Research Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 4
Electronic Banking Service Quality and its Impact on Customer Satisfaction (CS): A Case Study from Jordan
Iyad A.A Khanfar, Zarqa University
Citation Information: Kanfar., Iyad A.A. (2023) Electronic Banking Service Quality and its Impact on Customer Satisfaction (CS): A Case Study from Jordan, International Journal of Entrepreneurship, 27(4),1-8
Abstract
Customer satisfaction is crucial for the success and growth of any business. This study examines the impact of e-Banking Service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction (CS) in Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa, Jordan. The study analyzed seven service quality dimensions, including Tangibles, Reliability, Empathy, Responsiveness, Assurance, Security, and Trust, using data collected from 421 electronic banking customers through a questionnaire. The research hypotheses were tested using SPSS and AMOS software, and the results showed that the five dimensions of Empathy, Responsiveness, Assurance, Security, and Trust had the most significant impact on CS. To improve customer satisfaction, we recommend that Jordan Islamic Bank prioritize these five quality dimensions by investing in employee training, enhancing security measures to increase customer trust, and ensuring reliable and accessible e-banking services. This strategy will give the bank a competitive edge in the Jordanian banking sector, where competition is intense.
Keywords
E-Banking, Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Jordan.
Introduction
In today's world, it is essential for all types of commercial banks to utilize technology to provide high-quality services (Bhatia & Jain, 2022). This has paved the way for customer satisfaction, particularly through the provision of electronic banking services (Nazir et al., 2021). The use of the internet has turned the world into a small global village and revolutionized the banking industry, leading to the emergence of a new and modern face of the sector by transitioning from traditional manual operations to internet-based facilities (Shaikh, et al., 2021). Over the years, the intensity of competition has increased, necessitating banks to adopt new tools and technologies to retain customers and obtain their satisfaction. Electronic banking services are an essential tool to achieve this goal (Shafiq, et al., 2020). According to (Karjaluoto, et al., 2002), banks have been freed from time and geographic constraints for the time being. Electronic banking services have been defined as the automatic and direct delivery of banking products to customers through interactive electronic communication channels (Giridhar & Thampi, 2021). E-banking services are crucial in meeting the expectations of customers, enabling banks to achieve customer satisfaction and gain their loyalty by providing high-quality services (Alam, et al., 2020). As the world rapidly adopts electronic banking services, the same holds for customers in Jordan, where automating banking procedures has opened new horizons for the banking sector (Alqatan & Al-Zoubi, 2021).
Study Objectives
The study aims to identify the influence of electronic banking service quality on (CS) of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city.
Literature Review
The use of electronic banking services has become crucial in meeting customer expectations and achieving satisfaction in the banking industry. According to a study by (Razaq, et al. 2021), the adoption of technology by commercial banks has become essential in providing high-quality services and improving customer satisfaction. In the Jordanian banking sector, the influence of internet banking service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction has been examined by (Alsharairi, et al. 2020), who found that reliability, responsiveness, and assurance were the most significant factors affecting customer satisfaction. Additionally, the study conducted by (Ahmad, et al. 2021) highlights the importance of web design, privacy, and security as critical factors that affect customer satisfaction with electronic banking services. Finally, the study of (Tantawi, et al. 2022) identifies convenience, quality of service, and empathy as significant dimensions that affect customer satisfaction in the context of electronic banking services.
Conceptual Framework
E-Banking
The introduction of the first automated teller machine (ATM) in Finland marked the beginning of a new distribution channel for banking services and established the country as a pioneer in electronic banking services (Taloussanomat, 2018). As a result of the rapid advancements in information technology and fierce competition among banks, e-banking and e-financial services have proliferated and are now distributed through electronic systems (Asare & Sacco, 2015). Today, customers can carry out banking transactions through a variety of electronic channels, including the internet, mobile phones, and computers, without having to physically visit a bank teller (Zahid, 2016). However, the slow development of Jordan's information and communication technology infrastructure has impeded the successful delivery of e-banking services, with only internet banking and mobile phone banking services currently permitted (Alawneh & Alghizzawi, 2018).
