Research Article: 2019 Vol: 23 Issue: 1
Entrepreneurial Passion Domains of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): A Case Study of Lower Northeastern, Thailand
Adisak Suvittawat, Suranaree University of Technology
Abstract
The objective of this research is; finding the entrepreneurial passion and enthusiasm variables which produces effect on enthusiasm for entrepreneurship and persistence of business for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Lower Northeastern Province, Thailand. The enthusiasm for entrepreneurship parameters have been identified in 5 variables; commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship, enthusiasm for opportunity and enthusiasm for development. This research found that enthusiasm for entrepreneurship consists of commitment to the product or service, with a mean value of 3.47 and S.D=1.21; enthusiasm for competition with a mean value of 3.46 and S.D=1.15, passion for entrepreneurship with a mean value of 3.67 and S.D=1.11, enthusiasm for opportunity with a mean value of 3.54 and S.D=1.10 and enthusiasm for development with a mean value of 3.66 and S.D=1.19. There is a correlation between persistence of business and, commitment to the product or service (r=-0.285**), persistence of business and enthusiasm for competition (r=- 195**), persistence of business and passion for entrepreneurship (r=-0.145**), persistence of business and enthusiasm for opportunity (r=-0.141**) and persistence of business and enthusiasm for development (r=-0.141**) Commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship, enthusiasm for opportunity, and enthusiasm for development have a correlation with persistence of business. The entrepreneur who has an enthusiasm for entrepreneurship keeps a persistence of business.
Keywords
Enthusiasm for Entrepreneurship, Enthusiasm for Competition, Passion for Entrepreneurship, Enthusiasm for Opportunity, Enthusiasm for Development.
Introduction
Entrepreneurs are a considerable force for economic development. Entrepreneurs create businesses or ventures by drawing together, resources and manpower in order to run the business. Research on the factors influencing entrepreneurial passion has a long historical background and extends to the fields of economics, sociology and psychology. Macro-level environmental conditions are the characteristics of entrepreneurial opportunities and the entrepreneurs’ behaviour which is related to entrepreneurial motives. The small and medium enterprises performance management process in Thailand consists of six processes such as preparation, planning, implementation, evaluation, revision and application. Small and medium enterprises performance management process in Thailand has a unique process which requires specific capital, personal and organizational management structure then Thailand SMEs require a determination direction and operation for high efficiency within industry to achieve a sustainable competition (Na-Nan, 2016).
Entrepreneurial passion involves extreme feelings and strong identification with entrepreneurial jobs and processes such as, how to influence opportunity or opportunity recognition. Passion is a critical factor in many cognitive and motivational elements of the entrepreneurial process such as entrepreneur’s effort (Gaglio & Katz, 2001). The entrepreneur needs to have an enthusiasm for development and competition, especially as the enthusiasm is related to entrepreneurial activity engagement. Enthusiasm provides the entrepreneur with workrelated self-efficacy and is positively related to work engagement of the entrepreneur.
The office of Small and Medium Enterprise Promotion of Thailand reported in 2016, that Thailand’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increased by 3.2% for small and medium enterprise when compared to 2015. It refers to the importance of small and medium enterprise for the Thai economy (Office of Small and Medium Enterprises Promotion, 2011). Government is a key player in disaster recovery process in any given affected economy. Government policies have an influence on any sectors of economy such as financial, social and managerial sectors. The interdepartment miscommunication, valuable resources mismanagement and lack of transportation facilities reduce the efficiency of management (Subthum & Ahmad, 2018).
Many entrepreneurial academics highlight the importance of passion and enthusiasm for entrepreneurs, due to the fact that passion and enthusiasm are the main factors of entrepreneurial efforts with reference to business goal commitment. We are also of the opinion that passion and enthusiasm are important, however, there is a limited knowledge in relation to existing literatures on passion and enthusiasm for entrepreneurial activities. Currently, the internet has an influence on business conducting which makes market and business reformed. Many business organizations attempt to get competitive advantages by selling and marketing through social media platforms (Clercq et al., 2013; Dolsopol, 2014).
