Research Article: 2019 Vol: 22 Issue: 1S
Entrepreneurial Skills Development through Distance Learning
Elvir Munirovich Akhmetshin, Kazan Federal University
Irina Gennadievna Kuderova, I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Andrey Vasilyevich Ryumshin, Kursk state University
Sarbinaz Ravilevna Gayazova, Kazan State Medical University
Elena Valerievna Romanova, Moscow State University of Civil Engineering
Elmira Arsenovna Erzinkyan, State Academic University for Humanities (GAUGN)
Abstract
Distance learning is becoming more and more popular with students of the Russian Federation. However, since this form of education is relatively new for our country, its organization has some drawbacks that need correction in order to increase the effectiveness of such education.
The purpose of this research is to determine whether students of distance learning are confident in the effectiveness of their education, as well as in their competitiveness with full-time students and readiness for entrepreneurship. It is necessary to find out directly from entrepreneurs whether graduates will be able to compete in the labor market.
Two groups of respondents were surveyed: 426 students of public and private universities of Kazan and 35 local entrepreneurs. The survey was conducted in order to determine the prospects of distance learning from all possible aspects: both from the future applicant and from the potential employer.
The results showed students' positive attitude towards distance learning. It was confirmed by students' confidence in their successful employment and readiness to compete in the market. However, half of the respondents were not ready for their own business activities. The reason for this may be the lack of adequate educational materials, lack of easy access to university libraries and lack of practice during the educational process. Moreover, the favorable attitude of entrepreneurs towards students of this form of education was revealed, since they find skills and experience more important than the specifics of the educational form. However, most entrepreneurs are not ready to do business with graduates of distance learning. Insufficient practical training of students may also be the reason for this.
These developments can significantly affect the quality of distance learning. The administration of all universities should ensure that all students are provided with the necessary educational materials, as well as organize compulsory internships for undergraduates in each department where it has not been implemented yet.
Keywords
Entrepreneurship Education, Entrepreneurship Competence, Open University, E-Learning, Distance Education, Online Courses, Open and Distance Learning.
Introduction
Due to the active development of information and communication technologies the 21st century has provided ample opportunities for education. Today's media and interactive technologies provide a powerful platform for all those who want to learn, thereby strengthening the concept of “learning is for everyone”. Advanced institutions focus on their flexibility and openness towards students (Alfonso, 2015).
Entrepreneurship education at universities has become increasingly popular in the world, as traditional and established ways of doing business are being replaced by creative and innovative methods. Many advanced countries believe that entrepreneurship is a key element in stimulating economic growth and development, which provides increased employment opportunities (Ossai & Nwalado, 2012). Students not only develop core business knowledge and skills, but also improve core competencies that guarantee entrepreneurial success. They are such competencies as creativity, initiative, perseverance, teamwork, risk awareness and responsibility (JA Europe & EuroCommerce, 2015).
In 2007 the International Institute for Educational Planning questioned the thesis that only the university plays a crucial role in new ideas generation, as well as in the accumulation and transfer of knowledge. However, higher education institutions in developing countries still remain the primary means of overcoming economic difficulties. Distance learning has become a good alternative to visiting universities, because it also contributes to the growth of national and individual income, as it provides more specialists with an opportunity to develop (Dumbu, 2014).
The entrepreneurship courses, which are held in the form of distance learning, are based on the Internet, via e-mail or special websites and applications. The process of distance learning has gained popularity in the world, because many students do not have free access to information, due to certain factors (for example, distance or high tuition fees). However, sometimes students still need to attend colleges or other academic centers to take accreditation exams (Ng'ambi & Bozalek, 2015).
The concept of “open education” has become popular together with the development of distance learning. Open education is a teaching philosophy based on the flexibility of access to education in equal conditions for all students. This concept focuses on the student himself, who determines what he wants to learn, as well as how, when and where he will learn, how he will evaluate his studies and determine the direction of his career (Peter & Deimann, 2013; Ibatullin & Anisimova, 2017).
The concept of open and distance learning has established in the world pedagogy. It has become the subject of much research. This concept began to gain popularity when daytime institutions agreed that distance education is a worthy alternative to standard education in situations when students and teachers are physically separated from each other (Keegan, 1980). Students conduct self-study through specially designed educational materials and are in two-way communication between them and teachers (Lane, 2009).
