Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 3S
Efficiency of the Accounting Information System and the Budget on the Administrative and Financial Performance of Universities: An Applied Study on a Sample of Colleges and Departments of Tikrit University
Emad Nayef Turki, Tikrit University
Saad Salih Hussein, Tikrit University
Hamad Abed Mustafa, Tikrit University
Keywords
Participation in the Strategic Decision, Administrative Performance, Clarity of Purpose in the Strategic Decision, Tikrit University
Abstract
The research aims to study the accounting information system to demonstrate the effect of participating in the strategic decision as an independent variable on the dependent variable (administrative performance) through the mediating variable (clarity of purpose of the strategic decision). To achieve this goal, the research adopted a questionnaire list, distributed to 39 employees from the colleges of Tikrit University (College of Administration and Economics, College of Law, College of Engineering and College of Petroleum Engineering), in addition to the Finance and Audit Department of the University Presidency. The target group included the deans of the colleges with the scientific and administrative dean assistants, as well as the heads of the scientific departments and the accounts and auditing departments in each college. Only 33 questionnaires (85%) were used in the statistical analysis process, while 6 questionnaires were neglected for not completing the analysis requirements. The simple linear regression model (OLS) was used to demonstrate the role of accounting information systems in rationalizing strategic decisions through research variables (participation in strategic decision, clarity of purpose of strategic decision and management performance). The research concluded that there is a moral relationship and a significant impact of participating in the strategic decision on administrative performance through the mediating variable, and thus, increasing the likelihood of a rational strategic decision.
Introduction
The accounting information system is one of the important systems that provide information of great importance to the organization, as the accounting information plays an important and major role in the management of business organizations, and the continuous development of accounting is due to the development of the business environment. Therefore, it was necessary to keep pace with the information systems, including the accounting information system from In order to contribute to the decision-making process, whether for the management of the organization or the external parties concerned and interested in this information. The accounting system is one of the most important systems producing accounting information that contributes to rationalizing administrative decisions, and the accounting system is closely related to various administrative processes, which affects the type of information produced through the system, and thus, contributes to rationalizing decisions, and makes the administrative process more effective in meeting the needs of management Organization, and raise the level of performance to achieve goals. Hence, the importance of providing effective and efficient accounting information systems to rationalize administrative decisions through high administrative performance resulting from participation in the decision-making process on the one hand, as well as assisting the administration in solving problems that may be encountered on the other hand. Accordingly, the accounting information system helps in providing useful information to relevant decision-makers that have a positive role in supporting and sustaining organizations
Effective administrative decisions are those decisions based on sufficient quality and accurate information, and this quality is only available with the presence of information systems on which the management depends when making these decisions. The decision-making process is one of the most important tasks for managers and workers in organizations, and this importance doubles and increases whenever the decision relates to a policy or strategic approach, as it maps and defines the general direction that the organization is taking in its economic operations. Accordingly, decisions represent the backbone of organizations, which in turn depend greatly on the quality and availability of information, and the importance of information systems has increased due to the need of different organizations for it. Information systems are no longer limited to business organizations only, but rather to different organizations that do not aim to Profit like universities and hospitals. These organizations, like business organizations, need information systems that enable them to make their decisions on sound grounds.
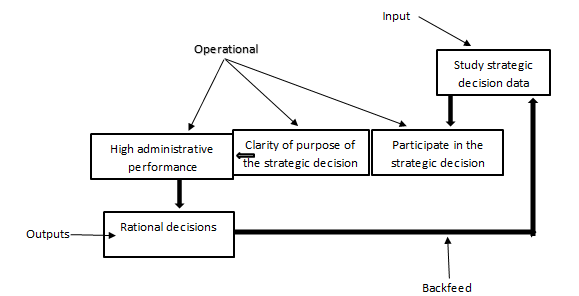
In general, information is a wealth, and the importance of information goes beyond the fact that it does not include only the decision-making process, but rather its importance lies in the fact that it is used in other administrative processes such as drawing up plans, drawing up and adjusting policies, monitoring and evaluating performance, etc. But the use of information and its systems in making decisions is one of the most important issues. Highly controversial, as it depends on the behavioral aspect in addition to the competence and experience of the employees. Without information, management decision-making becomes unscientific and rational. Accordingly, this research is distinguished by that it addresses the problem of the relationship between participation in strategic decisions of Tikrit University through high administrative performance as a dependent variable and clarity of purpose as an intermediate variable as shown in Figure (1).
Based on the foregoing, this research is concerned with demonstrating the efficiency and effectiveness of accounting information systems used by participating in the strategic decision and their impact on administrative performance through the clarity of the decision-making process as an intermediate variable on a sample of the colleges of Tikrit University, and to achieve this, the research was divided into the aspect The theoretical and previous studies. The third paragraph was devoted to data and research methodology, while the fourth paragraph was devoted to results and discussion, while the fifth and final paragraph was for conclusions.
