Research Article: 2024 Vol: 27 Issue: 6
Future Leadership Challenges and Opportunities Amidst Global Dynamics
Shankar Subramanian Iyer, Faculty, Westford University College
Citation Information: Subramanian, I.S. (2024). Future Leadership Challenges and Opportunities Amidst Global Dynamics. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 27(6), 1-29.
Abstract
The rapidly evolving global landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for future leaders. This study explores the leadership competencies and strategies necessary to navigate and thrive amidst complex global dynamics. Utilizing qualitative methodology, this research involves in-depth interviews with 20 leaders from various industries and regions. The study examines emerging trends such as technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, cultural diversity, and economic uncertainties. Key themes include adaptability, cross-cultural competence, ethical leadership, and strategic foresight. Insights from the interviews highlight the critical importance of continuous learning, resilience, and inclusive leadership practices in addressing global challenges. The findings provide a nuanced understanding of the leadership skills required for future success and offer practical recommendations for current and aspiring leaders. This study contributes to the ongoing discourse on leadership development and prepares leaders to capitalize on opportunities while mitigating the risks associated with global change.
Keywords
Future Leadership, Global Dynamics, Qualitative Research, In-Depth Interviews, Leadership Competencies, Adaptability, Cross-Cultural Competence, Ethical Leadership, Strategic Foresight, Technological Advancements, Geopolitical Shifts, Cultural Diversity, Economic Uncertainties, Resilience, Inclusive Leadership.
Introduction
In an increasingly interconnected and rapidly changing world, the nature of leadership is undergoing a profound transformation. Leaders today must navigate a complex landscape characterized by technological advancements, economic uncertainties, geopolitical shifts, and social changes. These global dynamics present both challenges and opportunities for future leaders. As the world becomes more volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA), leaders must adapt to new paradigms, develop innovative strategies, and cultivate a diverse range of skills to guide their organizations and societies effectively. This study aims to explore the future leadership challenges and opportunities amidst these global dynamics, providing insights into the competencies and approaches required for effective leadership in the 21st century. Future leaders will face a multitude of challenges in navigating global dynamics. Technological advancements, while offering numerous opportunities, also pose challenges such as cybersecurity threats, ethical dilemmas related to artificial intelligence, and the need for continuous learning to keep up with rapid technological changes. Economic uncertainties, including fluctuations in global markets, trade tensions, and economic inequality, can create instability and require leaders to be adaptable and strategic in their decision-making. Geopolitical shifts, such as changing alliances, political instability, and conflicts, can impact global supply chains, regulatory environments, and business operations. Social changes, including increasing demands for social justice, diversity, and inclusion, require leaders to be empathetic, inclusive, and proactive in addressing social issues. Additionally, the ongoing impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic have highlighted the need for leaders to be resilient and capable of managing crises effectively.
Background
The concept of leadership has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Traditional hierarchical models are being replaced by more collaborative and adaptive approaches. Technological advancements such as artificial intelligence, big data, and digital communication tools are reshaping the business landscape, requiring leaders to be tech-savvy and agile. Additionally, the rise of globalization has increased the interconnectedness of economies and cultures, making cross-cultural competence and global awareness essential for effective leadership. Social movements advocating for diversity, equity, and inclusion are also influencing leadership practices, emphasizing the need for ethical and inclusive leadership. Furthermore, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of resilience and crisis management, underscoring the need for leaders who can navigate unprecedented challenges and drive sustainable change (). Despite the challenges, global dynamics also present numerous opportunities for future leaders. Technological advancements can drive innovation, improve efficiency, and create new business models. Leaders who can harness the power of big data, artificial intelligence, and digital tools can gain a competitive edge and drive organizational success. Economic uncertainties, while challenging, also create opportunities for strategic thinking, innovation, and growth. Leaders who can navigate these complexities can identify new markets, optimize operations, and create value. Geopolitical shifts can open up new opportunities for collaboration, partnerships, and expansion into new regions. Social changes, including increasing demands for diversity, equity, and inclusion, present opportunities for leaders to create more inclusive and equitable organizations, enhancing employee engagement, innovation, and overall performance. Furthermore, the ability to lead effectively during crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, can build resilience, trust, and a strong organizational culture (). The benefits of effective leadership amidst global dynamics are substantial. Leaders who can navigate the complexities of the modern world can drive organizational success, innovation, and growth. Effective leadership can enhance employee engagement, satisfaction, and retention, creating a positive and productive work environment. Inclusive leadership practices can foster diversity, equity, and inclusion, leading to a more innovative and competitive organization. The ability to leverage technological advancements can improve efficiency, decision-making, and overall performance. Strategic leadership can help organizations navigate economic uncertainties, geopolitical shifts, and social changes, ensuring long-term sustainability and success. Furthermore, resilient and adaptive leaders can build trust, credibility, and a strong organizational culture, enabling their organizations to thrive in the face of challenges and disruptions.
Research Scope
This research will examine the future leadership challenges and opportunities in the context of global dynamics. It will explore the key factors influencing leadership, including technological advancements, economic uncertainties, geopolitical shifts, and social changes. The study will identify the competencies and skills required for future leaders to navigate these challenges and leverage opportunities. It will also analyze the impact of different leadership styles and approaches on organizational and societal outcomes. The research will cover a range of sectors, including business, government, and non-profit organizations, providing a comprehensive understanding of leadership in various contexts. By taking a holistic perspective, the study aims to offer practical insights and recommendations for developing effective leaders in a rapidly changing world.
Research Questions
1. How do technological advancements impact leadership practices and strategies?
2. How do economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts shape leadership challenges and opportunities?
3. How can future leaders develop resilience and crisis management capabilities?
4. What are the implications of global dynamics for leadership development and training programs?
Research Objectives
1. To assess the impact of technological advancements on leadership practices and strategies, examining how leaders can leverage technology to drive organizational success.
2. To analyze the role of economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts in shaping leadership challenges and opportunities, providing insights into how leaders can navigate these complexities.
3. To examine how future leaders can develop resilience and crisis management capabilities, providing strategies for leading effectively in times of uncertainty and disruption.
4. To provide insights and recommendations for leadership development and training programs, ensuring they are aligned with the demands of the future leadership landscape.
Review of Literature
The contemporary landscape of leadership is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by a confluence of global dynamics. Existing literature underscores the increasing complexity of the leadership role, characterized by rapid technological advancements, economic globalization, demographic shifts, and geopolitical uncertainties. Researchers have extensively explored the challenges associated with these trends, including the need for enhanced digital literacy, cross-cultural competence, and adaptability to volatile environments. A significant body of research has focused on the implications of technological advancements for leadership. Studies have examined the emergence of new leadership roles, such as digital transformation leaders and data-driven decision-makers. Simultaneously, concerns about the ethical implications of technology, including issues of privacy, bias, and job displacement, have been highlighted. The impact of globalization on leadership has also been a subject of considerable interest, with scholars investigating the challenges of managing diverse workforces, operating in multiple cultural contexts, and navigating geopolitical risks. Moreover, demographic shifts, such as aging populations and increased workforce diversity, have been identified as critical leadership challenges. Research has emphasized the importance of intergenerational leadership, inclusive practices, and the ability to leverage diversity as a competitive advantage. The literature also acknowledges the growing significance of sustainability and corporate social responsibility in the leadership agenda. Leaders are increasingly expected to balance economic performance with environmental and social impact.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Leadership
A burgeoning body of literature underscores the transformative influence of technology on leadership. Research has delved into the emergence of digital leadership, characterized by competencies such as digital fluency, data analytics, and the ability to foster innovation. Studies have also explored the implications of artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and virtual work environments on leadership roles and responsibilities. While these advancements offer new opportunities for efficiency and productivity, they also present challenges related to job displacement, ethical considerations, and the need for upskilling the workforce. Scholars have extensively explored the impact of technological innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and digital transformation on leadership. For instance, AI has been identified as a crucial tool for enhancing decision-making processes, optimizing operational efficiency, and driving innovation within organizations (Al-Surmi et al., 2022). Similarly, digital transformation is seen as a catalyst for redefining leadership roles, requiring leaders to adopt new strategies that leverage technology for competitive advantage (Rajagopal et al., 2022).
Role of Economic Uncertainties and Geopolitical Shifts
The dynamic interplay of economic fluctuations and geopolitical tensions has been a focal point in leadership research. Scholars have examined the impact of economic crises, trade wars, and political instability on organizational performance and leadership effectiveness. Studies have highlighted the importance of strategic foresight, risk management, and adaptability in navigating such complex environments. Additionally, research has explored the role of cultural intelligence and cross-cultural leadership in building relationships and managing operations across diverse markets. Economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts also present significant challenges and opportunities for contemporary leaders. Research highlights how global economic crises, trade tensions, and political instability can disrupt organizational strategies and necessitate adaptive leadership (Kramskyi et al., 2024). Leaders are increasingly expected to possess risk management skills and the ability to pivot strategies in response to fluctuating market conditions and geopolitical changes (Iriani et al., 2024). This requires a deep understanding of global markets and the agility to respond to both threats and opportunities that arise from economic and political shifts (Tarba et al., 2023).
