Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 1
Ethical Leadership Influence on Employees Loyalty Mediating Role of Transformational Leadership Characteristics
Salah A. A. Alabduljader, Kuwait University
Citation Information: Alabduljader, S.A. A. (2021). Ethical leadership influence on employees' loyalty mediating role of transformational leadership characteristics. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(S1), 1-15.
Abstract
The current study aimed at examining the influence of ethical leadership dimensions including (Ethical guidance, Fairness, Leader integrity, Caring behaviour, Power sharing, Role clarification and Concern for sustainability) in increasing employees' loyalty through the mediating role of transformational leadership. Quantitative approach was adopted in that sense and an online questionnaire was distributed on (483) employees within private health care sector in Kuwait. Results of study indicated that acceptance of the main hypotheses and there appeared an influence of ethical leadership on employees' loyalty, in addition to that, it appeared that transformational leadership mediates the relationship between ethical leadership and employees loyalty, meaning that adopting a transformational leadership style and running it based on ethical conduct can increase the possibility of employees' loyalty and connection to the organization based on their feelings of security, justice, positive behaviour that stems from their ethical leadership. Study recommended the necessity of adopting an organizational culture that emphasizes ethical values and standards and disseminating them within the organization in a manner that places ethical values at the top of the organizational value ladder.
Keywords
Ethics, Leadership, Transformational, Conduct, Justice, Security, Loyalty, Organization, Culture, Morals.
Introduction
Business organizations have an important role in serving people and leadership is considered one of the most important issues concerning the organization in this era ( Davidson & Hughes, 2020) , and the organization today seeks to raise the performance of workers and increase their productivity, here there must be a leader who leads them towards achieving its goals, and from here lies the dilemma of many organizations in analyzing the nature of the relationship between leadership and performance or leadership and job satisfaction, or even organizational leadership and loyalty, and does the organization that has distinctive or ethical leadership differ in performance from other organizations ( Duan et al., 2018) . Is there a clear effect that the leader has in raising the performance of workers and increasing their productivity and loyalty to their organization? Therefore, the importance of research stems from the importance of the topic in itself and being an effective addition to the formation of the leadership entity because of its importance in organizations, and in being the real challenge of the organization today in its ability to choose the leader, the ability of the leader to deliver the organization to the goals it aspires to, and being an audit of the most important skills And leadership behaviors affecting the performance of the organization (Kim & Brymer, 2011; Dradkeh & Al-Mutairy, 2017; Cetin et al., 2015).
Problem Statements
It is obvious and natural for a human being that dealing with morals is acceptable to others, as dealing with good manners has a positive effect in attracting the other towards a cause and imposing good faith in order to complete the required tasks (Yozgat & Meşekıran, 2016)). From the viewpoint of Sikorsky (2019), dealing with ethics in the field of work has a great impact on the organization and its members including management, leaders and workers, as dealing ethically can lead to enhancing organizational symmetry and increasing employees' sense of belonging to the organization and their adherence to achieving its goals and ambitions
It was indicated by Asif et al. (2019) that leadership is one of the most important levels that need to be on high ethics in dealing, as leadership has a direct link and immediate interaction with working individuals - who are the basis of the success of the organization - and therefore the ethics of leaders will have a positive or negative impact on Individuals working and thus harm either the image of the organization in front of them, or its identity, importance and the degree of their affiliation and loyalty to it.
Among the studies that dealt with the impact of ethical leadership in the organization, Salami & Qa'odah (2017), which stated that ethical leadership has a significant impact on the organizational commitment of working individuals in terms of increasing their level of understanding and awareness of the organization's laws and deepening their communication with the organization and its management And thus reducing their desire to leave work.
