Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 1
Factors Affecting the Development of Non-Credit Services: A Case Study of Commercial Banks in Ho Chi Minh City
Nguyen Van Trai, University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City (UEH)
Ha Van Son, University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City (UEH)
Abstract
In the context of complicated developments in the financial market, credit activities are too risky. The credit revenues are still very volatile; commercial banks must accelerate non-credit services to increase their revenues. Besides, non-credit service development has become one of the goals of the commercial banking system restructuring program. However, compared to other countries in the region and worldwide, the product of financial services in general and non-credit services, particularly in Vietnam, is still too far away, requiring concentration. All resources for investment and growth. Therefore, this study determines the factors affecting commercial banks’ non-credit services in Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC). The study surveyed 800 staffs working for commercial banks in HCMC, but 775 samples processed and answered 35 questions. The data collected from July 2020 to October 2020. The authors tested with Structural Equation Model (SEM). Finally, eight factors affect the development of non-credit services of commercial banks in HCMC with a significance level of 0.01.
Keywords
Non-credit, Services, Development, Commercial bank, UFM.
Introduction
One of the restructuring financial activities’ contents is credit institutions in the Scheme on restructuring the credit institutions system for the period 2011-2015. The Prime Minister has approved it under Decision No. 254/QD-TTG, dated March 1, 2012, is: “Gradually changing the business model of commercial banks towards reducing dependence on credit activities and increasing income from non-credit services”. This content showed that Vietnam has been aware of non-credit services’ role in bringing more stable and safer revenue for commercial banks. The development of non-credit services plays a significant role, deciding the existence of a bank in the process of international economic integration, namely: (i) Contributing to the diversification of banking products and services, thereby attracting and expanding to many types of customers; (ii) Optimal response to the needs of the economy, contributing to consolidating the growth and enhancing the reputation and position of commercial banks in the economy; (iii) Distributing risks to banks, bringing stable income for banks, increasing profits of commercial banks and (iv) Promoting international cooperation and economic integration in the banking sector.
On the other hand, international economic integration forces Vietnamese commercial banks to cope with international competition pressure with commercial banks’ penetration, healthier technology, financial capacity, type, and quality. Service quality, business professionalism. Vietnamese commercial banks are forced to strengthen their competitiveness by diversifying and improving financial services, primarily commercial banks. Non-credit service, while credit services always contain high risks. Non-credit services are less risky and bring additional sources of income with an increasing proportion for commercial banks. In many countries, the reality shows that in periods when credit is difficult, such as after the crisis and economic recession, the development of non-credit services is necessary, even the salvation of many commercial banks.
Literature Review
The Development of Non-Credit Services (DNCS)
Non-credit services
These are the services associated with the fee collection performed by commercial banks; through the provision of banking services to businesses, organizations, and individuals to gain profits, typically for this service is paid service. Guarantee services, electronic banking services, foreign currency trading services, gold, silver, and gemstones. Non-credit service is a service provided by a bank to customers to meet customers’ financial and monetary needs to directly or indirectly bring the bank an income by specific fees - receipts from customers, excluding credit services by Bhadury (2019).
The development of non-credit service
It is an increase in the size and number of non-credit products and services. Diversification of many benefits is considered a necessary criterion for the broad-based development of non-credit banking services. That said, the development process continues to work with traditional services and has to update and develop modern non-credit services in addition to conventional non-credit services such as payment, treasury, and money transfer. From a micro-perspective, diversifying non-credit services helps banks diversify their income structure, minimize business risks, and strengthen brand and reputation in the market by Santouridis & Kyritsi (2014). From a macro perspective, diversifying non-credit services contributes to providing benefits to the economy and the population, and economic development by Thofack (2015).