Although, passion and enthusiasm are relevant to entrepreneurship literature, a deeper and more detailed explanation is still required. For instance, what is the influence of passion and enthusiasm on entrepreneurship? It is more important for us to cultivate passion and enthusiasm for entrepreneurship as passion and enthusiasm play a major role in the entrepreneurship development process. Globalization provides many changes for business operations which creates business opportunities for small and medium enterprises. It is a huge opportunity for SMEs which have a support for economic development. One of the biggest challenges for SMEs is social commerce; however more opportunities are generated from population structure and new innovation changes. Business environment changed has direct effect on SMEs future business performance and model (Vongsruluang & Bhatiasevi, 2016).
The research on entrepreneurial passion and enthusiasm is very important for better understanding of entrepreneurship and the development of entrepreneurs. These are among the questions that will contribute to the entrepreneurial academic knowledge and managerial practice throughout this research. This research provides the entrepreneurial academic knowledge on entrepreneurship in the province which is considered the backbone of Thailand’s economic development.
Literature Review Commitment to the Product or Service
Entrepreneurial success depends on entrepreneurial performance which is determined by efficiency and company growth; and it is a vital issue in entrepreneurship because it separates an entrepreneurial venture from others (Tasnium & Singh, 2016). Entrepreneurial commitment refers to behavioural concepts such as endurance, perseverance and passion and selfdetermination. These behavioural concepts have positive impact on start-up and venture performance (Suliman & IIes, 2000). In order to become highly successful in business, entrepreneurs need to have a high passion and commitment. Commitment is the weapon that encourages the entrepreneurial mind set and directs the entrepreneur to maintain his entrepreneurship and to take the right and important steps to success (Kor, 2001; Nordstrom, et al., 2016). The study of three dimensions of leadership, workplace value ethic and workplace innovation among Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Thailand and Vietnam find that workplace value ethic has high influence on leadership behaviour and design leadership also has a significant effect on workplace innovation. The workplace value ethic and workplace innovation has direct relationship which creates high competitive advantage (Muenjohn & McMurray, 2017).
Enthusiasm for Competition
Excitement and enthusiasm are very important for small business operators. Small business operators without excitement and enthusiasm may not be successful. Entrepreneurs need to create a business plan to gain further perspectives and, must understand their product, market and competition (Savita, 2015). To be excited about the work, entrepreneurs must be passionate from within. One way to develop enthusiasm is to find something connected with your passion and could give you excitement. Real enthusiasm will be engendered and great achievements come from enthusiastic their work (Pell, 1994; Warnick, 2016). The high competitive market makes small and medium enterprises management changes dramatically in Thailand. The entrepreneurship, corporate brand management and competitive environment has direct influence on corporate performance of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). Competitive environment, entrepreneurship and corporate brand management under Thai society and culture of SMEs have a specific characteristics for corporate performance management (Kamkankaew et al., 2017). Passion for entrepreneurship Passion for entrepreneurship is an intense felling and it refers to entrepreneurial activities and processes such as opportunity recognition and venture creation (Nordstrom et al., 2016). Passion is strong at the initial stage of the venture and it might decrease at the actual stage of doing the business. Entrepreneurial intensity has five dimensions such as autonomy focus, innovation orientation, proactive capability, risk-taking competency, and competitive aggressiveness mind set. The entrepreneurial intensity and firm performance of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) has a relationship through customer response efficiency, market reaction competency, competitor learning effectiveness and business advantage for Thai small and medium enterprises (Dolsopol, 2014) Entrepreneurs within the passion domain often create innovation and solve specific problems. Passionate entrepreneurs have high aspirations for business growth and love to work (Warnick, 2016). Entrepreneurial passion plays a critical role for venture success and funding decision. Entrepreneurial passion has a strong positive relationship with entrepreneurial intentions, even when the entrepreneur’s self-efficacy has been introduced as a mediator. The relationship between creativity and entrepreneurial intentions has been mediated by entrepreneurial self-efficacy (Biraglia & Kadile, 2017).
