Research Article: 2023 Vol: 26 Issue: 3S
Financial technology and its role in achieving economic development in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
Mohammed Khairy Tawfiq, Al-Balqa Applied University
Hamed Al Sheikh Abdullah, Al-Balqa Applied University
Citation Information: Khairy Tawfiq, M., & Sheikh Abdullah, H.AL. (2023). Financial technology and its role in achieving economic development in the hashemite kingdom of jordan. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 26 (S3), 1-8.
Abstract
This study aimed to identify the role of financial technology in the development of the economy in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, and this study spoke at the beginning of the concept of financial technology, and the most prominent stages of the development of this technology, as was the talk about financial technology and its development in the countries of the world, and at the end of the research was talking about financial technology In Jordan and how financial technology is increasingly developing thanks to special conferences and seminars in this field, and the role of the Central Bank of Jordan in developing this sector, which contributes positively to the development of the economy in Jordan.
Keywords
Financial Technology, Economic Development, The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, The Central Bank of Jordan.
Introduction
Financial technology, often abbreviated as FinTech or fintech, is technology and financial innovation that strives to eliminate old financial methods when providing any financial service to individuals, institutions and companies. It is considered as a new industry in which technology plays a major role in improving economic activities in the financing aspect. For example, smart and developed phones can be used in financial services or what is known as cellular banks, as well as investment services via mobile phone, and emerging and encrypted digital currencies, which seek to make banking services accessible to all individuals. FinTech firms are made up of financial start-ups, banking institutions and established technology firms seeking to make it possible for individuals to use or change the financial services offered by existing financial firms. Also, many banking institutions apply special financial technology solutions and technologies in order to improve customer service and work on developing it (Aldridge & Krawciw, 2017).
Financial technology provides huge opportunities, such as lower costs for customers, immediate payment, more choices and facilitation of services. Fintech will facilitate access to finance for individuals and owners of small and medium enterprises who lack adequate banking services, thus achieving higher and more inclusive growth for all segments of the population (Hussain & Carnemo, 2013).
Financial innovations are still spreading rapidly as a result of the accelerating pace of financial globalization in the world, and the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan cannot stand far from these developments at a time when the business environment in the Jordanian markets still needs further improvement and progress to keep pace with developments and events and achieve high economic development. This requires the support of financial technology, as its support and the provision of all its requirements helps to improve the business environment and improve the economic situation in Jordan (Fouad & Mustafa, 2021).
In this research, we will shed light on the role of financial technology in achieving economic development in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and what are the main challenges that stand in the way of its application (Warsame & Ireri, 2022).
Research Problem
Financial innovations are still spreading rapidly as a result of the accelerating pace of financial globalization in the world, and the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan cannot stand far from these developments at a time when the business environment in the Arab countries still needs further improvement and progress to keep pace with developments in events and achieve economic development. High, which requires the support of financial technology, as its support and the provision of all its requirements helps to improve the business environment and improve the economic situation in the Arab countries (Naz et al., 2022).
Research Aims
The research aims to study the improvement of the business environment and the status of the economy in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan through modern financial technology. The research also aims to identify the requirements for improving the situation in Jordan in order to improve the economy and the business environment in the Jordanian markets (Nishmitha, 2016).
The First Topic: The Concept of Financial Technology
The concept of financial technology can be defined as any technological development that is used in banking services in order to influence financial markets and institutions and provide better financial services. It can be defined as a natural product of merging financial operations with the uses of modern technology. Proposing technical solutions according to different business situations, and newly innovative ideas may also lead to finding new businesses, as well as all institutions that develop innovative financial services and products based on the extensive use of information technology, and among those services are electronic payment and electronic wallets, and the money transfer process, Insurance, borrowing and financing, investment services and financial trading platforms (Schueffel, 2016).
After reviewing many scientific papers that defined the term "fintech" as: a term in the new financial industry that works on applying modern technology to develop various financial services. It can also be considered that fintech is any innovative new idea that in turn improves the operations of various financial services, by developing technological solutions and suggestions according to what is required by the business, while these ideas can lead to new business models (Kanaan, 2009).