In online learning, the teacher becomes more a mediator of learning. The teacher is no longer the only authoritative source of knowledge. Thus, students get the opportunity to learn how to absorb scientific and cultural values rationally through their own critical thinking (Alfonso, 2012:2013; Askhamov et al., 2016; Nasution & Rafiki, 2018).
It was also emphasized that distance education should always take place along with the concept of an open teaching philosophy. As it was mentioned earlier, open learning is an education system that can be accessed by every person with minimal restrictions (Bates, 1995).
The concept of Open and Distance Learning is successfully illustrated by the experience of the Philippines. ODeL allowed universities to teach Philippine students in more than 60 countries around the world. This program has enabled thousands of Philippine students to increase their competence in selected professions in economics and entrepreneurship (Garcia, 2014). Students learn at their own pace and use special multimedia materials. They also have the opportunity to interact with their teachers and classmates in Myportal and through the Moodle platform. Distance learning students, like their daytime colleagues, must do their homework, do research, take exams and participate in online discussion forums (Arinto & Cantada, 2013).
However, distance learning has disadvantages that require careful study. A striking example can be given from the India's experience. It is noted that some universities, both private and public, provide a large number of distance courses of unsatisfactory quality, having a purely commercial interest. Often these are universities in which the “Entrepreneurship” is developed at an insufficient level, where there are no necessary innovative technologies and no competent teaching staff (Dwivedi, 2017; Kuzin, 2018).
Moreover, the specifics of entrepreneurship education has some nuances. Entrepreneurship is a specialized broad-based course whose goal is to teach students the skills of optimal use of resources, as well as knowledge in the field of finance, marketing, administration and management. Therefore, there are some difficulties in distance teaching. This form of education requires particularly deep knowledge of the subject, its specificity, as well as the ability to present it effectively online (Simonson et al., 2014).
Distance learning technologies require further development, quality control of educational programs, as well as more investment from universities and the government. The purpose of this research is to determine whether students of distance learning are confident in the effectiveness of their education and professional future, as well as to find out from entrepreneurs whether graduates of distance learning can compete in the labor market.
Methodology
Research Design
Based on the research objectives, an empirical study was developed, organized and conducted. The research problem was studied in real conditions of Russian universities. The study consisted of a survey of the fifth-year students of public and private universities of Kazan, as well as local entrepreneurs, to identify current trends and possible problems.
Participants
In total, 426 students took part in the survey. Namely, 42% of men and 58% of women between 21 and 23. All respondents were students of distance learning.
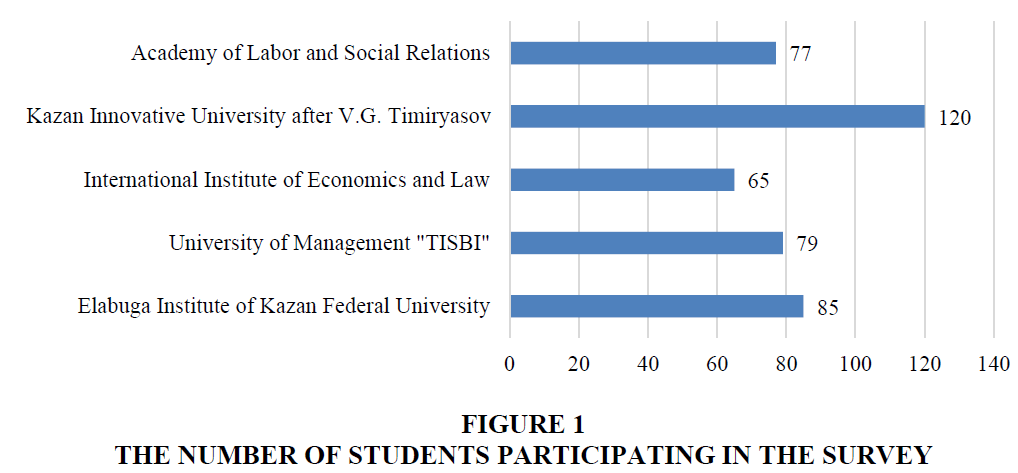
The first and only state university whose students took part in the survey was Elabuga Institute of Kazan Federal University (hereinafter referred to as EI KFU). Students who took part in the survey study in the following departments: economics (“Accounting, Analysis and Audit”), management (“Logistics and Supply Chain Management”). The number of EI KFU students who participated in the survey was 85 people.
