Research Article: 2022 Vol: 25 Issue: 1
Effects of Occupational Health and Safety Strategies on the Organizational Performance: A Case Study on Electric Power Corporation in Wolaita Sodo District, Ethiopia
Ashenafi Abebe Bitire, Mizan Tepi University
Legese Lemma Chuma, Wolaita Sodo University
Citation Information: Bitire, A.A., & Chuma, L.L. (2022). Effects of occupational health and safety strategies on the organizational performance: A case study on electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 25(1), 1-11
Abstract
The main objective of this study was to assess the effects of OHS strategies of organizational performance; a case study was Ethiopian electric power corporation at Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia. Descriptive and inferential statistical techniques were used for data analysis. The study discovered that Ethiopian electric power corporation have significant effects in increasing organization performance through providing social welfare, accident prevention of employees, and, providing adequate training about health and safety to increase organization productivity. Based on the result of the study the researcher concludes that, occupational health and safety strategies have positive significant effect on organizational performance. Finding of this study posited that all occupational health and safety strategies almost similar mean and standard deviation value. Generally, scores in all OHSs were found to be strongly correlated with organization performance. Based on the finding of the study the correlation analysis value showed the occupational health and safety strategies in electric power corporation are positive effects on organization performance. However, further research continuous pre- requisite for the financial performance of occupation health and safety strategies in Electric Corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia.
Keywords
Occupational Health Strategies, Safety, Organizational Performance.
Introduction
Health and safety strategies are protective with caring employees and people suffering from what the corporate produces and do against the hazards arising from their employment or their links with the corporate (Armstrong, 2012).
Occupational health entails the promotion and maintenance of the best degree of physical and mental state and social well-being of employee’s altogether occupations (Taderera, 2012). According to identify a number of benefits to the organization from promotion of health and safety workplace as improvements of productivity as a result of reduced sickness absence, enhanced corporate image and staff turnover. Safety measures prevent accidents and ensure regular flow of work which helps to improve the morale and productivity of workers.
As highlighted in their study, In the 1960s, something like a thousand employees were killed at their work in the UK. each year of that decade about 500,000 workers suffered injuries in varying degrees of severity, and 23 million working days were lost annually on account of organizational injury and disease. Such statistics led investigators to argue that 'for both humanitarian and financial reasons, no society can accept with satisfaction that such levels of death, injury, disease and waste must be regarded as the expected price of meeting its needs for goods and services. There are also indirect expenses related with occupational accidents. The indirect expenditures include overtime payments necessary to make up for lost production, cost of retaining a replacement employee, a wage cost for the time spent by HRM personnel recruiting, selecting and training the new employee and, in less typical cases, the cost associated with loss of revenue on orders cancelled or lost if the accident causes a net long-term reduction on sales, and attendance at court hearings in contested cases.
The major valuable impact of job-related health and safety on performance is reduced absenteeism. The major concern of this study was to assess the OHS strategies on performance of Ethiopia Power Company in Wolaita Sodo district. Actually, the study examined how the organization keep its place of work healthier and safe, and assess how the strategies applied as a catalyst to attain organizational goals and propagate sustainable performance to employees in specific and organization in general.
In economic terms, the ILO has estimated that 4% of the world's annual GDP is lost as a consequence of occupational diseases and accidents. In past three year slightly more than three (3) million US workers suffered from occupational injuries and illnesses resulting from accidents at work number of fatal accidents. This statistics results in an incidence rate of 3.3 cases per 100 equivalents to full time workers.
The Significance of the Study
The findings of the studies are also expected to be useful to other public and private organization. It will shade lights on how useful the OHS strategies are on the organization performance well-growing. It will help to reduce the risk of hazard or harm caused by either new technologies or poor occupational health and safety to enhance organizational performance. It is expected to help policy maker to design and devising health and safety policies which will support the international attempts to reduce number of work related accidents, diseases and hazards at workplace (Jane and Esther, 2017).
Problem Statement
Occupational safety and health is an important strategy not only to ensure the health and safety of workers, but also contribute positively to productivity, quality of products, work motivation, job satisfaction and thereby to the overall quality of life of individuals and society (Joan, 2013).
The electric power corporation is a significant sector of any national economy, especially regarding its employment and organizational performance. But accidents, incidents, injuries and fatalities continue to occur unabated on electric power sites around the world at consistently high rates (Watkins et al., 2017).
The electric power corporation tends to have a little consciousness of the long-term benefits of occupational safety strategies, while the tendering process often gives little attention to safety, resulting in cost and corner cutting.