Enthusiasm for Opportunity
Identifying opportunities in the marketplace is necessary for successful entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurs must therefore evaluate the business objectives that exist in the marketplace. Opportunity recognition must be an acceptable entry barrier which is a competitive advantage as well as a profit potential for entrepreneurs (Meenakshi & Harini, 2012). There are three main strategies for large and medium enterprises to maintain profitability. One very innovative strategy is the use of a new product introduction to replace or create new market, which comes from opportunity captured by enterprises (Chitakornkijsil, 2011). The entrepreneurial creativity strategy on marketing performance and product advantage consists of saturated skill accumulation, supplier information sharing and advanced learning capacities has a moderate influence on customer requirements responsiveness. Saturated skill accumulation, supplier information sharing and advanced learning capacities have a positive relationship with product strategy (Seakoo et al., 2013).
The innovativeness of opportunity has a positive effect on business growth; it is related to entrepreneurship enthusiasm for identifying opportunities. High innovative entrepreneurship opportunity comes from uncertainties in the business environment; entrepreneurs must respond to the rapidly changing environment (Long et al., 2016; Chitakornkijsil, 2011). Opportunity identification refers to a unique entrepreneurial behaviour which is dynamic and process driven. Entrepreneurial alertness is a distinctive set of perceptual and informative processing skills that drives opportunity identification. Understanding the opportunity identification process is one of the main intellectual questions for the domain of entrepreneurship (Gaglio & Katz, 2001).
Enthusiasm for Development
Working without limitation, customer preference changes and global processes integrations have changed the traditional business operations of various enterprises. A focus on innovative methods of process development such as improving business operations represent the main competitive advantage for modern entrepreneurship (Lettl & Gemunden, 2005). The accelerations of technology, communication technology and information development are the basis of globalization in any area and aspect of business operations for entrepreneurs. The development of new entrepreneurship in tourism enterprise represents the new forms of business conduct, teamwork encouragement and human resource emphasis. Continued process of human resource development creates the value for competitive advantage of enterprise (Postolov et al., 2016). The creative economy and creative industry refers to emerging models of economic development. The creative economy and creative industry have direct influence on creativity and intellectual capital for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) economic development and creative value chain is play as the most straightforward in creative industry (Bhatiasevi & Dutot, 2014).
Problem Statement
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are considered as the fundamentals of economic development for Thai economy. SMEs have 3 main sectors such as services sector, production sector and trading and maintenance sector. The services sector is an important sector for the Thai economic growth and, it continuously drives the Thai economy. However, there is little or no knowledge of the entrepreneurship passion and enthusiasm of Thai SMEs. The big question is; why would an entrepreneur need passion or enthusiasm and how does it influence entrepreneurial success. It is very important to study entrepreneurial passion and enthusiasm under the Thai SMEs circumstance.
Research Objectives
1. To study the entrepreneurial passion and enthusiasm factors of small and medium enterprises of Lower Northeastern, Thailand.
2. To study on the relationship between entrepreneurial passion and enthusiasm with respect to persistence of business.
Research Methodology
This is an exploratory research which focuses on new factors with effect on enthusiasm for entrepreneurship and persistence of business in Thai’ s small and medium enterprises. The research also explores the degree of impact that each factor has on enthusiasm for entrepreneurship and persistence of business. This research adopted a quantitative approach, by using questionnaires. Qualitative contextual tools were also used as first parameter identification. A secondary data was drawn from the review of various existing literatures as well as from the confirmation of research finding.
The research process was started with a review of existing literature. Based on this literature review, a parameter termed ‘measurements of procurement skills related issues’ was created, which was used to consult with supervisors and experts, before conducting the pilot surveys with the entrepreneurs. The measurements were certainly applied to the final results of the survey. The survey results were analysed using a mean and SD. The correlation testing was done on persistence of business and enthusiasm for entrepreneurship parameters. The conclusions were drawn from the study’s findings.
This exploratory research was focused on 335 small and medium enterprises entrepreneurs who are in the service, production and trading businesses, using the questionnaires developed specifically for the sole purpose of this research. After the data were analysed, the observations of their behaviours were done to confirm the results finding.