The Theoretical Side and Previous Studies
In order to achieve the goal of the research, a group of studies related to the topic has been reviewed through two sections of studies at the local level and another at the international level, as follows:
Studies Related to the Research Topic at the Local Level
There may be many variables studied for each study at the local level, but they do not differ or deviate from the general framework, and the general result of these research and studies is that they center on appropriate and inappropriate costs, differential decisions and decision-making theories, as well as the effect of the behavioural aspect on the administrative performance of employees, and thus, performance. For example, studies (Al-Nuaimi, 1994; Amer, 1994; Ismail, 1999; Al-Dhahabi, 2001; Al Kaabi, 2003; Al-Rabie & Al-Rakabi, 2007 Hamidi, 2009; Jawad & Al-Rifai, 2010; Al-Zubaidi, 2010; Judy, 2011; Salman, 2012).
Al-Nuaimi's (1994) study tried to determine the appropriate cost for the purpose of making private decisions in order to help the administration in rationalizing its decisions. The study tried to test a basic hypothesis that “a good distinction between the cost elements appropriate to a particular decision and the inappropriate cost elements helps the management in making rational decisions.” The study found that the appropriate costs differ according to the alternatives, and thus, affect the decision-making.
As for Amer’s (1994), study it focused on showing the collective impact of investors ’decisions on stock prices. The study concluded that there is a difference in the level of understanding accounting information according to the demographic variables of the investors.
As for study of Ismail's (1999), it tried to determine the characteristics of the beneficiaries (individual, functional and professional) in the industrial sector organizations in Nineveh Governorate, as well as to determine the nature of the beneficiaries' need for information, and to identify the nature of the link and the effect between the characteristics of the beneficiaries and their attitudes towards information systems, and the study concluded that there is a relationship The characteristics of the beneficiaries and their attitudes towards information systems is influenced by the attitudes of the beneficiaries towards the adoption of the account in the applications of management information systems.
Whereas the study of Al-Dhahabi (2001) came with the aim of demonstrating the role of accounting information in rationalizing investment decisions by studying and evaluating the investment project, and the study tested the hypothesis of adopting a rational investment decision on the extent to which adequate and reliable accounting information is provided for the costs and returns of the investment alternative, and the study concluded that the process Making and making decisions is not an easy process, it is a complex process, as many factors and parties with multiple and different interests affect it, in addition to the investment decision is one of the important decisions as it is related to the process of employing huge resources for more than one financial year as well as its impact on the financial position and competitive position
As for the study of Al-Kaabi (2003), it tried to clarify the role of strategic management accounting methods in providing financial information to operational decision-makers for the purpose of rationalizing the decision-making process in business organizations, and tested the hypothesis of applying modern systems and methods in strategic cost management that provide useful information for the purposes of making operational decisions. That the existence of an information system in the organization is efficient and rapid and helps to provide useful information to guide strategic decisions.
The study of Al-Rubaie & Al-Rikabi (2007) came to try to determine the appropriate costs for the purpose of making non-recurring private decisions in order to help the administration in rationalizing its decisions, and the study tested the hypothesis that appropriate costs help the administration in rationalizing investment decision-making, and the study concluded that the importance of a rational decision lies in the use of appropriate data. In the differentiation process for decision-making.
Hamidi's (2009) study focused on clarifying the availability of qualitative characteristics of accounting information in financial reports and their impact on assessing war damages, and the study concluded that the information resulting from damage assessment lacks some or all of the qualitative characteristics of accounting information because it depends largely on personal judgment.
The study of Jawad & Al-Rifai (2010) tried to show how to assist the management in making operational decisions according to scientific foundations by conducting a differential analysis of costs in order to distinguish between the appropriate and inappropriate elements for their impact on the organization’s decisions and in order to achieve the desired objectives of the decision, and the study reached the importance of the differential decision in Rational decision making.
As for study of Al-Zubaidi's (2010), it tried to know the effect of accounting information contained in financial reports when making investment decisions in terms of buying and selling shares of local companies in the Iraq Stock Exchange, and based on the opinions of 92 individual investors, the study concluded that investors have sufficient awareness of the importance of information. Accounting in the investment decision-making.
