Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 6S
Employee Performance and Compensation: Evidence from Indonesia
Gazali, Universitas Madura
Adriani Kusuma, Universitas Madura
Muslimatul Aina, Universitas Madura
Zef Risal, Universitas Madura
Zainurrafiqi, Universitas Madura
Rusdiyanto, Universitas Airlangga and Universitas Madura
Muhammad Miftah Farid, IKIP Widya Darma Surabaya
Siti Mazilatus Sholikha, IKIP Widya Darma Surabaya
Vina Budiarti Mustika Sari, IKIP Widya Darma Surabaya
Sultan Syah, Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Ekonomi Tri Dharma Nusantara
Abstract
The study seeks to examine the impact of salary and work discipline on regional public employees. The study employs quantitative approaches and collects data via questionnaires. The sample of this study consisted of 80 staff of public agency enterprises owned using a Purposive Sampling approach. Multiple linear regression employing statistical programs is utilized in the data analysis technique. The results of this research revealed that salary and work discipline affect on the performance of staff of publicly owned firms belonging to the area. Meanwhile, parallel test findings were obtained indicating salary and cooperation discipline affect the performance of staff in regional public held firms. The discipline of work is the variable whose impact is most dominant. Results of this research indicate that remuneration and discipline are believed to boost employee performance in order to achieve better the objectives of the firm. Previous research has examined the effect of compensation and discipline on employee performance, as well as the effect of compensation and discipline on employee performance in manufacturing companies in Indonesia, with the conclusion that compensation and work discipline have an effect on company performance. This scientist took over the research item at the corporation's Regional Public Agency.
Keywords
Employee Performance, Discipline, Compensation
JEL Classification Code
F65, Q34, L25, G20, O15
Introduction
Human resources are the one resources with a sense of feeling, skill, desire, encouragement, knowledge, power and work (Ahn & Huang, 2020; Bushkova-Shiklina & Musikhina, 2020; Gulzar, 2020; Afanasyev, 2020; Bodrova, 2020; Markhgeym, 2020). All potential human resources impact the organization's efforts in achieving goals. Regardless of technological advances, the development of information, the provision of capital and adequate materials are difficult for the organization to achieve its objectives without human resources. Human beings are the main investment in every organization; therefore, it must be managed accordingly (Bush, 2020; Chambers, 2020; Habig, 2020; Jackson, 2020; Markard & Rosenbloom, 2020; Wanka, 2020).
Compensation is a major reason for employees to work and motivate them. Staff do not only dedicate themselves to the organisation, but also to dedicate their skills, knowledge, energy, time and commitment, but there is another goal that it wants to achieve, namely to expect rewards or performance rewards and productivity of the work that is earned (Almutairi, 2015; Alomran, 2019; Cerka et al., 2015; Loginov et al., 2017). When compensation is not in accordance with the expectations of employees, then what happens is a subtle rejection until the rejection is loudly through demonstrations.
Work discipline could be considered as a big advantage, to the company as well as to employees (Durrant, 1991). Discipline is essential for organizational growth, primarily to educate employees to comply with and enjoy existing regulations, procedures, and policies, to produce a good performance. Good discipline reflects a person's great sense of responsibility for his or her tasks. This encourages the passion of work, the spirit of work, and the realization of the company's objectives (Cortés & Cruz, 2011; Green, 1973; Miller & Cripps, 2005). Therefore, every manager always strives for his subordinates to have good discipline. Disciplined and orderly employees comply with all the company standards and rules to enhance productivity.
Literarure Review and Hypothesis Development
Compensation
Compensation means all revenues in money, indirect or direct goods that employees receive in exchange for the company's services (Mezzapesa et al., 2020; Park, 2020; Vibhakar, 2020; Zhao, 2020; Zhou, 2020; Gao, 2020). Compensation is the cost of the company. The Company expects that the compensation paid is in exchange for greater employment achievement from employees. Compensation is something employees receive in lieu of their service contributions to the organization. They distinguish compensation from wages that are fair and worthy of being given to workers for their services in achieving the company's goals (Almohaimeed & Abdel-Akher, 2020; Basha, 2020; Civelli, 2020; Mou, 2020; Rodin, 2020; Xiang, 2020).