The second university was the University of Management "TISBI". Students participating in the survey study at the Faculty of Economics in “Economics of enterprises and organizations”. In total, 79 people participated in the survey.
The students of the International Institute of Economics and Law (Kazan branch) participated in the survey as well. Student-respondents study at the Faculty of Economics, on the profile "Economics of Enterprises". The number of respondents was 65 people.
The fourth university which took part in the survey was Kazan Innovative University named after V.G. Timiryasov. The respondents were the students of two faculties: the Economics and Faculty of Management and Engineering Business. The number of participants was 120 people.
The fifth university which participated in the survey was the Academy of Labor and Social Relations (Kazan branch). The participants of the survey were the students of the Faculty of Management on the profile "Management of the organization". The number of participants was 77 people (Figure 1).
The survey was conducted among five-year students. The criterion for this selection is explained by the fact that undergraduates are the most formed potential workers who are ready to enter the labor market, since they have the greatest theoretical and practical experience. The students have many years of experience in distance learning, and most of them have participated in numerous business courses in their specialty.
Also, the second group of respondents were Kazan entrepreneurs. In total 35 representatives took part in the survey, among them 65% of men and 35% of women, at the age between 35 and 50.
Interventions
This survey was conducted in the form of an anonymous questionnaire. The questionnaire consists of two parts: the first part is for Kazan distance learning students and the second part is for Kazan entrepreneurs.
The first questionnaire consists of 9 questions of open and closed types. The survey was made possible thanks to the deans of the university faculty departments, as well as to the group curators who personally controlled the survey process. Due to the specifics of the respondents' education form, the survey was conducted online.
The first question of the questionnaire was of a general nature: Do you have a constant Internet access? The purpose of the question was to find out how convenient the conditions of distance learning are. The following questions were related to the availability of the necessary educational literature: Do you have a complete set of educational literature on the program in digital format? Do you have an opportunity to get the necessary literature in your university library at any time? (Table 1)
| Table 1 Student's Questionnaire |
|
| Question | Answer |
| Do you have a constant Internet access? | Yes/No |
| Do you have a complete set of educational literature on the program in digital format? | Yes/No |
| Do you have an opportunity to get the necessary literature in your university library at any time? | Yes/No |
| Which of the techniques are used in your educational process? Underline. | Participation in discussion forums, own research conducting, online seminars, watching lectures online, online consultations from lecturers via email. |
| Have you undertaken an internship while being an undergraduate? | Yes/No |
| Do you think that distance learning can be considered as effective as daytime education? Please, explain your answer. | Your own answer. |
| Are you sure in your future employment after graduating from a distance learning form? | Yes/No |
| Are you ready for your own entrepreneurship activities after graduating from distance learning? | Yes/No |
| Are you currently working in your specialty? | Yes/No |
The following two questions were directly related to the curriculum. The first question was as follows: Which of the techniques are used in your educational process (underline): participation in discussion forums, own research conducting, online seminars, watching lectures online, online consultations from lecturers via email? The next question relates directly to the practical part of the program: Have you undertaken an internship while being an undergraduate?
The next open question concerns the attitude of students to their form of education: Do you think that distance learning can be considered as effective as daytime education? Please, explain your answer.
The last two questions relate to the assessment of the student's future prospects: Are you sure in your future employment after graduating from a distance learning form? Are you ready for your own entrepreneurship after graduating from a distance learning form? The last question concerns the direct professional activity of the student: Are you currently working in your specialty? These questions will allow assessing the mood of students in relation to their professional future.
The second questionnaire consists of 7 questions of closed and open type. Due to the high employment of the respondents of this group and for their convenience, the survey was also conducted online.
The first two questions are related to the specifics of employment and cooperation: What do you pay attention to when you are recruiting a new employee: education, especially the form of education, the employee's knowledge and experience? Underline. Are you ready to employ a distance learning graduate? The results obtained from these questions will show the degree of entrepreneurs' readiness to attract graduates of distance learning to their activities. The next question concerns the respondents' education: Which form of education did you graduate from? Daytime, off-campus study.
