Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 3
Directions for Research In Halal Certification: A Bibliometric Analysis
Noopur Agrawal, Shaheed Bhagat Singh College, University of Delhi
Aditya P Tripathi, Shyam Lal College (Evening), University of Delhi
Citation Information: Agrawal, N., & Tripathi, A.P. (2022). Directions for research in halal certification: a bibliometric analysis. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(3),1-17.
Abstract
In the series of standards and certifications to be followed and obtained by the marketers, Halal Certification has drawn significant attention of marketers across the globe. Halal certification is no more confined to food products or cosmetics only but it is widespread now. The purpose of this paper to offer a systemic review of existing literature on halal-certification highlighting the scope, composition and direction of researches conducted on this topic. Bibliometric analysis was performed on a database of 341 documents published during 2003-2021 downloaded from the repository of Scopus with intent to offer meaningful directions for further research.
Keywords
Halal Certification, Halal, Bibliometric Analysis, Citation Analysis, Thematic Map, Three-Field Plot.
Introduction
With the increase in global Muslim population which constitutes world’s second largest religious group ‘Halal’ Branding or ‘Halal certification’ has become a branding strategy of mainstream. As per a study by Adroit Market research (2020), the global halal market is valued at 7.2 trillion dollars which, if we make a comparison, is much ahead of the GDP of countries like Germany, India and United Kingdom.
The established and simplest meaning of ‘halal’ may be attributed to compliance with the principles of Islam. Whatever is allowed or defined as legitimate in Shariah is termed as ‘Halal’ and the forbidden ones are termed as haram. General perception about the term ‘halal’ limits this term to the area of products especially food items which is devoid of alcohol, pork and follows the defined process for slaughtering of the animals as per ritual but in reality it is not so. A clear distinction is made between ‘halal’and ‘Jhatka’ in case of meat and it is said that when an animal is slaughtered by a single strike of a weapon, the meat is termed as ‘meat after Jhatka’ and is forbidden (called as‘haram’) as per Islam.
Nevertheless, existing literature on halal indicates the widening dimension of researches being conducted on the topic. Researches indicate that products with halal certification have emerged as a symbol of trust because it has the power to influence consumer behavior (Lada et al., 2009; Khan & Haleem, 2016).
Understanding Halal Certification
Extensive review of existing literature is performed to observe the findings of different key researches conducted in the area and identify the research gaps to contribute to the body of knowledge significantly (Sufiyan et al., 2019).
It is very important for the certification seeking individuals to have a clear understanding of the key elements of certification process so as to enable them to comply with the process of certification. To provide a conceptual clarity on the topic of halal certification, key researches conducted by the different researches have been detailed as follows Table 1.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Retrieved from Scopus database by Authors.
*JAKIM is the acronym used for Department of Islamic Development, Malaysia which is the competent authority for Halal Certification in Malaysia.
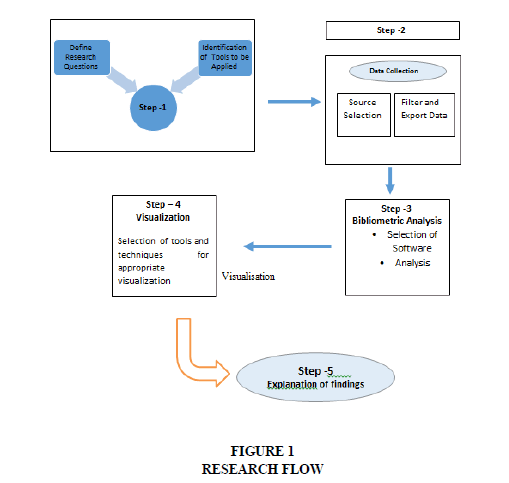
Research Flow
Present research adopts five-step process suggested by Zupic & Cater (2015). Cater which is popularly called as bibliometric workflow(Figure 1).
Research Design & Methodology
Step -1 Defining Research Question and Identification of Tools to be Applied
Research Questions: The objective of present study is to answer following research questions:
1. To identify the key aspects of ‘halal certification’ in the existing literature. 2. To explore the existing literature on ‘halal certification’ and identify key trends and themes.