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a well-researched concept in marketing, and several studies have provided insights into its nature and determinants. For instance, a study by Lai, Griffin, and (Babin, 2009) found that perceived value, service quality, and product quality were the most significant determinants of customer satisfaction in the retail industry. Another study by (Jiang etal., 2019) found that perceived service quality, product quality, and trust significantly influenced customer satisfaction in the online shopping context. Similarly, a study by (Chen & Hu 2020) identified customer expectations, perceived service quality, and perceived value as critical factors affecting customer satisfaction in the hospitality industry. These studies demonstrate the multidimensional nature of customer satisfaction and highlight the importance of understanding the factors that influence it in different contexts. By focusing on these factors, businesses can enhance their customers' satisfaction According to this study and consistent with these definitions mentioned earlier, customer satisfaction is an attitude Crafted by the customer in response to his use of any form of electronic banking service.
Accordingly, the features of electronic banking services can increase, decrease or maintain the same customer satisfaction.
Customer Satisfaction and E-Banking
Customer satisfaction is a critical factor for success in the banking industry, and the quality of electronic banking services is one of the key determinants of customer satisfaction. A study conducted by (Al-Hawari & Ward, 2006) found a positive relationship between electronic service quality and customer satisfaction in the banking industry. Similarly, another study by (Yang & Jun, 2002) found that the quality of electronic banking services positively influenced customer satisfaction. Moreover, a study by (Wang, et al., 2017) demonstrated that customer satisfaction with electronic banking services was positively influenced by factors such as perceived usefulness, ease of use, and security. Additionally, a study by (Uppal & Kaur, 2021) found that electronic banking service quality significantly affected customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. Therefore, it is crucial for banks to prioritize the quality of their electronic banking services to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Dimensions of E-Banking Service Affecting Customer Satisfaction
Electronic banking services have become an integral part of the banking industry, and customer satisfaction is a crucial aspect for the success of these services. The dimensions of e-banking services that affect customer satisfaction can be grouped into Tangibility, Reliability, Empathy, Responsiveness, Assurance, Security, and Trust. Speed in performing e-banking services is critical in achieving customer satisfaction, according to (Parasuraman et al., 1985). Tangibility refers to the physical environment, such as equipment, personnel, and means of communication used to provide e-banking services, and it should be attractive to the customer. Studies have shown that the tangibility dimension has a positive effect on customer satisfaction (Soltani, et al., 2020). Reliability is another important dimension that customers use to evaluate the quality of e-banking services they use. It includes aspects such as system availability, accuracy, and consistency in service delivery. Research has shown that reliability has a significant impact on customer satisfaction (Nguyen, et al., 2020). Empathy involves individual and personal attention to customers, including knowing their preferences, name, and needs. Studies have found that empathy is positively related to customer satisfaction (Wu & Li, 2020). Responsiveness is concerned with the willingness to help customers and provide them with prompt services, as well as dealing with customer requests, questions, and complaints with interest and speed. Research has shown that responsiveness has a significant impact on customer satisfaction (Nguyen, et al., 2020). Assurance, Security, and Trust are also critical dimensions that affect customer satisfaction with e-banking services. Assurance involves the knowledge and courtesy of employees, while Security and Trust involve the protection of customer information and funds. Research has shown that these dimensions have a positive effect on customer satisfaction (Soltani, et al., 2020). In conclusion, e-banking services have many dimensions that affect customer satisfaction. Banks should focus on improving these dimensions to enhance the overall customer experience and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Study Model
Service Quality generally referred to the quality of service model developed by (Parausaman, et al., 1985), as a concept way of defining the impact of service elements and customer satisfaction from a customer's point of view. Tmodel has seven main aspects, such as (Tangibles, Reliability, Empathy, Responsiveness, Assurance, Security and Trust).
Based on the (SERVQUAL) service quality model, hypotheses were derived as follows
H1 Tangibles statistically impacts the customers’ satisfaction of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city - Jordan.
H2 Reliability statistically impacts the customers’ satisfaction of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city – Jordan.
