Research Article: 2020 Vol: 24 Issue: 1
Factors Influencing Customers Buying Decision towards Shopping Online and Offline with Reference to Coimbatore City
Nedunchezhian, V.R, Kumaraguru College of Technology Business school
Suresh Babu, R, Bharathiar University
Abstract
In recent years the technology plays a vital role towards making the consumers purchase the products. The online portals and offline shopping varieties play a key role in deciding the buying behaviour of a customer. The main objective of the study is to analyse the factor influencing customers buying decision towards shopping online and offline. For this purpose a sample of 150 was collected from the respondents were percentage analysis, descriptive statistics, multiple regression and one way anova were used as tools to analyse the data. The conclusion is that the consumers are often purchasing from online and offline sources because of the revolution in the technology and most of them are purchasing to their need towards a particular product. More effort can be initiated towards influencing the buying behaviour of customers by promoting a product both in online as well as offline so that the companies can satisfy the consumers based on convenience, Personalisation and making the consumers purchase through reviews and feedback.
Keywords
Online Shopping, Offline Shopping, Buying Behaviour, Purchase, Anova and Customers.
Introduction
The increase in technology provides good opportunities to the seller to reach the customer in much faster, easier and in economic way. Online shopping is emerging very fast in recent years. Now a day the internet holds the attention of retail market. Millions and millions of people shop online. On the other hand the purchasing of product from traditional market is continuing since years (Lu et al., 2011). Many customers go for purchasing offline so as to examine the product and hold the possession of the product just after the payment for the product. In this contemporary world customer’s loyalty depends upon the consistent ability to deliver quality, value and satisfaction. Some go for offline shopping, some for online and many go for both kind of shopping. The focus of the study is on the consumer’s choice to shop on internet and at the traditional stores at the information gaining period. However online shopping is easier for the people and less price than the offline shopping (Chu et al., 2010; Mehta et al., 2013). While making any purchase decision consumer should know the medium to purchase whether online shopping or the offline shopping. Consumer should decide the channel for them which can best suit to their need and wants and which can satisfy them. In this competitive world how consumer can decide the particular medium for their purchase of goods is very important to understand in a managerial point of view (Sivanesan et al., 2017).
Statement Of Problem
This research may fill the gap between the choice of online shopping and offline shopping. This study reflect the problems and factors of online and offline shopping (Levin et al., 2005). There are certain problems, why people do not do online shopping and go for market to shop things? What are the major reasons behind the online and offline shopping? This study helps the consumer to get an idea about the online shopping (Iyer & Jacqueline, 2014; Koo & Lee, 2011). In Coimbatore, there is less number of people who do shopping online as compared to the other districts. The study makes the consumer clear about which option should be taken by the consumer to get more benefit out of it and that has been taken as problem towards the study (Sinha et al., 2002).
Objectives Of The Study
1.To study about the demographic variables of the respondents.
2.To evaluate the perception of customers towards online and offline shopping based on their buying decision.
3.To find out the impact of buying decision towards online and offline shopping.
Scope of the Study
The consumers in today’s era have not only many stores choice, but they also have a wide variety of channels to choose from. Pauwels et al. (2013) with the start of numerous channels (e.g. Mobile Commerce, E-Commerce) and a continuous increase in the competition among channels, the understanding of what incites consumers to purchase from one channel rather than another becomes progressively important channel design and management (Kar, 2010). The main scope of the study is to it will be useful for the companies to know about the perception and their shopping behaviour towards online and offline.
Research Methodology
Type of research: Descriptive research has been used analyzing the customers buying decision towards shopping online and offline.
Type of methodology used: As the population is undefined stratified random sampling has been used towards the study.
Data Collection
Primary data: The primary data is been using questionnaire method.
Secondary data: The secondary data has been collected from Journals, websites and Articles.
Sample size: The sample size for the study was 150 and the data was collected from the respondents who are residing in Coimbatore city.
Tools used for the study: Percentage analysis, Descriptive statistics, Multiple regression and Oneway Anova.
Limitations Of The Study
1.The sample size is limited to 150 respondents.
2.The study area is limited to Coimbatore city.
3.There may be a bias towards the primary data collected from the respondents.
