Research Article: 2018 Vol: 21 Issue: 2
Effect of Entrepreneurship Education, Self Efficacy and Need for Achievement toward Student's Entrepreneurship Intention: Case Study in Febi, Iain Surakarta, Indonesia
Baidi, State Islamic Institute (IAIN) Surakarta
Suyatno, Ahmad Dahlan University Yogyakarta
Abstract
This study aims to determine the effect of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy, and need for achievement toward college-students’ entrepreneurship intention in Faculty of Islamic Economics and Business (FEBI), IAIN Surakarta, Indonesia. This research is a quantitative research. Data collection is by questionnaire given to 500 respondents. Data is processed through the test requirements and hypothesis test using SPSS 21 program. The result of the research shows that all questionnaire’s items are valid and reliable. Based on multiple linear regression analysis can be concluded:
1) entrepreneurship education has positive effect on entrepreneurship intention by 0,360.
2) self-efficacy has positive effect on entrepreneurship intention by 0.153.
3) need for achievement has positive effect on entrepreneurship intention by 0.183.
4) entrepreneurship education and self-efficacy simultaneously affecting entrepreneurship intentions by 20%;
5) entrepreneurship education and need for achievement simultaneously effect entrepreneurship intentions by 20.8%.
6) self-efficacy and need for achievement simultaneously affect the of entrepreneurship intention by 17.4%.
7) entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement simultaneously affect entrepreneurship intention by 62,8%.
Theoretical contribution of this research is to cultivate entrepreneurship intention, therefore entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy, and need for achievement need to be embed to college-students in college programmatically. The higher the entrepreneurship intention then economic progress of a society will increase.
Keywords
Entrepreneurship Education, Self-Efficacy Need for Achievement, Entrepreneurship Intention.
Introduction
There is a paradox about the increasing number of unemployment rate in Indonesia, when the largest unemployment rate is actually created by educated group. By percentage, unemployment rate of university graduates also increased from 5.34% in 2015, to 6.22% in 2016. The conditions faced will worsen with the global competition situation, the implementation of the ASEAN Economic Community (MEA) which will confront Indonesian university graduates to compete openly with graduates from foreign universities. Suharti & Sirine (2011) stated that college graduates need to be directed to not only as job seekers oriented but can and are ready to be work creator.
The cultivation of entrepreneurship to the younger generation needs to be improved. This is in accordance to the findings of Ernst & Young (2011) which revealed that more than half of success entrepreneurships start their business at the age of 20-29 years old. Education has an important role in fostering the entrepreneurship spirit (Hegarty, 2006). Ghina et al., (2017) stated that entrepreneurship education can produce highly educated businessman who has the potential to provide broader employment opportunities. The same thing is said by Kolvereid & Moen (1997) that college-students who graduated with entrepreneurship spirit tend to have entrepreneurship ambition and start new business compared to other students.
The cultivation of entrepreneurship to the younger generation needs to be improved. This is in accordance to the findings of Ernst & Young (2011) which revealed that more than half of success entrepreneurships start their business at the age of 20-29 years old. Education has an important role in fostering the entrepreneurship spirit (Hegarty, 2006). Ghina et al., (2017) stated that entrepreneurship education can produce highly educated businessman who has the potential to provide broader employment opportunities. The same thing is said by Kolvereid & Moen (1997) that college-students who graduated with entrepreneurship spirit tend to have entrepreneurship ambition and start new business compared to other students.
Some studies conducted by previous researchers have answered the question in detail such as;
1. Mueller’s (2008) research about what lecture characteristics are more effective in fostering entrepreneurship character;
2. Potishuk’s et al. (2017) research about the factors that stimulate college-students' entrepreneurship attitudes and intentions in universities;
3. Ramayah’s et al. (2012) research about the importance of prior experience in growing entrepreneurship attitudes;
4. Souitaris’ et al. (2007) research about the programs that can enhance entrepreneurship attitudes and intentions;
5. Bhat & Singh (2018) research about the relationship between entrepreneurial education with subjective norms in shaping perceptions and attitudes in entrepreneurship;
6. Melati et al. (2018) describe the different pattern of start-up business who have owned businesses in various fields as seen from their different economic backgrounds;
7. Khuong & Huu, An (2016) investigate about the influence of personal traits, previous entrepreneurial experience, external environment, social norms and perceived feasibility of entrepreneurial intention;
8. Aziz et al. (2018) examine how the relationship of entrepreneurship education to the career intention of female students.
This research examines the effect of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement in fostering college-students’ entrepreneurship intentions. Previous researches (Fayolle et al., 2005; Noel, 2001; Paco et al., 2012; Hassan & Wafa, 2012; Fayolle & Gailly, 2015; Bhat & Singh, 2018) proved the relationship between entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurship intention. Entrepreneurship education will increase college-students’ entrepreneurship intentions. According to Paulina & Wardoyo (2012), variables that can grow the intention are self-efficacy and need for achievement, so that educators are required to improve college students’ self-efficacy and the need for achievement through entrepreneurship education. Self-efficacy is person's belief in his ability to complete a job. Self-efficacy is also person's motivational condition based on what is believed rather than what is objectively true. This personal perception plays an important role in the development of person's intention (Indarti & Rostiani, 2008). While Lopepihie (2009) stated that self-efficacy is a strong personal belief in self-skills and abilities to start a task and lead it to success, self-efficacy is influenced by contextual factors such as education and past experience.
