Research Article: 2020 Vol: 24 Issue: 1
Factors Affecting Talent Retention: Case Study of Universities in Ho Chi Minh City
Lan Chi Le, Saigon University
Tam Thanh Phan, Lac Hong University
Abstract
In the recent years, many universities have the application of the industrial revolution achievements (4.0) in education. This shows that talent retention is very important job and talented people are considered a source of competitive strength. Human capital is increasingly becoming a valuable source of organization. Managers have talent management methods; it is necessary to have appropriate human resource management. Because talented people are rare, precious and difficult to replace. Therefore, the main objective of this paper is to explore factors affecting talent retention of universities in Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC). The researchers surveyed 800 people who are working at eight universities in HCMC. The researchers applied simple random sampling technique. The researchers had tested Cronbach's Alpha, the exploratory factor analysis and Structural Equation Modelling (SEM). The paper had used questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale. Finally, there were four various factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
Keywords
Talent, Retention, University, Human Resource, HCMC.
Introduction
Organization needs in order to achieve success in its operations; it must focus on the important role of the human element. First of all, the organization needs to have a strong leadership; it must ensure the leadership throughout the organization. Second, that organization needs to be effectively managed. Third, the organization must have a staff with sufficient knowledge, skills, aptitudes, and work attitudes to a high degree appropriate for the organization's mission. Besides, talented people play a very important role in the success or failure of that organization. Therefore, domestic and non-state agencies and organizations must find suitable and effective measures to attract develop and retain talented people to ensure the maintenance and development of organizations. There are many factors affecting the attraction and retention of talented people that including the two most important factor groups that any organization must pay special attention to: related to the organization and its group of peoplerelated factors (Bidisha & Mukulesh, 2013). Organization must choose the right people, right job placement ensures the fit between organization and people, between people and jobs; have appropriate remuneration and reward regime with competence, qualifications and personal contributions to the organization. Training and professional development of individuals in the organization create opportunities for each individual, especially those who have the ability (talented people) to have the opportunity to try themselves with difficult, challenging, etc... are important elements in the source element group. At the same time, the team of leaders, managers who are good, dynamic and creative in agencies and organizations; suitable working environment; reasonable organizational structure with good coordination inside and outside organizations that are extremely important conditions for attracting and retaining talented people that any organization needs to pay special attention to during construction and development. Above mentioned things, the main objective of this paper is to find out factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC to maintain universities’ talent.
Literature Review
Talent Retention (TR)
A talent is someone who is able to surpass others and does not need to try his best to use it, they excel easily (Govaerts et al., 2015). A talent has a certain strength that others want to achieve. Talented people have outstanding qualities and capabilities to be able to undertake a difficult or complex job or field of operation and achieve results. They have effectively, very high quality, sometimes highest in a certain range. Talents are people with broad knowledge, high intelligence, skilled career (Irshad, 2014). They have the purpose of living in accordance with the development trend of society. Besides, they are people with political ideals and have motives to live in a bright society. Talents are people who have high professional qualifications and professional ethical qualities as well as good human dignity that are respected by the intelligence and scientific working methods (Sinha & Sinha, 2012). They have good ideas to business executives, have the ability to create innovative initiatives or solve timely problems if any in the business activities (Schuler et al., 2011). Maintaining talent requires managers to consider ensuring that talented people always want to be dedicated and committed to sticking to their organization, promoting all their capabilities to the organization (Kossivi, 2016). Maintaining talent needs to create opportunities for them to develop ideas for their own initiative to work, ensure working conditions for them, affect their loyalty and commitment (Mohammed, 2015).
