Review Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 1
Food Quality, Price Fairness, Location and Physical Environment and Customer retention: An Evidence from the Oriental Food Chains in Egypt
Khaled Gad, The Arab Academy for Science and Technology & Maritime Transport, Alexandria, Egypt
Citation Information: Gad, K. (2024). Food quality, price fairness, location and physical environment and customer retention: evidence from the oriental food chains in egypt. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(1), 1-13
Abstract
The goal of this study is to empirically investigate the relations between food quality, price fairness, location and physical environment, and customer retention in the oriental food chains in Egypt. In addition to that, this paper validates a model regarding the relations between the variables. The study's data were gathered through a survey with 410 valid answers. The results were analysed by employing Structural Equation Modelling technique (SEM) using Analysis Moment of Structures (AMOS) software. The main conclusions drawn from this study are: the direct effect between (perceived food quality, perceived price fairness, location & physical environment) and customer retention is statistically significant. The direct effect between (perceived food quality, perceived price fairness, location & physical environment) and customer satisfaction is statistically significant. The direct effect between customer satisfaction and customer retention is statistically significant. And finally, customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between (perceived food quality, perceived price fairness, location & physical environment) and customer retention.
Keywords
Food Quality, Price Fairness, Location and Physical Environment, Satisfaction, Retention.
Introduction
Egypt's GDP rose by 6.6% in fiscal year 2021/2022, compared to 3.3% the previous year. The restaurant industry is a rapidly growing and complex type of business all over the world. Egypt is a developing and overpopulated country where many individuals visit oriental food restaurants on a regular and infrequent basis. Building relationships with customers and offering quality service are essential in the restaurant industry (Saleem and Raza, 2014). Services are intangible; they cannot be measured and counted. In restaurants, food is delivered. Food services related to speed and reliability of delivery. Customer feelings, perceptions, and expectations are crucial in the restaurant industry for customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. Food category or a variety of food and service quality is both essential antecedents for restaurant choice and customer loyalty (Han et al., 2018).
In the restaurant industry, a highly competitive business climate makes it essential for businesses to exceed customer expectations in order to survive in the long run. Customer satisfaction is essential to the restaurant business since it may impact customer loyalty and retention at a low cost (Shariff et al., 2015). Customer perceived value of any product or service plays an important role in brand loyalty. Making customers loyal in a service factory, such as an oriental-food restaurant, is the ultimate objective of offering value-based service and food (Izquierdo-Yusta et al., 2019). Customer satisfaction is increased by the quality of food and service, competitive prices, and a pleasant environment (Jani and Han, 2015). Gaining loyal customers requires achieving high levels of customer satisfaction. Although they are also customers, managers and owners of restaurants view loyal customers as being significantly more important than casual ones (Espinosa et al., 2018). Restaurants can benefit from improved profitability, positive word of mouth, frequent visits from loyal customers, and reduced marketing and promotional expenses when customer satisfaction levels are higher. The importance of service quality in exceeding customers' expectations for a given service has long been recognized (Raza et al., 2020). More loyal customers are attracted when a greater degree of service quality is provided, as this improves consumer confidence in the product or service (Liu et al., 2017). Price has been observed to be a key component in evaluating the value of a certain service (Malik et al., 2020). The concept of perceived price fairness has also achieved substantial prominence among professionals in the field of service marketing (Yieh et al., 2007). The value received affects the customer's perception of a service's price fairness (Andres-Martnez et al., 2014).
Currently, restaurant owners are giving much attention to customer satisfaction and retention because it is very much related to their business profitability. There is a dearth of research regarding customer satisfaction and retention in a service factory like oriental food restaurant business in Egypt till date.
Literature Review
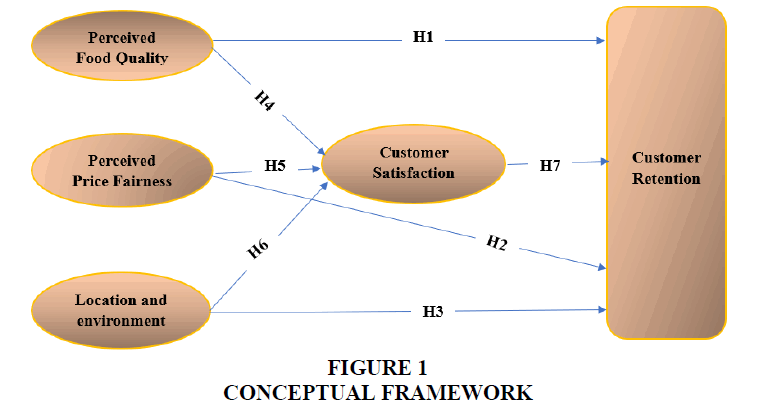
Food quality, price fairness, location and physical environment are considered the independent variables, customer satisfaction is considered the mediator variable and customer retention is considered the dependent variable.
Location and Physical Environment, Price Fairness, Food Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is the evaluation or feelings a customer has about a product, service, or experience after comparing their expectations to the actual performance or outcome (Kotler and Keller, 2016; Cuison et al., 2021). Customer satisfaction is essential to a company's success because satisfied consumers are more likely to repurchase products or services and recommend the company to others, whereas dissatisfied customers are more likely to switch to rivals and share their negative experiences. Satisfying customer needs is a company's objective, which increases its competitive advantage (Cuong, 2020).