Human Resources (HR)
According to Yu (2017) the human factor is appreciated, even the most essential aspect of all success. Banks want to provide adequate services with high quality and attract customers need to have a capable staff. Competence is shown in quality and quantity: The quality of human resources is shown in professional expertise; it is necessary to master, have professional knowledge, understand professional aspects. Simultaneously, the bank officials also need to be active, agile, with a human-style in the new era. Because these are compassionate services, the care and customer service become even more critical by Lehtinen (2016). Therefore, with the direct transaction department with customers, in addition to the above factors, bank staff should have a warm, thoughtful, dedicated attitude to customer service. With those as mentioned above, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H1 Human resources positively impact the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
Distribution Channel Network (DCN)
According to Köhler (2014) commercial banks worldwide have built their network of distribution channels with the combination of electronic distribution channels. The distribution network has domestic and foreign branches - banks affiliated companies, agents, transaction offices such as ATM, POS, SMS banking. They have often played an essential role in providing services to customers and in developing operations. Besides, internet banking is creating a significant influence in attracting customers because it brings convenience to customers, minimized travel effort and transaction time. The information is updated fastest anytime, anywhere by Nicholas (2014). Non-credit service action creating diversified distribution channels to maximize the provision of services and information to customers to meet each population class’s increasingly diverse needs by Tamran (2020). For the above-mentioned human resources, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H2 The distribution channel network has a positive impact on developing non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
Service Quality (SQ)
According to Westhuizen (2019) Service quality is assessed through the bank staff’s service quality and the safety, accuracy, and update in professional processing, convenient and straightforward procedures transaction and fast transaction processing speed. Service quality is an invisible factor but has vital significance in commercial banks’ service business today by Tremraj (2019). Commercial banks aim to care for customers with services to support customers using their services. At the same time, this is also a sales channel and modern banking operations. The researchers have hypothesis following:
H3 Service quality has a positive impact on developing non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
Customer Policy (CP)
According to Williams (2017) as competition increases, banking technology has many significant changes. It is increasingly diversified, as foreign banks and financial institutions’ penetration makes the competition increasingly fierce. Along with changing traditional capital markets and increasingly diversifying customer need. It is time that banks need to pay more attention to their pricing and customer policies. Customer policy is the policy that banks apply to express their marketing strategy at the customer level or customer segment. Based on decisions made to allocate the bank’s existing resources, the ultimate goal is to provide a service to satisfy the maximum increasing demand of customers, thereby achieving its maximum profitability by Nguyen (2012). The mentioned above, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H4 Customer policy has a positive impact on developing non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
Marketing Advertising Activities (MAA)
According to Maudos & Solís (2019) the essential banking marketing elements are market research, formulation, and execution based on market strategy. Today, the banking sector’s marketing concept includes clarifying the current market and its trends for service delivery, selecting more profitable areas, and identifying customer need in those areas. For service delivery, to develop short-term and long-term goals for developing and launching new services by Abbas et al. (2020). Marketing is about implementing the service and the strategy and philosophy of each bank and it requires meticulous preparation, thorough analysis, and positive analysis of all departments from leadership to staff. The mentioned above thing, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H5 Marketing advertising activities positively impact the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
Reputation and Brand (RB)
According to Zouari (2014) prestige and brand name are significant factors in attracting and developing commercial banks’ customers. Customers often trust banks with a long history of development and reputation in the market to use non-credit services. Although the service quality is not completely good, there are banks because of their firm and reputable brands, customers still choose to use the service by Zofio (2015). The bank’s reputation is reflected in the following aspects: solvency, professional processing techniques, payment time, ability to respond to payment instruments, variety of services. The mentioned above thing, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H6 Reputation and brand positively impact the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
Executive Management Capacity (EMC)
According to Badar et al. (2013) a commercial bank’s management capacity is expressed through development orientation and strategy, new business thinking to minimize operating costs, using available resources to achieve results optimal. Non-credit service operations can only be successful if they have the right direction and development strategy. The service system must be tied to each bank’s governance and governance capacity to ensure stable, safe, sustainable, and self-controlled development of the service. Bank executives and executives know to comply with the law. Still, they must have professional knowledge about banking operations and know-how to analyze and evaluate each type of service’s possible risks - customer strategy, market penetration marketing strategy, improved by Trump (2019). The development trends of each profession to have appropriate preventive measures and steps by Thomas (2020). The mentioned above thing, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H7 Executive management capacity has a positive impact on developing non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
Development Goals and Strategies (DGS)
According to Demirgüç-Kunt (1989) any organization has its own goals and operating principles. In each particular stage, organizations often set their purposes. The ultimate goal is that all banking activities can bring income to the bank. From that goal, new banks develop a strategy to achieve the set goals. A process is to create specific plans, a program of action that includes the effective use of resources to achieve individual goals.