Job Satisfaction (JS)
Job satisfaction is defined as the degree to employees like their jobs. Based on perceptions, an employee develops a positive or negative attitude towards their job and the working environment (Loan-Clarke et al., 2010). It is talented people, when a talented person is satisfied with his new job, he can become a talented person committed to the universities (Safiullah, 2015). When they are satisfied, they increase their loyalty and work more effectively to create value. Therefore, it is essential to have the right policies for the job. The career goals of a talented person are to experience job satisfaction. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
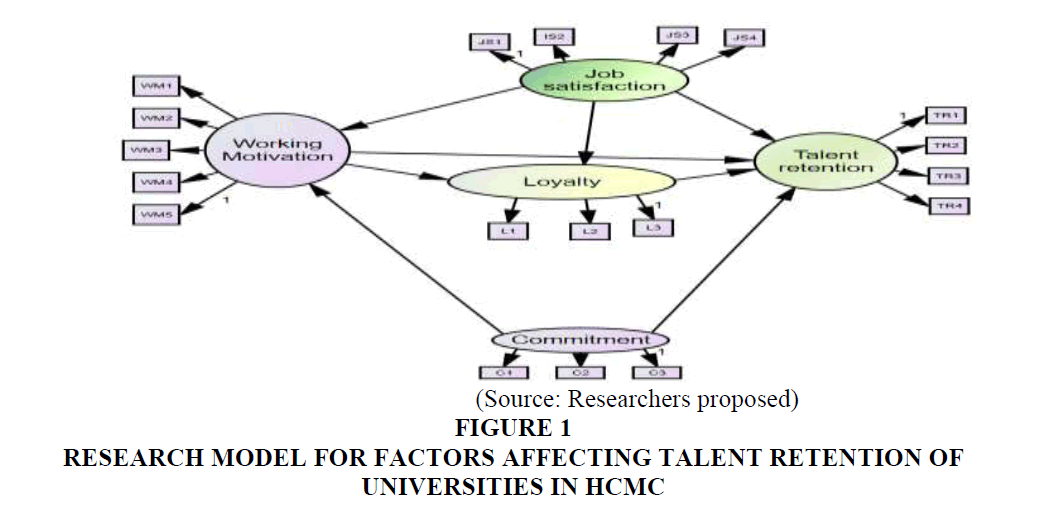
Hypothesis H1: Job satisfaction has a positive impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC.
Working Motivation (WM)
The motivation for working of talents is the effort of each talent itself. Therefore, the goal of the universities’ managers is to create a motivation for talented people to work to achieve the highest working efficiency for the universities (Mehta et al., 2014). It can be said that the motivation to work is the voluntariness, the desire of employees to try to strive to achieve the goals set by the organization (Raziq & Maulabakhsh, 2015). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H2: Working motivation has a positive impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC.
Loyalty (L)
Talent loyalty is often connected with the way an organization treats their talents. If talented people feel that they are treated fairly and have the best opportunities in the organization (Umamaheswari & Krishnan, 2016). They will rarely want to move to work at other organizations. An organization will gain talent loyalty by satisfying the various aspects of talent for work related needs (Turkyilmaz et al., 2011). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H3: Loyalty has a positive impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC.
Commitment (C)
An employee's commitment is an emotional and intellectual connection of an employee to his/her job, organization, management or colleagues (Loan-Clarke et al., 2010). This is affecting him/her to applying effort to your work. According to another study by (Singh & và Dixit, 2011), stated that employees 'commitment is a measure of their employees' energy and passion for their businesses. Committed employees are individuals who take action to improve the business results of the organization which they work (Sergio et al., 2013). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H4: Commitment has a positive impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC.
Hypothesis H5: Commitment has a positive impact on working motivation of universities in HCMC.
Hypothesis H6: Working motivation has a positive impact on loyalty of universities in HCMC.
Hypothesis H7: Job satisfaction has a positive impact on loyalty of universities in HCMC.
Hypothesis H8: Job satisfaction has a positive impact on working motivation of universities in HCMC.