Development of Resilience and Crisis Management
The literature on leadership resilience and crisis management has grown significantly in recent years. Studies have investigated the personal attributes, organizational factors, and leadership behaviors associated with effective crisis response. Researchers have emphasized the importance of building psychological resilience, developing robust crisis communication plans, and fostering a culture of preparedness. Moreover, the concept of "anticipatory leadership" has gained traction, highlighting the need for leaders to proactively identify and address potential challenges. Resilience and crisis management have emerged as critical competencies for future leaders in response to the growing frequency of global disruptions. Studies on crisis leadership emphasize the importance of resilience, adaptability, and emotional intelligence in navigating crises effectively (Uy et al., 2023). Leaders who can maintain composure, communicate effectively, and inspire confidence during times of uncertainty are better equipped to guide their organizations through challenges. Moreover, crisis management research suggests that preparedness and proactive planning are essential for mitigating the impact of crises and ensuring organizational continuity (Jerab, 2023).
Leadership development and training programs have traditionally focused on building foundational skills such as strategic thinking, communication, and team management. However, recent literature points to the need for these programs to evolve in line with the demands of the future leadership landscape. Scholars argue for the incorporation of new content areas such as digital transformation, global risk management, and crisis leadership into training curricula (Behie et al., 2023). The importance of experiential learning and continuous development is also emphasized, with a focus on preparing leaders to handle the complex and dynamic challenges of the future.
Literature Gaps
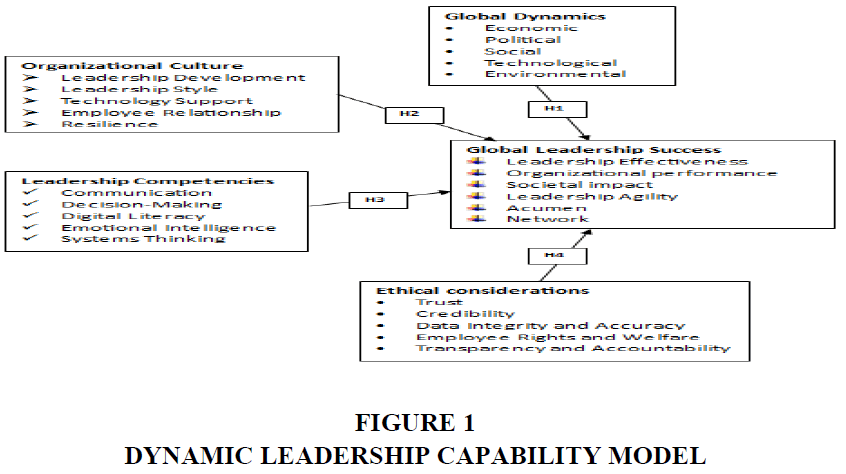
Despite the extensive research on leadership, several gaps remain in the context of future leadership challenges and opportunities amidst global dynamics. First, while there is considerable literature on the impact of technology on leadership, there is limited research on how leaders can integrate multiple emerging technologies simultaneously to drive organizational success. The interplay between AI, big data, blockchain, and other technologies in leadership contexts is underexplored, leaving a gap in understanding how leaders can effectively harness these tools in combination. Secondly, the literature on economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts tends to focus on reactive strategies, with less emphasis on proactive leadership approaches. There is a need for more research on how leaders can anticipate and prepare for economic and geopolitical disruptions, rather than merely responding to them. Additionally, the impact of cultural differences on leadership strategies in navigating global challenges is not sufficiently addressed, particularly in the context of multinational organizations. The field of resilience and crisis management in leadership also presents gaps, particularly in the area of long-term resilience building. While existing studies focus on immediate crisis response and short-term resilience, there is a limited exploration of how leaders can cultivate sustained resilience over extended periods of disruption. Research on the integration of resilience training into leadership development programs is also scarce, highlighting a need for more comprehensive studies that link resilience-building practices with leadership training. Finally, there is a noticeable gap in the literature regarding the alignment of leadership development programs with the rapidly changing global landscape. While there are calls for updating curricula to include new content areas, there is insufficient empirical research on the effectiveness of these updates in preparing leaders for future challenges. Moreover, the role of technology in enhancing leadership training and development remains underexplored, with few studies examining the potential of digital tools and platforms to support leadership growth. Addressing these gaps will require interdisciplinary research that bridges the fields of leadership, technology, global studies, and crisis management. By filling these gaps, future studies can provide more comprehensive insights into the evolving demands on leaders and the strategies they can employ to navigate an increasingly complex global environment figure 1.
Hypotheses
H1: There is a significant relationship between Global Dynamics Factors and Global Leadership Success Factors
H2: The Global Leadership Success Factors are influenced by the Organizational Culture Factors
H3: There is a significant relationship between Leadership Competencies Factors and Global Leadership Success Factors
H4: The Global Leadership Success Factors are influenced by the Ethical Considerations Factors
Methodology
This study on "Future Leadership Challenges and Opportunities Amidst Global Dynamics" aims to investigate how leaders can effectively navigate the complexities of technological advancements, economic uncertainties, and geopolitical shifts to drive organizational success. The research will employ a qualitative design, focusing on in-depth interviews as the primary data collection method. A purposive sampling technique will be used to select a diverse group of 20 respondents, ensuring that participants are highly knowledgeable and experienced in leadership roles across various industries and global contexts. The sample will include senior executives, leadership development experts, industry analysts, and strategic consultants, each chosen for their direct experience with and insights into leadership challenges in dynamic environments. The respondents will represent a range of sectors, including technology, finance, manufacturing, and international trade, providing a comprehensive view of how different industries are impacted by global dynamics. Data will be collected through semi-structured interviews, allowing for flexibility in exploring the unique perspectives of each respondent while maintaining a focus on the core research objectives. These interviews, conducted either in person or via virtual platforms, will each last approximately 20-30 minutes and will be recorded and transcribed for detailed analysis. Thematic analysis, following the approach outlined by Naeem et al., (2023), will be used to systematically identify, analyze, and report patterns or themes within the data. This process will begin with an initial coding phase, where recurring ideas and concepts are identified, followed by the grouping of these codes into broader categories or themes that reflect the key issues related to future leadership challenges and opportunities. Anticipated themes include the integration of technology into leadership practices, strategies for managing economic and geopolitical uncertainties, the development of resilience and crisis management capabilities, and the alignment of leadership development programs with the demands of the future leadership landscape table 1. The findings will offer actionable insights and recommendations for leaders and organizations, providing practical strategies to enhance leadership effectiveness in a rapidly evolving global environment (Braun et al., 2023).
