Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 1
Directions of Regulations and Management of the Financial and Banking Sector
Serik Sultanbaiuly, Bohemian Central University of the Czech Republic
Arsen Nasyrhanov, Almaty Management University
Yury Khan, Kazakh Research Institute for Economics of Agro-Industrial Complex and Territories Development
Karlygash Kenenova, Almaty Management University
Ruslan Konuspayev, Shokan Ualikhanov Kokshetau University
Assylbek Bazarbayev, Narxoz University
Citation Information: Sultanbaiuly, S., Nasyrhanov, A., Khan, Y., Kenenova, K., Kenenova, R., & Bazarbayev, A. (2021). Directions of regulations and management of the financial and banking sector. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(1), 1-8.
Abstract
The article examines the main directions of regulation of the financial and banking sector in the context of the crisis of the world economic system. The analysis of the current state of the banking sector is given: participation in the formation of the country's GDP, the dynamics and structure of total assets and liabilities in recent years. The main problems of development of banks in the context of a pandemic are revealed. An assessment of the current state of the lending activities of commercial banks in Kazakhstan is presented. The analysis of the influence of the banking sector on the development of the economy of Kazakhstan is carried out and its problems and factors that affect the current situation are identified, and a forecast for future development is made. Indicators of investment activity of the economy are given. Recommendations are given to improve the efficiency of the bank's management activities and the main priorities of stabilization measures of the Government and the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan is highlighted. It is noted that the impact of investments in general is multifaceted. They can act as a tool for managing crisis situations and financial stabilization of the economy, play a significant role in solving strategic and tactical tasks at the macroeconomic level, such as combating inflation, reducing unemployment, restructuring, and eliminating the technological and managerial backwardness of the economy. One of the most important conditions for attracting investment and subsequent economic growth of the country is the creation of a favorable investment climate. The results of this work can contribute to expanding the boundaries of research on the development of the financial and banking sector, as well as serve as an analytical basis for further developments.
Keywords
Second-tier Banks, Banking Regulation, Banking Sector, Financial Institutions, Financial and Banking Sector, Investment Climate, Economy, Pandemic, Assets, Loan Portfolio, Credit.
Introduction
The most important condition for full and high-quality financing of the modernization process is the task of achieving the stability of the financial system of Kazakhstan. In the conditions before the pandemic, the development of the financial sector of the Republic of Kazakhstan took place in conditions of sustainable economic growth, strengthening of the national currency against the US dollar, strengthening of the country's foreign economic position in the world geopolitical arena.
One of the difficult economic challenges is maintaining the pace of economic development during the global financial instability, which has proved to be a kind of important test and taught a good lesson. The financial sector and the real estate market have been most negatively affected by the global crisis. Despite this, the domestic economy continues to work and show positive dynamics during this difficult time. Investors' perceptions of Kazakhstan are changing for the better, but we do not fall into the group of the most attractive countries in terms of foreign direct investment.
At the moment, in order to increase investment attractiveness, work is underway in Kazakhstan to create reforms aimed at increasing transparency and an understandable regulatory framework, improving the key characteristics of the business sector, diversifying the economy and more active coverage of investment opportunities in the country. According to analysts, the investment climate in Kazakhstan will improve over the next three years.
Literature Review
Today, it is the banks that have the money capital accumulated and constantly growing in the pension system in the form of deposit funds and savings deposits, and it is the banks that have the greatest experience in financing and servicing investment projects (Rakhmetova et al., 2020).
In Kazakhstan, scientists such as Zhuirikov (2017); Esentugelov (2005); Sadvokasova (2017); Nakipova (2020); Rakhmetova et al. (2020), considering the problems of investment diversification. Research concerning the improvement of the structure of financial sources, including the problems of banking regulation, influencing the creation of a favorable investment climate, were carried out by such Kazakhstan scientists as Zeynelgabdin (2018); Khamitov (2018); Chelekbai (2017).
Domestic scientists Khamitov & Baybulatov (2018) note that the methods of banking supervision ensure the organizational unity of the existing instruments of monetary policy according to unified regulatory and regulatory principles, are provided with a unified regulatory methodology (systematic observation - monitoring of activities, identification of deviations, detailed inspection, decision-making to prevent excessive, excessive risks).