Discipline
Good discipline reflects a person's great sense of responsibility for the duties given to him (Cortés & Cruz, 2011; Green, 1973; Miller & Cripps, 2005). The organization has difficulty achieving ideal performance without a good employee discipline. Discipline is the sixth operative function of Human Resource Management (Abdalla et al., 2015; Hausdörfer et al., 2018; Kraus et al., 2018). Discipline is the main operational function of managment of human resources, as the better the employee discipline and the better the job performance. It is difficult for the company to achieve optimum results without good employee discipline (Han, 2020; Listiani, 2020; Nechanska, 2020; Puranik, 2020; Schleu & Hüffmeier, 2020; Soetjipto, 2020).
Performance
All human resources, managers as well as employees, perform in an organization. Many factors affect the performance of human resources. Certain factors come from both within and outside the human resources. Each employee is capable of referring to knowledge, job satisfaction, motivation and skills. Workers also have characteristics, attitudes and conduct that can impact their work. (Al Hosani, 2020; Arubayi, 2020; Iqbal, 2020; Soumyaja & Sowmya, 2020; Upadhyay, 2020; Wibowo & Mochklas, 2020). Performance is the execution of the plan prepared. Performance is implemented by staff who have skills, skills, motivations and interests. How organizations value and treat their staff will affect their attitudes and conduct (Iqbal et al., 2020; Marín & Del Carmen, 2020; Mishra et al., 2020; Pudjiarti & Darmanto, 2020; Suryakumar et al., 2019; Tavares et al., 2020).
The Relationship between Compensation to Employee Performance
The company can provide compensation as expected, then the compensation will help the company to achieve its goals and take good care of employees (Abugre & Nasere, 2020; Chakrabarty, 2020; Idris et al., 2020; Kim, 2020; Lenda, 2020; Lill, 2020). Conversely, when compensation is not in accordance with the expectations of employees, then what happens is a subtle rejection until a violent rejection through demonstrations. Because compensation is one of the main reasons and motivations why employees work (Aboramadan, 2020; Aburumman, 2020; Bao, 2020; Cappelli, 2020; Chitra Rekha, 2020; Haleema, 2020). Employees work not only to dedicate or devote themselves to the organization, but there is another goal that he wants to achieve, namely to expect rewards or performance rewards and productivity of the work he earns. Compensation is a reward or reward given by the organization to the workforce, because the workforce has contributed energy and thought for the progress of the organization in order to achieve the goals that have been set (Ahmad et al., 2019; Ahmad et al., 2019; Campbell & Im, 2019; Hooi, 2020; Khandakar & Pangil, 2019; Mohd Nasurdin et al., 2020).
The Relation between Work Discipline & Performance of Employees
Discipline is the willing and willing attitude of a person to follow and respect the rules that apply in his or her environment. Work discipline could be considered as something of considerable advantage for both the organization and its personnel (Laksana, 2020; Mariappanadar, 2020; Mowbray, 2020; Müceldili, 2020; Sinambela, 2020; Tentama, 2020). Discipline is essential for organizational growth, used primarily to educate employees to comply with and enjoy existing regulations, procedures, and policies, so as to produce good performance. Therefore, every manager always strives for his subordinates to have good discipline (Krishnakumar et al., 2019; Lyons & Bandura, 2016; Mercado et al., 2017; Park et al., 2018; Razzaq et al., 2019; Shan et al., 2017; Sugiono & Vitaloka, 2019).