A strong predictor of future success is the location in which a restaurant operates. Parsa et al. (2011) suggested that factors such as service quality, price fairness, and expert administration may be ineffective if a restaurant does not have a superior location. The main characteristics of an ideal location for a restaurant are simple access, volume, the total number of residents in the area, the level of rivalry, and the population's financial position (Hanaysha, 2016). Location and physical environment (decoration, layout, illumination, color, etc.) affect a customer's expectations and perceptions, and consequently their level of satisfaction (Belal, 2019).
According to Campbell (2007), price fairness is "a consumer's subjective perception that a price is fair, just, or legitimate as opposed to incorrect, unjust, or illegitimate." Occasionally, consumer’s judge the fairness of a price based on a rival's pricing (Xia et al., 2004). Surprisingly, the growing acceptance of pricing justice may also result in increased consumer satisfaction and loyalty (Jin et al., 2019). Similarly, if the price is considered unfair or unreasonable, dissatisfaction will result. This type of behavioural connection tends to occur in the food service restaurant industry, where reasonable or equitable pricing is associated with increased customer loyalty and commitment (Nikbin et al., 2016). Indeed, prices that are competitive or reasonable have a substantial impact on consumer repurchase intentions and satisfaction (Kotler and Keller, 2012).
A difficult task for restaurant businesses involves providing fresh, high-quality food. A satisfied customer may be a valuable referral source, but only if the food is of a satisfactory standard. The quality of food is a major priority for both consumers and businesses (Ryu and Han, 2010). It is expected that food quality is related to customer satisfaction (Bujisic et al., 2014).
Location and Physical Environment, Price Fairness, Food Quality and Customer Retention
Customer retention is defined as a company's capacity to maintain favourable customer relations sufficient for customers to continue purchasing its products or services (Kotler et al., 2008). According to Wertz (2018), customer retention is more cost-effective than acquiring new customers. As a result of businesses' customer retention strategies, retained loyal customers are willing to pay more, make more purchases, and resist switching brands (Evanschitzky et al., 2012). Therefore, retaining loyal customers is essential for businesses (Shsarma et al., 2020).
The well-located and ample parking space is advantageous for both the restaurant management and the customers, who frequently view the cost of obtaining parking near a restaurant as a non-revenue-generating expense. This explains the value of convenient parking as well as the direct effect it has on consumer intentions to dine at a restaurant (Warraich et al., 2013). All of these factors increase the customer retention rate and loyalty to that restaurant (Bateson and Hoffman, 1999). The restaurant's physical environment is another factor that can contribute to its competitive advantage. The physical environment of a restaurant comprises all the tangible and intangible elements that exist inside and outside. These expenditures are the most essential investments for attracting customers (Azim et al., 2014), so restaurant managers should make substantial investments in interior designs, decorations, floor cleanness, and other accessories that will improve the physical environment.
A well-maintained physical environment in a restaurant should then provide customers with a memorable experience and make them willing to return frequently. Choi et al. (2013) highlighted that the physical environment consists of aesthetics, surrounding, functionality, and convenience. Several scholars and restaurant managers have emphasised the significance of constructing a visually stunning physical environment as a significant factor in enhancing the retention and satisfaction of customers in the hospitality industry (Ryu and Han, 2010).
According to the Price Fairness literature, customer price fairness evaluations directly influence post-purchase attitudes and behaviours (Rothenberger, 2015) and result in positive or negative word-of-mouth and repurchase intentions. Empirical studies have also supported a strong, positive relationship between perceived price fairness and customer retention (Mansuthi and Han, 2020).
According to Namkung and Jang (2007), food quality was linked to utilitarian values. The concept of food quality is determined by price, flavour, menu choice, portion size, and healthiness options. The empirical study confirmed that the numerous food characteristics serve as genuine indicators of quality. From the perspective of customers, food quality is the key determinant in restaurant selection, according to Susskind and Chan (2000). Mattila and Wirtz (2001) further stated that restaurant food quality is the key determinant of customer loyalty in casual dining restaurants. In support, Grunert (2005) stated that consumer choice and demand are related to food quality. According to these studies, there may be an important relationship between food quality, customer satisfaction, customer retention, and customer loyalty.
Customer Satisfaction and Customer Retention
According to Kumar (2012), Lombard (2009), Santouridis & Trivellas (2010), customer satisfaction with services is defined as the extent to which service performance meets or exceeds the customer's expectations. In a similar vein, Hui and Zheng (2010) defined satisfaction as an assessment of a particular transaction as a result of perceived quality. However, customer retention is characterised by Danesh, Nasab, and Ling (2012) as "the future propensity of a customer to stay with the service provider". They argued that there are other factors that participate in the retention of customers in addition to customer satisfaction. Customer retention was defined by Ramakrishnan (2006, cited in Molapo and Mukwada, 2011) as the marketing objective of keeping a customer from switching to a rival. According to Edward and Sahadev (2011), "customer retention indicates customer's intention to repurchase a service from the service provider." The customer's intention to stay loyal to the service provider was identified by customer retention. For them, customer satisfaction and service quality are crucial antecedents of customer retention.
