Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
Effects of Organizational Communication Climate and Employee Retention Toward Employee Performance
Indra Prasetyo, Universitas Wijaya Putra and Akademi Sekretari dan Manajemen Indonesia Surabaya
Nabilah Aliyyah, Universitas Wijaya Putra and Akademi Sekretari dan Manajemen Indonesia Surabaya
Rusdiyanto, Universitas Airlangga, Universitas Gresik, Universitas Madura
Woro Utari, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Sri Suprapti, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Chandra Kartika, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Ruddy Winarko, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Chamariyah, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Dwi Lesno Panglipursari, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Muninghar, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Nur Halimah, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Aminatuzzuhro, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Mei Indrawati, Universitas Wijaya Putra
Onong Junus, Universitas Airlangga, Universitas Gorontalo
Mohammad Herli, Universitas Airlangga, Universitas Wiraraja
Hafidhah, Universitas Wiraraja
Nanik Kustiningsih, Universitas Airlangga
Gazali, Universitas Madura
Adriani Kusuma, Universitas Madura
Muslimatul Aina, Universitas Madura
Isnain Bustaram, Universitas Madura
Zef Risal, Universitas Madura
Zainurrafiqi, Universitas Madura
Siti Salama Amar, Universitas Madura
Khoiroh Umah, Universitas Gresik
Susan Novitasari Khadijah, Universitas Gresik
Mono Pratiko Gustomi, Universitas Gresik
Hendra Irawan, Universitas Gresik, PT.Rachmad Barokah Jaya
Arif Syafi'ur Rochman, Universitas Gresik
Dini Ayu Pramitasari, Universitas Gresik
Muhammad Miftah Farid, IKIP Widya Darma
Nawang Kalbuana, Politeknik Penerbangan Indonesia Curug
Keywords
Organizational Communication Climate, Organizational Culture, Employee Performance
JEL Classifications
G20, L25, F65, O15, Q34
Abstract
The purpose of this research is to analyze the effect of organizational communication climate and employee retention toward employee performance with organizational culture as an intervening variable. The research sample used Company employees was 65 respondents. The research information analysis method uses path analysis using the PLS-SEM application. The results of research findings explain that the influence of organizational culture has an influence on employee performance in the company. Organizational communication climate hasn’t an influence on employee performance. Employee retention hasn’t an influence on employee performance, conversely, the indirect effect of organizational culture if it is included to improve employee's performance has a very large effect on improving influence of organizational communication climate and employee retention has a significant to increase performance in the company.
Introduction
The business world has a very tight competitive climate that keeps the quality of its products and services competitive, produces high quality goods and services and is a priority that cannot be diverted from the key role that the performance of human resources plays. One way to solve the problem is through organizational communication. This human tendency to communicate continues and is carried out in an organizational environment while at work. Employees who work for a company have an obligation to communicate with each other. One aspect that can influence the success of a company is the communication climate created in the company. Changes in communication climate that occur in an organization can affect the performance and productivity of employees (Alseiari & Farrell, 2020; Chakraborty & Biswas, 2020; Dartey-Baah et al., 2020).
In addition to the organizational communication climate, another important point in an organization is the organization’s culture. Exploring organizational culture issues is essential for an organization or company, because it will always be interconnected and related to the company's life. Organizational culture is a common and binding philosophy, assumptions, beliefs, ideology, values, expectations and rules. In particular, the culture of the organization shall be determined by team working conditions, organizational management, character and administrative processes applicable. Organizational culture is highly regarded because it is an organization’s practice which represents the standards of behavior followed by the members of the organization’s hierarchy. A productive organizational culture is one that can make an organization stronger (Balanagalakshmi & Kumari, 2019; Budie et al., 2019; Horváthová et al., 2020).
The problem that often arises with weak employee retention is employee turnover, but can be solved through various pro-active employee retention strategies so that the organizational culture has a positive impact on employee performance.
Literature Review
Organizational Communication Climate Relations and Employee Performance
Communication that occurs in an organization is called organizational communication. The purpose of communication in the organization is to form mutual understanding so that there is an equality of reference framework and similar experience among the members of the organization. Human beings as social beings need to communicate to build relationships with the exchange of messages/information in an effort to achieve certain goals. This communication involves yourself, between individuals, small groups and organizational groups. The human tendency to communicate continues and is repeated in the organizational environment while they are at work (Diamantidis & Chatzoglou, 2019; Jiang & Shen, 2020; Sopow, 2020).