To answer the first question a descripting analysis has been done to identify top sources, countries, authors and countries related to the research papers on ‘halal certification’. In order to find the key authors and sources total citations and source impact have been used. Further, by using Bradford’s Law key sources of articles on halal certification have been identified.
This law classifies sources into three different zones indicating differing levels of their productivity. Zone one is considered to be highly productive and named as nuclear zone followed by Zone two which is considered to be moderately productive. Zone three is considered to be a low productivity zone. Based on total citations and frequency of publication top countries and affiliations are considered for the analysis.
In order to identify key trends and themes of study technical tools viz; thematic map, thematic evolution and co-occurrence maps have been used. For the purpose of analysis we have used keywords plus because it not only explains the knowledge structure of the research but also helps in linking differing research areas. Author’s Keywords reflect the central point of the research whereas the keywords plus provided by repositories express the contents of the research briefly. Keywords plus always offer more descriptive trends than that of keywords mentioned by authors.
In order to conduct the bibliometric analysis we have used ‘biblioshiny’, a bibliometric analysis tool offered by the R-program.
Step-2: Data Collection – Source Selection, export and Filter of Data
Present research makes an attempt to conduct bibliometric analysis in order to identify, examine and systematically classify the existing research on Halal. Bibliometric analysis is performed on a database of 341 documents downloaded from the repository of Scopus. Systematic review of existing literature on ‘Halal certification’ has been conducted with the inclusion of research papers published in journals and conference proceedings during a period of 2003-2022.
We opted for Scopus because the papers in these databases reflect scholarly attention towards ‘Halal Certification’. While searching the term “Halal Certification, Halal Standards or Halal Verification as a title/abstract key, we found a total of 341 documents.
Filters Applied: Year and Document Type.
1. Year Wise – 2003-2022 Limit to documents of English language only.
2. Document Type considered: Articles, Conference Papers, Review, Book Chapter and Conference Review.
3. Scopus Final Search query path : TITLE-ABS-KEY ( "halal Certification" OR "halal standards" OR "halal verification" ) AND ( LIMIT-TO ( LANGUAGE , "English") .
Step-3 Bibliometric Analysis: Selection of Software and Analysis
Analysis has been performed on Biblioshiny and titles, abstracts and content of the papers were considered for drafting future scope of research.
Key Results and Description
The key results of analysis indicates that in a time-span of 20 years 169 sources offered 341 documents recording an average publication of 3.94 per annum which approves that the topic of halal certification is still evolving. There is a significant and robust presence of collaborative research in this field with the score of 3.25 Co-authors per document. Collaboration index of 2.94 approves the high degree of collaboration in halal publications (Table 2).
| Table 2 Key Results With Description |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Results |
| MAIN INFORMATION ABOUT DATA | |
| Timespan | 2003:2022 |
| Sources (Journals, Books, etc) | 169 |
| Documents | 341 |
| Average years from publication | 3.94 |
| Average citations per documents | 10.21 |
| Average citations per year per doc | 1.69 |
| References | 11757 |
| DOCUMENT CONTENTS | |
| Keywords Plus (ID) | 822 |
| Author's Keywords (DE) | 924 |
| AUTHORS | |
| Authors | 901 |
| Author Appearances | 1108 |
| Authors of single-authored documents | 40 |
| Authors of multi-authored documents | 861 |
| AUTHORS COLLABORATION | |
| Single-authored documents | 48 |
| Documents per Author | 0.378 |
| Authors per Document | 2.64 |
| Co-Authors per Documents | 3.25 |
| Collaboration Index | 2.94 |
Source: Generated from Analysis by Authors.