Studies Related to the Research Topic at the International Level
Several studies at the international level have dealt with the importance and quality of accounting information By participating in the investment decision-making process by understanding the mechanism of reaching that decision (Gharaibeh & Naber, 1987; Matar, 1988; Kaplan, 1990; Jayyousi & Gharaibeh, 1990; Hopkins et al., 1998; Al-Ajlouni, 1998; Saleh, 2000; Al-Hussain, 2006; Hamza, 2007; Suleiman, 2010; Ahmad, 2010). On the other hand, many studies dealt with evaluating the reality of accounting information systems and their efficiency by assisting decision-makers in accessing the required information in several countries, including Jordan (2001); Saudi Arabia (Saleh, 2000; Saadi, 2000), Palestine (Ahmed, 2006; Shabir, 2006; Jerboa, 2007; Musa, 2010), Sudan (Al Hussein, 2006) & Thailand (Boonmak, 2007).
In addition to these studies, the study of Gharaibeh & Al-Naber (1987) came to show the extent of providing explanations in the annual financial reports of industrial public shareholding companies in Jordan through two categories of users: the individual investor and the financial analyst, the extent of providing explanations in the financial reports and the relationship between these explanations and some other variables such as the number Shareholders, total assets and return on shareholders ’equity. The study found the similarity of the needs of the two groups of information, and showed a direct relationship between the percentage of clarification, the total assets and the number of shareholders. As for Matar's study (1988), it tried to identify the importance of financial information in audited financial statements issued by public shareholding companies for investment decision makers in Kuwait. These lists
As for the study of Kaplan (1990), it aimed to demonstrate the importance of the board of directors' report for companies registered in the stock market, as well as the importance of investments made by brokerage offices in investment decisions related to the sale and purchase of shares. Brokers in investment decisions are more important than other accounting information contained in corporate financial reports
The study of Al-Jayyousi & Gharaibeh (1990) was to demonstrate the suitability of the financial reports information of the Jordanian industrial public joint-stock companies to the investment decisions. The study concluded that the amount of information published by the Jordanian industrial companies in their annual reports is small although the information of the disclosure scale used can be published without incurring additional costs. To these companies.
As for Brunson's (1990) study, it aimed to explain the responsibility and the implicit details of decision-making in organizations, and concluded that many decision-makers predetermine the best alternative among the available alternatives, while continuing to evaluate additional solutions is done for the purpose of distinguishing and determining the preference of the alternative as a result of the preference of the alternative that Was chosen.
A Lot of Accounting Research and Studies have tried to Measure the Financial Performance of Joint-Stock Companies, For Example:
Hussein (2008) studied the process of achieving profits in joint-stock companies and its money of importance, as its realization requires great efforts on the part of the company's management. The process of holding money and not distributing it is not desirable to the shareholders. The questionnaire was approved by a number of companies and through descriptive statistics. The researcher concluded that there is a positive relationship between investment opportunities and the profit retention process in companies.
Daden (2012) studied the extent of the impact of the dividend policy on the market value of the share, and the researcher used the simple and multiple linear regression method to find out the extent of an effect between the cash distributions and the market value of the share, and the study concluded that there is a significant effect between the market value of the share and the policy of Cash dividends.
As for Abd al-Qadir & Issa (2013), he stressed not to ignore and take into account the policy of distributing profits in financial institutions, and counting them from strategic financial decisions, such as the availability of liquidity that covers the distribution of profits, taxes and others. The researcher relied on a set of theories in explaining the behaviour of institutions towards the profit distribution policy. The researcher concluded that the total profits of the corporation and taxes on profits are among the most important determinants of the percentage of profit distribution in Algerian private institutions.
The study of Zarqoun (2010) also aimed that the profit distribution policy in the economic institutions listed on the stock exchange is affected by the public offering by governments. The researcher used a number of financial indicators on the stock exchange to arrive at the results. The researcher concluded that the relationship between the public offering and the profit distribution policy is a positive moral relationship.
As for the study of Shabita & Haddad (2010), it aimed to measure the impact of the systemic risks of companies, their size and the type of sector to which the companies belong to the relationship between dividends and returns of shares listed on the Amman Financial Market. The researcher used multiple linear regression model to arrive at the results. The researcher concluded that the relationship between distributed profits and stock returns is statistically significant in the industrial sector only in the Amman Financial Market.
The study of Youssef (2012) aimed to find out the appropriateness of the accounting profits information resulting from the independence of the board of directors and their impact on the decisions of investors in the financial markets. The researcher used the program) to test the assumptions and reach the required results. The researcher concluded that SPSS investor decisions are positively affected by the presence of the majority of non-executive board members in accounting profit information, and that the appropriateness of accounting profit information is negatively affected by the chairman of the board of directors playing a dual role in management, and the appropriateness of accounting profit information is not affected by the size Board of Directors.
The study of Zoroub & Sherrab (2007) also aimed to find out the extent to which the share prices of companies listed on the Palestine Stock Exchange are affected by those companies announcing these distributions. The researcher used the simple and multiple linear regression method in testing the hypotheses. The researcher concluded that the relationship between the variables in the stock market is statistically significant.