As for Daradken & Mtairi (2017), they found through their study that ethical leadership positively affects organizational trust through ethical interaction that brings together leaders and working individuals, which in turn increases individuals’ standing in their leadership and motivates them to achieve the required goals. Al-Qarni (2016) previously agreed with the results of this study and supported them, indicating that ethical leadership is not only able to stimulate organizational trust, but also has a significant impact on reducing the rate of organizational silence. Where, through moral leadership, workers are more away from silence and a desire to state their point of view on organizational matters, and to speak in a clear and frank manner without sensitivity or fear
As for Al-Saqer (2018), he found through his study that a significant impact of ethical leadership on organizational loyalty among workers, as the study showed that employee loyalty is higher in organizations whose leaders have an ethical approach to work compared to others. Al-Saqer (2018) stated that reaching the stage of employee loyalty is through adopting an ethical approach to leadership and work
Aim and Objectives
Based on problem formulating above, current study sought to examine the influence of ethical leadership on employees' loyalty through the moderating effect of transformational leadership. In other meaning, it was set to examine how and ethical transformational leadership is more able to achieve organizational loyalty among employees and increase the level of their connectedness to their organization
Achieving such aim was done depending on following objectives:
1. Identify the nature of ethical leadership
2. Highlight the relationship that gathers between ethics and transformational leadership
3. Examine the level of organizational loyalty among sample of study
4. Examine the influence of transformational ethical leadership on employees' loyalty
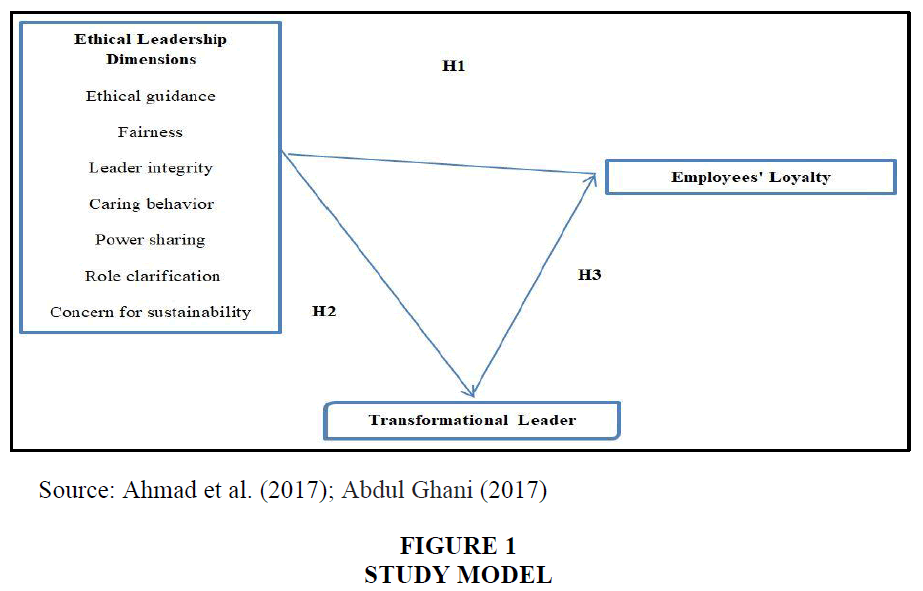
In order to better clarify the relationship between variables, researcher built the following model (Figure 1):
From model above, researcher was able to extract the following set of hypotheses:
H1: Ethical leadership dimensions has a positive influence on employees' loyalty
H2: Ethical leadership dimension has a positive relationship with transformational leadership
H3: Transformational leadership mediates the relationship between ethical leadership and employees' loyalty
Literature Review
Ethical Leadership
Leadership is defined as the ability to influence subordinates to achieve common goals and objectives (Hayat Bhatti et al., 2020). Generally speaking, leaders are accountable to the bodies associated with the corporation from stakeholders, shareholders and employees in relation to achieving the objectives of the organization, and the degree of their commitment to responsibility and ethics when doing so depends on several factors (Karabey & Aliogullari, 2018). A leader's values are important in terms of ethics and effectiveness because they usually become the values that the organization as a whole embraces ( Elçi et al., 2012).
With the continuous development of the term “leadership”, many scholars and researchers have gone into deeply understanding the concept of leadership and try to find a suitable and generalized definition for the term. Of course, all of these efforts went without reaching the most suitable definition for leadership as everyone sees the term in their own eye, and there couldn't be one unified definition for a term that is universal in its nature ((Riaz, 2018).
However, many characteristics, types, styles and forms of leadership appeared on the surface with the increased research on this term, many aspects began to rule it, and many ideas and investigations began to take place on the term leadership reaching to the state of considering leadership as a human behavior which has to be ruled and governed by ethics (Altahat & Atan, 2018). From that point, the term ethical leadership appeared, and it was defined as acting according to ethical principles every day in practical life and in the decision-making process, that is to put it simply: ethical leadership means doing the right thing.
From a managerial point of view, ethical leadership means for the leader to be committed to their ethical principles, and to be aware at the same time of the complexity of some ethical issues, and to take intoaccount the different views of employees, and to work to settle disputes that may arise Hu & Bentler, 1999.