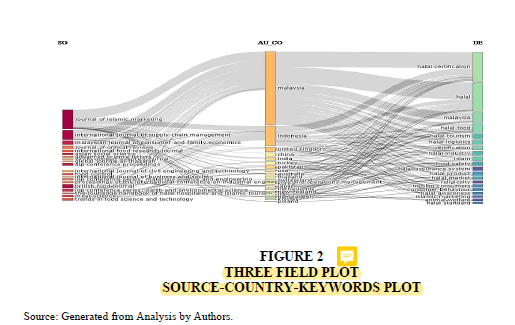
Apart from key descriptions of the articles viz; author’s keywords, average citations per documents and collaboration index, it is important to conduct three fold analyses of sources, countries and keywords. Figure – provides the three field plot with source on the extreme left of the figure, country at the middle and keywords on the right. Three field plot shows that Malaysia is actively working with key sources viz; Journal of Islamic Marketing, International Journal of Supply Chain Management and Malaysian Journal of Consumer and Family Economics on the topic of halal certification followed by Indonesia, United Kingdom, China and India respectively having important contributions to the body of knowledge by their research on different dimensions of halal certification (Figure 2).
Document by Subject Area
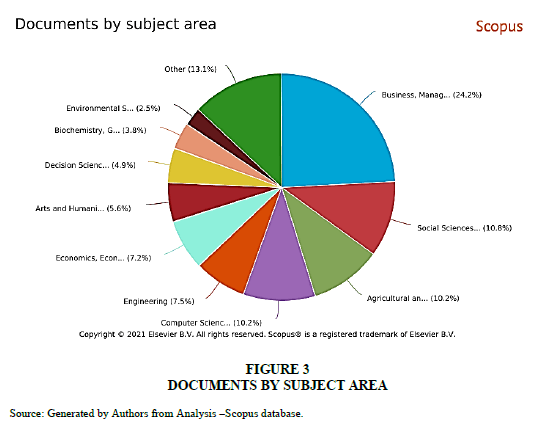
Subject –wise analysis of research articles published indicates that the highest 24.2% articles were published in the area of business and management making the topic of halal certification an important one from business and market perspective followed by 10.80% in social sciences, 10.2% in Agriculture and allied areas,7.5% in Engineering and 7.2% in economics. Only 3.8% researches were conducted on halal certification in the subject of Biochemistry and 2.5% in environment studies. 13.1% articles were published in multidisciplinary areas.
This analysis reveals the representation of studies conducted on halal from the lens of different streams of studies making the topic of research a truly multi-disciplinary one Figure 3.
Source Analysis
Analysis of most relevant source publishing researches on halal certification identified Journal of Islamic Marketing to be a top journal having the highest number of 54 articles followed by International Journal of Supply Chain Management -20, British Food Journal -9, Malaysian Journal of Consumer and Family Economics -9 and AIP Conference proceedings -9 respectively. This indicates and approves the concentration of publication to selected journals(Table 3).
| Table 3 Most Relevant Sources |
|
|---|---|
| Sources | No. of Articles |
| Journal of Islamic Marketing | 54 |
| International Journal of Supply Chain Management | 20 |
| British Food Journal | 9 |
| Malaysian journal of consumer and family economics | 9 |
| Aip conference proceedings | 6 |
| Asian social science | 5 |
| Iop conference series: earth and environmental science | 5 |
| Meat science | 5 |
| The Routledge handbook of halal hospitality and islamic tourism | 5 |
| Trends in food science and technology | 5 |
| Food control | 4 |
| International food research journal | 4 |
| Iop conference series: materials science and engineering | 4 |
| Journal of critical reviews | 4 |
| Proceedings of the international conference on industrial engineering and operations management | 4 |
| World applied sciences journal | 4 |
Source: Generated from Analysis by Authors.
Ranking of Journal’s as Per Bradford’s Law
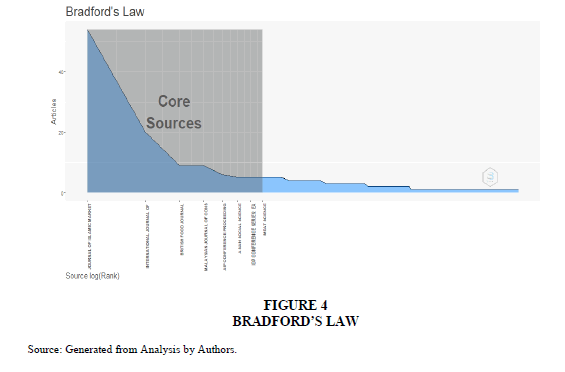
Samuel C. Bradford (1934) was the first to describe a law which estimates the exponentially diminishing returns of search for references in the journals of sciences. Journal of Islamic Marketing, International Journal of Supply Chain Management, British Food Journal, Malaysian Journal of Consumer And Family Economics ,AIP Conference Proceedings and Asian Social Science were clustered in zone 1 i.e. highly productive source through Bradford’s Law. (Figure-4). It reflects the concentration of articles in these journals.
