Research Article: 2020 Vol: 19 Issue: 5
Evaluating the Factors Influencing Customer Perception on Online Buying Behavior of Sub Urban People of Bangladesh
Md. Al Amin, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University
Sabiha Matin, Daffodil International University
Md. Rakibul Islam, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University
Israt Jahan, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University
Md. Hafizur Rahman, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University
Abstract
The research aims at analyzing the consumer online buying behavior of Sub Urban People of Bangladesh regarding the social media and online marketing platforms. The study, conclusive in nature, uses quantitative research methods and collected data through survey questionnaires by five Likert scales through online-offline basis from 285 respondents and in-depth interviews from 10 experts in this field having snowball sampling techniques. The relationship among the series of variables was done by sophisticated statistical tools including factor Analysis, regression, correlation, and hypothesis testing by t-statistics overcoming the limitations in the availability of data, financial problems, and time.
The researchers have found nine factors (Psychological factor, Personal Factors, Peer Influence, Web Influence, Brand Personality, Promotion, Environmental forces, Convenience, Process) which influence the Online Buying Behavior of Sub Urban People of Bangladesh. The relationship among the internal factors and processing factors are related; the external factors have also the correlated with processing factors (security, privacy or Trust issues) and positive Consumer Perception Or Consumer Buying Behavior is the results of this process factor which means psychological factor, personal factors, peer influence, web influence, brand personality, promotion, environmental forces, convenience factors generate Consumer perception for online buying behavior being loyal. The identified factors have significant relationship creating positive or negative consumer perception and convincing customers to purchase the products through internal factors & external factors which influence on security, privacy, and trust disposition attitude of the consumers. The organizations should not be focusing on ‘technologically’ only; instead, they need proper judgment on how consumers perceive their efforts in the process. The use of online marketing platforms has a positive perception in consumers’ minds.
The implications are to attract sub-urban people to use social media and other online platforms. Also, using online marketing platforms, a positive perception of the consumers can be understood by the companies. The research conforms to developing a new theory called Input Processing output (IPO) Model, methodological improvement, and practical implications of how organizations can capture the sub-urban as their customer through online.
Keywords
Sub-Urban People, Online Buying Behavior, Customer perception, Social Media Marketing, Motivations.
Introduction
With the advent of technology, social media, as well as other online marketing platforms, have proven to be very effective for the marketing efforts of the companies (Ngai et al., 2015). Although they are overwhelmingly popular among the city dwellers, there are vast implications of these platforms in the urban areas (Misirlis & Vlachopoulou, 2018). This study aims to evaluate the factors influencing consumer perception on the online marketing platforms for the Sub Urban people in Bangladesh. In doing this study, it has been assessed whether these platforms are appropriate for the promotion of products to the Sub Urban people of Bangladesh.
Problem Statement
The companies are continuously targeting urban people to conduct their marketing activities-besides, plenty of customers in the online market who are dwelling in the Sub Urban region. Therefore, the promotion of products to these people can be a massive success since companies are primarily entering in the online industry. Besides, the companies can target these people for a better result in the market, which plays a significant role in providing them with a competitive advantage (Amatulli et al., 2018). Online marketing platforms can make a difference because Sub Urban people are firmly enthusiastic about online marketing platforms. This study is needed to understand factors attracting the Sub Urban people and tapping into this vast market to gain a high profit.
Rationale Statement
Many types of research have been conducted on consumers' perceptions of online marketing. Several types of research have been conducted on online marketing platforms and their prospects for companies (Stephen, 2016). However, few of these researches fundamentally focused on measuring the influence on customer perception on the online buying behavior of Sub Urban People of Bangladesh. Since many people are newly using social media and other online platforms, they can be attracted by the companies more effectively. It is a vast scope for the companies that these factors can be positively used in the decision making of the companies (Amatulli et al., 2018; Al Amin et al., 2020). Therefore, this research will have a greater significance in the academic field and pave new possibilities. Furthermore, it will also be a new dimension for the companies to focus on. That is why this research bears great significance for the companies and researchers in this field.
Research Aims
The major aim of the research is to analyze the perception of the customers dwelling in the Sub Urban region regarding the online marketing platforms. To reach these objectivs, some specific objectives are needed.
There are some specific objectives of this research which are provided below:
• To find out the factors that influence consumers for purchasing from different online platforms in the Sub Urban people of Bangladesh;
• To evaluate how the online platforms are used by the companies directed towards the Sub Urban people of Bangladesh;
• To assess the effectiveness of the use of online marketing platforms in the Sub Urban people of Bangladesh.
Literature Review
Online Marketing
Online Marketing Platforms have drastically altered the orthodox notions of marketing practices, and there are abundant works of literature to bolster this proclamation. According to Reddy (2013), online marketing platforms can craft a profound and yet lucrative relationship with the customers in sales, marketing, and customer support. Dlodlo & Mafini (2014) stated that the use of online marketing could amend the marketing and operations efficiency of a firm. Furthermore, following the statement of Boyles (2011), it is grasped that online marketing platforms offer an assortment of prospects for firms that support it to attain marketing and operational proficiency by sinking costs. Moreover, Sharma (2011) states that the usage of online platforms such as websites, e-mails, online advertising, viral marketing, social media, etc. allows the companies to escalate the responsiveness of the customers about their brand and sustain their loyalty with professed quality and brand associations. Besides, Morgan-Thomas & Veloutsou (2013) depict that because of the virtual nature of the World Wide Web, possessing an established and trusted brand perceived in the cognizance of the customers, which provide acquaintance and reduce the perceived risk. However, various factors of online marketing are presumed to influence the perception of consumers. According to Schivinski & Dabrowski (2015), large companies like Coca-Cola have used Facebook to effectively connect with their customers and created a positive change in the perception of these customers about their products. However, Burke & Kraut (2016) stated that companies need a robust online marketing plan along with the usage of effective online marketing platforms to connect effectively with the consumers. Hence, it can be argued that the use of online marketing platforms can be effective for the positive perception of consumers. Still, it should be done according to a robust plan and effective implementation of the plan (Jung, 2017).
Consumer Buying Behavior
Consumer Buying Behaviour is coordinated towards understanding the path in which the people, associations, and gatherings pick, buy, and discard the products (Cruz-Cárdenas & Arévalo-Chávez, 2018). As per the examination led by Kotler & Keller (2012), different elements impact the buying behavior of the purchasers, including past involvement, taste, value, marking, and so on (Al Amin & Bhuiyan, 2019). The general execution of a business is fundamentally dictated by the comprehension of the consumer buying behavior by the organizations in the market (Bae & Lee, 2011) like different wares made by the organizations, comprehension of customer purchasing conduct for the stock is additionally vital (Haque & Faruquee, 2013). For this, they need data about share. Since there is no use for utilization, the purchasers of offers consider whether they will get adequate come back from their venture (Stephen, 2016). They might want to produce better benefits from their venture of offers (Raunaque et al., 2016).
