Research Article: 2023 Vol: 26 Issue: 2
Effect of Value Creation and Adaptive Capacity to Transformation, with Organizational Performance as An Intervening Variable
Furtasan Ali Yusuf, University of Bina Bangsa
Basrowi, University of Bina Bangsa
Citation Information: Ali Yusuf, F., & Basrowi. (2023). Effect of value creation and adaptive capacity to transformation, with organizational performance as an intervening variable. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 26 (2), 1-18.
Abstract
Keywords
Higher Education Performance, Value Creation, Adaptive Capacity, Transformation of Private Universities.
Introduction
The world of higher education, especially private higher education, really needs institutional transformation to obtain a more meaningful national education order in accordance with the demands of the times and generations. This is marked by changes in several private universities (PTS) changing their status from high schools or institutes to transforming into universities. The idea of changing the status of this university, began with a change in the status of various private universities (PTS), especially in the city of Serang. Suprayogo & Rasmianto mentions that there are several strong reasons why universities change their status to universities, including: (1) To provide wider opportunities for structuring higher education. (2) So that University graduates can access a wider world of employment. (3) To increase the dignity of higher education institutions so that they are equal to the dignity of public universities.
According to Fadjar the birth of the University is an effort to renew, sharpen, and emphasize the existence of education in the field of service to basic needs for humans, namely presentative education. Also as a model of scientific reintegration aimed at one form of development, improvement, and strengthening of professional academic status. The university is predicted to be a model of an education system that has high quality compared to before the status transfer to a university that has the same status, role, and function, besides having wider autonomy both in academic development, management, and administration.
According to Suprayogo, higher education institutions in order to progress and have a competitive advantage must be able to develop the following: 1) a clear vision, mission, core values, core belief; 2) clear and directed planning; 3) Strong leadership; 4) strong and broad networking; 5) support from all parties, namely the government and the community including alumni; 6) strong and broad sources of funding; and 7) strong commitment and enthusiasm from all existing components.
From the description above, it can be concluded that to become a competitive university as an effort to maintain existence in this competitive era, universities are required to have the will, willingness, and ability to carry out reformulation, revitalization, and reorientation and transformation as a whole, both at its fair, structural and operational aspects. Universities that are not able to do it all, sooner or later will be abandoned by the community because they are unable to compete.
The organizational transformation agenda is characterized by changes in business practices that are oriented towards significant performance leaps. These changes are a response to the rapid dynamics of the organization's external environment which must also be responded quickly from the internal side. Organizational transformation is a must for organizations that want sustainable growth (Handoko, 2012). Organizational transformation has an impact on competitiveness and business performance (McKeown & Philip, 2003). The company is carrying out business transformation amid the acceleration of economic dynamics as a result of globalization, technological advances, government regulations, and ever-changing consumer preferences. Therefore, organizations must develop their capacity to review work patterns, organizational values, and strategies so that these components can be transformed into new organizational life that is able to respond to organizational changes and challenges.
In Indonesia, organizational transformation in public organizations is generally carried out through flexibility in governance with the organization. Therefore, the proposition is that the innovation ecosystem affects the adaptive capacity of the company. The adaptive capacity of companies is related to their ambidexterity (Lange & Schüßler, 2018). Indeed, the sustainability of the innovation ecosystem stems from continuous improvements in value creation and the ability of companies to reorganize and adapt to changing markets and technologies. Thus, the innovation ecosystem requires exploitation and exploration capabilities in order to remain sustainable.
Disclosure of disruptive innovation is a signal of strategy, adaptive power, value creation, and sustainability of an institution or organization. Activities related to revolutionary innovations can provide a plus for the reputation of the institution or company, because it is related to adaptive power, value creation, and sustainability of an institution or organization. This potential, both financial potential and non-financial potential (including those that are intangible), plays an important role in increasing the level of sustainability of the Institution. Therefore, it is important to continue to communicate (including voluntary disclosure) with all stakeholders.
This study uses a theory that is believed to provide answers to the creation of competitive advantage and value creation for an institution, known as the Resources-Based View (RBV) (Barney, 2001). Globalization and advances in science, knowledge and technology have changed human behavior in an effort to meet various needs. Advances in information and communication technology bring people in any part of the world to easily and quickly obtain information and communicate in all things. Humans as customers of various goods and services are now becoming more thorough because they have extensive and up-to-date information. As a result, organizations need to adapt to the dynamics of the environment through changes that are in accordance with the strengths and needs of the organization.
Any organization or institution must make the right choice of organizational change model, because not all organizational change models offered by various parties can be implemented in all organizational forms, because it depends on the field of activity, size or size of the organization, capabilities, and organizational environment. Organizational transformation or change is a challenge that requires the organization to develop its ability to adapt to the external environment, and integrate it within by empowering its own resources, especially human resources as the most important asset of the organization. Organizational transformation aims to improve organizational capabilities in accordance with the demands of the business environment (Sisibintari, 2015).
The transformation that occurs requires institutions as an appropriate instrument in providing a framework for interpreting information into usable knowledge and enabling individuals and groups to create coordination, social interaction, and establish boundaries in the interaction process (Hudson, 1988; North, 1990). Institutions are generally recognized as a form of organizational structure for policy and legal scope (policies, laws, procedures, both formal and informal) and include the processes and mechanisms of planning, decision making, coordination, and negotiation.