Conceptual Framework
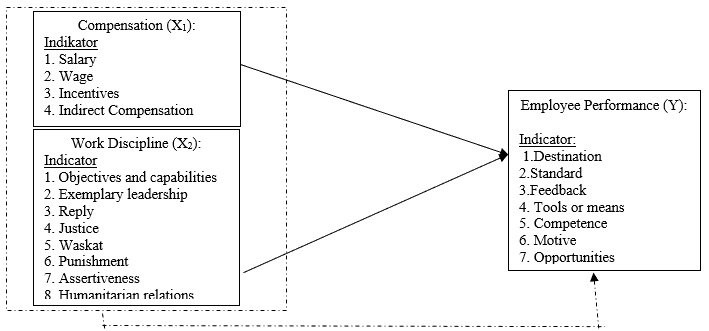
The Conceptual Framework theoretically explains the linkages between the variables studied, so the theoretical explanation must be given to the relation between dependent and independent variables. Compensation and adequate work discipline may influence the performance of publicly held enterprises in the region. In an organization compensation and discipline of work is certainly necessary to improve employee performance. The relationship between dependent and independent variables in this study on the impact of compensation and work discipline on the employee performance of regional public bodies can be conceptually seen in the figure 1 below
Hypothesis
Hypothesis constitutes a temporary response to research problems in which research problems are formulated in the form of question phrases. While responses are based only on relevant theories, it is stated that it was not based on empirical data collected. Using the above conceptual framework, the study hypothesis is as follows:
H1: It is alleged that compensation (X1) partially affects employee performance (Y)
H2: It is alleged that work discipline (X2) partially affects employee performance (Y)
H3: It is alleged that compensation (X1) and work discipline variables (X2) simultaneously affect employee performance (Y)
Research Methods
Types and Approaches to Research
This research uses quantitative research method because the data will be taken in the form of numbers and processed using statistics, (Abadi et al., 2021; Aliyyah et al., 2021; Endarto, Taufiqurrahman et al., 2021; Endarto et al., 2021; Indrawati et al., 2021; Juanamasta et al., 2019; Kalbuana et al., 2021; Kalbuana et al., 2021; Luwihono et al., 2021; Prabowo et al., 2020; Prasetyo et al., 2021; Prasetyo et al., 2021; Prasetyo et al., 2021a, 2021b; Rusdiyanto et al., 2020; Rusdiyanto et al., 2020; Rusdiyanto et al., 2021; Rusdiyanto et al., 2020; Shabbir et al., 2021; Susanto et al., 2021; Utari et al., 2021; Nabilah Aliyyah et al., 2021; Bahtiar Prabowo et al., 2021; Prasetio et al., 2021; Prasetyo et al., 2021). Quantitative methods could be considered methods of research based on a positivist philosophy, data collection using research tools, quantitative data analysis to test established hypotheses for research in a specific population or sample.
Variable Operational Definitions
Independent Variables (Y)
A variable that freely affects or causes modifications or the start of dependent variables is a variable. Bound variables are variables which, due to the presence of free variables, are influenced or result.
a Employee Performance (Y)
Performance is the execution of the plan prepared. Performance is implemented by staff who have skills, skills, motivations and interests. How organizations value and treat their staff will affect their attitudes and conduct ( Khaled et al., 2020; K & Ranjit, 2020; Elangovan & Rajendran, 2020; Sangeetha, 2020; Wolff, 2020).
Dependent Variables (X)
Bound variables are variables which, due to the presence of free variables, are influenced or result.
a)Compensation (X1)
Compensation means all revenues in money, indirect or direct goods that employees receive in exchange for the company's services (Duan et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2020; Hernandez-Martin et al., 2020; Kataoka et al., 2020; Li et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020).
a)Work Discipline (X2)
Discipline is Human Resource Management's sixth operational function. Discipline is a human resources management operational function. Most importantly, because the better employees' discipline, the better they can achieve their work. The company's organization cannot achieve optimal results without good employee discipline (Kluger & Bartzke, 2020; Leonida, 2020; Martino, 2020; Soleymanjahan, 2020; Urdan & Luoma, 2020; Farley-Ripple, 2020).