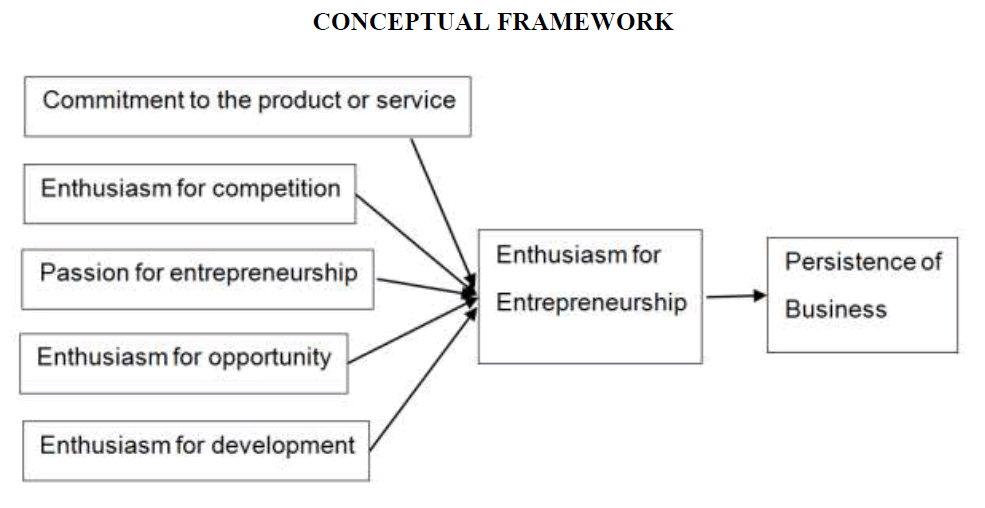
Conceptual Framework
A conceptual framework for studying entrepreneurial enthusiasm and persistence of business was developed according with the update with literature review and with several studies in above (Figure 1). The main constructs leading to enthusiasm for entrepreneurship and persistence of business involve five variables: commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship, enthusiasm for opportunity and enthusiasm for development (Ho & Pollack, 2014; Gaglio & Katz, 2001; Warnick, 2016).
To examine the effects of enthusiasm for entrepreneurship variables and persistence of business, the following hypotheses are proposed:
1. H1: Commitment to the product or service is positively related to the persistence of Business.
2. H2: Enthusiasm for competition is positively related to the persistence of business.
3. H3: Passion for entrepreneurship is positively related to the persistence of business.
4. H4: Enthusiasm for opportunity is positively related to the persistence of business.
5. H5: Enthusiasm for development is positively related to the persistence of business.
Results
Table 1 shows the mean and S.D results for these variables: Commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship, enthusiasm for opportunity and enthusiasm for development. The results found that the entrepreneurs’ responses were in the agreed level in which the mean=3.56 and S.D=1.15. The mean value of Commitment to the product or service is 3.47 and S.D=1.21. Based on customer values, sales people and entrepreneurial behaviours such as innovativeness, pro- activeness and risk taking have a positive relationship with customers’ trust in the product and, satisfaction come from sales people who have a product commitment (Douglas et al., 2016; Biraglia & Kadile, 2017). The mean value of Enthusiasm for competition is 3. 46 and S. D=1.15. Entrepreneurship within the firm is the best and most cost effectiveness way to increase the competition in global marketplace. Firms have more entrepreneurial employees who will be given the right support and provided the enthusiasm for their works (Pryor & Shays, 1993). The mean value of Passion for entrepreneurship is 3.67 and S.D=1.11. Passion for work is an emotional aspect of people’s approach to work and is also related to the cognition of the people who are passionate about their work and tend to engage more intensive knowledge processing when it is required (Clercq et al., 2013). Lately, the increasing attention of researchers has become more concentrated on the role of passion in the entrepreneurial process, which is a means of exploiting profitable chance and shaping entrepreneurial objectives and real performance. Passion, for the entrepreneur, is greater persistence, effort, enthusiasm and overall achievement (Ho & Pollack, 2014). The mean value of Enthusiasm for opportunity is 54 and S.D=1.10. Theoretically, enthusiasm, commitment and preparedness are all a demonstration of passion. Enthusiasm, commitment and preparedness relate to an entrepreneurs’ motivation for work engagement. It has a considerable influence on entrepreneurial success (Cardon et al., 2017; Clercq et al., 2013). The mean value of Enthusiasm for development is 3.66 and S.D=1.19. The successful entrepreneurs have an experience structure which is formed by the various experiences gained over time. We should develop talented entrepreneurs with a sense of enthusiasm which will then lead to success (Oh, 2018; Gaglio & Katz, 2001).