The Second Topic: The Development of Financial Technology
The financial technological development went through several stages, which we will learn about in this aspect, according to what was reported by the Central Bank of Egypt, 2023.
The First Stage (1866-1967)
This stage emerged with the passage of the first transatlantic communications cable, followed by the emergence of giant mainframe computers, which produced a number of financial technology-related products such as the Swift system (Kasim & Hussainey, 2022).
The Second Stage (1967-2008)
This stage appeared with the launch of Barclays Bank for the first ATM machine in 1967, the first appearance of the mobile phone in 1983, followed by the first appearance of online banking services in 1985, to end that stage with the global financial crisis in 2008 to make room for the emergence of a larger For fintech innovations in the next phase.
The Third Stage (2008 - Until Now)
The beginning of the emergence of new players, which are emerging companies specialized in the field of financial technology, and the emergence of a number of non-banking institutions that have become playing the role of banks in some functions. Also, the emergence of digital currencies in 2009, with the aim of providing payment solutions over the phone and the Internet, in 2011, transfer services appeared for the first time. Funds are transferred directly from one individual to another, as well as payment services via mobile phones. This stage can be called the stage of optimal exploitation of the most important technology resources, which is data.
The Third Topic: The Main Areas of Financial Technology
Financial technology has been used in many electronic businesses, which are industries, insurance, e-commerce, various financial services, and electronic risk management (Aldridge & Krawciw, 2017).
Financial services may originate from various independent service providers, including at least one licensed bank or insurance company. Communication is also activated through smart application programming pages that are open and available to all, and financial services provided by banks that are open to individuals and supported by regulations and laws.
In the global capital markets trading activity, innovative electronic trading platforms facilitate trading via Internet platforms and at the same time. Digital trading networks allow investors to monitor the trading activity and behavior of their peers, expert traders, and can follow their investment plans in the digital currency and capital markets. These platforms require little or no knowledge of financial markets and have been described by the World Economic Club as “disruptors” that provide a sophisticated, low-cost alternative to traditional wealth managers (McWaters et al., 2015).
Robo-advisors are a group of automated financial advisors that provide financial advice to individuals or manage investment via the Internet without the presence of an intermediary in order to reduce human intervention. These advisors also provide digital financial advice using mathematical rules or algorithms, and thus can provide lower-cost alternatives to human advisors (Lieber, 2014).
Global investment in the use of financial technology has increased by more than 2,200%, from $930 million in 2008 to nearly $22 billion in 2015 Accenture, 2017. The emerging financial technology industry in London has also grown significantly over the past years, and according to the Mayor of London’s office, 40% of the workforce in the City of London works in financial services and banking technology (hot topics. July 2014).
In continental Europe, nearly $1.5 billion was invested in financial technology companies and institutions in 2014, with companies located in London investing nearly $538 million, Amsterdam in the Netherlands $306 million, and Stockholm $266 million, and Stockholm ranked second after London in terms of financing in the financial sector in Europe over the last ten years, and financial technology deals in the continent of Europe increased fivefold, increasing from 47% in the last quarter of fiscal year 2015 to 47% in the first quarter of 2016 (Hussain & Carnemo Janlind, 2013).
As for the United States of America, investments in financial technology companies increased significantly, as investments reached $12.4 billion in 2018, up 43% from what they were in 2017.
In the Asia-Pacific region, a new financial technology hub opened in Australia, specifically in Sydney, in April 2015. According to KPMG, in 2017 Sydney's banking services sector contributed 9% of the national GDP, much more than the financial services sector. Based in Hong Kong and Singapore. And in 2015, the FinTech Innovation Lab was opened in Hong Kong. In 2015, the Monetary Authority of Singapore launched an initiative called FinTech and Information Suite to attract startups around the world. It pledged to spend $225 million in the financial technology sector over the next five years.
The Fourth Topic: Financial Technology in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
(According to what was stated in a statement by the Central Bank of Jordan, 2023), the Central Bank of Jordan believes that it is necessary to keep pace with the rapid developments, especially in the financial technology sector, in a way that serves the financial and banking sector and in a way that guarantees its protection, prevention and stability. The Central Bank opens channels of dialogue and cooperation to enhance the participatory approach, encourage youth capabilities, and support entrepreneurs.
