Research Article: 2019 Vol: 23 Issue: 3
Factors Affecting the Audit Quality and the Competitive Capability of Auditing Enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City
Nguyen Anh Hien, Saigon University
Huynh Vu Bao Tram, Saigon University
Doanh Thi Ngan Ha, Saigon University
Nguyen Chuong Thanh Huong, Saigon University
Nga Phan Thi Hang, University of Finance - Marketing
Abstract
Audit is a special activity; a type of service activities is to ensure that customers using audited information can be assured and reliable about the quality of the service, the truthfulness, the right, the legal. It is full of audited information. The success of auditing enterprises depends on many factors but audit quality is one of factors that are very important. Therefore, the main objective of this study is to explore factors impacting the audit quality and the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC). The researchers surveyed 800 persons related the auditing activities in HCMC (They including: 150 lecturers teaching accounting and auditing, 150 managers of auditing, 200 auditors, 50 enterprises of auditing, 150 officers working in auditing and 100 enterprises using auditing service). 19 items and 788 samples processed and Data collected from July 2018 to July 2019 in Ho Chi Minh City. The researchers get simple random sampling technique. Cronbach's Alpha and the exploratory factor analysis (EFA) which used for Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) technique and using partial least squares method. Persons’ responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5- point Likert scale. The findings of the paper have factors affecting the audit quality and the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in (HCMC) with significance level 0.01.
Keywords
Audit, Quality, Capability, Competitive, Enterprise.
Introduction
Quality in general and audit quality in particular is always the top concern of many enterprises. Several researchers have tried to define the audit quality for more than 30 years; the ways of measurement these factors affect quality, and the impact of quality to competitive capabilities (Hosseinniakani et al., 2014). However, so far, these concepts have not been united yet and researches on this topic are continued. This caused because audit quality is a multifaceted concept, difficult to observe and measure, depends on feeling and judgment of each individual, therefore it is difficult to have a unified viewpoint. Vietnam officially joined WTO, and is a member of CPTPP, ASEAN Economic Community (AEC); According to the committed roadmap, Vietnam officially open all financial services from 2015; In the trend of globalization, the success of Audit Firms in Vietnam depends much on Audit quality and Competitive Capabilities in the market. Meanwhile, according to the Ministry of Finance: "The size and quality of independent auditors have not reached the expectation yet and are also struggling to be recognized by regional and international, the competition among the auditing firms derive from local interests, arising unhealthy competition such as reducing audit fees that leads the audit quality uncertainty". This situation requires more researches on audit quality oriented enhance the competitive capability of Audit Firms in Vietnam in terms of economic integration that is increasing intensive now.
Audit Auditing is a special activity, a type of service activities to ensure that the objects using audited information are safe and reliable about the quality of certification services, honesty, correctness and legality, full of audited information. Like other activities, audit results must meet certain quality standards (Amahalu Nestor Ndubuisi, 2017). On the other hand, as a service of certifying and ensuring to provide reliable, honest, objective information for users to make the right decision, the quality of auditing needs to be enhanced. Auditing agencies need to ensure regular provision of high quality audit results at reasonable costs. Based on mentioned above things, the researchers to explore factors affecting the audit quality and the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in (HCMC). This study helps audit enterprise managers who apply the research results for improving the audit quality better in the future.
Literature Review
Audit Quality (AQ)
Quality reflects the value in terms of the benefits of products and services. It is evaluated by the customers. Combining the purpose and meaning of the audit with the survey results, it is possible to give the following concept of audit quality: Auditing quality is the level of satisfaction of objectivity and credibility in mind and audit opinions of auditing service users at the same time satisfy the desire to get comments to improve the effectiveness of financial and accounting management of audited units (Bell et al., 2015). Audit quality is a complex and multifaceted concept; therefore, many researches have been done in order to define audit quality. There are many factors affecting audit quality as well as measure audit quality. However, according to the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board, the concept of audit quality has reached no consensus; many studies are continuing to be done. Although there are many different ways to approach audit quality. In recent years, all the global researchers mainly focused on three main points. Audit quality is the level of guarantee the ability to detect and report errors on financial statement. Audit quality is the Level of compliance with auditing standard and audit quality combining level of compliance with standards and the level of assurance about the ability to detect and report on essential errors in the financial statement (Brown et al., 2016).