Research model for factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC (Figure 1):
Methods Of Research
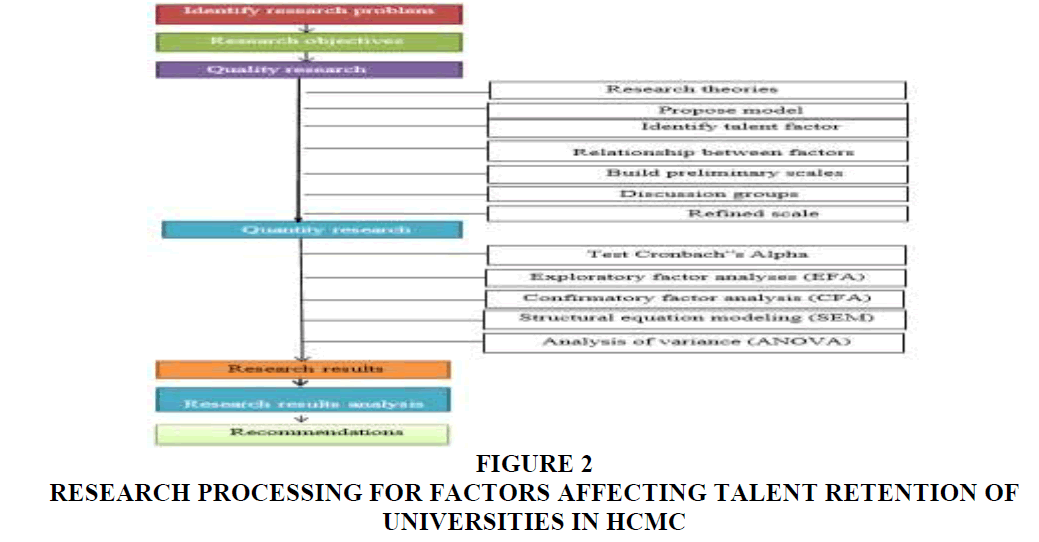
The research process for factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC (Figure 2 ((Source: Researchers proposed))).
Factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC that had many steps following: Step 1: It is to identify research problem. This paper is usually chosen through experience, accumulated knowledge and practical needs of society. Step 2: The researchers found the objectives of research. Step 3: The researchers found the research theories. Step 4: The researchers built the research model. Step 5: The researchers identified talent factors of the research model. Step 6: The researchers tested relationship between talent factors of the research model. Step 7: The researchers built preliminary scales based on 10 experts’ consultation about education to improve the scale and design of the questionnaire. The results of surveying 10 experts who showed that all factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC. Step 8: The researchers had adjustment and refined scale by testing a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. The researchers surveyed 300 people working for 8 universities in HCMC. The research results built questionnaire for quantitative research (n = 800 people). Step 9: The researchers surveyed 800 people working for 08 universities by questionnaires and tested a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. Each university has 100 people including 30 lecturers, 30 staffs and 40 managers. There are 19 items and 765 samples processed and data collected from January 2019 to October 2019 at 8 universities in HCMC. Step 10: The researchers had simple random sampling technique and spent 30 minutes for a survey. All data collected from the questionnaire are coded, processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos. The researchers had to test a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. This method is based on the eigenvalue, the appropriate factorial analysis and the observed variables in the whole which are correlated when Average Variance Extracted is > 50%, the KMO coefficient is within 0.5 to 1, Sig coefficient ≤ 5%, the loading factors of all observed variables are >0.5. In addition, the researchers tested exploratory factor analyses (EFA) were performed (Hair, Anderson, Tatham, & Black, 1998). Step 11: The researchers continued to confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). EFA's next step is to test if there is a prior theoretical model that underlies a set of observations. CFA is also a form of SEM. When developing CFA, the observed variables are also indicator variables in the measurement model. The purpose of CFA helps to clarify: (1) Unilaterality, (2) Reliability of scale, (3) Convergence value, and (4) Difference value. A research model is considered relevant to market data if Chi-square testing is P-value > 5%; CMIN/df ≤ 2, some cases CMIN/df may be ≤ 3 or < 5 (Hair, Anderson, Tatham, & Black, 1998); GFI, TLI, CFI ≥ 0.9. However, according to recent researcher’ opinion, GFI is still acceptable when it is greater than 0.8; RMSEA ≤ 0.08. Apart from the above criteria, the test results must also ensure the synthetic reliability > 0.6; Average Variance Extracted must be greater than 0.5 (Hair, Anderson, Tatham, & Black, 1998). Step 12: The researchers tested SEM model based on the results of step 11 and ANOVA analysis. Step 13: The researchers had research result analysis and had recommendations.