Satisfied customers are typically more likely to return to a firm and make repeat purchases, resulting in customer retention (Singh et al., 2021; Slack et al., 2020c). Customer satisfaction has been shown to have a direct, positive effect on customer retention in several studies (Byun and Jang, 2019; Kim et al., 2020; Singh and Slack, 2020). This result that customer satisfaction is related positively to customer retention has been supported by various empirical studies of the restaurant business (Ryu et al., 2012; Zhong and Moon, 2020). Numerous studies have linked customer satisfaction with retention, and it has been suggested that in order to keep customers, managers must understand this relationship (Sim et al., 2006).
Conceptual Framework
Based on the literature review discussed above, the research conceptual framework was formulated as below Figure 1.
Measurement
The independent variables (food quality, perceived price fairness, location and physical environment) are adapted from (Belal Uddin, 2019; Ahmed et al., 2023; Singh et al., 2022). The mediator variable (customer satisfaction) is the measured by (Belal Uddin. 2019). In addition to that, the dependent variable customer retention is adapted from (Singh et al., 2022; and Al-Tit, 2015).
Research Methodology
This research aims to examine the relationship between food quality, price fairness, location, physical environment as well as customer retention, with the customer satisfaction of oriental food establishments in Egypt serving as a mediator. Quantitative research based on an online survey was chosen as the methodological approach (Creswell, 2013). The questionnaire data is analysed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) for quantitative data analysis, including descriptive statistics (frequencies and percentages), and Structural Equation Model analyses (SEM) using Analysis Moment of Structures (AMOS) software for the hypothesised model analysis.
Results
Seven hundred (700) respondents received the research questionnaire, 482 questionnaires representing 68.9% were returned, 72 questionnaires representing 10.3% were incomplete, ineligible, or refusals, and 218 (31.1%) were unable to be reached. With 410 valid responses and a response rate of 58.6%, the response rate for this study is more than adequate. Measurement items have standardised loading estimates of at least 0.5 (ranging from 0.607 to 0.912 at the 0.05 alpha level), indicating the convergent validity of the measurement model. Discriminant validity shows how different a construct is from other constructs (Hair et al., 2019).
According to Hair et al. (2019), the Average Variances Extracted (AVE) has to be greater than 0.50 at all times. The AVEs of the constructs are higher than 0.50 (Perceived Food Quality = 0.720, Perceived Price Fairness =0.575, Location and physical Environment= 0.620, Customer Satisfaction =0.789, and Customer Retention =0.698). Generally speaking, these measurement findings are adequate and support continuing with the structural model testing. The reliability of a construct in a measurement model is calculated using Composite Reliability (CR). CR (Food Quality Perceived = 0.928, Price Fairness Perceived = 0.843, Location and Physical Environment Perceived = 0.889, Customer Satisfaction Perceived = 0.937, and Customer Retention Perceived = 0.920). All constructs in the measurement model were found to have high reliability, as was expected. Overall, CR is a more presentable technique of reliability since it demonstrates the construct's consistency (Hair et al., 2019).
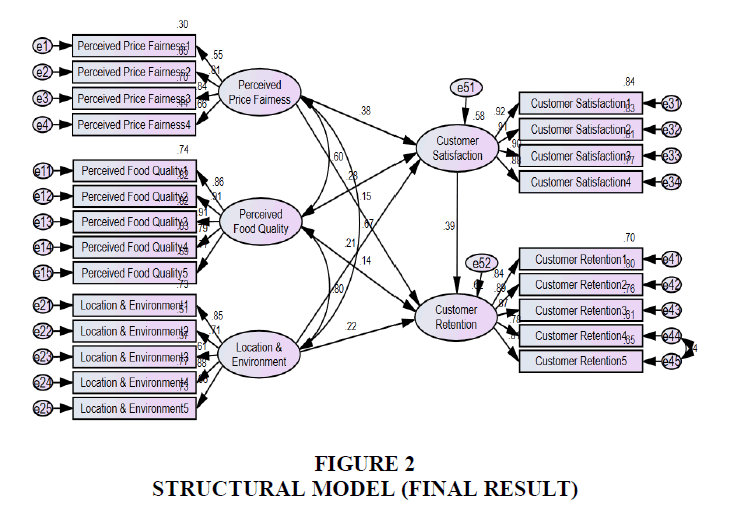
Hair et al. (2019) claim that the relationships between the latent variables show that each of the hypothesised effects generated for this research model accurately reflects the significance and degree of each impact, resulting in a good model fit. Overall, a model's fitness measurement was higher than what was considered to be acceptable because each test for the significance of the relationship between the variables was conducted individually. It demonstrates that there is a relationship between customer retention and perceived food quality (=0.136, CR (Critical Ratio) = 1.992, CR>1.96, p=0.046, p=0.05). Therefore, it is supported that (H1: Perceived food quality has an impact on customer retention in Egyptian oriental food chains) Figure 2.