In case of credit financing, SMEs undergo a thorough qualification examination by STB employees (second-tier bank). The main criteria for such selection are the economic analysis of the enterprise from the standpoint of its creditworthiness. By definition Gilyarovsky (2017) creditworthiness can be characterized as the ability of small and medium-sized businesses to settle accounts with creditors in full at the time when such a need arises. In general, creditworthiness is understood as the financial condition of the enterprise, which gives confidence in the efficiency of the use of borrowed funds and the readiness to return.
Methodology
The methodological and theoretical basis of the research was the fundamental works, theories, which are set forth in modern studies of financial and banking regulation of the economy. In the process of the research, the following were used: the method of desk research with analysis of open sources of information and statistical data, the method of interviewing with the main financial institutions that finance investment projects, the method of financial modeling, the method of technical analysis for constructing a trend line, as well as a graphical method for constructing an analysis based on statistical data. Data analysis and processing was carried out using Microsoft Excel application software.
The information base of the study was legislative and regulatory data, domestic and foreign statistical sites, official sites of banks and financial institutions to support entrepreneurship.
Research Results
The function of the JSC Investment Fund of Kazakhstan is to rehabilitate enterprises by attracting investments to private sector entities in order to create competitive industries in the non-resource sector of the economy. The main goals are the development of business entities of industrial and innovative development, as well as investment projects implemented within the framework of government programs, public-private partnerships.
The Foundation's activities are aimed at:
- Repayment of debts on projects by carrying out claims work and rehabilitation procedures;
- Work with problem projects through debt restructuring;
- Sale of assets, or lease of assets to domestic and foreign investors (Nakipova et al., 2013).
Table 1 shows the action plan of the venture fund of QazTech Ventures JSC until 2021.
| Table 1 Events of JSC of Qaztechventures | |||
| Indicators | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Attracting external investment to venture capital funds | ratio 0.8:1 | ratio 1:1 | ratio 1.2:1 |
| Number of venture funds created | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Share of business incubator projects that received funding | 15% | 15% | 15% |
| Number of companies, projects for which technological expertise services were provided | 6 | 7 | 8 |
The COVID-19 pandemic and the quarantine restrictions that followed led to a 2.6% contraction in the economy in real terms at the end of 2020. The rate of contraction of the economy of Kazakhstan in the fourth quarter of 2020 slowed down to (-) 2.0% in annual terms. Investment activity indicators in 2020 have also been linked to the negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. At the end of 2020, the decline in investment in fixed assets amounted to 3.4% (Table 2). The decline in investment in 2020 is primarily due to a 26.4% decline in investment in the mining industry due to the temporary suspension of a large investment project in the Tengiz oil field. Against this background, the share of the mining industry in the total investment volume has significantly decreased from 44.6% in 2019 to 33.6% in 2020.
| Table 2 Indicators of Investment Activity, in % | ||||||
| Year | Months | Fixed capital investments | Construction and overhaul works | Machinery, equipment and transport | Other expenses | Housing investment |
| 2019 | 1 | 7.0 | -1.0 | -9.0 | 17.0 | 16.2 |
| 2 | 13.8 | 15.5 | 7.1 | -8.0 | 19.0 | |
| 3 | 6.8 | 8.7 | 1.8 | -6.3 | 30.1 | |
| 4 | 5.9 | 0.8 | -3.2 | 7.4 | 22.5 | |
| 2020 | 1 | 6.0 | 12.3 | 2.0 | -9.3 | 17.8 |
| 2 | -7.6 | -0.5 | -19.2 | 4.0 | 33.2 | |
| 3 | -8.6 | 7.3 | -10.9 | -6.0 | 22.6 | |
| 4 | -0.2 | -0.9 | 11.5 | -13.3 | 69.3 | |
However, according to the analysis of the current figure of the category of bank credit sector account of Kazakhstan, the management remains in the million still billion, the discrepancy remains the largest and the dominant direction of the credit segment of the financial current sector of the country's relations, the moment about the mechanism of this production is evidenced by the narrow data forced by Table 3.