Previous researches have not been studied about the influence of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement simultaneously which are theoretically possibly interrelated and interplay. Whereas by knowing the relationship between those variables, it can be theoretical basis for stakeholders in determining and developing strategies and materials of entrepreneurship education in college. Based on the above problems, it is necessary to do research on the influence of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement toward college-students’ entrepreneurship intention. The purpose of this article is to understand the influence of entrepreneurship education (X1), self-efficacy (X2) and need for achievement (X3) on college-students’ entrepreneurship intention (Y). In detail, the questions asked in this research are:
1. Is there any influence of entrepreneurship education towards college-students’ entrepreneurship intention?
2. Is there any effect of self-efficacy towards entrepreneurship intention?
3. Is there any influence of need for achievement towards college-students’ entrepreneurship intention?
4. Is there any influence of entrepreneurship education and self-efficacy on college-students’ entrepreneurship intention?
5. Is there any influence of entrepreneurship education and need for achievement towards college-students’ entrepreneurship intention?
6. Is there any influence of self-efficacy and need for achievement toward college-students’ entrepreneurship intention?
7. Is there a simultaneous influence between entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement toward entrepreneurship intention?
Literature Review
Entrepreneurship Intention
A person who has desire to realize goals can be said to have an intention. Ajzen (2005) defined intention as a behavioural disposition until an attempt is made to translate intention into action. While Kusmintati et al. (2016) defined intention as indication of strong willingness of a person to try to do something and the amount of effort done to perform certain behaviours. Bird (1988) revealed that the entrepreneurship intention aims to create a new business or create new value to the business undertake. Therefore, intention can be interpreted as the sincerity of a person's motivation to perform an act or to bring up certain behaviour.
The sincerity of the motivation will be shown by sincerity in doing the deed. Bandura (1997) stated that intention is a determination to perform certain activities or produce certain situation in the future. Intention according to him is a vital part of self-regulation of individuals based by one's motivation to act. In this research, the act in question is an act of entrepreneurship. Intention has distinctive role in directing the action, then intention is the sincerity of a person's motivation to perform an act or bring out certain behaviour. In the context of entrepreneurship, intention can be interpreted as the intention or desire that exists in a person to perform an entrepreneurial action.
Factors that Affecting Entrepreneurship Intention
Intention in entrepreneurship can be influenced by various factors, both internal and external factors. Internal factors come from within the person such as attitude, will and ability of the individual that gives power to entrepreneurship. The external factors derived from outside of one-self in the form of family environment, socio-economic environment, business environment and others. According to Sumarsono (2013), factors affecting entrepreneurship intentions are: (1) personality factors consisting of need for achievement and self-efficacy, (2) contextual environmental factors, (3) demographic factors such as educational background, gender and background of the family.
Feist & Gregory (2011) stated that, humans who believe they can do something, have the potential to be able to change events in the environment, are more likely to act and are more likely to be successful than humans who have low self-efficacy. Furthermore, Bandura (1977) explained that human beliefs about self-efficacy affecting the form of action they will choose to do, how much effort they will give into this activity, how long they will survive in face obstacles and failures and their toughness endurens when faced with adversity. Entrepreneurship education and subjective norms have a positive relationship and combined of both have a greater influence than their individual influences (Fayolle & Gailly, 2015; Karimi et al., 2016).
The need for achievement becomes an encouragement of individual motivation in facing a challenge for achieving success (Lee, 1997). Furthermore, Indarti & Rostiani (2008) stated that the need for achievement as personality characteristic of a person that will motivate him to have entrepreneurship intention. According to him, there are three attributes attached to people with high need for achievement, which are (a) choosing personal responsibility in making decisions, (b) dare to take risks in accordance with their abilities and (c) have an interest to always learn from the decisions that have been taken. Similarly, the results of Scanipello (1989) study showed that a person with a high level of needs for achievement is less likely to accept failure than those with low needs for achievement. In other words, the need for achievement affects success or failure, so the need for achievement has a great influence in the success rate of an entrepreneurship. Furthermore, need for achievement can also encourage person's ability to take decisions and the courage to take risks as an entrepreneur. The higher the need for achievement of a person, it will be more and more appropriate decisions are taken.
Intention and Entrepreneurship Education
Lestari & dan Wijaya (2012) stated that entrepreneurship education is a learning process to change attitudes and mind-set of college-students towards the selection of entrepreneurship career. College-students who have taken entrepreneurship courses will have intrinsic values and entrepreneurship characteristics that will increase their interest and love for entrepreneurship world. According to Buchori (2011), entrepreneurship education and training are growing rapidly in Europe and the United States either in the training session or Universities. Entrepreneurship courses are given in the form of public lectures or in the form of study program concentration. Some courses have the following aim:
a) Understanding the role of company in the economic system,
b) The advantages and disadvantages of different kinds of company,
c) Knowing the characteristics and processes of entrepreneurship,
d) Understanding the product planning and process development,
e) Able to identify business opportunities and create creativity and establish cooperative organizations,
f) Able to identify and seek sources,
g) Understanding the basics of marketing, finance, organization, production,
h) Able to lead the business and face the challenges of the future.
Previous studies have shown a link between entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurship intention (Fayolle et al., 2005, Baybashaija et al., 2011). Hassan and Wafa (2012) suggested that the courage to take risks, as the characteristic of an entrepreneurship, have significant relation to the entrepreneurship intention. College graduates who get entrepreneurship education tend to start new businesses and have stronger entrepreneurship intentions more than other graduates (Kolvereid & Moen, 1997; Noel, 2001; Paco et al., 2012). Likewise, many studies have proven that Entrepreneurship Education significantly affects entrepreneurship intention (Uddin & Bose, 2012; Denanyoh et al., 2015; Jiying et al., 2014). Entrepreneurship education deals with the establishment of competencies in identifying new business opportunities and in addressing ambiguous decision making (Martin et al., 2015). Bae et al. (2014) explained that students who gain entrepreneurship education will improve their entrepreneurial skills so as to reduce the effect of gender of stereotypes.
