Research Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 2
Financial Performance Measurement of Public Sector Banks with Special Reference on NPA
Nidhi Sharma, Manipal University Jaipur
Tailor R.K, Manipal University Jaipur
Citation Information: Sharma, N., & Tailor, R.K. (2024). Financial performance measurement of public sector banks with special reference on npa. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(2), 1-7.
Abstract
Banking sector is an important integral part of the financial system. It works as an effective tool in the growth of economy. Indian economy largely depends on the services providing by the banks as investment, infrastructure, credit and deposits. The banking industry works as a backbone for the whole economic activities. It helps in the development and GDP growth of the economy. Hence it is essential for banks to increase their profit by providing best services to their customers. In this paper an attempt has made to compare the NPA performance of selected public sector banks (SBI Bank, Punjab National Bank, Bank of India and Canara Bank). The period for the study is for five years i.e., from 2018-19 to 2022-23.
Keywords
Economy, Public Sector Banks, Banking Sector, Profit, Development, Growth.
Introduction
In recent years, the performance of public sector banks in India has garnered significant attention due to various challenges they have faced, particularly in managing non-performing assets (NPAs). ( Kumar & Singh, 2014)NPAs are loans and advances that have not been repaid by borrowers for a specified period, leading to a deterioration of banks' asset quality and financial stability. ( Siraj & Pillai, 2013) Analysing the performance of public sector banks and their handling of NPAs is crucial for understanding the overall health and efficiency of the banking sector in India. ( Agarwala & Agarwala, 2019)This comparative study aims to delve into the performance analysis of public sector banks in India, with a specific focus on NPAs. Public sector banks play a vital role in India's banking landscape, accounting for a significant market share and serving as the backbone of the country's financial system. ( Agrawal & Goyal, 2021)Understanding their performance and the factors influencing their NPA levels is crucial for formulating effective policies and strategies to address these challenges. (Biswas, 2014).
Therefore, this study on the performance analysis of public sector banks in India, with a focus on NPAs, holds significant importance in assessing the health of the banking sector and identifying measures to address the challenges faced by public sector banks, ultimately contributing to the overall stability and growth of India's economy. ( Chaudhary & Sharma, 2011)
Identifying Measures to Address the Challenges Faced by Public Sector Banks
Public sector banks in India have encountered several challenges in recent years, ranging from high levels of non-performing assets (NPAs) to operational inefficiencies. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving various stakeholders, including policymakers, regulators, bank management, and the banks themselves. (Das & Dutta, 2014)Here are some key measures that can be implemented to tackle these challenges:
1. Strengthening Credit Appraisal and Risk Management: Improving credit appraisal processes is crucial to identify potential risks and ensure that loans are granted to borrowers with sound financial positions. Banks should enhance their due diligence processes, adopt robust risk assessment models, and strengthen collateral and security mechanisms. Implementing effective risk management practices can help prevent the creation of new NPAs. (Hafsal, Suvvari, & Durai, 2020).
2. Enhanced Recovery Mechanisms: Public sector banks need to streamline and strengthen their loan recovery mechanisms. This includes adopting a proactive approach to identify and resolve stressed assets, employing specialized teams for recovery, utilizing legal frameworks effectively, and exploring alternative mechanisms such as asset reconstruction companies. Timely and efficient recovery of NPAs can help in reducing their overall burden on the banks' balance sheets. ( Ibrahim & Thangavelu, 2014).
3. Recapitalization and Adequate Capital Buffer: Public sector banks should maintain an adequate capital buffer to absorb losses arising from NPAs. Recapitalization measures, both from the government and through other means such as market capitalization or asset sales, can enhance banks' capital positions and strengthen their ability to withstand financial shocks. Adequate capitalization can also improve the banks' lending capacity and confidence in the market. (Joseph, 2014).
4. Governance and Accountability: Strengthening corporate governance practices within public sector banks is essential to enhance transparency, accountability, and risk management. This includes appointing qualified and experienced professionals in key management positions, ensuring the independence of boards, conducting regular audits, and establishing clear performance evaluation metrics. Good governance practices can help improve decision-making processes and minimize the occurrence of NPAs. (KAUR, 2012).