| Table 1 Interview Summary | |
| Interviewee no, (Experience in years), Designation, Location | Main Comments on “Future Leadership Challenges and Opportunities Amidst Global Dynamics” (Other Interviewees agreeing to these comments) |
| 1. (10) Chief Technology Officer (CTO), Mumbai | - Technological advancements, like AI, big data, and digital communication tools, empower leaders to make informed decisions, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. - Technologically adept leaders can quickly adapt to changing market dynamics and innovate to meet evolving demands. Their understanding of digital tools and trends equips them with the acumen to anticipate and respond to challenges and opportunities. - Economic volatility, such as recessions or inflation, and geopolitical events like trade wars or conflicts, present significant challenges for leaders. These factors can disrupt markets, supply chains, and financial stability, requiring leaders to be strategic and adaptable. - Social dynamics, including demographic changes, cultural shifts, and societal expectations, influence leadership resilience. Leaders must be culturally aware, empathetic, and capable of managing diverse teams, especially during crises or periods of social upheaval. - Environmental factors, including climate change and sustainability challenges, are increasingly important in leadership. Leaders must integrate sustainable practices into their strategies and operations to meet regulatory demands and societal expectations. - Future leadership development programs must incorporate sustainability and environmental awareness, equipping leaders with the skills to navigate and address environmental challenges. This focus ensures that leadership practices are aligned with global sustainability goals and the demands of the future leadership landscape. - Leadership programs should focus on digital literacy, technological acumen, and innovation management, ensuring leaders can leverage technology for organizational success. - Digital transformation, remote leadership, AI-driven decision making, data-driven leadership, Innovation focus, digital literacy, cybersecurity, agile methodologies. - Organizational Performance leads to Increased efficiency, enhanced customer experience, and new business models. Leadership Agility ensures adaptability to technological shifts, and willingness to learn new technologies. - Global Dynamics serve as the external pressures shaping the leadership landscape, while Leadership Outcomes represent the desired results influenced by leadership actions in response to these dynamics (Interviewees 2, 5, 8, 13, 17, 19, 20) |
| 2. (11), Sustainability Officer in Tokyo, Japan | - Leaders who embrace and leverage these technologies can gain a competitive edge, optimize organizational processes, and create more agile and responsive teams. - Leaders must navigate these complexities by being agile and resilient, capable of making swift decisions under pressure. They need to develop strategies to mitigate risks, manage resources effectively, and maintain organizational stability amidst uncertainty. - Leaders who are attuned to social changes can foster inclusive, ethical, and socially responsible organizational cultures. This alignment with societal values enhances the organization’s reputation and impact. - Leaders who prioritize environmental considerations can drive positive societal impact, enhance organizational reputation, and contribute to long-term success. - Incorporate modules on navigating economic and geopolitical uncertainties, building resilience, and effective crisis management. - Technology enhances efficiency, scalability, and market responsiveness, leading to improved organizational performance. - Leadership Acumen enhances understanding of technology trends and the ability to leverage technology for competitive advantage. Leadership Network builds relationships with technology experts, fostering digital collaboration. - Technological advancements significantly influence leadership practices and strategies. Digital transformation, remote leadership, AI-driven decision-making, and data-driven leadership are becoming increasingly prevalent. - Leaders must focus on innovation, digital literacy, cybersecurity, and agile methodologies to drive organizational success. Technological proficiency enhances leadership agility, acumen, and network building. - Economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts present both challenges and opportunities for leaders. Market volatility, supply chain disruptions, geopolitical risks, and regulatory changes demand effective crisis management, risk mitigation, and strategic partnerships (Interviewees 1, 4, 7, 11, 13, 16), (Pawar et al., 2024). |
| 3. (10), Global Trade Compliance Manager, Oman | - Leaders who harness technology effectively can streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth. - Economic and geopolitical dynamics can directly impact an organization's performance, affecting revenue, market position, and long-term sustainability. Leaders must understand these factors to make informed decisions and steer their organizations through turbulent times. - Social dynamics also shape leadership networks, encouraging collaboration across diverse groups and communities. Leaders who build and leverage these networks can enhance their influence and access new opportunities. - Develop leaders' cultural competence, empathy, and social responsibility to manage diverse teams and align with societal values. - Leaders must possess a deep understanding of economic and political trends to navigate these complexities successfully. Organizational performance, leadership agility, and acumen are directly impacted by the ability to respond to rapid market changes and geopolitical fluctuations. - Building resilience and crisis management capabilities is essential for effective leadership in an unpredictable world. - Economic downturns, natural disasters, pandemics, and political instability highlight the need for trust, empathy, collaboration, and strategic planning. Leaders must demonstrate agility, acumen, and strong networks to navigate crises effectively and protect organizational performance. - Global Dynamics serve as the external forces shaping the leadership landscape, while Leadership Outcomes represent the desired results influenced by leadership actions in response to these dynamics. - To prepare for the future leadership landscape, leadership development, and training programs must focus on technological literacy, global mindset, strategic thinking, resilience, and adaptability. - Crisis management simulations, digital transformation workshops, and intercultural competence training are essential components of effective leadership development. - By aligning leadership competencies with future challenges, organizations can enhance their performance, foster innovation, and build a future-ready workforce. - Technology, economic uncertainties, geopolitical shifts, and societal challenges demand a new breed of leaders who are agile, adaptable, and equipped with a global mindset (Interviewees 5, 7, 8, 15, 18, 20) (Walters et al., 2023); (Figueiredo et al., 2023) |
| 4. (10) Logistics Director, Spain | - Embed sustainability and environmental considerations into leadership training to prepare leaders for the challenges of a rapidly changing world. - Leadership development programs cultivate essential skills, competencies, and behaviors needed for effective global leadership. These programs can focus on strategic thinking, cross-cultural communication, and adaptability, which are critical for navigating the complexities of global dynamics. - By investing in leadership development, organizations can create a pipeline of capable leaders who can drive performance and innovation, ensuring long-term organizational success. - Leadership style also shapes the organization’s culture and values, influencing how the organization is perceived by external stakeholders and its broader societal impact. - Technology support enables leaders to stay informed about global trends, economic changes, and geopolitical developments, enhancing their decision-making agility and strategic acumen. - Positive employee relationships extend beyond the organization, influencing leadership networks and the organization’s reputation. Leaders who foster strong internal relationships are often more successful in building external networks and partnerships, enhancing their societal impact. - In times of crisis, strong employee relationships contribute to organizational resilience. Leaders who have built trust and open communication can mobilize their teams more effectively, navigating challenges and maintaining stability (Interviewees 2, 6, 9,11, 13, 17,18, 19) (Hashimy et al., 2023). |
| 5. (9) HR Director Private Energy, Kuwait | - Well-structured leadership development fosters agility and acumen, enabling leaders to respond proactively to technological advancements, economic shifts, and geopolitical challenges. - Well-developed leaders in ethics, social responsibility, and sustainability can enhance their organization's societal impact, aligning their practices with broader societal goals. - The availability and support of advanced technology within an organization empower leaders to implement data-driven strategies, streamline operations, and foster innovation. Leaders who leverage technology effectively can enhance both organizational performance and leadership effectiveness. - Technology also plays a critical role in resilience, providing tools for real-time communication, data analysis, and scenario planning, which are vital during crises or disruptions. - Strong employee relationships create a foundation of trust, collaboration, and engagement, which are essential for leadership effectiveness. Leaders who prioritize positive employee relations can enhance team performance, morale, and organizational outcomes. - Resilience is a critical trait for global leadership, enabling leaders to withstand and recover from challenges such as economic downturns, geopolitical shifts, or technological disruptions. Resilient leaders can maintain effectiveness even in the face of adversity. - Develop programs that encourage flexibility in leadership styles, preparing leaders to adapt their approach based on situational demands, economic conditions, and cultural contexts. - Include modules on resilience-building, both at a personal and organizational level, to prepare leaders for economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts. Focus on strategies for maintaining effectiveness during crises. - Train leaders on fostering strong, trust-based relationships with employees, which are critical for organizational cohesion, performance, and resilience. - A culture that prioritizes leadership development fosters leaders equipped to tackle complex global challenges. Effective development programs enhance leadership capabilities, enabling leaders to leverage technology, navigate economic uncertainties, and build resilience. - Leadership style is pivotal to organizational success. Transformational leadership, characterized by employee empowerment, innovation, and ethical conduct, aligns well with the demands of a globalized world. (Interviewees 3, 4, 8, 11, 12, 16, 20), (Rozell et al., 2024); (Mohammed et al., 2023). |
| 6. (12) Dean of Business School, Toronto, Canada | - Leadership style—whether transformational, transactional, or servant leadership—greatly affects how leaders engage with their teams, make decisions, and drive results. For example, transformational leaders may be more adept at leveraging technological advancements to inspire innovation and drive organizational success. - The flexibility of a leader’s style can enhance their ability to navigate economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts. A flexible, adaptive leadership style can foster resilience in both the leader and their organization, enabling effective crisis management. - A resilient organizational culture, led by resilient leaders, fosters an environment where adaptability and agility are ingrained. This enhances the organization’s ability to respond to changes, maintain performance, and capitalize on new opportunities. - Leadership fosters a positive organizational climate, crucial for navigating economic downturns and geopolitical shifts. Technology support is essential for leadership agility. A culture that embraces technology empowers leaders to utilize digital tools for innovation, decision-making, and global networking. - Strong employee relationships contribute to organizational resilience. A collaborative culture enhances innovation, employee engagement, and the ability to weather economic storms. - Resilience, as a cultural value, equips leaders and employees to overcome challenges. By fostering adaptability and continuous learning, organizations can navigate disruptions effectively. - To achieve organizational goals, organizational culture must align with strategic objectives. A culture supporting technology adoption and employee development empowers leaders to leverage technology for organizational success. - A culture emphasizing adaptability and resilience is crucial for navigating economic and geopolitical challenges. By investing in leadership development and fostering a supportive environment, organizations can cultivate leaders capable of meeting future demands. - Organizational culture is a cornerstone of global leadership success. A culture that nurtures leadership talent embraces technology, fosters strong employee relationships, and builds resilience is essential for navigating the complexities of the global landscape (Interviewees 2, 4, 7, 10, 11, 12, 18), (Moşteanu, 2024) |