For this reason, they consider the organizations with a better brand picture and remarkable notoriety of making a critical measure of benefit in the business (Pushpa Bhatt & Sumangala, 2012). Additionally, word to mouth preparation is essential for urging individuals to buy securities exchange partakes in the nation. If a few buyers can pick up benefits with their interests in the offer market even, they may suggest the offers of a similar organization (Bae & Lee, 2011). And the offer of that organization might be extremely famous among the customers, which they have closer and better associations with and tend to pull in a more considerable amount of offer for them (Haque & Faruquee, 2013).
The Theory of Reasoned Action can be considered here, which was created by Martin Fishbein & Ajzen in 1967 (Fishben and Ajzen, 1975). This theory depicts that consumers carry out actions based on their intention to create or attain a specific outcome (Lamb et al., 2011). Consumers only take particular actions when a specific result is expected. The consumers will purchase a product when they are convinced that their desires and needs will be fulfilled by that product (Kapoor & Kulshrestha, 2014). When all the factors of consumer perception are in favor of the decision making, the consumers are likely to purchase the products.
Factors of Consumer Perception
To contemplate the consumer perception of the online marketing efforts, the researcher has discovered some factors which have a closer connection with it. These factors are two types,' i.e., internal factors and external factors.
Some psychological factors like motivation, learning, attitude, beliefs, ego, and super-ego are also included among internal factors. Motivation is a factor that encourages a person to purchase a specific product. Attitude and beliefs also shape the potential consumer's perception regarding a product. These three factors can create positive customer perception (Dlodlo & Mafini, 2014 and ). Some psychosocial factors, which include ID, ego, and super-ego, may also be linked to the problem. ID comprises the unconscious and subconscious minds and the instincts of the individuals (Haque & Faruquee, 2013).
Superego is primarily associated with all levels of consciousness, and consumers tend to be attracted to socially acceptable commodities. Finally, the ego is the part of the whole personality of an individual, which compels one to decide on the purchase of the product (Singh, 2016). Then there are the personal factors which include age, income level, lifestyle, and personality (Hemsley-Brown & Oplatka, 2016). People of different ages tend to perceive their needs and the product's capacity to fulfill those needs differently (von Helversen et al., 2018). Furthermore, peer influence includes reference groups, family, roles and status, social values (Kapoor & Kulshrestha, 2014). Reference groups are the ones who have been satisfied after using the product of the company (Lamb et al., 2011). Also, social roles and status can shape their needs and demands of particular products (Singh, 2016). Lastly, social values can also promote these people to purchase the products.
Web influence includes factors like easy to read, easy to navigate, comfortably viewed, and quick to download (Lee, 2016). If the website is easy to read and easy to navigate, the potential customers will be satisfied with their encounter. The speed of the website should also be up to the market. It should not turn slow when there is high traffic. Any items should be downloaded quickly (Boyles, 2011).
Regarding the external factors, four categories have been selected for this research. They are brand personality, promotion, PESTEL, and convenience. Brand personality includes sincerity, excitement, competence, sophistication, and ruggedness (Bairrada et al., 2019). The company can flourish its brand image by doing marketing functions effectively and ensuring that the products are promoted honestly and sincerely (Güse, 2011). They want to ensure that the products that they bought will fulfill their needs. Also, the products have to be rugged as in sturdy and durable (Kapoor & Kulshrestha, 2014).
In the promotion category, various online promotional platforms are included, which can provide the company with a competitive edge. The factors that are included are Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, Twitter, Google+, etc. Among these, Facebook is the most prominent one, with more than 2 billion monthly active users (Lee, 2016 and Al Amin, 2018). There is a considerable scope for companies to reach out to more and more customers. Also, YouTube has gained much popularity in recent years (Singh, 2016). LinkedIn is a social media for professionals who are also used to promote various kinds of products. Twitter is used to provide public posts called tweets, which can be seen by the followers along with others. Lastly, Google+ has benefits that have other Google accounts such as Gmail (Lamb et al., 2011).
PEST/environmental factors are also crucial external factors. Firstly, political factors are essential, which include political turbulence, election, protests, terrorism, etc. When the political condition of a country is unstable, the consumers tend to avoid going to shops to purchase goods (Reic, 2016). The economic factors include economic policies, tax policies, income levels, unemployment rates, etc. The social factors include social values, ideologies, culture, religion, etc. At present, technological factors are more important than ever (Lamb et al., 2011). They include modern innovation, communication platforms, online devices and websites, databases, etc. Ecological factors are also important; the companies must ensure that environmental pollution and degradation is not accelerated with the manufacturing process (Reddy, 2013). Lastly, the legal factors indicate various kinds of legislation that are imposed by the government.
Convenience factors are also significant to consider. In this category, the major factors include distribution channels, distribution points, delivery time, and placement of order (Güse, 2011). The consumers like those companies which have convenient arrangements for order placement (Kapoor & Kulshrestha, 2014). After placing the order, the goods also need to be delivered timely.
Three significant factors are there, which are reinforced by the input factors. They consist of security, privacy, and trust disposition attitude (Al Amin, 2017). Security refers to be free from any threat, danger, or loss, which can incur from the transactions (Singh, 2016). There is also a risk of hacking the data, which can negatively influence consumer perceptions (Raunaque et al., 2016). Moreover, privacy refers to the situation where the private information of the consumers, such as ID number, bank account number, passwords, etc. is protected (Usmani, 2012). The consumers only decide to purchase items from a company that offers a higher level of privacy. Lastly, trust refers to the sense of reliance, conviction, and faith that an individual has on a particular company or a product (Coelho et al., 2018; and Al Amin & Mozid, 2017).
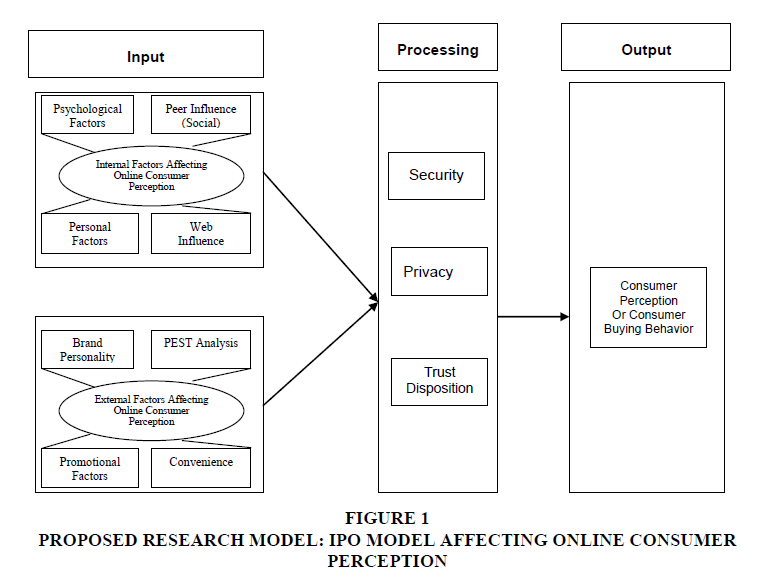
Conceptual Framework of the Study
The conceptual framework provides an idea about the overall perception and standpoint of the researcher and the pathway for deriving information. Using the existing knowledge and the information from different sources, the researcher has created the following conceptual framework in this research. There are three major dimensions of this conceptual framework which is related to the research. These three dimensions are Input, processing, and output of the model.