The electric power company can benefit from an improved attitude change that cultivates a vision for the future which elevates safety concerns and effectively integrates them into the overall organization performance. High charge of injury are mainly due to insufficient or non-existence of an OSH personal protective equipment’s. Many occupational accidents and injuries are due to a breakdown in the existing OSH strategy. Therefore, the application of ‘effective’ strategies can lead to safer systems of Power Company and reduce incidence of injuries and work related diseases in organization.
Research Questions
This study attempts to address the following research questions.
1. What is the effect of health and safety strategies on organizational performance in electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district?
2. What is the effect of social welfare strategies on organizational performance?
3. What is the effect of accident prevention strategy on organization performance?
4. Do occupational health and safety training strategies affect organization performance?
Objectives of the Study
1. To assess the effect of health and safety strategy that determines organizational performance in the electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district.
2. To assess the effects social welfare strategies that contributes to the success of organization.
3. To assess the effect of accident prevention strategy on organization performance.
4. To identify the effects occupational health and safety training strategies in the organization.
Limitations of the Study
This study has limitations as with all the research fields. Effects of occupational health and safety on organizational performance were investigated through a single research model. Its effects on workers’ motivation, alienation, commitment, working hours, employee attitude towards OSH training and intention to cease employment may be involved in further studies. The effects of occupational health and safety on social welfare, accident prevention strategy and occupational health training, on organizational performance can also be investigated on the bases of sex, educational level, age, culture, white- and blue-collared, and payment. Moreover, the selfreporting methods a can be employed to collect data and better to employee multiple methods to collect data. Better to use data analysis methods such as partial list square SEM model for purpose of shading line on examining interrelationship. Keeping qualified human capital to compete in today’s stiffly competitive working life is very imperative. According to the principle of reciprocity, employee’s occupational health and safety strategies as perceived organizational support will yield work from employees for the benefit of the organization. The employees acting with a sense of commitment will increase their efforts for the performance of the organization.
Literature Review
The study address relevant conceptual, theoretical framework and empirical review related on the literature review on occupational safety and health strategies on organizational performance. Foundation of occupational safety and health strategies, and the effects of occupational safety and health strategies on organization performance.
Occupational health and safety is relatively a new conception as during the industrial revolution labour activities pointed out the problems of workplace or occupational health and safety showing interest in health and safety related problems of work force.
Improving employee efficiency, productivity, occupational health and safety (OHS) has been a significant area of interest of industry particularly in developing countries. Some common features of such industries consist of inappropriate workplace design, ill-structured jobs, mismatch between job demands and worker’s abilities, adverse environments, poor humantechnology system design, and inappropriate management system.
Recently occupational and safety strategies has been get attention from different authors. Recent occupational accidents urged enterprises to put more importance on occupational health and safety practices. The pressure by both the public authority and the business and social milieu has played an important role in it. Providing a healthy and safe working environment has the potential to increase labour productivity and in turn increase business profits (Ojiem, 2012).
Human capital is one of the most treasured assets an organization has and efficient use of human resource anticipates any organization at top level due to high human resource capital job performance and consequently, it is vital for employers to have a healthy and secure workplace for its workers. Investing in health and safety at work has to be looked upon as an investment on capital rather a cost.
The European Union defines health and safety, in a wider sense, as going beyond the avoidance of accidents and prevention of disease to include all aspects of the worker's well-being. Accident is an unplanned event/incident
That happens suddenly and unintentionally resulting damage to property or injury and loss of life; short and long term effects or incidents due to exposure on installing electric power site and consequently interruption to power process.
In developed nations there are good practices and standardized ways of providing timely and reliable information about work related accidents and diseases from which worker force of world is suffering. But in developing countries do not have such standardized ways of recording and keeping work accidents and resulting ill health consequences to help obtain relevant data in order to withstand.
Annually, throughout the world, an estimated number of 271 million people suffer with work-related injuries and about 2.3 million die as a consequence of these work related diseases and injuries. While industrial disasters, especially those resulting in multiple fatalities, make global headlines; the reality is that many thousands of people die from their work activities every day and numerous fatalities are unreported or ignored.
The present rapid economic growth has brought changes in workplaces in developing countries, including Ethiopia. The organization of occupational health and safety strategies is not yet resilient enough to handle the growing demands for workers’ health in the context of organization. There is limited information on the gaps and needs of occupational health strategies in workplaces in Ethiopia (Kumie et al., 2016; Ramaan et al., 2016).