Employees who work for a company have an obligation to communicate with each other. An organizational communication climate is very important because the organizational communication climate can affect the way of life of its members, to whom it speaks, to whom it is liked, how it works, how it develops, what it wants to achieve and how it adapts. When running the wheels of an organization, the human resources of the organization will interact with each other in the organization and with the inter-organizational parts, it is necessary harmony in the communication between people in the organization or institution for organizational communication to run effectively and efficiently to achieve the objectives of the organization (Kellner et al., 2016; Maamari & Majdalani, 2017; Steers & Lee, 2017).
Meanwhile, social interaction between employees and superiors through effectively intertwined communication will create job satisfaction and foster a sense of organization. This sense of ownership is very important because it can produce genuine devotion from its workers. Conversely, ineffective communication due to personal problems, competition between work units, lack of superiors' willingness to hear, understand and acknowledge employee opinions or achievements will trigger the onset of job dissatisfaction (Halter et al., 2009; Jo & Shim, 2005; Rapert et al., 2001).
Climate Relations of Organizational Communication with Organizational Culture
The organization's culture that arises when an organization is formed is one of the factors that can influence the organizational climate. Existing systems can influence an organization’s existing climate in the organization, norms, or disciplines in the organization or company. Language or pattern of behavior, even clothing can affect the existing climate in the organization because it becomes a tangible form or character that is highlighted to distinguish the organization from each other (Alzahrani et al., 2019; Araujo & Figueiredo, 2019; Azim et al., 2019).
In the process, each member of the organization will learn and adjust to the values in their work environment. The culture in an organization becomes the foundation studied and implemented by each member in all activities related to the organization. Different cultures in each organization form a different organizational climate in each organization (Ali et al., 2019; Brandis et al., 2017; Chug & Vibhuti, 2017).
Employee Retention Relationship with Organizational Culture
Retention of employees is the task of keeping employees as key experts in a company, while retention of employees can also be carried out to find solutions to reduce turnover and to increase staff comfort in an enterprise and not just to position them. Employees should however also be able to adapt to the organizational culture, supervisors, managers and co-workers within a company (Basnyat & Clarence Lao, 2019; Dechawatanapaisal, 2019).
Companies with engaged employees have high employee retention resulting from declining employee turn-overs, reduced intention to exit the company, improving productivity, profitability, growth and customer satisfaction (Anggraeni, 2018; Crossman, 2018; Dechawatanapaisal, 2018b). Companies can sustain the workforce using a retention approach that combines organizational culture, salary or compensation, as well as employee training and development (Hume & Hume, 2017; Nkomo et al., 2017; Vijay Anand et al., 2017).
Employee Retention Relationship with Performance
The company's effort to minimize the level of employee turnover, the human resources department has an important task that is to create good employee retention. The development of employee retention program must be a crucial component for the organization. If Employee Retention is bad, it will increase Turn over Intention which negatively affects employee performance(Ayodele et al., 2020; Chakraborty & Biswas, 2020).
In general, the relationship between Employee Retention to employee performance is very complex, there is evidence that performance can decrease if employee retention is bad and vice versa if employee retention is good employees then performance will improve. One way to improve employee performance is to optimize employee retention in order to remain loyal to the company (Anil & K.P, 2019; Blouch & Azeem, 2019; Dash & Roy, 2020).
Organizational Cultural Relationship with Employee Performance
One of the important roles of values organizational culture is increased motivation for employee performance. Organizational with strong philosophical and fundamental values both within the company's internal and external environments have a clear connection between high performance and organizational culture through motivation. The employees' performance as the drivers of the organizational activities will also increase if the employees' performance is good. Many variables affecting the performance of employees, including organizational culture (Cadden et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2020; Markovic et al., 2020; Russen et al., 2020; Shahriari & Allameh, 2020; Tagliabue et al., 2020).