According to Mike (2016) the bank must clearly define the goals and develop a banking service development strategy to ensure the banking service development is carried out effectively, with a long-term plan, not activities. Small and discrete movement, creating an active position for the bank. The mentioned above thing, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H8 Development goals and strategies positively impact the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City.
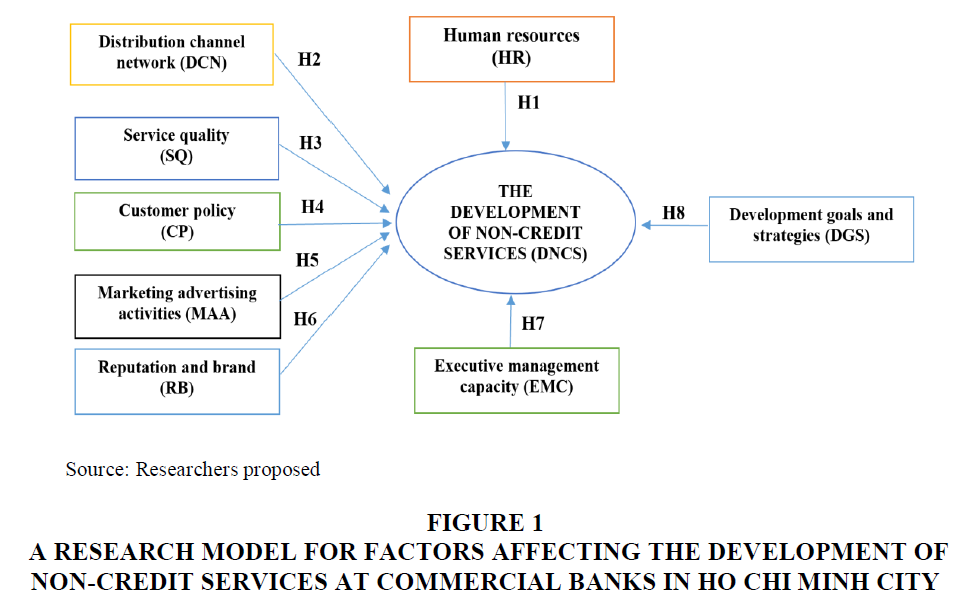
A research model for factors affecting the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City following (Figure 1):
Figure 1 A Research Model for Factors Affecting the Development of Non-Credit Services at Commercial Banks in HO CHI MINH City
Methodology
To carry out the research, the protocol established by the authors’ team based on the reference and development from the standard research consists of 09 steps of implementation as follows: (1) identifying research problem; (2) consider a priori studies; (3) identify research gaps; (4) develop research models and hypotheses; (5) develop draft scales of the factors in the model; (6) preliminary assessment of the scale; (7) official data collection; (8) data analysis and (9) conclusions and policy implications are as follows by Hair & Anderson (2010).
The researchers applied preliminary research carried out by available theoretical research methods and through in-depth interview techniques to explore, correct, and develop critical elements and components of non-credit services development. The researchers interviewed 13 leaders of 13 commercial banks in HCMC. The surveying results had 13 leaders who agreed that all of the factors affecting non-credit services’ development.
Quantitative methods: The researchers surveyed the completed questionnaires, which were directly collected from 800 staffs working for commercial banks in HCMC, but 775 samples processed and answered 35 questions. The data collected from July 2020 to October 2020. The authors applied simple random sampling, tested Cronbach’s Alpha, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), and tested with Structural Equation Model (SEM) (Hair & Anderson, 2010).
Finally, the purpose of confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) helps the authors to clarify: (1) Unilaterality, (2) Reliability of scale, (3) Convergence value, and (4) Difference value. A research model considered relevant to the data if Chi-square testing is P-value > 5%; CMIN/df ≤ 2.0, some cases CMIN/df maybe ≤ 3.0 or < 5.0; GFI, TLI, CFI ≥ 0.9. However, according to recent researchers’ opinions, GFI is still acceptable when it is greater than 0.8; RMSEA ≤ 0.08. Apart from the above criteria, the test results must also ensure synthetic reliability > 0.6; the Average variance extracted must be greater than 0.5 (Hair & Anderson, 2010). To test the research hypotheses, the authors used SEM with path analysis method through regression weights and p-value values to test. Factor analysis is a structural model analysis, so the model’s conformity with actual data is considered the scale’s official assessment.