Dessler (2000) suggests that changes in the organizational environment will affect the role of human resource management in the organization. Today's organizations are required to put more emphasis on the ability to work better, faster and more competitively. Meyerson explained that organizational change can be carried out in two ways, namely drastic action and evolutionary adaptation. Drastic action change, is a discontinuous change and will deal with the organization or top management tasks. In a situation, change may occur quickly and always result in significant difficulties. While evolutionary change is a step by step change, decentralized and does not require upheaval. These two approaches encourage organizations to have a future-oriented culture of change. The choice of whether change is made by drastic action, or evolution depends on the capabilities, needs, and market size of the organization.
Basically every organization must be able to develop its capabilities in anticipating environmental changes by actively looking at the future of the organization. Changes in one environmental element or simultaneously will interfere with the existence of other environments. Change can take the form of various areas of the organization depending on the size of the organization and the type of activity. Stoner (1995) states that there are three important areas of change, namely, technology, structure, and people. Whereas Robbins & Judge add one more field that is spatial. Organizations must be able to develop their capabilities in anticipating environmental trends by actively looking at the future of the organization.
Morgan in his book, Riding the Waves of Change, calls it Proactive Mindsest, namely the activities: 1) Looking ahead; 2) Identify problems and opportunities; 3) Find ways to overcome negative problems and open up opportunities for organizational development; and 4) Understanding, determining, and developing opportunities that can be implemented. To realize the four proactive thoughts, organizations must improve the attitudes and capabilities of their human resources by positioning and repositioning their capabilities.
Organizational change can be understood as organizational operational changes in an effort to adjust the dynamics of the organizational environment. Human resources are capital which is one of the important determinants of the success or failure of the overall organizational performance. The process of organizational transformation will face various challenges caused by interests both organizationally and individually which can be in the form of rejection. Considerations of organizational resistance include structural, work groups, expertise, power relations, and the allocation of established resources. While individual rejection includes factors of habit or establishment, ignorance, position, and reluctance.
Constructive and exploratory action by combining the required resources and capabilities both from within and outside the organization will enable the company to create value. From the point of view of the study, valuable resources are the result of elaboration between internal and external factors including access to information Schmidt & Keil (2013) which are complementary by combining relevant information and then exploiting it based on the knowledge and experience of the organization. In this context, information which is then processed into knowledge of customers becomes an important basic ingredient in generating value or value creation.
Previous studies have done a lot of research on the transformation of an organization has been done. One of the research conducted by El-Haddadeh et al. (2021); Mavri et al. (2021) which explains that in transforming an institution or institution is significantly influenced by value creation. Therefore, the important role of value creation in a developing institution is very necessary. However, another study conducted by Gero et al. (2015) and Minucci explained that the effect of value creation is not significant on the transformation of an institution or institution.
Besides that Sehrsweeney & Fischer (2022); Zhang (2021) in his research explains that adaptive capacity can significantly affect the transformation of an institution or institution. This is also a reference in transforming an institution, so the adaptive capacity in the university must be considered. However, in contrast to the findings of research conducted by Giezen and which explains that adaptive capacity does not significantly affect the transformation of an institution.
From several previous research findings, there are still inconsistencies in the research, therefore this research is considered feasible to be carried out in order to become a reference for private universities that specifically want to change their status to become a university.
The novelty of this research is to find the effectiveness of organizational performance variables as intervening variables, especially in mediating the effect of value creation and adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities.
Research Question are
1. How is the effect of value creation on the organizational performance of private universities in Banten,
2. How is the influence of adaptive capacity on the organizational performance of private universities in Banten,
3. What is the effect of value creation on the transformation of private universities in Banten,
4. How is the influence of adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Banten,
5. How is the influence of higher education performance on the transformation of private universities in Banten,
6. What is the indirect effect of value creation on the transformation of higher education through the performance of private universities in Banten
7. How is the indirect effect of adaptive capacity on the transformation of higher education through the performance of private universities in Banten
Theory
The effect of value creation on organizational performance
Value creationis a determinant of the performance of an institution/organization. Aspara & Tikkanen (2013) revealed that value creation refers to the empowerment of the value generated or the value benefits of the institution's offering for users having a positive impact on the performance of the institution. Study conducted by Killa find the important role of value creation in bridging risk-taking orientation in encouraging the improvement of an institution's performance. The study of value is often associated with satisfaction and service quality which will ultimately lead to user behavior itself. Abdullah & Rosliyati (2020) found that value creation capability is a variable that affects the performance of an institution stronger than product strategy and competitive advantage itself.
On the other hand, Rahman et al., (2016) revealing the role of value creation in an organization resulting from acquisitions and mergers will have an impact on increasing differentiation and cost efficiency which in turn will have an impact on improving institutional performance. The findings of research conducted by El-Haddadeh et al. (2021); Mavri et al. (2021) which explains that value creation significantly affects organizational performance. In addition it is confirmed and strengthened by research conducted by Elia et al. (2022); Kim et al. (2020) who also explained that the importance of value creation in an organization, where value creation plays an important role in building good performance in an organization. Therefore, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
H1: It is suspected that there is an influence of value creation on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
Effect of Adaptive Capacity on Organizational Performance
This research also focuses on the component of adaptive capacity, which can be defined as the ability to respond to challenges through learning, risk and impact management, developing knowledge and formulating effective approaches (Marshall et al., 2010). Then according to Walker adaptive capacity is broadly defined as the ability of a socio-ecological system (or components of that system) to be resilient to disturbances and able to respond to change (Walker et al., 2006).