The study of Ahmed (2012) aimed to know the extent to which cash dividends in the Egyptian joint-stock companies are affected by the quality of profits, then to identify the relationship between the quality of profits and the quality of the external audit. The researcher used simple and multiple linear regression analysis in testing hypotheses. The researcher found that there is a positive effect between the quality of profits represented by the decrease in total receivables in the Egyptian joint-stock industrial companies and the professional qualification of the references. Also, the quality of profits is negatively affected by the period of retention of the customer by the joint-stock companies.
The study of Abu Al-Rub & Al-Zahir (2006) also aimed to find out the extent to which the market value and trading volume of public shareholding companies traded on the Palestine Stock Exchange are affected by profit distribution decisions. The researcher used the SPSS test to show the effect of distribution decisions before and after a month on trading prices and their volume through the (t) program. Statistically
Based on what was stated in previous studies at the local and international levels, the following hypothesis can be formulated:
H1: The relationship between accounting information systems and budget efficiency is significant.
Data and Research Methodology
The University of Tikrit is one of the central universities in Iraq. It was established in Salah al-Din Governorate in 1987. The university includes 21 colleges with various specializations (College of Medicine, College of Dentistry, College of Pharmacy, College of Veterinary Medicine, College of Nursing, College of Engineering, College of Petroleum and Mineral Engineering, College of Agriculture, College of Science, College of Islamic Sciences, College of Law, College of Business and Economics, College of Political Sciences, College of Education for Human Sciences, College of Education for Pure Sciences, College of Education for Girls, College of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, College of Basic Education/Sharqat, College of Education/Toz, College of Arts) as well as three research centers And a central
A specialized and proposed list of questionnaire was adopted to measure the research variables involved in the investment decision through seven Likert scale levels diverging between (1 strongly disagree to 7 strongly agree) proposed by Milani (1975) and used by Brownell (1983); Hassel & Cunningham ( 2004) as well as by Mahjoub & Halioui (2012); Hussein, et al., (2016). In the same direction, the objective clarity variable of the investment decision was measured, as seven levels of Likert scale were adopted, varying between (1 strongly disagree to 7 strongly agree) and suggested by Kenis (1979) and later used by Yang (2010). As for administrative performance, it was measured through 8 trends (planning, investigation, coordination, evaluation, supervision, recruitment, negotiation, and representation) and the measure was suggested by Mahoney, et al., (1963) and was used by Tsui (2001). The financial colleges ’budget information for the period from 2015 to 2019 was also used.
As for the questionnaire, 39 employees were targeted in the four colleges, the research sample (College of Business and Economics, College of Law, College of Engineering, College of Petroleum Engineering and the Department of Financial Affairs and Auditing at the University). The questionnaires were distributed to the deans and assistants of the deans and heads of scientific departments in the colleges, as well as the finance and auditing departments of the university presidency. Of these, 33 (85%) questionnaires were used only in the statistical analysis process, while 6 questionnaires were not complete, so they were neglected from the questionnaire analysis process, as shown in Table (1).
| Table 1 Questionnaire forms Distributed and Received |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of good forms to total forms% | Damaged forms | Forms received | Distributed forms | Statement |
| 60 | 4 | 6 | 10 | Faculty of Administration and Economics |
| 100 | 0 | 5 | 5 | collage of rights |
| 80 | 2 | 8 | 10 | College of Engineering |
| 100 | 0 | 4 | 4 | College of Petroleum Engineering |
| 100 | 0 | 5 | 5 | Department of Financial Affairs |
| 100 | 0 | 5 | 5 | Audit Department |
| 85 | 6 | 33 | 39 | Total |
| Source: Prepared by researchers based on the distributed questionnaire forms | ||||
Study Model
In order to measure the strength of the relationship between information systems through the production of the investment budget and its impact on strategic decisions at the university, the following regression model was used:
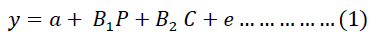
Whereas:
y=managerial performance represented by strategic decisions
B1 P=Participation in the investment decision
B2 C=the degree of clarity of the investment decision
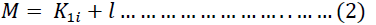
Whereas:
M=Performance efficiency
K=the rate of change in the balance from one year to the next.
