Research Article: 2023 Vol: 22 Issue: 3
Evaluating Factors Influencing Consumers Satisfaction towards online shopping in India
Rohini Baghel, Banasthali Vidyapith
Citation Information: Baghel, R. (2023). Evaluating Factors Influencing Consumers’ Satisfaction towards Online Shopping in India. Journal of International Business Research, 22(3), 1-11.
Abstract
With the growth of the Internet, online shopping is developing speedily in India as a new way of shopping. Consequently, this research paper needs to identify determinates of consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India. A total 100 numbers of consumers have participated in this research in India. The findings of this research paper show that some factors are more effective on the consumers. I.e. Websites Deigns, Quality Information, Product Variety, Product Quality, Pricing, Securities. Websites design means are more updates available, and any information is easily accessible for consumers. E-retailers offer many product varieties from e-commerce portals then product quality is a critical role play for every consumer. The finding website design, security, information quality, pricing, product quality, and product variety affect consumers' satisfaction level towards online shopping in India.
Keywords
Consumer Satisfaction, Website Design, Information Quality, Security, Product Variety, Product Quality and Pricing.
Introduction
Online shopping has become prevalent; exploiting the "next generation" service is highly suitable. It refers to the consumers' shopping behaviour in an online store or a website used for online purchasing purposes. Technological innovation is helpful to online shopping, and traditional shopping is time-consuming.
Many e- retailers deal with many products in India, i.e. Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra, e-bay, Homeshop18, Yebhi.com etc. They are provided with many facilities for many consumers. Online shopping is the process whereby consumers directly buy goods, services through the internet. They allow purchasing any product & services through the internet, i.e. clothes, electronics, smartphones, gadgets, e- retailers are increasingly selling goods and services before availability through prevail for testing, building and managing demand.
The e-commerce industry in India, which grew by 33% last year and saw goods and services worth $3.5 billion exchanging hands, is poised for more significant growth and touch new highs; the three most prominent e-commerce players have driven it; Flipkart, Amazon and snap deal. The trio achieved $ 4 billion in 2014, where Flipkart alone accounted for almost half that amount.
Review of the Literature
According to Li & Zhang (2002), this study had shown that most consumers purchase electronics products through Amazon and Flipkart. Three main factors are affecting consumers’- gender, income and price. The paper finds out the males are more interested in purchasing electronics products compare to females. However, people are interested in acquiring electronics goods online only when exposed to offers, irrespective of their age and income.
Consumer Satisfaction
Consumers satisfaction outcome from comparing the expectations and the experience; in other words, the consumers are happy while they meet or deliver the product and fulfil the expectations (Jun et al., 2004; Ballantine, 2005; Cappelli et al., 2011). Satisfaction and loyalty is the critical element influential the success of the market concept of implementation. Satisfaction factors are an essential aspect of consumer buying because the customers are satisfied with the product. They would repeat purchase the product if the service provider reached or exceeded their expectations. According to Guo et al. (2012) this study is shown that Eight factors are influence the consumers' satisfaction level; web design, security, quality information about the product & services, product range, product quality, payment method, service provision and product variety etc.
Website Design
Website design is the critical role play for online shopping, effective website design to attract consumers to buy the product online. Effective website designs are included in the websites' navigation capability or visual appeal (Cyr, 2008). Customer satisfaction in ecommerce is related to the quality of website design (Cho & Park, 2001); Lee & Lin (2005), this study found that website design positively impacts the consumers’ satisfaction level and perceived service quality. Websites design impacts the consumers' minds and creates the visual appeal of the websites. As antecedents to website trust, website satisfaction and e- loyalty in graphic design and information design positively influenced consumer satisfaction.
Security
Another critical factor is affecting online shopping is security. This study had found that security is the website ability to protect the consumers' personal information. Consumers are ready to pay online, i.e. online bank transfer, online transactions from unauthorized disclosure. However, consumers are concern about the security, liabilities and privacy of online websites (Gefen, 2000). Security concerns about e-commerce can be divided into user authentication and worry about data and transaction security (Ratnasingham, 1998; Rowley, 1996).