Research Results
The scale reliability tests for factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC.
Table 1 showed that factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC that had all of 19 variables surveyed corrected item-total correlation greater than 0.3 and Cronbach's Alpha if Item deleted greater than 0.6 and Cronbach’s Alpha is very reliability. Such observations make it eligible for the survey variables after testing scale. This showed that data was suitable and reliability for researching.
| Table 1: The Scale Reliability Tests For Factors Affecting Talent Retention Of Universities In Hcmc | |||
| Items | Content | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| JS1 | I am satisfied with the job | 0.891 | |
| JS2 | I find it really interesting at work | 0.885 | |
| JS3 | I feel happy to be appreciated | 0.902 | |
| JS4 | I feel satisfied because I have the opportunity to develop and advance | 0.876 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for job satisfaction (JS) | 0.914 | ||
| WM1 | I find the job interesting | 0.968 | |
| WM2 | I often get rewarded for a good job | 0.975 | |
| WM3 | University has performance feedback that helps me work harder | 0.975 | |
| WM4 | I learn new things from my organization | 0.965 | |
| WM5 | I often get praised for the good work | 0.971 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Working motivation (WM) | 0.976 | ||
| L1 | I think the organization deserves to be loyal | 0.946 | |
| L2 | High level relationships attract me | 0.896 | |
| L3 | I feel obligated to stay with this organization | 0.944 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Loyalty (L) | 0.952 | ||
| C1 | I feel valued at my organization | 0.803 | |
| C2 | I feel proud to be part of the organization | 0.736 | |
| C3 | I cannot leave the organization right now because I feel obligated to everyone in the organization | 0.729 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for commitment (C) | 0.823 | ||
| TR1 | I enjoy working for this organization | 0.806 | |
| TR2 | The work I do is very important | 0.755 | |
| TR3 | I have no intention of leaving this organization | 0.783 | |
| TR4 | I see my future in this organization | 0.696 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for talent retention (TR) | 0.810 | ||
| (Source: The researchers’ collecting data and SPSS 20.0) | |||
Table 2 showed that extraction sums of squared loadings of Cumulative % is 80.828% (>60%) and Initial Eigenvalues is 1.181 (>1.0). This result is suitable for next step.
| Table 2: Total Variance Explained | |||||||
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadingsa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | |
| 1 | 7.330 | 38.581 | 38.581 | 7.330 | 38.581 | 38.581 | 6.352 |
| 2 | 2.952 | 15.537 | 54.118 | 2.952 | 15.537 | 54.118 | 3.553 |
| 3 | 2.188 | 11.514 | 65.632 | 2.188 | 11.514 | 65.632 | 4.178 |
| 4 | 1.706 | 8.979 | 74.611 | 1.706 | 8.979 | 74.611 | 5.229 |
| 5 | 1.181 | 6.217 | 80.828 | 1.181 | 6.217 | 80.828 | 2.368 |
| 6 | 0.624 | 3.286 | 84.115 | ||||
| ? | ? | ? | ? | ||||
| 19 | 0.030 | 0.156 | 100.000 | ||||
| (Source: The researchers’ collecting data and SPSS 20.0) | |||||||
Table 3 showed that KMO coefficient is 0.872 and the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000. Result showed that there are six components. Extraction sums of squared loadings are % of Variance coefficient is 80.828 with the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000.