In this context, the Central Bank seeks to make Jordan a platform for financial technology in the region, as the Central Bank of Jordan announces its commencement of establishing a Regulatory Sandbox to enable pioneers and owners of innovative ideas in the financial technology sector to apply to the Central Bank and obtain regulatory guidance and the possibility of examining these ideas technically. Before launching it to enhance the chances of success of these creative ideas, the Central aims to launch the regulatory laboratory at the end of June 2018.
The Central Bank of Jordan affirms its support for initiatives and innovations that use the latest global technology, including Blockchain technology, with priority for applications that enhance access to digital financial services easily, efficiently, and safely, while taking into account the controls to enhance cybersecurity for financial services in general.
In the same context, the Central Bank of Jordan reaffirms the prohibition of dealing in virtual currencies due to their high risks to their dealers, financial institutions and the national economy. The Central Bank carefully monitors all developments on virtual currencies, and conducts research and studies on them in cooperation with other central banks and international institutions (Warsame et al., 2022).
The Central Bank of Jordan also launched the regulatory laboratory for financial technology and innovation on 10/2018, as an initial step to keep pace with the financial technology that the world is witnessing, and for Jordan to always be supportive of this technology.
And in an article he published Titled "Financial Technology in Jordan Emerging but Promising", in which he spoke on the lips of the young Ali Tabbalat, On February 5th, the Jordanian fintech startup, GreenWallet, launched an online money-lending platform that allows users to request and receive a loan within 15 minutes. Behind this idea, which relies on a mathematical equation about ownership to assess the creditworthiness of the user, is the young Ali Tabbalat.
Tabbalat points out that the possibility of solving the global dilemma called 'financial inclusion' with practical methods encouraged him to establish a company in the field of financial technology.
He added that "the presence of more than 2.5 billion people in the world without formal financial services is a major problem, and a large percentage of them are located in the Middle East and Africa."
In North America and Europe, people take a bank account for granted, which is not the case in many emerging economies.
For example, Jordan, as well as several countries in the Middle East and North Africa, still rely on cash transactions and many of its citizens still do not deal with banks. According to Tabbalat, the percentage of Jordanians who own a bank account is 24%, while the percentage of those who can obtain loans is even lower.
This is due to several factors, including the cost of opening a bank account, the lack of branches in rural areas, and tedious bureaucratic hurdles.
According to Tabbal, “Traditional banks find it costly to serve these individuals, so the best solutions for that are those that rely on technology to serve a larger number of potential users.”Despite the lack of bank accounts in Jordan, the country's young population is growing, and Internet use is increasing.Young people under the age of 30 constitute more than 70% of the population, and 86% of the total population uses the Internet, and this will create a large consumer market that is preparing to look beyond the current financial sector and demand alternatives to a life that depends on cash.In addition, the economy of this country depends partly on remittances, as in 2015 the value of remittances to it reached nearly $900 million. This is mainly due to the emigration of skilled Jordanian workers to the Gulf countries and abroad and filling high-paid jobs. However, sending money to their families comes at a high cost, amounting to 10% of the value of the transfer in general (Vijai, 2019).
Therein Lie the Problems that Fintech is Trying to Address
MadfooatCom, EMB and Green Wallet, as well as other entrepreneurs in Jordan, are actively working in this field, offering consumers different ways to change the status quo in the financial sector.
In an interview conducted by TV Kingdom, 2022 with the Minister of Digital Economy and Entrepreneurship Ahmed Al-Hananda, where he said that Jordan is one of the first countries in adopting financial technology, and in pioneering, innovation and creativity in financial technology and providing solutions (Kauflin, 2019).
On the sidelines of his participation in the first Jordanian Financial Technology Conference and Exhibition, he added that Jordanian companies operating in the field of financial technology provide their services to more than 60 markets around the world. This is thanks to Jordan's geographical location and what distinguishes its youth working in this field in terms of knowledge and knowledge of all the surrounding markets (Vijai, 2019).