L=error ratio
Results and Discussion
Table (2) shows the correlation matrix for the study variables, and it is noted from the table that there is a high and significant correlation between all the study variables (administrative performance, clarity of purpose of the investment decision, and contribution to the investment decision). Where the relationship between the contribution to the investment decision and the clarity of the objective of the investment decision was higher than the relationship between other variables, to reach 0.865, with a 5% level of significance. This is followed by the relationship between the clarity of the objective of the investment decision and the administrative performance of 0.796 with the level of 10% morale, while the relationship between the contribution to the investment decision and the administrative performance was 0.610 with the level of 5% morale, which indicates that for participation in the investment decision formation process, represented in the investment budget. It has a moral and high impact on the university's administrative performance by understanding the nature and quality of the decision and its importance. The higher the participation in the formation of the investment decision, the higher the understanding and clarity of that decision among university employees, and this leads, as a result, to higher performance for the same employees. This proves the research hypothesis that there is a moral relationship between accounting information systems and strategic decisions.
| Table 2 Matrix of Correlation Between Study Variables |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Contribution to the Investment Decision | Clarity of Purpose of the Decision | Administrative Performance | Variables |
| 1 | Administrative performance | ||
| 1 | 0.796* | Clarity of purpose of the decision | |
| 1 | 0.865** | 0.610** | Contribution to the investment decision |
| And ** represent 10% and 5% level of significance, respectively* | |||
The result of applying the regression model (1) was shown in Table 3. It is noted from the table that the significant relationship between the independent variables (contribution to the investment decision and clarity of purpose in the investment decision) on the one hands and the dependent variable (administrative performance) on the other hand.
Although the correlation coefficients between the study variables were few, their significance cannot be overlooked. Where the strength of the relationship of the correlation coefficient between the contribution in the investment decision and the administrative performance was (0.582) at a level of 10%, while the strength of the relationship between the clarity of the objective of the investment decision on the one hand and the administrative performance on the other hand was (0.447) at the level of 5%. And the value of t supports this significant relationship.
It is also noticed from the table that the value of F is significant at the level of 5%, and this confirms the validity of using the regression model proposed in this study. Despite the small size of the study sample, the value of DW confirms that there is no self-correlation problem in the research data used in the statistical analysis. As for the value of explanatory strength R2, it confirms that the study variables have dealt largely with the role of information system operational processes in helping to make strategic decisions at the university.
| Table 3 The Results of the Regression Model |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 value | DW value | F value | P value | T value | Correlation coefficient B | Variables |
| 0.81 | 1.45 | 16.17** | 0.08 | 17.44 | 0.582 | Contribution to the investment decision |
| 0.02 | 11.11 | 0.447 | Clarity of purpose of the decision | |||
| Management performance is the dependent variable. | ||||||
Efficiency of Financial Performance by Measuring the Efficiency of the Budget
| Table 4 Data of (Actual) Expenditures and (Planned) Allocations for Tikrit University |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expense logarithm - previous year's expenses | Logarithm of assignments - specializations of the previous year | Logarithm of assignments | Expense Logarithm -1 | Expense logarithm | Expense logarithm | Logarithm of assignments | Expenses | Customizations | Years |
| 25.36465 | 25.32181 | 25.32181 | 25.36465 | 99,33,91,83,553 | 1,03,68,78,06,421 | 2015 | |||
| 0.089815 | -0.08642 | 25.41162 | 25.32181 | 25.23539 | 25.23539 | 25.41162 | 91,11,51,93,323 | 1,08,67,42,19,248 | 2016 |
| 0.151133 | 0.008865 | 25.38652 | 25.23539 | 25.24426 | 25.24426 | 25.38652 | 91,92,65,54,165 | 1,05,98,07,84,202 | 2017 |
| 0.084405 | 0.055456 | 25.32866 | 25.24426 | 25.29971 | 25.29971 | 25.32866 | 97,16,84,52,459 | 1,00,02,24,70,728 | 2018 |
| 0.066981 | 0.079438 | 25.36669 | 25.29971 | 25.37915 | 25.37915 | 25.36669 | 1,05,20,22,09,175 | 1,03,89,98,29,071 | 2019 |
It is noticed from Table (4) that the data has been converted into natural data using its natural logarithm, and the reason is mainly due to the magnitude of the mentioned financial data and thus the possibility of error occurring is greater. The value of the difference was found by allocations for the previous year, as well as the difference in expenditures for the previous year, and as shown at the end of Table (4). By applying the regression equation to the data mentioned in Table (4), the results mentioned in Table (5) were obtained.
| Table 5 Results of Regression Analysis |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | F | R Square | |
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||||
| Constant (1) | 0.064 | 0.141 | 0.454 | 0.004 | 0.1137** | 0.064 | |
| xit | 0.506 | 1.366 | 0.254 | 10.1371 | 0.046 | ||
| a. Dependent Variable: yit | |||||||
It is noticed from Table (5) that the value of F is significant at the level of 5%, which gives an indication that the regression model used is appropriate to know the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It is also noted that the value of beta (0.254), although it is relatively small, but the significance cannot be ignored with the value of t 10.13. This means that the use of budgets for the years from 2015 and 2019 was efficiently, which gives the researcher tangible evidence that the efficiency of the budget represents the university’s efficiency in dealing with annual financial expenditures.