Results
Testing Cronbach’s alpha for factors affecting the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City following:
Table 1 showed that Cronbach’s alpha of the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City is 0.943 and 0.871 > 0.6.
| Table 1 Cronbach’s Alpha of the Development of Non-Credit Services | |
| The development of non-credit services (DNCS) | Cronbach’s Alpha if Item Deleted |
| DNCS1: The bank has all conditions to develop non-credit services in the coming time | 0.933 |
| DNCS2: The bank’s non-credit services are taking steps of sustainable development | 0.885 |
| DNCS3: Banks conditionally centralize Non-credit service to ensure growth | 0.933 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.943 | |
| Human resources (HR) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| HR1: The bank has an abundant and stable financial source | 0.844 |
| HR2: Professionally qualified human resources good service | 0.809 |
| HR3: The management system is implemented on the platform of modern technology | 0.860 |
| HR4: Facilities for service deployment are present great, complete | 0.824 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.871 | |
Table 2 showed that Cronbach’s entire Alpha is greater than 0.7. Cronbach’s Alpha for Service quality (SQ) is 0.938; for Customer policy (CP) is 0.964 and for the Marketing advertising activities (MAA) is 0.855; for reputation and brand (RB) is 0.958; for Executive management capacity (EMC) is 0.949 and for development goals and strategies (DGS) is 0.946.
| Table 2 Cronbach’s Alpha of Factors Affecting the Development of Non-Credit Services | |
| Distribution channel network (DCN) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| DCN1: The system of transaction offices is extensive and capable of high service force | 0.902 |
| DCN2: The quantity and quality of ATM, POS, meeting are required for customers | 0.883 |
| DCN3: ATM and POS machines are distributed reasonably and conveniently | 0.905 |
| DCN4: Internet and electricity payment systems Phone brings many benefits to customers | 0.866 |
| DCN5: Non-credit services are implemented with few errors through the E-banking system | 0.870 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.907 | |
| Service quality (SQ) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| SQ1: Non-credit services show concern and understanding of customers’ needs | 0.927 |
| SQ2: Non-credit services are highly secure | 0.876 |
| SQ3: Non-credit services bring customers comfort and convenience | 0.926 |
| Customer policy (CP) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| CP1: The bank offers a wide range of customer policies | 0.940 |
| CP2: Customer policies bring many benefits for customers | 0.964 |
| CP3: The customer policy is highly relevant to the wishes of customers | 0.959 |
| CP4: Highly competitive customer policies compared with other banks | 0.945 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.964 | |
| Marketing advertising activities (MAA) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| MAA1: The bank’s an advertising and marketing activities are carried out regularly | 0.804 |
| MAA2: Various advertising forms are available | 0.814 |
| MAA3: Advertising content provides complete information about service to customers | 0.845 |
| MAA4: Promotion programs are informed promptly past time marketing activities | 0.801 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.855 | |
| Reputation and brand (RB) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| RB1: Banks demonstrate a high reputation for safety and confidentiality in service delivery | 0.941 |