In general perception of the organization, culture belongs to all organization members, the culture of the organization will ensure that each employee of the organization conforms to its values, beliefs, and behavior. On the basis of this definition known that recognize that employee performance is very important, since a decrease in the performance of individuals and groups within a company can have a significant influence on the organization (Moore et al., 2020; Noviantoro et al., 2020a, 2020b; Palmer et al., 2020; Vomberg et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020). Climate Communication Organization is a collection of perceptions of the members of the organization of what is happening in the organization in which they work (Brawley Newlin & Pury, 2020; Hobbs, 2020; Martín-Santana et al., 2020; Mathis, 2020; Prasad et al., 2020; Sopow, 2020). Interactions that occur between members of the organization whether between colleagues, superiors and subordinates or vice versa will increase knowledge and understanding for members of the organization regarding the background, experience, attitudes and behaviors of others (De Clercq & Belausteguigoitia, 2020; Gaspary et al., 2020; Jiang & Shen, 2020; Schulz-Knappe & Ter Hoeven, 2020; Shulga, 2020; Zahidul Islam et al., 2020).
Organizational Communication Climate is a combination of perceptions of a macro evaluation of communication events, human behavior, employee response to other employees, expectations, conflicts between personas, and opportunities for growth in the organization (Brawley Newlin & Pury, 2020; Hobbs, 2020; Martín-Santana et al., 2020; Mathis, 2020; Prasad et al., 2020; Sopow, 2020). O’Connor, et al., (2008) there are 4 (four) dimensions of organizational climate, namely: There are 4 (four) dimensions of organizational climate, namely 1. Responsibility, namely the degree of delegation of experience experienced by employees, Standards, namely expectations about the quality of work, Rewards, namely recognition and exhortation for good work and otherwise punishment for bad workers, Closeness and support, namely good friendship and trust.
Goals & Abilities, Role Models, Remuneration, Justice
Research Hypothesis
Based on the formulation of the problem, the research objectives and the conceptual framework that have been formulated to the following hypothesis:
1. H1: Organizational communication climate has a positive effect on the Employee Performance at company.
2. H2: Organizational communication climate has a positive effect on organizational culture at company.
3. H3: Employee retention has a positive effect on organizational culture.
4. H4: Employee retention has a positive effect on Employee Performance at company.
5. H5: Organizational culture has a positive effect on the Employee Performance at company.
6. H6: Organizational culture mediates the relationship between Organizational Communication Climate and employee’s performance.
7. H7: Organizational culture mediates the relationship between Organizational Communication Climate and employee’s performance.
Research Methods
Type of Research, Population and Sample, Sampling Technique
The type of research used is causal research, research that uses a quantitative approach using statistics to respond to problems or research hypotheses that are specific in nature to carry out predictions if a certain variable affects other variables (Juanamasta et al., 2019; Kunaifi et al., 2021; Luwihono et al., 2021; Prabowo et al., 2020; Prasetyo et al., 2021; Rusdiyanto et al., 2021; Rusdiyanto, Agustia, et al., 2020; Rusdiyanto, Hidayat, et al., 2020; Shabbir et al., 2021; Susanto et al., 2021). The research population of all employees at company, on the other hand, the sample in the study used 80 male and female employees. This research sampling method uses non- probability sampling. The sampling method used was purposive sampling where the sampling was based on the criteria described by the researcher for the sample (Ahmad & Chowdhury, 2020; de Leon, 2020; Endiana et al., 2020; Koul et al., 2020; Narayanasamy et al., 2020; Tutar et al., 2020).
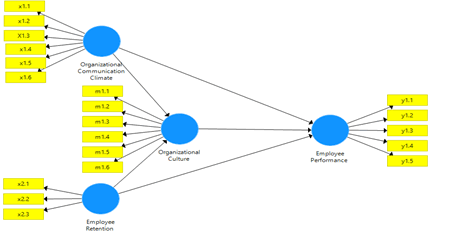
Operational Definition of Variables
The operational definition in this research consists of three work discipline variables, compensation variables and employee performance variables.
Organizational Communication limite (Mokhayeri et al., 2015)
x1.1: Trust, x1.2: Decision-making, x1.3: Honesty, x1.4: Openness in downward communication, x1.5: Listening in upward communication, x1.6: Attention to high-performance goals.