| Table 1: Enthusiasm For Entrepreneurship Parameters |
||
| Factors | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Commitment to the product or service | ||
| 1. In the last 2- 3 years, you have the new product or service Development. |
3.14 | 1.22 |
| 2. You are interesting on product or service differentiation. | 3.63 | 1.14 |
| 3. Product or service development takes into account the need of the customer. |
4.24 | 0.98 |
| 4. Social media for communication with customer. | 2.89 | 1.52 |
| Average | 3.47 | 1.21 |
| Enthusiasm for competition | ||
| 1. Price discount strategy for sales improvement. | 3.25 | 1.24 |
| 2. Competitive advantage by focus on niche segments. | 3.22 | 1.14 |
| 3. You are continuing to develop new products or services. | 3.52 | 1.06 |
| 4. You are focusing on sales targets. | 3.87 | 1.16 |
| Average | 3.46 | 1.15 |
| Passion for entrepreneurship | ||
| 1. You like the challenge of running a business. | 3.71 | 1.17 |
| 2. You are a people like to meet people. | 4.04 | 0.99 |
| 3. Your business goal is a victory. | 3.21 | 1.17 |
| 4. You are brave and do not fell tried. | 3.72 | 1.12 |
| Average | 3.67 | 1.11 |
| Enthusiasm for opportunity | ||
| 1. You always find information on the business. | 3.94 | 1.01 |
| 2. You are the leader in product or service change. | 3.25 | 1.16 |
| 3. You always change your product or service offering methods. | 3.59 | 1.09 |
| 4. You always have a market analysing. | 3.41 | 1.15 |
| Average | 3.54 | 1.10 |
| Enthusiasm for development | ||
| 1. You allocate the budget for new product or service Development. |
3.43 | 1.25 |
| 2. You offer products or services to customer needs. | 3.94 | 1.00 |
| 3. You employ an enthusiastic staff. | 3.42 | 1.49 |
| 4. You offer better quality products or services than Competitors. |
3.85 | 1.04 |
| Average | 3.66 | 1.19 |
| All parameter average | 3.56 | 1.15 |
| Note: *Number of respondents=335. | ||
The assessment of convergent and discriminate validity has focused on Pearson productmoment correlation coefficient. Results show that all observed variables have high loading on their related factors and low crossing loadings. They relate highly to each other and less highly to measures of other constructs. The loadings were significant at 0.01% level. This indicated good convergent and discriminant varidities (Hair, 1998). From Table 2, the correlation between Persistence of Business and Enthusiasm for Entrepreneurship Parameters.
| Table 2: Pearson Correlation Between Persistence Of Business And Enthusiasm For Entrepreneurship Parameters | |||||
| (Pearson Correlation) | Commitment to the product or service |
Enthusiasm for competition | Passion for entrepreneurship | Enthusiasm for opportunity | Enthusiasm for development |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persistence of Business Pearson Correlation Sig. (2- tailed) N |
-0.285** 0.000 335 |
-0.195** 0.000 335 |
-0.145** 0.008 335 |
-0.141** 0.010 335 |
-0.141** 0.010 335 |
| Note: **Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). | |||||
H1: Commitment to the product or service is positively related to the persistence of business. The result shows that persistence of business and commitment to the product or service r=-0.285** and Sig. (2- tailed (=0.000 due to Sig. (2-tailed))) less than 0.05 then commitment to product or service has a significant level of persistence of business elements.
H2: Enthusiasm for competition is positively related to the persistence of business persistence of business and enthusiasm for competition r=-0.195** and Sig. (2-tailed (=0.000 due to Sig. (2-tailed))) less than 0.05, then enthusiasm for competition has a significant level of persistence of business elements.
H3: Passion for entrepreneurship is positively related to the persistence of business Persistence of business and passion for entrepreneurship r=-0.145** and Sig. (2- tailed (=0. 008 due to Sig. (2- tailed))) less than 0. 05 then passion for entrepreneurship has a significant level of persistence of business elements.