Adaptive capacity is the ability of a social system to remain ready and resilient in the face of shocks and respond to changes from internal and external factors (Plummer & Armitage, 2010). Adaptive ability is also seen as the resilience, stability, and flexibility of the social system's resilience from threats or dangers that can adapt to the environment. The process of developing adaptive capacity is also determined through the use of resources or potential as well as modification of institutional systems and rules or norms. The term adaptive capacity is used in this study to measure the extent to which a private university is resilient in the face of change or a particular shock. In this context, how does a set of laws, institutions and regulations regarding organizational performance have an adaptive capacity to situations that have a significant impact on various dimensions of life.
From the various statements above, it can be seen that the important role of adaptive capacity in the performance of an organization is something that must be considered. Because in overcoming certain unfavorable circumstances for the organization, the role of adaptive capacity is very important for the stability of an organization or institution. The findings of research conducted by Kang et al. (2022); Rinsky-Halivni et al. (2022); Zhang (2021) and Zheng et al. (2022) which shows that adaptive capacity can significantly affect organizational performance. Therefore, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
H2: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
The Effect of Value Creation on the Transformation of Higher Education
The essence of value creation is an effort to create a "new offer" to the market. The new offer consists of: core offer, expected features, added features, and symbolic features. Core features are the main products offered by the company to the market as a potential exchange. Expected features are additional features/services provided by the company to its customers that are not expected by the customer in principle. These added features can be used by companies to differentiate the products offered by competitors' products. While symbolic features are efforts to provide emotional benefits to customers, such as: brand name, country of origin, symbolic status, feeling of pride as a member of a particular community/social group.
Value creation is also an organization's ability to provide new benefits to consumers, by using the organization's core advantages as an alternative to focusing on customers, domains, and the organization's partner network.
So in this case value creation is very important in supporting the transformation of an institution/organization. In essence, the better the value creation in an institution/organization, the change in an institution to a better direction is also very well-opened. The findings of research conducted by Chiu & Lin (2022); Mavri et al. (2021) which shows that value creation significantly affects the transformation of an institution/organization. Therefore, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
H3: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
The Influence of Adaptive Capacity on the Transformation of Higher Education
Adaptive capacity to strategically adjust thinking and actions in response to changing circumstances based on relevant knowledge and better understanding. Adaptive capacity relies on networks that connect individuals, organizations, institutions, and institutions at different levels of the organization. The principle of adaptive management in critical security of complex organizations contributes to safety management by bringing ideas from the theory of organizational complexity. Organizations as complex adaptive systems have focused on how to generate new innovations or how to increase effectiveness.
Adaptive is a form of organizational response to changes and differences that occur in the environment. Organizational adaptation design can be in the form of company maneuvers in the face of change, both internal organizational changes, new technologies and market competition. The dynamics of the interaction between organizations and the market to suit the changing environment need to be adapted by senior management at the company level to achieve a better fit. The adaptation process requires several stages with incremental changes in response to changes in environmental conditions. Adaptability is used to identify and take advantage of emerging markets and technologies as indicated by changes in the company's posture (Plugge et al., 2016).
The success of an organization to meet the demands of the environment, requires the organization to have the resources and skills that become the adaptive capacity in adapting to the dynamics, turbulence and complexity of the environment. Environmental dynamics reflect unpredictable changes or environmental instability and are difficult to predict. The complexity of the environment reflects the geographical distribution of activities. A turbulent environment is described as a turbulent environment in which the interaction effects of complexity and rate of acceleration exceed the predictive capacity of the organizational system on the environment. Environmental shifts and turbulence require the development of dynamic adaptation processes and adaptive response mechanisms (Vohra, 2011).
The findings of this study conducted by Sehrsweeney & Fischer (2022); Zhang (2021) explained that adaptive capacity has a significant effect on the transformation of an institution. The role of adaptive capacity in the progress of an institution is very necessary considering that adaptive capacity is a very important role, especially in the transformation of a higher education institution that specifically transfers functions from a high school or institute to a university. Therefore, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
H4: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
The Influence of Higher Education Performance on the Transformation of Higher Education
Transformation in an institution or an organization is the dynamics of the environment of profit and non-profit organizations such as competition, globalization, market changes, and technology which are continuously the principal reasons for organizational transformation to improve human resource capabilities. Beer argues, as a consequence of environmental changes, organizations must find themselves in managing human resources continuously. The hierarchical bureaucratic organization was replaced with a flat and open organization. More importantly, organizations must improve their capabilities in order to be competitive. This statement indicates that transformation or also referred to as organizational change is the basis for improving the quality of human resources in the face of a wave of change.
Poerwanto explained that the organization in the present and in the future whatever the form and type of activity will continue to face change and change itself. The needs of individual life will affect the needs of the organization where the individual works and or vice versa. The individuals and organizations in which people work are two inseparable sides of the same coin, both of which require change. Furthermore, Poerwanto explained that organizations are now facing the challenges of global change in various aspects of life that will never stop. Consequently, every organization must be able to anticipate and adapt to changes that occur in its environment or the organization concerned changes its operating system through innovations that are relevant to the needs of its existence.