| Table 3: Kmo And Bartlett's Test For Factors Affecting Talent Retention Of Universities In Hcmc | |||||
| Code | Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| WM4 | 0.981 | ||||
| WM1 | 0.974 | ||||
| WM5 | 0.966 | ||||
| WM2 | 0.959 | ||||
| WM3 | 0.875 | ||||
| JS4 | 0.931 | ||||
| JS1 | 0.901 | ||||
| IS2 | 0.882 | ||||
| JS3 | 0.855 | ||||
| TR2 | 0.857 | ||||
| TR4 | 0.823 | ||||
| TR1 | 0.814 | ||||
| TR3 | 0.679 | ||||
| L3 | 0.976 | ||||
| L2 | 0.960 | ||||
| L1 | 0.854 | ||||
| C3 | 0.883 | ||||
| C2 | 0.876 | ||||
| C1 | 0.821 | ||||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy: 0.872 | |||||
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity; Sig. is 0.000 | |||||
| (Source: The researchers’ collecting data and SPSS 20.0) | |||||
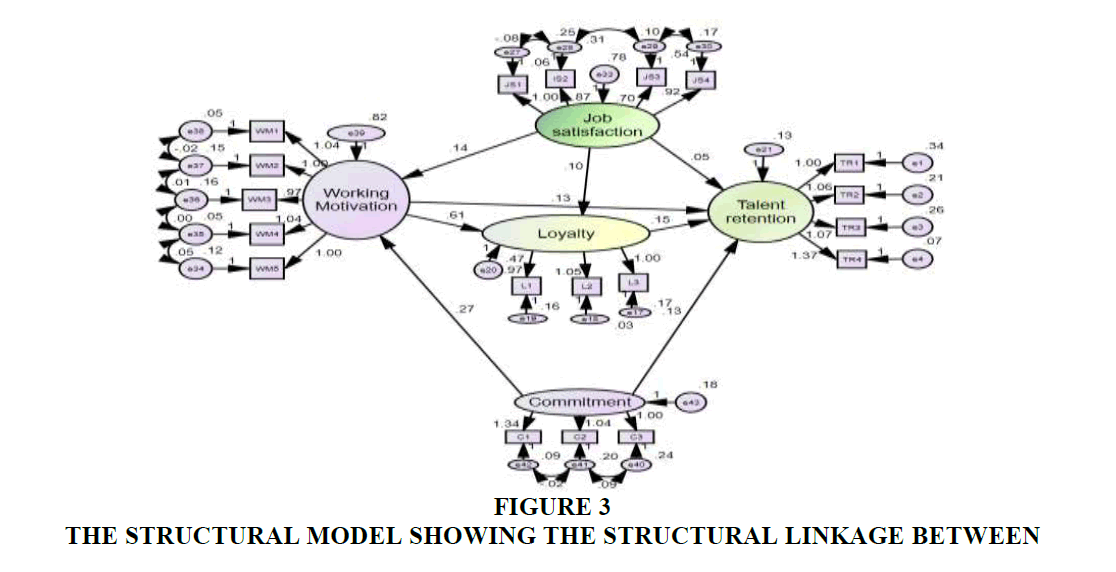
Table 4 showed that the objective of this paper is to identify factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC and identify the relationship of factors and detect the influence of these factors. The theoretical model is built on the specific basis of Vietnamese culture including the following components: Job satisfaction, work motivation, commitment, loyalty and relationship review of them. Besides, Table 4 showed that column “P” < 0.01 with significance level 0.01 and column “Conclusion” following:
| Table 4: Coefficients From Structural Equation Modelling (Sem) | |||||||
| Relationships | Estimate | Standardized Coefficient | C.R. | P | Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working motivation | <--- | Job satisfaction | 0.145 | 0.139 | 3.005 | 0.003 | H8: Accepted |
| Working motivation | <--- | Commitment | 0.272 | 0.126 | 3.187 | 0.001 | H5: Accepted |
| Loyalty | <--- | Job satisfaction | 0.098 | 0.096 | 3.257 | 0.001 | H7: Accepted |
| Loyalty | <--- | Working motivation | 0.611 | 0.625 | 19.524 | *** | H6: Accepted |
| Talent retention | <--- | Loyalty | 0.154 | 0.318 | 6.781 | *** | H3: Accepted |
| Talent retention | <--- | Job satisfaction | 0.047 | 0.094 | 2.795 | 0.005 | H1: Accepted |
| Talent retention | <--- | Commitment | 0.126 | 0.123 | 3.223 | 0.001 | H4: Accepted |
| Talent retention | <--- | Working motivation | 0.126 | 0.266 | 5.772 | *** | H2: Accepted |
| Note: ***Significant at 1.0 percent (All t-tests are one-tailed) (Source: The researchers’ collecting data, SPSS 20.0 and Amos) |
|||||||
H1: supported: Job satisfaction impacted on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
H2: supported: Working motivation impacted on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
H3: supported: Loyalty impacted on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
H4: supported: Commitment impacted on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
H5: supported: Commitment impacted on working motivation of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
H6: supported: Working motivation impacted on loyalty of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
H7: supported: Job satisfaction impacted on loyalty of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
H8: supported: Job satisfaction impacted on working motivation of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01.
This showed that four factors affecting talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01 (Figure 3 (Source: The researchers’ collecting data and Amos)).
Figure 3:The Structural Model Showing The Structural Linkage Between Chi-square = 397.413; df = 135; p = 0.000; Chi-square/df = 2.944; GFI = 0.948; TLI = 0.976; CFI = 0.981; RMSEA = 0.056.
Conclusions And Managerial Implications
Conclusions