Auditor Quality (AU)
Auditor is an accountant with a degree assigned to check the accuracy of the accounts and financial statements that give a company. Based on this, auditor drafted an independent report (for appointed agencies, shareholders) about whether the accounts reflect the company's activities properly. Auditors have been granted the audit registration certificate (Amahalu Nestor Ndubuisi, 2017). Besides, there is a real time for an audit of thirty-six months or more. Auditor participates fully in the knowledge update programs. Auditor fully meets the conditions prescribed above shall register for audit practice and be granted audit practice registration certificates according to the regulations of the Ministry of Finance (Dimas Dwi Oktavianto, 2018). The certificate of audit practice registration is only valid when the auditor who is granted has a labour contract to work full time for an auditing enterprise, a foreign invested enterprise branch in Vietnam. Within three years from the effective date of the Law on Independent Auditing, auditor has been certified as an auditor before the effective date of the independent Auditing Law that is entitled to register for audit practice in accordance with the Law on Inspection (Eko Suyono, 2012). Independent math without having to ensure conditions for the actual time to do an audit of thirty-six months or more. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
H1: Auditor quality has a positive impact on the audit quality of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
H2: Auditor quality has a positive impact on the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
Internal Factors of Auditing Enterprise (IF)
Auditing enterprise is an enterprise that is qualified to conduct auditing services business in accordance with this Law and other relevant laws (Khasharmeh et al., 2018). Today, the skepticism needs for a thorough assessment of the financial statements of an increasingly large company. Investors lose confidence in corporate governance and reports. They expect more: higher reliability, more control and clearer evidence of internal control systems. Auditing enterprise meet investors' expectations that should begin with the fullness and accuracy of the information on the company's financial statements (Gonthier-Besacier et al., 2016). With auditing tools, resources and auditing procedures that meet high standards, audit firm is committed to providing the best service for customers. The audit helps customers to judge the complex risks that are increasing in today's business world and how those risks can be reflected in a business's financial statements. Audit firm is at the forefront of helping customers improve transparency, improve corporate governance and business models based on principles of sustainability (Krishnan, 2005).
Moreover, the competitive capability of auditing enterprises is affected by many different factors. According to the Diamond model of M. Porter, it can be seen that there are at least 4 groups of factors affecting the competitiveness of enterprises, demand (market) conditions, factor conditions (input resources), supply and related sectors (industry competition), random factors and state factors (Goodwin & Kent, 2006). However, it is possible to divide the factors affecting enterprises' competitive capability into two groups: internal factors and external factors. Internal factors including labour qualifications in enterprises, financial capacity of enterprises, ability to link and cooperate with other businesses and international economic integration, level of equipment and technology and Marketing capacity (Eko, 2012). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
H3: Internal factors have a positive impact on the audit quality of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
H4: Internal factors have a positive impact on the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
External Factors (EF)
There are many external factors affecting the competitive capability of auditing enterprises. The World Economic Forum (WEF) is based on external factors affecting the competitive capability of auditing enterprises under the business environment title of enterprises” with 56 specific targets (these indicators are quantified to rank for countries) in 4 groups of factors as follows. Firstly, the conditions of input factors, including 5 sub-groups: physical-technical infrastructure; administrative infrastructure, human resources, technology infrastructure, financial market (Yeghaneh et al., 2015). Secondly, demand conditions: buyers' preferences, legal situation of consumption, information technology... Third, the supply and related industries: the quality and number of local suppliers, on-the-spot capabilities of specialized research and training services, the degree of cooperation among economic sectors, ability to provide onsite details and machinery accessories (Vanstraelen, 2000). Fourthly, the context for corporate strategy and competition, consisting of two categories is motivation and competition (invisible barriers, competition of local manufacturers, the effectiveness of antitrust and rights). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
H5: External factors have a positive impact on the audit quality of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
H6: External factors have a positive impact on the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
Competitive Capability (CC)
According to (Usman, 2016) the competitive capability of auditing enterprises can be understood as the ability to dominate the market to consume the same products (or alternative products) of that company. The ability to seize and dominate the high consumption market is that enterprise has high competitiveness. Michael Porter is not confined to direct competitors but he extends to both potential competitors and alternative products. According to (Nopmanee & Ling, 2015) competitive capability of enterprises is the ability and capacity that enterprises can maintain in a long-term way in the competitive market and progress by making a low profit margin. It is enough to cover the realization of the goals of the business. The Competitive capability of enterprises is also defined as the competitiveness of enterprises to meet and fight competitors in providing products and services in the longest way (Husam Al-Khaddash , 2013).