| 7. (11) General Manager Cooperative Retail, Ahmedabad, India | - Effective communication is fundamental to global leadership success. Leaders who can articulate vision, strategy, and expectations clearly are more likely to inspire and align their teams, driving organizational performance and achieving strategic goals. - Transparent and inclusive communication fosters trust within the organization and with external stakeholders, enhancing reputation and societal impact. - A resilient organizational culture, led by resilient leaders, fosters an environment where adaptability and agility are ingrained. This enhances the organization’s ability to respond to changes, maintain performance, and capitalize on new opportunities. - Incorporate training on leveraging technology for strategic decision-making, innovation, and crisis management. Ensure leaders are proficient in using digital tools to enhance organizational success. - Leaders who communicate effectively can build strong relationships, both internally and externally, which contributes to a positive organizational culture and broader societal influence. - In rapidly changing environments, communication is key to maintaining agility. Leaders who communicate well can swiftly adapt messages, strategies, and directives to respond to economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts, ensuring alignment and coherence in action. - Strong communication skills enable leaders to build and maintain extensive networks, facilitating collaboration and resource sharing across diverse contexts. - Decision-making is at the heart of leadership. Leaders who make informed, timely, and strategic decisions can drive organizational success, particularly when leveraging technological advancements. - Effective decision-making ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, risks are managed, and opportunities are seized. - The ability to make swift and sound decisions is crucial in times of economic uncertainty and crisis. Leaders who excel in decision-making can navigate complex challenges, maintaining organizational stability and performance even in volatile environments (Interviewees 1, 4, 8, 12, 15, 17, 19), (Huda et al., 2023) |
| 8. (11) Head of Healthcare Organization, Bahrain | - Strategic decision-making is closely tied to leadership acumen and systems thinking. Leaders who understand the broader systems within which they operate can make decisions that account for multiple variables and long-term implications, enhancing organizational resilience and success. - As technological advancements reshape industries, digital literacy becomes increasingly important for leaders. Digitally literate leaders can effectively leverage technology to optimize processes, drive innovation, and enhance organizational performance. - Digital literacy enables leaders to stay ahead of technological trends and adapt to new tools and platforms. This agility is crucial for navigating economic shifts and ensuring the organization remains competitive and resilient. - Digitally literate leaders can leverage digital platforms to build and maintain networks, fostering global collaboration and information sharing. This competency is key to expanding influence and access to resources in a connected world. - Emotional intelligence is critical for understanding and managing emotions—both one’s own and others. Leaders with high EI can foster a positive organizational culture, enhance employee engagement, and build strong, trust-based relationships. - Leaders with strong EI are more likely to lead with empathy and social responsibility, contributing to a positive societal impact. They are also better equipped to handle stress and guide their teams through crises, enhancing organizational resilience. - EI contributes to leadership agility by enabling leaders to read and respond to emotional and social cues effectively, which is crucial in dynamic and complex environments. This awareness enhances decision-making and strategic foresight. - Systems thinking enables leaders to understand the interconnections between various components of their organization and the external environment. - The holistic perspective allows for more effective strategic planning and problem-solving, driving long-term organizational success. - Effective communication is essential for building trust, fostering collaboration, and navigating complex global environments. Strong communication skills enhance leadership effectiveness, agility, and network building (Interviewees 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 16, 19), (Kolasani, 2023) |
| 9. (7) Leadership Development Coach, Johannesburg, South Africa | - Leaders who excel in systems thinking can anticipate the ripple effects of their decisions, ensuring that actions are aligned with organizational goals and external realities. This competency enhances leadership acumen, particularly in navigating complex global dynamics. - Systems thinking is critical for building resilience, as it enables leaders to identify potential vulnerabilities and interdependencies within the organization. This understanding allows for proactive crisis management and the development of robust contingency plans. - Training programs should emphasize the development of advanced communication skills, including active listening, clarity in messaging, and the ability to communicate across diverse cultural contexts. - Include modules on strategic decision-making, risk assessment, and scenario planning to equip leaders with the skills needed to navigate complex challenges and uncertainties. - Ensure that leaders are proficient in using digital tools and technologies, with a focus on leveraging data analytics, AI, and digital platforms to drive innovation and organizational success. - Incorporate training on emotional intelligence, focusing on self-awareness, empathy, and relationship management to enhance leadership effectiveness and resilience. - Develop leaders’ ability to think systemically, understanding the broader context of their decisions and actions, which is crucial for strategic planning and long-term success. - Sound decision-making is crucial for navigating economic uncertainties, geopolitical shifts, and technological advancements. Leaders with strong decision-making abilities can effectively allocate resources, mitigate risks, and seize opportunities. - In today's digital age, digital literacy is paramount. Leaders proficient in technology can drive innovation, improve decision-making, and build global networks. - Emotional intelligence is equally important for building relationships, resolving conflicts, and inspiring teams. - Leaders with high emotional intelligence can effectively navigate crises, foster positive organizational cultures, and build trust (Interviewees 1, 2, 8, 11, 14, 17, 19) (Chauhan et al., 2024) |
| 10. (13) E-commerce Director in Dubai, UAE, | - Systems thinking is essential for understanding the interconnectedness of elements within complex systems. Leaders with strong systems thinking abilities can anticipate trends, make informed decisions, and develop effective strategies. - A strong emphasis on digital literacy, emotional intelligence, and systems thinking is essential to equip leaders with the skills needed to navigate the complexities of the global landscape. - Ethical considerations are fundamental to effective global leadership. Trust, credibility, data integrity and accuracy, employee rights and welfare, transparency, and accountability are essential components of ethical leadership. These factors significantly influence leadership outcomes and organizational performance. - Trust and credibility are foundational for building strong relationships with stakeholders. These elements are crucial for navigating complex global challenges and enhancing leadership effectiveness, organizational performance, and societal impact. - Data integrity and accuracy are paramount in a data-driven world. Leaders must prioritize ethical data handling to maintain trust and credibility while making informed decisions and driving innovation. - Prioritizing employee rights and welfare fosters a positive organizational culture, enhances employee engagement, and contributes to organizational performance and societal impact. - Transparency and accountability are essential for building trust and maintaining credibility. Open communication and accountability ensure that leaders are held responsible for their actions, which is crucial for effective crisis management. - By integrating ethical considerations into leadership practices, organizations can build stronger reputations, enhance organizational performance, and create a positive societal impact. - Ethical factors shape the way leaders interact with stakeholders, make decisions, and manage their organizations in a globalized and technologically advanced world. - Trust is the cornerstone of effective leadership. - Leaders who cultivate trust within their teams and with external stakeholders can drive engagement, loyalty, and collaboration, which are essential for global leadership success. - Trust facilitates smoother implementation of strategies and acceptance of leadership decisions (Interviewees 1, 5, 6, 9, 11, 15, 18), (Woodhill et al., 2023); (Singh et al., 2023). |
| 11. (10) Vice President, Environmental Agency, London, UK | - Trustworthy leadership enhances organizational performance by creating a positive work environment where employees feel valued and motivated. - Externally, it builds the organization’s reputation, contributing to its societal impact by promoting ethical practices and fostering community trust. - Trust allows leaders to act with agility, as they can rely on the support of their teams and networks when making swift decisions in response to technological advancements or geopolitical shifts. It also strengthens networks, as trust is a key factor in building and maintaining long-term professional relationships. - Credibility is essential for leaders to be taken seriously and respected. Leaders with credibility are more likely to inspire confidence, influence others, and achieve organizational goals. - Credibility ensures that the strategies and directives set by leaders are followed and implemented effectively. - Credible leaders can more effectively navigate challenges and uncertainties, as their decisions are trusted by stakeholders. This enhances their leadership agility, allowing them to lead through crises with authority and composure. - Credibility extends beyond the organization to how leaders are perceived in the broader industry and society. - Credible leaders attract valuable partnerships and alliances, expanding their networks and increasing their societal impact through ethical leadership. - In an era where data drives decision-making, the integrity and accuracy of data are crucial. - Leaders who prioritize data integrity ensure that decisions are based on reliable information, leading to better outcomes and enhanced organizational performance (Interviewees 1, 3, 4, 12, 13, 16, 19, 20), (Blanchard et al., 2023); (Khokhar et al., 2023). |
| 12. (16) Operations Manager, Renewable Energy, Copenhagen, Denmark | - Data accuracy also bolsters leadership effectiveness, as decisions are perceived as well-founded and justified. - Leaders with access to accurate and trustworthy data can make informed, agile decisions in response to technological advancements and economic changes. This enhances their strategic acumen and ability to navigate complex environments. - Ensuring data integrity and accuracy also has ethical implications for societal impact. - Leaders who handle data responsibly contribute to the organization’s transparency and accountability, which in turn fosters public trust and supports the organization’s ethical reputation. - Ethical leaders who prioritize employee rights and welfare create a supportive and fair work environment. This leads to higher employee satisfaction, retention, and productivity, directly enhancing organizational performance. - Respecting employee rights also builds leadership effectiveness by fostering a culture of mutual respect and trust. - Leaders who champion employee rights contribute positively to society by setting standards for fair treatment and ethical behavior in the workplace. - The commitment to ethical labor practices enhances the organization’s societal impact and holds leaders accountable for their decisions and actions (Interviewees 2, 3, 8, 12, 15, 16, 19), (El Ouarzadi et al., 2023); (Nejati et al., 2020). |