Geographical Distribution of the Data Source: Most Cited Countries
As far as most cited countries are concerned, Malaysia emerged as a top cited country with total citations of 1719 followed by united Kingdom (283), Indonesia (160), Canada (121), India (87), Ireland (70) respectively. This indicates that this topic has widely been analyzed in Asian countries Table 4.
| Table 4 Most Cited Countries (Top 10) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Country | Total Citations | Average Article Citations |
| MALAYSIA | 1719 | 15.08 |
| UNITED KINGDOM | 283 | 35.38 |
| INDONESIA | 160 | 5.00 |
| CANADA | 121 | 60.50 |
| INDIA | 87 | 17.40 |
| IRELAND | 70 | 70.00 |
| USA | 62 | 12.40 |
| AUSTRALIA | 50 | 8.33 |
| TURKEY | 41 | 10.25 |
| SAUDI ARABIA | 34 | 34.00 |
Source: Generated from Analysis by Authors.
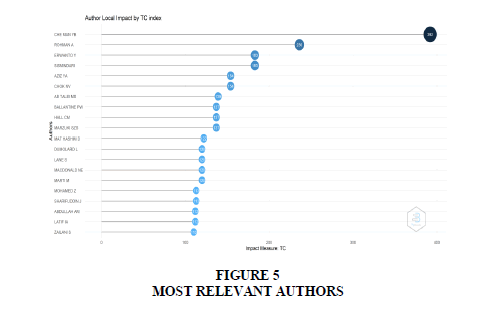
Most Relevant Authors
Most relevant authors have been identified on the basis of citations of their respective research papers. CHE MAN YB (Total Citation of 392), Rohman et al. (2011) (Total Citation of 236), Erwanto. (Total Citation of 183) and Sismindari (Total Citation of 3183) emerged as authors having the highest impact by total citation index with total citation as impact measure and number of authors to be 20 for researches on halal certification Figure 5.
Most Relevant Affiliations
Analysis of most relevant affiliation based on their productivity in terms of number of articles published, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,Universiti Teknologi Mara and Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia emerged as most relevant affiliations for publishing research papers on halal certification. Out of top 15 affiliations more than 10 universities were alone from Malaysia recording the highest contribution to the body of knowledge on halal certification (Table 5).
| Table 5 Most Relevant Affiliations |
|
|---|---|
| Affiliations | Articles |
| Universiti Putra Malaysia | 46 |
| Universiti Teknologi Malaysia | 42 |
| Universiti Teknologi Mara | 41 |
| Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia | 38 |
| Universiti Utara Malaysia | 26 |
| Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) | 17 |
| University Of Malaya | 17 |
| International Islamic University Malaysia | 16 |
| Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia | 14 |
| Universiti Malaysia Sabah | 12 |
| Universitas Airlangga | 10 |
| Sokoine University Of Agriculture | 9 |
| Universitas Padjadjaran | 9 |
| Universitas Sebelas Maret | 9 |
| Universiti Sains Malaysia | 9 |
Source: Generated from Analysis by Authors.
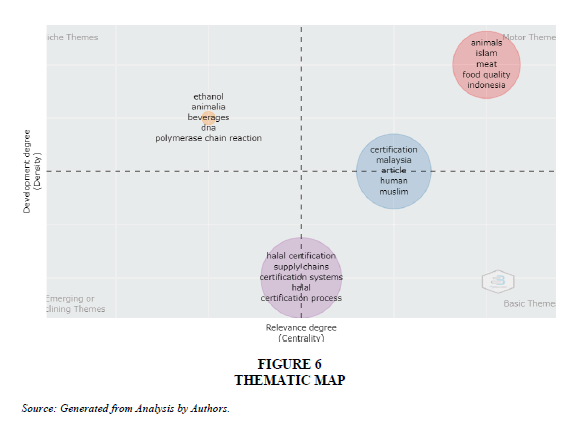
Conceptual Structure: Thematic Map
In order to draw comparatively better inferences from the analysis it is always better to identify key research themes. The identified research themes are then classified into a strategic diagram which is called as thematic map. Figure 5 presents the thematic map having centrality on X-axis indicating the significance of the theme and density which examines the development of selected theme on Y axis. Thematic map divides the entire map in four quadrants. The top left quadrant of the map indicates high density with low centrality inferring that such themes are highly developed but are isolated that is why they are called as niche themes.