| Table 3 Dynamics of Relative Indicators Characterizing the Role of Lending the Bank Values in the Sector OF The Economy | |||
| кот Indicator contract name | 01.01.2019 | 01.01.2020 | 01.01.2021 |
| денежных GDP, billion tenge | 59 614 | 68 639 | 70 134 |
| Assets, billion tenge | 25 213,6 | 26 526,1 | 31 298,9 |
| Liabilities, billion tenge | 22 093,6 | 22 807,8 | 27 271,7 |
| Equity capital, billion tenge | 3 119,9 | 3 718,4 | 4 027,2 |
Based on the data in the table, it can be seen that the share of banking sector assets in GDP occupies a significant part. The ratio of assets to gross domestic product was 42.3% in 2018, 38.6% in 2019 and 44.6% in 2020.
Active operations are the most important banking operations, therefore it is important to study their structure, which is shown in Table 4.
| Table 4 The Structure of Total Assets of the Banking Sector of the Reoublic of Kazakhstan | ||||||||
| странах Indicators | 01.01.2018 | 01.01.2019 | 01.01.2020 | 01.01.2021 | ||||
| процента billion tenge | in % to total | процента billion tenge | in % to total | процента billion tenge | in % to total | процента billion tenge | in % to total | |
| снижениCash, correspondent accounts | 3605,5 | 13,6 | 3753,4 | 13,8 | 3049,7 | 10,5 | 3293,2 | 9.9 |
| Deposits with obankDeposits with other banks | 955,6 | 3,6 | 1267,2 | 4,7 | 2449,8 | 8,5 | 4777,7 | 14.4 |
| purpose Securities | 4812,5 | 18,2 | 5335,7 | 19,7 | 5977,1 | 20,7 | 6650,4 | 20.0 |
| средств Bank loans and reverse repos | 13590,5 | 51,4 | 13762,7 | 50,7 | 14743,0 | 50,9 | 15792,1 | 47.6 |
| Capital investmentCapital investment | 527,5 | 2,0 | 370,7 | 1,4 | 484,3 | 1,7 | 581,8 | 1.8 |
| ссудного Other assets | 2943 | 11,1 | 2653,4 | 9,8 | 2236,0 | 7,7 | 2096,1 | 6.3 |
| потребностиTotal assets excluding reserves | 26435,0 | 100 | 27143,2 | 100 | 28940,0 | 100 | 33191,4 | 100 |
| банкир Reserves | -2277,1 | -8,6 | -1902,3 | -7,0 | -2154,0 | -7,4 | -2019,7 | -6.1 |
| банки Total assets | 24157,9 | - | 25241,0 | - | 26785,9 | 31171,7 | ||
Application Functionality
In order to assess the impact of the development of the banking sector on the country's economy, methods of economic and mathematical modeling were used, which made it possible to link the ratio of banks' assets and deposits to the value of gross domestic product. Taking into account the forecasting algorithm, we will carry out the necessary calculations.
Among the collected indicators, the indicator of gross domestic product has the highest value of the correlation coefficient with the effective indicator, which has a corresponding value at the level of -0.98. This indicates a high degree of dependence between the effective indicator and the factor.
Using the “Data Analysis” add-in in the Microsoft Excel software package and its “Regression” function, we determine the form of the linear regression equation.
Next, you need to predict the dynamics in the near future.
To do this, we will use two options:
- Use in forecasting the obtained multiple regression equation, which describes the dynamics of the level of economic development;
- Use a linear trend goods are non-financial.
For the second option, it is necessary to build a linear trend line using the time factor as a defining feature.
The resulting equations are as follows:
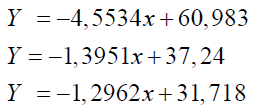
Where: x - is the ordinal number of the study period (starting from zero).