Structural Model
Furthermore, the hypothesis (H2: Perceived price fairness has an impact on Customer Retention in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported as the result shows that ( = 0.148, CR (Critical Ratio) = 8.308, CR > 1.96, p=0.000, p0.05), as it predicts that " There is a relationship between Perceived price fairness and Customer Retention ". The result shows that (H3: location and physical environment have an impact on customer retention in oriental food chains in Egypt) is supported because (β = 0.217, CR (Critical Ratio) = 3.036, CR > 1.96, p = 0.002, p0.05), as it predicts that "There is a relationship between location and physical environment and customer retention".
The finding indicates that (H4: perceived food quality has an impact on customer satisfaction in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported as the result shows that ( = 0.279, CR (Critical Ratio) = 8.128, CR > 1.96, p = 0.000, p0.05), as it predicts that " There is a relationship between Perceived food quality and the Customer Satisfaction ". In addition, the fifth hypothesis (H5: perceived price fairness has an impact on customer satisfaction in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported as the result shows that ( = 0.376, CR (Critical Ratio) = 26.384, CR > 1.96, p = 0.000, p0.05), as it predicts that " There is a relationship between perceived price fairness and customer satisfaction ". Furthermore, (H6: location and physical environment have an impact on customer satisfaction in oriental food chains in Egypt) is supported as the result shows that ( = 0.205, CR (Critical Ratio) = 3.917, CR > 1.96, p = 0.000, p0.05), as it predicts that "There is a relationship between Location and Physical Environment and Customer Satisfaction ".
Furthermore, (H7: customer satisfaction has an impact on customer retention in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported by the result, which shows that (=0.391, CR (Critical Ratio) = 8.128, CR > 1.96, p = 0.000, p0.05), as it predicts that "There is a relationship between customer satisfaction and customer retention ". The results demonstrate that customer satisfaction has a statistically significant indirect impact on perceived food quality and customer retention (P = 0.003, P0.05). The mediation effect results show that there is a partial mediation effect of customer satisfaction between the relationship between perceived food quality and customer retention. As a result, the hypothesis (H8: customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between perceived food quality and customer retention in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported. The findings also demonstrate that perceived price fairness has a statistically significant indirect impact on customer retention via customer satisfaction (P = 0.002, P0.05).
The mediation effect results show that there is a partial mediation effect of customer satisfaction between the perceived price fairness and customer retention. As a result, the hypothesis (H9: customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between perceived price fairness and customer retention in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported. Finally, results demonstrate that location and physical environment have a statistically significant indirect impact on customer retention via customer satisfaction (P = 0.037, P0.05). The mediation effect results show that there is a partial mediation effect of customer satisfaction between the relationship between location and physical environment and customer retention. As a result, (H10: customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between location, physical environment, and customer retention in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported.
Discussion
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the relationship between food quality, price fairness, location and physical environment, as well as customer retention, with the mediation role of customer satisfaction in oriental food chains in Egyptian. Additionally, a model explaining the relationships between the variables is validated in this paper. Hair et al. (2019) claim that the relationships between the latent variables show that each of the hypothesised effects generated for this research model accurately reflects the significance and degree of each effect, resulting in a good model fit. Overall, a model's fitness measurement was higher than what was considered to be acceptable. The hypothesis (H1: Perceived Food Quality Has an Impact on Customer Retention in Oriental Food Chains in Egypt) is supported by the individual tests of significance of the relationship between the variables. This result is consistent with claims made by Namkung and Jang (2007) and Grunert (2005) that consumer food quality is linked to consumer utilitarian values.
The idea of food quality is determined by the cost of food, tastiness, food quantity, menu choice, and healthiness alternatives since it is regarded as the key determinant in restaurant selection (Susskind and Chan, 2000). Furthermore, the results show that (H2: perceived price fairness has an impact on customer retention in the oriental food chains in Egypt ) is supported. This is compatible with the findings of Manosuthi and Han (2020), who found a strong, positive relationship between customer perception of price fairness and customer retention, as well as that customer perceptions of price fairness impact consumer engagement in frequent purchases. Furthermore, studies in the restaurant business (Singh et al., 2022; Clemes et al., 2010; Han and Ryu, 2009; Hyun, 2010) confirmed the positive effect of customer-perceived price fairness on customer retention, as well as the risk to customer retention when customers consider pricing to be unfair. According to Hanaysha (2016), Nawaz (2013), and Aksel (2013), price fairness is a strong predictor of customer retention in the restaurant business. According to the findings of Rothenberger (2015), clear pricing is the most crucial element in the success of a restaurant. The result shows that (H3: location and physical environment have an impact on customer retention in Egyptian oriental food chains) is supported. Previous studies supported the idea that a restaurant's location is a key factor in customer retention and revisit intentions.
According to studies (Ahmed et al. 2019; Minai and Lucky, 2011), restaurants that are located in prominent locations with ample parking and a positive physical environment attract customers. Furthermore, a study done by Voon (2017) revealed that these aspects contribute to customer retention since fair prices cannot attract customers if the physical surroundings of the restaurant are inadequate. Hanaysha (2016) examined the drivers of customer retention in the restaurant business. The study revealed that the accessibility and visibility of a restaurant are significant factors affecting customer retention. According to Canny (2014), a restaurant's physical environment is a key marketing factor for differentiating itself by providing a memorable customer experience in a nice and comfortable environment. As a result, the physical environment has a greater impact on both acquiring and sustaining existing customers.