| RB2: The Bank complies with the regulations on information disclosure and transparency in its operations | 0.956 |
| RB3: The bank implements effective branding and development strategies | 0.947 |
| RB4: The bank’s brand name is highly likely to be recognized by customers | 0.933 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.958 | |
| Executive management capacity (EMC) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| EMC1: The bank has good risk management capacity | 0.924 |
| EMC2: The Bank complies with international standards of risk management | 0.938 |
| EMC3: The bank has a good organizational structure and management apparatus | 0.943 |
| EMC4: The bank has a good customer information management system | 0.928 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.949 | |
| Development goals and strategies (DGS) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| DGS1: The Bank develops a fully detailed non-credit service development strategy | 0.926 |
| DGS2: Development strategies are characteristic and terms of the bank | 0.934 |
| DGS3: Các chi?n l??c phát tri?n phù h?p v?i xu th? phát tri?n d?ch v? ngân hàng trên th? gi?i | 0.933 |
| DGS4: Development goals are specified; the tasks of each department are specified clear | 0.924 |
| Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.946 | |
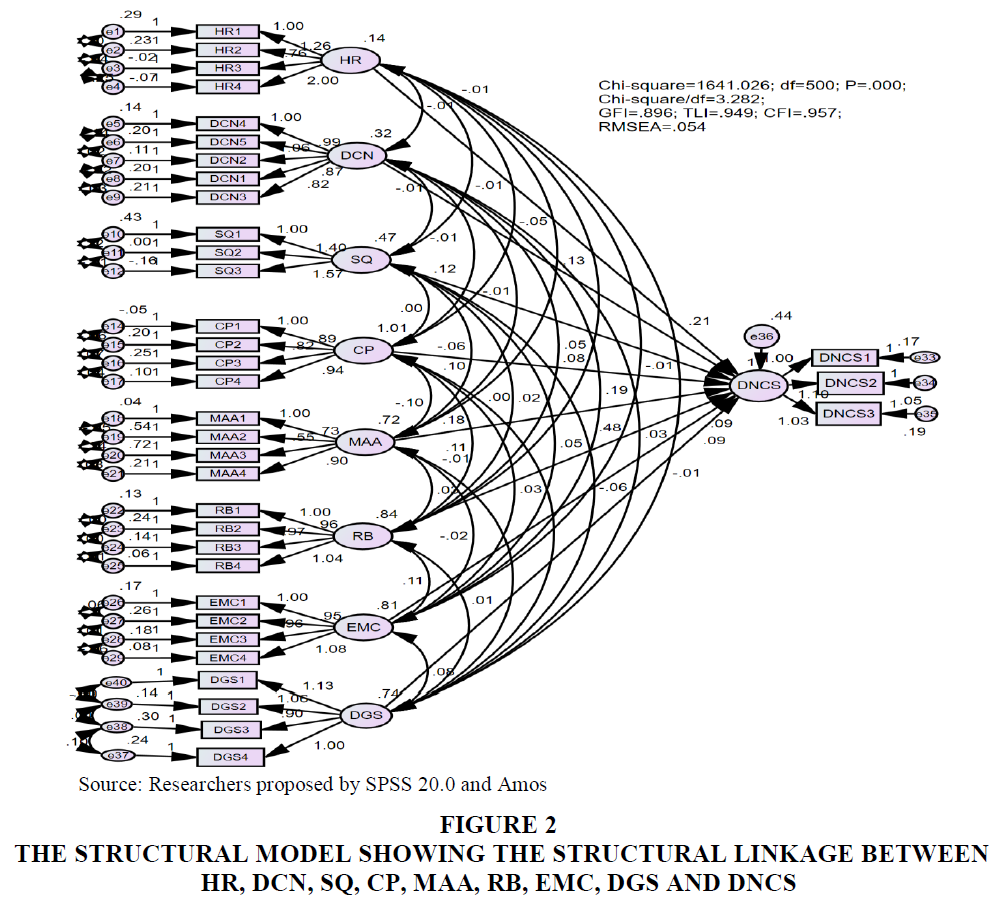
Table 3 showed that column “P” < 0.01 with significance level 0.01. This result indicated that eight factors affected the development of non-credit services at commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City with a significance level of 0.01 (Figure 2).
| Table 3 Factors Affecting the Development of Non-Credit Services | |||||||
| Relationships | Coe. | Standardized Coefficient | SE. | CR. | P | ||
| DNCS | <--- | HR | 0.208 | 0.092 | 0.054 | 3.820 | *** |
| DNCS | <--- | DCN | 0.133 | 0.088 | 0.051 | 2.601 | 0.009 |
| DNCS | <--- | SQ | 0.119 | 0.095 | 0.033 | 3.579 | *** |
| DNCS | <--- | CP | 0.081 | 0.096 | 0.025 | 3.304 | *** |
| DNCS | <--- | MAA | 0.176 | 0.175 | 0.033 | 5.336 | *** |
| DNCS | <--- | RB | 0.484 | 0.522 | 0.030 | 16.209 | *** |
| DNCS | <--- | EMC | 0.085 | 0.090 | 0.031 | 2.751 | 0.006 |
| DNCS | <--- | DGS | 0.087 | 0.088 | 0.029 | 3.001 | 0.003 |
Figure 2 The Structural Model Showing The Structural Linkage Between HR, DCN, SQ, CP, MAA, RB, EMC, DGS and DNCS
Conclusions
Non-credit service is an indispensable business activity for commercial banks. Along with the development of the economy, commercial banks continually expand their branches to operate and develop non-credit services to meet the demand for assistance in the context of increasingly fierce competition. Customers are considered an indispensable part of the economy. With a correct orientation of banks in developing non-credit services provided to customers, banks will attract customers, increase the proportion of service revenue, and contribute to promoting social work. Non-cash payments. The study surveyed 800 staffs working for commercial banks in HCMC, but 775 samples processed and answered 35 questions. The data collected from July 2020 to October 2020. The authors applied simple random sampling, tested Cronbach’s Alpha, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), and tested with Structural Equation Model (SEM). Finally, eight factors affect the development of non-credit services of commercial banks in HCMC with a significance level of 0.01. Research results are an essential scientific basis for commercial banks to refer to and apply in practice.