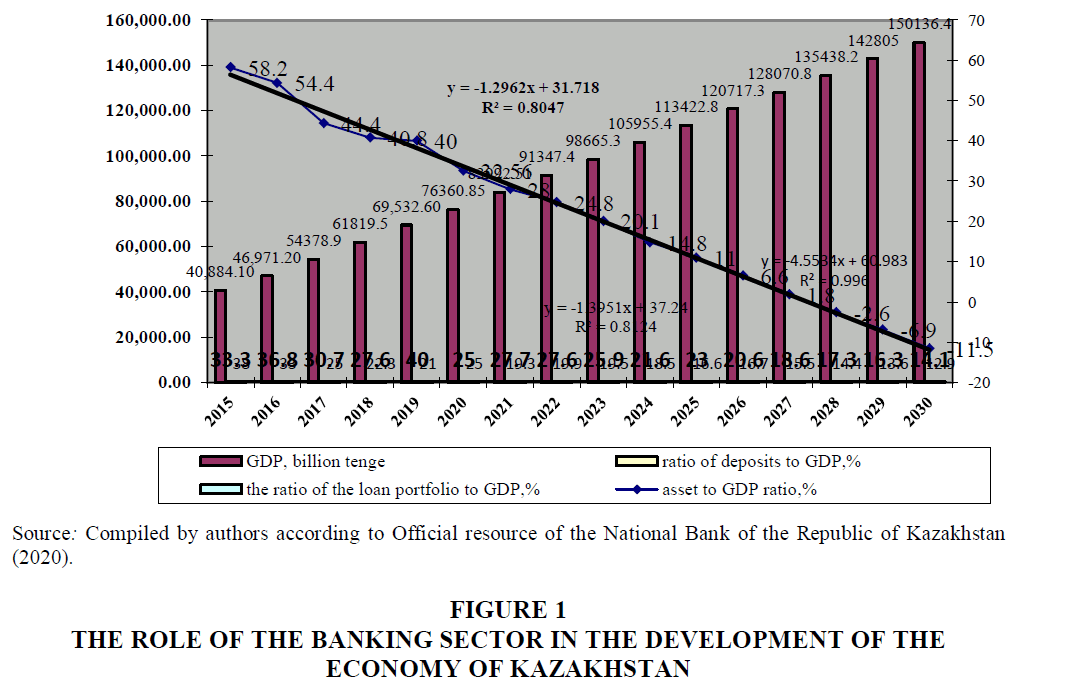
The obtained forecast values of these indicators are used to calculate the level of forecasting indicators of the impact of the development of the banking sector on the economy of Kazakhstan. Let's enter the data into the table given in Figure 1.
The analysis of this graph shows that the time series model, chosen as a linear trend, in principle adequately describes the real process, the approximation reliability coefficients are equal to 0.996, 0.8124, and 0.8047. This indicates a high degree of dependence between the effective indicator and the factor. The calculation of the trend line equations for these indicators was carried out using the “Regression” function in the Data Analysis of the Microsoft Excel application program (Table 5).
| Table 5 Forecast of the Impact of the Development of the Banking Sector on the Economy of Kazakhstan | ||||||||
| Indicator | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| GDP, billion tenge | 40884,10 | 46971,20 | 54378,9 | 61819,5 | 69532,60 | 76360,85 | 83992,51 | 91347,4 |
| asset to GDP ratio, in % | 58,2 | 54,4 | 44,4 | 40,8 | 40 | 32,56 | 28 | 24,8 |
| ratio of deposits to GDP, in % | 33,3 | 36,8 | 30,7 | 27,6 | 40 | 25 | 27,7 | 27,6 |
| loan to GDP ratio,% | 38 | 33 | 25 | 22,3 | 21 | 25 | 19,3 | 19,9 |
| Indicator | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 |
| GDP, billion tenge | 98665,3 | 105955,4 | 113422,8 | 120717,3 | 128070,8 | 135438,2 | 142805 | 150136,4 |
| asset to GDP ratio, in % | 20,1 | 14,8 | 11 | 6,6 | 1,8 | -2,6 | -6,9 | -11,5 |
| ratio of deposits to GDP, in % | 25,9 | 21,6 | 23 | 20,6 | 18,6 | 17,3 | 16,3 | 14,1 |
| loan to GDP ratio,% | 19,5 | 18,5 | 16,6 | 16,7 | 15,5 | 14,4 | 13,6 | 12,9 |
In accordance with the baseline scenario of economic development for the period 2015-2030. The growth of the gross domestic product of the Republic of Kazakhstan is expected by almost 3.7 times. At the same time, the development of the banking sector will continue to have a positive impact on GDP growth.