The top right quadrant of the map shows high density and high centrality of themes indicating that such themes are essential and developed and are labeled as ‘Motor theme’.The lower left quadrant of the map shows the themes which are emerging or declining indicating that these themes may emerge to be a good one or eliminate from the research area.
The fourth or the lower right quadrant of the map lists the themes which are basic in nature and extensive research had been conducted on the themes listed in this quadrant. They show high level of centrality but density is low. Thematic map is generated with the articles published during 2003-2022 using … keywords. Items shown in the clusters were set at a frequency of 4 in ‘biblioshiny’ software and representative label in each theme was set at ‘5’.
The research themes identified were ‘halal certification’ as Basic themes followed by ‘certification’ as Motor theme and ‘ethanol’ as a niche theme (Figure 6 and Table 6).
| Table 6 Themes And Keywords In Thematic Map |
||
|---|---|---|
| Themes | Cluster Representation | Keywords in Clusters |
| Basic Theme | Halal Certification | Halal Certification, Supply Chains, Certification Systems, Halal, Certification Process, Food Supply, Surveys, Halal Products, Food Safety. |
| Motor Theme | Certification | Certification, Malaysia, Article, Human, Muslim, Structural Equation Modeling, Food Industry, Catering Service. |
| Niche Theme | Ethanol | Ethanol, Animalia, Beverages, DNA, Polymerase Chain reaction, Bakery Products. |
| Motor Theme | Animals | Animals, Islam, Meat, Food Quality, Indonesia, Animal, Meats, Swine, Pork |
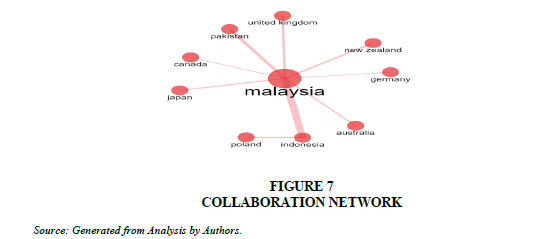
Collaboration Network
Analysis of collaborative world map for researches conducted on the topic of ‘halal certification’ witnessed the key collaboration between Malaysia and Indonesia (12), Malaysia and Pakistan (6), Malaysia and New Zeland (4) and Malaysia and Germany (2) respectively. Malaysia also collaborated with Japan, Canada, Australia and Poland. It ratifies the centrality of Malaysia as a hub for research on halal certification Figure 7.
Word Cloud
In order to identify the most significant and impactful key word on the topic, we tried to identify the most frequently used word on parameters like ‘keyword Plus’, ‘Author’s Keywords’ ,’title’ and ‘abstracts’. Certification is found to be the most frequently used word as per key words plus, ‘halal Certification’ as per author keywords and ‘halal’as per titles and abstracts. Details about terms and frequency on different parameters are provided in the table (Table-7) along with the word cloud generated from the data based on keyword plus (Figure-8) is shown as per the followings:
| Table 7 Most Frequent Words In Word Cloud |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Words Plus | Author Keywords | ||
| Terms | Frequency | Terms | Frequency |
| Certification | 24 | Halal Certification | 80 |
| Malaysia | 20 | Halal | 76 |
| Article | 18 | Malaysia | 26 |
| Human | 18 | Halal Food | 23 |
| Animals | 13 | Certification | 14 |
| Islam | 13 | Islam | 14 |
| Halal Certification | 12 | Halal Logistics | 12 |
| Meat | 12 | Halal Industry | 11 |
| Food Quality | 10 | Halal Tourism | 11 |
| Principal Component Analysis | 10 | Food Safety | 10 |
| Titles | Abstracts | ||
| Terms | Frequency | Terms | Frequency |
| Halal | 322 | Halal | 2374 |
| Food | 101 | Food | 751 |
| Certification | 97 | Certification | 653 |
| Malaysia | 48 | Study | 463 |
| Products | 42 | Products | 399 |
| Study | 30 | Muslim | 321 |
| Chain | 27 | Research | 301 |
| Muslim | 27 | Consumers | 245 |
| Supply | 25 | Industry | 225 |
| System | 25 | Malaysia | 222 |
Source: Generated by Authors from Analysis.