5. Technology Adoption and Digital Transformation: Embracing technology and digitization can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer experience for public sector banks. Implementing robust core banking systems, online platforms for loan applications, and digital payment solutions can streamline processes and reduce the risk of errors. Additionally, leveraging data analytics and artificial intelligence can aid in early detection of potential NPAs and enable proactive measures for risk mitigation. ( Lahaa & Biswas, 2019).
6. Training and Skill Development: Continuous training and skill development programs are crucial for employees of public sector banks to stay updated with industry trends, best practices, and emerging risks. Fostering a culture of learning and innovation can enhance the banks' ability to adapt to changing market dynamics and effectively address the challenges they face (Rastogi, et al. 2022).
7. Policy and Regulatory Reforms: Policymakers and regulators play a significant role in creating an enabling environment for public sector banks. Implementing reforms that facilitate ease of doing business, promote healthy competition, and strengthen regulatory oversight can contribute to the overall stability and performance of the banking sector. Regular monitoring and timely policy interventions can address systemic issues and promote a level playing field (Singh, 2013).
By implementing these measures, public sector banks in India can address the challenges posed by NPAs and enhance their overall performance and stability. It requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders to create a robust and resilient banking system that supports economic growth and financial inclusion. (Singh, 2016).
Objectives
Following are the main objective of the study:
To analyse the performance of selected public sector banks.
To Rank the selected banks by comparing their performance.
Data Collection
The present study is based on the secondary data of selected public sector banks. The secondary data has been collected through, published reports, annual reports and websites of the selected banks.
Period of Study
The study is based on the period from 2018-19 to 2022-23.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The data collection and analysis are as followed-
Interpretation
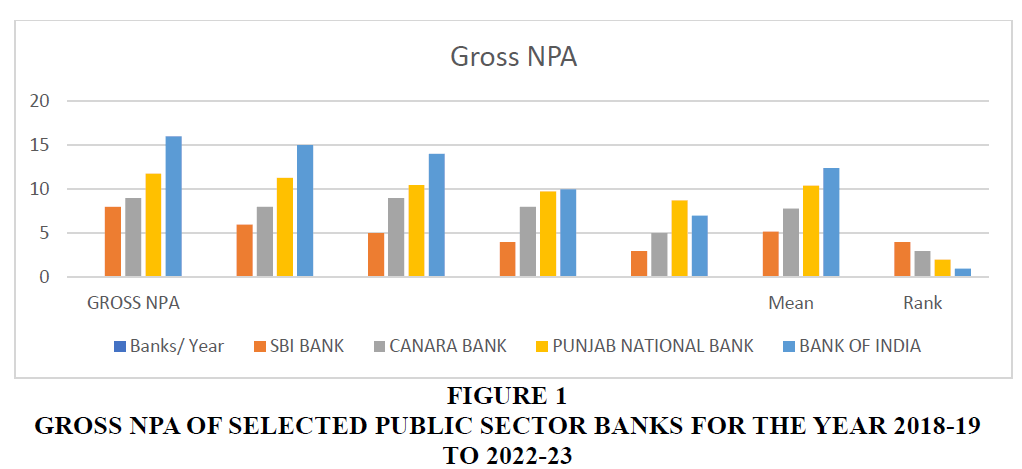
The above table 1 exhibits the gross NPA of public sector banks. As per the figure shown in the table the average of selected banks is SBI Bank 5.2, Canara Bank 7.8, Punjab National Bank 10.4 and Bank of India 12.4. Rank has allotted on the basis of their mean i.e., SBI Bank on 4th, Canara Bank 3rd, Punjab National Bank 2nd and Bank of India is on 1st rank Figures 1-4.