The result shows that (H4: Perceived food quality has an impact on customer satisfaction in the oriental food chains in Egypt). This is aligned with the findings of Namkung and Jang (2007), who found that the quality of food experienced a high impact on both repeated customer patronage and customer satisfaction. The degree of customer satisfaction has a relationship with both food and service quality. A higher level of satisfaction cannot be guaranteed by high-quality service without high-quality food. (Belal, 2019; Kim and Ham, 2016) Offering excellent standards of food and service quality could improve customer satisfaction.
In addition, the fifth hypothesis (H5: perceived price fairness has an impact on customer satisfaction in the oriental food chains in Egypt) is supported. This result is consistent with Kim et al., 2015; and Wang et al., 2018, who emphasised that consumers' perceptions of price fairness can have a substantial impact on their product or service satisfaction. If consumers perceive a product or service's price to be reasonable, they are more probable to be satisfied with their purchase. In turn, this increases the probability of retention and positive word-of-mouth recommendations (Liu & Jang, 2020; Wang et al., 2020; Jia et al., 2021). In addition, (H6: Location and physical environment have an impact on customer satisfaction in the oriental food chains in Egypt) is supported. Location and physical environment (decoration, layout, illumination, colour, etc.) affect a customer's expectations, perception, and consequently satisfaction (Belal, 2019). Due to Lam (2001) and Kwon et al., (2016), a customer’s entrance into a place and their emotions are both highly influenced by a good location and a pleasant atmosphere.
In addition, there is evidence to support (H7: customer satisfaction affects customer retention in the oriental food chains in Egypt). According to the literature (Berezina et al., 2012), retention is a result of service quality, customer satisfaction, and brand loyalty. Customer retention "indicates customer's intention to repurchase a service from the service provider," as stated by Edward and Sahadev (2011). Consequently, happy consumers are more likely to return to a restaurant and make further purchases (Singh et al., 2021; Slack et al., 2020c). Several prior studies (Byun and Jang, 2019; Kim et al., 2020; Singh and Slack, 2020) have assured the direct positive effect of customer satisfaction on customer retention. Our data supports the hypothesis that (H8: customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between perceived food quality and customer retention in oriental food chains in Egypt). Specifically between service quality and customer retention, customer satisfaction has been found to have a mediating role in several studies (Daz, 2017; Al-Tit, 2015; Jiang & Zhang, 2016).
Findings also show that (H9: customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between perceived price fairness and customer retention in the oriental food chains in Egypt) is supported. This is in line with Dawes (2009) and Han and Hyun (2015), who stated that customer satisfaction influences customers' perceived price fairness. El-Adly (2019) further suggested that customer satisfaction partially mediates the interrelationship between price and post-purchase behaviour. Results also show that (H10: customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between Location and physical environment and customer retention in Oriental food chains in Egypt) is supported. One of the most important variables that encourage consumers to choose a certain restaurant that satisfies their needs and wants about the quality of the food, the location of the restaurant, its accessibility easiness, and the environment of the restaurant. The location of a restaurant is a significant factor in customer retention and intentions to revisit. According to studies, consumers are more likely to revisit a restaurant that is conveniently located, has ample parking, and has a clean physical environment (Ahmed et al., 2019).
Model Validation
This paper developed and validated a model regarding the relationship between food quality, price fairness, location and physical environment and customer retention with mediation role of customer satisfaction of oriental food chains in Egypt using structural equation modelling. This is done through two steps:
First step, measurement model: the measurement model which consists of 5 latent variables, namely, Perceived Food Quality, Perceived Price Fairness, Location and physical Environment, Customer Satisfaction and Customer Retention.These 5 latent variables are measured by 23 observed variables. The standardized loading of the measurement items is performed to assess the internal consistency of the constructs in the measurement model. The level of internal consistency for each construct was acceptable, with the standardized loading ranging from 0.670 to 0.912 which exceeded the minimum hurdle of 0.50.
Second step, structural model summary: The 5 factor was subjected to CFA using the AMOS software. DF was 219 (it should be more than 0), χ2 /DF has a value of 2.328, that is less than 3.0 (it should be less than or equal 3.0). The RMSEA was .057 (it should be less than 0.08). The TLI index was .957 which is very close to 1.0 (a value of 1.0 indicates perfect fit). The CFI was .963. All indices are close to a value of 1.0 in CFA, indicating that the measurement models provide good support for the factor structure determined through the CFA.
Based on the outcome of the measurement model analysis and the structural model analysis, the research model was re-arranged to conform to the outcome of the two analyses, the final model is validated.
Author Contribution
This study is important both academically and practically. Academically, the current research fills the gap and adds to the body of knowledge. The research generated a model that provides knowledge to other models that have recommended expanding the area of the investigation using structural equation modeling. The results show that the estimated structural model corroborated the seven hypotheses,as Perceived Food Quality, Perceived Price Fairness and Location and physical Environment constructs explained 58.3 % of Customer Satisfaction variance (R2 = 0.583), Besides, Perceived Food Quality, Perceived Price Fairness and Location and physical Environment constructs through Customer Satisfaction explained 62 % of Customer Retention variance (R2 = 0.620).