H3 Empathy statistically impacts the customers’ satisfaction of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city - Jordan.
H4 Responsiveness statistically impacts the customers’ satisfaction of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city – Jordan.
H5 Assurance statistically impacts the customers’ satisfaction of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city – Jordan.
H6 Security statistically impacts the customers’ satisfaction of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city - Jordan.
H7 Trust statistically impacts the customers’ satisfaction of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city – Jordan.
In this section, the research design will be discussed, including the study population, sample size, sampling method, study hypotheses, questionnaire design, method of analysis, and reliability results. The study population consisted of clients of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city, and 450 questionnaires were distributed. A total of 421 valid questionnaires were retrieved for statistical analysis, which is considered an acceptable number according to (Sekaran, 2016).
To ensure the questionnaire's clarity, a pretest was conducted with 35 clients of Jordan Islamic Bank in Zarqa city, and their feedback was taken into account. A convenience sample was selected, as it is a common method in social science research (Mohr, 1990) and provides an acceptable database for statistical inference techniques.
The questionnaire consisted of three parts: the first part collected personal information such as age, education, income, and marital status. The second part focused on the independent variables: tangibles, reliability, empathy, responsiveness, assurance, security, and trust. The third part assessed the dependent variable, customer satisfaction, with 27 questions. The Likert scale was used to measure the variables, as it is widely used in marketing and social sciences (Burns & Bush, 2020), and a seven-point format was used to reduce participant disturbance (Churchill & Iacobucci, 2019).
In summary, the research design involved a convenience sample of Jordan Islamic Bank clients in Zarqa city, who completed a questionnaire with three parts assessing personal information, independent variables, and customer satisfaction. The Likert scale with a seven-point format was used to measure the variables, and 421 valid questionnaires were retrieved for statistical analysis.
Reliability Test
The reliability of the variables was assessed, and all variables met the minimum threshold of 0.70, as recommended by (Hair et al. 2019). Table 1 displays the Cronbach's alpha coefficient for each factor, indicating high reliability for all variables. The study examined seven independent variables and one dependent variable, customer satisfaction, as shown in Table 1.
| Table1 Results of Reliability |
||||
| Construct | Original Items | Total Mean | Items after CFA | Composite Reliability |
| Tangibility | 5 | 3.9 | 2 | .73 |
| Reliability | 4 | 3.7 | 2 | .81 |
| Empathy | 5 | 3.5 | 2 | .76 |
| Responsiveness | 6 | 3.7 | 2 | .87 |
| Assurance | 6 | 3.6 | 3 | .84 |
| Security | 4 | 3..3 | 2 | .88 |
| Trust | 4 | 3.3 | 3 | .72 |
| Customer Satisfaction | 5 | 3.8 | 2 | .85 |
| 39 | 18 | |||
Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
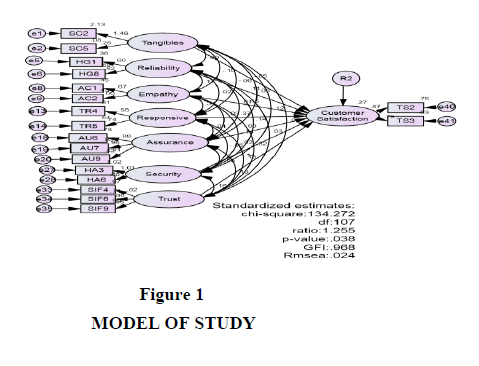
According to many recent analytical studies, the study indicator model focuses on measuring CFA, which is considered the first step in structural equation modelling (SEM). CFA is a measure that shows whether the number of variables and the elements' load corresponds to what is expected,SEM used the CFA technique, AMOS 20.0 was used to find out the proposed factors for analysis and how they match the data collected for the structural equation study, according to Hair et al. (2006). (SEM) is a set of statistical models that looks for details regarding relationships among multiple variables. Confirmation Factor Analysis (CFA) is used for the first time to confirm the load factor for the seven structures (tangibility, reliability, empathy, responsiveness, assurance, security, trust and customer satisfaction). The results of the suitability of fit for the generation model are shown in Fig.1 The chi-square has a value of 134.272 with 107 degrees of freedom. GFI is 0.968, AGFI 0.949, IFI 0.992, TLI 0.988, NFI 0.960, CFI 0.992, RMSEA is 0.024, CMIN / DF of 1.255<3. Most of the factors confirmed and accepted in this study are based on the appropriate quality results for the model generation. They were higher than the recommended values Hair et al., (2006).