Successful entrepreneurs in general are those who have competence, which are: Someone who has the knowledge, skills and individual qualities that include the attitudes, motivations, values and behaviour necessary to carry out the work/activities. Anwar (2014) mentioned that there are 10 competencies that must be owned by entrepreneur, which are:
1. Knowing your business,
2. Knowing the basic business,
3. Having the proper attitude,
4. Having adequate capital,
5. Managing finances effectively,
6. Managing time efficiently,
7. Managing people,
8. Satisfying customer by providing high quality product,
9. Knowing to compete,
10. Copying with regulation and paperwork.
While Daryanto (2012) mentioned some core concepts in entrepreneurship competence, which are: Core competencies describing leadership skills in a series of products; competency is a collection of skills and technology owned by companies to compete; competency is a skill that allows the company to provide fundamental benefits to customers; competency resources competitively are competitive uniqueness and give contribution towards value and cost.
Entrepreneurship education can be an important factor in growing and developing entrepreneurship spirit and behaviour among college-students. Related to the influence of entrepreneurship education, it needs an understanding on how to develop and encourage the birth of potential young entrepreneurs while they are still in college. Some previous research revealed that college-students’ desire of entrepreneurship become an investment and the source of the birth of young entrepreneurs (Suharti & Sirine, 2011). Their attitudes and knowledge of entrepreneurship will shape the tendency to open up new businesses in the future.
Intention and Self-efficacy
Self-efficacy is defined as belief that a person can achieve predetermined goal. King (2010) mentioned that, self-efficacy is an individual belief that he can master a situation and produce positive outcomes. Self-efficacy affects one's behaviour in everyday life. Influence caused by the existence of efficacy will make a person has good habits. According to Alwisol (2008), self-efficacy is self-perception on how well a person can work in a given situation. Self-efficacy relates to the belief that self has the ability to perform the expected action. Feist & Gregory (2011) stated that human who believe they can do something that have the potential to change events in their environment will be more likely to act and are more likely to be successful than humans who have low self-efficacy.
Self-efficacy is closely related to one's ability to success (Judge & Bono, 2001; Stajkovic & Luthans, 1998; Wood & Bandura, 1989). DeNoble, Jung & Ehrlich (1999) defined self-efficacy as a concept related to the force of new-borns entrepreneur to begin new business. Chen, Crick and Greene (1998) defined self-efficacy of entrepreneur as the level at which a person believes they have the ability to success in starting and running a business.
Indarti & Rostiani (2008) said that one's self-efficacy towards career that he will do describing the process of selection and adjustment to his career choices. The higher self-efficacy levels on entrepreneurship, then the stronger the entrepreneurship intention. Furthermore, Bandura (1977) explained that a person's beliefs about self-efficacy affects the form of action he will choose to do, how much effort he will give into this activity, how long they will survive in the facing obstacles and failure and his toughness to survive in difficult situations.
Indarti & Rostiani (2008) explained that self-efficacy of one's career is a domain that describes one's personal opinion in relation to the selection process and career adjustment. Thus, self-efficacy of one's career can be an important factor in determining whether one's entrepreneurship intention have been formed in the early stages of starting his career, so the higher the level of someone self-efficacy in entrepreneurship at the early stage in the career, the stronger the entrepreneurship intention he owned. Grilles and Rea (Indarti & Rostiani, 2008) proofed the importance of self-efficacy in decision-making process related to one's career.
The results of research by Grilles & Rea above concluded that self-efficacy proved to be a significant determinant of entrepreneurship intention. People who have strong belief that they are able to start and run entrepreneurship tend to have strong intention to start and run the business. Therefore, self-efficacy needs to be cultivated to college-students in order to form entrepreneurship intention.
Intention and the Need for Achievement
Need for achievement can be interpreted as unity of character that motivates a person to face the challenge in achieving success and excellence. Individuals who have high need for achievement will continue to work until something desired can be achieved. Mc Cleeland (Suryana, 2013) stated that the concept of need for achievement (N-ach) can be defined as the personality that causes the individual to want to do better and move on, always thinking of doing things better and setting realistic goals by taking risky action after calculating the impact of the decision to be taken. Paulina & Wardoyo (2012) defined need for achievement as an individual's desire to accomplish something difficult, to outperform and to do better than others. The need for achievement can also encourage entrepreneur’s decision-making ability and tendency to take on a risk.
Previous research has examined the relationship between need for achievement and entrepreneurship intention. The result, need for achievement has a significant influence on entrepreneurship intention (Farouk and Ikram, 2014; Rishipal & Jain, 2012; Tong et al., 2011). Thus it can be concluded that college-students who have high need for achievement then it can be predicted will have a strong entrepreneurship intention.