Employee Retention (Tranquillo, 2006)
x2.1: Organizational career opportunities, x2.2: Award given, x2.3: Employee relations.
Organizational Culture (Syafii et al., 2015)
m1.1: process orientation, m.1.2: employee orientation, m1.3: professional, m1.4: tight control, m1.5: open system, m1.6: pragmatic.
Employee’s Performance (Y) (Elangovan & Rajendran, 2020)
y1.1: Goal, y1.2: Standard, y1.3: Feedback, y1.4: Tool or Means y1.5: Competence y1.6: Motive.
Data Analysis Techniques
The research used PLS-SEM analysis with the following stages (Azam, 2015; Garrido & Zambrano, 2019): 1) A reliability assessment session was conducted which was divided into two sessions, namely an assessment of markers of reliability and an assessment of internal consistency reliability. 2) Conducting an assessment of the validity of information using convergent validity and discriminant validity. 3) Carry out a bootstrapping test to obtain a statistical value and a P value. 4) Testing of indirect influence mediation.
Analysis and Discussion
Initial Outer Model
| Table 1 Test of Convergent Validity |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | AVE | Information |
| Organizational Communication Climate | 0,136 | Not Valid |
| Employee Retention | 0,662 | Valid |
| Organizational Culture | 0,474 | Not Valid |
| Employee Performance | 0,576 | Valid |
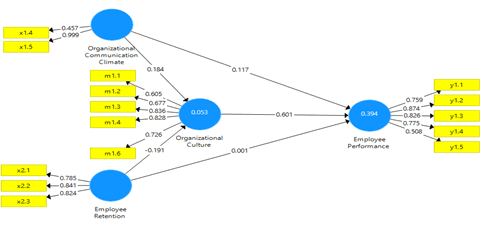
Based on the test table above the AVE value for organizational culture, the value is below the standard for the feasibility of testing the fit model, which must be above 0.5, while in the first stage of the initial test the outer value is 0.412. Therefore, it is necessary to remove the indicators that are not valid against the variables until the model becomes fit (Goodness of Fit).
Retesting to the Fit Model Obtained
| Table 2 Test of Second Convergent Validity |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | AVE | Information |
| Organizational Communication Climate | 0,603 | Valid |
| Employee Retention | 0,668 | Valid |
| Organizational Culture | 0,547 | Valid |
| Employee Performance | 0,576 | Valid |
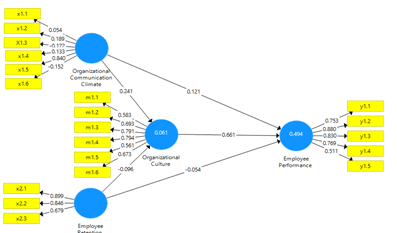
In the second convergent validity test, the AVE value for each variable has met the requirements above 0.5, whereas if we look at the Figure above, five indicators are omitted, namely x1.1 (Trust), x1.2 (decision making), x1.3 (honesty), x1.6 (attention to high performance goals) and m1.5 (open system).
| Table 3 Test of Reliable Internal Consistency |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | Composite Reliability | Information |
| Organizational Communication Climate | 0,728 | Reliable |
| Employee Retention | 0,858 | Reliable |
| Organizational Culture | 0,856 | Reliable |
| Employee Performance | 0,868 | Reliable |
The table above shows the totality of latent variables in the study that had composite reliability values above 0.6, so it was concluded that all of these variables had a high degree of internal consistency reliability. After being declared a fit model, then doing testing by bootstrapping produces the following model:
From the bootstrapping model above, the T-statistic value and Hypothesis Test are used to draw conclusions. The T-table value with a significance level of 5% for 80 respondents explains that the inner model is significant if the T-Statistic value is greater than the T-Table of 1,6759.
| Table 4 T-Statistics |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Sample | Sample Mean | Standard Error | T- | P Value | |
| Statistic | |||||
| Organizational Communication Climate -> Employee Performance | 0.117 | 0.101 | 0.14 | 0.838 | 0.402 |
| Organizational Communication Climate -> | 0.184 | 0.183 | 0.19 | 0.966 | 0 |
| Organizational Culture | |||||
| Employee Retention -> Organizational Culture | -0.191 | -0.183 | 0.194 | 0.986 | 0.012 |
| Employee Retention -> | 0.001 | -0.012 | 0.185 | 0.006 | 0.005 |
| Employee Performance | |||||
| Organizational Culture -> Employee Performance | 0.601 | 0.625 | 0.09 | 6.663 | 0.432 |
In the above table, a coefficient value may be shown in the original sample value that displays the influence force of one latent variable on another variable, while the value in a mean column (m) shows the mean value of the path coefficient, or the standard deviation and the default error (stderr) display the default and error value in the sample.