The research findings have various practical implications for the development of the oriental food chains in Egypt. From the perspective of management, this research recognises the significance of various customer satisfaction criteria in predicting customer retention. Thus, restaurant owners and managers of oriental food chains should create an attractive environment and provide the necessary facilities to give customers a high perceived value, which will positively influence their satisfaction and willingness to continue eating and recommend the restaurant to others. Restaurant managers should pay close attention to the quality of service in their restaurants. Service quality is not directly measurable ; rather, it is the consumer's perception immediately following service delivery. Training for front-line workers, as well as time to deliver meals and receive a bill, are essential for improving service quality. Restaurants should deliver decent and healthy meals in terms of food quality. Price competitiveness plays an important role in the restaurant sector. Customers are extremely price sensitive, thus pricing strategies should be based on the competitor's pricing strategy as well as other internal and external concerns. client satisfaction factors such as food quality, price fairness, location, and environment are linked to client patronage and repeat purchase intentions. Customer retention is more likely when they are more satisfied.
References
Ahmed, S., Al Asheq, A., Ahmed, E., Chowdhury, U. Y., Sufi, T., & Mostofa, M. G. (2023). The intricate relationships of consumers’ loyalty and their perceptions of service quality, price and satisfaction in restaurant service.The TQM Journal,35(2), 519-539.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ahmed, u., kura, k. m., umrani, w. a., & pahi, m. h. (2019). modelling the link between developmental human resource practices and work engagement: the moderation role of service climate. Global Business Review,21(1), 31-53.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Al-Tit, A. A. (2015). The effect of service and food quality on customer satisfaction and hence customer retention.Asian social science,11(23), 129.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Andrés-Martínez, M. E., Gómez-Borja, M. Á., & Mondéjar-Jiménez, J. A. (2014). A model to evaluate the effects of price fairness perception in online hotel booking.Electronic Commerce Research,14, 171-187.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Azim, A., Shah, N. A., Mehmood, Z., Mehmood, S., & Bagram, M. M. M. (2014). Factors effecting the customers selection of restaurants in Pakistan. International Review of Management and Business Research,3(2), 1003.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bateson, J. E., & Hoffman, K. D. (1999). Managing services marketing: Text and readings.
Berezina, K., Cobanoglu, C., Miller, B. L., & Kwansa, F. A. (2012). The impact of information security breach on hotel guest perception of service quality, satisfaction, revisit intentions and word‐of‐mouth.International journal of contemporary hospitality management,24(7), 991-1010.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bujisic, M., Hutchinson, J., & Parsa, H. G. (2014). The effects of restaurant quality attributes on customer behavioral intentions.International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management,26(8), 1270-1291.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Byun, J., & Jang, S. (2019). Can signaling impact customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions in times of service failure?: Evidence from open versus closed kitchen restaurants.Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management,28(7), 785-806.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Campbell, M. C. (2007). “Says who?!” How the source of price information and affect influence perceived price (un) fairness.Journal of Marketing Research,44(2), 261-271.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Canny, I. U. (2014). Measuring the mediating role of dining experience attributes on customer satisfaction and its impact on behavioral intentions of casual dining restaurant in Jakarta.International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology,5(1), 25-29.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Choi, G., & Chung, H. (2013). Applying the technology acceptance model to social networking sites (SNS): Impact of subjective norm and social capital on the acceptance of SNS.International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction,29(10), 619-628.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Clemes, M. D., Gan, C., & Ren, M. (2011). Synthesizing the effects of service quality, value, and customer satisfaction on behavioral intentions in the motel industry: An empirical analysis.Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research,35(4), 530-568.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017).Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
Cuison, R. R., Ingalla, R. M. V., Amor, J. H. R. B., Remigio, J. L., Guerra, K. X., Arellano, G. A. D., & Francisco, C. D. (2021). The effects of perceived value and customer satisfaction in online businesses.International Journal of Academic Multidisciplinary Research,5(1), 41-45.
Cuong, D. T. (2020). The role of brand trust as a mediator in the relationship between brand satisfaction and purchase intention.International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation,24(6), 14726-14735 .
Danesh, S. N., Nasab, S. A., & Ling, K. C. (2012). The study of customer satisfaction, customer trust and switching barriers on customer retention in Malaysia hypermarkets.International Journal of business and Management,7(7), 141-150. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v7n7p141.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dawes, J. (2009). The effect of service price increases on customer retention: The moderating role of customer tenure and relationship breadth.Journal of service research,11(3), 232-245.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Edward, M., & Sahadev, S. (2011). Role of switching costs in the service quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction and customer retention linkage. Asia pacific journal of marketing and logistics,23(3), 327-345.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
El-Adly, m.i. and eid, r. (2016), “an empirical study of the relationship between shopping environment, customer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty in the UAE malls context.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services,31, 217-227.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Espinosa, J. A., Ortinau, D. J., Krey, N., & Monahan, L. (2018). I’ll have the usual: how restaurant brand image, loyalty, and satisfaction keep customers coming back.Journal of Product & Brand Management,27(6), 599-614.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Evanschitzky, H., Ramaseshan, B., Woisetschläger, D. M., Richelsen, V., Blut, M., & Backhaus, C. (2012). Consequences of customer loyalty to the loyalty program and to the company.Journal of the academy of marketing science,40, 625-638.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Grunert, K. G. (2005). Food quality and safety: consumer perception and demand.European review of agricultural economics,32(3), 369-391.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Babin, B. J., & Black, W. C. (2010). Multivariate data analysis: A global perspective (Vol. 7).