The research results of the paper are help to propose management implications for the purpose of developing appropriate policies, propose to increase the motivation to work for talented people by satisfying job satisfaction, improving the commitment of talented people. This supports them to enhance the loyalty of those talents. Theoretically, the research's contribution is to identify criteria for identifying talents in the field of education, thereby paper is helping administrators accurately identify the talents they need to maintain in the team and his position. Besides, the relationship of 4 factors affecting the retention of talent in universities in Vietnam determined. In practical terms, the article has added the model of talent retention through factors of job satisfaction, work motivation, commitment and loyalty of talents. Based on the above mentioned things, the researchers had managerial implications following:
Managerial Implications
Managerial implication for loyalty (β=0.318) had the strongest impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01. Leaders need to take actions to strengthen the trust of talented people, support their work when they need to increase trust in them, treat and recognize equity in a timely manner that is also a way to increase trust in the level. Talents will feel their importance to the organization they are dedicated and cannot leave the organization because of the responsibility to do business with the trust of their leaders. Besides, they feel the organization deserves their loyalty, they will always be satisfied with what their superiors and colleagues do treating yourself when leaders create a fair and professional working environment. If other organizations are attracting talent, they are not paying much attention; they will wholeheartedly propose improvements to bring high performance to the organization.
Managerial implication for working motivation (β=0.266) had the second impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01. University leaders need to develop this strong point to increase the motivation to work for talented people. Every day they go to work, they are interested in their work, with students and with colleagues. Because this environment has created an interest in their work, it is necessary to promote and maintain the ways of creating excitement in the university. In building working motivation, leaders need to build internal and external motivation. A motivated employee will meet the clear goals set by the organization and will be achieved with unyielding efforts. Employees are motivated to work for the organization to be more successful because they will constantly look for innovative ways to do a better job. Therefore, universities need to have policies to motivate their employees, create excitement in work for talented people to work.
Managerial implication for commitment (β=0.123) had the third impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01. Leaders need to pay attention to the issue of developing career programs for talented people, helping them to have specific directions and plans for their career development at the universities, thereby helping them to have a good feeling and inspired to work and more responsible for the job. Leaders should pay more attention to building a sense of responsibility in the work of each individual working in the university, in order to overcome this weakness in universities. Besides, it is necessary to build a professional university image so that talented people feel proud of choosing this university to work. Leadership and colleagues continue to be a factor to increase the commitment of talented people, thanks to their support that talented people are more interested in work, more eager to work, contribute to the organization. This is increasing commitment to leadership needs to focus on the need to inspire work for talent.