| 13. (13) Senior HR Director, Tourism Company, Scotland | - By ensuring that employee welfare is prioritized, leaders build resilient organizations where employees are more willing to go the extra mile, especially in times of crisis. This strengthens the organization’s ability to adapt and thrive in challenging environments. - Transparency in leadership practices builds trust and credibility, both internally and externally. - Leaders who are transparent about their decisions, processes, and challenges are more likely to be effective, as they foster an open culture where issues can be addressed proactively. - Transparency also contributes to organizational performance by reducing misunderstandings and fostering alignment towards common goals. - Transparent leaders can respond more effectively to technological advancements and geopolitical shifts because they maintain clear communication channels and foster trust. This transparency also aids in building strong, trustworthy networks. - Transparency in operations and decision-making enhances an organization’s societal impact by demonstrating ethical leadership and fostering public trust. It also reinforces accountability, as transparent leaders are more likely to be held to high ethical standards by their stakeholders (Interviewees 2, 4, 8, 9, 14, 16, 18, 20), (Martinez et al., 2023) |
| 14. (13) President, Healthcare Group, Turkey | - Accountability ensures that leaders are responsible for their actions and decisions, which is critical for building a culture of integrity and performance. - Leaders who hold themselves and their teams accountable are more likely to achieve global leadership success, as they set clear expectations and follow through on commitments. - Accountability supports agile leadership by fostering a culture of responsibility where quick decisions are balanced with careful consideration of their implications. This balance enhances leadership acumen, allowing leaders to navigate complex environments with confidence and foresight. - Leaders who demonstrate accountability are more likely to be trusted and respected, which enhances their societal impact and strengthens their professional networks. - Accountability also ensures that leaders and organizations are aligned with ethical standards, reinforcing their reputation and influence. - Incorporate training that emphasizes ethical considerations in communication and decision-making, ensuring that leaders understand the importance of trust, credibility, and transparency. - Provide training on data ethics, focusing on the importance of data integrity and accuracy in decision-making and how to manage data responsibly in a technology-driven world. - Include modules on upholding employee rights and welfare, teaching leaders to balance organizational goals with ethical labor practices, and fostering a supportive work environment. - Develop programs reinforcing the importance of accountability and transparency in leadership, helping leaders build trust and credibility with their teams and stakeholders. - By integrating these ethical considerations into leadership practices and development programs, leaders can enhance their effectiveness and resilience while navigating the complexities of the global leadership landscape (Interviewees 3, 5, 8, 11, 13, 17, 19) (Gorman et al., 2023); (McKenzie et al., 2023); (Deng et al., 2023). |
| 15. (18) Operations Director, Stuttgart, Germany | - Leadership effectiveness is fundamental to achieving global leadership success. - Effective leaders can inspire, motivate, and align their teams with organizational goals, driving performance and innovation. They can also make informed, strategic decisions that capitalize on technological advancements, ensuring their organizations remain competitive and relevant. - Effective leaders leverage technology to enhance their leadership practices, using tools like AI and data analytics to optimize decision-making and strategy formulation. - Leaders with a high level of effectiveness are better equipped to address economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts, as they possess the skills needed to steer their organizations through complex challenges. - Effective leaders are also resilient, capable of leading their teams through crises and ensuring that the organization can recover and thrive amidst disruption. - Satya Nadella has transformed Microsoft’s culture by focusing on empathy, collaboration, and innovation. Under his leadership, Microsoft has embraced a growth mindset and a more inclusive work environment. - Strong organizational performance is a clear indicator of successful leadership. - Leaders who can drive their organizations to achieve high levels of productivity, profitability, and innovation are more likely to be recognized as global leaders. This performance is often the result of strategic planning, effective resource management, and the ability to harness technological advancements. - Leaders who can integrate and leverage technology within their organizations are better positioned to drive performance, ensuring that the organization stays ahead of competitors. - High organizational performance during periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical shifts is often a sign of a leader's ability to adapt and make strategic decisions that mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities. - Organizations that perform well even in challenging times reflect the resilience and crisis management capabilities of their leaders. - Societal impact goes beyond organizational boundaries, influencing how leaders are perceived on a global scale (Interviewees 2, 3, 6, 9, 10, 13, 16, 20), (Rayets et al., 2023); (Murphy, 2024); (Siddiqui, 2024) |
| 16. (10), Islamic Bank, Head, Malaysia | - Leaders who prioritize ethical practices, sustainability, and social responsibility contribute positively to society, thereby enhancing their reputation and legitimacy as global leaders. This impact is increasingly important in a world where corporate social responsibility (CSR) and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria are becoming critical to business success. - Leaders who use technology not only for profit but also for societal good—such as reducing environmental impact or improving community well-being—strengthen their societal impact. - In times of economic or geopolitical instability, leaders who maintain a focus on societal impact help build trust and loyalty among stakeholders, contributing to long-term success. - Leaders who can navigate crises while maintaining their commitment to societal impact are seen as more credible and trustworthy, which reinforces their global leadership status. - The CEO of General Motors (GM) provides another compelling example of global leadership success. Barra’s leadership effectiveness is reflected in her ability to transform GM into a company that is forward-thinking and innovative, particularly in the areas of electric vehicles and autonomous driving technology. This strategic shift has bolstered GM’s organizational performance, positioning it as a leader in the future of mobility. Barra’s leadership has also made a significant societal impact. - Leadership agility refers to a leader’s ability to adapt to changing circumstances, embrace innovation, and respond swiftly to challenges. Agile leaders can quickly adjust their strategies in response to technological advancements, market shifts, or crises, ensuring that their organizations remain resilient and competitive on a global scale. - Agile leaders can quickly adopt and integrate new technologies, ensuring their organizations are at the forefront of innovation and performance. - Leadership agility is crucial in navigating economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts. Agile leaders can pivot their strategies and operations to align with new realities, mitigating risks and seizing new opportunities. - Agility is essential in crisis management, enabling leaders to respond rapidly and effectively to disruptions, minimizing negative impacts, and steering their organizations toward recovery - Arvind Krishna (CEO) has positioned IBM as a leader in hybrid cloud, AI, and quantum computing. His focus on client-centricity and sustainability has driven organizational performance and societal impact (Interviewees 3, 4, 8, 12, 15, 17), (Akhtar et al., 2023); (Kurniawan et al., 2024) |
| 17. (12) Sustainability Group, HOD, Sweden | - Leadership acumen encompasses a deep understanding of global markets, strategic foresight, and the ability to make informed decisions that drive long-term success. - Leaders with strong acumen are better equipped to navigate the complexities of the global business environment, making strategic choices that ensure organizational growth and sustainability. - Leaders with high acumen recognize the potential of technological advancements and strategically implement them to enhance organizational capabilities and competitive advantage. - Acumen allows leaders to anticipate and prepare for economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts, making decisions that mitigate risks and leverage opportunities. - Leaders with strong acumen are adept at crisis management, drawing on their deep understanding of the business landscape to guide their organizations through challenges. - Cook has demonstrated exceptional agility in navigating challenges and opportunities, from supply chain disruptions to the expansion of Apple's product line. His strategic acumen has been instrumental in maintaining Apple's market dominance. - A robust professional network is vital for global leadership success. Networks provide leaders with access to resources, information, and opportunities that can enhance organizational performance and expand their influence. - Global networks also facilitate collaboration and partnerships that are essential for navigating the complexities of the international business environment. - Leaders with strong networks can tap into a wealth of knowledge and expertise, enabling them to stay ahead of technological trends and integrate innovations into their organizations. - Networks provide leaders with insights and support that are crucial for navigating economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts. Collaborative relationships can offer alternative perspectives and solutions to complex challenges. - During crises, networks are invaluable in providing the support and resources needed to manage disruptions and ensure organizational continuity (Interviewees 1, 3, 4, 7, 9, 12, 13) (Anwari et al., 2024); (Longenecker et al., 2024); (Tarba et al., 2023). |
| 18. (12) CEO, Hospitality sector, Abu Dhabi | - Programs should focus on developing core leadership skills, including strategic thinking, communication, and decision-making, to enhance overall leadership effectiveness. - Training should emphasize performance management, operational excellence, and the integration of technology to drive organizational success. - Leaders should be educated on the importance of CSR, sustainability, and ethical practices, aligning their leadership approach with societal expectations. - Development programs should include modules on adaptive leadership, innovation management, and change management to build leadership agility. - Leaders should be equipped with the knowledge and tools to enhance their strategic foresight, market understanding, and decision-making capabilities. - Programs should encourage leaders to build and maintain strong networks, emphasizing the value of collaboration, mentorship, and global partnerships. - Jacinda Ardern, former Prime Minister of New Zealand, is renowned for her compassionate and empathetic leadership style, particularly during crises such as the Christchurch mosque shootings and the COVID-19 pandemic. While Ardern’s leadership is not within a corporate setting, her effectiveness in governance and crisis management has led to significant societal impact in New Zealand (Interviewees 2, 3, 6, 12, 13, 20) (Wallace et al., 2021); (Carvalho et al., 2023); (Bonaconsa et al., 2024). |
| 19. (14) Quality Control Manager in Hongkong | - Ginni Rometty, the former CEO of IBM, exemplifies how leadership effectiveness can drive a company through transformation. Under Rometty’s leadership, IBM focused on emerging technologies such as cloud computing and AI, which were pivotal in the company’s organizational performance during her tenure. Rometty also made a significant societal impact by championing diversity and inclusion initiatives within IBM. Her leadership agility was crucial as she guided IBM through the shifting technology landscape, ensuring the company’s relevance in a rapidly evolving industry. - Strong performance is often a result of effective leadership, which can be enhanced by the strategic use of technology, adaptability to economic and geopolitical shifts, and a focus on resilience and crisis management. In turn, strong organizational performance contributes to societal impact - Effective leaders can leverage technology to drive innovation, navigate economic uncertainties, and build resilience. - Successful global leaders prioritize societal impact and integrate it into their organizational strategies. By leveraging technology, addressing societal challenges, and building strong relationships, leaders can create a positive impact. - Agile leaders can effectively navigate technological advancements, economic uncertainties, and geopolitical shifts. They can also respond effectively to crises and build resilience within their organizations. - Leaders with strong acumen can leverage technology to gain competitive advantages, identify emerging opportunities in economic and geopolitical landscapes, and develop effective crisis management strategies. - A strong network is essential for global leadership success. It provides access to information, resources, and diverse perspectives. Leaders can leverage their networks to drive innovation, mitigate risks, and build resilience. - Pichai's leadership in AI and digital transformation has positioned Google as a leader in the tech industry. His ability to build strong partnerships and collaborations has expanded Google's global reach (Interviewees 5, 8, 10, 13, 15, 17, 19) (Orozco et al., 2023); (Vera et al., 2020); (Joel et al., 2024). |