In the conceptual framework psychological factors have been adpapted from (ref) while the authors have adapted peer influence (social) from (ref), personal factors from (ref), and web influence from (ref). In accordance with (ref) brand personality was extracted for the research model while environmental factors (pest analysis) from (ref). Moreover, promotional factors from (ref), convenience from (ref), security from (ref), privacy from (ref), trust disposition from (ref); consumer perception from (ref). and consumer buying behavior from (ref) were taken.
Input factors affecting online consumer perception
Firstly, psychological factors such as motivation and learning create a greater sense of trust in the company (Jeong & Kim, 2017). Also, the attitude and beliefs of the consumers determine how secure they feel while using the website. Secondly, personal factors, such as the age and personality of the consumers, delineate their trust in the company. Besides, income level and lifestyle determine how much privacy they need while seeking the product. Also, peer influence such as reference groups and families etc. encourages consumers to try new products in the market (Kapoor & Kulshrestha, 2014). Therefore, Hypothesis 1: The internal factors are positively related to security, privacy, or Trust of Consumer perception.
Again, the external factors such as brand personality consisting of sincerity, excitement, competence, sophistication, and ruggedness may influence the trusting attitude of the consumers. For instance, consumers are willing to trust the companies that are sincere to them and show competence in delivering sophisticated services to them (Martín-Consuegra et al., 2019). Besides, the promotion also plays a pivotal role in this case as the social media platforms can be frequently used to reach to the consumers conveniently. Consequently, the PESTEL factors also influence the consumers. Lastly, distribution channels, distribution points, and the delivery time as part of the convenience factors influence the degree of trust of the consumers (Lamb et al., 2011). Thus Hypothesis 2: The external factors (Brand Personality, Promotional, PEST Factors, and Convenience) are positively related to security, privacy or Trust issues of Consumer perception.
Processing elements of affecting online consumer perception
The three processing elements are security, privacy, and trust disposal attitude, which are presumed to affect the consumer perception of online products. Firstly, security is a fundamental component of any transaction between consumers and businesses. It involves providing better products, reasonable prices, avoiding fraudulent actions, using secure means of transaction, etc. (Misirlis & Vlachopoulou, 2018; and Al Amin et al., 2020). The companies, which are able to provide these benefits to the consumers, are primarily ahead in the competition of the business. Secondly, privacy is another major factor affecting consumer perception since a substantial number of deceitful actions are seen in the era of online business (Obar & Oeldorf-Hirsch, 2020). The companies that can provide a significant amount of privacy are, therefore, preferred by the consumers. Lastly, the trust disposal attitude of the consumers is indispensable in the process of better consumer perception and purchase. Consumers frequently purchase from the companies that they trust, and they often stick with the same company if they are satisfied with the deal (Choi et al., 2017).
Final output
As per the conceptual framework, the input and processes interact to deliver a final output, which is a positive perception and purchasing of the product. When all the pieces of the framework fall in the appropriate places, the consumer may make a favorable decision to purchase the product (Yerasani et al., 2019). Emanating from security, privacy, and trust as part of the process, the positive consumer perception is the prime desire of the companies working in the online business sector. As all the companies are working to increase their consumer base, they would like to ensure that a large number of consumers purchase their products. To do so, their perceptions regarding the brand need to be positively changed (Shiau et al., 2017). Thus the Hypothesis 3: There is an impact of Security, privacy or Trust on customer for buying goods and services through online (Figure 1).
Thus, it is evident from the literature the consumer perception of online shopping differs between individuals with a feeling that the quality of appropriate access and accessibility is limited to some degree in online shopping. However, evaluating each hypothesis statement, several techniques are required, which has been done to a later portion of the study (Misirlis & Vlachopoulou, 2018). To be sure, the researcher mentioned all the relevant crucial information to strengthen the significance of the conceptual framework concerning online shopping behavior.
Research Methodology
In the quantitative method, both the primary and secondary data has been used in this conclusive research. For collecting primary data, the researchers chose the convenience sampling method (Hossain & Al Amin, 2016). Using the method, the researcher selected 285 respondents as a sample based on the preference of the researchers who they thought would be suitable for the study (Shanahan et al., 2019; and Al Amin, 2020).). These respondents were dwellers of the Sub Urban areas in Bangladesh with different occupations and ages. The secondary information was collected from different kinds of research papers, journals, articles, magazines, newspapers, brochures, websites, blogs, and social media. Besides, the author utilized SPSS software for data analysis & Microsoft word application for data presentation (Liu et al., 2018). For identifying Sub Urban people of Bangladesh, the researcher considered some criteria which are i) the area where the internet facilities (Broadband and Wi-Fi) are not readily available, but people are using the internet for online shopping either through Mobile internet or by coming near Upazila ICT centers (Kabir & Roy, 2015); ii) the area where people as consumers have significantly grown usage interest and moderate knowledge of social media advertising. The authors have selected these 2nd criteria of the respondents as the city people, or urban people are losing faith in social media advertising. In contrast, the first criteria were chosen so that researchers could understand the real suburban people’s perceptions as there have already been a lot of studies have been conducted on urban population. On the other hand they Researchers primarily selected areas are i) Cumurdi Union, Bhanga, Faridpur, ii) Gava Union, Baniripara, Barisal, iii) Tujerpur, Bhanga, Faridpur. These are were convenient for researchers.
The authors used both metric (nominal and ordinal level data) and non-metric (Interval and ratio level data) data for the analysis of the research project (Mishra et al., 2018 and Al Amin, 2020). Besides, an in-depth interview with ten experts was considered. After that, the researcher analyzed the collected data employing the following statistical Models:
Regression Equation-1
Y= β0+β1X1 +β2X2 +β3X3 +β4X4 + β5X5+ β6X6 + β7X7+ β8X8 + β9X9 + β10X10+ β10X10 + β11X11+ β12X12 + β13X13 + β14X14 + β15X15 + β16X16 + β17X17 + β18X18 + e
Here, Y = Security Process Factors, X1= Motivation, X2= Learning, X3 = Attitude & beliefs, X4= ID, X5 = ego, X6 = super-ego, X7= Age, X8 = Income Level, X9= Lifestyle, X10 = Personality, X11 = Reference Groups, X12 = Family, X13 = Roles and Status, X14= Social values, X15 = Easy to read, X16 = Easy to navigate, X17= Comfortably viewed, X18 = Quick to download.