| Table 1 Gross NPA of Selected Public Sector Banks for the year 2018-19 to 2022-23 | |||||||
| GROSS NPA | Mean | Rank | |||||
| Banks/ Year | 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | ||
| SBI BANK | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 5.2 | 4 |
| CANARA BANK | 9 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 7.8 | 3 |
| PUNJAB NATIONAL BANK | 11.78 | 11.27 | 10.48 | 9.76 | 8.74 | 10.4 | 2 |
| BANK OF INDIA | 16 | 15 | 14 | 10 | 7 | 12.4 | 1 |
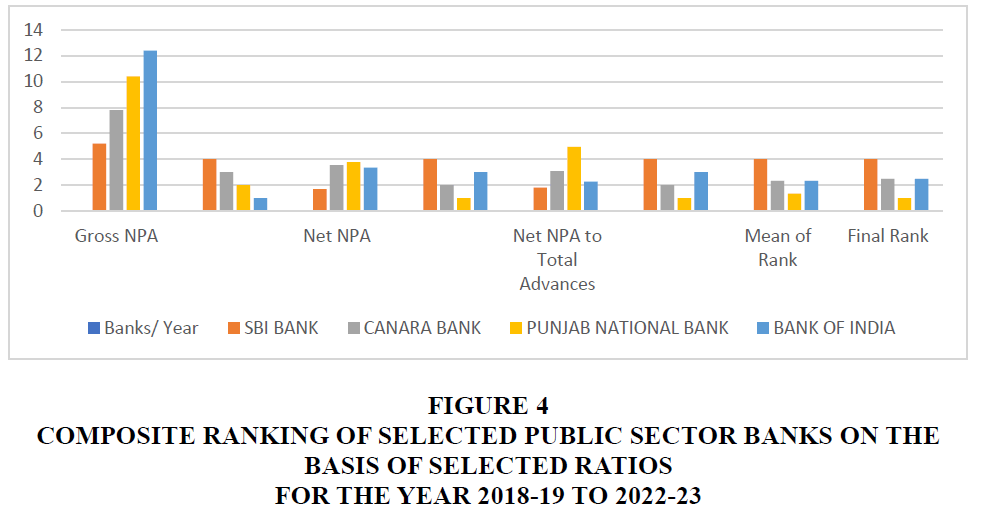
Figure 4 Composite Ranking of Selected Public Sector Banks on the Basis of Selected Ratios for the year 2018-19 to 2022-23
Interpretation
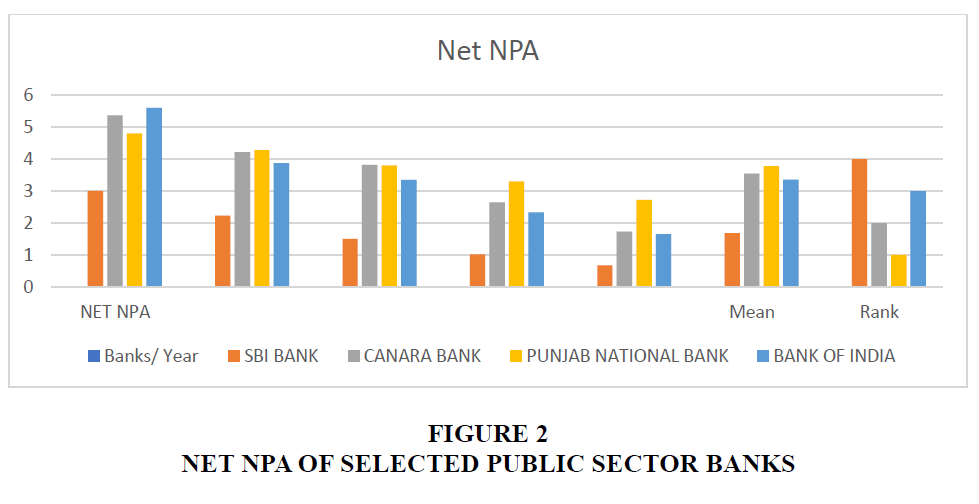
The above table 2 exhibits the Net NPA of public sector banks. As per the figure shown in the table the average of selected banks is SBI Bank 1.68, Canara Bank 3.55, Punjab National Bank 3.78 and Bank of India 3.36. Rank has allotted on the basis of their mean i.e., SBI Bank on 4th, Canara Bank 2nd, Punjab National Bank 1st and Bank of India is on 3rd position.