He stressed that Jordan has qualified human resources and cadres that make it a pioneer in dealing with financial technology. He added that the conference discusses important issues that are essential pillars in the processes of digital transformation and the transition to the digital economy, the most important of which are: digital and electronic payments and cybersecurity, indicating that the conference included a large group of companies and expertise working in these areas, which constituted an opportunity to exchange experiences, especially with The great development witnessed by these areas in terms of creativity and innovation in the solutions provided.
Al-Hananda pointed out the importance of financial inclusion as a basic pillar of digital transformation and the transition to the digital economy, which requires these digital tools in payments, as well as innovations and creativity in providing solutions, and that the financial sector in all countries of the world works to develop itself to support financial inclusion plans and facilitate access. To the digital and electronic payments of citizens.
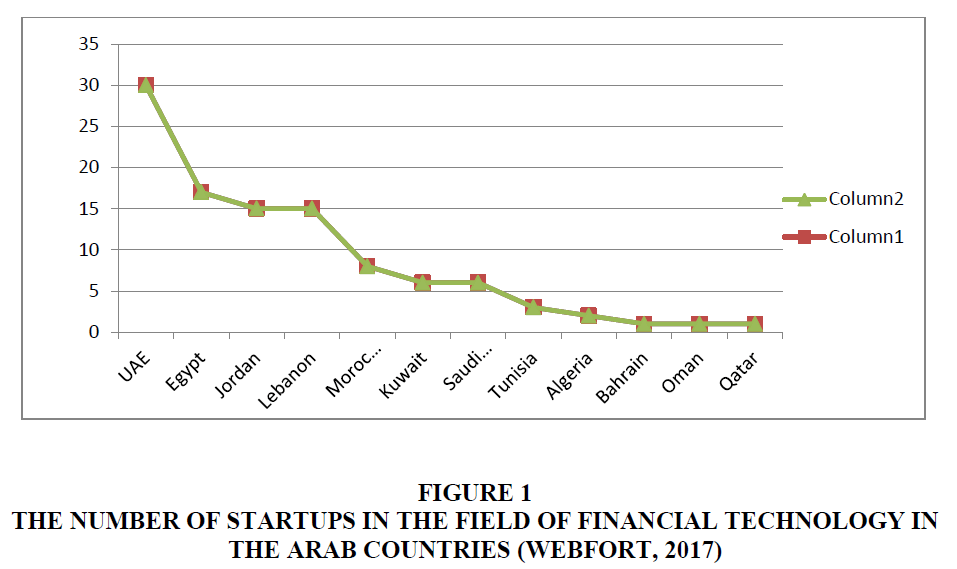
Through the previous Figure 1, it is clear to us that Jordan occupies a strong position in establishing companies specialized in financial technology, and this came by 15 companies, according to the Webfort report, which is therefore a positive result compared to the rest of the Arab countries, in which the United Arab Emirates ranked first in the list, and Egypt came third.
Figure 1 The Number of Startups in the Field of Financial Technology in the Arab Countries (Webfort, 2017)
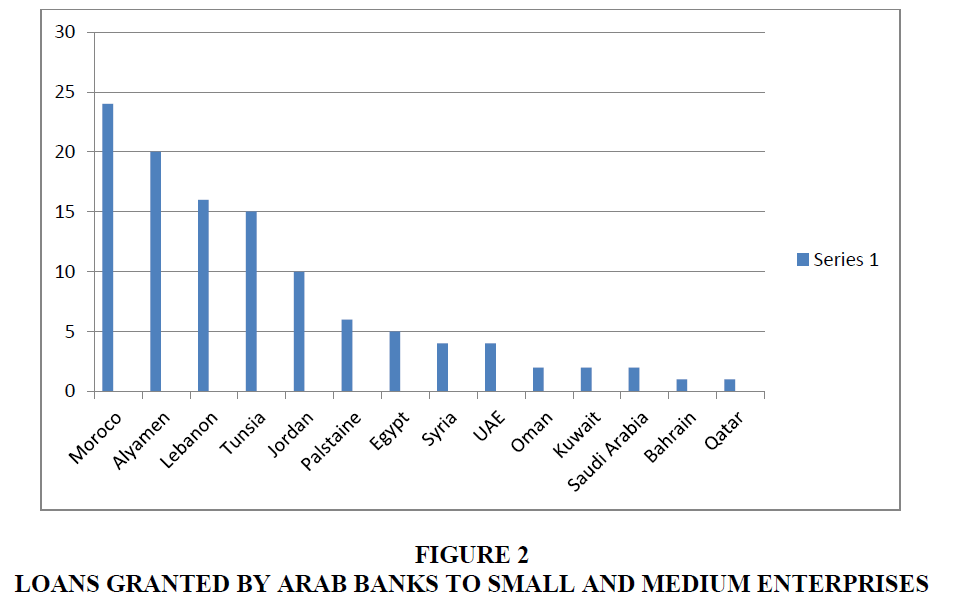
Loans are considered one of the most important things that large banks can offer to smaller banks in order to develop their work and use financial technology to the fullest extent, thus abandoning traditional methods of payment.