Many large organizations have been bankrupt due to ethical scandals, and it has become clear after the investigation and examination of many scandals that have befallen organizations over the years that these errors could have been avoided had the ethical leadership been in place and if the managers had questioned the wrongdoers or prevented mistakes from occurring before it gets worse (Wang & Liu, 2017). Accordingly, it can be said that ethical leadership has benefits that the organization can reap; only ethical leadership is positively related to a large extent with the performance of employees, while Basoro & Tefera (2021) he emphasized that ethical leadership reduced the likelihood of employees leaving work, and this is a great benefit considering the cost. Increase in employee turnover
Generally speaking, ethical leadership revolves around creating a culture in which people do the right thing as there are many benefits that come from this, ranging from small things like reducing the likelihood of employees stealing office supplies to much bigger things like treating customers in an appropriate way and making decisions that will benefit in the long term for a wide range of stakeholders rather than short-term personal gain ( Kalshoven, 2011; Men, 2015).
Organizational Loyalty
The word loyalty has many connotations. Loyalty in the language “means covenant, closeness and victory, love and commitment.” The concept of loyalty is an ancient concept that sociologists and behaviorists have discussed in earlier times, as they tried to give explanations and jurisprudence based on the fact that a person lives with individuals in an organized social environment in which life requires cooperation, belonging and devotion to reach goals and objectives as according to Okan & Akyüz (2015).
According to Philipp & Lopez (2013), individuals live in societies in which they are exposed to situations that contribute to the formation of their attitudes and patterns of behavior, and if individuals have negative feelings, they will live in work environments dominated by the character of conflict and organizational tension that will lead to the inevitable result of a low and low level of loyalty and affiliation. But if the individuals’ feelings are positive as a result of a sound organizational climate, this will encourage and develop the factor of loyalty and affiliation with them, and then increase their productivity and thus the organization can maintain its survival and achieve its goals (Ponnu & Tennakoon, 2009; Rabie & Malek, 2020;Saleem et al., 2020;Tabechnick & Fidell, 2007).
Many scholars have defined the concept of loyalty in organizational environment,Wang & Liu (2017) defined it as greatly effective coupling between the individual and the organization, although they get less return, Hassan et al. (2013) defined organizational loyalty as a situation in which the individual embodies the values and goals of the organization, and the individual wishes to maintain their membership in it to facilitate the achievement of their goals. As for Tseng & Wu (2017), organizational loyalty was defined as employee's strong desire to continue as a member of a particular organization and the employee's willingness to make a high effort for the organization.
As for the supporters of behavioral school, they tried to clarify and define organizational loyalty, and they described it from the behavioral perspective as the individual's representation of the values and goals of the managerial organization, the fusion of the individual within work environment through functional and organizational role, the desire and willingness to work and remain in work environment and readiness to present the organizations for the benefit of the organization (Khuong & Nhu, 2015). In this direction, behaviorists tried to define organizational loyalty as the direction or orientation towards the organization, or it can be seen as the drift of individuals or their effective attachment to the goals and values of the organization regardless of the material value achieved by the organization ( Alshammari et al., 2015;Hair et al., 2006;Engelbrecht et al., 2017; Bachmann, 2015).
Boteet (2018) argued that there might be thousands of definitions for organizational loyalty, and it would be impossible to settle on one universal definition, however, for an employee to be considered as loyal; all definitions which were presented focused on the existence of the following elements:
1. Acceptance of the goals and values of the administrative organization.
2. Contribute positively to achieve the goals of the administrative organization.
3. Provides a high level of loyalty to the organization.
4. Strong desire to stay and continue the existing organization.
5. Sincerity and willingness to evaluate the organization positively.
Transformational Leadership
According to Jada & Mukhopadhyay (2019);O’Reilly & Chatman (2020), leadership is a necessary matter necessitated by interactions between individuals and groups, for the leader is a watchdog, organizer and directs to individuals in their behavior and attitudes towards specific common goals that they aim to achieve without breaching public order, law, customs and traditions, and the goal of that is to reach the group to achieve what they aspire to without tampering with the system or breach the security of others.