According to Elliot & Fowell (2000); Szymanski & Hise (2000), this study is founded that, perception of the consumers related to the e-commerce security risk decrease and satisfied the online store services expected information is increasing. Therefore, the security factor increases the level of customers’ satisfaction. They have identified the critical element of securities, and they are helpful to manipulate the consumers buying and e- satisfaction level of consumers, technology, shopping etc. Security and e- satisfaction of the consumers have a positive relationship of the both.
Information Quality
Accuracy of information quality is concerned about the retailers and customers relationship and trustworthiness of the websites or e-retailers. According to Katerattanakul, (2002), the reliability of the online retailers then customers have to perceived risks, better justification for their decisions and ease in reaching the best judgments. Therefore, there is a positive and negative impact on customers’ satisfaction and interest in purchasing the products online. This deviation is consistent with the media richness theory that emphasized the importance of the quality, accuracy and reliability of the information exchanged across a medium (Daft & Lengel, 1986). Information quality significantly impacts customer satisfaction, accuracy, internet shopping, content and format, etc. A higher level of information quality will improve the customer satisfaction level related the online shopping and the accuracy of the information quality (Liu et al., 2008).
Product Quality
Quality is an essential property of a product. Product quality is the expected standard of development or service excellence (Jarvenpaa & Todd, 1996). Product quality is crucial for every consumer because there are positive and negative aspects of the product & services. The Sproles and Kendall’s Consumers Style Inventory (CSI) model highlighted the influence of highquality development. Some consumers consider the quality product as their first consider when to shop online. However, online shopping has some negative aspects, i.e. consumers have no touch and smell the products. They only see the effect on the websites or pictures. Furthermore, they are only read the comments or reviews on the website can be indicating the quality of the product to some extent.
Product Variety
E-retailer has offered many products to the customers, and there will be a higher chance of selling the product. Consumers expect online retailers to offer a wide range of product variety because of the reach of the internet and the potential to track down specialty goods and services (Jarvenpaa & Todd, 1996). According to Szymanski & Hise (2000) this study indicated that a wider variety of the product is helpful to attract the customers and e-satisfaction would have a more positive impact on consumers.
According to Liu et al. (2008), this study is founded that eight factors impact consumers' buying or consumer satisfaction level (Website design, quality information, payment method, security, privacy, delivery, product quality, product variety). Therefore, the product is a solid factor for influence customer satisfaction in an online shopping environment.
Pricing
Professional literature is described that pricing is an essential role play to manipulate the consumers buying the product online (Kang Lo et al., 2013). E-Commerce portals give the chances to compare the price quickly because many e- retailers are offered many types of development and different prices (Lo et al., 2014).
Pricing is directly impacted on consumers perception, the delivery cost of the products, transaction cost etc. Due to better purchase conditions, consumers use the internet to buy the same product at a lower price than in the traditional store (Sam & Sharma, 2015). Discounts while purchasing influenced the consumer buying, and ultimate, they affect their immediate customer satisfaction. As online stores are offered many products range in the e-commerce portals, they easily compare the price and quality of the product and services. Therefore, pricing can be a reason to satisfy the customers (Guo et al., 2012).
H1: Product Quality has a positive impact on consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India.
H2: Product Variety has a positive impact on consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India
H3: Pricing factors have positive impact on consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India
H4: Quality Information has a positive impact on consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India.
H5: Security has a positive impact on consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India.
H6: Website Design has a positive impact on consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India.
Research Methodology
Population: We target customers to bring the products through online portals, i.e. Amazon, Flipkart snap deal, etc.
Research Design
This study has been based on the descriptive method or primary data.
Tools for data collection: Collect the data through a questionnaire; it is based on 5 points Likert scale method.
Sample Size: A total number of 100 questionnaires are distributed among the customers in Delhi or NCR.
Data Collection
Primary Data: This data was collected through a questionnaire from the customer who buys the products through online portals.
Secondary Data: The data was collected from secondary sources, i.e. books, internet sources, journals and research studies etc.
Data Analysis Methodology
The data was collected from the specific cities Delhi & NCR, and then fill the questionnaire who buys the products online.
