Research Article: 2020 Vol: 24 Issue: 1
Entrepreneurial Leadership: Midwife Competence and Performance
Endang Suswati, Gajayana University
Abstract
Midwife is not only a health worker who helps deliveries, but also be charged to be able to become an entrepreneur in order to empower the potential capabilities of midwife and others, able to create jobs and reduce unemployment. An entrepreneur must be a leader; a leadership owned by an entrepreneur is called as an entrepreneurial leadership. The purposes of this study are to examine the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on midwife competency, to examine the effect of competency on midwife performance, to examine the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on midwife performance, to examine the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on midwife performance through midwife competency. This research was conducted in Banyuwangi with midwives who have practical businesses privately or independently as respondents. Analytical tools used by path analysis using the AMOS (Analysis of Moment Structure) program in order to test the first, second, third and fourth hypotheses. The results of this study are: First, entrepreneurial leadership has a significant effect on midwife competence; Second, entrepreneurial leadership has a significant effect on midwife performance; Third, midwife competence has a significant effect on performance; and Fourth, entrepreneurial leadership has a significant effect on performance through midwife competence.
Keywords
Entrepreneurial Leadership, Competence, Midwife Performance.
Introduction
Midwife is a woman who has graduated from midwife education that is recognized by the government and professional organizations in the territory of the Republic of Indonesia and has the competencies and qualifications to be registered, certified and or legally licensed to carry out midwifery practices according to the Indonesian Midwives Association. The profession as a midwife is not solely due to the income earned from the work, but because of dedication as a midwife in devoting herself to the community, a noble profession with knowledge that she has is such a her own pride with all its attributes that able to carry out good duties and professionals which able to help others with a full sense of responsibility (Manuaba, 1998; Suswati, 2012).
The Indonesian will advance if many of them become entrepreneurs who have creative and innovative characters, never be give up, dare to take calculated risks and have a leadership spirit (Susanto, 2009). Secretary of the Ministry of Cooperatives and Small and Medium Enterprises (UKM), explains their data that the number of entrepreneur in Indonesia advance sharply from 0.24 percent to 1.56 percent of the population. The Ministry is optimistic that in 2016 entrepreneurship growth to an ideal figure of at least 2 percent can be achieved. The number of Indonesian entrepreneurs is still far below that of neighbouring countries, Singapore by seven percent, Malaysia by five percent, and Thailand by four percent, while developed countries such as the United States and Japan even have entrepreneurs more than 10 percent of the population (Muharram, 2016).
Entrepreneurship is an ability possessed by human resources in order to be able to think creatively and innovative behavioural approaches that are used as the basis, as a driving force, tactics, tips and processes in facing life's challenges (Alma, 2004). Jong & Wennekers (2008) said that the concept of entrepreneurship as a risk taker in running one's own business and taking advantage of opportunities to create new businesses with an innovative approach, so that businesses are able to develop, succeed and be independent in facing the challenges of competition that is full of uncertainty. States a midwife who opens an independent practice is called an entrepreneur. An entrepreneur is a person who has expertise in selling, offering ideas to commodities, which are namely services. Midwives must be able to provide qualified health services and be able to manage service management professionally as midwives who open private or independent practice who must have an entrepreneurial spirit.
Being professional is the main demand to support the midwifery competency improvement process since what the community needs right now is midwife excellent services, whether it is delivery service or other health services (Suyat, 2006). Midwife professionalism is a demand that must be fulfilled. Indonesian midwives certainly must constantly increase their competence so that they are able to adjust themselves according to service standards in the community. Midwife competency that must be possessed is a standard in giving services to the community. However, there are still many problems faced, particularly the quality of midwives in Indonesia nowadays tends to decline compared to years before. The statement of the Minister of Health of Indonesia is based on the results of the Midwife competency test held at the end of 2013, among 3,171 prospective Midwives who took the competency test in East Java, 40% of them were declared not to have passed (Nurjasmi, 2014).