Documents by Funding Sponsor
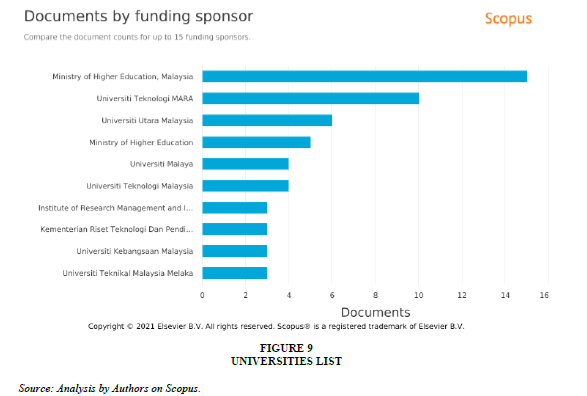
Analysis of documents by funding sponsors shows the highest number of research papers was produced with the funding by Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia followed by Universiti Teknologi, Mara, Universiti Utara, Malaysia many other institutions from Malysia justifying the reason for highest number of research publications from the country Figure 9.
Findings and Conclusion
Present research has witnessed key aspects of existing literature on ‘halal certification’. Analysis reveals that Journal of Islamic Marketing, International Journal of Supply Chain Management and British Food Journals emerged as the topmost journals contributing significantly to the body of knowledge on ‘halal’ certification. ‘Certification’ is found to be the most frequently used word as per key words plus, ‘halal Certification’ as per author keywords and ‘halal’ as per titles and abstracts.
CHE MAN YB (Total Citation of 392), Rohman et al. (2011) (Total Citation of 236), Erwanto Y (Total Citation of 183) and Sismindari (Total Citation of 3183) emerged as authors having the highest impact by total citation index with total citation as impact measure and number of authors to be 20 for researches on halal certification.
As per Bradford’s law Journal of Islamic Marketing, International Journal of Supply Chain Management, British Food Journal, Malaysian Journal of Consumer And Family Economics ,AIP Conference Proceedings were clustered in zone 1 i.e. highly productive source.
Universiti Putra Malaysia, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,Universiti Teknologi Mara and Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia emerged as most relevant affiliations for publishing research papers on halal certification.
Malaysia emerged as most cited country with highest number of citations (1719) followed by United Kingdom (283), Indonesia (160), Canada (121) and India (87) respectively. South Africa, Ghana and Belgium were reported to have zero citations of researches on halal certification.
Collaborative world Map indicates the key collaboration between Malaysia and Indonesia (12), Malaysia and Pakistan (6), Malaysia and New Zeland (4) and Malaysia and Germany (2) respectively. Malaysia also collaborated with Japan, Canada, Australia and Poland. The Conceptual Structure of ‘Biblioshiny’ identifies the themes and key research areas by using thematic map. The research themes identified were ‘halal certification’ as Basic themes followed by ‘certification’ as Motor theme and ‘ethanol’ as a niche theme.
Implications of the Study
Present study with a systematic review of existing literature on ‘halal certification’ has attempted to reveal the key aspects of existing researches along with the conceptual framework. Findings of our study sets the way forward for academicians, researchers and policy makers to explore in detail the identified basic and motor themes of ‘halal certification’ as per thematic map generated in this study. Some key areas of research on the subject are explained as follows:
1. Most of the studies have focused upon the need of halal –certification and its process but we could rarely find a study listing some products that does not require such certification due to the very nature and type of the product.