Gender of the respondents Figure 1, we are collecting the random sampling of the data Table 1. 43 males have preferred the online shopping output of 100 no of sampling, and 57 females prefer online shopping between the 100 no of sampling through the purchase of the product onlineTable 2.
| Table 1 Gender of Respondents | ||||
| S.No | Characteristics | Category | Frequency | Percentage |
| 1. | Gender | Male | 43 | 43 |
| Female | 57 | 57 | ||
| Total | 100 | 100 | ||
| Table 2 Age of Respondents | ||||
| S.No | Characteristics | Category | Frequency | Percentage |
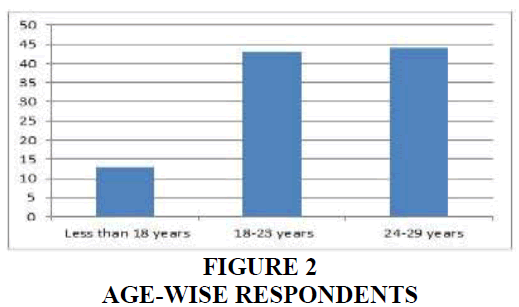
| 2. | Age | Less than 18 years | 13 | 13 |
| 18-23 years | 43 | 43 | ||
| 24-29 years | 44 | 44 | ||
| Total | 100 | 100 | ||
Age-wise respondents Figure 2, we are collecting the random sampling. Less than 18 years of the respondents are 13 numbers of respondents Table 3. 18-23 years of the respondents are 43 numbers respondents. 24-29 years of the respondents are 44 numbers of the respondents Figure 3.
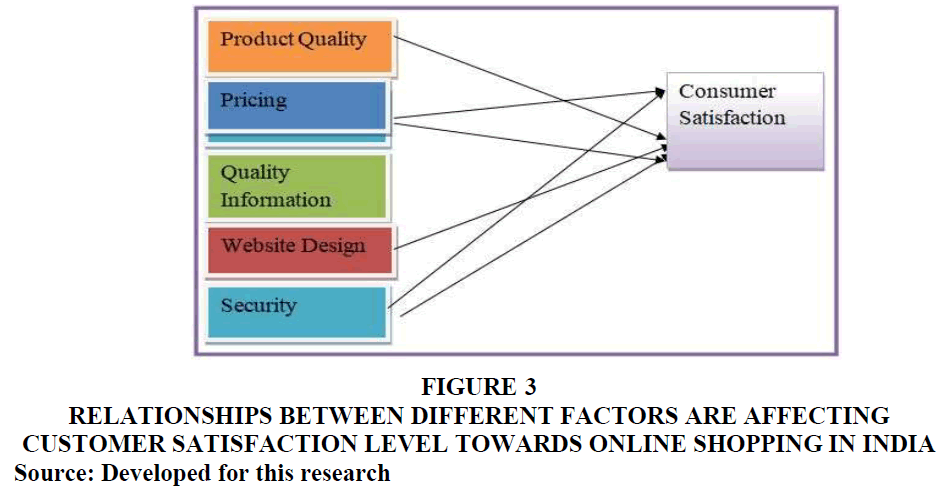
Figure 3 Relationships Between Different Factors are Affecting Customer Satisfaction Level Towards Online Shopping in India
Source: Developed for this research
| Table 3 Case Processing Summary | |||
| Case | N | % | |
| Valid | 99 | 100.0 | |
| Excluded | 0 | 0.0 | |
| Total | 99 | 100.0 | |
| Note: List wise deletion based on all variables in the procedure | |||
Reliability Statistic: It has shown that the Cronbach’s Alpha for the analysis tool applied is 0.882 (Greater than 0.7), hence it is acceptable for current analysis Table 4.
| Table 4 Reliability Statistics | |
| Cronbach’s Alpha | No of items |
| 0.882 | 15 |
Factor Analysis
As discussed, the total number of questionnaires is 15; it is calculated in different aspects of a study on customers’ satisfaction level towards online shopping in India Figure 3. We are analyzing the problems and collect the 17 no of variables Table 5. Each variable are closed related to other variables and using the factor analysis techniques. It is helpful to reduce the number of variables in the research problem to a concise or manageable number by combining selected ones into factors. The principal component analysis method of extraction and the Varimax process of rotation have been used. Before using factor techniques, the appropriateness of the data set the factor model was tested using Kaiser Meyer Olkin (KMO). As a result, the value of KMO statistics 0.797 was founded, which is greater than the desired value of 0.5 Table 6.