The findings of research conducted by, Gao et al. (2021); Islam et al. (2021); Moran et al. (2021) revealed that the performance of an organization is highly correlated with the transformation of an institution or organization, because the progress or decline of an organization depends on the performance of the human resources of each institution itself. Therefore, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
H5: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
H6: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on organizational performance through the performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
H7: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on organizational performance through the performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
Method
Research Design
The type of research used in this research is quantitative research with a structural equation modelling (SEM) approach.
Population and Sample
The population of private universities that have transformed/transferred status to universities in Serang City, Banten Province, Indonesia is 5. Determination of the sample for this study uses saturation sampling, which uses the entire research population as a sample.
Data and Data Collection Methods
Primary data was obtained by using a questionnaire which was developed based on the dimensions and indicators that have been put forward by the experts. These dimensions and indicators are then compiled into a questionnaire which is distributed to all predetermined samples.
Validity and Reliability Test
The cross loading value shows the magnitude of the correlation between each construct and its indicators and indicators from other block constructs. A measurement model has good discriminant validity if the correlation between the construct and its indicators is higher than the correlation with indicators from other block constructs. After processing the data using Smart PLS 3.0 the results Table 1.
| Table 1 Discriminant Validity Cross Loading |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | Y | Z | |
| KO1 | 0.518 | 0.635 | 0.756 | 0.860 |
| KO2 | 0.550 | 0.626 | 0.810 | 0.776 |
| KO3 | 0.454 | 0.549 | 0.647 | 0.770 |
| KO4 | 0.544 | 0.603 | 0.687 | 0.792 |
| KO5 | 0.462 | 0.604 | 0.737 | 0.817 |
| KO6 | 0.432 | 0.560 | 0.683 | 0.782 |
| KO7 | 0.392 | 0.531 | 0.659 | 0.760 |
| AC1 | 0.467 | 0.884 | 0.643 | 0.645 |
| AC10 | 0.419 | 0.733 | 0.549 | 0.559 |
| AC2 | 0.534 | 0.968 | 0.715 | 0.700 |
| AC3 | 0.479 | 0.872 | 0.698 | 0.652 |
| AC4 | 0.543 | 0.879 | 0.628 | 0.649 |
| AC5 | 0.559 | 0.824 | 0.681 | 0.660 |
| AC6 | 0.505 | 0.874 | 0.642 | 0.648 |
| AC7 | 0.504 | 0.785 | 0.625 | 0.587 |
| AC8 | 0.360 | 0.710 | 0.500 | 0.483 |
| AC9 | 0.445 | 0.775 | 0.558 | 0.567 |
| VC1 | 0.822 | 0.507 | 0.550 | 0.546 |
| VC2 | 0.814 | 0.447 | 0.422 | 0.418 |
| VC3 | 0.814 | 0.486 | 0.542 | 0.552 |
| VC4 | 0.747 | 0.319 | 0.375 | 0.368 |
| VC5 | 0.786 | 0.449 | 0.477 | 0.446 |
| VC6 | 0.740 | 0.484 | 0.462 | 0.473 |
| VC7 | 0.807 | 0.494 | 0.493 | 0.465 |
| VC8 | 0.749 | 0.428 | 0.491 | 0.492 |
| TPT1 | 0.442 | 0.559 | 0.798 | 0.746 |
| TPT2 | 0.538 | 0.603 | 0.790 | 0.731 |
| TPT3 | 0.450 | 0.543 | 0.751 | 0.660 |
| TPT4 | 0.546 | 0.638 | 0.793 | 0.703 |
| TPT5 | 0.425 | 0.572 | 0.741 | 0.642 |
| TPT6 | 0.433 | 0.571 | 0.760 | 0.682 |
The cross loading results show that the correlation value of the construct with its indicators is greater than the correlation value with other constructs. Thus, all constructs or latent variables already have good discriminant validity, where the indicators in the construct indicator block are better than indicators in other blocks.
Reliability Test
In this study, the reliability test was carried out using composite reliability and Cronbach's alpha. The following is the result of the calculation of composite reliability.
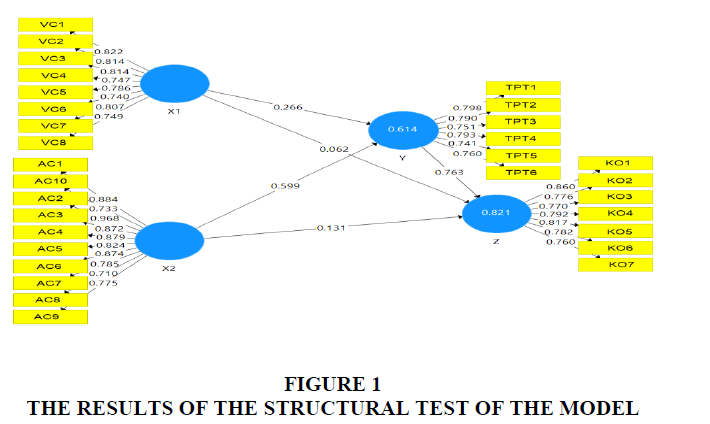
From the results of composite reliability as shown in the table 2 above, it can be seen that all composite reliability values in each construct have a value greater than 0.7, which means that all constructs are reliable Figure 1.
| Table 2 Composite Reliability |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cronbach's Alpha | rho_A | Composite Reliability | AverageVariance Extracted (AVE) | |
| X X1 | 0.911 | 0.916 | 0.928 | 0.617 |
| X X2 | 0.950 | 0.955 | 0.958 | 0.695 |
| Y Y | 0.865 | 0.866 | 0.899 | 0.597 |
| Z Z | 0.902 | 0.905 | 0.923 | 0.631 |
Result
Test the First Hypothesis
H0:1= 0:H1: It is suspected that there is an influence of value creation on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia Figure 2.