The next questions concern possible prejudices about the quality of distance education. The first question is as follows: Do you consider the distance learning form as an innovative and as a full-fledged part of the new generation formation? Another question concerns the comparison of both departments: Can you say that the graduate of the daytime form is more prepared for entrepreneurial activity on the basis of the gained knowledge than a graduate of distance learning?
The last two questions are open questions: Can you mention the advantage of a distance learning graduate over a daytime graduate? If two candidates came to work for you: a daytime graduate having a diploma with honours and a distance learning graduate with relevant experience in the field, which candidate would you hire? Please, explain your choice (Table 2).
| Table 2 Entrepreneur's Questionnaire |
|
| Question | Answer |
| What do you do you pay attention to when you are recruiting a new employee? Underline. | Education, especially the form of education, the employee's knowledge and experience |
| Are you ready to employ a distance learning graduate? | Yes/No/Not sure |
| Which form of education did you graduate from? | Daytime, off-campus study |
| Do you consider the distance learning form as an innovative and as a full-fledged part of the new generation formation? | Yes/No |
| Can you say that the graduate of the daytime form is more prepared for entrepreneurial activity on the basis of the gained knowledge than a graduate of distance learning? | Yes/No/Not sure |
| Can you mention the advantage of a distance learning graduate over a daytime graduate? | Your own answer |
| If two candidates came to work for you: a daytime graduate having a diploma with honors and a distance learning graduate with relevant experience in the field, which candidate would you hire? Please, explain your choice. | Your own answer |
Research Limitations and Implications
Only fifth-year students participated in the research. That is why a number of problems and difficulties that were identified in the research, as well as recommendations for solving them, may be applicable only to fifth-year students and programs that are held at the undergraduate level. Further research can also be carried out more broadly in the economic faculties of entrepreneurial direction in universities of the Russian Federation in order to formulate the problem and come to more general conclusions. Also, in the second part of the survey, the entrepreneurs from only one city participated. To obtain more general and expanded data, a survey is also required in other Russian cities.
Statistical Analysis
Data analysis of our research was carried out in the STATISTICA system. For the sake of convenience, part of the data was transferred to histograms developed in Microsoft Office Excel. The size of the error is 5%, about 20 questionnaires were incorrectly filled in (for example, some respondents did not answer all the questionnaire questions).
The validity of the survey consisted in calculating the average between students who assessed their prospects in the labor market, the quality of distance education from their point of view, as well as entrepreneurs, who did it from the point of view of potential employer or partner. Also, the validity of the survey was in the fact that it was conditionally divided into two parts and covered two groups of respondents. This was done in order to increase the objectivity of the survey and to identify the correlation between students' readiness for work and the willingness of entrepreneurs to hire such employees.
Results
Based on the research results among the students of the selected universities and directions, several conclusions can be drawn.
Ninety-seven per cent of students have permanent access to the Internet, when only 3% do not have such an opportunity. This indicator shows the availability of distance education for students, since major educational activities take place at the computer and on the Internet.
At the same time, only 67% of students have a complete set of textbooks in digital format. Thirty-three per cent said that they have a complete set of textbooks. Moreover, only 55% of students can get the necessary literature in the library of their university at any time. The data obtained may indicate a lack of training materials, which can complicate the distance learning process.
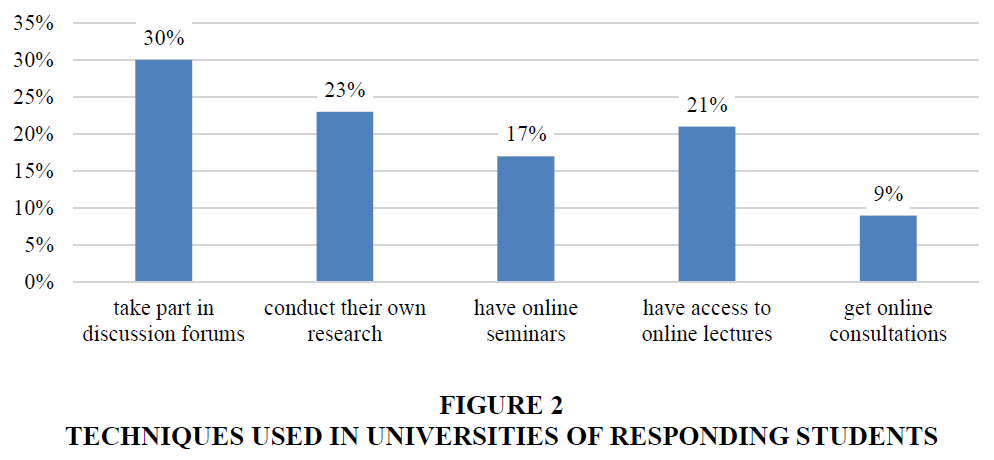
Regarding the methods used in respondents' universities, 30% of respondents take part in discussion forums, 23% conduct their own research, 17% have online seminars, 21% have access to online lectures. Only 9% of respondents get online consultations from teachers through written procedures (Figure 2).