Analysis and Interpretation
In the Table 1 out of 150 respondents taken for the study 56% are male and 44% are female. 92% are from the age group between 15-35, 8% are from the age group between 36-55. 6% have completed their school level, 72% have completed their UG and PG, 4% have completed their M.phil and PhD and 20% have completed other courses. 4% are students, 24% are self-employed and 72% are private employee. 64% are earning monthly income less than Rs. 20,000, 24% are earning between Rs.20,001-40,000, 4% are earning between Rs.40,000 – 60,000 and 8% are earning between Rs. 60000 – 80000. 68% of the consumers taken for the study are single and 32% are married. 60% are preferring offline shopping and 40% are preferring online shopping.
| Table 1: Demographic Variables Of The Respondents | |||
| Demographic variables | Particulars | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 84 | 56 |
| Female | 66 | 44 | |
| Total | 150 | 100 | |
| Age | 15 - 35 | 138 | 92 |
| 36 - 55 | 12 | 8 | |
| Total | 150 | 100 | |
| Educational qualification | School Level | 6 | 4 |
| UG /PG | 108 | 72 | |
| MPhil / PhD | 6 | 4 | |
| Others | 30 | 20 | |
| Total | 150 | 100 | |
| Occupation | Student | 6 | 4 |
| Self Employed | 36 | 24 | |
| Pvt. Employee | 108 | 72 | |
| Total | 150 | 100 | |
| Monthly Income in INR | < 20000 | 96 | 64 |
| 20001-40000 | 36 | 24 | |
| 40000 - 60000 | 6 | 4 | |
| 60000 - 80000 | 12 | 8 | |
| Total | 150 | 100 | |
| Marital Status | Single | 102 | 68 |
| Married | 48 | 32 | |
| Total | 150 | 100 | |
| Preference towards shopping | Offline (Market) | 90 | 60 |
| Online | 60 | 40 | |
| Total | 150 | 100 | |
In the Table 2 out of 150 respondents taken for the study 28% are frequently and occasionally shopping with online, 8% re shopping at festival time, 12% are shopping during for celebrations and 24% are shopping online based on their need. With offline shopping 44% are shopping frequently, 28% are shopping occasionally, 12% are shopping during festival time, 4% are shopping during for celebrations and 12% are shopping offline based on their need.
| Table 2: Frequency Of Purchasing Through | ||||
| Online | Offline | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Percent | Frequency | Percent | |
| Frequently | 42 | 28 | 66 | 44 |
| Occasionally | 42 | 28 | 42 | 28 |
| Festivals | 12 | 8 | 18 | 12 |
| Celebrations | 18 | 12 | 6 | 4 |
| Need Based | 36 | 24 | 18 | 12 |
| Total | 150 | 100 | 150 | 100 |
In the Table 3 out of 150 respondents taken for the study 8% said that they are shopping only with offline rather than preferring online, 8% said that they are preferring online rather than preferring offline, 24% said that they are preferring 50% online and 50% offline, 32% said that they are preferring 70% online and 30% offline and 28% said that they are preferring 30% online and 28% offline.
| Table 3: Ratio Of Purchasing Online Vs Offline | ||
| Frequency | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| A- Online 0% & Offline 100% | 12 | 8 |
| B- Online100% & Offline 0% | 12 | 8 |
| C Online 50% & Offline 50% | 36 | 24 |
| D Online 70% and Offline 30% | 48 | 32 |
| E Online 30% and Offline 70% | 42 | 28 |
| Total | 150 | 100 |
It depicts that the respondents agree towards convenience in seeing and feeling the product when purchasing offline (1.40), convenience in seeing and accessing to variety of products and brands on online screen (1.72), instant delivery of their choice making them feel happy with offline than planning for online shopping previously and waiting for the product (1.40), shopping online for good brands and for good price increasing the respect to their volume of purchase with their budget which makes them happy (1.56) and returning of goods having a very minimum chances as they check and buy through offline than online (1.56) in Table 4.
| Table 4: Descriptive Statistics Convenience | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE1 | 150 | 1.4 | 0.635 |
| CE2 | 150 | 1.72 | 0.778 |
| CE3 | 150 | 1.4 | 0.695 |
| CE4 | 150 | 1.56 | 0.807 |
| CE5 | 150 | 1.56 | 0.755 |
The respondents agree towards accessing any brands with online and offline store (1.44), Preferring familiar brands (1.24), preferring known sellers for trust ability (1.64), recognizing the new brands on advertisement and trying it (1.80) and recommending their friends and relatives about the new brand used (1.48) in Table 5.
| Table 5 : Recognition | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RN1 | 150 | 1.44 | 0.64 |
| RN2 | 150 | 1.24 | 0.514 |
| RN3 | 150 | 1.64 | 0.744 |
| RN4 | 150 | 1.8 | 0.751 |
| RN5 | 150 | 1.48 | 0.642 |
| 150 | 1.52 | 0.31602 | |
The respondents agree towards Instant purchasing of any brand at their budget (1.64), instant purchasing of any brand to their need (1.28), purchasing what impress them than the brands and price (1.60), purchasing only preferred and selective brands (1.72), looking more choices over their preference (1.64) in Table 6.