Conclusion
Members of the economic community have always been interested in researching the problems of financial and banking activities, as well as investment activities. All countries at different levels of development are involved in a kind of work to attract investment. This is not only about foreign direct investment, but also about domestic ones. Establishing and increasing the inflow of investment investments is one of the priority tasks of any state. The importance of improving the investment climate for Kazakhstan is reflected in all strategically important documents.
Thus, for the economy of modern Kazakhstan, bank lending is of great importance, allowing organizations to use significant borrowed resources to expand production and circulation of products. Lending as a fundamental component of the bank's activities is a significant source of investment, contributes to the continuity and acceleration of the reproduction process, strengthening the economic potential of organizations and is able to take a major place in the volume of banking operations that generate income.
The state of emergency introduced in Kazakhstan on March 16 due to the coronavirus pandemic has clearly affected the country's banking sector. First of all, its profitability suffered. The fall in the exchange rate of the national currency put pressure on the state of affairs in the banking system of Kazakhstan. The growth of problem loans and provisions for possible loan losses resumed.
The main priorities of the stabilization measures of the Government and the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan:
1. In order to ensure the stability of the financial sector of our country, it is necessary to take measures to restore confidence in the banking sector on the part of the population and business, second-tier banks to attract short-term financing from the National Bank, to ensure the stability of the resource base of the banking system.
2. The government and akims of local self-government, within the framework of the program, to implement measures to increase income and employment of the population of the country.
3. In order to raise the growth of employment of the population in the economy and increase the business activity of citizens of the country, it is necessary to use funds from national companies and banks to launch domestic enterprises in all sectors.
4. To further expand financial support for small and medium-sized businesses, link support with government procurement of national companies.
5. Hyperactive investment policy.
6. Make the most of the country's potential in the energy, chemical and agricultural sectors.
7. Fulfill all orders for social support of the population.
8. The strategic program for the development of the country until 2050 must be strictly implemented.
Summing up, we can say that the main means of giving banks their true economic role is the formation of a high-quality portfolio of financial assets and the creation of a set of regulators for this, allowing them to keep them within the framework of such a view. A very important place should be occupied by self-regulation mechanisms, which should be developed by commercial banks themselves, taking into account their mission, a well-founded strategy for their development.
References
Rakhmetova, A., Kalkabayeva, G., Kurmanalina, A., Gusmanova, Zh., Serikova, G., & Aimurzina, B. (2020). Financial-credit and innovative economic sectors: evaluation of macroeconomic effects of regulation and interaction sectors. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 8(1), 1224-1237.
Nakipova, G.N., Ahmetova, K.A., & Kamenova, M.J. (2013). Marketing-management in the complex socio-economic systems: Basic ideas, aims, tasks. World Applied Sciences Journal, 27(6), 723-728.
Zhuirikov, K.K. (2017). Methods and sources of financing investment projects. Banks of Kazakhstan, 1(235), 13-16.
Sadvokasova, K.Zh. (2017). Improving banking regulation and supervision in the Republic of Kazakhstan: theory and practice. Astana: BILIM, 50p.
Zeynelgabdin, A.B. (2018). Financial system: Kazakhstan: formation and development: monograph. Astana:KazUEFiMT, 226p.
Khamitov, N.N., Baybulatov, D.Zh. (2018). Banking supervision in Kazakhstan. Almaty: Economics, 250p.
Chelekbai, A.D. (2017). Risk management in monetary and investment activities: theory, world experience and practice in Kazakhstan. Almaty: Economics, 187p.
Gilyarovsky, L.T. (2017). Economic analysis. Moscow: Prospect, 360p.
Official resource of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan. (2020). Retrieved from www.nationalbank.kz
Official resource of the JSC "QaztechVentures". (2020). Retrieved from https://qaztech.vc/