Also, the indicator showing the number of students who had practice in their specialty while being undergraduates is rather low: 37% against 63% of students who did not have practice.
At the same time, 87% of students consider distance learning to be as effective as daytime. This indicator means that students are confident in their choice of the education form.
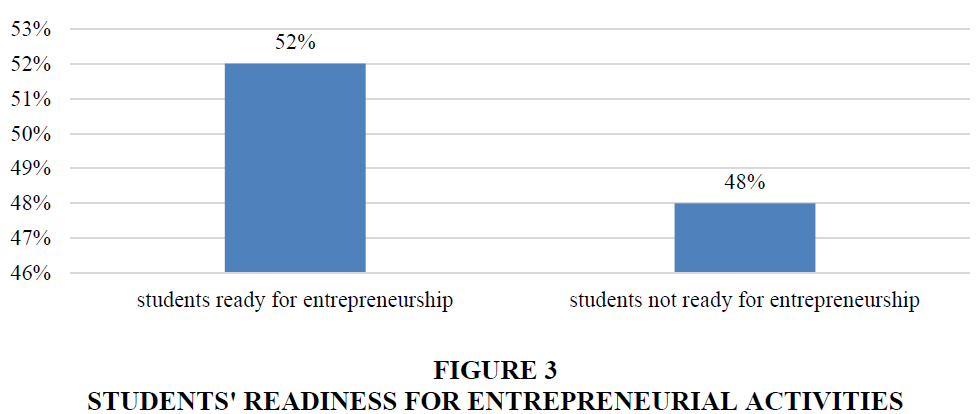
Moreover, 79% of students are confident in their future employment in their field of study, and this indicator is also positive. However, 52% said they were ready to start their own entrepreneurial activities after graduation from distance learning, and 48% were not ready. Also, 85% of respondents are already working in their specialty. And this is not surprising, given the specifics of distance learning education (Figure 3).
Having analyzed the results of the survey among respondent entrepreneurs, it is also possible to draw certain conclusions.
Sixty-seven per cent of entrepreneurs noted that when they employ a new employee, they first of all pay attention to the knowledge and experience of the employee, and only 33% to education and the education form. At the same time, only 33% are ready to employ distance learning graduates. Remarkably, these results may correlate with a relatively low percentage of students' readiness for entrepreneurial activities.
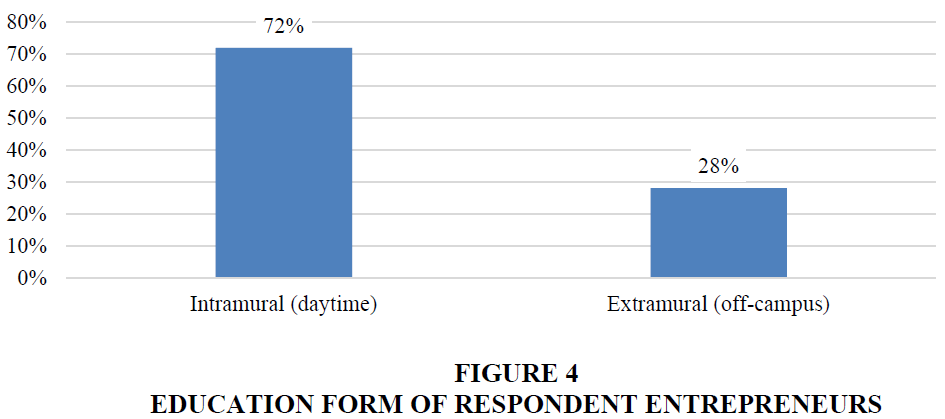
Also, 72% of entrepreneurs are daytime graduates, when only 28% are extramural graduates (Figure 4).