| Table 6: Personlisation | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PR1 | 150 | 1.64 | 0.744 |
| PR2 | 150 | 1.28 | 0.532 |
| PR3 | 150 | 1.6 | 0.751 |
| PR4 | 150 | 1.72 | 0.828 |
| PR5 | 150 | 1.64 | 0.744 |
The respondents agree towards reviews influencing and ensuring their confidence in brands (1.60), reviews influencing and ensuring the confidence in shops (1.52), preferring with good review and feedback easing their decision (1.60), review and suggestions recommending new brands and new shops (1.56) and Review & feed backs saving time in process of decision making (1.64) in Table 7.
| Table 7: Reviews And Feedback | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF1 | 150 | 1.6 | 0.695 |
| RF2 | 150 | 1.52 | 0.642 |
| RF3 | 150 | 1.6 | 0.695 |
| RF4 | 150 | 1.56 | 0.64 |
| RF5 | 150 | 1.64 | 0.627 |
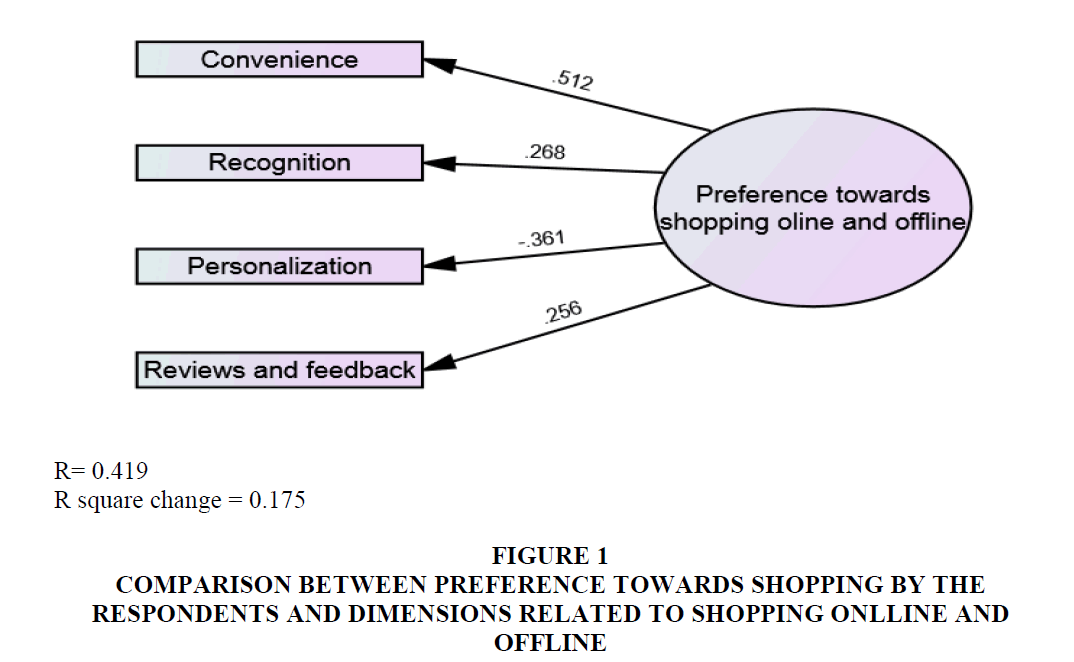
The R square change describes that there is a low relationship between the compared variables as the value is less than 0.3 at 0.175. It also depicts that there is relationship between preference towards shopping online and offline and convenience towards shopping (0.512), recognition (0.268) and shopping based on reviews and feedback (0.256) in Figure 1.
Figure 1:Comparison Between Preference Towards Shopping By The Respondents And Dimensions Related To Shopping Onlline And Offline.
H1: There is a significant difference between age and dimensions related to shopping online and offline.
There is no significant difference between age and personalization of shopping online and offline (0.000) and shopping based on reviews and feedback (0.000). There is a significant difference between age and convenience towards shopping (0.137) and recognition towards shopping online and offline (0.362) in Table 8.
| Table 8: One Way Anova | ||||||
| Comparison Between Age And Dimensions Related To Shopping Online And Offline | ||||||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | F | Sig | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convenience | 15 - 35 | 138 | 1.5391 | 0.32114 | 2.239 | 0.137 |
| 36 - 55 | 12 | 1.4 | 0 | |||
| Total | 150 | 1.528 | 0.31025 | |||
| Recognition | 15 - 35 | 138 | 1.513 | 0.32864 | 0.835 | 0.362 |
| 36 - 55 | 12 | 1.6 | 0 | |||
| Total | 150 | 1.52 | 0.31602 | |||
| Personalization | 15 - 35 | 138 | 1.5478 | 0.31443 | 13.857 | 0 |
| 36 - 55 | 12 | 1.9 | 0.31334 | |||
| Total | 150 | 1.576 | 0.32763 | |||
| Reviews and feedback | 15 - 35 | 138 | 1.5478 | 0.3088 | 25.571 | 0 |
| 36 - 55 | 12 | 2 | 0 | |||
| Total | 150 | 1.584 | 0.32067 | |||
Personalization
The respondents who are from the age group between 15-35 (1.54), 36-55 (1.90) agree towards personalization on online and offline shopping.