| Table 5 Rotated Component Matrix | ||||||
| Component | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| S.Q1 | 0.755 | |||||
| S.Q3 | 0.735 | |||||
| S.Q4 | 0.788 | |||||
| S.Q5 | 0.618 | |||||
| S.Q6 | 0.772 | |||||
| S.Q7 | 0.717 | |||||
| P.Q5 | 0.618 | |||||
| P.Q7 | 0.772 | |||||
| P.Q9 | 0.717 | |||||
| P.Q10 | 8.16 | |||||
| S.Q2 | 6.68 | |||||
| P.Q4 | 5.44 | |||||
| P.Q6 | 7.70 | |||||
| P.Q2 | 5.52 | |||||
| P.Q3 | 6.52 | |||||
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. Rotation Method: Varimax with Kaiser Normalization. |
||||||
| Table 6 KMO and Bartlett’s Test | ||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy. | 0.797 | |
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 782.201 |
| Df | 136 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
The variables or statements of questionnaire clubbed under factors were under:
Factor 1 (Product quality): This factor has Total Initial Eigenvalues of 6.120 and explains 36.002% of total variance Table 7. This factor includes three variables or three different dimensions namely:
| Table 7 Total Variance Explained | |||||||||
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 6.120 | 36.002 | 36.002 | 6.120 | 36.002 | 36.002 | 3.945 | 23.206 | 23.206 |
| 2 | 1.960 | 11.531 | 47.533 | 1.960 | 11.531 | 47.533 | 2.907 | 17.099 | 40.305 |
| 3 | 1.420 | 8.355 | 55.887 | 1.420 | 8.355 | 55.887 | 2.237 | 13.161 | 53.466 |
| 4 | 1.257 | 7.393 | 63.280 | 1.257 | 7.393 | 63.280 | 1.668 | 9.814 | 63.280 |
| 5 | 1.954 | 5.614 | 68.894 | ||||||
| 6 | 1.841 | 5.945 | 73.839 | ||||||
| 7 | 0.816 | 4.800 | 78.639 | ||||||
| 8 | 0.630 | 3.707 | 82.346 | ||||||
| 9 | 0.553 | 3.253 | 85.599 | ||||||
| 10 | 0.496 | 2.920 | 88.519 | ||||||
| 11 | 0.438 | 2.578 | 91.098 | ||||||
| 12 | 0.365 | 2.148 | 93.246 | ||||||
| 13 | 0.330 | 1.939 | 95.185 | ||||||
| 14 | 0.277 | 1.631 | 96.815 | ||||||
| 15 | 0.239 | 1.405 | 98.221 | ||||||
| 16 | 0.153 | 0.902 | 99.123 | ||||||
| 17 | 0.149 | 0.877 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. | |||||||||
• Online shopping provides better quality products.
• When I shop online more positive feedback indicates better quality of products.
• When shopping on the internet pictures and colors are clear and representative of the products.
Factor 2 (Product variety): This factor has Total Initial Eigenvalues of 1.960 and explains 11.531 % of total variance. This factor includes three variables or three different dimensions namely:
• Internet shopping provides more variety of the products
• The service quality of sellers is important
• I will consider all comprehensive factors to choose the best products when I shop online.
Factor 3 (Pricing): This factor has Total Initial Eigenvalues of 1.420 and explains 8.335 % of total variance. This factor includes three variables or three different dimensions namely:
• The price is important when you shopping online.
• Online shopping helps me to saving money.
• Shopping online permits me to buy an item at a relatively lower price.
Factor 4 (Quality information): This factor has Total Initial Eigenvalues of 1.257 and explains 7.393 % of total variance. This factor includes three variables or three different dimensions namely:
• Concerns over what information retailers are storing about customers, e.g. buying habits.
• Not being able to physically inspect the goods before purchase.
Factor 5 (Security): This factor has Total Initial Eigenvalues of 1.954 and explains 5.614 % of total variance. This factor includes three variables or three different dimensions namely:
• I trust the security of online payment methods such as credit/ debits cards etc...
• Goods getting damaged during transport.