T- Statistics on the effect of organizational communication climate on employee performance show a number 0,838 smaller than T- Table 1,6759 with a probability value of 0, 402 which is greater than 5%, meaning that organizational communication climate hasn’t a significant positive effect on employee’s performance. T- Statistics on the effect of organizational communication climate on organizational culture show a number 0,966 smaller than T- Table 1, 6759 with a probability value of 0,334 that is greater than 5%, meaning that organizational communication climate hasn’t a significant positive effect on organizational culture. T- Statistics on the effect of employee retention on organizational culture shows the number 0,986 is smaller than T- Table 1, 6759 with a probability value of 0.325 which is greater than 5%, meaning that employee retention hasn’t a significant positive effect on organizational culture.
T- Statistics on the effect of employee retention on employee performance show a number 0,006 smaller than T- Table 1, 6759 with a probability value of 0,996 that is greater than 5%, meaning that employee retention hasn’t a significant positive effect on employee performance. But T- Statistics on the effect of organizational culture on employee's performance shows the number 6,663 is greater than T- Table 1, 6759 with a probability value of 0.000 which is smaller than 5%, meaning that organizational culture has a significant positive effect on employee's performance
Indirect Effect Evaluation
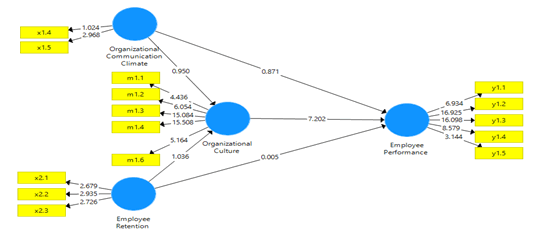
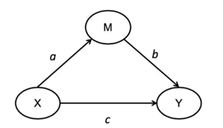
Smart PLS includes the results of calculating the indirect effect which is useful in analyzing the strength of the relationship between the mediator variable and other variables. Mediation is established when a variable affects the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. Changes in the based variables lead to changes in the mediator variable and the conclusion also causes changes in the dependent variable. In this paper, the authors use a simple mediation model because there is one mediator variable. In order to analyze this simple mediation model, the author adopts the flow created by (Al Idrus et al., 2020; Haider & Kayani, 2020; Mivehchi & Rajabion, 2020; Siahaan et al., 2020; Vu, Tran, Le & Nguyen, 2020; Vu, Tran, Le, Nguyen, et al., 2020) The picture above is a simple mediator model. The mediation effect analysis uses the following values: c is the direct impact, the multiplication of axb equals the indirect impact, c+(axb) is the total effect.
Explained that the impact of mediation is divided into 5 groups, namely: 1) Complementary (partial mediation) if axb is significant, c is significant, and axbxc is significant. 2) Competitive (partial mediation) if axb is significant, c is significant, but axbxc is not significant. 3) Indirect-only (full mediation) if axb is significant, but c is not significant. 4) Direct-only (mediation number) if axb is not significant, but c is significant, 5) effect number (mediation number) is if axb is not significant and c is not significant (Chukwuedo & Ogbuanya, 2020; Hauser et al., 2018; Kim & Beehr, 2017; Obedgiu et al., 2020; Shoaib & Baruch, 2019; Solimun & Fernandes, 2017; Tournois & Djeric, 2019; Zhang et al., 2019).
| Table 5 Evaluation of Indirect Effects |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Axb notation | Indirect effect | Direct effect | Mediation effect status |
| (T statistic axb) | (value c) | ||
| (X1 -> M) | 6,436 | (X1 -> Y) 0,838 | Indirect-only (Full Mediation) |
| (M -> Y) (0,966) (6,663) | (No-Significant) | ||
| (Significant) | |||
| (X2 -> M) | 6,569 | (X2 -> Y) 0,006 | Indirect-only (Full Mediation) |
| (M -> Y) (0,986) (6,663) | (No-Significant) | ||
| (Significant) | |||
Based on the indirect effect evaluation table, the indirect effect through the organizational culture mediation variable has a T-statistic value greater than 6,436 than the value of the direct effect of organizational communication climate on employee performance, which is 0,838. This is convincing that organizational culture can increase employee performance as a result that the positive is bigger.