Population and Techniques Sampling
The population in this study is employees of locally owned public agency companies numbering 100 people. The size of the samples in this study used the Slovin formula, as follows:
Slovin formula: n=
So: n== = =n=80
Based on the results of the calculation of the formula Slovin, it is known the number of samples used in this study as many as 80 public agency employees in the region.
Research and Discussion Results
Research Results
Respondents in this research as many as 80 people, namely selecting samples from all operational employees. The number of samples obtained is based on the Slovin formula. Population data is obtained from employees of regional public agency companies numbered 1 to 80 people. Descriptive analysis of respondents in this study will descriptive data on respondent characteristics based on age, gender, length of work, and education. Disclosure of descriptive analysis of respondents in the form of percentage data.
Age
The following table shows the characteristics of age-based respondents:
| Table 1 Respondent Characteristics Based On Age |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Age | Amount | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | 17-25 | 26 | 32.7 % |
| 2 | 26-45 | 36 | 45.5% |
| 3 | 46-65 | 18 | 22.8% |
| TOTAL | 80 | 100% | |
The table 1 above shows that respondents aged 17-25 years as many as 26 people or 32.7% of respondents, then respondents between the ages of 26 and 45 years, namely 36 persons or 45.5% of respondents and respondents aged 46-65 as many as 18 people or 22.8% of respondents. It identifies that the majority of workers in publicly owned corporate entities.
Gender
The following table shows the characteristics of gender-based respondents
| Table 2 Respondent Characteristics Based on Gender |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Gender | Amount | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Male | 56 | 70% |
| 2 | Female | 24 | 30% |
| Total | 80 | 100% | |
The table 2 above shows that the majority of respondents are male, namely 56 people or 70% of respondents and female respondents as many as 24 people or 30% of respondents.
Working Period
The following table 3 shows the respondents' characteristics based on their working period
| Table 3 Characteristics of Respondents Based on Working Period |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Working period | Amount | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | 1-5 Year | 63 | 78.9% |
| 2 | 6-10 Year | 17 | 21.4% |
| TOTAL | 80 | 100% | |
The table 3 above shows the length of work of respondents in regional public agency companies, most of which have worked for 1-5 years as many as 63 people or 78.9% of respondents and who have long worked for 6-10 years as many as 17 people or 21.4% of people.
Education
The following table 4 shows the characteristics of respondents based on their education:
| Table 4 Respondent Characteristics Based on Education |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Education | Amount | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | SD-SMP | 30 | 37.6% |
| 2 | SMK/SMU | 50 | 62.7% |
| TOTAL | 80 | 100% | |
According to the table above, of the 80 respondents, most of them are educated smk / equivalent, namely as many as 50 people or 62.7% of respondents and respondents who are educated elementary-junior high school as many as 30 people or 37.6% of respondents.
Descriptive Statistics
| Table 5 Descriptive Statistical Test Results |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| Compensation | 80 | 14 | 25 | 20.42 | 2.560 |
| Work Discipline | 80 | 26 | 40 | 35.08 | 3.314 |
| Employee Performance | 80 | 21 | 35 | 29.60 | 2.954 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 80 | ||||
Based on the table 5 above, there are three research variables (Compensation, Discipline and Employee Performance) with a sample of 80 samples. With the lowest value and the highest value in the study. The lowest value. In the table can also be seen mean, in addition can also be seen the standard deviation of values from the data of each variable.
Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
| Table 6 Test Results for Multiple Linear Regression Analysis |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | |||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 13.554 | 3.521 | 3.849 | .000** | ||||
| TOTAL_X1 | 0.231 | 0.122 | 0.2 | 1.893 | 0.062 | ||||
| TOTAL_X2 | 0.323 | 0.094 | 0.362 | 3.431 | .001** | ||||
| a. Dependent Variable: TOTALLY | |||||||||
From the table 6 above, multiple linear regression equations can be created as follows:
Y=a+β1 X1+ β2 X2, Y=13.554+0,231 X1+0,323 X2
a)Constants of 13,554, can be interpreted if the compensation variable (X1), work discipline (X2) is zero then the employee performance value is 13,554 assuming other variables that can affect the performance of employees are considered fixed.
b)The value of the regression coefficient of compensation variables, if compensation increases by 1 unit, then the performance of employees will increase by 0.231, assuming a fixed value.
c)The coefficient of regression of work discipline variables, If the discipline of work increases by 1 unit, then the performance of employees will increase by 0.323, assuming a fixed value.