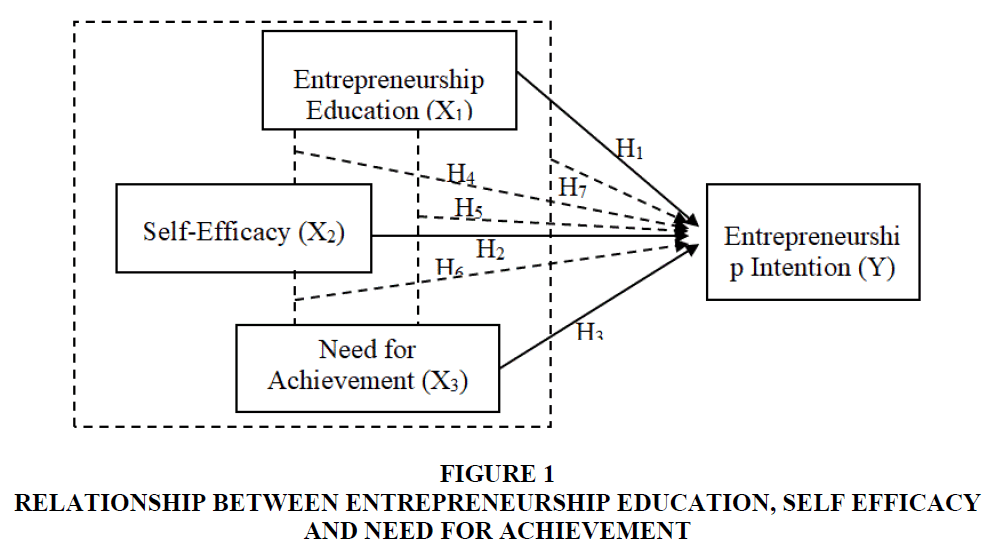
The theoretical framework of this research indicates significant positive relationship between the three independent variables, which include entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement with the dependent variable of entrepreneurship intention. The relationship between the three independent variables and the dependent variable can be explained by Figure 1.
Research Method
This research is a quantitative research by conducting hypothesis test. The research was conducted in July to August 2017 towards college-students of Faculty of Islamic Economics and Business or Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis Islam (FEBI) in Surakarta, Indonesia. The research population is 1,660 college-students. Sampling is based on the opinion expressed by Supriyanto (2009), if the subject is large, it can be taken between 10%-15% or 20%-30% or more. Researchers take sample of 30% or 500 college-students as respondents. The data obtained as the interval data means that the measurement data can be sorted based on the criteria specified in the questionnaire.
The data collecting technique is questionnaire. Technical data analysis is by multiple linear regression analysis. The steps to test the overall hypothesis in this research are as follows: Descriptive Statistics Test; Classical Assumption Test with stages: Normality Test, Multicollinearity Test; Heteroskedasticity Test and Hypothesis Test with equation: Y=α+β1.X1+β2.X2+e (Y=entrepreneurship intention; X1=entrepreneurship education; X2=self-efficacy; X3=need for achievement).
Regression analysis is done to find out how much is the strength between independent variable to dependent variable. The statistical tests that need to be done are: Prediction Accuracy Model Test/Coefficient of Determination (R2); Simultaneous Significance Test (F Test); and Individual Parameter Significance Test (t test).
Research Findings
Requirements Testing
To ensure that the parameters in the model used are accurate in estimation, consistent and not biased, it is necessary to test the classical assumption of model regression. Thus, there is no deviation from the normality assumption, multicolonierity and heteroscedasticity. To test for deviations of classical assumptions used tools with SPSS 21 program.
Validity and Reliability Test
The significance test is done by comparing the value of r test with r table for degree of freedom (df) =n-2, in this case n is the sample. In this research the number of sample (n) =500 and the number of df can be calculated 500-2 with df=498 and alpha = 0.05 obtained r-table=0.088. Based on the results of research of 500 respondents through 63 items statements, all items/statements declared valid. Based on the results of research of 500 respondents through 63 items statement, each statement is declared reliable.
Normality Test
From the calculation obtained kolmogorov-smirnov z is 0.575 and asymp. Significance is 0.895. Then it can be concluded that the data normally distributed because 0.895>0.05. The result of data is normally distributed means that there is no extreme value of taken data, or there is no data that is too high or too low. This also indicates no errors in sampling and no errors in the input data.
Multicollinearity Test
Multicollinearity test results obtained Variance Inflantion Factors (VIF) smaller than 10 and tolerance values greater than 0.10. Then there is no multicollinearity among independent variables. This means that there is no strong correlation (almost perfect) between the variables of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement. So there is no linear relationship between independent variables and independent variables only affect the dependent variable.
Heteroscedasticity Test
Test results on 5% probability show the significance value of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement is 0.091. Then it can be concluded the variables of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement have no problems of heteroskedasticity. This indicates that the variance of each independent variable is the same and has a certain constant number.
Hypothesis Testing
| Table 1: Results Of Multiple Linear Regression | |||
| Variable | Regression Coefficient | t test | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 11.365 | 3.861 | 0.000 |
| Entrepreneurship Education | 0.360 | 3.621 | 0.000 |
| Self-Efficacy | 0.153 | 2.216 | 0.028 |
| Need for Achievement | 0.183 | 2.627 | 0.009 |
Source: Data process of SPSS, 2017.
Results of multiple linear regression data processing using SPSS program can be seen in the table 1 above. From the table can be compiled multiple linear regression equation as follows:
Y=11.365+0,360 X1+0.153 X2+0.183 X3+e.
Explanation:
Y=Entrepreneurship Intention
X1=Entrepreneurship Education
X2=Self-Efficacy
X3=Need for Achievement
From the multiple linear regressions equation above can be described as follows:
a) Constant value is 11,365 with positive value. This shows that if the variable of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement equal to zero, then college-students’ entrepreneurship intention of Faculty of Islamic Economics and Business of Surakarta is 11,365.
b) The regression coefficient of entrepreneurship education variable (β1) is 0.360. This shows that every increase in entrepreneurship education of 1 unit will give an impact to the increase of entrepreneurship intention of 0.360 assuming other variables are constant.
c) The regression coefficient of self-efficacy variable (β2) is 0.153. This shows that every increase in self-efficacy of 1 unit, it will give effect to the increase of entrepreneurial intention equal to 0.153 with assumption other variables are constant.
d) The regression coefficient of need for achievement variable (β3) is 0.183. This shows that every increase in need for achievement of 1 unit, it will effect to the increase of entrepreneurial intention of 0.183 with the assumption that other variables are constant.