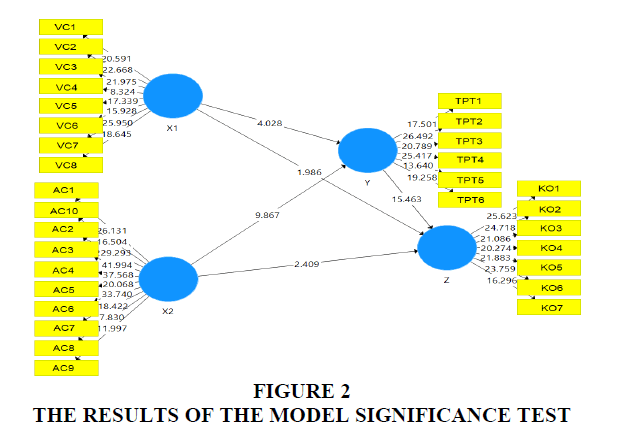
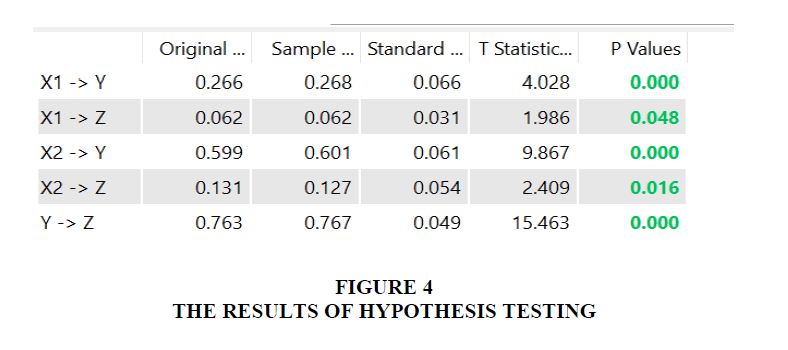
The first hypothesis examines whether there is a direct influence between value creation on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia. From the results of hypothesis testing, the coefficient R2 is 0.266 with a t-statistic of 4.028 > 1.96 with a p-value of 0.000 <0.05, so Ho1 is rejected and Ha1 is accepted. There is a significant direct effect between value creation on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia Figure 3.
Second Hypothesis Test
H0:2 = 0 : It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
The second hypothesis examines whether there is a direct influence between adaptive capacity on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia. From the results of hypothesis testing, the coefficient R2 is 0.599 with a t-statistic of 9.867 > 1.96 with a p-value of 0.000 <0.05, so Ho2 is rejected and Ha2 is accepted. There is a significant direct influence between adaptive capacity on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
Third Hypothesis Test
H0:3 = 0: It is suspected that there is an influence of value creation on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
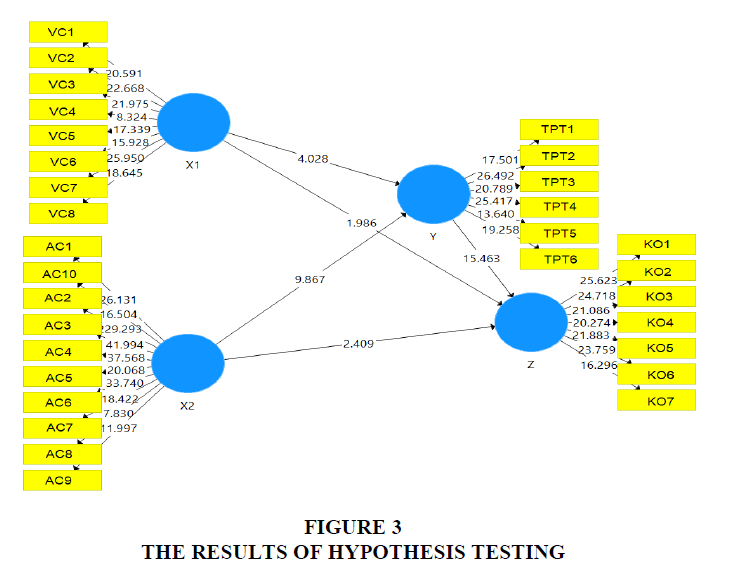
The third hypothesis examines whether there is a direct influence between adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia. From the results of hypothesis testing, the coefficient R2 is 0.062 with a t-statistic of 1.986 > 1.96 with a p-value of 0.000 < 0.048, so Ho3 is rejected and Ha3 is accepted. There is a significant direct influence between adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia, Figure 4.