Hypothesis Testing
T Test (Partial Test)
| Table 7 Test Result T (Partial Test) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | T | Sig. | |||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 13.554 | 3.521 | 3.849 | 0.000 | ||||
| TOTAL_X1 | 0.231 | 0.122 | 0.200 | 1.893 | 0.062 | ||||
| TOTAL_X2 | 0.323 | 0.094 | 0.362 | 3.431 | 0.001 | ||||
| Dependent Variable: TOTALLY | |||||||||
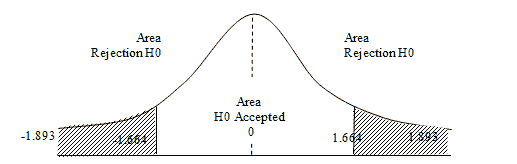
In this study the test rule: If tcount>ttable then significant, known number of n is 80 people and k (variable) is 2, then the amount is 77 (df= n-k-1) with a significance level of α=0.01 or α=0.05. Based on the calculation obtained tcount of 1,893 greater than ttable of 1,664. And obtained the value t significance=0.62 greater than α=0.05. Because tcount (1,893)>ttable (1,664) the compensation variable (X1) affects employee performance (Y). These results prove that H0 was rejected and H1 was accepted. It can therefore be concluded that compensation effects but the performance of regional publicly held companies’ employees is not significant.
The Effect of Compensation on Employee Performance
H0: ß1=0; Means there is no significant impact between compensation variables on partial employee performance variables.
H1: ß1 ≠ 0; Means there is a significant influence between compensation variables on partial employee performance variables.
The results obtained from the comparison of sig values with the level of significance α=0.01 or α=0.05. So it can be concluded that H1 is received and H0 is rejected, meaning that the regression coefficient on the compensation variable partially affects the performance of employees of regionally owned public bodies.
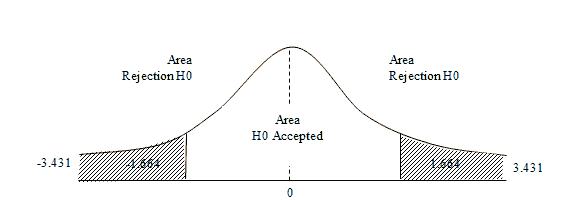
In this study the test rule: If tcount>of ttable then significant, known number of n is 80 people and k (variable) is 2, then the amount is 77 with a significance level of α=0.01 or α=0.05. Based on the calculation obtained tcount of 3,431 greater than the ttable of 1,664. And the value t significance=0.001 is less than α=0.05. Because tcount (3,.431)>ttable (1,664) so that the variable discipline of work (X2) has a significant effect on employee performance (Y). These results show that H0 has been rejected and H1 has been accepted. Therefore, the discipline and performance of the employees of public enterprises in the region can be inferred and made relevant (Figure 3).
The Effect of Work Discipline on Employee Performance
H0: ß1=0; Means there is no significant impact between work discipline variables on partial employee performance variables.
H1: ß1 ≠ 0; Means there is a considerable impact on partial employee performance factors between work discipline variables.
From the results obtained from the comparison of sig values with the level of significance α=0.01 or α=0.05. So it can be concluded that H1 is accepted and H0 is rejected, meaning that the regression coefficient on work discipline variables partially affects the performance of employees of regional publicly owned companies.