Published information on the status of OSH at the national level is very limited. Even the limited amount that is available is not updated to contain the dynamics of workplace exposures and the introduction of new technologies.
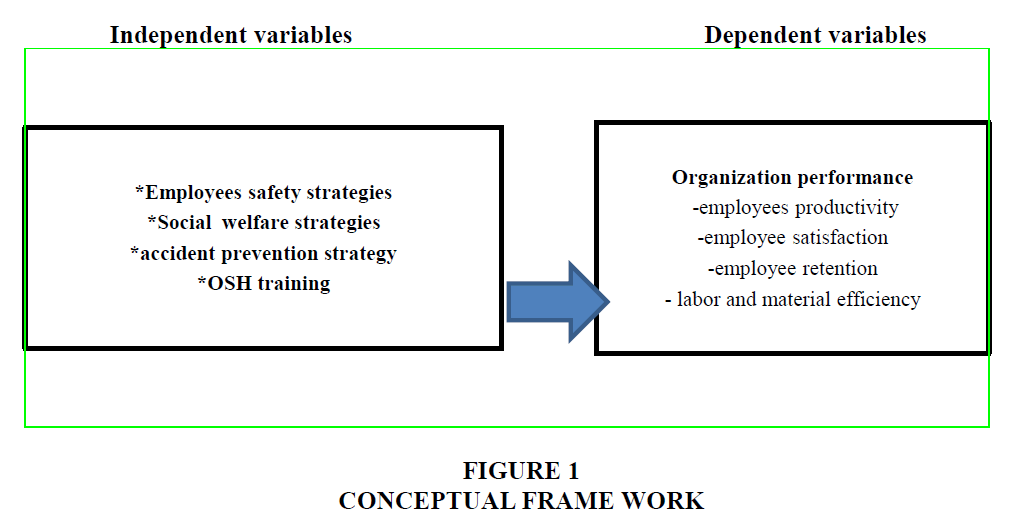
Conceptual Framework
The conceptual framework of these variables was a guide to this research on how they determine organization performance. Organizational performance of electric power company across space and time are influenced by different strategies and their associations. Strategies such as health and safety strategies, social welfare strategies, accident prevention and health and safety training determine the probability of organizational performance. It is obvious that different studies have been conducted to look into the direction and magnitude of the influence of different strategies on organizational performance (Fekele et al., 2016; McCunney, 1994).
Methods and Materials
This study was conducted to assess the effects of occupational health and safety strategies to the organization performance in Ethiopia electric power company the case of Wolaita Sodo district. In explanatory design; researcher is only interested in explaining the situation or case under the research study. The study used both qualitative and quantitative approaches and obtained the relevant data through structured questionnaire survey and formal interview. The target populations of this study were administrative and employees of electric corporation of Sodo district and they are 112 in number, (90 employees and 22 administrative members).
From the literature the following conceptual frame work is developed to indicate independent and dependent variables in the study (Figure 1).
The sample of respondents was selected from the sampling frame as shown in the Table 1 below.
| Table 1 Sample of Respondents | ||
| Name of selected departments | Number of employees | Selected sample size |
| Organization employees | 110 | 90 |
| administrative members | 46 | 22 |
| Total | 156 | 112 |
In order to determine the sample size from total population, researcher used the following formula of Yamane, 1967 which asserts that the sample size can be determined by:
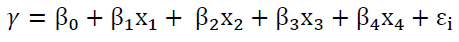
Where,
n = is the sample size,
N = is the total population under study
e = is the level of precision assumed to be 5%.
This study basically depends on primary data in which the researcher prepared the questionnaires that were distributed to employees of electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia. The secondary data was used only for supporting the finding obtained from analysis of primary data.
The researcher employed primary data which were collected through self-administered questionnaires with closed ended questions. As much as possible, a 5-point liker scale was used to investigate effect of occupational health and safety strategies on organizational performance of electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia.
All research questions were analyzed with the help of Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) Version 23 that was used to aid in the analysis. In order to analyze the data, the two sets of Statistics: Descriptive and Inferential statistics was used. Descriptive statistics summarizes and describes quantitative information in the form of mean and percentage, whereas inferential statistics (multiple linear regressions and correlation) was taken from this tool.
The model built around two sets of variables, specifically dependent variable (organizational performance) and independent variables (employee’s safety strategies, social welfare strategies, accident prevention strategies, and health and safety training strategies). The basic objective of using regression equation on this study is to make the study more effective at explaining, understanding and predicting the stated variables. The following regression model is formulated with four independent variables and one dependent variable.