2. Sources of research (Journals) identified under zone 1 as per Bradford law may produce application based researches but it requires more funding to get more number of publications.
3. Collaborative research with top cited authors and affiliation shall avoid repeated version of same work and contribute significantly to the body to knowledge.
4. As per the findings of our study Malaysia and Indonesia along with some other countries have emerged as central hub for research on ‘halal certification and products’ Product-wise need assessment of ‘halal certification’ may be another dimension of future research.
References
Ab Talib, M.S., Sawari, S.S.M., Hamid, A.B.A., & Chin, T.A. (2016). Emerging Halal food market: an Institutional Theory of Halal certificate implementation.Management Research Review,39(9), 987-997.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ab Talib, M.S. (2017). Motivations and Benefits of Halal Food Safety Certification.Journal of Islamic Marketing,8(4), 605-624.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Adroit Market Research (2020), Halal Market by Product and by Region: Global Forecast 2019 to 2028.
Badruldin, B., Mohamed, Z., Sharifuddin, J., Rezai, G., Abdullah, A. M., Abd Latif, I., & Mohayidin, M.G. (2012). Clients' perception towards JAKIM service quality in Halal certification.Journal of Islamic Marketing,3(1), 59-71.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hanzaee, K.H., & Ramezani, M.R. (2011). Intention to halal products in the world markets.Interdisciplinary Journal of research in Business,1(5), 1-7.
Ireland, J., & Rajabzadeh, S.A. (2011). UAE consumer concerns about halal products.Journal of Islamic Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Khan, M.I., & Haleem, A. (2016). Understanding “Halal” and “Halal Certification & Accreditation System”-A Brief Review.Saudi Journal of Business and Management Studies,1(1), 32-42.
Lada, S., Tanakinjal, G.H., & Amin, H. (2009). Predicting intention to choose halal products using theory of reasoned action.Management,2(1), 66-76.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Latif, I.A., Mohamed, Z., Sharifuddin, J., Abdullah, A.M., & Ismail, M.M. (2014). A comparative analysis of global halal certification requirements.Journal of Food Products Marketing,20(sup1), 85-101.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Marzuki, S.Z.S., Hall, C.M., & Ballantine, P.W. (2012). Restaurant managers’ perspectives on halal certification.Journal of Islamic Marketing,3(1), 47-58.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Prabowo, S., Abd Rahman, A., Ab Rahman, S., & Samah, A.A. (2014). Revealing factors hindering halal certification in East Kalimantan Indonesia.JIMA,6, 2.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rajagopal, S., Ramanan, S., Visvanathan, R., & Satapathy, S. (2011). Halal certification: implication for marketers in UAE.Journal of Islamic Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Razalli, M.R., Yusoff, R.Z., & Mohd Roslan, M.W. (2013). A framework of halal certification practices for hotel industry.Asian Social Science,9(11), 316-326.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rohman, A., Erwanto, Y., & Man, Y.B.C. (2011). Analysis of pork adulteration in beef meatball using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy.Meat Science,88(1), 91-95.
Soon, J.M., Chandia, M., & Mac Regenstein, J. (2017). Halal integrity in the food supply chain.British Food Journal.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sufiyan, M., Haleem, A., Khan, S., & Khan, M.I. (2019). Evaluating food supply chain performance using hybrid fuzzy MCDM technique.Sustainable Production and Consumption,20, 40-57.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Tieman, M., & Ghazali, M.C. (2013). Principles in halal purchasing.Journal of Islamic Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zailani, S., Iranmanesh, M., Aziz, A.A., & Kanapathy, K. (2017). Halal logistics opportunities and challenges.Journal of Islamic Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zailani, S., Omar, A., & Kopong, S. (2011). An exploratory study on the factors influencing the non-compliance to halal among hoteliers in Malaysia.International Business Management,5(1), 1-12.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zupic, I., & Čater, T. (2015). Bibliometric methods in management and organization.Organizational research methods,18(3), 429-472.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 08-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-11589; Editor assigned: 10-Mar-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-11589(PQ); Reviewed: 24-Mar-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-11589; Revised: 26-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-11589(R); Published: 29-Mar-2022