Because of the rapid developments that have occurred in business organizations today, and the urgent need to keep pace with these developments and confront them and increase the complexities in the business environment in all its aspects, in addition to the need for change at all levels of work and increase the effectiveness of the relationship between the leader and the subordinates, it was necessary to think about finding more leadership styles that are more appropriate, the concept of transformational leadership was the most important of these types, which is considered one of the modern concepts in leadership thinking (Neves & Coimbra, 2019)
According to Bello (2012), the concept of transformational leadership was coined by the American scientist (Burns) in 1978 A.D., and then the concepts of transformational leadership emerged as contributions to the work of (Burns) by a number of scholars thanks to the emergence of transformational leadership in education to (Sergeiovanni). However, transformational leadership was defined by Bahzar (2019) as the ability to align means and ends for individuals and organizations as they are shaped to achieve great humanitarian purposes andethical aspirations, while Berkovich & Eyal (2019) defined it as the ability to realize the apparent and latent needs of the subordinates and work to satisfy those needs and invest the maximum energies of the subordinates in order to achieve an intended change
Many definitions appeared for transformational leadership, among these definitions:
1. Leadership that achieves results far beyond what was envisaged and beyond what was expected, as it seeks to bring about an integrated qualitative leap in values, convictions, trends, visions and goals, which depend on real change and creativity ((Khuong & Nhu, 2015)
2. Prepare in advance by providing technical, behavioral, administrative and cognitive skills to use the available resources efficiently and effectively, to transform from the current reality to the desired future reality within a specific period with the least possible negative aspects for individuals and institutions in the shortest time and the least effort and cost ( Yasir & Mohamad, 2016)
3. A process by which both the leader and his subordinates strive to elevate each other to the highest levels of motivation and ethics ( Jambawo, 2018)
4. A leadership style that facilitates the redefinition of people's vision and mission, the renewal of their commitment to the spirit of the profession, and the re-modification of the structure of the systems under which they work in order to achieve the required goals ( Hoch et al., 2018)
Hypotheses Development
In a study by Wang & Liu (2017), researchers aimed at examining effect of ethical leadership on loyalty to leadership by employees by examining the effect of ethical leadership characteristics as mediating variables, which include justice and collectivistic orientation. Through the study, the tool was applied to a sample of (395) employees within (74) work teams in various organizations in China. The results of the study found that there is a positive effect of ethical leadership on motivating employees towards loyalty and belonging to their leadership, as it appeared that there is mediating relationship of justice between ethical leadership and loyalty, and the study also found that collectivistic orientation moderated the relationship between ethical leadership and justice Kim & Thapa (2018). To say based on the results of the study that ethical leadership has a positive effect on motivating employees towards loyalty to leadership, which would lead to loyalty to the organization as a whole.
Another study by Elçi et al. (2012) aimed at determining the effect of ethical leadership on the effectiveness of leadership in reducing job turnover through the mediating role of work stress. And by collecting data from (1093) employees within (70) organizations operating in (9) sectors, the study came to the conclusion that there is no direct relationship between ethical leadership and employee turnover, except that the actual relationship appeared between ethical leadership and work stress, Where the ethical leadership helped to prepare the employees to withstand the work stress and thus reduced the job turnover in the organization, on the other hand, the study found that there is a direct effect of the ethical leadership on the performance of the employees, and this matter affected the performance of the studied organizations in general Shevlin & Miles (1998).
On the other hand, Asif et al. (2019) aimed in their study to highlight the influence of ethical leadership on work engagement, effective commitment, and employee creativity, and through the application of the survey study on a sample of (233) government sector employees in Chinese organizations, the study demonstrated that there is a clear impact of ethical leadership on work engagement and effective commitment. Primarily and apparently, MacCallum et al., (1996) the study also demonstrated that an effective commitment mediates the relationship between ethical leadership and work engagement, which has led to a direct impact on employee creativity. That is, the study generalized the idea of the impact of ethical leadership on each of the variables of work engagement, effective commitment, and employee creativity.
Sikorsky (2019) also examined the characteristics of ethical leadership effect on employees' behavior in the organization, results of study indicated that the characteristics of ethical leadership play a role in deviating employees away from misbehavior based on dealing with them through traits of fairness, power sharing and role clarification. On the other hand, researcher found that traits of ethical leadership interconnect with many traits of transformational leadership which includes charisma or idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation and individualized consideration
Another study by Yozgat & Meşekıran (2016) shed the light on the influence of ethical leadership and trust in leader on job satisfaction. Through applying a questionnaire on middle management within organizations in Turkey, it was indicated that ethical leadership and trust positively influence employees' satisfaction towards their job; this in its turn facilitates the process of increasing employees' loyalty to their leadership which can be motivating to be loyal to the organization as a whole. Study also demonstrated the better effect that ethical leadership has in case it was merged with traits of transformational leadership, it is widely known that transformational leadership is more accepted among employees compared to other style of leadership; this can help in increasing satisfaction and loyalty.