Model Specifications

Where,
Y = organizational performance
b1, b2, b3, b4 = coefficient of independent variables
X1= occupational health and safety strategy
X2 = social welfare strategy
X3 = accident prevention strategy
X4 = health and safety training strategy
£ = error
The significance of the analytical model is checked by the use of ANOVA statistical model which is analysis of variance and a multiple linear regression analysis were done to find out the relationship between occupational safety strategies and organizational performance. A pilot study was conducted to refine the methodology and test instrument such as a questionnaire before administering the final phase. Questionnaires were tested on potential respondents to make the data collecting instruments objective, relevant, suitable to the problem and reliable.
The closer the reliability coefficient to 1.00 is the better. In general, reliabilities below 0.60 are considered weak; those ranged from 0.60 to 0.80 are considered good and acceptable.
Results and Discussion
This Part presents the analysis and interpretation which carried out based on the data collected through questionnaire from respondents and interview made with administrative staffs of respective departments. From the total 112 questionnaire distributed to employees of Ethiopian electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, all questionnaires were returned and used for analysis. The study used descriptive statistics to present the frequency and the percentages of the gathered data on the effect of occupational health and safety strategies on organizational performance of electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia (Table 2).
| Table 2 Correlation Analysis Results | ||
| OSH strategies | Organization performance | |
| Pearson correlation | Sig. (2- tailed ) | |
| Health and safety strategies | .695** | .000** |
| Social welfare strategies | .841** | .000** |
| Accident prevention strategies | .867** | .000** |
| Health and safety training strategies | .477** | .000** |
Also the results of correlation analysis shows that all the independent variables i.e. health and safety strategies, social welfare strategies, accident prevention strategies, and health and safety trainings are positively and significantly correlated with the dependent variable i.e. organizational performance at 99 percent confidence level (P<0.01). The highest correlation is signified by accident prevention strategies focus(r=0.867), followed by social welfare strategies (r=0.841), occupational health and safety strategies (r=0.695) and health and safety training strategies (r=0.477). Regarding the reliability of the questionnaire illustrates that all the quaternaries were reliable with Cronbach's Alpha result 0.855 and acceptable.
Pearson’s r (the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient) is a statistic that measures the direction and strength of the linear relation between two variables that have been measured on an interval or ratio scale. Pearson’s r can range from values of +1.00 to −1.00, with the plus or minus indicating a positive or negative correlation, respectively Michael, (2014).
The absolute values of Pearson’s of .10 to .29 reflect a small association, .30 to .49 reflects a medium-sized association, and .50 to 1.00 represents a large association. Therefore the following Pearson Correlation allows us to estimate the strength of connection between determining factors (independent variables) and success factors (dependent variable). The result of correlation analysis results shows that all the independent variables was positively and significantly correlated with the dependent variable of organizational performance at 99 percent confidence level (P<0.01) (Michie and Williams, 2003). The highest correlation is signified by accident prevention strategies(r=0.867), followed by social welfare strategies (r=0.841), occupational health and safety strategies (r=0.695) and health and safety training (r=0.477) Based on Pearson test the accident prevention strategies with the organization performance has highest correlation this means the accident prevention strategies improve the organization performance, the electric corporation function become well performed. Therefore the accident prevention strategies have power to determine the organization performance in corporation.
Regression Analysis
The below Table 3 indicates that the multiple linear regression models revealed that 81 % of independent variable in the dependent variability on the study affects the organization performance. The p-value is equal to 0.000<0.05. This indicates the dependent variable used in the linear regression is affecting the occupational health and safety strategies in the organization performance. All independent variables were statistically significant. However the variables those affecting the organization performance in well- functioning are in positive effect on corporation.
| Table 3 The Coefficients Table of Multiple Regression Analysis Coefficients | |||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coeff-icients | Standardized Coefficients | T | Sig. | |
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| (Constant) | 0.240 | 0.170 | 1.408 | 0.162 | |
| Occupation health and safety strategy |
0.155 | 0.046 | 0.188 | 3.375 | 0.001 |
| Social welfare strategy | 0.226 | 0.088 | 0.237 | 2.565 | 0.012 |
| Accident prevention strategy |
0.506 | 0.094 | 0.492 | 5.367 | 0.000 |
| Health and safety training strategy |
0.076 | 0.030 | 0.126 | 2.582 | 0.011 |
The Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) results of the regression between Independent variables and organization performance shows the probability value of 0.000 (p<0.05) indicates that occupational health and safety strategies was statistically significant in predicting organizational performance. In order to ensure the content validity, discussion with experts in area was made. Regarding the right to privacy of the respondents, all participants were briefed about the research and joined with their full consent, maintained the confidentiality of the identity of each participant and also the researcher reported the findings in complete honesty.