| 20. (15), CEO, Mall, Hyderabad, India | - Global Dynamics, including economic, political, social, technological, and environmental factors, significantly influence leadership practices and outcomes. Leaders who successfully navigate these dynamics are often those who can anticipate changes, adapt their strategies, and lead their organizations through uncertainty. - Christine Lagarde, President of the European Central Bank, has demonstrated exceptional leadership by navigating the economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts in Europe. Her ability to manage the economic fallout from Brexit and the COVID-19 pandemic, while maintaining stability in the Eurozone, showcases how understanding and responding to global dynamics can lead to leadership success. - A positive organizational culture fosters collaboration, innovation, and adaptability, which are essential for global leadership success. - Leadership Competencies such as communication, decision-making, digital literacy, emotional intelligence, and systems thinking are vital for effective global leadership. These competencies enable leaders to make informed decisions, communicate effectively across cultures, and leverage technology to enhance organizational performance. - Sheryl Sandberg, COO of Meta (formerly Facebook), exemplifies strong leadership competencies, particularly in communication and emotional intelligence. Her ability to navigate the complexities of managing a global social media platform, while advocating for women in leadership through initiatives like Lean In, highlights how these competencies contribute to leadership success. - Ethical considerations, including trust, credibility, data integrity, employee rights, transparency, and accountability, are fundamental to building a strong reputation and fostering long-term success. Ethical leadership builds trust with stakeholders, enhances organizational reputation, and ensures sustainable success - Paul Polman, former CEO of Unilever, is known for his commitment to ethical leadership. Polman’s focus on sustainability, transparency, and social responsibility during his tenure helped Unilever gain trust among consumers and stakeholders, while also driving long-term business success. His ethical approach to leadership has been a key factor in his global leadership success. - Leaders who can effectively manage global dynamics, cultivate a strong organizational culture, demonstrate key leadership competencies, and adhere to ethical standards are more likely to achieve sustained success on a global scale (Interviewees 1, 3, 5, 7, 12, 13, 19) (Ekemezie et al., 2024); (Jerab et al., 2023); (Bagga et al., 2023). |
Qualitative Methodology
Navigating future leadership challenges and opportunities amidst global dynamics requires a strategic blend of adaptability, foresight, and ethical stewardship, where understanding the impact of economic, political, social, technological, and environmental factors becomes essential for global leadership success. Leaders must leverage technological advancements to drive organizational innovation and performance, while also navigating economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts with agility and informed decision-making. Developing resilience and crisis management capabilities enables leaders to effectively steer their organizations through times of disruption, ensuring stability and growth. Ethical considerations, such as transparency, trust, and accountability, are crucial in maintaining credibility and fostering stakeholder confidence. By integrating these elements, leaders can build robust networks, enhance organizational effectiveness, and create a positive societal impact, ultimately positioning themselves for long-term success in an increasingly complex global landscape (Shahi, 2024).
Findings and Discussions
This section explores the hypotheses developed to understand the relationship between various factors in the context of Future Leadership Challenges and Opportunities Amidst Global Dynamics. These hypotheses are supported by an analysis of the benefits and challenges posed by Global Dynamics, a review of the latest literature, and insights drawn from the summary table of the interviewees (Iyer et al., 2024).
Hypothetical Decisions
H1: The research strongly supports the hypothesis that there is a significant relationship between Global Dynamics factors and Global Leadership Success factors. Global dynamics such as technological advancements, economic fluctuations, and geopolitical shifts directly impact the effectiveness and adaptability of leaders on a global scale. The study demonstrates that leaders who are attuned to these dynamic factors are better equipped to navigate complexities, anticipate challenges, and seize opportunities in a rapidly changing global environment. By staying informed and responsive to global trends, leaders can make more strategic decisions, foster innovation, and build resilient organizations that thrive in diverse markets. This relationship underscores the importance of global awareness and adaptability as key components of leadership success in today’s interconnected world (Holbeche, 2023).
H2: The research findings confirm that Organizational Culture factors significantly influence Global Leadership Success factors. A supportive organizational culture that promotes collaboration, inclusivity, and continuous learning creates a fertile ground for leadership success. The study reveals that leaders operating within cultures that value diversity, encourage open communication, and align with ethical principles are more likely to succeed on a global stage. Such cultures enable leaders to effectively harness the strengths of their teams, drive performance, and achieve organizational goals. Moreover, the alignment between organizational culture and leadership practices enhances employee engagement and fosters a positive work environment, contributing to sustained leadership effectiveness and organizational success (Bermeo et al., 2023).
H3: The research also supports the hypothesis that there is a significant relationship between Leadership Competencies factors and Global Leadership Success factors. The competencies that leaders possess, such as strategic thinking, emotional intelligence, and cross-cultural communication skills, are critical in achieving leadership success in a global context. The study highlights that leaders who exhibit strong competencies in these areas are better positioned to lead diverse teams, navigate complex international landscapes, and drive organizational success. Effective leaders leverage their competencies to inspire and motivate their teams, build trust, and execute strategies that align with both local and global objectives. This relationship emphasizes the need for leaders to continually develop and refine their competencies to remain effective in a globalized world (Groves et al., 2023).
H4: Finally, the research provides strong evidence that Ethical Considerations factors influence Global Leadership Success factors. Leaders who prioritize ethics, transparency, and accountability are more likely to achieve long-term success in their global leadership roles. The study shows that ethical leadership fosters trust, enhances organizational reputation, and mitigates risks associated with unethical behavior. Leaders who integrate ethical considerations into their decision-making processes are better equipped to handle ethical dilemmas, build sustainable relationships with stakeholders, and create a positive organizational culture. This influence underscores the critical role that ethical leadership plays in achieving and sustaining global leadership success, particularly in a world where ethical breaches can have widespread and lasting consequences (Hyatt et al., 2023).
In recent years, leaders in the Asian-Middle East region have adeptly navigated global dynamics by leveraging opportunities and addressing challenges unique to this geopolitical landscape. For instance, UAE leaders have capitalized on the region's strategic location as a global trade hub by fostering economic ties with Asian economies, particularly China and India. At the same time, these leaders have faced challenges such as geopolitical tensions and shifting economic conditions. In response, they have implemented strategies to diversify their economies, enhance diplomatic relations, and invest in technology and sustainability to ensure resilience and long-term growth. These efforts reflect a nuanced understanding of the complex interplay between global opportunities and regional challenges, demonstrating a forward-thinking approach to leadership in the context of global dynamics. Leaders in the UAE are also leveraging opportunities presented by the region's economic growth and geopolitical significance while addressing challenges such as navigating cultural sensitivities and fostering an inclusive corporate culture amidst rapid globalization. These efforts not only enhance organizational performance but also contribute to the UAE's reputation as a progressive and inclusive society on the global stage. (Pontes et al., 2023).
Scrutiny of Future Leadership Facing Global Dynamics
Objective 1: Assessing the Impact of Technological Advancements on Leadership Practices and Strategies
The research effectively meets this objective by conducting a thorough analysis of how emerging technologies, such as AI, big data, and digital communication tools, are transforming leadership practices. Through interviews and a literature review, the study explores how leaders are leveraging these advancements to drive organizational success, enhance decision-making, and foster innovation. The findings underscore the importance of technological literacy for leaders and provide practical insights into integrating technology into leadership strategies to maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving global landscape. This involves examining how leaders are leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, and digital tools to enhance decision-making and drive innovation. Technological advancements offer leaders new ways to streamline operations, improve strategic planning, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. By integrating these technologies into leadership strategies, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, adaptability, and competitive advantage. This objective shows how embracing technological innovations can reshape leadership practices and contribute to achieving organizational goals.
Objective 2: Analyzing the Role of Economic Uncertainties and Geopolitical Shifts in Shaping Leadership Challenges and Opportunities
This objective is achieved by examining the complex interplay between global economic fluctuations, trade tensions, and geopolitical shifts, and their impact on leadership. The research highlights how leaders are adapting their strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities arising from these uncertainties. The study's analysis of recent global events provides a comprehensive understanding of how leaders navigate these challenges, offering valuable insights into the strategies and mindset required to lead effectively in a volatile global environment. Leaders must navigate these complexities by adapting their strategies to mitigate risks and seize emerging opportunities. By exploring recent global events and their implications for leadership, this objective seeks to provide insights into effective strategies for managing uncertainties and leveraging geopolitical dynamics to achieve organizational success.
Objective 3: Examining Resilience and Crisis Management Capabilities in Leadership
Developing resilience and crisis management capabilities is vital for effective leadership, particularly in times of uncertainty and disruption. This objective focuses on understanding how leaders build and utilize these capabilities to navigate crises such as economic downturns, natural disasters, or global pandemics. By exploring case studies and interviews, the research identifies key behaviors and strategies that enable leaders to maintain organizational stability and guide their teams through challenging situations. This objective aims to provide practical insights into enhancing resilience and crisis management skills, ensuring leaders are well-prepared to handle future disruptions and lead effectively in times of crisis. Through qualitative data, the study identifies key traits and behaviors that enable leaders to maintain stability and guide their organizations through turbulent times. The findings suggest that developing resilience and crisis management skills is essential for future leaders, providing actionable strategies to enhance these capabilities and ensure effective leadership during crises.