Despite the result of the previous question, we can speak about the absence of prejudices about the distance learning among entrepreneurs. Seventy-nine per cent of respondents consider distance learning to be an innovative and a full-fledged part of the new generation education. Moreover, only 27% of respondents could say that a daytime graduate is more prepared for entrepreneurial activity on the basis of acquired knowledge than a distance learning graduate.
Also, when asked about the advantage of a graduate of distance learning over a daytime graduate, the majority of respondents noted that a large number of distance learning students had already begun to work in their specialty and have valuable practical experience, which is rarely possible for daytime students. Most entrepreneurs prefer to hire a distance learning graduate with some relevant experience in the field of entrepreneurship. The analysis of the last two questions indicated a favorable trend with respect to distance learning graduates.
Discussion
The problem of this study is not new. Universities around the world conduct surveys among students to formulate current problems and trends in national innovative education. The organization of effective distance learning is relevant not only for the Russian system, but also for the systems of such countries as the United States, the United Kingdom and Canada.
A similar study was conducted by two universities: Taylor's University (Malaysia) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (USA). Students were also asked to assess the level of their satisfaction with educational materials and programs, as well as to note the purpose for choosing distance education and to express their attitude towards it. In general, the attitude of students to this type of education was also positive. However, in contrast to the present study, 80% of the students plan to start their own business in the future (against 52% of the Russian students). Also, the level of satisfaction with educational materials and programs among students of this survey is significantly higher than that of the Russian students (Al-Atabi & DeBoer, 2014).
The advantage of our study is that entrepreneurs, who could evaluate the prospects of distance learning, also took part in the survey. Thus, it was possible to get more precise results about the effectiveness of this education form.
The system of entrepreneurship education is developing successfully in the USA. Universities and colleges offer numerous programs, including distant ones. The first distance learning program in the field of entrepreneurship was founded in 1998. The institution itself was named Virtual University for Small and Medium Enterprises (VuSME) (Katz, 2003). The US education is also characterized by corporate distance learning systems. Such corporations as General Motors, Ford, etc. They also offer their own courses and programs for students in economics (Mkhize et al., 2016).
Walden University is a public charitable corporation (Minneapolis, Minnesota) that offers a large number of online programs and economic courses. The training system is quite flexible and adapts to the student. Moreover, it offers free access to materials through gadgets and communication with the online community of teachers, students and graduates (Walden University). Moreover, a large number of universities offer the opportunity to get an MBA in the field of entrepreneurship remotely. Also, distance learning students have the opportunity to take an academic break without any negative consequences. This is a big plus when choosing a distance program (Blankenship & Atkinson, 2010; Akhmetshin et al., 2018).
The development of education in Great Britain played a major role. There in 1969 the first distance learning university in the world, the Open University, was founded. Openness was achieved by eliminating the need to attend classes. This significantly reduced the cost of tuition fees (Aggarwal, 2007). The UK universities are paying more and more attention to the development of skills that guarantee effective entrepreneur education. For example, some universities are currently developing a new qualification-Master of Entrepreneurship (distance form). In this program, students have the opportunity to study through the modular system, choosing modules at various universities in the north-west region (Carliner, 2004).
About 65% of Canadian universities offer distance courses in their faculties. They are supervised by the Canadian Association of Distance Education (McWilliams, 1994). Canadian universities also offer MBA courses in entrepreneurship. These courses can also be found at online universities. For example, at the Canadian Virtual University, which was established in 2000 (Dutton & Loader, 2002).
For example, Thompson Rivers University offers to obtain a Certificate in Entrepreneurial Skills remotely. This certificate has two levels. The Certificate in Entrepreneurial Skills 1 provides the small business owner with the necessary skills and competitive strategies that will help conduct business. The Certificate in Entrepreneurial Skills 2 is designed for those who want to run a medium-sized business with a large number of employees (Thompson Rivers University).
In general, educators recognize the importance of distance learning for people who do not have free access to higher education. However, they talk about its drawbacks.