Managerial Implications
Based on the results mentioned above, to enhance commercial banks’ non-credit services in Ho Chi Minh City.
(1) Managerial implication for the reputation and brand (RB). Commercial banks need to improve the importance and brand name of a bank has the most significant influence on developing non-credit services according to survey results of bank staff. Building a reputation and a valuable brand includes service improvement, customer service, and error reduction, solving customer questions and complaints. At the same time, thoroughly is building a strong brand in the ability to recognize the brand and loyalty to the brand. With the influence of prestige and brand name on developing a bank’s non-credit services, enhancing the reputation and brand value of a bank should be very focused on contributing to the development of non-credit services at banks.
(2) Managerial implication for the Marketing Advertising Activities (MAA). Commercial banks need to improve advertising factor has the second most significant influence on developing non-credit services at banks. This commendation demonstrated through the benefits of expanding the market and promoting the service to customers, thereby attracting customers so that the bank can develop its non-credit services. The bank’s current status of an advertising and marketing work has been assessed as not high by its staff. Weaknesses exist in terms of content, advertising form, updating, and efficiency of information to customers. As such, the bank should focus on overcoming these shortcomings in advertising activities in the coming time.
(3) Managerial implication for customer policy (CP). Commercial banks need to improve the process of building and implementing new customer policies, increasing the diversity of these policies so that customers of many types can choose the best approaches. Banks must have a team of qualified market analysts and assessors and recognize and analyze customer opinions well, thereby giving the right idea to leaders. Plan to build new customer policies for the bank. At the same time, it is necessary to have a team of specialists in charge of planning, testing the implementation of customer policies in each area before deploying on the whole system.
(4) Managerial implication for the service quality (SQ). Commercial banks need to improve the quality of customer service. In addition to researching and improving services provided, retail banks need to pay more attention to the quality of direct transactions with customers, ensuring customers’ satisfaction when using banking services. The bank’s operations are more professional. The bank’s management level is more scientific, with generous support from the banking technology (Core banking), so the banks have to simplify the documents and procedures. To transact with the bank more quickly and accurately, creating comfort for customers when using the bank’s non-credit service.
(5) Managerial implication for human resources (HR). Commercial banks need to improve personnel allocation appropriately, and creating motivation for employees is also a measure to improve bank employees’ working efficiency. For employees performing non-credit services, it is necessary to have a selection process according to the employee’s wishes, the requirements of the job, and there is a regular assessment of job suitability. Doing with that employee. To motivate employees to work, the bank may be interested in staff remuneration with salaries, bonuses, and welfare regimes - additional health care benefits for relatives of employees, such as husbands or children.
(6) Managerial implication for the executive management capacity (EMC). Commercial banks need to improve the quality of administration and administration of non-credit services. Separate the Departments and Centers at Head Office’s powers and responsibilities and strengthen the coordination between these departments and branches in the development of non-credit services. Researching and building an income-cost distribution model for each specific service can compare each service’s efficiency and then have appropriate development measures.
(7) Managerial implication for the development goals and strategies (DGS). Commercial banks need to improve the creation of new ideas for the development of non-credit services is very rich, diverse, but very difficult and can be formed from inside or outside the bank. In the bank, groups are responsible for developing the original idea of a new non-credit service. Banks must create a new non-credit service from professional staff. Or from market research results and information gathered from customers, or from sources outside the bank through collecting ideas from new service development organizations, or learning from other banks’ experiences, maybe even copying ideas services of domestic and foreign banks.