Conclusions
The research dealt with the issue of participation in the investment decision in a sample of Tikrit University's colleges (College of Management and Economics, College of Law, College of Engineering, College of Petroleum Engineering, Department of Financial Affairs and Auditing Department in the Presidency of the University). 39 questionnaires were distributed to the four colleges for the research sample (College of Administration and Economics, College of Law, College of Engineering, College of Petroleum Engineering and the Financial Affairs and Auditing Departments of the University). Of these, 33 (85%) were used for lack of completeness of information on 6 questionnaires. The simple linear regression model was adopted by considering the managerial performance as a dependent variable and participation in the strategic decision as an independent variable with the presence of clarity of purpose from the strategic decision (investment) as an intermediate variable. It can be seen that the accounting information system depends heavily on operational processes through studied research variables. The study also showed, based on the results of the statistical analysis, that participation in the investment decision-making process has a significant and high impact on the administrative performance of the university through understanding the nature and quality of the decision and its importance. The study found that the higher the participation in the formation of the investment decision, the higher the understanding and clarity of that decision among university employees, and this leads to a high performance of the employees. The researchers also concluded that the university was using the budget efficiently, despite the small value of the beta, but it was found to be significant. The researchers believe that one of the obstacles related to the research was the availability of data in total at the university level, and it would have been better to give a clearer picture if the data were analyzed at the level of colleges and departments in the university.
References
- Ahmed, B.M. (2006). The role of accounting information systems in rationalizing administrative decisions in palestinian business establishments: An applied study on private limited joint stock companies in the Gaza strip. GazaL: Islamic University.
- Ayoub, N. (2000). The efficiency of information technology systems from the point of view of the beneficiary in small Saudi industrial establishments. Journal of Administrative Sciences Studies, 27(1), 161-180.
- Al-Bashabshah, S. (2005). The impact of quality management information systems in raising the level of job performance in the Jordanian social security corporation. The Accountant, Management and Insurance Journal, Amman, 10(1), 267-380.
- Al-Kaabi, B.R. (2003). The role of modern management accounting methods in rationalizing operational decisions, an applied study in the General Company for Leather Industries.
- Al-Loghani, N.I. (2001). Investment performance of value shares and growth shares in the Kuwait stock exchange. The Arab Journal of Administrative Sciences, 8(2), 217-233.
- Al-Mahasna, M.A. (2005). The impact of information systems efficiency on effective decision-making in the customs department. The Jordanian Journal of Business Administration, 1(1), 78-100.
- Al-Abaji, M.A. (2021). Cuckoo search algorithm: Review and its application. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 26(2), 137-144.
- Al-Naimi, H.F. (1994). The role of appropriate costs in rationalizing administrative decisions an applied study in the light industries company. University of Baghdad.
- Al-Hazaymeh, A.S. (2009). The role of the information system in making decisions in government institutions, a field study in the public institutions of Irbid Governorate. Damascus Journal of Economic and Legal Sciences, 25(1), 379-408.
- Alobaidi, M.H., & Omar, I.K. (2019). Dynamical behavior of some families of cubic functions in complex plane. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 24(7), 122-128.
- Alsammarraie, S., & Nazar, K.H. (2020). A new hybrid grasshopper optimization-backpropagation for feedforward neural network training. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(1), 118-127.
- Arif1, G.E. (2020). Constructing mathematical models to find a relationship between physical compounds using the graph theory. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(6), 126-129.
- Al-Jayousi, M., & Gharaibeh, F. (1990). The annual financial reports published for industrial public shareholding companies in their relevance to the financial investment decision. Dirasat Journal, 17(1), 143-165.
- Al-Hussein, A. (2006). The role of accounting information in rationalizing financing decisions in sudanese commercial banks. Sudan University of Science and Technology: Sudan.
- Al-Dhahabi, J.I. (2001). The role of accounting information in rationalizing investment decisions, a study in the light of the strategic approach to cost management systems, an applied study in the General Company for the Vegetable Oil Industry. University of Baghdad: Iraq.
- Al-Rubaie, J., & Al-Rikabi, N. (2007). The role of appropriate costs in rationalizing special administrative decisions: An applied study in the general establishment for Woolen Industries. Al-Taki Journal, 20(2), 1-14.
- Al-Zubaidi, F.K. (2010). The impact of accounting information on investment decisions in shares of companies listed in the Iraqi stock exchange. Al-Qadisiyah Journal for Administrative and Economic Sciences, 12(3), 105-119.
- Al-Saadi, M. (2000). The role of accounting information in administrative control. King Abdulaziz University: Saudi Arabia.