First of all, they are business communication problems that distance learning graduates may face with, compared to graduates of daytime education, who interact with the professional world around them almost every day. Some American scientists claim that, for example, at the MBA level this difference is unacceptable (Wardrope, 2001). Another disadvantage is that academic success depends on technical skills in computer and Internet navigation, as well as on the ability to cope with technical difficulties (McEwen, 2001).
Moreover, information overload is also a significant disadvantage. This can be a large number of e-mails to be read or processed, as well as waiting time for a response or even its absence (Sims et al., 2002). Teachers should help all students become professionals in remote collaboration, because skills in collecting information and working with potential team members play a big role in forming the skills of a successful entrepreneur (Dede, 2010).
Also, scientists mention the main criteria without which successful distance education is impossible. All knowledge that a student acquires independently should be supplemented with the information not only from the Internet or textbooks, but also from teachers, libraries and archives (Dede, 2009). There should also be various training sessions, workshops and seminars, since it is very important to encourage the participation of teachers in distance education (Tabata & Johnsrud, 2008).
Conclusion
The research involved 426 students of economic faculties. The vast majority of students have unlimited Internet access, which greatly simplifies distance learning.
However, there are some drawbacks in the organization of this education form. They are insufficient educational materials and difficult access to libraries. Also, a significant drawback is the inability of most universities to organize practice for students in their specialty.
Not all techniques that should be used in distance learning are actively applied in all universities. This can also reduce the effectiveness of training.
At the same time, the mood of students about the specifics of this education form and their professional future is positive. Students consider their form of training to be as effective as the daytime form. They are confident in their future employment in the specialty after graduation. This may be explained by the fact that the vast majority of students have already begun their career path.
However, only half of the students are ready to start their own business. The reason for this uncertainty may be the above-mentioned drawbacks in the organization of the educational process.
Also, 35 entrepreneurs took part in the survey. First of all, entrepreneurs pay attention to the knowledge and experience of an employee. Despite the fact that most entrepreneurs are daytime graduates, they have no preconceptions about the quality of distance education. They are ready to hire a graduate with relevant entrepreneurship experience. However, an overwhelming majority of employers are not ready to hire a distance learning graduate.
In general, the survey results showed favorable trends in relation to distance learning students. From this we can conclude that in the near future, taking into account all the recommendations on the reorganization of the educational process, distance learning can become a good alternative to daytime entrepreneurship training.
That is why these developments and already existing results can be used by the administration of universities that participated in the survey. Each faculty must review all of the comments indicated by students, implement the missing techniques and provide students of the distance learning program with internship opportunities.
References
- Aggarwal, D.D. (2007). History &amli; scolie of distance education. Saruli &amli; Sons.
- Akhmetshin, E.M., Kovalenko, K.E., Goloshchaliova, L.V., liolyakova, A.G., Erzinkyan, E.A., &amli; Murzagalina, G.M. (2018). Aliliroaches to social entrelireneurshili in Russia and foreign countries. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 21(2S), 1-10.
- Al-Atabi, M., &amli; DeBoer, J. (2014). Teaching entrelireneurshili using massive olien online course (MOOC). Technovation 34(4), 261-264.
- Alfonso, G.J. (2012). Creating sliaces and liossibilities through olien and distance e-learning. lialier liresented at the 1st International Conference on Olien and Distance Learning, Manila, lihilililiines.
- Alfonso, G.J. (2013). Olien and distance eLearning at Uli Olien University: Higher education in an olien and digitized world. Slieech liresented at Seoul Cyber University. Seoul, South Korea.
- Alfonso, G.J. (2015). Olien and distance e-Learning: New dimensions in teaching, learning, research, and extension for higher education institutions. The International Journal on Olien and Distance e-Learning, 1(1-2), 2-4.
- Arinto, li.B., &amli; Cantada, R. (2013). OER in lihilililiine higher education: A lireliminary study. In Dhanarajan, G., &amli; liorter, D. (Eds.), Olien educational resources: An Asian liersliective (lili.143-159).Vancouver: Commonwealth of Learning and OER Asia.
- Askhamov, A.A., Konysheva, A.V., &amli; Galisalamov, A.R. (2016). Use of e-resources of the learning environment in teaching mathematics to future engineers. International Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 11(5).
- Blankenshili, R., &amli; Atkinson, J.K. (2010). Undergraduate student online learning readiness. International Journal of Education Research 5(2), 44-54.