Fourth Hypothesis Test
H0:4 = 0: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
The fourth hypothesis examines whether there is a direct influence between adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia. From the results of the hypothesis test, the coefficient R2 is 0.131 with a t-statistic of 2.409 > 1.96 with a p-value of 0.000 <0.05, so Ho4 is rejected and Ha4 is accepted. There is a significant direct influence between adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
Fifth Hypothesis Test
H0:5 = 0: It is suspected that there is an influence of organizational performance on transformation private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
The fifth hypothesis examines whether there is a direct effect of adaptive capacity on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia. From the results of the hypothesis test, the coefficient R2 is 0.763 with a t-statistic of 15.463 > 1.96 with a p-value of 0.000 <0.05, so Ho5 is rejected and Ha5 is accepted. There is a significant direct influence between adaptive capacity on organizational performance at private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia Figure 5.
Sixth Hypothesis Test
H0:6 = 0: It is suspected that there is an effect of value creation on the transformation universities through the organizational performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
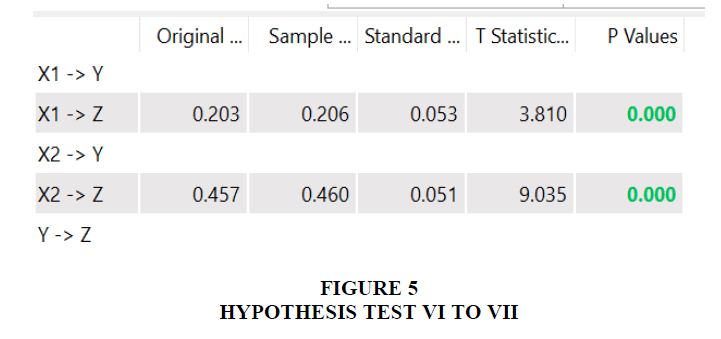
The sixth hypothesis examines whether there is an indirect effect between value creation on the transformation of universities through the organizational performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia. From the results of hypothesis testing, the coefficient R2 is 0.203 with a t-statistic of 3.810 > 1.96 with a p-value of 0.003 < 0.05, so Ho6 is rejected and Ha6 is accepted. There is a significant indirect effect between value creation on the transformation of universities through the organizational performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
The seventh hypothesis test
H0:7 = 0: It is suspected that there is an influence of adaptive capacity on the transformation universities through the organizational performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia
The seventh hypothesis examines whether there is an indirect effect between adaptive capacity on the transformation of universities through the organizational performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
From the results of hypothesis testing, the coefficient R2 is 0.457 with a t-statistic of 9.035 > 1.96 with a p-value of 0.002 < 0.05, so Ho7 is rejected and Ha7 is accepted. There is a significant indirect effect between adaptive capacity on the transformation of universities through the organizational performance of private universities in Serang Banten, Indonesia.
Discussion
The Effect of Value Creation on Organizational Performance
The output of the data analysis that has been carried out, it is found that the first hypothesis explains that value creation has a significant effect on organizational performance in a positive direction. This explains that, the higher the level of value creation in an institution or organization, the higher the level of performance of the institution. In other words, in maximizing organizational performance, the important role of value creation in an organization becomes a very important concern in the progress of an institution.
Aspara & Tikkanen (2013) revealed that value creation refers to the empowerment of the value generated or the value benefits of the institution's offering for users having a positive impact on the performance of the institution. Study conducted by Killa find the important role of value creation in bridging risk-taking orientation in encouraging the improvement of an institution's performance. The study of value is often associated with satisfaction and service quality which will ultimately lead to user behavior itself. Abdullah & Rosliyati (2020) found that value creation capability is a variable that affects the performance of an institution stronger than product strategy and competitive advantage itself.
This research is in line with research conducted by El-Haddadeh et al. (2021); Mavri et al. (2021) which explains that value creation significantly affects organizational performance. In addition, it is confirmed and corroborated the research conducted by Elia et al. (2022); Kim et al. (2020) who also explained that the importance of value creation in an organization, where value creation plays an important role in building good performance in organizational performance. In improving optimal institutional performance, especially private universities, value creation needs an important role in doing so. The creation of a value is seen as very important in improving the performance of the institution, considering that the value creation of employees can become the image of the university.
Effect of Adaptive Capacity on Organizational Performance
The output of the data analysis that has been carried out, it is found that the second hypothesis explains that adaptive capacity has a significant effect on organizational performance in a positive direction. This explains that, the higher the level of adaptive capacity in an institution or organization, the higher the level of performance of the institution. In other words, in maximizing organizational performance, the important role of adaptive capacity in an organization becomes a very important concern in the progress of an institution. Adaptive capacity is the ability of a social system to remain ready and resilient in the face of shocks and respond to changes from internal and external factors. Adaptive ability is also seen as the resilience, stability, and flexibility of the social system's resilience from threats or dangers that can adapt to the environment.
The process of developing adaptive capacity is also determined through the use of resources or potential as well as modification of institutional systems and rules or norms. The term adaptive capacity is used in this study to measure the extent to which a private university is resilient in the face of change or a particular shock. In this context, how does a set of laws, institutions and regulations regarding organizational performance have an adaptive capacity to situations that have a significant impact on various dimensions of life. This research is in line with the research conducted by Kang et al., (2022); Rinsky-Halivni et al., (2022); Zhang (2021) which shows that adaptive capacity can significantly affect organizational performance.