Regression Equation-2:
Y= β0+β19X19 +β20X20 +β21X21 +β22X22+ β23X23+ β24X24+ β25X25+ β26X26+ β27X27+ β28X28+ β29X29 + β30X30+ β31X31+ β32X32 + β33X33 + β34X34 + β35X35+ β36X36 + β37X37+e
Here, Y = Security Process Factors, X19= Sincerity, X20 = Excitement, X21 = Competence, X22= Sophistication, X23= Ruggedness, X24= Facebook, X25= YouTube, X26= LinkedIn, X27 = Twitter, X28 = Google+, X29 = Political issues, X30= Economic, X31 = Social, Technological, X32 = Ecological, X33 = Legal, X34= Distribution Channel, X35 = Distribution Points, X36 = Delivery time, X37 = Placement of order.
Regression Equation-3
Y= β0+β38X38 +β39X39+β40X40+ e
Here, Y = Consumer perception, X38= Security, X39 = Privacy, X40= Trust e = error associated
Data Analysis and Presentation
Introduction
In this chapter, the researcher presents analyses and interprets data that were collected from the primary source, questionnaires. Statistical methods have been used to analyze and interpret quantitative data and have also tested hypotheses to prove the arguments brought in this chapter.
Reliability and validity
The reliability and validity of the study have ensured through AVE, CR and Cronbach's Alpha given in Table 1.
| Table 1: Average Variance Extracted (AVE) and CR | |||
| Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
Composite Reliability(CR) | Cronbach's alpha | |
| Psychological factor (PSF) | 0.609 | 0.823 | 0.715 |
| Personal Factors (PF) | 0.604 | 0.820 | 0.790 |
| Peer Influence (PI) | 0.700 | 0.823 | 0.912 |
| Web Influence (WI) | 0.505 | 0.750 | 0.772 |
| Brand Personality (BP) | 0.580 | 0.805 | 0.791 |
| Promotion (PRO) | 0.513 | 0.758 | 0.701 |
| Environmental forces (EF) | 0.627 | 0.834 | 0.769 |
| Convenience (CON) | 0.791 | 0.883 | 0.727 |
| Process Factors (PRS) | 0.668 | 0.857 | 0.735 |
The AVE for each construct must be greater than 0.5 which stands that the construct explains more than 50% of the variance of the items in the research model while Hair et al. (2014) and (Malhotra & Das, 2016) Composite reliability (CR) must be more than 0.7 which explains 70% of the variance in the items. Both criteria are fulfilled for all of our variables. According to Malhotra & Das, (2016) the cut of value for Cronbach's alpha 0.7 while 0.6 is acceptable by the rule of thumb, which matched with the study of (Cronbach, 1951 and Cho, 2016). This study also matched the required cut value for Cronbach's alpha given in the Table 1.
Factor Analysis
The author has organized an exploratory factor analysis by considering the 37 variables. Initially, the PCA), a principal component analysis, was performed, where all the 37 variables were extracted to the maximum possible extent. The extraction score of more than (0.5) was only considered for the calculation. The value below 0.5 is eliminated during the principle component analysis (PCA).
Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis
Ref to the above Table 2, the variables with loading factor less than 0.5 is eliminated during the EFA. The iterative process able isolates almost 40 components or variables. Ref to Table 4 total of eight components or factor was identified under different constructs. Out of 40 components, only 9 Components has able to deliver the Eigenvalue score >1. The source of cumulative variance has captured almost (71.15) % (Table 3). So consideration of these nine components based on Eigenvalue is justified (Schweingruber & McPhail, 1999). The component matrix is given in the Appendix-Table A1.
| Table 2: Total Variance Explained | ||||||
| Dimension | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 9.608 | 27.451 | 27.451 | 9.608 | 27.451 | 27.451 |
| 2 | 3.461 | 9.889 | 37.340 | 3.461 | 9.889 | 37.340 |
| 3 | 2.870 | 8.199 | 45.538 | 2.870 | 8.199 | 45.538 |
| 4 | 2.000 | 5.715 | 51.254 | 2.000 | 5.715 | 51.254 |
| 5 | 1.688 | 4.822 | 56.076 | 1.688 | 4.822 | 56.076 |
| 6 | 1.496 | 4.275 | 60.351 | 1.496 | 4.275 | 60.351 |
| 7 | 1.398 | 3.994 | 64.345 | 1.398 | 3.994 | 64.345 |
| 8 | 1.198 | 3.421 | 67.767 | 1.198 | 3.421 | 67.767 |
| 9 | 1.184 | 3.382 | 71.149 | 1.184 | 3.382 | 71.149 |
| 10 | 0.964 | 2.753 | 73.902 | |||
| 11 | 0.947 | 2.705 | 76.606 | |||
| . . |
||||||
| 38 | 0.300 | 0.856 | 6.017 | |||
| 39 | 3.723E-16 | 1.064E-15 | 100.000 | |||
| 40 | -2.526E-16 | -7.216E-16 | 100.000 | |||
| Table 3: Communalities | |||||
| Initial | Extraction | Initial | Extraction | ||
| Motivation | 1.000 | 0.688 | Competence | 1.000 | 0.705 |
| Learning | 1.000 | 0.606 | Sophistication | 1.000 | 0.711 |
| Attitude & beliefs | 1.000 | 0.708 | Ruggedness | 1.000 | 0.667 |
| ID | 1.000 | 0.723 | 1.000 | 0.789 | |
| Ego | 1.000 | 0.625 | YouTube | 1.000 | 0.710 |
| super-ego | 1.000 | 0.665 | 1.000 | 0.760 | |
| Age | 1.000 | 0.656 | 1.000 | 0.628 | |
| Income Level | 1.000 | 0.686 | Google+ | 1.000 | 0.689 |
| Lifestyle | 1.000 | 0.733 | Political issues | 1.000 | 0.968 |
| Personality | 1.000 | 0.694 | Economic | 1.000 | 0.762 |
| Reference Groups | 1.000 | 0.579 | Social Media | 1.000 | 0.720 |
| Family | 1.000 | 0.550 | Ecological | 1.000 | 0.745 |
| Roles and Status | 1.000 | 0.682 | Legal | 1.000 | 0.690 |
| Social values | 1.000 | 0.685 | Distribution Channel | 1.000 | 0.968 |
| Easy to read | 1.000 | 0.826 | Distribution Points | 1.000 | 0.968 |
| Easy to navigate | 1.000 | 0.613 | Delivery time | 1.000 | 0.620 |
| Comfortably viewed | 1.000 | 0.649 | Placement of order | 1.000 | 0.665 |
| Quick to download | 1.000 | 0.693 | Security | 1.000 | 0.690 |
| Sincerity | 1.000 | 0.548 | Privacy | 1.000 | 0.680 |
| Excitement | 1.000 | 0.813 | Trust | 1.000 | 0.687 |
Source: Computed data, SPSS 22 output file
Results and Discussion on Factor Analysis