Studied by Suswati (2010; 2015), the result shows that democratic leadership style has the greatest influence on employee performance. Moreover, other empirical study result shows that competence has a positive and significant effect on the performance of midwives. It proves that the higher the competence owned by midwives, the higher their performance. Thus, when it is observed based on the research results conducted by previous researchers, particularly research on entrepreneurial leadership, competency creates great performance.
Midwives must have professional competency, so that they are able to improve performance which is very necessary to face competition as entrepreneurs, particularly facing the Asian Economic Community in 2015. If Indonesian midwives have high and professional performance, the midwives will be able to compete internationally. Based on the background that has been described, the purposes of this study are to examine the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on midwife competencies, to examine the effect of competency on midwife performance, to examine the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on performance, and to examine the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on performance through midwife competencies.
Literature Review
Entrepreneurship Leadership
According to Kuratko & Hodgetts (2004); Thornberry (2006); Renko et al., (2013), entrepreneurship is dynamic prose in creating vision, changes, and creation. Entrepreneurship also requires the application of spirit through the creation and implementation from a new idea as well as the creative solution. In the study by Meyer & Allen (1991) on organizational commitment stated that organizational commitment is a multi-concept. They suggested that organization commitment consists of three components namely: Affective Commitment, Continuance Commitment, and Normative Commitment.
Entrepreneurial leadership helps the organization members to comprehend and understand the mission, vision, purpose of the organization achieved through employees commitment (Cunningham & Lischeron, 1991; Gupta et al., 2004; Renko, et al., 2013). Organizational commitment has been related to performance both theoretically and empirically (Meyer & Allen, 1991; Yiing & Ahmad, 2009). Specifically, Dirani (2009) stated that organizational commitment is a significant factor affecting the output of the employees and it is also an important indicator of performance.
According to Greef de Annique (2014); Yiing & Ahmad (2009), entrepreneur leadership has a direct and positive influence on employee’s commitment. This is in line with the type theory of McGregor (1960) in Greef de Annique (2014) stating that employees who can work in the organization, employees who love their job, those who are creative, motivated, proud on their work results, fully responsible and happy to face challenges.
Standard Performance and Competence of Midwives in Indonesia
According to Bernandin & Russel (1993), performance is something related to the work results achieved by the employees in a certain period of time, in this case, performance is related to the quantity or quality of the work results. Midwife performance, standard performance of midwives in Indonesia has been stipulated through the Minister Health Decree of the Republic of Indonesia Number 900/MENKES/SK/VII/2002 on the Midwife Registration and Practice as well as the description on performance, performance understanding of a midwife is the work results achieved by the midwife in completing her task in relation to the quality of the health service for mother and children consisting of the coverage antenatal care, delivery services, postpartum and neonatal services (after birth).
Hmieleski & Ensley (2007) stated that entrepreneurial leadership behaviour can be achieved through empowerment to achieve performance. Businessmen will not be able to develop his business without showing the effective leadership behaviour (Bryant, 2004; Cogliser & Brigham, 2004). The study by Suswati et al., (2015) showed that entrepreneurial midwives have a positive and significant influence on performance, meaning that the better the entrepreneurial orientation with entrepreneurial spirit, the better the performance, it is also stated that organizational commitment has a positive effect on employee performance, the more committed they are on duty the better the performance (Suswati & Budianto, 2013).
Methodology
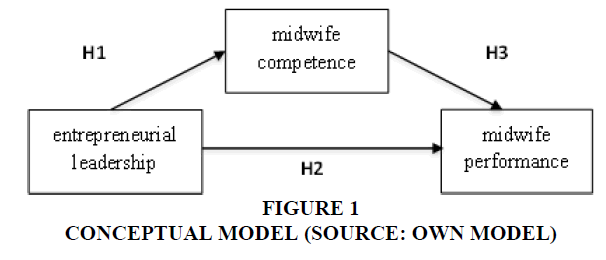
The population of this research is 200 midwives who open independent practices in Banyuwangi, East Java, based on statistical data in 2016, as one of developed districts in health sector. This research is an explanatory research. The sampling method uses random sampling method as primary data. Researcher in determining the sample uses the Slovin formula justification in Umar (2003), with an alpha value (α) of 5%, the number of samples in this study is 133 Midwives. The primary data collection method in this study uses questionnaire. The data analysis method used is path analysis using the AMOS (Analysis of Moment Structure) program in order to test several hypotheses (Figure 1).