These definitions show that the competitive capability of auditing enterprises must first be created from the capabilities. An enterprise is considered to have competitive competence when that enterprise dares to accept the convenient conditions which are beneficial for the business itself. Enterprises need to have strong enough resources to ensure in competition (Ilaboya & Okoye, 2015). The competitive capability of auditing enterprises based on many factors such as: use value and high product quality, stable production conditions due to production based mainly on modern techniques, advanced technology, large scale production and thus lower prices and product prices. The social factors such as maintaining trust (prestige) in the market, propaganda, consumer guidance, advertising also have an important influence now manufacturers also use some forms such as selling instalment payments (instalment payments) to stimulate consumption, on the basis of increasing competitiveness (Noor Adwa Sulaiman, 2018). Finally, Competitive capability theory based on enterprise resources, competitive theory based on business capabilities with the impact of audit quality and factors of audit quality affecting competitive capability, as the basis for determining the factors affecting audit quality and competitive capability of auditing firms (Hussein & Hanefah, 2013). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
H7: Audit quality has a positive impact on the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
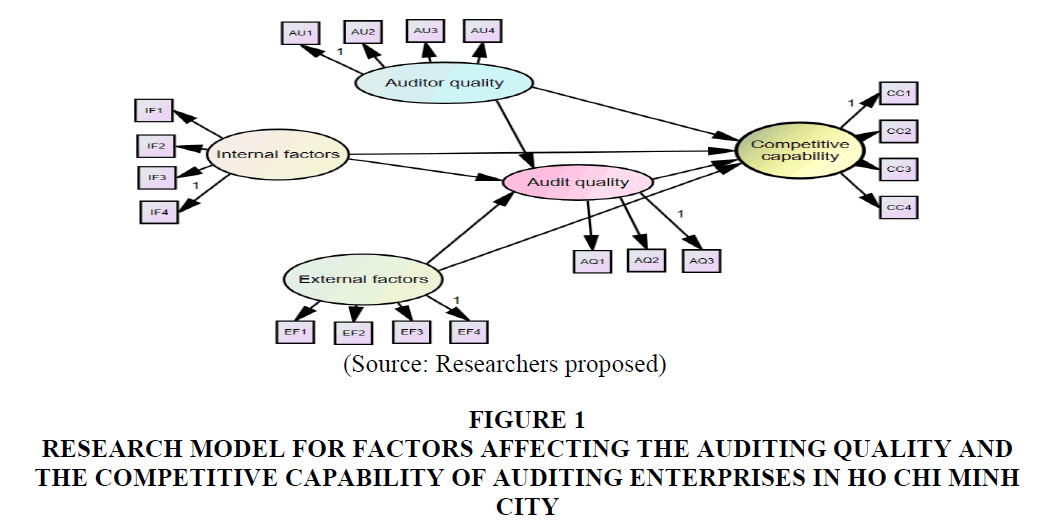
Research model for factors affecting the auditing quality and the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Research Model For Factors Affecting The Auditing Quality And The Competitive Capability Of Auditing Enterprises In Ho Chi Minh City.
Methods Of Research
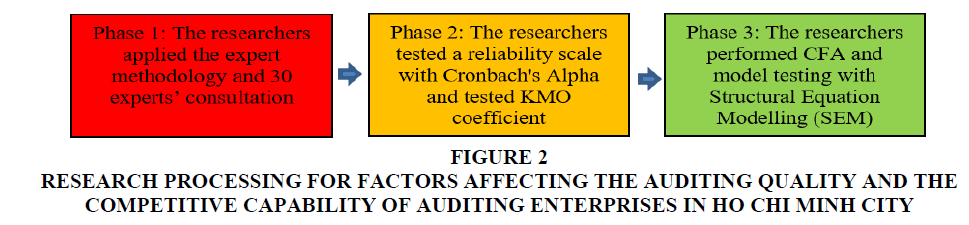
The research process for for factors affecting the auditing quality and the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City (Figure 2).