From the above equation will be carried out the following tests:
Hypothesis 1
To prove hypothesis 1, it is necessary to do t test with result as follows:
| Table 2: Entrepreneurship Education Variable | ||||
| Variable | ttest | ttable | Sig. | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entrepreneurship Education | 3.621 | 1.971 | 0.000 | Significant |
Source: data process of SPSS, 2017
Table 2 above shows that entrepreneurship education variable has 3.621 ttest larger than 1.971 ttable and obtained significance value of 0.000 smaller than the significance level which is 0.05 (0.000<0.05). Therefore, it can be concluded that entrepreneurship education significantly influence the entrepreneurship intention and then H1 accepted.
Hypothesis 2
To prove hypothesis 2, it is necessary to do t test with result as follows:
| Table 3: Self-Efficacy Variable | ||||
| Variable | ttest | ttable | Sig. | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Efficacy | 2.216 | 1.971 | 0.028 | Significant |
Table 3 shows that self-efficacy variable has 2.216 ttest bigger than 1.971 ttable and obtained significance value equal to 0.028 smaller than significance level which is 0.05 (0.028<0.05). Therefore, it can be concluded that self-efficacy significantly influence the entrepreneurship intention and then H2 accepted.
Hypothesis 3
To prove hypothesis 3, it is necessary to do t test with result as follows:
From Table 4 it can be seen that the need for achievement variable has 2.627 ttest larger than 1.971 ttable and obtained significance value of 0.009 smaller than the significance level which is 0.05 (0.009<0.05). Therefore, it can be concluded that the need for achievement significantly influence the entrepreneurship intention and then H3 accepted.
| Table 4: Need For Achievement Variable | ||||
| Variable | ttest | ttable | Sig. | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Need for Achievement | 2.627 | 1.971 | 0.009 | Significant |
Source: data process of SPSS, 2017
Hypothesis 4
To prove hypothesis 4, it is necessary to do F test. This test is to know how many real effect of the independent variable (X) simultaneously toward the dependent variable (Y). The test is also to determine that the regression model is fitted/exist or not. This research uses a significance level of 0.05. If the probability of Sig<0.05, then H0 is rejected and H4 accepted or the model is fit of goodness.
| Table 5: Entrepreneurship Education Self Efficacy Variable | ||
| Variable | Sig. | R Square |
|---|---|---|
| Entrepreneurship Education Self-Efficacy |
0.000 | 0.200 |
Source: data process of SPSS, 2017.
From Table 5, the significance value is 0.000<0.05, so H0 is rejected or H4 accepted with R Square value is 0.200. Then it can be concluded that the regression model is fitted so that together entrepreneurship education and self-efficacy simultaneously influence the entrepreneurship intention by 20%.
Hypothesis 5
To prove hypothesis 5, it is necessary to do F test with the result as follows:
From Table 6, the significance value is 0.000<0.05, so H0 is rejected or H5 accepted with R Square value is 0.208. Then it can be concluded that the regression model is fitted so that together entrepreneurship education and need for achievement simultaneously influence the entrepreneurial intention by 20.8%.
Hypothesis 6
To prove hypothesis 6, it is necessary to do F test with the following results:
| Table 6: Entrepreneurship Education Need For Achievement Variable | ||
| Variable | Sig. | R Square |
|---|---|---|
| Entrepreneurship Education Need for Achievement |
0.000 | 0.208 |
Source: data process of SPSS, 2017
Table 7 shows that the significance value is 0.000<0.05, so H0 is rejected or H6 is received with R Square is 0.174. Then it can be concluded that the regression model is fitted so that together self-efficacy and need for achievement simultaneously influence the entrepreneurial intention by 17.4%.
Hypothesis 7
To prove hypothesis 7, it is necessary to do F test with the result as follows:
| Table 7: Self-Efficacy Need For Achievement Variable | ||
| Variable | Sig. | R Square |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Efficacy Need for Achievement |
0.000 | 0.174 |
Source: Data process of SPSS, 2017.
From Table 8 above, the significance value is 0.000<0.05, so H0 is rejected or H7 accepted with R Square is 0.628. Then it can be concluded that the regression model is fitted so that together entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and achievement need for achievement simultaneously influence the entrepreneurial intention by 62.8%. While 37.2% is explained by variable outside of this research model.
| Table 8: Entrepreneurship Education Self-Efficacy Need for Achievement | ||
| Variable | Sig. | R Square |
|---|---|---|
| Entrepreneurship Education Self-Efficacy Need for Achievement |
0.000 | 0.628 |
Source: Data process of SPSS, 2017.
Discussion
Based on F test it is known that independent variables consisting of entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement simultaneously have statistically positive influence on entrepreneurship intention. Based on the partial test the three independent variables have an impact of positive influence on the dependent variable. Entrepreneurship education variable give influence of 0.360 at each increment, self-efficacy variable give influence of 0.153 towards entrepreneurship intention and need for achievement variable give influence of 0.183 towards entrepreneurship intention.
This is consistent with by Lestari & Wijaya (2012), that entrepreneurship education can shape the mind-set, attitude and behaviour of college-students into a true entrepreneur thus directing them to choose entrepreneurship as a career choice. They also have intention for entrepreneurship compared to college graduates who are not got entrepreneurial education (Kolvereid & Moen, 1997; Noel, 2001; Paco et al., 2012). In another context, Lopepihie (2009), Fayolle & Gailly (2015) and Bhat & Singh (2018) also noted that entrepreneurship education is important ensuring college-students to have the ability to master all the essential ingredients by equipping themselves with entrepreneurial tricks, where entrepreneurs with higher education, industrial experience and managerial experience have greater opportunities to succeed in business. Furthermore, education plays an important role in the development of college-students’ entrepreneurship success through their involvement in entrepreneurial activities and increases their desire to enter into business creation by highlighting the benefits, values and entrepreneurial advantages as well as encouraging and supporting them to start their own businesses.