Objective 4: Providing Insights and Recommendations for Leadership Development and Training Programs
The study successfully meets this objective by offering targeted recommendations for leadership development and training programs based on the analysis of current and future leadership demands. The research emphasizes the need for programs that focus on technological proficiency, adaptability, and strategic thinking to prepare leaders for the challenges of the future. The insights gathered from the study inform the design of training initiatives that are aligned with the evolving leadership landscape, ensuring that future leaders are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to thrive in a dynamic global environment. By assessing the need for technological proficiency, adaptability, and strategic thinking, the research aims to inform the design of training programs that prepare future leaders for emerging challenges. This objective seeks to offer actionable insights and recommendations for developing comprehensive leadership training programs that equip leaders with the necessary tools and knowledge to excel in an evolving global landscape.
The Contribution and Originality (Value of the Research)
This research offers significant contributions and originality in the study of leadership amidst global dynamics, highlighting how emerging factors influence leadership practices and strategies. By exploring the impact of technological advancements, economic uncertainties, geopolitical shifts, and the development of resilience and crisis management capabilities, the research provides a comprehensive understanding of contemporary leadership challenges and opportunities. The originality of this research lies in its multi-dimensional approach, integrating technological, economic, and geopolitical factors to offer a holistic view of modern leadership dynamics. Firstly, the research advances the field by presenting a nuanced analysis of how technological advancements can transform leadership practices. It explores how leaders can harness emerging technologies to drive innovation, streamline operations, and achieve strategic goals, filling a critical gap in existing leadership literature. Secondly, by examining the role of economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts, the research provides valuable insights into how these global factors shape leadership strategies. It offers practical guidance for leaders to navigate complex and volatile environments, contributing to a deeper understanding of leadership in a global context. Thirdly, the focus on resilience and crisis management capabilities adds a unique dimension to leadership studies. The research identifies key strategies and behaviors that enable leaders to effectively manage crises and maintain organizational stability, providing actionable recommendations for enhancing leadership training and development. Finally, the research contributes by offering targeted recommendations for leadership development programs. By aligning these programs with the evolving demands of the global leadership landscape, it ensures that future leaders are well-equipped to handle emerging challenges and leverage opportunities for organizational success. Overall, the research's originality and contribution lie in its comprehensive examination of contemporary leadership dynamics, offering valuable insights and practical recommendations for enhancing leadership effectiveness in a rapidly changing global environment.
Implications of This Research
The research on leadership amidst global dynamics underscores the need for a paradigm shift in how leadership is conceptualized and practiced in today’s complex and evolving global environment. It highlights the profound influence of technological advancements, economic uncertainties, and geopolitical shifts on leadership strategies. This broader understanding encourages academic and professional discourse on the evolving nature of leadership and the importance of adaptive, forward-thinking approaches. The findings suggest a re-evaluation of traditional leadership theories and practices, advocating for a more integrated approach that considers the multifaceted challenges and opportunities leaders face globally.
Practical Implications
Practically, the research provides actionable insights for leaders and organizations seeking to navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing global landscape. By demonstrating how technological advancements can be leveraged for organizational success, the study guides leaders in adopting innovative tools and strategies to enhance operational efficiency and drive growth. The examination of economic and geopolitical factors offers practical advice on how to adapt strategies in response to global uncertainties, ensuring organizational resilience. Additionally, the focus on developing resilience and crisis management capabilities provides concrete strategies for leaders to effectively handle disruptions, thereby enhancing their preparedness and adaptability.
Social implications
Socially, the research emphasizes the importance of leadership practices that foster resilience, inclusivity, and adaptability in the face of global challenges. It highlights how effective leadership can drive positive social outcomes by promoting equitable practices, enhancing organizational culture, and addressing societal issues. By advocating for leadership that is responsive to economic and geopolitical changes, the research encourages leaders to contribute to social stability and cohesion. This approach not only benefits organizations but also has broader societal impacts by promoting ethical leadership practices and supporting community well-being during times of uncertainty.
Managerial implications
For managers, the research provides valuable guidance on how to align leadership development and training programs with the demands of the future leadership landscape. It emphasizes the need for integrating technological competencies, economic foresight, and crisis management skills into managerial training. Managers are encouraged to adopt flexible and innovative leadership strategies that respond effectively to global dynamics. The insights on resilience and crisis management also guide managers in preparing for and addressing potential disruptions, thereby improving organizational agility and competitiveness. Overall, the research equips managers with practical tools and strategies to enhance their leadership effectiveness in a complex global environment.
Limitations
This research, while providing valuable insights into leadership amidst global dynamics, has several limitations. Firstly, the study’s focus on qualitative methods, including interviews and case studies, may introduce subjectivity and potential bias in the analysis of leadership practices and strategies. The reliance on self-reported data from leaders and managers might not fully capture the objective challenges and opportunities they face. Secondly, the research is context-specific to the current global dynamics and may not account for rapid changes in technology, economic conditions, or geopolitical situations that could emerge in the near future. Additionally, the study's focus on specific regions and industries might limit the generalizability of its findings to other contexts or sectors. Lastly, the research may not fully explore the intersectionality of global dynamics with other organizational factors such as internal culture or individual employee experiences.
Future Research Directions
Future research could address these limitations by incorporating a mixed-methods approach that combines qualitative and quantitative data to provide a more comprehensive analysis of leadership practices. Longitudinal studies could be conducted to assess how leadership strategies and their effectiveness evolve over time in response to changing global dynamics. Expanding the research to include diverse geographical regions and industries would enhance the generalizability of the findings and offer a broader perspective on leadership challenges and opportunities. Additionally, exploring the intersectionality of global dynamics with organizational culture and employee experiences could provide deeper insights into how leaders can effectively address internal and external challenges. Future research could also examine emerging trends in technology, economic shifts, and geopolitical changes to ensure that leadership practices remain relevant and adaptive in an evolving global landscape.
Conclusion
This research has provided a comprehensive exploration of leadership practices amidst global dynamics, utilizing a qualitative methodology to gain deep insights into the intricate relationship between technology, economic uncertainties, geopolitical shifts, and leadership strategies. Through in-depth interviews and case studies, the study has effectively addressed the research objectives, offering valuable perspectives on how leaders can navigate and leverage global challenges and opportunities.
The qualitative approach has allowed for a nuanced understanding of the impact of technological advancements on leadership practices, revealing how leaders can harness technology to drive organizational success. It has also illuminated the role of economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts in shaping leadership challenges, providing actionable insights into how leaders can adapt to these complexities. The research further examined the development of resilience and crisis management capabilities, identifying strategies for effective leadership in times of uncertainty. Finally, the study has offered recommendations for aligning leadership development and training programs with future demands, ensuring that leaders are well-equipped to handle emerging global dynamics.
The hypotheses supported by this research—demonstrating the significant relationships between technological advancements, economic uncertainties, leadership competencies, and ethical considerations with global leadership success—validate the study's framework and contribute to the existing body of knowledge. By meeting its objectives, the research has not only deepened understanding of the factors influencing global leadership but also provided practical guidance for leaders seeking to thrive in an increasingly complex and dynamic global environment. This conclusion underscores the research's value in advancing leadership practices and preparing organizations for future challenges and opportunities.
References
Al-Surmi, A., Bashiri, M., & Koliousis, I. (2022). AI based decision making: combining strategies to improve operational performance. International Journal of Production Research, 60(14), 4464-4486.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Akhtar, M. W., Garavan, T., Javed, M., Huo, C., Junaid, M., & Hussain, K. (2023). Responsible leadership, organizational ethical culture, strategic posture, and green innovation. The Service Industries Journal, 43(7-8), 454-474.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Anwari, A., & Suzianti, A. (2024). Mapping future competencies: a comprehensive review of organizational challenges, competencies, and strategies to survive and compete in the digital era. Journal of Syntax Literate, 9(3).
Bagga, S. K., Gera, S., & Haque, S. N. (2023). The mediating role of organizational culture: Transformational leadership and change management in virtual teams. Asia Pacific Management Review, 28(2), 120-131.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Behie, S. W., Pasman, H. J., Khan, F. I., Shell, K., Alarfaj, A., El-Kady, A. H., & Hernandez, M. (2023). Leadership 4.0: The changing landscape of industry management in the smart digital era. Process safety and environmental protection, 172, 317-328.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bermeo, J. O., & Perez, M. A. (2023).Trends in human talent management of and impact on inclusive organizational culture. In Handbook of Research on Promoting an Inclusive Organizational Culture for Entrepreneurial Sustainability (pp. 241-263). IGI Global.
Blanchard, P. N., & Thacker, J. W. (2023). Effective training: Systems, strategies, and practices. SAGE Publications.