| Table 2 Net NPA of Selected Public Sector Banks for the year 2018-19 To 2022-23 | |||||||
| NET NPA | Mean | Rank | |||||
| Banks/ Year | 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | ||
| SBI BANK | 3.01 | 2.23 | 1.5 | 1.02 | 0.67 | 1.68 | 4 |
| CANARA BANK | 5.37 | 4.22 | 3.82 | 2.65 | 1.73 | 3.55 | 2 |
| PUNJAB NATIONAL BANK | 4.8 | 4.28 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 2.72 | 3.78 | 1 |
| BANK OF INDIA | 5.61 | 3.88 | 3.35 | 2.34 | 1.66 | 3.36 | 3 |
Interpretation
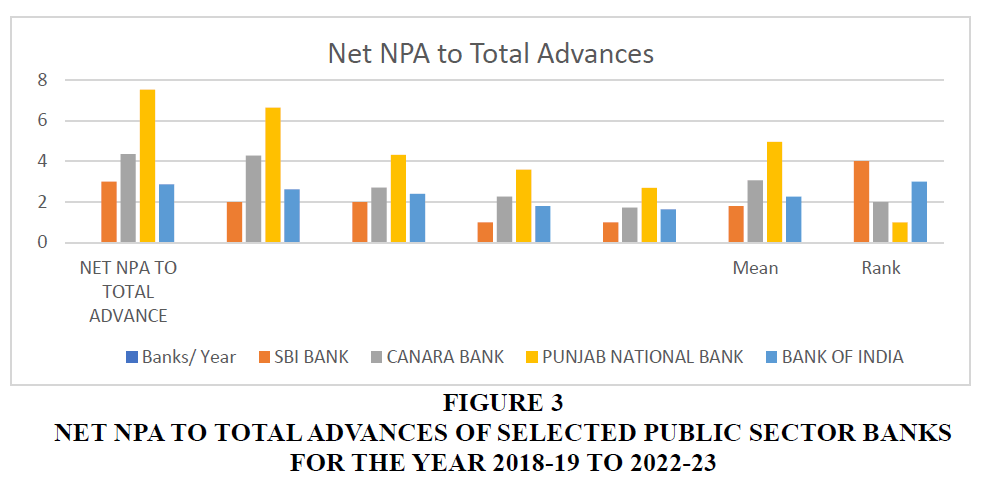
The above table 3 depicts the Net NPA to Total Advances of public sector banks. As per the figure shown in the table the average of selected banks is SBI Bank 1.8, Canara Bank 3.07, Punjab National Bank 4.96 and Bank of India 2.27. Rank has allotted on the basis of their mean i.e., SBI Bank on 4th, Canara Bank 2nd, Punjab National Bank is on 1st and Bank of India is on 3rd rank.
| Table 3 Net NPA to Total Advances of Selected Public Sector Banks for the year 2018-19 to 2022-23 | |||||||
| NET NPA TO TOTAL ADVANCE | Mean | Rank | |||||
| Banks/ Year | 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | ||
| SBI BANK | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1.8 | 4 |
| CANARA BANK | 4.36 | 4.28 | 2.7 | 2.27 | 1.72 | 3.07 | 2 |
| PUNJAB NATIONAL BANK | 7.54 | 6.65 | 4.32 | 3.59 | 2.69 | 4.96 | 1 |
| BANK OF INDIA | 2.87 | 2.63 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 1.64 | 2.27 | 3 |
Interpretation
The above table 4 shows the Composite Ranking of selected public sector banks. As per the figure shown in the table the mean of rank of selected banks is SBI Bank 1.8, Canara Bank 3.07, Punjab National Bank 4.96 and Bank of India 2.27. Final Rank has allotted on the basis of their mean of rank i.e., SBI Bank on 4th, Canara Bank 2.5th, Punjab National Bank is on 1st and Bank of India is on 2.5th rank.