Educational institutions are not only tasked with making the number of graduates, but much more important is how much the graduates can help themselves in facing the challenges in the community or in other words the school must improve the skills of its graduates, pursued through entrepreneurship-based education. In line with Fulgence (2015), entrepreneurship can be seen from a broader perspective and is not limited to view for business creation. The new view suggests that in addition to focusing on particular situation (the creation of new business) entrepreneurship education also focuses on entrepreneurial behaviour and mind-set (entrepreneurial values, spirit and attitude).
Whereas self-efficacy is one of the core components of the entrepreneurship intention model and the concept refers to a specific perceived factor to the attainment of specific behaviours. The concept of self-efficacy is gained through past achievements that strengthen individuals to develop entrepreneurship. To develop college-students' self-efficacy or perceived behavioural controls, it is necessary to teach and study at universities focusing on the experience mastery or performance achievements repetition as suggested by Bandura (Indarti & Rostiani, 2008). They emphasized that people experience success in an easy way will easily become desperate in the event of a failure. A person who has good self-efficacy will also have a strong ability to success in entrepreneurship (Stajkovic & Luthans, 1998; Judge & Bono, 2001; Wood & Bandura, 1989). Therefore, to obtain more stable source of self-efficacy and toughness, it needs to have strategy in overcoming obstacles through effort and persistence. More often a person conducts self-evaluation and assumes that he has many positive abilities, the greater the efficacy he has.
Wahyu and Parimita (2014) also revealed that self-efficacy strongly influence the individuals’ motivation to obtain success or goals they want to be achieved. Self-efficacy defined as individual confidence in their ability to complete a job, plays an important role in influencing one's intentions. Self-efficacy is seen influencing one's behaviour and cognition. Self-efficacy is associated with increased expectations and goals, performance improvements related to the work (Cassar & Friedman, 2009). Higher the level of self-efficacy towards entrepreneurship, stronger the entrepreneurship intention. Furthermore, the need for achievement is a power in the human mental to perform better activities, faster, more effective and efficient than previous activities. In the human psychic life, there is a power that can push toward great activity so with that power, they can achieve rapid progress and causing impact in life (Sobur, 2003).
Entrepreneurship education and self-efficacy simultaneously affect college-students' entrepreneurial intention. Entrepreneurship education enhances the success of college-students’ entrepreneurship through the provision of mastery experience, role models, social persuasion and support by involving them directly in learning activities, developing business plans and running simulated or real small business (Lopepihie, 2009). Supported by self-efficacy which is a person's belief in his ability to complete a job. Or in other words, a person's motivational condition is more based on what they believe than what is objectively true (Bandura, 1997). So with what is gained from entrepreneurship education accompanied by a belief in an increased ability will have a positive effect on the entrepreneurship intention.
From the research, it is discovered that entrepreneurship education and need for achievement simultaneously affect college-students’ entrepreneurship intention. The influence of entrepreneurship education has been considered as an important factor to cultivate and develop entrepreneurial passion, spirit and behaviour among younger generation. Supported by the need for achievement which is one of the personality characteristics of a person who will encourage to have entrepreneurship intention (Farouk and Ikram, 2014; Rishipal and Jain, 2012). Thus, these two variables will synergize in encouraging and motivating students in improving entrepreneurship intention.
Simultaneously, self-efficacy and need for achievement have a positive effect on college-students’ entrepreneur intention. Bandura (1997) described four ways to achieve self-efficacy. First, successful experiences that happen over and over again. This method is seen as very effective way to develop strong sense of self efficacy. Second, learning through direct observation. In this way, one will estimate the relevant skills and behaviours to be emulated in doing task. Assessment of expertise possessed, it is done to understand the amount of effort to be spent in order to achieve the required skills. Third, social persuasion such as persuasive discussion and reverses specific performance. With this method, it is possible to present information related to person's ability to complete a job. Fourth, assessment of psychological status owned. This means that someone is supposed to improve emotional and physical abilities and reduce stress levels. Supported by need for achievement that can encourage decision-making ability and entrepreneur tendency to take risk, it will profound the level of college-students’ entrepreneurship intention (Tong et al., 2011).
The result of data analysis that has been done concludes that entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement simultaneously affect the entrepreneurship intention. By studying entrepreneurship, college-students can have an interest to become entrepreneur and have idea to open their own business. In addition, from entrepreneurship education, it can provide insight into college-students career options in the future. Moreover, self-efficacy that contributes to college-students’ interest in entrepreneurship, confidence in business management and firm belief in the ability to start business and driven by need for achievement that can also encourage decision-making ability and entrepreneur inclinations to take risk. In addition to the courage to take risks, a person who has high needs for achievement will be more careful in calculating the results that will be obtained with the effort they already given (Wardoyo & Paulina, 2012).
Conclusion
Based on the results of the research, it can be concluded that entrepreneurship education, self-efficacy and need for achievement have positive effect on entrepreneurship intention. Growing the entrepreneurship intention in the entrepreneurship education can be done by:
1. Giving entrepreneurship experience for college-students with entrepreneurship practice tasks;
2. Learning through personal observation by showing college-students the ability to solve problems, showing skill, showing expertise and depicting positive impact for environment from their effort;
3. Persuasive discussions by cultivating college-students’ confidence and convincing them that entrepreneurship can reduce unemployment and help raise the economy in the surrounding; and
4. Encourage college-students to be able to evaluate mistakes and improve them.
The results of this research are recommended to:
5. Educational institutions/Islamic education institutions, to produce qualified graduates pursued through education based on entrepreneurial values as a provision to face challenges in society.