F Test
| Table 8 Test Result F (Simultaneous Test) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F | Sig | |
| 1 | Regression | 147.276 | 2 | 73.638 | 10.463 | .000b |
| Residual | 541.924 | 77 | 7.038 | |||
| Total | 689.2 | 79 | ||||
| a. Dep. Variable: TOTALLY | ||||||
| b. Predictors: (Constant), TOTALLY X2, TOTALLY X1 | ||||||
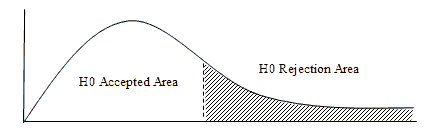
Based on the result of table 8, shows the value of Fcount is 10.463 and the Sig value in the table is 0.000. The value of Fcount we compare with Ftable, how to calculate Ftable=F (k: n-k) F (2:78)=3.11, and the level of significance α=0.01 or α=0.00. It appears that the value of Fcount is greater than Ftable, then H0 is rejected and H1 is accepted, this means that compensation and discipline of work jointly affect the performance of employees of regional public bodies (Figure 4).
H0 : ß 1,2 =0 ; Means there is no effect between compensation and discipline on employee performance.
H1 : ß 1,2 ≠ 0 ; Means there is an influence between compensation and discipline on employee performance.
Conclusions can be obtained from the comparison of sig values with a significant α=0.01 or α=0.00. It can then be concluded that H1 is accepted and H0 is rejected. This means that both independent variables, kompensai (X1), and Work Discipline (X2) simultaneously affect employee performance dependent variables (Y). The results of the investigation showed that compensation and discipline of the labor market had an undesirable impact on the performance of employees of public enterprises in the region.
Analysis of Coefficients of Determination (R2)
| Table 9 Test Results Analysis of Coefficients of Determination (R2) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate |
| 1 | 0.462a | 0.214 | 0.193 | 2.653 |
| a. Predictors: (Constant), X2, X1 | ||||
The determination coefficient is from zero (0) to one (1). A small R2 value suggests that the ability to explain dependent variables is relatively limited. An approaching value (1) suggests that independent factors supply almost all information needed to predict dependent variables. The R Square value obtained is 0.214 or 21.4%. The figure means that Employee Performance is affected by compensation and discipline of 21.4%. While 78.6% was influenced by other factors studied in this study.
Discussion
This study discussed the influence of compensation and work discipline affecting the performance of employees in publicly held enterprises.
The Effect of Compensation on Employee Performance
In this study, t-test has a test rule: If tcount>of the ttable then significant, known number of n is 80 people and k (variable) is 2, then the amount is 77 with the level of significance α=0.01 or α=0.05. Based on the calculation obtained thitung of 1,893 greater than the tybel of 1,664. And obtained the value t significance=0.62 greater than α=0.05. Because tcount (1,893)>ttable (1,664) the compensation variable (X1) affects employee performance (Y). These results show that H0 has been rejected and H1 has been accepted. It can therefore be inferred that compensation has a favorable impact on the performance of employees of enterprises controlled by public companies in the region, which means that the better the compensation provided, the better the employee performance will be increased.
For employees, compensation is one of the main reasons and motivations why they work. Employees work not only to dedicate or devote themselves to the organization, but there is another goal that he wants to achieve, namely to expect rewards or rewards for the performance and productivity of the work he earns.
This is in accordance with the comparative theory that explains that the rewards or rewards given by the organization to the workforce, because the workforce has contributed energy and thought for the progress of the organization in order to attain the objectives that are set.
The Effect of Work Discipline on Employee Performance
In this study, t-test has a test rule: If tcount>of the ttable then significant, known number of n is 80 people and k (variable) is 2, then the amount (df=n-k-1) is 80-2-1=77 with the level of significance α=0.01 or α=0.05. Based on the calculation obtained tcount of 3,431 greater than the ttable of 1,664. And the value t significance=0.001 is less than α=0.05. Because tcount (3,.431)>ttable (1,664) so work discipline (X2) has a strong impact on employee performance (Y). These results prove that H0 was rejected and H1 was accepted. It can therefore be concluded that working discipline impacts greatly on the performances of employees of public companies in the area, thus enhancing employee performance by increasing discipline of work.