The second indirect effect through the organizational culture mediation variable has a T-statistic value greater than 6,569 than the value of the direct effect of employee retention on employee performance, which is 0,006. This is convincing that organizational culture can increase employee performance as a result that the positive is bigger.
Conclusion
Based on the results of the analysis, it explains that the influence of employee's organizational communication climate hasn’t an influence on employee's performance, which means that employee's organizational communication climate at work can’t improve employee's performance at the company. Employee retention hasn’t an influence on employee's performance, meaning that retention employee in the company can’t increase the employee’s performance receive from the company. Meanwhile, organizational culture has an influence on the employee's performance. While the indirect effect of organizational culture if it is included to improve employee’s, performance has a very large effect on improving influence of organizational communication climate and retention employee to increase performance in the company.
References
- Azam, M.S. (2015). Diffusion of ICT and SME performance. Advances in Business Marketing and Purchasing, 23A, 7–290.
- Azim, M.T., Fan, L., Uddin, M.A., Abdul, K.J.M.M., & Begum, S. (2019). Linking transformational leadership with employees’ engagement in the creative process. Management Research Review, 42(7), 837–858.
- Balanagalakshmi, B., & Kumari, S.S. (2019). Employees’ perception on diversity in management. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 8(1C2), 7–11.
- Basnyat, S., & Clarence Lao, C.S. (2019). Employees’ perceptions on the relationship between human resource management practices and employee turnover: A qualitative study. Employee Relations, 42(2), 453–470.
- Blouch, R., & Azeem, M.F. (2019). Effects of perceived diversity on perceived organizational performance: Mediating role of perceived organizational justice. Employee Relations, 41(5), 1079–1097.
- Brandis, S., Rice, J., & Schleimer, S. (2017). Dynamic work place interactions for improving patient safety climate. Journal of Health, Organisation and Management, 31(1), 38–53.
- Brawley, N.A.M., & Pury, C.L.S. (2020). All of the above?: an Examination of overlapping organizational climates. Journal of Business and Psychology, 35(4), 539–555.
- Budie, B., Appel-Meulenbroek, R., Kemperman, A., & Weijs-Perree, M. (2019). Employee satisfaction with the physical work environment: The importance of a need based approach. International Journal of Strategic Property Management, 23(1), 36–49.
- Cadden, T., Millar, K., Treacy, R., & Humphreys, P. (2020). The mediating influence of organisational cultural practices in successful lean management implementation. International Journal of Production Economics, 229.
- Chakraborty, D., & Biswas, W. (2020). Articulating the value of human resource planning (HRP) activities in augmenting organizational performance toward a sustained competitive firm. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 14(1), 62–90.
- Dunford, B.B., Mumford, K.J., Boss, R.W., Boss, A.D., & Boss, D.S. (2020). Integrated conflict management systems pay off with lower levels of formal grievances and lower turnover rates. ILR Review, 73(2), 528–551.
- Elangovan, N., & Rajendran, S. (2020). Impact of functional interdependency on employee satisfaction with performance appraisal in the real estate industry. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 18(4), 213–227.
- Guzeller, C.O., & Celiker, N. (2019). Examining the relationship between organizational commitment and turnover intention via a meta-analysis. International Journal of Culture, Tourism, and Hospitality Research, 14(1), 102–120.
- Horváthová, P., Kashi, K., Štverková, H., & Mikušová, M. (2020). Wellbeing as a core area of line managers’ work in cross-border organizations [Satisfaction as the main area of work for line managers in cross-border organizations]. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 22(1), 186–199.