H4: Enthusiasm for opportunity is positively related to the persistence of business persistence of business and enthusiasm for opportunity r=-0.141** and Sig. (2-tailed (=0.010 due to Sig. (2-tailed))) less than 0. 05 then enthusiasm for opportunity has a significant level of persistence of business elements.
H5: Enthusiasm for development is positively related to the persistence of business Enthusiasm for development r=-0.141** and Sig. (2-tailed (=0.010 due to Sig. (2-tailed))) less than 0. 05, then enthusiasm for development has a significant level of persistence of business elements.
Discussion and Conclusions
The study of entrepreneurial passion domains of small and medium enterprises, and their notion on enthusiasm for entrepreneurship and persistence of business. The factors responsible for enthusiasm for entrepreneurship are commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship, enthusiasm for opportunity and enthusiasm for development.
Commitment to product or service refers to the intention of entrepreneurs for their products or service development in the last 2-3 years. Product or service differentiation plays an important role in providing competitive advantage as it will give the product differentiation from competitor (Suliman & IIes, 2000). Now, social media is a common way for customer engagement then product or service communication throughout social media is necessary (Dolsopol, 2014).
Enthusiasm for competition is one of key success factor that gives the entrepreneur more advantage. An entrepreneur who has enthusiasm for competition will focus on niche segments and continuously develop new products or services (Pell, 1994). Sales target is a crucial success factors for entrepreneurship since it refers to revenue achievement. Passion for entrepreneurship has become one of success factor for entrepreneurship because, an entrepreneur is someone who love the challenges of running a business, love to meet people, focuses on business goal and is very brave (Nordstrom et al., 2016). Due to the rapid change in the business environment, an entrepreneur must have a passion for entrepreneurship which is a fundamental aspect of business activities and goal achievement.
Enthusiasm for opportunity is a key success factor in entrepreneurial activities and process. This is especially true as entrepreneurs always find business information that will change business plan accordingly (Chitakornkijsil, 2011). An entrepreneur who has enthusiasm for opportunity is a leader in product or service change with respect to customer needs. Due to the fact that customers’ needs always changes, products or services must changes for customer satisfaction.
Enthusiasm for development refers to the budget allocation for new products and services development, in order to offer better quality products or services than competitors and according to customers’ needs (Lettl & Gemunden, 2005). Furthermore, enthusiasm for development is an enthusiastic staff employment as high potential staff will have high work efficiency.
Commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship and enthusiasm for opportunity, have a significant correlation with persistence of business (Bhatiasevi & Dutot, 2014). The entrepreneur who has an enthusiasm for entrepreneurship keeps a persistence of business.
The relationship between entrepreneurial passion and enthusiasm with respect of persistence of business found that commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship, enthusiasm for opportunity and enthusiasm for development are positively related to the persistence of business.
Directions for Further Investigation
This research finds significant parameters for Thai Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) such as commitment to the product or service, enthusiasm for competition, passion for entrepreneurship, enthusiasm for opportunity and enthusiasm for development factors. The next research or investigation needs to consider the specific parameters such as enthusiasm for competition; it also need to investigate social media communication plan or practice as the internet is becoming an influential tool in customer communication.
References
- Bhatiasevi, V., & Dutot, V. (2014). Creative industries and their role in the creative value chain-a comparative study of SMEs in Cannada and Thailand. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation Management, 18(6), 466-480.
- Biraglia, A., & Kadile, V. (2017). The role of entrepreneurial passion and creativity in developing entrepreneurial intentions: Insights from American home brewers. Journal of Small Business Management, 55(1), 170-188.
- Cardon, M., Mitteness, C., & Sudek, R. (2017). Motivation cues and angel investing: Interactions among enthusiasm, preparedness and commitment. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 41(6), 1057-1086.
- Chitakornkijsil, P. (2011). Perspectives on entrepreneurship opportunities and internationalization. International Journal of Organizational Innovation, 3(3), 184-202.
- Clercq, D., Honig, B., & Bruce, M. (2013). The roles of learning orientation and passion for work in the formation of entreperneurial intention. International Small Business Journal: Researching Entrepreneurship, 31(6), 652-676.
- Dolsopol, K. (2014). Effects of entrepreneurial intensity on firm performance of SMEs in Thailand. International Journal of Business Research, 14(2), 75-90.