Results and Discussion
Entrepreneurial Leadership and Midwife Competence
The estimated result obtains path coefficients (Standardized Regression Weights) of 0.562 for the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on midwife competency. Significant coefficient test obtained a CR critical ratio value of 7.804 with a probability (p) of 0.000. Entrepreneurial leadership has a positive and significant impact on the competency of midwives. The results of this study explain that the better the entrepreneurial leadership possessed by a midwife, the higher the competency possessed. This research produces entrepreneurial leadership as its profession is a future-oriented leader who has a vision, creative thinking and innovative behaviour, as a motivator to motivate subordinates and dare to take risks with full responsibility in order to achieve professional business success (Tables 1 & 2).
| Table 1 Regression Weights | ||||
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | P | |
| Sum_Y1 <--- Sum_X1 | 0.657 | 0.084 | 7.804 | *** |
| Sum_Y2 <--- Sum_X1 | 0.439 | 0.140 | 3.142 | 0.002 |
| Sum_Y2 <--- Sum_Y1 | 1.052 | 0.120 | 8.802 | *** |
| Table 2 Standardized Regression Weights | |
| Estimate | |
| Sum_Y1 <--- Sum_X1 | 0.562 |
| Sum_Y2 <--- Sum_X1 | 0.217 |
| Sum_Y2 <--- Sum_Y1 | 0.609 |
This is supported by the research result of Harris (2000), successful entrepreneurs are entrepreneurs who have competencies, knowledge, individual qualities and skills according to the profession. Leadership and competency of village midwives in carrying out the duties of maternal and child health services, before birth, childbirth services, after birth services affect the performance, which means midwife leadership in carrying out their duties must have competency, with great responsibilities to make them perform well.
Susanto (2009), People who have high quality entrepreneurial leadership are those who are able to convert resources that were initially low in value to high-value resources that have competence through measured risk taking and effective leadership. Entrepreneurial success and failure depends very much on the personal abilities of the entrepreneur (Suryana, 2003). Several studies have shown that companies with an entrepreneurial orientation tend to be more successful (Suci, 2009).
Entrepreneurial leadership makes organizational members understand and comprehend related to the vision, mission, and goals of the organization. Hmieleski & Ensley (2007) explains that entrepreneurial leadership behaviour is able to achieve good performance results by empowering and directing subordinates as employees. Entrepreneurs are not able to be success in developing their businesses without exhibiting effective entrepreneurial leadership behaviours. This is proven by research (Bryant, 2004; Cogliser & Brigham, 2004).
In research related to midwife entrepreneurship, it is explained that midwives always think creatively for new ideas related to midwife practice, as stated that a successful midwife is a midwife who used to think creatively in order to innovate gymnastics for pregnant women, baby photos, massages and baby spas. Midwives are expected to have insight and foresight. Dam et al. (2010) wrote the result of their research that individual entrepreneurial competency is related to entrepreneurial behaviour, particularly is able to adapt and think creatively. This result reinforces the research results that midwives are ready to face challenges, looking the problem as an opportunity, and having perseverance in carrying out the task, and not be easy to give up as an entrepreneurial midwife.
Entrepreneurial Leadership and Midwife Performance
The estimated result obtains path coefficients (Standardized Regression Weights) of 0.217 for the effect of entrepreneurial leadership on midwife performance. Significant coefficient test obtained a CR critical ratio value of 3.142 with a probability (p) of 0.002. That means that entrepreneurial leadership has a positive and significant impact on the performance of midwives. The results of this study indicate that the better the entrepreneurial leadership possessed by a midwife, the higher the performance will be.
Peltier et al. (1999) competencies or abilities that include knowledge, experience, and midwifery care skills affect performance in providing services to patients. Entrepreneurial leadership makes organizational members understand and comprehend related to the vision, mission, and goals of the organization. Hmieleski & Ensley (2007) entrepreneurial leadership behaviour is able to achieve good performance results by empowering and directing subordinates as employees.