- Amer, K. (1994). The impact of accounting information on stock prices. University of Baghdad.
- Abdul Razzaq, H. (1993). The extent to which accounting information is used in administrative decisions related to planning and control functions. University of Jordan.
- Al-Ajlouni, A.M. (1998). Evaluation of management information systems applications in selected companies from the private and public sectors in Jordan.
- Al-Issa, Y.A. (1991). The importance of accounting information and its availability in the financial reports published for joint stock companies in Jordan for investors in the Amman Stock Exchange. Mutah Journal for Research and Studies, 6(2), 385-415.
- Abdul Jalil, T. (2014). The impact of the capital structure on the performance of Jordanian public shareholding industrial companies. The Jordanian Journal of Business Administration, 10(3), 390-403.
- Abu Risha, K.A., Hemeidat, M.M., & Al-Issa, M.S. (2015) Factors affecting accrual settlements under management control - An applied study on industrial shareholding companies listed in the Amman stock exchange. The Jordanian Journal of Business Administration, 11(3), 727-744.
- Abdelkader, B., & Issa, B. (2013). Determinants of the policy of profit distribution in Algerian private institutions. Academy Journal for Social and Human Studies, 10, 12-22.
- Badrani, O.A., & Faris, N.H. (2021). Calcareous nannofossils bioevent throughout the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary in kh-4 well, Northern Iraq. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 26(1), 60-66.
- Barik, R.K., Patra, S.S., Kumari, P., Mohanty, S.N., & Hamad, A.A. (2021). A new energy aware task consolidation scheme for geospatial big data application in mist computing environment.
- Bouchet, M.L., Hopkins, T., Kinnell, M., & McKnight, C. (1998). The impact of information use on decision making in the pharmaceutical industry. Library Management, 19(3), 196-206.
- Brownell, P. (1983). Leadership style, budgetary participation and managerial behavior. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 8(4), 307-321.
- Daoud, S.J. (2011). Computerized information systems in Iraqi oil companies in Basra governorate. Basra Literature Journal, 56, 301-330.
- Daden, A.W., & Badida, H. (2012). The impact of the policy of dividend distribution on the value of priced institutions. Al-Bahith Journal, 10, 225-238.
- Elawi, M.A., Noori, H.N., & Auday, T.S. (2021). Comparison btween the relations of HPGE detector efficiency curve and background “Spectrum Shape”. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 26(1), 96-100.
- Gharaibeh, F., & Naber, R. (1987). Availability of clarifications in the annual financial reports of industrial public shareholding companies in Jordan. Dirasat Journal, 14(8), 9-32.
- Hussein, H.H. (2008). Factors affecting the dividend policy in joint stock companies. Journal of Baghdad College of Economic Sciences, 17, 209-230.
- Hassel, L.G., & Cunningham, G.M. (2004). Psychic distance and budget control of foreign subsidiaries. Journal of International Accounting Research, 3(2), 79-93.
- Hussein, S.S., Maji, S.G., & Panda, N.M. (2016). The association between budget goal clarity and managerial performance in Iraqi oil refinery: The role of budget goal difficulty and budget participation. Middle East Journal of Management, 3(4), 343-358.
- Hamza, M. (2007). The role of accounting information in rationalizing investment decisions in the Amman stock exchange: An applied study. Damascus Journal of Economic and Legal Sciences, 23(1), 145-174.
- Ismail, H.K. (1999). Measuring the beneficiaries’ attitudes towards management information systems. Al-Mustansiriya University.
- Jarbou, Y.M. (2007). Areas of the contribution of accounting information to financial statements in improving the administrative decisions of public shareholding companies in Palestine, an applied study on public shareholding companies in Palestine. Islamic University Journal, 15(2), 507-555.
- Jawad, S., & Al-Rifai, H. (2010). The role of appropriate costs in rationalizing operational decisions an applied study in Al-Furat general company for chemical industries. Babel Journal/Human Sciences, 18(1), 62-74.
- Khalaf, H.H. (2018). The impact of electronic money on the effectiveness of monetary policy. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 24(3), 1-16.
- Matar, M. (1988). The relative importance of audited financial statements issued by joint stock companies in the State of Kuwait as a source of information for investment and lending decision-makers. Dirasat Journal, 8, 23-65.
- Musa, O. (2010). The role of accounting information in rationalizing credit decisions. Islamic University Library: Gaza Palestine.
- Muthanna, M.M., Hameed, H.K., & Omar, A. (2021). Monetary policy responses to the global financial crisis: What did emerging economies do differently? Academy Of Entrepreneurship Journal, 27(5).
- Maria Antony, L.T., & Abdullah, H.A. (2020). A theoretical implementation for a proposed hyper-complex chaotic system. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 38(3), 2585-2590.