Through the previous table, it is clear that the emerging banks in Jordan granted them the equivalent of 10% by the large Arab banks, which is a high percentage compared to the rest of the Arab countries. It is not clear, and there is no central record of bank guarantees, and there are no credit agencies, as we notice from the previous Figure 2 that the percentage ranges between 1% to 4% only, and Morocco ranked first in the classification, with the support of emerging banks by 24%.
Conclusion
Jordan is one of the emerging countries in the use of financial technology and is trying hard to reach the knees of developed countries in this field, and this is evident through the attempts of the Central Bank of Jordan to work on developing financial technology in large and small banks, which contributes to supporting the economy, and the Ministry of Digital Communication works to hold conferences and seminars aimed at developing work in financial technology, and we do not rule out that Jordan will be one of the first Arab countries in the field of financial technology in the coming years.
References
Aldridge, I., & Krawciw, S. (2017). Real-time risk: What investors should know about FinTech, high-frequency trading, and flash crashes. John Wiley & Sons.
Fouad, I., & Mustafa. (2021). The role of financial technology in improving the business and economic environment in the arab countries. Scientific Journal, Faculty of Commerce, Assiut University, 71, 47-68.
Hussain, N., & Carnemo Janlind, S. (2013). The nature of business relationships towards suppliers in an international context: A quantitative study of the companies within the Stockholm Business Region and the Automation Region.
Kanaan, R. K. (2009). Making sense of e-government implementation in Jordan: A qualitative investigation.
Kasim, M., & Hussainey, K. (2022). Independence of Central Bank of Egypt and exchange rate regimes. In Handbook of Banking and Finance in the MENA Region. World Scientific.
Kauflin, J. (2019). The 11 biggest fintech companies in america 2019.
Lieber, R. (2014). Financial advice for people who aren’t rich. The New York Times, B1.
McWaters, R.J., Bruno, G., Lee, A., & Blake, M. (2015). The future of financial services: How disruptive innovations are reshaping the way financial services are structured, provisioned and consumed. In World economic forum 125,1-178.
Naz, F., Karim, S., Houcine, A., & Naeem, M. A. (2022). Fintech growth during COVID-19 in MENA region: current challenges and future prospects. Electronic Commerce Research, 1-22.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Nishmitha, N. (2016). Financial technology implications: indian context.
Schueffel, P. (2016). Taming the beast: A scientific definition of fintech. Journal of Innovation Management, 4(4), 32-54.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Vijai, C. (2019). FinTech in India–opportunities and challenges. SAARJ Journal on Banking & Insurance Research (SJBIR), 8.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Warsame, M. H., & Ireri, E. M. (2022). Fintechs’ Future in Kenya: Does Social Influence Matter?. Journal of African Business, 23(4), 1067-1087.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 04-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-13233; Editor assigned: 06-Feb-2023, Pre QC No. JMIDS-23-13233(PQ); Reviewed: 06-Feb-2023, QC No. JMIDS-23-13233; Revised: 21-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-13233(R); Published: 27-Feb-2023