The Influence of Value Creation on the Transformation of Universities
The output of the data analysis that has been carried out, it is found that the third hypothesis explains that value creation has a significant effect on the transformation of higher education in a positive direction. This explains that, the better the level of value creation in an institution or organization, the better the transformation of the university in the progress of the institution. In other words, in the transformation of universities to universities, the important role of value creation in an organization becomes a very important concern in the progress of an institution. Value creation is also an organization's ability to provide new benefits to consumers, by using the organization's core advantages as an alternative to focusing on customers, domains.
This research is in line with research conducted by Chiu & Lin (2022); Mavri et al. (2021) which shows that value creation significantly affects the transformation of an institution/organization. It is clear that the role of value creation in transformation, especially in private universities in Serang, Banten, is very important, because if a university has excellent value creation, the image of the university can be raised well too, which allows private universities to transform or change the status of the college into a university.
The Influence of Adaptive Capacity on the Transformation of Higher Education
The output of the data analysis that has been carried out, it is found that the fourth hypothesis explains that adaptive capacity has a significant effect on the transformation of higher education in a positive direction. This explains that, the better the level of adaptive capacity in an institution or organization, the better the transformation of the university in the progress of the institution. In other words, in the transformation of universities to universities, the important role of adaptive capacity in an organization becomes a very important concern in the progress of an institution.
Adaptive is a form of organizational response to changes and differences that occur in the environment. Organizational adaptation design can be in the form of company maneuvers in the face of change, both internal organizational changes, new technologies and market competition. The dynamics of the interaction between organizations and the market to suit the changing environment need to be adapted by senior management at the company level to achieve a better fit. The adaptation process requires several stages with incremental changes in response to changes in environmental conditions. Adaptability is used to identify and take advantage of emerging markets and technologies as indicated by changes in the company's posture (Plugge et al., 2016).
The success of an organization to meet the demands of the environment, requires the organization to have the resources and skills that become the adaptive capacity in adapting to the dynamics, turbulence and complexity of the environment. Environmental dynamics reflect unpredictable changes or environmental instability and are difficult to predict. The complexity of the environment reflects the geographical distribution of activities. A turbulent environment is described as a turbulent environment in which the interaction effects of complexity and rate of acceleration exceed the predictive capacity of the organizational system on the environment. Environmental shifts and turbulence require the development of dynamic adaptation processes and adaptive response mechanisms (Vohra, 2011).
This research is confirmed and strengthens the research conducted by Sehrsweeney & Fischer (2022); Zhang (2021) which states that adaptive capacity has a significant effect on the transformation of an institution. The role of adaptive capacity in the progress of an institution is very necessary considering that adaptive capacity is a very important role, especially in the transformation of a higher education institution that specifically transfers functions from a high school or institute to a university.
The influence of higher education performance on the transformation of higher education The output of the data analysis that has been carried out, it is found that the fifth hypothesis explains that the performance of universities has a significant effect on the transformation of universities in a positive direction. This explains that, the better the level of performance at the tertiary institution, the better the transformation of the tertiary institution in the progress of the institution, which is specifically in terms of the status of the college carrying out the transfer of functions from a high school or institute to a university. In other words, in the transformation of private universities in Serang Banten to universities, the important role of higher education performance becomes a very important concern in the progress of an institution. Poerwanto explains that the organization in the present and in the future whatever the form and type of activity will continue to face change and change itself. The needs of individual life will affect the needs of the organization where the individual works and or vice versa. The individuals and organizations in which people work are two inseparable sides of the same coin, both of which require change. Furthermore, Poerwanto explained that organizations are now facing the challenges of global change in various aspects of life that will never stop.
Consequently, every organization must be able to anticipate and adapt to changes that occur in its environment or the organization concerned changes its operating system through innovations that are relevant to the needs of its existence. This research is in line with the study. previously suggested by Gao et al. (2021); Islam et al. (2021); Moran et al. (2021) and who explained that the performance of an organization is highly correlated with the transformation of an institution or organization, because the progress or decline of an organization depends on the performance of the human resources of each institution itself.
Conclusion
The results of the analysis show that the seven hypotheses analyzed are all significant, there is a direct effect of value creation on organizational performance, there is a direct effect of adaptive capacity on organizational performance, there is an effect of value creation on the transformation of higher education both directly and through higher education performance, there is an influence of adaptive capacity on transformation of tertiary institutions both directly and through the performance of universities and, there is a direct influence of the performance of universities on the transformation of universities. The novelty of this research is the discovery of the effective role of the intervening variable of higher education performance in mediating the effect of value creation and adaptive capacity on the transformation of private universities in Banten.
References
Abdullah, Y., & Rosliyati, A. (2020). The product market strategy, value creation, and competitive advantages as a determinant factor of marketing performance.Int. J Sup. Chain. Mgt Vol,9(3), 13.
Aspara, J., & Tikkanen, H. (2013). Creating novel consumer value vs. Capturing value: strategic emphases and financial performance implications.Journal of Business Research,66(5), 593-602.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Barney, J. B. (2001). Resource-based theories of competitive advantage: A ten-year retrospective on the resource-based view.Journal of management,27(6), 643-650.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chiu, M. L., & Lin, C. N. (2022). Developing supply chain open innovation capability: the mediating role of the knowledge creation process, governance mechanism and technology as a driver.Journal of Innovation & Knowledge,7(4), 100264.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dessler, G. (2000).Human resource management. Pearson Educación.