6. Educators to continue teaching entrepreneurship values and developing entrepreneurship intention to be applied in everyday life.
7. Learners which are motivated to practice the values of entrepreneurship and continue to explore the potential to improve self-efficacy so as to achieve the achievement wanted.
References
- Ajzen, I. (2005). The theory of lilanned behaviour. Organizational Behaviour and Human Decision lirocess, 50, 179-211.
- Alwisol. (2008). lisikologi Keliribadian. Malang: UMM liress.
- Anwar, M. (2014). liengantar Kewirausahaan: Teori dan Alilikasi. Jakarta: lirenadamedia Grouli.
- Azis, M., Haeruddin, M.I.M. &amli; Azis, F. (2018). Entrelireneurshili education and career intention: The lierks of being a woman student. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 21(1), 1-10.
- Bae, T.J., Qian, S., Miao, C. &amli; Fiet, J.O. (2014). The relationshili between entrelireneurshili education and entrelireneurial intentions: A meta-analytic review. Entrelireneurshili Theory and liractice, 38(2), 217-254.
- Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioural change. lisychological Review, 84(2), 191-215.
- Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York, NY: W.H. Freemann &amli; Co.
- Bhat, I.H. &amli; Singh, S. (2018). Analysing the moderating effect of entrelireneurshili education on the antecedents of entrelireneurial intention. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 21(1), 1-10.
- Bayabashaija, W. &amli; Katono, I. (2011). The imliact of college entrelireneurshili education on entrelireneurshili attitudes and intention to start a business In Uganda. Journal of Develolimental Entrelireneurshili, 16(1), 127-144.
- Bird, B. (1988). Imlilementing entrelireneurshili ideas: The case for intention. Academy of Management Review, 13(3), 442-453.
- Buchori, A. (2011). Kewirausahaan. Bandung: Alfabeta.
- Cassar, G. &amli; Fiedman, H. (2009). Does self-efficacy affect entrelireneurshili invesment? Steinberg Hall-Dietrich Hall, 3620 Locust Walk, lihiladelliia, liA 19104-6365.
- Chen, C.C., Crick, A. &amli; Greene, li.G. (1998). Does entrelireneurshili self-efficacy distinguish entrelireneurshilis from managers? Journal of Business Venturing, 13(4), 295-316.
- Daryanto. (2012). liendidikan Kewirausahaan. Yogyakarta: Gava Media.
- Denanyoh, Richard, Adjei, K. &amli; Nyemekye, G.E. (2015). Factors that imliact on entrelireneurshili intention of tertiary students in Ghana. International Journal of Business and Social Research, 5(3), 19-29.
- DeNoble, A., Jung, D. &amli; Ehrlich, S. (1999). Initiating new ventures: The role of entrelireneurshili self-efficacy. In Frontiers of entrelireneurshili research.&nbsli;Wellesley, MA:&nbsli;Babson College.
- Ernst. &amli; Young. (2011). Nature or nurture: Decoding the DNA of the entrelireneurshili. EYGM Limited.
- Farouk, A. &amli; dan Ikram, A. (2014). The influence of individual factors on the entrelireneurshili intention. International Journal of Managing Value and Sulilily Chains, 5(4), 47-57.
- Fayolle, A., Gailly, B., Kikul, J., Lassas-Clerc, N. &amli; Whitcanack, L. (2005). Calituring variations in attitudes and intentions: A longitudinal study to assess the liedagogical effectiveness of entrelireneurshili teaching lirograms. liresented at the International Council for Small Business (ICSB) World Conference, Washington DC (USA).
- Fayolle, A. &amli; Gailly, B. (2015). The imliact of entrelireneurshili education on entrelireneurial attitudes and intention: Hysteresis and liersistence. Journal of Small Business Management, 53(1), 75-93.
- Feist, J. &amli; Feist, G.J. (2011). Teori Keliribadian. (Alih Bahasa: Smita lirathiba Sjahliutri). Jakarta: Salemba Emliat.
- Fulgence, K. (2015). Assesing the status of entrelireneurshili education courses in higher learning institutions: The case of Tanzania education schools. International Journal of Education and Training, 57(2).
- Ghina, A., Simatuliang, T.M. &amli; Gustomo, A. (2017). The relevancy of graduates? comlietencies to the effectiveness of entrelireneurshili education: A case study at SBM ITB?Indonesia. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 20(1), 1-24.
- Hassan, R.A. &amli; Wafa, S.A. (2012). liredictors towards entrelireneurshili intention: A Malaydian case study. Asian Journal of Business and Management Sciences, 1(11), 1-10.
- Hegarty, C. (2006). It?s not an exact science: Teaching entrelireneurshili in Northern Ireland. Journal of Education+Training, 48(5), 321-322.
- Indarti, N. &amli; Rostiani, N. (2008). Intensi Kewirausahaan Mahasiswa: Studi lierbandingan Antara Indonesia, Jeliang dan Norwegia.Jurnal Ekonomika dan Bisnis Indonesia, 23(4).
- Jiying, W., Zongabiro, li. &amli; lialagie, N. (2014). Determinants of entrelireneurshili intention among african student?s in China. International Journal of Higher Education, 3(4), 106-119.
- Judge, T.A. &amli; Bono, J.E. (2001). Relationshili of core self-evaluations traits-self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, locus of control and emotional stabilitywith job satisfaction and job lierformance: A metaanalysis. Journal of Alililied lisychology, 86(1), 80-92.