Factor 6 (Website design): This factor has Total Initial Eigenvalues of 1.841 and explains 5.954 % of total variance. This factor includes three variables or three different dimensions namely:
• The website design helps me in searching the products easily.
• Please indicate which one affects you satisfaction most during your previous shop online experience.
The ANOVA is given in the Table 8 below (B), Table 9, Table 10 and the significant value is 0.000, which is less than the critical value of 0.05; therefore, the consumer satisfaction level has a significantly different mean than Online Shopping factors, i.e. Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, and Websites consequently, has a linear relationship. Henceforth, the null hypothesis “Different types of factors are not affecting the customer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India is rejected”. Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, and Websites have no significant value is less than 0.005. The Total Variance is divided into the variance, which is possibly explained by Consumer shopping factors, i.e. Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, and Websites, i.e. 4.880 and the variance, which is not explained by Consumer Shopping factors, i.e. 75.680.
| Table 8 Anovas | ||||||
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 4.880 | 6 | 0.813 | 0.999 | .000b |
| Residual | 75.680 | 93 | 0.814 | |||
| Total | 80.560 | 99 | ||||
| a. Dependent Variable: Consumer Satisfaction b. Predictors: (Constant), Websites, Quality Information, Pricing, Product Quality, Security, Product Variety, |
||||||
| Table 9 Model Summary | |||||||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | Change Statistics | ||||
| R Square Change | F Change | df1 | df2 | Sig. F Change | |||||
| 1 | 0.246a | 0.061 | 0.000 | 0.902 | 0.061 | 0.999 | 6 | 93 | 0.431 |
| a. Predictors: (Constant), Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, Websites b. Dependent Variable: Consumer Satisfaction |
|||||||||
| Table 10 Variables Entered/Removed | |||
| Model | Variables Entered | Variables Removed | Method |
| 1 | Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, Websites | 0 | Enter |
| a. Dependent Variable: Consumer Satisfaction b. All requested variables entered. |
|||
The t value is statistically significant, being less than 0.05 for Individual different forms of online shopping, i.e. Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, and Websites. The coefficient value of the consumer satisfaction level represents the changes in the mean response for one unit of change in online shopping factors. At the same time, the other terms in the model are held constant. The relationship between Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, and Websites and consumer satisfaction level can be expressed in the equation forms as:
Consumer Satisfaction= 0.082 Product Quality + 0.044 Product Variety + 0.018 Pricing + 0.128 Quality Information + 0.205 Security + 0.118 Websites.
The equation (1) is defined when Consumer Satisfaction is measured on five point Likert Scale.
Show the Regression Table 11 below: Online Shopping, i.e. Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, Websites, has a significant relationship between consumer satisfaction levels. The standard error of estimate measures the dispersion of Consumer Satisfaction factors around their means which is 0.902. This is the standard deviation of the error term and the square root of the mean square for the Residual in the ANOVA table given below.
| Table 11 Coefficients | ||||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 3.676 | 0.668 | 5.501 | 0.000 | |
| Product Quality | 0.082 | 0.111 | 0.081 | 0.743 | 0.000 | |
| Product Variety | 0.044 | 0.124 | 0.045 | 0.351 | 0.002 | |
| Pricing | 0.018 | 0.101 | 0.022 | 0.177 | 0.000 | |
| Quality Information | 0.128 | 0.148 | 0.105 | 0.865 | 0.003 | |
| Security | 0.205 | 0.130 | 0.197 | 1.577 | 0.001 | |
| Websites Design | 0.118 | 0.108 | 0.127 | 1.098 | 0.004 | |
| a. Dependent Variable: Consumer Satisfaction | ||||||
Conclusion
Conclusion of this paper, according to the review of literature below, some factors are more affecting the consumer’s satisfaction level towards online shopping in India.
Product Quality, Product Variety, Pricing, Quality Information, Security, Websites Design.
• Product quality is a more critical factor for every consumer buying; mostly, women search for more products and branded products. Because product quality is crucial for every consumer and there are positive and negative aspects of every product & services. Then e-commerce portals are offered many types of products & services. However, sometimes, branded products are an essential role play for a consumer’s life.
• Product Variety: Consumers expect online retailers to offer a wide range of product variety because of the reach of the internet and the potential to track down specialty goods and services. The product variety is an essential role play for every consumer because every consumer has different tastes and preferences of the product & services.