Managerial implication for job satisfaction (β=0.094) had the least impact on talent retention of universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01. Universities need to increase job satisfaction of the staff, the administrators at the university in HCMC. Universities should pay attention to the following issues: Improve the working relationship between employees and between employees and management units; pay attention to the arrangement of job characteristics suitable to the capacity of employees; develop policies on salary and proper management methods, apply welfare and reward regimes, trainings, promotions and appointments appropriately. Administrators need to appreciate the value of their contribution to the job so that their job satisfaction will be increased. In particular, they will feel happy to be appreciated.
Finally, the study was conducted by a convenient sampling method so the results brought about subjective factors of the author, reducing the objectivity and generalization. Therefore, the following studies should consider the use of probability sampling methods because it ensures a higher degree of representativeness and increases the size of the sample for more accurate analysis results.
References
- Bidisha, L.D., & Mukulesh, B. (2013). Employee retention: A review of literature. Journal of Business and Management, 14(1), 8-16.
- Govaerts. (2015). Influence of learning and working climate on the retention of talented employees. Journal of Workplace Learning, 23(1), 37-48.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., & Black, W. (1998). Multivariate data analysis with readings. US: Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Irshad, M. (2014). Factors affecting employee retention: Evidence from literature review. Abasyn Journal of Social Sciences, 4(1), 84-97.
- Kossivi, B. (2016). Study on determining factors of employee retention. Journal of Social Sciences, 4(1), 261-268.
- Loan-Clarke, J., Arnold, J., Coombs, C., Hartley, R., & Bosley, S. (2010). Retention, turnover and return - A longitudinal study of allied health professionals in Britain. Human Resources Management Journal, 20(1), 391-406.
- Mehta, M., Kurbetti, A., & Dhankhar, R. (2014). Study on Employee Retention and Commitment. International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies, 2(2), 1-15.
- Mohammed, A. (2015). The impact of talent management on employee engagement, retention and value addition in achieving organizational performance. International Journal of Core Engineering v� Management, 1(12), 142-152.
- Raziq, A., & Maulabakhsh, R. (2015). Impact of working environment on job satisfaction. Procedia Economics and Finance, 23(1), 717-725.
- Safiullah, A.B. (2015). Employee motivation and its most influential factors: A study on the Telecommunication Industry in Bangladesh. World Journal of Social Sciences, 5(1), 79-92.
- Schuler, R.S., Jackson, S.E., & V� Tarique, I. (2011). Global talent management and global talent challenges: Strategic opportunities for IHRM. Journal of World Business, 46(4), 506-516.
- Sergio, R.P., Al-Rawahi, S.M.H., & V� Gernal, L.M. (2013). Managing talent for competitive advantage: Perspective from Gulf Cooperation Council nationals. Asian Journal of Business and Governance, 2(1), 125-137.
- Singh, S., & V� Dixit, P.K. (2011). Employee retention: The art of keeping the people who keep you in business. VSRD International Journal of Business v� Management Research, 1(7), 441-448.
- Sinha, R., & Sinha, C. (2012). Factors affecting employee retention: A comparative analysis of two Organizations from heavy engineering industry. European Journal of Business and Management, 4(3), 145-162.
- Turkyilmaz, A., Akman, G., Ozkan, C., & V� Pastuszak, Z. (2011). Empirical study of public sector employee loyalty and satisfaction. Industrial Management v� Data Systems, 111(5), 675-696.
- Umamaheswari, S., & Krishnan, J. (2016). Work Force Retention: Role of work environment, organization commitment, supervisor support, and training and development in ceramic sanitary ware house industries in India. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, 9(3), 612-633.