(8) Managerial implication for the distribution channel network (DCN). Commercial banks need to enhance the efficiency and self-service capabilities of the ATM system to provide various types of services with cheaper costs, upgrade the ATM system to modern and convenient transaction points spread across the provinces. At the same time, to develop a network of point-of-sale points (POS) and strengthen the link between banks to improve efficiency and expand the usability of ATM and POS cards.
References
- Abbas, S., Nguyen, V.C., Yanfu, Z., & Nguyen, H.T. (2020). The impact of china exchange rate policy on its trading partners evidence based on the GVAR model. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business, 7(8), 131-141.
- Badar, M., Javid, A.Y., & Zulfiquar, S. (2013). Impact of macroeconomic forces on nonperforming loans: An empirical study of commercial banks in Pakistan. wseas Transactions on Business and Economics, 10(1), 40-48.
- Bhadury, S. (2019). Non-interest income-growing importance. SIES Journal of Management, 6(1), 37-46.
- Demirgüç-Kunt, A. (1989). Deposit-institution failures: a review of empirical literature. Economic Review, 25(4), 2-19.
- Hair, B.B., & Anderson (2010). Multivariate data analysis. New York: US: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Köhler, M. (2014). Does non-interest income make banks more risky? Retail-versus investment-oriented banks. Review of Financial Economics, 23(4), 182-193.
- Lehtinen, J.R. (2016). Service quality a study of quality dimensions. Review of Financial Economics, 4(1), 50-61. Maudos, J., & Solís, L. (2009). The determinants of net interest income in the Mexican banking system: An integrated model. Journal of Banking & Finance, 33(10), 1920-1931.
- Mike, T. (2016). Determinants of non-performing loans: Evidence from Euro-area countries. Finance Research Letters, 18(3), 116-219.
- Nguyen, J. (2012). The relationship between net interest margin and noninterest income using a system estimation approach. Journal of Banking & Finance, 36(9), 2429-2437.
- Nicholas, A. (2014). The long-term role of non-traditional banking in profitability and risk profiles: Evidence from a panel of US banking institutions. Journal of International Money and Finance, 45(3), 61-73.
- Santouridis, I., & Kyritsi, M. (2014). Investigating the determinants of internet banking adoption in Greece. Procedia Economics and Finance, 9, 501-510.
- Tamran, H.W. (2020). Climate change and bank stability: The moderating role of green financing and renewable energy consumption in ASEAN. Talent Development and Excellence, 2(2), 13-23.
- Thofack, H.L. (2015). Non-performing loans in sub-Saharan Africa: Causal analysis and macroeconomic implications. International Journal of Financial and Business Research, 1(2), 41-49.
- Thomas, T.T. (2020). Factors affecting the competitive capacity of commercial banks: A critical analysis in an emerging economy. International Journal of Financial Research, 11(4), 241-249.
- Tremraj, T.S. (2019). The determinants of non-performing loans: An econometric case study of Guyana. International Journal of Financial and Economics, 4(2), 4-12.
- Trump, T.F. (2019). Predicting bank failure using DEA to quantify management quality. Journal of Financial and Economics, 2(3), 140-148.
- Westhuizen, G. (2019). The role of interest income and non-interest income on bank regions’ relative efficiency: The case of a large South African bank. Journal of Asian Economics, 55(2), 3-23.
- Williams, B. (2017). Bank risk and return: The impact of bank non-interest income. International Journal of Managerial Finance, 6(3), 220-244.
- Yu, Z. (2017). Are there diversification benefits of increasing non-interest income in the Chinese banking industry? Journal of Empirical Finance, 24(1), 151-165.
- Zofio, J.L. (2015). How to properly decompose economic efficiency using technical and allocative criteria with non-homothetic DEA technologies. European Journal of Operational Research, 240(3), 882-891.
- Zouari, N. (2014). Macroeconomic and bank-specific determinants of household’s non-performing loans in Tunisia: A dynamic panel data. Procedia Economics and Finance, 13(1), 58-68.