El-Haddadeh, R., Osmani, M., Hindi, N., & Fadlalla, A. (2021). Value creation for realising the sustainable development goals: Fostering organisational adoption of big data analytics.Journal of Business Research,131, 402-410.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Elia, G., Raguseo, E., Solazzo, G., & Pigni, F. (2022). Strategic business value from big data analytics: An empirical analysis of the mediating effects of value creation mechanisms.Information & Management,59(8), 103701.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gao, Y., Zhao, X., Xu, X., & Ma, F. (2021). A study on the cross level transformation from individual creativity to organizational creativity.Technological Forecasting and Social Change,171, 120958.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gero, A., Fletcher, S., Rumsey, M., Thiessen, J., Kuruppu, N., Buchan, J., ... & Willetts, J. (2015). Disasters and climate change in the pacific: adaptive capacity of humanitarian response organizations.Climate and Development,7(1), 35-46.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Handoko, TH. (2012). Personnel Management and Human Resources, Third Edition. BPFE Publisher. Yogyakarta.
Hudson, A. (1988).The premature reformation: wycliffite texts and lollard history. Clarendon Press.
Islam, M. N., Furuoka, F., & Idris, A. (2021). Mapping the relationship between transformational leadership, trust in leadership and employee championing behavior during organizational change.Asia Pacific Management Review,26(2), 95-102.
Kang, Y., Zhao, C., & Battisti, M. (2022). Organizational learning in SMEs’ internationalization: A moderated mediating effect of absorptive capacity.Long Range Planning, 102220.
Kim, D. W., Trimi, S., Hong, S. G., & Lim, S. (2020). Effects of co-creation on organizational performance of small and medium manufacturers.Journal of Business Research,109, 574-584.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lange, B., & Schüßler, E. (2018). Unpacking the middleground of creative cities: spatiotemporal dynamics in the configuration of the Berlin design field.Regional Studies,52(11), 1548-1558.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Marshall, N. A., Marshall, N. A., Marshall, P. A., Tamelander, J., Obura, D., Malleret-King, D., & Cinner, J. E. (2010).A framework for social adaptation to climate change: sustaining tropical coastal communitites [sic] and industries. iucn.
Mavri, A., Ioannou, A., & Loizides, F. (2021). Value creation and identity in cross-organizational communities of practice: A learner's perspective.The Internet and Higher Education,51, 100822.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
McKeown, I., & Philip, G. (2003). Business transformation, information technology and competitive strategies: learning to fly.International Journal of Information Management,23(1), 3-24.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Moran, V., Allen, P., Sanderson, M., McDermott, I., & Osipovic, D. (2021). Challenges of maintaining accountability in networks of health and care organisations: A study of developing Sustainability and Transformation Partnerships in the English National Health Service.Social Science & Medicine,268, 113512.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
North, D. C. (1990).Institutions, institutional change and economic performance. Cambridge university press.
Plugge, S., Landau, L. A., Sela, E., Altland, A., Flensberg, K., & Egger, R. (2016). Roadmap to Majorana surface codes.Physical Review B,94(17), 174514.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rahman, M., Lambkin, M., & Hussain, D. (2016). Value creation and appropriation following M&A: A data envelopment analysis.Journal of Business Research,69(12), 5628-5635.
Rinsky-Halivni, L., Hovav, B., Christiani, D. C., & Brammli-Greenberg, S. (2022). Aging workforce with reduced work capacity: From organizational challenges to successful accommodations sustaining productivity and well-being.Social Science & Medicine,312, 115369.
Schmidt, J., & Keil, T. (2013). What makes a resource valuable? Identifying the drivers of firm-idiosyncratic resource value.Academy of Management Review,38(2), 206-228.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sehrsweeney, M., & Fischer, A. P. (2022). Governing ecosystem adaptation: An investigation of adaptive capacity within environmental governance networks.Environmental Science & Policy,134, 46-56.
Sisibintari, I. (2015). Organizational transformation: the base for increasing human resources in strengthening competitiveness. Journal of Al-Azhar Indonesia Social Institution Series, 2(2), 119–132.
Stoner, J. A. (1995).Management. Pearson Education India.
Vohra, J. (2011). Diagnosis and management of Brugada syndrome.Heart, Lung and Circulation,20(12), 751-756.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Walker, B., Gunderson, L., Kinzig, A., Folke, C., Carpenter, S., & Schultz, L. (2006). A handful of heuristics and some propositions for understanding resilience in social-ecological systems.Ecology and society,11(1).
Zhang, F. (2021). Evaluating public organization performance under extreme weather events: Does organizational adaptive capacity matter?.Journal of Environmental Management,296, 113388.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 09-Nov-2022, Manuscript No.JMIDS-22-12836; Editor assigned: 12-Nov-2022, Pre QCNo. JMIDS-22-12836(PQ); Reviewed: 26-Nov-2022, QC No. JMIDS-22-12836; Revised: 19-Jan-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-22-12836(R); Published: 27-Jan-2023