This is in accordance with the theory of discipline that explains that the willingness and A person's willingness to comply with the standards of his or her rules.
The Effect of Compensation and Discipline on Employee Performance
Based on the results of the study showed the value of Fcount of 10,463 and the value of Sig in the table of 0.000, and the level of significance α=0.01 or α=0.00. It appears that the value of Fcount is greater than Ftable, then H0 is rejected and H1 is accepted, It states that compensation and co-operation discipline effect (at the same time) the work of employees of public held firms belonging to the region, it can be interpreted if the compensation provided by the company is getting better and the discipline of work is increasing then the employee performance will be improved.
Conclusion
Based on t-test results on compensation variables partially affecting the performance of employees of regional public bodies, t-test results on work discipline variables partially affect the performance of employees of regional public bodies, f-test results can be concluded that both independent variables, Compensation (X1) along with work discipline (X2) have a considerable effect on factors in employee performance (simultaneously) (Y).
Meanwhile, based on the test results of the coefficient of determination of R Square value obtained is 0.214 or 21.4%. The figure means that Employee Performance is affected by compensation and discipline of 21.4%.
Acknowledgements
The authors say many thanks to the Faculty of Economics, Universitas Madura Indonesia, for all the facilities provided during the research process.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Funding
This research uses personal funds from all authors in this journal
References
- Abadi, S., Endarto, B., Aji, R.B.T., Kurniawan, W., Daim, N.A., … & Kalbuana, N. (2021). Indonesian desirious finality of the community in regard. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24(Special Issue 1), 1–10.
- Aliyyah, N, Prasetyo, I., Rusdiyanto, R., Endarti, E.W., Mardiana, F., … & Tjaraka, H. (2021). What affects employee performance through work motivation? Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24, 1–14.
- Aliyyah, Nabilah, Siswomihardjo, S.W., Prasetyo, I., Rusdiyanto, … & Kalbuana, N. (2021). The effect of types of family support on startup activities in indonesia with family cohesiveness as moderation. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(1), 1–14.
- Endarto, B., Kurniawan, W.T, Indriastuty, D.E., Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., … & Kalbuana, N. (2021). Global perspective on capital market law development in Indonesia. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(Special Issue 1), 1–8.
- Endarto, B., Suhartono, S.T., Setyadji, S., Abadi, S., Aji, R.B., … & Kalbuana, N. (2021). The obligations of legal consultants in the independent legal diligence of the capital market supporting proportion of legal prepparement. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24(Special Issue 1), 1–8.
- Indrawati, M., Utari, W., Prasetyo, I., Rusdiyanto, & Kalbuana, N. (2021). Household business strategy during the covid 19 pandemic. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(Special Issue 1), 1–12.
- Juanamasta, I.G., Wati, N.M.N., Hendrawati, E., Wahyuni, W., Pramudianti, M., … & Umanailo, M.C.B. (2019). The role of customer service through Customer Relationship Management (CRM) to increase customer loyalty and good image. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 8(10), 2004–2007.
- Kalbuana, N., Prasetyo, B., Asih, P., Arnas, Y., Simbolon, S.L., … & Mahdi, F.M. (2021). Earnings management is affected by firm size, leverage and roa: Evidence from Indonesia. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(SpecialIssue2), 1–12.
- Kalbuana, N., Suryati, A., Rusdiyanto, R., Azwar, A., Rudy, R., & … Hidayat, W. (2021). Interpretation of sharia accounting practices in Indonesia. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24, 1–12.
- Luwihono, A., Suherman, B., Sembiring, D., Rasyid, S., Kalbuana, N., … & Rusdiyanto. (2021). Macroeconomic effect on stock price: Evidence from Indonesia. Accounting, 7(5), 1189–1202.