Ref to Appendix-Table A1, the result of the exploratory factor analysis revealed that for each of the 37 factors. The first component for consideration is the Psychological factor extracted from Maslow's (1958) hierarchy of needs theory and Freud’s psychoanalytic theory (1920). The significance value of the factor’s variables ‘motivation’ (0.792), ‘learning’ (0.670), ‘attitude and beliefs’ (0.406), and ‘id’ (0.482), ego and super-ego’ (0.261). So, consumers have to be motivated by informing more about the product that will lead to more purchases. The second component to consider in this case is Personal Factorsextracted from Kotler’s (2004) buyer black-box model, where the significance value of variables ‘income’ (0.691), ‘age’ (0.556), ‘lifestyle’ (0.535), and ‘personality’ (0.513). From the result, it is seen that high-income persons in society tend to be intrigued more easily using online marketing, and online attractions vary from age to age. Besides, the third component is Peer Influenceextracted from Sociological model by Brim (1968), where the significance value of variables are ‘Social roles and statuses’ (0.711), ‘social values’ (0.628), ‘reference groups’ (0.625), and ‘family’ (0.458). Consequently, the result illustrates that individuals with higher social status tend to be attracted more by the online for being convenient. After that, the fourth factor is Web Influenceextracted from the model of online consumer behavior by Kumar & Dange (2012), where the significance value of variables ‘speed of the website’ (0.639), ‘easy to read’ (0.636), and ‘user friendly’ (0.603). So, the consumers are satisfied with the company if its website provides a steady speed, and they can surf it conveniently. The fifth factor to be taken into consideration is Brand Personalityextracted from Aaker's (1997) Dimensions of Brand personality, where the significance value of variables ‘sincerity’ (0.691), ‘reliability’ (0.618), ‘exciting’ (0.590), ‘competence’ (0.516) and ‘sophistication’ (0.184). The result exhibits that consumers always like to associate themselves with the companies that show sincerity to them. The sixth factor is Promotion extracted from social media marketing communication model by Castronovo & Huang (2012), where the significance value of variables ‘Facebook’ (0.766), ‘Google+’ (0.208), ‘YouTube’ (0.205), ‘Twitter’ (0.104), and LinkedIn (-0.035). The result shows that Facebook’s rapidly growing popularity is an excellent opportunity for online promotion. The seventh-factor is Aguilar's (1967) Environmental forces (PEST Forces) that include ‘political, economic, social, and technological’ (Ramya & Ali, 2016). The significance values of these variables are ‘technological’ (0.651), ‘economic’ (0.615), ‘social’ (0.461), and ‘political’ (0.372). The eighth factor is Convenienceextracted fromLauterborn's (1990) 4C model, where the significance value of ‘convenient arrangements’ is 0.629, and ‘distribution channel and point’ is 0.481, which means it has a moderate level of connection with the eighth factor. Lastly, the ninth factor is Process extracted from the Privacy-trust-behavioral intention model by Liu et al. (2005). In this case, ‘security,’ ‘privacy,’ and ‘trust disposition’ have a significance value of 0.667, 0.461, and 0.461, respectively, and have the most connection level with this component. So, these three factors have a substantial amount of significance with the ninth factor.
Correlation Analysis (CA)
Pearson correlation (r) is 0.900; which means that there is a positive and very strong relationship between internal factors and process factors (Table 4). It means that environmental forces (internal) have an influence on process factors (security, privacy and trust) to buy their desired products on these platforms. However, the second Pearson correlation (r) is .858; which means that there is a positive and very strong relationship between external factors and processing factors. It means that environmental forces (external) influence process factors (security, privacy, and trust) to enhance customers to makes a transaction for making a loyal customer. Moreover, the third Pearson correlation (r) is 0.662, which means that there is a positive and strong relationship between process factors and consumer perception. This results also mean that process factors (security, privacy and trust) changes the perceptions or buying attitudes of the customers.
| Table 4: Correlation Analysis (CA) | ||
| Variables | r | Strength of association |
| Internal Factors and Process Factors | 0.900 | Very strong |
| External factors and processing factors | 0.858 | Very Strong |
| Process factors and Consumer perception | 0.662 | Strong |
Coefficient of Determination (R2): Results and Discussion
From equation – 1, the value of R2 is 0.810, which means that 81% variance of dependent variables can be changed concerning the independent variables. The value of adjusted R2 also denotes is.780, in which the dependent variables can be caused 78% variance due to additional independent variables. Whereas the equation – 2 shows that the value of R2 is 0.722, which means that 72% variance of dependent variables can be changed concerning the independent variables. The value of adjusted R2also denotes is 0.717, in which the dependent variables can be caused 71% variance due to additional independent variables. So, this study explains that a customer’s perceived value influences confirmation.
Moreover, from the equation- 3, the value of R2 is 0.930, which means that 93% variance of dependent variables can be changed concerning the independent variables. At the same time, the value of adjusted R2 also denotes 0.921, in which the dependent variables can be caused by 921% variance due to additional independent variables (Table 5).
| Table 5: Model Summary | ||||
| Equation No. | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Standard error | Independent and dependent variables |
| 11 | 0.810 | 0.780 | 0.732 | Internal Factors and Process Factors |
| 22 | 0.722 | 0.717 | 0.649 | External factors and processing factors |
| 33 | 0.930 | 0.921 | 0.709 | Process factors and Consumer perception |
Hypothesis Testing: Results and Discussion
From the above Table 6, the value of b is 0.830 t statistic value is 6.883, critical value is 1.976, at the level of significance of 0.05, df value is 283, which means that t-statistic value is > critical value which is (6.883> 1.976). However, it proves that the hypothesis (H1) is supported. Therefore, it can be expected that psychological factors, peer influence (social), personal factors from and web influence have a significant impact on processing factor (security privacy and trust) that matches literature provided by (ref)
| Table 6: t Statistic For Hypothesis Testing | ||||||
| t- statistic: Hypothesis | ||||||
| Hypotheses | b | t Value | Critical value | Sig | Result | Remarks |
| H1 | 0.830 | 6.883 | 1.976 | 000 | 6.883> 1.976 | Supported |
| H2 | 0.643 | 4.548 | 1.976 | 000 | 4.548> 1.976 | Supported |
| H3 | 0.562 | 3.876 | 1.976 | 000 | 3.876> 1.976 | Supported |
α = 0.05, df = 283
In hypothesis (H2), the value of b is 0.643, t statistic value is 4.548, critical value is 1.976, at the level of significance of 0.05, df value is 283 which means that the t statistic value is more than critical value which is (4.548> 1.976) that supports H2. Therefore, brand personality, environmental factors, promotional factors, and convenience have a significant impact on processing factor (security privacy and trust) that matches literature provided by found by (ref).