Figure 2:Research Processing For Factors Affecting The Auditing Quality And The Competitive Capability Of Auditing Enterprises In Ho Chi Minh City.
Phase 1: The researchers applied the expert methodology and based on 30 experts’ consultation about auditing and accounting to improve the scale and design of the questionnaire. The results of surveying 30 experts who showed that all factors affecting the auditing quality and the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City. The researchers created a list of possible factors gathered from the literature reviews as mentioned in the above studies.
Phase 2: The researchers tested a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. The researchers surveyed 800 persons related the auditing activities in HCMC (They are including 150 lecturers teaching accounting and auditing, 150 managers of auditing, 200 auditors, 50 enterprises of auditing, 150 officers working in auditing and 100 enterprises using auditing service). 19 items and 788 samples processed and Data collected from July 2018 to July 2019 in Ho Chi Minh City. The researchers got simple random sampling technique and having 30 minutes for the survey. 19 questions answered and 788 samples processed and surveyed by hard copy distributed among more than 60.000 persons related to audit and accounting. All data collected from the questionnaire are coded, processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos. This method is based on the Eigenvalue, the appropriate factorial analysis and the observed variables in the whole which are correlated when Average Variance Extracted is>50%, the KMO coefficient is within 0.5 to 1, Sig coefficient≤5%, the loading factors of all observed variables are>0.5. In addition, the researchers tested exploratory factor analyses (EFA) were performed.
Phase 3: The researchers performed CFA and model testing with Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) analysis. The purpose of CFA helps to clarify: (1) Unilaterality, (2) Reliability of scale, (3) Convergence value, and (4) Difference value. A research model is considered relevant to market data if Chi-square testing is P-value>5%; CMIN/df ≤ 2, some cases CMIN/df may be ≤ 3 or <5 (Hair et al., 1998); GFI, TLI, CFI ≥ 0.9. However, according to recent researcher’ opinion, GFI is still acceptable when it is greater than 0.8; RMSEA ≤ 0.08. Apart from the above criteria, the test results must also ensure the synthetic reliability > 0.6; Average Variance Extracted must be greater than 0.5 (Hair et al., 1998).
Research Results
The scale reliability tests for factors affecting the auditing quality and the competitive capability of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
Table 1 showed that all of 19 variables surveyed Corrected Item-Total Correlation greater than 0.3 and Cronbach's Alpha if Item deleted greater than 0.6 and Cronbach’s Alpha is very reliability. Such observations make it eligible for the survey variables after testing scale. This showed that data was suitable and reliability for researching.
| Table 1: The Scale Reliability Tests For Factors Affecting The Auditing Quality And The Competitive Capability Of Auditing Enterprises | |||
| Items | Content | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AU1 | Labor qualifications in enterprise and management capacity | 0.936 | |
| AU2 | Financial capacity of enterprise and enterprise size | 0.956 | |
| AU3 | Audit enterprise has ability to link and cooperate with other enterprises and international economic integration | 0.960 | |
| AU4 | Audit enterprise has level of equipment and technology and Marketing capacity | 0.937 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for auditor quality (AU) | 0.960 | ||
| IF1 | Auditor’ knowledge requires extensive specialized knowledge such as auditing methodology and reach international and regional qualifications | 0.801 | |
| IF2 | An auditor in charge of management has often been trained in specialized subjects such as awareness of adherence to professional ethics | 0.809 | |
| IF3 | We know that the responsibility of auditor must not only monitor and improve the quality of services provided | 0.844 | |
| IF4 | Auditor’ skills must have some specialized subjects such as ability to apply technology and techniques and solving problems | 0.799 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for internal factors of auditing enterprise (IF) | 0.853 | ||
| EF1 | Legal system such as the completeness and synchronization of legal regulations | 0.936 | |
| EF2 | Quality of human resource auditing such as training program updated and the quality of training meets practical requirements | 0.951 | |
| EF3 | Quality control organization from outside such as remedies for violations | 0.945 | |
| EF4 | Strengthen inspection and supervision of service quality for companies providing independent audit services | 0.930 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for external factors of auditing enterprise (EF) | 0.955 | ||
| Code | Content | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted | |
| AQ1 | Auditor quality has a positive impact on the audit quality of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City | 0.934 | |
| AQ2 | Internal factors have a positive impact on the audit quality of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City | 0.886 | |
| AQ3 | External factors have a positive impact on the audit quality of auditing enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City | 0.935 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for audit quality (AQ) | 0.944 | ||
| CC1 | External factors have a positive impact on the competitive capability | 0.859 | |
| CC2 | Internal factors have a positive impact on the competitive capability | 0.829 | |
| CC3 | Auditor quality has a positive impact on the competitive capability | 0.880 | |
| CC4 | Audit quality has a positive impact on the competitive capability | 0.841 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for competitive capability (CC) | 0.886 | ||
| (Source: The researchers’ collecting data and SPSS 20.0) | |||
Table 2 showed that KMO coefficient is 0.861 and the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000. Result showed that there are five components. Extraction sums of squared loadings are % of Variance coefficient is 82.539 with the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000.