- Douglas, A., Shahid, B., & Shows, D. (2016). Customer-salespeople relationship: Influence of sales people entrepreneurial behaviours. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 34(5), 586-604.
- Gaglio, C., & Katz, J. (2001). The psychological basis of opportunity identification: Entrepreneurial alertnes. Small Business Economics, 16(2), 95-111.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., & Black, W. (1998). Multivariate data analysis (5th ed.). New York: Prentice Hall.
- Ho, V., & Pollack, J. (2014). Passion isn't always a good thing: Examining entrepreneur's network centrality and financial performance with a dualistic model of passion. Journal of Management Studies, 51(3), 433-459.
- Kamkankaew, P., Thanitbenjasith, P., & Sribenjachote, S. (2017). How do firm characteristics, entrepreneurship, competitive environment and corporate brand management impact on corporate performance? A case of Thailand SMEs perspective. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 15(26), 267-279.
- Kor, Y. (2001). The entrepreneurial mindset: Strategies for continuously creating opportunity in an age of uncertainty. Academic of Management. The Academic of Management Review, 26(3), 457-459.
- Lettl, C., & Gemunden, H. (2005). The entrepreneurial role of innovative users. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 20(7), 339-346.
- Long, D., Geng, L., & Shakeel, M. (2016). Antecedent factors of business planning in the new venture emergence in China. Chinese Management Studies, 10(3), 510-526.
- Meenakshi, T., & Harini, V. (2012). Entrepreneurship opportunities in managing e-waste. Asia Pacific Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research, 1(3), 47-55.
- Muenjohn, N., & McMurray, A. (2017). Design leadership, work values ethic and workplace innovation: an investigation of SMEs in Thailand and Vietnam. Asia Pacific Business Review, 23(2), 192-204.
- Na-Nan, K. (2016). Perfomance management for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in Thailand. International Journal of Economic Research, 13(4), 1641-1658.
- Nordstrom, C., Charlotta, A., Thorgren, S., & Wincent, J. (2016). Passion in hybrid entrepreneurship: the impact of entrepreneurial teams and tenure. Baltic Journal of Management, 11(2), 167- 186.
- Office of Small and Medium Enterprises Promotion. (2011). Small and medium enterprises' promotion plan (3rd) (2012-2016). Bangkok: Office of Small and Medium Enterprises Promotion.
- Oh, H.J. (2018). A qualitative case study on success of fashion retail start-up by young entreperneurs. Journal of the Korean Society of Clothing and Textiles, 42(1), 133-148.
- Pell, A. (1994). Enthusiasm. Manager's Magazine, 69(2), 30.
- Postolov, K., Sopova, M., Ivanovska, L., Petkova, T., & Josimovski, S. (2016). Modern entreperneurship as a factor for success in the operation of tourism enterprises. CBU International Conference on Innovations in Science and Education (pp.1-5). Prague, Czech Republic: CBUNI.
- Pryor, A., & Shays, M. (1993). Growing the business with intrapreneurs. Business Quaterly.
- Savita, A. (2015). Curbing their enthusiasm: A careful merger of enthusiasm and realism fuels success. Bank Investment Consultant, 23(9).
- Seakoo, A., Pansuppawatt, P., & Jitrawang, P. (2013). Entrepreneurial creativity strategy of SMEs in Thailand. International Journal of Business Research, 13(4), 105-116.
- Subthum, P., & Ahmad, M. (2018). Role of government in flood disaster recovery for SMEs in pathumthani province, Thailand. Natural Hazards, 9(2), 957-966.
- Suliman, A., & IIes, P. (2000). Is continuance commitment beneficial to organizations? Commitment- performance relationship: A new look. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 15(5), 407-426.
- Tasnium, R., & Singh, H. (2016). What, Exactly, is entrepreneurial commitment? Journal of Applied Management and Entrepreneurship, 21(3), 6-35.
- Vongsruluang, N., & Bhatiasevi, V. (2016). The determinants of social commerce system success for SMEs in Thailand. Information Development, 33(1), 80-96.
- Warnick, B. (2016). Passion for product, process, or both? Expanding our conception of passion in entrepreneurship. Indiana: ProQuest.