Research on the performance of women entrepreneurs is still very few (Brush, 1992; Lerner et al., 1997). So far, studies related to the performance of entrepreneurs have not been distinguished between male and female entrepreneurs. Chaganti & Parasuraman (1994) in Lerner (1997) suggest that women entrepreneurs show a desire to emphasize quality over male entrepreneurs. Shastri & Rao (2014) with an increase in a woman's academic qualifications, social awareness, and the desire to be independent, make women choose to become entrepreneurs.
Midwife Competence and Midwife Performance
The estimated result obtains path coefficients (Standardized Regression Weights) of 0.609 for the effect of competency on the performance of midwives. Significant coefficient test obtained a CR critical ratio value of 8.802 with a probability (p) of 0.000. It means that the midwife's competence has a positive and significant effect on the midwife's performance. The results of this study indicate that the better the competency possessed by a Midwife, the higher the performance will be (Tables 3 & 4).
| Table 3 Standardized Direct Effects | ||
| Sum_X1 | Sum_Y1 | |
| Sum_Y1 | 0.562 | 0.000 |
| Sum_Y2 | 0.217 | 0.609 |
| Table 4 Standardized Indirect Effects | ||
| Sum_x1 | Sum_y1 | |
| Sum_y1 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Sum_y2 | 0.342 | 0.000 |
Fort & Voltero (2004) Research on Factors Affecting the Performance of Maternal Health Care Providers in Armenia, with the aim of explaining the five main factors that affect the performance of midwives and nurses in Armenia, there are: Employee expectations, performance feedback, supporting environment and work equipment, incentives and motivation, as well as skills and knowledge. The result shows that training with the use of clinical equipment, knowledge, skills, and workers motivation have a strong influence on performance.
Competency has a positive and significant influence on the performance of midwives. This explains that the higher the competency possessed by midwives, the higher the performance. Suswati (2015) states that midwives who have good competency will improve performance, this performance are not only personal but also company performance. State that entrepreneurial competency supports company performance and economic development.
Conclusions
Entrepreneurial leadership has a positive and significant effect on competency. This explains that the leadership of midwives who are entrepreneurial proves that the higher entrepreneurial orientation, the more competent midwives. Moreover, midwives entrepreneurship has a positive and significant effect on performance. This shows that the midwife who is entrepreneurial has a proof that the higher the entrepreneurial orientation, the higher the level of performance in carrying out the task will be.
Competency has a positive and significant effect on performance. This explains that the higher the midwife's competency, the higher the performance. Entrepreneurial leadership has a significant effect indirectly on the performance of midwives through midwife competencies. Independent practice midwife programs are being developed continuously (continuous improvement) in order to improve competency. Midwives more use information technology through internet and social media.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank all Midwives who open independent practice in the Banyuwangi Regency of Indonesia for contributing to data collection. Furthermore, the author would like to thank Mrs. U. Werdiningsih SKM MPH as a Chief of the Indonesian Midwife Association (IBI) of Banyuwangi Regency for the research facilities provided as well as guidance for the implementation of the research.
References
- Alma, B. (2004). Entrepreneurship. Bandung, Alfabeta.
- Bernandin, H.J., & Russell, J.E. (1993). Human Resources Management. Singapore, Mc. Grow Hill Inc.
- Bryant, T.A. (2004). Entrepreneurship. In G.R. Goethals, G.J. Sorenson, & J.M. Burns (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Leadership, 1, 442-448.
- Cogliser, C.C., & Brigham, K.H. (2004). The intersection of leadership and entrepreneurship: Mutual lessons to be learned. Leadership Quarterly, 15, 771-799.
- Cunningham, J.B., & Lischeron, J. (1991). Defining entrepreneurship. Journal of Small Business Management, 29(1), 45-62.
- Dam, K.V., Schipper, M., & Runhaar, P. (2010). Developing a competency-based framework for teachers: Entrepreneurial behavior. Teaching and Teacher Education, 24(4), 965-971.
- Dirani, K.M. (2009). Measuring the learning organization culture, organizational commitment and job satisfaction in the Lebanese banking sector. Human Resource Development International, 12(2), 189-208.