| Table 2: Kmo And Bartlett's Test For Factors Affecting The Auditing Quality And The Competitive Capability Of Auditing Enterprises In Ho Chi Minh City |
|||||
| Code | Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| EF2 | 0.938 | ||||
| EF1 | 0.936 | ||||
| EF4 | 0.932 | ||||
| EF3 | 0.870 | ||||
| AU4 | 0.971 | ||||
| AU1 | 0.967 | ||||
| AU2 | 0.922 | ||||
| AU3 | 0.920 | ||||
| CC4 | 0.911 | ||||
| CC1 | 0.874 | ||||
| CC2 | 0.858 | ||||
| CC3 | 0.791 | ||||
| IF4 | 0.854 | ||||
| IF1 | 0.851 | ||||
| IF2 | 0.841 | ||||
| IF3 | 0.795 | ||||
| AQ2 | 0.948 | ||||
| AQ3 | 0.942 | ||||
| AQ1 | 0.860 | ||||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy is 0.861 | |||||
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity; Sig. is 0.000 | |||||
| (Source: The researchers’ collecting data and SPSS 20.0) | |||||
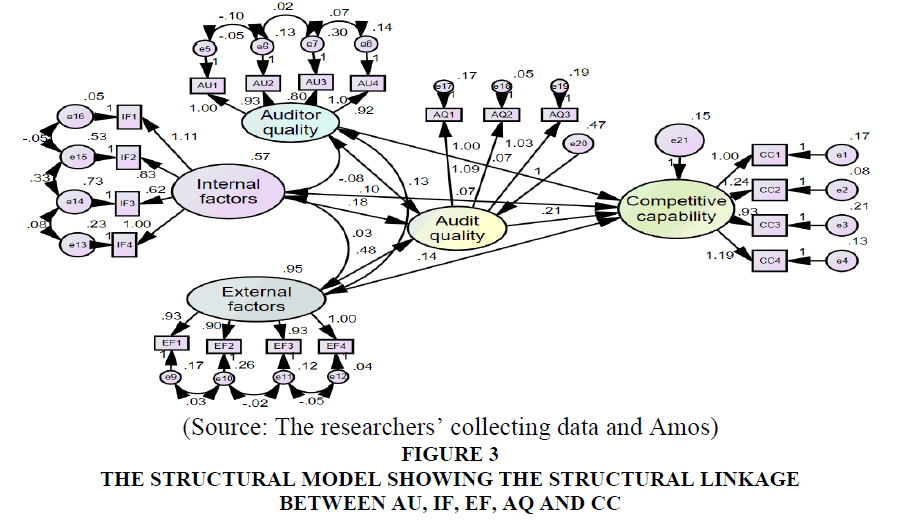
Table 3 showed that column Sig<0.01 with significance level 0.01 and column Conclusion H1: supported; H2: supported; H3: supported H4: supported; H5: supported; H6: supported and H7: supported. This showed that three factors affecting the management capacity and four factors affecting the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam with significance level 0.01 (Figure 3).