Kalshoven et al. (2021) in their study examined the general traits of ethical leadership and its influence in supporting a better work environment, variables of fairness, integrity, ethical guidance, people orientation, power sharing, role clarification, and concern for sustainability) were taken into consideration, results indicated that regardless of employees' influence by each of such variables, they are still influencing in presenting a good work environment for employees which can support their ability to work better and be more productive
Methods
Current study was carried out during COVID19 pandemic which managed in limiting the approach of applying study tools and framed the research process with health precautionary measures due to multiple laws that are related to lockdown, quarantine and the prevention of gatherings, not to mention the laws of remote working and operating for many organizations. For that reason, current study adopted the quantitative approach through employing a questionnaire as a tool. The questionnaire was built by researcher with the help of previous studies including Ahmad et al. (2017); Abdul Ghani (2017). The questionnaire consisted of two main sections, the first took into perspective demographics of study sample, while the other consisted statements that are related to study variables including (Ethical guidance, Fairness, Leader integrity, Caring behavior, Power sharing, Role clarification and Concern for sustainability). The study tool was designed based on Liker 5 scale (1 strongly disagree, 2 disagree, 3 neutral, 4 agree, 5 strongly agree). However, the questionnaire was arbitrated by a group of specialists in the field in order to check its suitability and consistency to the main aim of study; in its final version it consisted of (40) statements to be answered by respondents through an online copy of the questionnaire which was distributed of the study sample.
Population of study was resembled by individuals working within private health sector in Kuwait through 2019-2020, a convenient sample of (600) respondents were chosen to represent the population. After application process researcher was able to retrieve (483) properly filled questionnaires which indicated a response rate of (80.5%) as statistically accepted.
SPSS v. 27th was used for the sake of data screening and analysis, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation were used to test authenticity of primary data, and in addition to thatCronbach Alpha was used in order to verify the study reliability. The alpha value=0.956, which is an excellent ratio, being higher than the acceptable percentage 0.60 (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016).
Analysis and Discussion
Demographic Results
In Table 1 below, characteristics of sample who responded to questionnaire was calculated, results indicated that majority of sample responding to study questionnaire was male forming 58.8% of total sample whose ages ranged between 40-45 years old forming 49.5% with educational qualifications of BA forming 52.4% of the total sample. It is worth to mention also that results indicated that majority of respondents were employees forming a big chunk of the sample 91.1% and with experience of 12-15 years forming 42% of total sample.
| Table 1 Descriptive Statistics of Respondents | ||
| Gender | ||
| f | % | |
| Male | 284 | 58.8 |
| Female | 199 | 41.2 |
| Age | ||
| 28-33 | 43 | 8.9 |
| 34-39 | 65 | 13.5 |
| 40-45 | 239 | 49.5 |
| 46 + | 136 | 28.2 |
| Qualifications | ||
| BA | 253 | 52.4 |
| Diploma | 67 | 13.9 |
| MA | 120 | 24.8 |
| PhD | 43 | 8.9 |
| Position | ||
| Employee | 440 | 91.1 |
| Leader/Manager | 43 | 8.9 |
| Experience | ||
| 4-7 | 24 | 5.0 |
| 8-11 | 200 | 41.4 |
| 12-15 | 203 | 42.0 |
| +15 | 56 | 11.6 |
| Total | 483 | 100.0 |
Questionnaire Descriptive Statistics
In analyzing responses of individuals towards statements of questionnaire, it was found out that all statements scored higher than mean of scale 3.00 and this is statistically considered as a positive indication. Going deeper into examination of Table 2 below, it can be seen that the highest mean was for the statement of “Equity in promotions and performance appraisal reports” scoring a mean of 4.59/5.00 compared to the lowest mean for the statement of “Transformational leaders empower their employees” with a mean of 3.86/5.00.
| Table 2 Respondents' Attitudes Towards Questionnaire | ||
| Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| Ethical Leadership Dimensions | ||
| Ethical Guidance | ||
| Ethical leaders usually highlights standards related to ethical behavior | 4.21 | 0.496 |
| Increase the subordinates' awareness of work instructions and directives | 4.29 | 0.551 |
| Clarify the rights and obligations through daily dealing behaviors | 4.07 | 0.783 |
| An ethical leader is always aware of the ethical side of the situation | 4.29 | 0.605 |
| Fairness | ||
| An ethical leader treats employees equally | 4.47 | 0.499 |
| Emphasizing the principle of laying down principles | 4.58 | 0.493 |
| Equitable distribution of rewards in proportion to performance | 4.32 | 0.744 |
| Equity in promotions and performance appraisal reports | 4.59 | 0.492 |