Hypothesis Testing of Generating Model
The direct relationship represents the direct effect of independent construction on dependent construction. Figure 1 and Table 2 show that the hypothesis test determines the significance of each path parameter to estimate the error and weight of the critical ratio of the regression standardized weight, (CR = weight division was used to estimate the regression by estimating the standard error).
| Table 2 Results of Hypotheses |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. | Regression Weights From | To | Estimate | SE | C.R. | P | Hypothesis |
| H1 | Tangibility | Customer Satisfaction | .024 | .075 | 0.325 | .745 | NO |
| H2 | Reliability | Customer Satisfaction | .077 | .057 | 1.355 | .175 | NO |
| H3 | Empathy | Customer Satisfaction | .236 | .069 | 3.44 | *** | YES |
| H4 | Responsiveness | Customer Satisfaction | .452 | .086 | 5.25 | *** | YES |
| H5 | Assurance | Customer Satisfaction | .336 | .078 | 4.300 | *** | YES |
| H6 | Security | Customer Satisfaction | .466 | .098 | 3.983 | .*** | YES |
| H7 | Trust | Customer Satisfaction | .266 | .098 | 2.983 | .*** | YES |
Table 2 presents each parameter's C.R., Estimate and S.E of the Generating Model. Hence, the (H3, H4, H5, H6 and H7) have positive significance and direct impact on customer satisfaction. While (H1 and H2) have insignificance positive and direct impact on customer satisfaction.
Discussion
Through study results achieved the study objectives, which help in the development of academic research to describe, understand and explain the state of clients’ satisfaction at Zarqa city - Jordan. This research focused on studying indicators of the impact of clients’ satisfaction at Zarqa banks. The results showed that the paths analysis showed that most of the hypotheses had a positive and direct insignificance impact on clients’ satisfaction in Jordan Islamic bank in Zarqa city - Jordan (H1, and H2). While five hypotheses have a significant direct positive effect on the clients’ satisfaction (H3, H4, H5, H6 and H7). Therefore, the Central Bank of Jordan should pay more attention to other variables that impact clients ‘satisfaction at Zarqa in Jordan in the future, especially during the Corona pandemic. Finally, most of the findings were supported by previous studies (Harout, 2007; Yan & Lee 2015; Dora & Ferlita, 2016; Mawwala, 2017).
References
Ahmad, S., Hanif, M., & Sial, M.S. (2021). Internet banking service quality and customer satisfaction: Evidence from Pakistan. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 39(1), 79-98.
Alam, M. N., Uddin, M. M., & Bhuiyan, M. N. (2020). The impact of electronic banking service quality on customer satisfaction in Bangladesh: An empirical study. Journal of Innovation and Business Best Practice, 2020, 1-17.
Alawneh, M.A., & Alghizzawi, M. (2018). E-banking and its impact on customer satisfaction in the banking sector in Jordan. International Journal of Business and Management, 13(7), 197-207.
Al-Hawari, M., & Ward, T. (2006). The effect of automated service quality on bank financial performance and the mediating role of customer retention. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 10(2), 168-182.
Alqatan, M.N., & Al-Zoubi, E.S. (2021). E-banking adoption in Jordan: The impact of trust, security, and perceived risk. Journal of Risk Research, 24(7), 941-960.
Alsharairi, M., Abuhashesh, M., & Alzoubi, E. (2020). The impact of internet banking service quality on customer satisfaction in Jordanian banks. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 25(2), 87-100.
Asare, S.K., & Sacco, K.P. (2015). Impact of e-banking on traditional banking services. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, 20(2), 1-10.