| Table 3: Coefficients From Structural Equation Modelling (Sem) | ||||||||
| Relationships | Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | S.E | T | Sig | Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audit quality |
<-- | Auditor quality |
0.103 | 0.120 | 0.026 | 4.004 | *** | H1: Supported |
| Audit quality |
<-- | Internal factors |
0.183 | 0.162 | 0.035 | 5.252 | *** | H3: Supported |
| Audit quality |
<-- | External factors |
0.478 | 0.543 | 0.030 | 16.120 | *** | H5: Supported |
| Competitive capability |
<-- | Audit quality |
0.214 | 0.366 | 0.024 | 8.906 | *** | H7: Supported |
| Competitive capability |
<-- | External factors |
0.137 | 0.266 | 0.020 | 6.786 | *** | H6: Supported |
| Competitive capability |
<-- | Internal factors |
0.072 | 0.108 | 0.022 | 3.320 | *** | H4: Supported |
| Competitive capability |
<-- | Auditor quality |
0.065 | 0.131 | 0.020 | 3.289 | 0.001 | H2: Supported |
| Note: Significant at 1 percent (All t-tests are one-tailed) (Source: The researchers’ collecting data, SPSS 20.0 and Amos) |
||||||||
Chi-square = 441.818; df = 133; p = 0.000; Chi-square/df = 3.322; GFI = 0.946; TLI = 0.972; CFI = 0.978; RMSEA = 0.054.
Conclusions And Managerial Implications
Conclusions
Quality and audit quality are always the top concern of many enterprises. Several researchers have tried to define the audit quality for more than 30 years. The ways of measurement these factors affect audit quality and the impact of audit quality to competitive capabilities. However, so far, these concepts have not been united yet and researches are continuing. This showed that audit quality is a multifaceted concept, difficult to observe and measure, depends on feeling and judgment of each individual. Therefore, it is difficult to have a unified viewpoint. The findings of the study have three factors affecting the audit quality and four factors affecting the competitive capabilities of auditing enterprises in HCMC with significance level 0.00. The researchers surveyed 800 persons related the auditing and accounting in HCMC. 19 items and 788 samples processed and Data collected from July 2018 to July 2019 in HCMC and the researchers get simple random sampling technique. The Cronbach's Alpha had been analysed, KMO test and the result of KMO analysis which used for structural equation modelling (SEM). Persons’ responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale (Conventions: 1: Completely disagree, 2: Disagree, 3: Normal; 4: Agree; 5: completely agree). The researchers had managerial implications for auditing enterprise policymaker of Vietnam continued to improve the management policies in the future.
Managerial Implications
Audit is also a service activity and thus it creates value for the economy, contributing to raising the national income, raising revenues for budget. Besides, the audit also attracted a large force of workers with high professional qualifications and especially foreign consultants working in international auditing companies. This force has passed many economic management experiences for enterprises, organizations as well as universities. Therefore, the researchers had managerial implications following.
External factors (β =0.543) has the strongest impact on the audit quality and the competitive capabilities of auditing enterprises in HCMC with significance level 0.01. Auditing has become an indispensable service in ensuring publicity and transparency of financial information of enterprises. However, it is in order to have good quality of audit services, ensure transparency and benefits for the customers, the inspection and control work of management agencies must be at the top. This has a great meaning to limit the phenomenon of letting false financial reports that released to the market, distorting the market and affecting the legitimate rights and interests of investors. Government should regularly monitor, inspect and supervise the implementation of recommendations after auditing of auditing firms and practicing auditors. Government should regularly strengthen handling of violations through auditing service quality according to competence or transferring competent agencies to handle according to law...
Internal factors (β =0.162) has the second impact on the audit quality and the competitive capabilities of auditing enterprises in HCMC with significance level 0.01. Audit enterprises should improve the training quality of auditing and accounting for auditors, updating knowledge, providing professional advice, quality control, providing support tools for all of auditors to improve quality and experience. Audit enterprises should regularly organize dissemination, propaganda, seminars, exchange, answer, policy, draw experience through checking the quality of annual auditing services for practicing auditors and auditing firms to real policies. Audit enterprises should continue to improve the quality of audit services to meet the requirements of international economic integration.