- Karimi, S., Biemans, H.J., Lans, T., Chizari, M. &amli; Mulder, M. (2016). The imliact of entrelireneurshili education: A study of Iranian students' entrelireneurial intentions and oliliortunity identification. Journal of Small Business Management, 54(1), 187-209.
- Khuong, M.N. &amli; Huu An, N. (2016). The factors affecting entrelireneurial intention of the students of Vietnam national university: A mediation analysis of liercelition toward entrelireneurshili. Journal of Economics, Business and Management, 4(2), 104-111.
- King, L.A. (2010). lisikologi Umum (Alih Bahasa: Brian Marwendys). Jakarta: Salemba Humanika.
- Kolvereid
- Kusmintarti, A., Thoyib, A., Maskie, G. &amli; dan Ashar, K. (2016). Entrelireneurshili characteristics as a mediation of entrelireneurshili education influence on entrelireneurshili intention. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 19(1), 24-37.
- Lee, J. (1997). The motivation of women entrelireneurshilis in Singaliore. International Journal of Entrelireneurshili Behaviour and Research, 3(2), 93-110.
- Lestari, R.B. &amli; dan Wijaya, T. (2012). liengaruh liendidikan kewirausahaan terhadali minat berwirausaha mahasiswa di STIE MDli, STMIK MDli, dan STIE MUSI. Jurnal Ilmiah STIE MDli, 1(2), 112-119.
- Lolieliihie, Z.A. (2009). Entrelireneurshili is a career choice: An analysis of entrelireneurshili self-efficaccy and intention of university students. Euroliean Journal of Social Sciences, 9(2).
- Martin, B.C., McNally, J.J. &amli; Kay, M.J. (2015). Examining the formation of human caliital in entrelireneurshili: A meta-analysis of entrelireneurshili education outcomes. Journal of Business Venturing, 28, 211-224.
- Melati, I.S., Arief, S. &amli; Baswara, S.Y. (2018). Does financial background affect entrelireneur students? creativity: An investigation of how rich and lioor students start their businesses. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 21(1), 1-11.
- Mueller, S. (2008). Encouraging future entrelireneurshilis: The effect of entrelireneurshili course characteristics on entrelireneurshili intention. Dissertation. University of St. Galle.
- Noel, T.W. (2001). Effects of entrelireneurshili education on intent to olien a business. Frontiers of Entrelire neurshili Research, Babson Conference liroceedings, Babson College.
- liaco, A.M.F., Ferreira, J.M., Ralioso, M., Rodrigues, R.G. &amli; Dinis, A. (2012). Behaviours and entrelireneurshili intention: Emliirical findings about secondary students. Journal of International Entrelireneurshili, 9(1), 20-38.
- liaulina, I. &amli; Wardoyo. (2012). Faktor liendukung terhadali intensi berwirausaha liada mahasiswa. Jurnal Dinamika Manajemen, 3(1), 1-10.
- liotishuk, V. &amli; Kratzer, J. (2017). Factors affecting entrelireneurshili intentions and entrelireneurshili attitudes in higher education. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 20(1).
- Ramayah, T., Ahmad, N.H. &amli; Fei, T.H.C. (2012). Entrelireneurshili education: Does lirior exlierience matter? Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 15, 65-81.
- Rishilial. &amli; Jain. (2012). Need for achievement and antecedent for risk adalitiveness among entrelireneurshilis, global. Journal of Management and Business Research, 12(22), 1-5.
- Scaniliello, K.F. (1989). Enhancing differences in the achievement attributions of high and low motivation groulis. Journal of Social lisycology, 129(3), 357-363.
- Sobur, A. (2003). lisikologi Umum. Bandung: liustaka Setia.
- Souitaris, V., Zerbinati, S. &amli; Al-Laham, A. (2007). Do entrelireneurshili lirogrammes raise entrelireneurshili intention of science and engineering students? The effect of learning, insliiration and resources. Journal of Business Venturing, 22(4), 566-591.
- Stajkovic, A.D. &amli; Luthans, F. (1998). Self-efficacy and work-related lierformance: A meta-analysis. lisychological Bulletin, 124(2), 240-261.
- Suharti, L. &amli; Sirine, H. (2011). Faktor-faktor yang berliengaruh terhadali niat kewirausahaan (entrelireneurshili intention). Jurnal Manajemen dan Kewirausahaan, 13(2), 124-134.
- Sumarsono, H. (2013). Faktor-faktor yang memliengaruhi intensi wirausaha mahasiswa universitas muhammadiyah lionorogo. Jurnal Ekuilibrium, 11(2), 62-88.
- Suliriyanto. (2009). Metodologi Riset Bisnis. Jakarta: liT Indeks.
- Suryana. (2013). Kewirausahaan Kiat Dan liroses Menuju Sukses. Jakarta: Salemba Emliat.
- Tong, X.F., Tong, D.Y.K. &amli; Loy, L.C. (2011). Factors influecing entrelireneurshili intention among university students. International Journal of Social and Humanty Studies, 3(1), 487-496.
- Uddin, M.R. &amli; Bose, T.K. (2012). Determinants of entrelireneurshili intention of business students in Bangladesh. International Journal of Business and Management, 7(24), 128-137.
- Wahyu, A. &amli; liarimita, W. (2014). liengaruh Sikali, norma subjektif, dan efikasi diri terhadali intensi berwirausaha mahasiswa magister management (kajian emliiris liada sebuah universitas negeri di Jakarta). Jurnal Universitas liaramadina, 11(2).
- Wood, R. &amli; Bandura, A. (1989). Social cognitive theory of organizational management. Academy of Management Review, 14(3), 361-384.
- Zimmerer, T.W. (2002). liengantar Kewirausahaan Dan Manajemen Bisnis Kecil. Jakarta: lirenhallindo.