Bhatia, P., & Jain, S. (2022). Role of technology in enhancing service quality in the banking sector: A review. Journal of Public Affairs, e2898.
Burns, A. C., & Bush, R. F. (2020). Marketing research. Pearson.
Chen, C.C., & Hu, Y.H. (2020). The effects of customer expectations, perceived service quality, and perceived value on customer satisfaction in the hospitality industry. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 21(1), 1-21.
Churchill, G.A., & Iacobucci, D. (2019). Marketing research: Methodological foundations. Cengage Learning.
Giridhar, K., & Thampi, S.M. (2021). Customer loyalty in Indian banking sector: The impact of service quality dimensions and customer satisfaction. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 39(2), 409-424.
Jiang, L., Wang, X., & Wang, Z. (2019). The impact of perceived service quality, product quality, and trust on customer satisfaction: A study of online shopping customers in China. Journal of Customer Behavior, 18(3), 219-239.
Lai, F., Griffin, M., & Babin, B.J. (2009). How quality, value, image, and satisfaction create loyalty at a Chinese telecom. Journal of Business Research, 62(10), 980-986.
Mohr, L. B. (1990). Marketing of high-technology products and innovations. Prentice-Hall.
Nazir, A., Rashid, Z., Naseer, M. M., & Khan, M.A. (2021). The impact of service quality on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty: Empirical evidence from Pakistan. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management.
Nguyen, H.Q., Vu, T.H., Vuong, T.D., Nguyen, D.D., & Vu, T.T. (2020). Impact of e-service quality on customer satisfaction: Evidence from Vietnamese commercial banks. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(6), 365-374.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1985). A con-ceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. The Journal of Marketing, 49(4), 41-50.
Razaq, A., Nazir, S., & Ali, M. (2021). E-banking and customer satisfaction: the role of technology acceptance and service quality. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 26(1), 21-33.
Sekaran, U. (2016). Research methods for business: A skill building approach. John Wiley & Sons.
Shafiq, M., Rahman, T., & Rahman, Z. (2020). Impact of electronic banking on customer satisfaction: Evidence from Pakistan. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 25(1), 33-47.
Shaikh, S., Mahesar, S.A., Jaffry, S.W., & Kalhoro, M.A. (2021). Impact of service quality on customer satisfaction and loyalty: The mediating role of customer perceived value in the banking sector of Pakistan. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 39(2), 349-368.
Soltani, Z., Jafari, M., & Esmaili, M. (2020). Assessing the impact of electronic banking quality on customer satisfaction: A case study of Sina Bank in Iran. Journal of Electronic Banking Systems, 2020, 1-10.
Taloussanomat. (2018). Finland invented the ATM - this is how it has changed the Finns' relationship with money.
Tantawi, H.A., Al-Jarrah, I.M., & AbuAli, A.S. (2022). Examining the impact of electronic banking service quality on customer satisfaction: evidence from Jordanian banks. International Journal of Electronic Customer Relationship Management, 13(1), 22-41.
Uppal, R.K., & Kaur, G. (2021). Impact of electronic banking service quality on customer satisfaction, loyalty and retention. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 39(1), 15-34.
Wang, Y.S., Chen, K.C., & Chen, H.Y. (2017). Investigating the determinants and age and gender differences in the acceptance of mobile banking services. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 18(2), 156-177.
Wu, M. L., & Li, S. L. (2020). Analyzing the effect of e-banking service quality on customer satisfaction in Taiwan. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(2), 28.
Yang, Z., & Jun, M. (2002). Consumer perception of e-service quality: from internet purchaser and non-purchaser perspectives. Journal of Business Strategies, 19(1), 19-41.
Zahid, A. (2016). Impact of e-banking on traditional banking services. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, 21(3), 1-10.
Received: 26-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. IJE-23-13567; Editor assigned: 29-Apr-2023, Pre QC No. IJE-23-13567 (PQ); Reviewed: 13-May-2023, QC No. IJE-23-13567; Revised: 17-May-2023, Manuscript No. IJE-23-13567(R); Published: 24-May-2023