Auditor quality (β =0.120) has the least impact on the audit quality and the competitive capabilities of auditing enterprises in HCMC with significance level 0.01. Audit enterprises need to develop a strong and transparent audit industry and to meet the practical requirements. Audit enterprises should focus on developing human resources. First of all, it is necessary to review, evaluate, train and cultivate and train a team of qualified auditors and employees who are bright about professional ethics and practice their skills while performing service tasks. Audit companies also need to complete the management model, corporate management professionally, openly and transparently so that officials and employees always agree consensus. Auditing industry is still quite young but it is becoming more and more mature. Audit quality has made significant progress and is trusted by customers. Audit enterprises continue training activities on auditing profession staffs that will also enhance the practicum and apply knowledge into practicum. Audit enterprises continue focusing on personality education, professional ethics, lifestyle, behavioural communication culture, legal knowledge and information technology with the achievements of the 4.0 revolution for auditors according to the process, in accordance with international audit practice and standards.
Despite the highlighted contributions of this paper, some limitations have to be taken in this research results, thereby serving as proposals for future research. First of all, our model is tested on a sample of other Cities in Vietnam, so that the level of representativeness of the sample can be affected. Secondly, despite the high explanatory power of the model, it could be reinforced by adding control variables such as corporate culture, corporate social responsibility, audit firm tenure... Finally, the analysis of the longitudinal databases available to foreign enterprises that should allow them to make comparisons over time as a result of eventual changes in the variables.
References
- Amahalu Nestor Ndubuisi. (2017). Determinants of audit quality: Evidence from deposit money banks listed on nigeria stock exchange. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 7(2), 117-130.
- Bell, T.B., Causholli, M., & Knechel, W.R. (2015). Audit firm tenure, non-audit services, and internal assessments of audit quality. Journal of Accounting Research, 53(3), 461-509.
- Brown, V.L., Gissel, J.L., & Neely, D.G. (2016). Audit quality indicators: Perceptions of junior-level auditors. Managerial Auditing Journal, 31(8), 949-980.
- Dimas Dwi Oktavianto. (2018). The factors affecting the audit quality with the understanding on information systems as the moderating variable. Accounting Analysis Journal, 7(3), 168-175.
- Eko Suyono. (2012). Determinant factors affecting the audit quality: An indonesian perspective. Global Review of Accounting and Finance, 3(2), 42-57.
- Gonthier-Besacier, N., Hottegindre, G., & Fine-Falcy, S. (2016). Audit quality perception: Beyond the role-perception gap. International Journal of Auditing, 20(2), 186-201.
- Goodwin, J., & P. Kent (2006). Relation between external audit fees, audit committee characteristics and internal audit. Journal of accounting and finance, 40(1), 387-404.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., & Black, W. (1998). Multivariate data analysis with readings. US: Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Hosseinniakani, S.M., Inácio H., & Mota, R. (2014). A review on audit quality factors. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 4(2), 243-254.
- Husam Al-Khaddash (2013). Factors affecting the quality of Auditing: The Case of Jordanian Commercial Banks. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 4(11), 206-222.
- Hussein, F.E., & Hanefah, M. M. (2013). Overview of Surrogates to Measure Audit Quality. International Journal of Business and Management, 8(17), 84-91.
- Ilaboya, O. J., & Okoye, F.A. (2015). Relationship between audit firm size, non-audit services and audit quality. DBA Africa Management Review, 5(1), 1-10.
- Khasharmeh, H., & Desoky, A.M. (2018). Does the provision of non-audit services affect auditor Independence and audit quality? Evidence from Bahrain. Asian Academy of Management Journal of Accounting and Finance, 14(1), 25-55.
- Krishnan, J. (2005). Audit committee financial expertise and internal control: An empirical analysis. The Accounting Review, 80(2), 649-675.
- Noor Adwa Sulaiman. (2018). Perspectives on audit quality. Asian Journal of Accounting Perspectives, 11(1), 1-27.
- Nopmanee, T., & Ling, L. (2015). Auditor independence and audit quality: A literature review. Journal of Accounting, Auditing and Finance, 30(1), 101-121.
- Usman. (2016). Effect of experience and accountability on the quality of internal audit. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 5(3), 85-90.
- Vanstraelen, A. (2000). Impact of renewable long-term audit mandates on audit quality. European Accounting Review, 9(3), 419-442.
- Yeghaneh, Y.H., Zangiabadi, M., & Firozabadi, S.M.D. (2015). Factors affecting information technology audit quality. Journal of Investment and Management, 4(5), 196-203.