- Prabowo, B., Rochmatulaili, E., Rusdiyanto, & Sulistyowati, E. (2020). Corporate governance and its impact in company’s stock price: Case study, 25(Extra10), 187–196.
- Prabowo, Bahtiar, Rochmatulaili, E., Sulistiono, H.R.H., Wijayanto, A., … & Article. (2021). The capital adequacy ratio and the loan to deposit ratio influence on the price of banking companies: Evidence from Indonesia. Multicultural Education, 7(6), 147–154.
- Prasetio, J.E., Sabihaini, Susanto, A.A., Rahmanda, G.A., Rusdiyanto, … & Kalbuana, N. (2021). Corporate social responsibility community development and empowerment program in Indonesia. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(1), 1–10.
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, Chamariah, Syahrial, R., … & Sulistiyowati. (2021). Discipline and work environment affect employee productivity: Evidence from Indonesia. International Journal of Entrepreneurship, 25(5).
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, Kalbuana, N., & Rochman, A.S. (2021). Corporate social responsibility practices in islamic studies in Indonesian. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24(Special Issue 1), 1–15.
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, Nartasari, D.R., Nugroho, S., … & Rochman, A. S. (2021a). Impact financial performance to stock prices: Evidence from Indonesia. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24, 1–11.
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, R., Nartasari, D.R., Nugroho, S., & … Rochman, A. S. (2021b). What affects audit delay in Indonesia? Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 27, 1–15.
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, Suprapti, S., Kartika, C., & … Al-asqolaini, M.Z. (2021). Performance is affected by leadership and work culture: A case study from Indonesia. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(SpecialIssue2), 1–15.
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, Tjaraka, H., Kalbuana, N., & Rochman, A.S. (2021). Vocational training has an influence on employee career development: A case study Indonesia. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(2), 1–14.
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, Utari, W., Suprapti, S., & … Kalbuana, N. (2021). Effects of organizational communication climate and employee retention toward employee performance. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24(Special Issue 1), 1–11.
- Prasetyo, I., Endarti, E.W., Endarto, B., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, … & Rochman, A.S. (2021). Effect of compensation and discipline on employee performance: A case study Indonesia. Journal of Hunan University Natural Sciences, 48(6), 277–298.
- Rusdiyanto, Agustia, D., Soetedjo, S., & Septiarini, D.F. (2020). The effect of cash turnover and receivable turnover on profitability, 36(Special Ed), 1417–1432.
- Rusdiyanto, Hidayat, W., Bahari, C., Susetyorini, Elan, U., Indrawati, M., & … Gazali. (2021). Company profitability is influenced by sales and administration & amp; General Costs: Evidence from Indonesia. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24.
- Rusdiyanto, Hidayat, W., Tjaraka, H., Septiarini, D.F., Fayanni, Y., & … Imanawati, Z. (2020). The effect of earning per share, debt to equity ratio and return on assets on stock prices: Case study Indonesian. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 26(2), 1–10.
- Rusdiyanto, R., Karman, J., Toyib Hidayat, A., Muli Peranginangin, A., Tambunan, F., & Hutahaean, J. (2020). Analysis of decision support systems on recommended sales of the best ornamental plants by type. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1566(1).
- Shabbir, M.S., Mahmood, A., Setiawan, R., Nasirin, C., Rusdiyanto, R., … & Batool, F. (2021). Closed-loop supply chain network design with sustainability and resiliency criteria. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12980-0
- Susanto, H., Prasetyo, I., Indrawati, T., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, … & Zainurrafiqi. (2021). The impacts of earnings volatility, net income and comprehensive income on share price: evidence from Indonesia stock exchange. Accounting, 7(5), 1009–1016.
- Zhao, J., Sun, X., Dong, J., Wang, C., Xu, J., & Wang, Z. (2020). Sliding mode decoupling control for electro-hydraulic multi-dimensional force loading system with parallel mechanism [Sliding mode decoupling control of multi-dimensional force loading system of hydraulic drive parallel mechanism]. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 51(12), 3407–3417.