| Focus on achieving the goals of the organization as a whole | 4.50 | 0.501 |
| Leader Integrity | ||
| An ethical leader is true to their promises | 4.53 | 0.654 |
| There is consistency between words and actions | 4.55 | 0.571 |
| An ethical leader commit to their words with their employees | 4.39 | 0.489 |
| Act honestly and responsibly with subordinates | 4.51 | 0.800 |
| An ethical leader won't change their attitude for personal gains | 4.15 | 0.717 |
| Caring Behavior | ||
| Ethical leader cares for others | 4.43 | 0.569 |
| They respect their team members and support them with their ability | 4.18 | 0.679 |
| They make sure that all needs of the team members are met | 4.43 | 0.569 |
| An ethical leader puts into perspective the need to develop employees' performance | 4.16 | 1.027 |
| An ethical leader has good communications with team members | 4.04 | 0.978 |
| Power Sharing | ||
| An ethical leader leans towards sharing decision making process | 4.00 | .999 |
| Employee engagement is important to an ethical leader | 4.34 | .475 |
| An ethical leader cares for hearing others | 4.55 | .497 |
| Being a part of the team is an important issue for an ethical leader | 3.87 | 1.258 |
| Role Clarification | ||
| An ethical leader treats employees with transparency | 4.04 | 0.977 |
| An ethical leader defines responsibility of each team member | 3.98 | 1.134 |
| There is always a clarification for roles of each team member | 4.13 | 1.017 |
| Ethical leaders clarify the aim of work and work priorities | 4.36 | 0.621 |
| Concern for Sustainability | ||
| An ethical leader is always ready to care for shareholders' rights in the organization | 4.10 | 0.760 |
| Directing others to take care of the environment | 4.00 | 0.768 |
| Encouraging work in an environmentally friendly environment is one of the ethical leader's concerns | 4.13 | 0.694 |
| Encouraging the recycling process of materials and tools used in the work | 4.30 | 0.539 |
| Employees' Loyalty | ||
| Ethical leadership increases job satisfaction among employees | 4.64 | 0.557 |
| Usually satisfied employees are more able to be loyal to their organization | 4.17 | 0.778 |
| With ethical leadership employees are more oriented towards committing to their leadership | 4.23 | 0.845 |
| Leadership can drive employees to prefer the work environment | 4.31 | 0.611 |
| With ethical leadership employees are more lean towards staying within the organization | 3.86 | 0.631 |
| Transformational Leader | ||
| Transformational leaders are more convinced with power sharing | 3.77 | 0.671 |
| Transformational leaders empower their employees | 3.86 | 0.777 |
| Integrity is one of transformational leader traits | 3.89 | 0.727 |
| Transformational leaders are more resilient towards ethics and ethical behavior | 3.92 | 0.697 |
| Transformational leadership isn't rigid when it comes to ethics in leadership | 4.08 | 0.732 |
Following Table 3, descriptive statistics of variables' means was presented; it appeared the highest variable which was answered positively was “fairness” scoring a mean of 4.49/5.00 compared to the least positively answered variable which was “transformational leadership” which scored a mean of 3.90/5.00.
| Table 3 Descriptive Statistics of Variables | ||
| Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| Ethical Guidance | 4.2164 | 0.39253 |
| Fairness | 4.4923 | 0.39625 |
| Leader Integrity | 4.4277 | 0.52170 |
| Caring Behavior | 4.2460 | 0.64605 |
| Power Sharing | 4.1925 | 0.69317 |
| Role Clarification | 4.1258 | 0.85326 |
| Concern for Sustainability | 4.1222 | 0.62998 |
| Employees' Loyalty | 4.2418 | 0.49006 |
| Transformational Leader | 3.9056 | 0.54433 |
Pearson correlation was used to test the relationship between the independent variables (ethical leadership dimensions), the dependent variable (employees loyalty) and mediating variable (transformational leadership), it was found that that there was a relationship between the ethical leadership dimensions and employees loyalty, as well as, there is a relationship between the ethical leadership and the transformational leadership as it appeared in Table 4 below:
| Table 4 Pearson Correlation | |||||||||
| Guidance | Fairness | Integrity | Caring | Power | Clarification | Sustainability | Transformational | ||
| Loyalty | Pearson Correlation | 0.220** | 0.645** | 0.715** | 0.697** | 0.636** | 0.583** | 0.798** | 0.381** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| N | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | |
| Transformational | Pearson Correlation | 0.195** | 0.396** | 0.275** | 0.322** | 0.373** | 0.456** | 0.376** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | 483 | |
| **Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed) | |||||||||
Hypothesis Testing
Before starting structural analysis, the proposed study model was validated by a set of indicators to check the suitability of the model of this study, as follows:
The results in Table 5 showed that above indicators have passed the values recommended by the relevant references, this leads to the hypothesis testing as follows:
| Table 5 Fit Model | ||||||