Reviews and Feedback
The respondents who are from the age group between 15-35 (1.54) agree and the respondents from the age group between 36-55 (2.0) are neutral towards purchasing online and offline based on reviews and feedback.
Findings
1.Maximum of the respondents are male.
2.Maximum of the respondents are between 15-35 years of age.
3.Maximum of the respondents have completed their under graduation and post-graduation
4.Majority of the respondents are working as private employees.
5.Majority of the respondents are earning less than Rs.20,000.
6.Maximum of the respondents are preferring offline shopping than online shopping.
7.Maximum of the respondents are frequently making purchase with both online and offline shopping.
8.Maximum of the respondents are preferring 70% online and 30% offline shopping.
9.There is relationship between preference towards shopping online and offline and convenience towards shopping, recognition and shopping based on reviews and feedback.
10.The respondents who are from the age group between 15-35, between 36-55 agree towards personalization on online and offline shopping. Whereas, the respondents who are from the age group between 15-35 agree and the respondents from the age group between 36-55 are neutral towards purchasing online and offline based on reviews and feedback.
Suggestions
It is suggested for marketers that the major benefit of online and offline retailing is the ability to attain consumers over many geographical locations, in a very short amount of time. So marketers should take advantage of this by using various promotional methods to increase sales all over the world. They can also market themselves by positive word-of-mouth through creating loyal customers. Different source of advertisement can be used to create customer loyalty by providing consistent promotions through not only their website, but also social media sites. Lastly, marketers should maintain a system to provide sufficient and easily attainable product information to guide online and offline transactions.
Conclusion
The conclusion is that the consumers are often purchasing from online and offline sources because of the revolution in the technology and most of them are purchasing to their need towards a particular product. More effort can be initiated towards influencing the buying behavior of customers by promoting a product both in online as well as offline so that the companies can satisfy the consumers based on convenience, Personalization and making the consumers purchase through reviews and feedback.
References
- Chu, J., Arce-Urriza, M., Cebollada-Calvo, J.J., & Chintagunta, P.K. (2010). An empirical analysis of shopping behavior across online and offline channels for grocery products: the moderating effects of household and product characteristics. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 24(4), 251-268.
- Iyer, R., & Jacqueline, E. (2014). The Elderly and Their Attitude Toward s the Internet: The Impact of Internet use, Purchases, and Comparison Shopping. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 14(1), 213-223.
- Kar, M. (2010). Consumer behaviour over the last 25 years. The Retail Digest, 46-53.
- Koo, D.M., & Lee, J.H. (2011). Inter-relationships among dominance, energetic and tense arousal, and pleasure, and differences in their impacts under online vs. offline environment. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(5), 1740-1750.
- Levin, A.M., Levin, I.P., & Weller, J.A. (2005). A multi-attribute analysis of preferences for online and offline shopping: Differences across products, consumers, and shopping stages. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 6(4).
- Lu, Y., Cao, Y., Wang, B., & Yang, S. (2011). A study on factors that affect users’ behavioral intention to transfer usage from the offline to the online channel. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(1), 355-364.
- Mehta, D., Soni, S., Mehta, N.K., & Yadav D.S. (2013). Review of Literature on Online Consumer Behavior, Innovative business practices for creating value in global reedited by S. Singh, A. Gwal and J. K. Sharma, published by acropolice Academy, Indore.11-15,
- Pauwels, K., Leeflang, P.S., Teerling, M.L., & Huizingh, K.E. (2011). Does online information drive offline revenues?: Only for specific products and consumer segments!. Journal of Retailing, 87(1), 1-17.
- Sinha, P.K., Banerjee, A., & Uniyal, D.P. (2002). Deciding where to buy: Store choice behaviour of Indian shoppers. Vikalpa, 27(2), 13-28.
- Sivanesan, R., Monisha, C., Babisha, P.V., & Abisha, S.A. (2017). Comparative Study on Factors Influencing Online and Offline Shopping, International Journal of Research in Management & Business Studies, 4(3), 26-34.