- Mark, A.C., & Michael, J.J. (2006). Differential patterns of textual characteristics and company performance in the chairman's statement. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 19(4), 493-511.
- Shahoodh, M.K. (2021). The adjacency matrix of the compatible action graph for finite cyclic groups of p-Power Order. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 26(1), 123-127.
- Saad, S.I., Hameed, H.K., Ahmed, R.A., & Essia, R.A. (2018). Effectiveness of inflation targeting based monetary policy. Opcion - Scimago Journal, 34(16), 1032-1057.
- Suhae, F.J., & Amera, I.H. (2020). Suitability evaluation of mudstone of Injana formation for dam filling materials in TaqTaq area/Erbil/Iraq. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(3), 49-56.
- Sukar, Y.I. (1999). The use of management information systems in the decision-making process in the business sector. Middlesex University: Cairo.
- Salman, M.A.R. (2012). The impact of decision-making theories on measurement of appropriate costs. Baghdad Journal of University Economics, 29, 299-328.
- Suleiman, E. (2010). The role of accounting information in making administrative decisions under conditions of uncertainty. Islamic University Library: Gaza Palestine.
- Shabeer, A.A. (2006). The role of accounting information in administrative decision-making, an applied study on public shareholding companies in Palestine. Gaza, Palestine: The Islamic University.
- Saleh, R.I. (2000). The role of accounting data in the stock market, an empirical study by application to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The Scientific Journal of Commerce and Finance, 1, 1-28.
- Siam, W., & Saadeh, Y. (1996). The role of accounting data in rationalizing substitution decisions, field study. Journal of Administrative Sciences Studies, 23(1), 1-6.
- Shubaita, D.F., & Haddad, F.S. (2010). The effect of systematic risk, company size and sector type on the relationship between dividends and stock returns- An applied study on the Amman stock exchange. Dirasat Journal for Administrative Sciences, 37(1), 204-221.
- Thanoon, S.R. (2020). A comparison between Bayes estimation and the estimation of the minimal unbiased quadratic Standard of the bi-division variance analysis model in the presence of interaction. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(2), 116-123.
- Thivagar, L.M., Hamad, A.A., & Ahmed, S.G. (2020). Conforming dynamics in the metric spaces. Journal of Information Science and Engineering, 36(2), 279-291.
- Tsui, J.L. (2001). The impact of culture on the relationship between budgetary participation, management accounting systems, and managerial performance: An analysis of Chinese and western managers. The International Journal of Accounting, 36(2), 125-146.
- Wuhaib, S.A., & N.F. Abd. (2020). Control of prey disease in stage structure model. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(2), 129-135.
- Winterman, C., & Smith, A. (1998). Impact of information on decision making in government departments. Library Management, 19(2).
- Wuhaib, S.A., & Bilal, A.Y. (2020). SIS model with harvesting in food chain model. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(1), 108-117.
- Yaseen, B.A. (2020). SIS model with harvesting in food chain model. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(2), 93-101.
- Yang, Q. (2010).The impact of the budgeting process on performance in small and medium-size firms in china. University of Twente: Netherlands.
- Younis, M.T., & Zeena, N.A. (2020). Application methods of linear feedback control on the modified Lorenz 3D chaotic system. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(3), 129-134.
- Youssef, A. (2012). The impact of the independence of the board of directors on the relevance of accounting profits information to the decisions of investors in the financial markets. Damascus University Journal
- Zhang, G., Guo, Z., Cheng, Q., Sanz, I., & Hamad, A.A. (2021). Multi-level integrated health management model for empty nest elderly people's to strengthen their lives.
- Zaben, R.A., & Rana, H.J. (2020). Geometry of concircular curvature tensor of Kahler manifolds. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(2), 110-115.
- Zagi, H.R., & Abeer, T.M. (2020). A novel serpent algorithm improvement by the key schedule increase security. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 25(6), 114-125.
- Zaid, D. (2021). Study of prevalence of Thalassemia trait among couples undergoing premarital examination in Al-Hamdaniya Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 26(2), 22-25.
- Zubair, Z.R.S. (2021). A deep learning based optimization model for based computer interface of wheelchair directional control. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science, 26(1), 108-112.
- Zorob, H., & Shurrab, S. (2007). The impact of announcing dividends on the stock prices of companies listed in the Palestine stock exchange “An Applied Study”. Islamic University Journal, 15(2), 557-579.
- Zargoun, M. (2010). The impact of the public offering on the policies of dividend distribution in the economic institutions quoted in the stock exchange - A comparative analytical study of the Al-Aurassi Hotel Corporation. Algeria - Al-Bahith magazine, 8, 81-96.