- Hume, C., & Hume, M. (2017). Key enablers for knowledge management for Australian not-for-profit organizations: Building an integrated approach to build, maintain, and sustain KM. In Organizational Culture and Behavior: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications, 2(4).
- Idris, A.K.R., Soetjipto, B.E., & Supriyanto, A.S. (2020). The mediating role of job satisfaction on compensation, work environment, and employee performance: Evidence from Indonesia. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 8(2), 735–750.
- Juanamasta, I.G., Wati, N.M.N., Hendrawati, E., Wahyuni, W., Pramudianti, M., Wisnujati, N.S., … & Umanailo, M.C.B. (2019). The role of customer service through Customer Relationship Management (CRM) to increase customer loyalty and good image. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 8(10).
- Kunaifi, A., Rahman, F., Rosyid, A., Mansur, Masithoh, F.N., Zainurrafiqi, R.R.A.S., & Kalbuana, N. (2021). Quantitative easing in overcoming the crisis: Criticism of QE in the monetary system of capitalism. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education, 12(3), 3703–3714.
- Luwihono, A., Suherman, B., Sembiring, D., Rasyid, S., Kalbuana, N., Saputro, R., Prasetyo, B., Taryana, T., Suprihartini, Y., & Asih, P. (2021). Macroeconomic effect on stock price: Evidence from Indonesia. Accounting, 7(5), 1189–1202.
- Mosquera, P., Soares, M.E., & Oliveira, D. (2020). Do intrinsic rewards matter for real estate agents? Journal of European Real Estate Research, 13(2), 207–222.
- Narayanasamy, M.J., Thomson, L., Coole, C., Nouri, F., & Drummond, A. (2020). Investigating the barriers and facilitators to implementing mental health first aid in the workplace: a qualitative study. Journal of Mental Health Training, Education and Practice, 16(2), 164–178.
- Osman, I., Jameelah, M.M.H., Noordin, F., & Daud, N. (2016). An analysis of intellectual capital and turnover intentions among Malaysian employees in the private organisations. Agriculture Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 24(May), 79–88.
- Prabowo, B., Rochmatulaili, E., Rusdiyanto, & Sulistyowati, E. (2020). Corporate governance and its impact in company’s stock price: Case study Corporate governance and its impact on company stock prices: Case study. Latin American Utopia and Praxis, 25(10), 187–196.
- Prasetyo, I., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, Tjaraka, H., Kalbuana, N., & Rochman, A. S. (2021). Vocational training has an influence on employee career development: A case study indonesia. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(2), 1–14.
- Rusdiyanto, A.D., Soetedjo, S., & Septiarini, D.F. (2020). The effect of cash turnover and receivable turnover on profitability. The effect of cash turn over and accounts receivable turn over on profitability. Option, 36(Special Ed), 1417–1432.
- Rusdiyanto, H.W., Fayanni, Y., Rahman, M.A., Rosyidi, A.A., Khadijah, S.N., Irawan, H., … & Rochman, A. (2021). Customer satisfaction is effected by the quality of service: A case study Indonesian. Turkish Journal of Computerand Mathematics Education, 12(3), 3560–3567.
- Rusdiyanto, H.W., Tjaraka, H., Septiarini, D.F., Fayanni, Y., Utari, W., Wars, I.M., … & Imanawati, Z. (2020). The effect of earning per share, debt to equity ratio and return on assets on stock prices: Case study Indonesian. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 26(2), 1–10.
- Shabbir, M.S., Mahmood, A., Setiawan, R., Nasirin, C., Rusdiyanto, R., Gazali, G., … & Batool, F. (2021). Closed-loop supply chain network design with sustainability and resiliency criteria. Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
- Susanto, H., Prasetyo, I., Indrawati, T., Aliyyah, N., Rusdiyanto, T.H., Kalbuana, N., … & Zainurrafiqi. (2021). The impacts of earnings volatility, net income and comprehensive income on share price: evidence from Indonesia stock exchange. Accounting, 7(5), 1009–1016.
- Syafii, L.I., Thoyib, A., & Nimran, U. (2015). The role of corporate culture and employee motivation as a mediating variable of leadership style related with the employee performance (studies in Perum Perhutani). Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 211, 1142–1147.