| Indicator | AGFI | 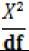 |
GFI | RMSEA | CFI | NFI |
| Value Recommended | > 0.8 | < 5 | > 0.90 | ≤0.10 | > 0.9 | > 0.9 |
| References | Shevlin & Miles (1998) | Tabachnick & Fidell (2007) | Shevlin & Miles (1998) | MacCallum et al. (1996) | Hu & Bentler (1999) | Hu & Bentler (1999) |
| Value of Model | 0.905 | 3.287 | 0.941 | 0.066 | 0.908 | 0.927 |
Structural equation analysis was used to test the research hypothesis. The hypothesis will be accepted if p-value is less than 0.05 (Table 6):
| Table 6 The Results of Testing Hypotheses | |||||||
| Standardized Indirect Effect | Standardied DirectEffect | PathCoefficients (β) | T-value | P | |||
| Transformational Leadership | <--- | Ethical leadership | 0.381 | 0.381 | 8.112 | *** | |
| Employees' Loyalty Loyalty | <--- | Ethical leadership | 0.047 | 0.673 | 0.721 | 13.872 | *** |
| Employees' Loyalty Loyalty | <--- | Transformational leadership | 0.125 | 0.125 | 3.641 | *** | |
H1 Ethical leadership dimensions has an influence on employees' loyalty
Above table shows that (β=0.673; P<0.05; =0.000). This means that Ethical leadership dimensions has an influence on employees' loyalty
H2 Ethical leadership dimension has a relationship with transformational leadership
Above table shows that (β=0.381; P<0.05; =0.000). This means that Ethical leadership dimension has a relationship with transformational leadership
H3 Transformational leadership has an influence on employees' loyalty
Above table shows that (β=0.125; P<0.05; =0.000). This means that Transformational leadership has an influence on employees' loyalty
H4 Transformational leadership mediates the relationship between ethical leadership and employees' loyalty
Above table shows that (β=0.721; P<0.05; =0.000). This means that Transformational leadership mediates the relationship between ethical leadership and employees' loyalty.
Discussion
Current study aimed at examining the influence of ethical leadership on employees' loyalty through focusing on the mediating role of transformational leadership. Depending on quantitative approach, a questionnaire was distributed electronically on (483) individuals working within the Kuwait private health sector. SPSS was used in order to screen and analyze primary data. Results of study was able to accept the main hypothesis confirming that there is a positive relationship between ethical leadership and employees' loyalty and transformational leadership mediates that relationship. Study was also able to reach following conclusions:
1. (β=0.673; P<0.05; =0.000) which means Ethical leadership dimensions has an influence on employees' loyalty
2. (β=0.381; P<0.05; =0.000) which means Ethical leadership dimension has a relationship with transformational leadership
3. (β=0.125; P<0.05; =0.000) which means Transformational leadership has an influence on employees' loyalty
4. (β=0.721; P<0.05; =0.000) which means Transformational leadership mediates the relationship between ethical leadership and employees' loyalty
Going deeply into analysis, results of study indicated that the relationship between ethics and employees is considered to be vital - as studies before have shown in addition to current study - that employees are more attracted to an ethical leadership and management. The fact that a leadership is being run on the bases on ethics makes more attractive to individuals as they tend to be more trustful in their leadership, this in many aspects operates an environment that is supportive for loyalty, study showed that being an ethical leader mean to be a leader who is guiding by ethics, a person who is fair, caring and makes informed decision based on equality and justice which agreed with Wang & Liu (2017) and Elçi et al. (2012). In addition to that, study results indicated that gathering between a transformational leadership style and an ethical leadership approach can make wonders in making employees more attached to their leadership, this feelings stems from their believe and trust, in addition to their sense of equality, fairness, integrity and justice at the work place as came before byAsif et al. (2019) ; Qa'odah (2017) and Daradken & Mtairi (2017).
The study also proved what came along with Asif et al. (2019); Sikorsky (2019) and Yozgat & Meşekıran (2016) that there is a strong relationship between the availability of ethical behavior among the leader and the ethical behavior practices of the leader and the organizational commitment of the workers, in addition to the level of moral leadership among the leaders and the level of commitment of the employees, where the leader must have a work ethic, that is, to act in an ethical manner. In addition to being a reinforcement of ethical behaviors, and deepening the leadership's awareness of the importance of ethical behavior, because of its prominent role in raising the degree of organizational commitment of management and workers, by finding appropriate mechanisms such as issuing official manuals that emphasize the importance of ethical behavior, as well as increasing the number of posters and panels that include standards of ethical behavior and its laws and the penalties that workers face when violating ethical standards.