The Table 6 explains that the value of b is 0.562 in H3, t statistic value is 3.876 critical value is 1.976, at the level of significance of 0.05, df value is 283 which means that the t statistic value is > critical value which is (3.876> 1.976) which proves the acceptance of the hypothesis. It stands that processing factor (security privacy and trust) leads to Customer perceptions, which is explained by (ref).
Limitations and Implications
Limitation of the Study
The author faced budget limitations since the study required traveling to collect data from Sub-Urban locations in Bangladesh. There is some degree of difficulty in finding the respondents as they are not always available. Besides, it could not be identified whether there are some other factors influencing consumer perception. Then, valid generalization is well-practiced to make sure the collected pieces of information are well appreciated by the researcher. Besides, it is expected from other researchers to conduct further study on additional factors of online marketing that can affect consumer perception of the product and ensuring that they purchase the product. By conducting further research, it will be understood which factors are most significant in affecting consumer perception (Jacobson et al., 2020).
Manegerial Implication
Online marketing platforms drastically improve the effectiveness of the marketing process (Boateng & Okoe, 2015). According to the research finding, the consumers of the sub-urban need to have the appropriate motivation and learning to make positive decisions to purchase the. Also, the results showed that online marketing is an essential part of executing the organizational marketing strategy to raise brand awareness since the manufactured products and services are available for a very long time to a more focused global consumer. The desire to purchase those products and services will remain escalated to the sub-urban consumer as long as the website still speedily functions and remains relevant. The outcomes of the marketing tools that are used online for targeting specific clients, carrying out more tasks, and saving a considerable resource for the company are essential findings of the study. So the companies need to enrich consumers providing reliable product information continuously. Moreover, the effectiveness of the online marketing process also depends on the consumer’s trust level. Peer influence incensement through online marketing strategies not only depends on the goods to roll in but also creates positive vibes to purchase. Each of the factors has a decent level of relationship with consumer perception, which is why the marketing managers can use these factors in their decision-making product (Chen & Lin, 2019; Arora & Sanni, 2019). It can improve the brand image of the company and gain it more profitability in the business (Kapoor et al., 2018).
Theoretical Contribution
The prior researchers do mention various factors that influence consumers’ perception and motivates their behavior through the Consumer behavior model. However, the author of this study illustrates specifically how consumers in the sub-urban influenced to purchase and re-purchase step by step through merging the IPO model in which Input, process, and output function as marketing efforts, purchase process, and consumer response to the marketing efforts. As consumers increasingly use social media and other online platforms, businesses can be more drawn to them. It is a comprehensive opportunity for companies to make effective use of these factors in company decision-making.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The conclusion was reached that the identified factors have a significant relationship with the processes that create positive or negative consumer perceptions and compelling them to purchase the company’s product (Algharabat et al., 2020). The internal factors, including psychological, personal, peer influence, and web influence, as well as the external factors involving brand personality, promotion, PEST, and convenience, significantly influence the security, privacy, and trust disposal attitude of the consumers. So, the companies have to emphasize these factors and provide better services so that consumers are encouraged to purchase from the companies frequently (Alalwan, 2018). They need to be technically savvy with the way they perceive their efforts in the process. For attracting the consumers, the following recommendations can be provided: Provide sufficient information of company background and product qualities to the consumers so that their learning is flourished and they have the motivation to purchase the products. The provision and promotion of product need to determine by age, income, and lifestyle of consumers to play a crucial role in their satisfaction.Companies should emphasize word of mouth in order to use a group of peers, one of the most effective methods of publicity. A robust brand personality has to be created with continual effectiveness in preserving. Promotion mode should be appropriate for the consumers in order to make the most of their cultural and attitudinal factors. The company website is convenient to distribute process should be efficient (Gucciardi & Jackson, 2015). This work will, therefore, be more important in the academic field and will pave the way for new opportunities. In addition, businesses will also concentrate on a new dimension.
Endnotes
1 Y = β0 + β1 X1 + β2 X2+ β3 X3 + e; 0.530 +0.314X1 + 0.505 X2 + 0.083 X3 + 301.735
2 Y = β0 + β4 X4+ β5 X5+ β6 X6 + e; 0.543 + 0.014 X4 + 0.000 X5 + 0.872 X6 +0 .24267
3 Y = β0+ β7 X7+ β8 X8+ β9 X9+ e; 0.662+ 0.810 X7 + 0.063 X8 + 1.502 X9 + 0.23894
Appendix
| Table A1 Component Matrixa |
|||||||||
| Component | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| Motivation | 0.892 | -0.21 | 0.196 | -0.256 | 0.056 | -0.281 | 0.085 | 0.212 | 0.502 |
| Learning | 0.67 | -0.207 | 0.599 | -0.05 | 0.083 | 0.131 | -0.039 | -0.007 | -0.202 |
| Attitude | 0.406 | -0.1 | 0.365 | 0.115 | 0.342 | -0.153 | -0.404 | -0.174 | 0.228 |
| ID | 0.482 | 0.073 | 0.43 | 0.169 | 0.104 | -0.428 | -0.063 | 0.022 | -0.272 |
| EGO and Super EGO | 0.61 | -0.007 | 0.52 | -0.229 | 0.012 | 0.44 | 0.021 | 0.179 | -0.091 |
| Age | -0.214 | 0.556 | 0.447 | -0.129 | 0.197 | 0.016 | -0.054 | -0.226 | -0.029 |
| Personality | -0.108 | 0.513 | 0.319 | -0.043 | 0.276 | -0.016 | 0.364 | -0.244 | -0.093 |
| lifestyle | -0.87 | 0.535 | 0.322 | -0.022 | -0.443 | -0.194 | 0.101 | 0.19 | -0.091 |
| Income | -0.189 | 0.691 | 0.013 | -0.006 | -0.418 | -0.194 | 0.048 | 0.027 | 0.062 |
| Reference Groups | -0.137 | -0.201 | 0.625 | -0.329 | -0.058 | 0.114 | 0.154 | 0.002 | 0.309 |