Bonaconsa, C., Nampoothiri, V., Mbamalu, O., Dlamini, S., Surendran, S., Singh, S. K., & Charani, E. (2024). Mentorship as an overlooked dimension of research capacity strengthening: how to embed value-driven practices in global health. BMJ Global Health, 9(1), e014394.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2023). Is thematic analysis used well in health psychology? A critical review of published research, with recommendations for quality practice and reporting. Health Psychology Review, 17(4), 695-718.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Carvalho, A. M., Sampaio, P., Rebentisch, E., McManus, H., Carvalho, J. Á., & Saraiva, P. (2023). Operational excellence, organizational culture, and agility: bridging the gap between quality and adaptability. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 34(11-12), 1598-1628.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Deng, C., Gulseren, D., Isola, C., Grocutt, K., & Turner, N. (2023). Transformational leadership effectiveness: an evidence-based primer. Human Resource Development International, 26(5), 627-641.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ekemezie, I. O., & Digitemie, W. N. (2024). Best practices in strategic project management across multinational corporations: a global perspective on success factorsand challenges. International Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research, 6(3), 795-805.
Figueiredo, P. C. N., Sousa, M. J., & Tomé, E. (2023). Integrative model of the leader competences. European Journal of Training and Development, 47(5/6), 533-564.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gorman, L., & Ward, A. M. (2023). Accountability. In Encyclopedia of Sustainable Management (pp. 22-28). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Groves, K. S., Feyerherm, A. E., & Sumpter, D. (2023). Cultural intelligence as a global leadership competency in disruptive contexts. In Handbook of Cultural Intelligence Research (pp. 214-231). Edward Elgar Publishing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hashimy, S. Q., Jahromi, A., Hamza, M., Naaz, I., Nyamwero, N. B., & HT, B. (2023). Nurturing Leadership and Capacity Building for Success: Empowering Growth. International Journal of Rehabilitation & Special Education, 3(2).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Holbeche, L. (2023). The agile organization: how to build an engaged, innovative and resilient business. Kogan Page Publishers.
Huda, M., Borham, A. H., Hashim, A., Ritonga, M., Almunawar, M. N., Anshari, M., ... & Hanafi, H. F. (2023, October). Strategic role of trust in digital communication: critical insights into building organizational sustainability. In Proceedings of the future technologies conference (pp. 387-403). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
Hyatt, J., & Gruenglas, J. (2023). Ethical Considerations in Organizational Conflict.
Iriani, N., Agustianti, A., Sucianti, R., Rahman, A., & Putera, W. (2024). Understanding Risk and Uncertainty Management: A Qualitative Inquiry into Developing Business Strategies Amidst Global Economic Shifts, Government Policies, and Market Volatility. Golden Ratio of Finance Management, 4(2), 62-77.
Jerab, D. (2023). How to Be an Effective Leader in Decision Making in an Unstable Environment. Available at SSRN 4525803.
Jerab, D., & Mabrouk, T. (2023). The role of leadership in changing organizational culture.
Joel, O. T.,& Oguanobi, V. U. (2024). Entrepreneurial leadership in startups and SMEs: Critical lessons from building and sustaining growth. International Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research, 6(5), 1441-1456.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Khokhar, M. S., Agashe, A., Deogaonkar, A., & Paralkar, T. A. (2023). Ethical Leadership and Corporate Social Responsibility in Diversified Business Groups: A Conceptual Model of Asian and Latin America. International Journal of Professional Business Review: Int. J. Prof. Bus. Rev.8(6), 19.
Kolasani, S. (2023). Leadership in business innovation and transformation, navigating complex digital landscapes and enterprise technology ecosystems and achieving sustainable growth in today’s rapidly evolving market. International Journal of Holistic Management Perspectives, 4(4), 1-23.
Kramskyi, S., Guo, X., Chmutova, I., Kryvobok, K.,& Lozova, T. (2024). The race for global leadership and its risks for world instability: Technologies of controlling and mitigation. Research Journal in Advanced Humanities, 5(1), 178-191.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kurniawan, D., Tambunan, D., & Dewi, G. C. (2024). Relationships Among Crisis Leadership, Innovation Capability, Implementation of Business Continuity Management, and Sustainable Performance in The Covid-19 Pandemic. The South East Asian Journal of Management, 18(1), 6.
Longenecker, C. O., & Wittmer, J. (2024). CEO reflections on leadership lessons from the global pandemic: back to basics during crisis. Leadership & Organization Development Journal.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Martinez, N., Kilag, O. K., & Macario, R. (2023). The Impact of Organizational Culture on Leadership Strategies in Crisis Management. Excellencia: International Multi-disciplinary Journal of Education (2994-9521), 1(5), 454-466.
McKenzie, C., Brophy, K., Konstanta, G., & Webster, L. (2023). A vision for change leadership: Trust, transparency and accountability at University of Wollongong Library. The Journal of Academic Librarianship, 49(3), 102710.
Mohammed, A. A., & AL-Abrrow, H. (2023). The impact of empowering and transformational leadership on organizational performance and innovation: the mediating role of shared leadership and moderating role of organizational culture in the Iraqi healthcare sector. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 31(7), 3532-3552.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Mosteanu, N. R. (2024). Adapting to the Unpredictable: Building Resilience for Business Continuity in an Ever-Changing Landscape. European Journal of Theoretical and Applied Sciences, 2(1), 444-457.
Murphy, M. C. (2024). Cultures of Growth: How the New Science of Mindset Can Transform Individuals, Teams and Organisations. Simon and Schuster.
Naeem, M., Ozuem, W., Howell, K., & Ranfagni, S. (2023). A step-by-step process of thematic analysis to develop a conceptual model in qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 22, 16094069231205789.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Nejati,M., Salamzadeh, Y., & Loke, C. K. (2020). Can ethical leaders drive employees’ CSR engagement?. Social Responsibility Journal, 16(5), 655-669.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Orozco, F., Kilag, O. K., & Parinasan, M. A. (2023). Navigating Unpredictability: Exploring Fundamental Components of Crisis Management in Organizational Settings. Excellencia: International Multi-disciplinary Journal of Education (2994-9521), 1(6), 1-11.
Pawar, S., & Dhumal, V. (2024). The role of technology in transforming leadership management practices. Multidisciplinary Reviews, 7(4), 2024066-2024066.
Pontes, D., Santos, V., Samões, O., Wang, S., & Figueiredo, R. (2024). Towards Internationalization: Exploring Economic Diplomacy in the Middle East (GCC). Economies, 12(4), 82.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rajagopal, N. K., Qureshi, N. I., Durga, S., Ramirez Asis, E. H., Huerta Soto, R. M., Gupta, S. K., & Deepak, S. (2022). Future of Business Culture: An Artificial Intelligence-Driven Digital Framework for Organization Decision-Making Process. Complexity, 2022(1), 7796507.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rayets, M., Tkachuk, V., Buryk, M., Kubitskyi, S., & Zhaldak, H. (2023). The role of leadership in stimulating innovation and the creative potential of the team.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rozell, E. J., & Spangler, H. (2024). Societal Impact: Beyond Frameworks. Electronic Journal of Business Ethics and Organization Studies, 29(1).
Shahi, S. G. (2024). Navigating Uncertainty: How Leaders Can Empower Employees in Times of Crisis. In Energy Crisis and Its Impact on Global Business (pp. 238-255). IGI Global.
Siddiqui, A. (2024). Managing Change in Organizational Culture: Strategies for Business Leaders. Advance Journal of Econometrics and Finance, 1(3), 56-62.
Singh, K., Abraham, R., Yadav, J., Agrawal, A. K., & Kolar, P. (2023). Linking CSR and organizational performance: the intervening role of sustainability risk management and organizational reputation. Social Responsibility Journal, 19(10), 1830-1851.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Tarba, S. Y., Frynas, J. G., Liu, Y., Wood, G., Sarala, R. M., & Fainshmidt, S. (2023). Strategic agility in international business. Journal of World Business, 58(2), 101411.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Uy, F., Kilag, O. K., Abendan, C. F., Macapobre, K., Cañizares, M. C., & Yray, F. (2023). Application of Adaptive Crisis Management Theory: The Dynamics of Leadership in Times of Crisis. Excellencia: International Multi-disciplinary Journal of Education (2994-9521), 1(5), 159-170.
Vera, D., Samba, C.,Kong, D. T., & Maldonado, T. (2020). Resilience as thriving: The role of positive leadership practices. Organizational dynamics.
Wallace, D. M., Torres, E. M., & Zaccaro, S. J. (2021). Just what do we think we are doing? Learning outcomes of leader and leadership development. The Leadership Quarterly, 32(5), 101494.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Walters, D. W., & Helman, D. A. (2023). The Value Chain Network: Unlocking Organizational Excellence Through Effective Operating Models. Springer Nature.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Woodhill, J., & Millican, J. (2023). Systems Thinking and Practice: A guide to concepts, principles and tools for FCDO and partners.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 23-Sep-2024, Manuscript No. AJEE-24-15287; Editor assigned: 25-Sep-2024, PreQC No. AJEE-24-15287(PQ); Reviewed: 02-Oct-2024, QC No. AJEE-24-15287; Revised: 09-Oct-2024, Manuscript No. AJEE-24-15287(R); Published: 16-Oct-2024