- Fort, A.L., & Voltero, L. (2004). Factors affecting the performance of maternal health care providers in armenia. Human Resource for Health.
- Greef, A.D. (2014). Entrepreneurial Leadership and its effect on the social performance of the organisation. Netherlands, university of twente, Faculty of Management and Governance.
- Gupta, V., MacMillan, I.C., & Surie, G. (2004). Entrepreneurial leaderships: Developing and measuring a cross-cultural construct. Journal of Business Venturing, 19, 214-260.
- Hariss, M. (2000). Human Recources Management. USA.
- Hmieleski, K.M., & Ensley M.D. (2007). A contextual examination of new venture performance: entrepreneur leadership behavior, top management team heterogeneity, and environmental dynamism. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 28, 865-889.
- Jong., & Wennekers. (2008). Conceptualizing Entrepreneurial Employee Behavior, SMEs and Entrepreneurship Programme Finance. by the Netherlands Ministry of Economic Affairs.
- Kuratko, D.F., & Hodget. (2004). Entrepreneurship. New York, John Willey & Son.
- Lerner, M., Brush, C., & Hisrich, R. (1997). Israeli women entrepreneurs: An examination of factors affecting performance. Journal of Business Venturing, 12(4), 315-339.
- Manuaba. (1998). Midwifery, Gynecology & Family Planning for Midwife Education. Jakarta, EGC.
- Meyer, J.P., & Allen, M.J. (1991). A three component conseptualizaion of organizational commitmen. Human Resource Management Review, 1(1), 61-89.
- Muharram, A. (2016). The Ministry of Cooperatives is optimistic the number of entrepreneurs will be 2% in 2016. Kantor Berita Politik.
- Nurjasmi, E. (2014). The Quality of Midwives Declines?. Majalah Bidan, X-97, CV Savira Hati.
- Peltie, J.W., Thomas, B., & John A.S. (1999). Obstetrical care and patient loyalty. Marketing Health Services.
- Renko, M., Tarabisby, A.E., Carsrud, A.L., & Brannback, M. (2013). Understanding and measuring entrepreneurial leadership style. Journal of Small Business Management, 53(1), 54-74.
- Shastri, D., & Rao, U.T. (2014). Women Entrepreneur of Gujarat. Procedia Economics & Finance, 11, 745-752.
- Suci, R.P. (2009). The effect of entrepreneurship orientation, environmental dynamics, management capabilities, and business strategy on performance. Sidoarjo, Dian Prima Lestari.
- Suryana. (2003). Entrepreneurship Practical Guidelines, Tips, and the Process to Success. Jakarta, Salemba Empat.
- Susanto, A.B. (2009). Leadership Strategic Management Approach in Entrepreneurship. Jakarta, Erlangga.
- Suswati, E. (2010). Leadership to Improve Employee Performance. Jurnal Ekonomi Arthavidya, Kajian Manajemen dan Keuangan, 11(1), 1-9.
- Suswati, E. (2012). Individual characteristics and organizational characteristics influence on motivation and performance of midwives at the general hospital of the tapal kuda regional government of East Java. Proceeding Call for Paper, Faculty of Economics and Business, Satya Wacana Christian University.
- Suswati, E., & Budianto. (2013). Organizational commitment as one determinant of employee performance. Surakarta, Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
- Suswati, E.D., Winarno., & Idrus, H.M.S. (2015). Entrepreneurship Midwife: Competence and Performance Work Environment as Determinant. Medwell Journals, International Business Management, 9(6), 1331-1338.
- Suyat. (2006). Globalization demands midwives must be qualified.
- Thornberry, N. (2006). Lead like an Entrepreneur: Keeping the Entrepreneurial Spirit Alive within the Corporation. Fairfield, PA, McGraw Hill.
- Umar, H. (2003). Applied Accounting Research Methods. Jakarta, Ghalia Indonesia.
- Yiing, L.H., & Ahmad, K.Z. (2009). The moderating effects of organizational culture on the relationships between leadership behaviour and organizational commitment and between organizational commitment and job satisfaction and performance, leadership and organization development. Journal Emerald, 30(1), 53-86.