• Pricing: E-Commerce portals give the chances to compare the price quickly because many e- retailers are offered many types of products for different prices. Pricing is directly impacted on consumers buying, i.e. The delivery cost of the products, extra transaction charges etc., but during festival time, e- retailers are offered many types of discounts and facilities, I.e. Coupons, free home delivery etc.
• Quality Information: Accuracy of information quality is concerned about the retailers and customers relationship and trustworthiness of the websites or e-retailers.
• Security: It is concerned that the consumers are not sharing the personnel information for other people or firms. Security is the website ability to protect the consumers' personal information. Consumers are ready to pay online, i.e. online bank transfer, online transactions from unauthorized disclosure. Consumers are concern about the security, liabilities and privacy of online websites.
• Websites Design: Website design is the critical role play for online shopping, effective website design to attract consumers to buy the product online. It is helpful to share accurate information for consumers about any product & service available in the market.
• These factors are more impact on the consumer satisfaction level towards online shopping in India.
References
Ballantine, P.W. (2005). Effects of interactivity and product information on consumer satisfaction in an online retail setting. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 35(6), 461-471.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cappelli, L., Guglielmetti, R., Mattia, G., Merli, R., & Renzi, M.F. (2011). Testing a customer satisfaction model for online services. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, 3(1), 69-92.
Cho, N., & Park, S. (2001). Development of electronic commerce user – consumer satisfaction index (ECUSI) for internet shopping. Industrial Management and Data Systems, 101(8), 400–405.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cyr, D. (2008). Modeling website design across culture: relationships to trust, satisfaction and E-loyalty. Journal of Management Information Systems, 24(4), 47-72.
Daft, R.L., & Lengel, R.H. (1986). Organizational information requirements, media richness and structural design. Management Science, 32(5), 554-571.
Elliot, S., & Fowell, S. (2000). Expectations versus reality: a snapshot of consumer experiences with Internet retailing. International Journal of Information Management, 20(5), 323-336.
Gefen, D. (2000). E-Commerce: the role of familiarity and trust. The International Journal of Management and Science, 28, 725-737.
Guo, X., Ling, K. C., & Liu, M. (2012). Evaluating factors influencing consumer satisfaction towards online shopping in China. Asian Social Science, 8(13), 40.
Jarvenpaa, S., & Todd, P. (1996). Consumer reactions to electronic shopping on the world wide web. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 1(2), 59-88.
Jun, M., Yang, Z., & Kim, D. (2004). Customers’ perceptions of online retailing service quality and their satisfaction. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 21(8), 817-840.
Kang Lo S., Chou Y., & Teng, C.H. 2013. Source effect of advertised reference price influences on transaction value in online shopping environments. Electronic Commerce Res, Vol. 13, p. 411–421.
Katerattanakul, P. (2002). Framework of effective website design for business-to-consumer Internet commerce. business library.
Lee, G.G., & Lin, H.F. (2005). Customer Perceptions of E-service quality in online shopping. Journal of Retail and Distribution Management, 33(2), 161-176.
Li, N., & Zhang, P. (2002). Consumer Online Shopping Attitudes and Behavior: An Assessment of Research. Eighth Americas Conference on Information Systems.
Liu, X., He, M.Q., Gao, F., & Xie, P.H. (2008). An empirical study of online shopping customer satisfaction in China: a holistic perspective. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 36(11), 919-940.
Lo S.H., Hsieh A., & Chiu Y. (2014). Why Expect Lower Prices Online? Empirical Examination in Online and Store-based Retailers. International Journal of Electronic Commerce Studies, 5, (1), 27-38.
Ratnasingham, P. (1998). The importance of trust in electronic commerce. Internet Research, 8(4), 313-321.
Rowley, J. (1996). Retailing and shopping on the Internet. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 24(3), 81-91.
Sam C.H., & Sharma C.H. (2015). An Exploration into the Factors Driving Conumers in Singapore towards or away from the Adoption of Online Shopping. Global Business and Management Research: An International Journal, 7(1), 60-73.
Szymanski, D.M., & Hise, R.T. (2000). E-Satisfaction: an initial examination. Journal of Retailing, 76(3), 309-322.