According to model summery of multiple regression analysis, the R value of the model as shown Was 0.904 which shows the highest degree of relationship between independent and dependent variables (Table 4). The adjusted R2 value of the regression model was 0.810 indicates that 81% of variance in affecting the organization performance was accounted by occupational health and safety strategies, social welfare strategies, accident prevention strategies and health and safety training strategies.
| Table 4 Model Summary | |||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | Durbin-Watson |
| 1 | 0.904 | 0.817 | 0.810 | 0.21251 | 1.855 |
It is apparent that the regression model was significant using between the independent variables and organization performance. An F statistic of 119.405 and a probability value of 0.000 clearly indicate that the model was significant or healthy (Table 5).
| Table 5 Anova | ||||||
| Model | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 21.570 | 4 | 5.392 | 119.405 | 0.000 |
| Residual | 4.832 | 107 | 0.045 | |||
| Total | 26.402 | 111 | ||||
Conclusion and Recommendations
From the total 112 questionnaire distributed to employees of Ethiopian electric power corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, all questionnaires were used in the data analysis. Also the results of correlation analysis shows that all the independent variables i.e. health and safety strategies, social welfare strategies, accident prevention strategies, and health and safety trainings are positively and significantly correlated with the dependent variable i.e. organizational performance at 99 percent confidence level (P<0.01). The highest correlation is signified by accident prevention strategies focus(r=0.867), followed by social welfare strategies (r=0.841), occupational health and safety strategies (r=0. 695) and health and safety training strategies (r=0.477). Regarding the reliability of the questionnaire illustrates that all the quaternaries were reliable with Cronbach's Alpha result 0.855 and acceptable.
Based on Multiple Regression Coefficients Result, the beta coefficient value of health and safety strategies is 188 which shows as health and safety strategies increase by 1% organization performance will increase by 18.8% keeping other factors constant. Also when social welfare strategies increase by 1% organization performance will increase by 23.7%. When accident prevention strategies increase by 1% organization performance will increase by 49.2%The same health and safety training increase by 1% of organization performance will increase by 12.6%generally when occupational health and safety strategies (OHS) increase by 1% organization performance will increase by 90.4% keeping other factors constant.
For clarity purpose, the conclusions are based on the research objectives of the study and recommendations are made to Ethiopia Electric Power Corporation in Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia based on the findings of the study.
The multiple regression analysis notifies that in Ethiopian electric power corporation Wolaita Sodo district more than eighty percent (80%) variance of organization performance is attributed. Therefore, the researcher can convincingly conclude that the independent variables occupational health and safety strategies, social welfare strategies, accident prevention strategies and health and safety training strategies has a positive and significant influence on the dependent variable of organization performance in electric corporation of Wolaita Sodo district, Ethiopia.
By relying on the study findings, the researcher initiated to provide the following recommendations for responsible body:
The researcher recommends that it is recommendable that Wolaita Sodo district Electric Corporation administrative and employees strive becomes role model for their customers regarding to the significance of occupational health and safety strategies on improving organizational performance.
The corporation should improve the stage of health and safety training by enabling ongoing and two-way communication, good organization practice, well trained and motivated employees, successful dissemination of knowledge detail knowledge of every procedures and ability to enhance organizational performance.
The study further recommends that corporation has to Continuous improvement of occupational safety and health should be promoted. This is necessary to ensure that electric company health and safety policy, regulations and technical standards to prevent occupational injuries, diseases and deaths are adapted periodically to social, technical and scientific progress and other changes in the world of work.
References
Armstrong, M. (2012). Strategic human resource management practice. Kogan Page, London.
Jane, W., & Esther, W. (2017). Influence of occupational health and safety on employees performance in flower industry in Kenya. Journal of Strategic Business and Change Management, 3(3), 191-208.
McCunney, R.A. (1994). Practical approach to occupational health and environment Medicine. Environmental health.
Ojiem, D. O. (2012). Occupational health and safety management practices among the electronic media houses in Kisumu County, Kenya. Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi.
Taderera, H. (2012). Occupational health and safety management systems: Institutional and regulatory frameworks in Zimbabwe. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 2(4), 99-114.