Han, H., & Hyun, S. S. (2015). Customer retention in the medical tourism industry: Impact of quality, satisfaction, trust, and price reasonableness. Tourism management,46, 20-29.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Han, H., & Ryu, K. (2009). The roles of the physical environment, price perception, and customer satisfaction in determining customer loyalty in the restaurant industry.Journal of hospitality & tourism research,33(4), 487-510.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Han, H., Xu, H., & Chen, H. (2018). Social commerce: A systematic review and data synthesis.Electronic Commerce Research and Applications,30, 38-50.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hanaysha, J. (2016). The importance of social media advertisements in enhancing brand equity: A study on fast food restaurant industry in Malaysia.International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology,7(2), 46.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hui, E. C., & Zheng, X. (2010). Measuring customer satisfaction of FM service in housing sector: A structural equation model approach.Facilities, 28(5/6), 306-320.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hyun, S. S. (2010). Predictors of relationship quality and loyalty in the chain restaurant industry.Cornell Hospitality Quarterly,51(2), 251-267.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Izquierdo-Yusta, A., Gomez-Canto, C. M., Pelegrin-Borondo, J., & Martínez-Ruiz, M. P. (2019). Consumers’ behaviour in fast-food restaurants: a food value perspective from Spain.British Food Journal,121(2), 386-399.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jani, D., & Han, H. (2015). Influence of environmental stimuli on hotel customer emotional loyalty response: Testing the moderating effect of the big five personality factors.International journal of hospitality management,44, 48-57.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jia, x., yang, x., & hu, m. y. (2021). impact of perceived price fairness on customer satisfaction and word of mouth intention: the moderating role of consumer expertise. journal of retailing and consumer services, 60, 102436.
Jiang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2016). An investigation of service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty in China's airline market.Journal of air transport management,57, 80-88.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jin, N., Merkebu, J., & Line, N. D. (2019). The examination of the relationship between experiential value and price fairness in consumers’ dining experience.Journal of Foodservice Business Research,22(2), 150-166.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kim, A. J., & Johnson, K. K. (2016). Power of consumers using social media: Examining the influences of brand-related user-generated content on Facebook.Computers in human behavior,58, 98-108.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kim, k., lee, y., & kim, h. j. (2015). consumer responses to price fairness: the effects of price presentation format. journal of business research, 68(4), 849-855.
Kim, W., Kim, H., & Hwang, J. (2020). Sustainable growth for the self-employed in the retail industry based on customer equity, customer satisfaction, and loyalty.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services,53, 101963.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kotler, p. and keller, k.l. (2012), marketing management, 14th ed., pearson education limited, upper saddle river, nj.
Kotler, p. and keller, k.l. (2016), marketing management, 15th ed., pearson, noida.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kumar, K. S. (2012). Expectations and Perceptions of Passengers on Service Quality with Reference to Public Transport Undertakings.IUP Journal of Operations Management,11(3).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kwon, H., Ha, S., & Im, H. (2016). The impact of perceived similarity to other customers on shopping mall satisfaction.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services,28, 304-309.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lam, S. Y. (2001). The effects of store environment on shopping behaviors: A critical review.ACR North American Advances.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Liu, S., & Jang, S. S. (2020). The influence of price fairness on customer satisfaction: The moderating roles of switching costs and perceived service quality. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 43, 21-31.
Liu, W. K., Lee, Y. S., & Hung, L. M. (2017). The interrelationships among service quality, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty: Examination of the fast-food industry.Journal of Foodservice Business Research,20(2), 146-162.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Roberts-Lombard, M. (2009). Customer retention strategies implemented by fast-food outlets in the Gauteng, Western Cape and KwaZulu-Natal provinces of South Africa: a focus on Something Fishy, Nando’s and Steers.African journal of marketing management,1(2), 70-80.
Malik, S. A., Akhtar, F., Raziq, M. M., & Ahmad, M. (2020). Measuring service quality perceptions of customers in the hotel industry of Pakistan.Total Quality Management & Business Excellence,31(3-4), 263-278.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Manosuthi, N., Lee, J. S., & Han, H. (2020). Impact of distance on the arrivals, behaviours and attitudes of international tourists in Hong Kong: A longitudinal approach.Tourism Management,78, 103963.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Mattila, A. S. (2001). Emotional bonding and restaurant loyalty.Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly,42(6), 73-79.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Minai, M. S., & Lucky, E. O. I. (2011). The moderating effect of location on small firm performance: Empirical evidence.International Journal of Business and Management,6(10), 178.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Molapo, M. E., & Mukwada, G. (2011). The impact of customer retention strategies in the South African Cellular Industry: the case of the Eastern Free State.International Journal of Business, Humanities and Technology,1(2), 52-60.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Namkung, Y., & Jang, S. (2007). Does food quality really matter in restaurants? Its impact on customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions.Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research,31(3), 387-409.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Nikbin, D., Marimuthu, M., & Hyun, S. S. (2016). Influence of perceived service fairness on relationship quality and switching intention: An empirical study of restaurant experiences.Current Issues in Tourism,19(10), 1005-1026.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Parsa, H. G., Gregory, A., & Terry, M. (2011). Why do restaurants fail? Part III: An analysis of macro and micro factors.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ramakrishnan, K. (2006). Customer retention: the key to business performance.Strategic Marketing .