On the other hand, the study has proven results of Kalshoven et al. (2021); Mukhopadhyay (2019) and O’Reilly & Chatman (2020) that transformational leadership mediates the relationship between moral leadership and employee loyalty, through the transformational leadership’s endeavor to advance the sense of employees through appealing to ethical ideas and values such as freedom, justice, equality, peace and humanity, and as the behavior of transformational leadership It starts from the personal values and beliefs of the leader and not on an exchange of interests with subordinates, the transformational leader moves in his work through well-established value systems such as justice and integrity, or the so-called internal values, and internal values are values that cannot be negotiated or exchanged between individuals, and through the expression of those standards. Personality The transformational leader unites his employees and is able to change their beliefs and goals.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Organizational loyalty is a recent topic, which has received great interest from researchers in industrial and management psychology. The emergence of interest in the issue of organizational loyalty is due to the important influence of organizational loyalty on many individuals' behaviors and its repercussions on the individual and the organization alike. It was seen through study that traits and characteristics of transformational leadership in addition to the ethical culture that the organization may have play a role in increasing employees loyalty through orienting their attitudes towards a more connected approach to the organization, this orientation is led by the smooth and ethical leadership behavior that gives them a sense of security and appeals them to be more productive and attached to their organization.
Based on discussion and conclusion, current study recommends:
1. The organization must consolidate ethical concepts, emphasize the fairness and integrity of the promotions system, gets rid of the financial and administrative corruption features available in the organization, and gives high precedence to ethical values in administrative work.
2. The necessity of adopting an organizational culture that emphasizes ethical values and standards and disseminating them within the organization in a manner that places ethical values at the top of the organizational value ladder.
References
Abdul Ghani, A. (2017). The impact of ethical leadership on the quality of work life an empirical study on Egyptian tax authority (Income tax sector). Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Ain Shams University, Egypt.
Ahmad, I., Gao, Y., & Hali, S.M. (2017). A review of ethical leadership and other ethics-related leadership theories. European Scientific Journal, 13(29), 10-23.
Al-Qarni, M. (2016). The ethical leadership of the heads and supervisors of academic departments at the university of tabuk and its relationship to the behavior of organizational silence. Journal of Pedagogy Faculty, Al-Azhar University, 170(4).
Al-Saqer, H. (2018). Ethical leadership and its relationship with organizational loyalty among the employees of general administration of education in Tabuk.
Bachmann, B. (2015). Concepts of ethical leadership and their potential implementation in organisations: An operational perspective.
Bahzar, M. (2019). Effects of green transformational and ethical leadership on green creativity, eco-innovation and energy efficiency in higher education sector of Indonesia.
Basoro, T.S., & Tefera, B. (2021). Ethical Leadership Practices and Factors Affecting It in South Addis Ababa District Commercial Bank of Ethiopia, 13(1).
Bello, S.M. (2012). Impact of ethical leadership on employee job performance. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(11).
Boteet, S. (2018). Organizational loyalty: Its development is a strategy aimed at influencing the performance of individuals and organizations. Journal of the Social and Human Sciences, 11(1).
Dradkeh, A., & Al-Mutairy, H. (2017). The Role of Ethical Leadership in Enhancing Organizational Trust Among Principals of Primary Schools in Taif City. Jordanian Journal of Educational Sciences, 13(2), 223-237.
Davidson, F.D., & Hughes, T.R. (2020). Moral dimensions of leadership. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Education.
Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., Anderson, R.E., & Tatham, R. (2006). Multivariate data analysis . Uppersaddle River, N.J.: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Khuong, M.N., & Nhu, N.V.Q. (2015). The effects of ethical leadership and organizational culture towards employees’ sociability and commitment–A study of tourism sector in Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam. Journal of Advanced Management Science, 3(4).
Men, L.R. (2015). The role of ethical leadership in internal communication: Influences on communication symmetry, leader credibility, and employee engagement. Public Relations Journal, 9(1), 1-22.
O’Reilly, C.A., & Chatman, J.A. (2020). Transformational leader or narcissist? How grandiose narcissists can create and destroy organizations and institutions. California Management Review, 62(3), 5-27.
Okan, T., & Akyüz, A.M. (2015). Exploring the relationship between ethical leadership and job satisfaction with the mediating role of the level of loyalty to supervisor. Business & Economics Research Journal, 6(4).
Salami, N., & Qa'odah, M. (2019). The impact of ethical leadership on organizational commitment: The mediation role for intention to leave work - a case study of the BATNA gas and electricity distribution directorate. Sustainability and Strategy Journal, 10(4).
Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2016). Research methods for business: A skill building approach. Haddington:John Wiley & Sons.Sikorsky, M. (2019). Ethical leadership: What is it and why does it matter?
Tabechnick, B.G., & Fidell, L.S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics 5th end. New York: Allyn and Bacon.
Yasir, M., & Mohamad, N.A. (2016). Ethics and morality: Comparing ethical leadership with servant, authentic and transformational leadership styles. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6(4), 310-316.
Yozgat, U., & Meşekıran, G. (2016). The impact of perceived ethical leadership and trust in leader on job satisfaction. Journal of Economics, Business and Management, 4(2), 125-131.