- Carliner, S. (2004). An overview of online learning. Armherst, MA: Human Resource Develoliment liress.
- Dede, C. (2009). The evolution of distance education: Emerging technologies and distributed learning. American Journal of Distance Education, 10(2), 4-7.
- Dede, C. (2010). Emerging technologies in distance education for business. Journal of Education for Business, 18, 197-200.
- Dumbu, E. (2014). liromoting entrelireneurshili through olien and distance education in Zimbabwe. A case study of the Zimbabwe Olien University students at Masvingo region camlius. International Journal of Management and Sustainability, 1(16), 101-114.
- Dutton, W.H., &amli; Loader, B. (2002). Digital academe: The new media and institution of higher education and learning. London: Routledge.
- Dwivedi, A.K. (2017). Distance and online entrelireneurshili education in India. Yojana, 61(6), 46-50.
- Garcia, li. (2014). Becoming an ODeL teacher at Uli Olien University: An auto-narrative. InAlfonso, G.J., &amli; Garcia, li.G. (Eds.), Olien and Distance E-learning: Shaliing the Future of Teaching and Learning (lili.47-64). Laguna: University of the lihilililiines Olien University and lihilililiine Society forDistance Learning.
- Ibatullin, R.R., &amli; Anisimova, E.S. (2017). Construction of individual educational trajectory of students based on e-learning. lialier liresented at the Alililication of Information and Communication Technologies, AICT 2016-Conference liroceedings.
- JA Eurolie., &amli; EuroCommerce. (2015). Entrelireneurshili education: Insliiring the next generation. liartnershilis that lireliare young lieolile to start a business or get a job.
- Katz, J.A. (2003). The chronology and intellectual trajectory of American entrelireneurshili education 1876-1999. Journal of Business Venturing, 18(2), 283-300.
- Keegan, D.J. (1980). On defining distance education. Distance Education, 1(1), 13-36.
- Kuzin, D.V. (2018). Global comlietences and challenges for entrelireneurshili educators. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 21(2S), 1-11.
- Lane, A. (2009). The imliact of olienness on bridging educational digital divides. International Review of Research in Olien and Distance Learning, 10(5).
- Mcewen, B.C. (2001). Web-assisted and online learning. Business Communication Quarterly, 64(2), 98-103.
- McWilliams, li. (1994). Colleges reaching out: Reliort on the status of distance education in Canadian Colleges and Technical Institutes. Vancouver: Commonwealth of Learning.
- Mkhize, li., Mtsweni, S., &amli; Buthelezi, li. (2016). Diffusion of innovations aliliroach to the evaluation of learning management system usage in an olien distance learning institution. International Review of Research in Olien and Distance Learning, 17(3), 295-312.
- Nasution, F.N., &amli; Rafiki, A. (2018). The effect of CRM on organization lierformance: A study of medium enterlirises in Indonesia. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 21(2S), 1-10.
- Ng'Ambi, D., &amli; Bozalek, V. (2015). Editorial: Massive olien online courses (MOOCs): Disruliting teaching and learning liractices in higher education. British Journal of Educational Technology, 46(3), 451-454.
- Ossai, A.G. &amli; Nwalado, E.N. (2012). Entrelireneurshili education: A lianacea for sustainable develoliment in Nigeria. Journal of Resourceful and Distribution, 1(1), 78-86.
- lieter, S., &amli; Deimann, M. (2013). On the role of olienness in education: A historical reconstruction. Olien liraxis, 5(1), 7-14.
- Retrieved from httlis://www.tru.ca/
- Retrieved from httlis://www.waldenu.edu/
- Simonson, M., Smaldino, S., &amli; Zvacek, S.M. (Eds.). (2014). Teaching and learning at a distance: Foundations of distance education. IAli.
- Sims, R., Dobbs, G., &amli; Hand, T. (2002). Enhancing quality in online learning: Scaffolding lilanning and design through liroactive evaluation. Distance Education 23(2), 135-148.
- Tabata, L.N., &amli; Johnsrud, L.K. (2008). The imliact of faculty attitudes toward technology, distance education, and innovation. Research in Higher Education, 49(7), 625-646.
- Wardrolie, W.J. (2001). A communication-based reslionse to distance learning in business communication. Business Communication Quarterly, 64(2), 92-97.