Raza, S. A., Umer, A., Qureshi, M. A., & Dahri, A. S. (2020). Internet banking service quality, e-customer satisfaction and loyalty: the modified e- SERVQUAL model.The TQM Journal,32(6), 1443-1466.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rothenberger, S. (2015).Fairness through transparency: The influence of price transparency on consumer perceptions of price fairness(pp. 1-32). Univ Libre de Bruxelles, Solvay Brussels School of Economics and Management, Centre Emile Bernheim. available at:
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ryu, K., Han, H., & Jang, S. (2010). Relationships among hedonic and utilitarian values, satisfaction and behavioral intentions in the fast‐casual restaurant industry.International journal of contemporary hospitality management,22(3), 416-432.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ryu, K., Lee, H. R., & Kim, W. G. (2012). The influence of the quality of the physical environment, food, and service on restaurant image, customer perceived value, customer satisfaction, and behavioral intentions.International journal of contemporary hospitality management,24(2), 200-223.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Saleem, H., & Raja, N. S. (2014). The impact of service quality on customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and brand image: Evidence from hotel industry of Pakistan.Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research,19(5), 706-711.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Santouridis, I., & Trivellas, P. (2010). Investigating the impact of service quality and customer satisfaction on customer loyalty in mobile telephony in Greece.The TQM Journal,22(3), 330-343.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ahmad Shariff, S. N. F., Omar, M., Sulong, S. N., Mohd Abd Majid, H. A., Mohamad Ibrahim, H., Jaafar, Z., & Ideris, M. S. K. (2015). The influence of service quality and food quality towards customer fulfillment and revisit intention.Canadian Social Science,11(8), 110-116.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sim, J., Mak, B., & Jones, D. (2006). A model of customer satisfaction and retention for hotels.Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 7(3), 1-23.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Singh, G., Slack, N. J., Sharma, S., Aiyub, A. S., & Ferraris, A. (2022). Antecedents and consequences of fast-food restaurant customers' perception of price fairness.British Food Journal,124(8), 2591-2609.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Singh, G., Slack, N., Sharma, S., Mudaliar, K., Narayan, S., Kaur, R., & Sharma, K. U. (2021). Antecedents involved in developing fast-food restaurant customer loyalty.The TQM Journal,33(8), 1753-1769.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Singh, R., & Söderlund, M. (2020). Extending the experience construct: an examination of online grocery shopping.European Journal of Marketing, 54(10), 2419-2446.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Slack, N., Singh, G., & Sharma, S. (2020). Impact of perceived value on the satisfaction of supermarket customers: developing country perspective. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management,48(11), 1235-1254.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Susskind, A. M., & Chan, E. K. (2000). How restaurant features affect check averages: a study of the Toronto restaurant market.The Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly,41(6), 56-63.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Uddin, M. B. (2019). Customer loyalty in the fast food restaurants of Bangladesh.British Food Journal,121(11), 2791-2808.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wang, C., Lee, M. K., & Hua, Z. (2015). A theory of social media dependence: Evidence from microblog users.Decision support systems,69, 40-49.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wang, h., lu, y., gupta, s., & kabadayi, s. (2020). impact of price fairness on customer satisfaction and repurchase intention in sharing economy: the roles of social presence and perceived risk. journal of business research, 110, 238-248.
Wang, Y., Yu, H., & Wu, J. (2018). How online consumer reviews affect consumer willingness to pay price: a perspective of fairness and product experience. Journal of Business Research, 90, 325-334.
Warraich, U. A., Ahmad, N., & Qureshi, F. (2013). Customer retention in fast food industry.Indus Journal of Management Sciences,1(1).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wertz, J. (2018). Don’t spend 5 times more attracting new customers, nurture the existing ones.Forbes. Retrieved November,19, 2019. available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/jiawertz/2018/09/12/dont-spend-5-times-moreattracting- new-customers-nurture-the-existing-ones/?sh545e5fc6d5a8e (accessed 13 december 2020).
Xia, L., Monroe, K. B., & Cox, J. L. (2004). The price is unfair! A conceptual framework of price fairness perceptions.Journal of marketing,68(4), 1-15.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yieh, K., Chiao, Y. C., & Chiu, Y. K. (2007). Understanding the antecedents to customer loyalty by applying structural equation modeling.Total quality management & business excellence,18(3), 267-284.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zhong, Y., & Moon, H. C. (2020). What drives customer satisfaction, loyalty, and happiness in fast-food restaurants in China? Perceived price, service quality, food quality, physical environment quality, and the moderating role of gender.Foods,9(4), 460.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 21-Jun-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13724; Editor assigned: 22-Jun-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13724(PQ); Reviewed: 29-Sep-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13724; Revised: 18-Oct-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13724R); Published: 20-Nov-2023