| Table 4 Composite Ranking of Selected Public Sector Banks on the Basis of Selected Ratios for the year 2018-19 to 2022-23 | ||||||||
| Gross NPA | Net NPA | Net NPA to Total Advances | Mean of Rank | Final Rank | ||||
| Banks/ Year | Mean | Rank | Mean | Rank | Mean | Rank | ||
| SBI BANK | 5.2 | 4 | 1.68 | 4 | 1.8 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| CANARA BANK | 7.8 | 3 | 3.55 | 2 | 3.07 | 2 | 2.33 | 2.5 |
| PUNJAB NATIONAL BANK | 10.4 | 2 | 3.78 | 1 | 4.96 | 1 | 1.33 | 1 |
| BANK OF INDIA | 12.4 | 1 | 3.36 | 3 | 2.27 | 3 | 2.33 | 2.5 |
On the basis of the above analysis, it can be said that in terms of Gross NPA Bank of India is on top position as compared to other selected public sector banks. On the other hand, Punjab National Bank is leading with 1st position according to Net NPA and Net NPA to Total Advances table and chats. As per the statement of composite analysis of Gross NPA, Net NPA and Net NPA to Total Advances the table shows that Punjab National Bank is on the top position followed by the other banks. Whereas, Canara bank and Bank of India got the same position with the 2.5th rank and State Bank of India (SBI) is on least position. So as per analysis SBI Bank needs to work towards the improvement of Gross NPA, Net NPA and Net NPA to Total Advances. Canara Bank and Bank of India is on average position. So, the banks should also work towards their loan sanction services and policies.
Future Scope of the study
1. Time-series Analysis- Conduct a longitudinal study over a more extended period to analyse the performance trends of public sector banks in India. This analysis would allow researchers to identify patterns, cyclical behaviour and long-term effects of NPAs on bank performance.
2. Impact of Regulatory Framework- Study the influence of regulatory policies on NPAs in Public Sector Banks. Analyse the effect of Basel Norms, loan classification norms and provisioning requirements on NPA level and its implications for bank performance.
References
Agarwala, V., & Agarwala, N. (2019). A critical review of non-performing assets in the Indian banking industry. Rajagiri Management Journal, 12-23.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Agrawal, R. B., & Goyal, D. M. (2021). Non- Performing Assets of Banks: A Literature Review. PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/ Egyptology, 330-340.
Biswas, D. M. (2014). Performance evaluation of andhra bank & bank of maharashtra with camel model. International Journal of Business and Administration Research Review, 220-226.
Chaudhary, K., & Sharma, M. (2011). International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, 249-256.
Das, S., & Dutta, A. (2014). A Study on NPA of Public Sector Banks in India. Journal of Business and Management, 75-83.
Hafsal, K., Suvvari, A., & Durai, S. R. (2020). Efficiency of Indian banks with non performing assets: evidence from two stage network DEA. Future Business Journal, 1-9.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ibrahim, M. S., & Thangavelu, D. R. (2014). A Study on the Composition of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) of Scheduled Commercial Banks in India. Journal of Finance and Bank Management, 31-48.
Joseph, A. L. (2014). A Study o n Analyzing t he Trend o f NPA Level in Private Sector Banks and Public Sector Banks. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications. 259-267.
Kaur, A. (2012). An empirical study on the performance evaluation of public sector banks in india. International Journal of Marketing, Financial Services & Management Research, 117-131.
Kumar, N., & Singh, A. (2014). Efficiency Analysis of Banks using DEA: A Review. International Journal of Advance Research and Innovation, 120-126.
Lahaa, S., & Biswas, S. (2019). A hybrid unsupervised learning and multi-criteria decision making approach for performance evaluation of Indian banks. Growing Science, 169-184.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rastogi, S., Sharma, A., Pinto, G., & Bhimavarapu, V. M. (2022). A literature review of risk, regulation, and profitability of banks using a scientometric study. Future Business Journal, 1-17.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Singh, M. A. (2013). Performance of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) in Indian Commercial Banks. International Journal of Marketing, Financial Services & Management Research, 86-94.
Singh, V. R. (2016). A Study of Non-Performing Assets of Commercial Banks and it’s recovery in India. Annual Research Journal of Symbiosis Centre for Management Studies, 4(1), 110-125.
Siraj, K., & Pillai, P. S. (2013). Efficiency of NPA Management in Indian SCBs –A Bank-Group Wise Exploratory Study. Journal of Applied Finance & Banking, 123-137.
Received: 08-Sep-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13988; Editor assigned: 11-Sep-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13988(PQ); Reviewed: 29-Oct-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13988; Revised: 29-Dec-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13988(R); Published: 16-Jan-2024