| Family | -0.75 | 0.231 | 0.458 | 0.195 | -0.078 | -0.113 | 0.134 | 0.224 | 0.279 |
| Social roles and status | -0.29 | 0.006 | 0.711 | -0.005 | 0.134 | -0.054 | -0.14 | -0.005 | -0.057 |
| Social values | -0.132 | 0.235 | 0.628 | 0.132 | 0.341 | 0.149 | -0.109 | -0.216 | -0.011 |
| easy to read | -0.2 | -0.299 | 0.81 | 0.636 | -0.093 | 0.368 | 0.079 | -0.167 | -0.111 |
| user friendly | 0.273 | -0.14 | 0.715 | 0.603 | -0.088 | 0.528 | 0.062 | 0.086 | -0.155 |
| The speed of the website | 0.194 | -0.168 | 0.102 | 0.639 | -0.203 | -0.017 | 0.09 | -0.048 | -0.277 |
| competence | -0.153 | -0.203 | 0.143 | 0.65 | 0.516 | 0.129 | -0.111 | -0.289 | 0.428 |
| Sincerity | -0.188 | -0.058 | -0.276 | 0.268 | 0.691 | 0.013 | 0.036 | 0.074 | -0.146 |
| Exciting | 0.145 | -0.075 | -0.025 | 0.035 | 0.59 | 0.205 | 0.088 | -0.264 | 0.229 |
| sophistication | -0.228 | 0.056 | 0.607 | -0.219 | 0.884 | 0.126 | -0.267 | 0.468 | -0.049 |
| Reliability | -0.118 | -0.043 | -0.474 | 0.267 | 0.618 | -0.054 | -0.051 | -0.029 | 0.071 |
| -0.89 | -0.239 | -0.102 | 0.057 | -0.1 | 0.766 | -0.112 | -0.131 | -0.082 | |
| YouTube. | -0.304 | 0.416 | 0.26 | 0.362 | 0.192 | 0.605 | 0.323 | -0.131 | 0.041 |
| 0.209 | 0.468 | 0.457 | 0.404 | 0.223 | 0.735 | 0.295 | 0.057 | 0.114 | |
| -0.128 | 0.468 | 0.24 | 0.542 | -0.296 | 0.704 | 0.055 | 0.089 | 0.119 | |
| 0.295 | 0.515 | -0.081 | 0.415 | 0.126 | 0.708 | 0.065 | 0.328 | 0.24 | |
| Political | 0.563 | 0.12 | -0.129 | -0.319 | 0.14 | -0.071 | 0.72 | -0.013 | -0.125 |
| Economical | 0.328 | 0.158 | -0.309 | -0.201 | 0.037 | -0.029 | 0.615 | 0.198 | -0.032 |
| Social | -0.136 | 0.778 | -0.01 | -0.303 | -0.16 | 0.017 | 0.861 | -0.117 | 0.001 |
| Technological | -0.048 | 0.108 | -0.299 | -0.259 | 0.262 | -0.221 | 0.651 | 0.22 | 0.032 |
| Distribution channel and point. | 0.335 | -0.054 | -0.13 | -0.107 | 0.539 | 0.174 | -0.145 | 0.481 | 0.059 |
| Convenient arrangements | 0.078 | 0.016 | -0.278 | 0.296 | 0.096 | -0.061 | -0.402 | 0.629 | -0.053 |
| The Security, | -0.251 | -0.079 | -0.208 | 0.021 | 0.224 | -0.208 | -0.103 | 0.168 | 0.667 |
| Privacy | 0.001 | 0.078 | -0.01 | -0.303 | -0.16 | 0.017 | -0.136 | -0.117 | 0.461 |
| Trust Disposition | 0.001 | 0.078 | -0.01 | -0.303 | -0.16 | 0.017 | -0.136 | -0.117 | 0.461 |
Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis.
a. 9 components extracted.
References
- Aaker, J. (1997). Dimensions of brand personality. Journal of Marketing Research, 34(3), 347-356.
- Aguilar, F. (1967). Scanning the Business Environment. New York: Macmillan.
- Al Amin, M. (2017). A five factor model of online purchase decision: A case study on bikroy.com, Bangladesh.
- Al Amin, M. (2018). An analysis on the impact of facebook marketing on brand awareness: A case study of glaxosmithkline bangladesh’s product,‘horlicks’. Journal of Business, 39(2).
- Al Amin, M., Nowsin, N., Hossain, I., & Bala, T. (2020). Impact of social media on consumer buying behaviour through online value proposition: A study on e-commerce business in bangladesh.
- Al Amin, M. (2020). Strategic analysis on diversity management to improve business performance: An empirical study.
- Al Amin M., & Mozid, A. (2017). Critical investigation of Customer Satisfaction: A case study on meena bazaar. Journal of Management and Entrepreneurship, 5(13).
- Al Amin M., & Bhuiyan, A.R. (2019). Online marketing platforms increase the customer engagement and understanding through online value proposition: A case study on e-commerce business in bangladesh
- Alalwan, A.A. (2018). Investigating the impact of social media advertising features on customer purchase intention. International Journal of Information Management, 42, 65-77.
- Algharabat, R., Rana, N.P., Alalwan, A.A., Baabdullah, A., & Gupta, A. (2020). Investigating the antecedents of customer brand engagement and consumer-based brand equity in social media. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 53.
- Amatulli, C., De Angelis, M., Korschun, D., & Romani, S. (2018). Consumers' perceptions of luxury brands’ CSR initiatives: An investigation of the role of status and conspicuous consumption. Journal of Cleaner Production, 194, 277-287.
- Arora, A.S., & Sanni, S.A. (2019). Ten years of ‘social media marketing’research in the Journal of Promotion Management: Research synthesis, emerging themes, and new directions. Journal of Promotion Management, 25(4), 476-499.
- Bae, S., & Lee, T. (2011). Product type and consumers’ perception of online consumer reviews. Electronic Markets, 21(4), 255-266.
- Bairrada, C.M., Coelho, A., & Lizanets, V. (2019). The impact of brand personality on consumer behavior: the role of brand love. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal, 23(1), 30-47.
- Boateng, H., & Okoe, A.F. (2015). Consumers’ attitude towards social media advertising and their behavioural response. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing.
- Boyles, T. (2011). Small business and Web 2.0: hope or hype?. The Entrepreneurial Executive, 16, 81.
- Brim Jr, O.G. (1968). Socialization through the life cycle.
- Burke, M., & Kraut, R.E. (2016). The relationship between Facebook use and well-being depends on communication type and tie strength. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 21(4), 265-281.
- Castronovo, C., & Huang, L. (2012). Social media in an alternative marketing communication model. Journal of Marketing Development and Competitiveness, 6(1), 117-134.
- Chen, S.C., & Lin, C.P. (2019). Understanding the effect of social media marketing activities: The mediation of social identification, perceived value, and satisfaction. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 140, 22-32.
- Cho, E. (2016). Making reliability reliable: A systematic approach to reliability coefficients. Organizational Research Methods, 19(4), 651-682.
- Choi, Y.G., & Hyun, S.S. (2017). Relationships between brand experiences, personality traits, prestige, relationship quality, and loyalty. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
- Coelho, P.S., Rita, P., & Santos, Z.R. (2018). On the relationship between consumer-brand identification, brand community, and brand loyalty. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 43, 101-110.
- Cronbach, L.J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16(3), 297-334.
- Cruz-Cárdenas, J., & Arévalo-Chávez, P. (2018). Consumer behavior in the disposal of products: Forty years of research. Journal of Promotion Management, 24(5), 617-636.
- Dlodlo, N., & Mafini, C. (2014). The relationship between Internet marketing paybacks and firm productivity: Perspectives from Zimbabwean SMEs. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 5(8), 21.
- Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention and behavior: An introduction to theory and research.
- Freud, S. (1920). A general introduction to psychoanalysis. New York, NY: Boni & Liveright.
- Gucciardi, D.F., & Jackson, B. (2015). Understanding sport continuation: An integration of the theories of planned behaviour and basic psychological needs. Journal of Science and Medicine In Sport, 18(1), 31-36.
- Güse, K.S. (2011). Brand personalities and consumer-brand relationships as elements of successful brand management. University of Bamberg Press.
- Haque, S., & Faruquee, M. (2013). Impact of fundamental factors on stock price: A case based approach on pharmaceutical companies listed with Dhaka stock exchange.
- Hemsley-Brown, J., & Oplatka, I. (2016). Personal influences on consumer behaviour. In Higher Education Consumer Choice (pp. 44-64). Palgrave Pivot, London.
- Hossain, M.S., & Al-Amin, M. (2016). Best model of CSR: An analysis of the impact of corporate social responsibility for improving the social development of the stakeholders-A study on four private commercial banks. International Journal of Information, Business and Management, 8(2), 74.
- Jacobson, J., Gruzd, A., & Hernández-García, Á. (2020). Social media marketing: Who is watching the watchers?. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 53.
- Jeong, Y., & Kim, Y. (2017). Privacy concerns on social networking sites: Interplay among posting types, content, and audiences. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 302-310.
- Jung, A.R. (2017). The influence of perceived ad relevance on social media advertising: An empirical examination of a mediating role of privacy concern. Computers in Human Behavior, 70, 303-309.
- Kabir, K.H., & Roy, D. (2015). Preferences of ICT tools by the Upazila Agriculture Officers (UAOs) for the information exchange in Bangladesh. Agriculture, Forestry & Fisheries, 4(2), 59-65.
- Kapoor, A. (2013). Dynamics of competitive advantage and consumer perception in social marketing. IGI Global.
- Kapoor, K.K., Tamilmani, K., Rana, N.P., Patil, P., Dwivedi, Y.K., & Nerur, S. (2018). Advances in social media research: Past, present and future. Information Systems Frontiers, 20(3), 531-558.
- Kotler, P., Keller, K., Brady, M., Goodman, M., & Hansen, T. (2012). Marketing management: A European perspective.
- Kotler, P., Armstrong, G., Saunders, J., & Wong, V. (2004). Consumer behaviour. Marketing Management.
- Kumar, V., & Dange, U. (2012). A study of factors affecting online buying behavior: A conceptual model. Ujwala, A Study of Factors Affecting Online Buying Behavior: A Conceptual Model.
- Lamb, C.W., Hair, J.F., & McDaniel, C. (2011). Essentials of marketing. Cengage Learning.
- Lauterborn, B. (1990). New marketing litany: four Ps passé: C-words take over.
- Lee, I. (2016). Encyclopedia of e-commerce development, implementation, and management. IGI Global.
- Liu, C., Marchewka, J.T., Lu, J., & Yu, C.S. (2005). Beyond concern—a privacy-trust-behavioral intention model of electronic commerce. Information & Management, 42(2), 289-304.
- Liu, L., Lee, M.K., Liu, R., & Chen, J. (2018). Trust transfer in social media brand communities: The role of consumer engagement. International Journal of Information Management, 41, 1-13.
- Malhotra, N. K., & Dash, S. (2016). Marketing research 7th ed.
- Martín-Consuegra, D., Díaz, E., Gómez, M., & Molina, A. (2019). Examining consumer luxury brand-related behavior intentions in a social media context: The moderating role of hedonic and utilitarian motivations. Physiology & Behavior, 200, 104-110.
- Maslow, A.H. (1958). A dynamic theory of human motivation.
- Mishra, P., Pandey, C.M., Singh, U., & Gupta, A. (2018). Scales of measurement and presentation of statistical data. Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia, 21(4), 419.
- Misirlis, N., & Vlachopoulou, M. (2018). Social media metrics and analytics in marketing–S3M: A mapping literature review. International Journal of Information Management, 38(1), 270-276.
- Morgan-Thomas, A., & Veloutsou, C. (2013). Beyond technology acceptance: Brand relationships and online brand experience. Journal of Business Research, 66(1), 21-27.
- Ngai, E.W., Tao, S.S., & Moon, K.K. (2015). Social media research: Theories, constructs, and conceptual frameworks. International Journal of Information Management, 35(1), 33-44.
- Obar, J.A., & Oeldorf-Hirsch, A. (2020). The biggest lie on the internet: Ignoring the privacy policies and terms of service policies of social networking services. Information, Communication & Society, 23(1), 128-147.
- Pushpa Bhatt, P., & Sumangala, J.K. (2012). Impact of earnings per share on market value of an equity share: an empirical study in Indian capital market. Journal of Finance, Accounting & Management, 3(2).
- Ramya, N., & Ali, S.M. (2016). Factors affecting consumer buying behavior. International Journal of Applied Research, 2(10), 76-80.
- Raunaque, N., Zeeshan, M., & Imam, M.A. (2016). Consumer Perception towards Online Marketing in India. International Journal of Advanced Engineering, Management and Science, 2(8), 239591.
- Reddy, J.S. (2003). Impact of E-commerce on marketing. Indian Journal of Marketing, 33(5), 18-20.
- Reic, I. (2016). Events marketing management: A consumer perspective. Taylor & Francis.
- Schivinski, B., & Dabrowski, D. (2015). The impact of brand communication on brand equity through Facebook. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing.
- Schweingruber, D., & McPhail, C. (1999). A method for systematically observing and recording collective action. Sociological Methods & Research, 27(4), 451-498.
- Shanahan, T., Tran, T.P., & Taylor, E.C. (2019). Getting to know you: Social media personalization as a means of enhancing brand loyalty and perceived quality. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 47, 57-65.
- Sharma, A. (2011). Take?off of online marketing: casting the next generation strategies. Business Strategy Series.
- Shiau, W.L., Dwivedi, Y.K., & Yang, H.S. (2017). Co-citation and cluster analyses of extant literature on social networks. International Journal of Information Management, 37(5), 390-399.
- Singh, A. (2016). Managing public relations and brand image through social media. IGI Global.
- Stephen, A.T. (2016). The role of digital and social media marketing in consumer behavior. Current Opinion in Psychology, 10, 17-21.
- Usmani, S. (2012). Factors Influencing Individual Investor Behaviour in Karachi. International Journal of Asian Social Science, 2(7), 1033-1047.
- von Helversen, B., Abramczuk, K., Kope?, W., & Nielek, R. (2018). Influence of consumer reviews on online purchasing decisions in older and younger adults. Decision Support Systems, 113, 1-10.
- Yerasani, S., Appam, D., Sarma, M., & Tiwari, M.K. (2019). Estimation and maximization of user influence in social networks. International Journal of Information Management, 47, 44-51.