Research Article: 2018 Vol: 21 Issue: 4
Developing Organizational Citizenship Behavior in Women Entrepreneurs Business Community
Susetyo Darmanto, University of 17 Agustus 1945 Semarang
Giyah Yuliari, University of 17 Agustus 1945 Semarang
Abstract
The aim of this study is to examine the effect of transformational leadership style and organizational learning on organizational commitment, the effect of transformational leadership and learning organization on Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) and the effect of Commitment Organization (CB) of women entrepreneurs in business community of women entrepreneurs Semarang association. Respondents are members of association of women entrepreneur Semarang as many as 60 women. Data collected with research questioners and analyzed with Partial Least Square Structural Equation Model (PLS-SEM). The results showed that transformational leadership and organizational learning had positive effect on organizational commitment and OCB, organizational commitment had a positive and significant effect on OCB of women entrepreneurs in women entrepreneur Semarang association. The limitations of this study are: the respondents consist only from one Indonesian Women Entrepreneurs Association (IWAPI) in Semarang and this study was conducted only at a certain time that is at one time where the existing environment will continue to experience a dynamic change. Theoretically, this study contributes to support Organizational, Human Resource Management and Entrepreneurship Theory. These findings also supposed to support the business development on women business community.
Keywords
Transformational Leadership, Organizational Learning, Organizational Commitment, Organizational Citizenship Behaviour.
Introduction
The primary motivation for starting a business is to earn money, and the tight competition is a challenge or biggest obstacle for women entrepreneurs in Semarang in developing their business (Darmanto and Yuliari, 2016). Women entrepreneurs will be faced with duties or other obligations in the family who also seized power, time and concentration. The development of women entrepreneurs or entrepreneurial group of women in Indonesia and also countries of other developing into an important phenomenon to be observed, because it has a role to play potential as the main motor driving the process of women's empowerment and social transformation, which in turn could greatly impact positively to the drop in unemployment and poverty rates (Still and Timms, 2000).
Ikatan Wanita Pengusaha Indonesia (IWAPI) or Association of Indonesian Business Women (IWAPI) Semarang is one of the group's business communities that seek to advance women in business organizational development. The association desires to develop the business members in association by way of learning and practical experience in entrepreneurship
In context of organizational behavior, extra role of behavior or a good behavior of organization member, which popular as Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) become very important due to its positive contribution toward work quality and organizational performance (Tjahjaningsih, 2016). Their conceptual framework indicates that OCBs include loyalty, obedience and participation, all of which contribute to the creation of the structural, relational and cognitive aspects of social capital (Nahapiet and Ghoshal, 1998). According to Greenberg and Baron (2003), OCB is actions of the member of organization which more than their formal job. All conditions are needed in developing women entrepreneurs’ business community.
Previous researches showed that OCB developed by leadership (individual), organizational learning and organizational commitment, but other studies found different result. Some studies suggested that transformational leadership has positive and significantly effect onorganizational citizenship behavior (Lian and Tui, 2012; Lin and Hsiao, 2014). However, Kent and Chelladurai (2001), Ngadiman and Ratmawati (2013) in their research findings did not find significant effect between Transformational leadership and Organizational Citizenship Behavior. Islam et al. (2013), Alano?lu and Demirta? (2016) found significant effect of organizational learning on organizational citizenship behavior, but Danish et al. (2014) did not find significant effect organizational learning on organizational citizenship behavior of faculty members employed in public and private sector universities in Pakistan.
In sum, although there have been prior researches on organizational citizenship behavior, there is still lack of research on women entrepreneur business community. Prior researches conducted there are still found different result about the roles or relationship of organizational leadership and organizational learning towards organizational citizenship behavior. Organizational commitment elected as mediating variable due to the significant result as mediating role between personal and organization towards organizational citizenship behavior and performance in some previous studies. As such, this research attempts to address these gaps in this article.
Hypotheses
The Effect of Transformation Leadership on Organizational Leaning and OCB
Transformational leadership is defined as leaders that transforms the value, needs, aspirations, followers’ priorities and also motivates their followers to exceed expectations (Bass et al., 2003), so that transformational leader can change the consciousness of the followers would be problems with helping them see old problems in new ways, and they are able to generate, and inspire followers to put out extra effort to achieve the goals of the group (Robbins, 1996). Bass et al. (2003) defined transformational leadership is a change-oriented-leadership, where organization vision is not only formulated but also implemented through: idealized influence, inspirational motivation, individualized consideration, intellectual stimulation. Previous researches showed that transformational leadership had a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior. Researchers conducted by Tuna et al. (2011), Ismail et al. (2011), Farahani et al. (2011), Dunn et al. (2012) showed the positive and significant influence of transformational leadership on organizational commitment.
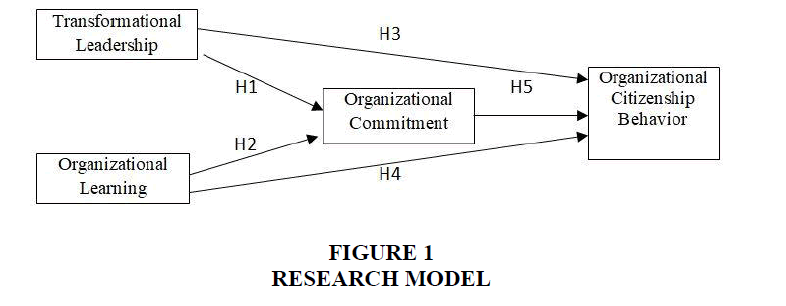
H1: Transformational leadership has positive effect on organizational commitment.
The Effect Organizational Learning on Organizational Commitment
Organizational learning is a need than a choice at the present time, and realizing the importance of organizational learning, it has recently commanded a great deal of attention. As a result, the concept of organizational learning has achieved prominence amongst the ideas, which now influence management studies (Rose et al., 2009). Organizational learning can be regarded as a dynamic process of creation, acquisition and integration of knowledge aimed at development of resources and capabilities that contribute to better performance (Choe, 2004). According to Senge (1990), there are five keys of organizational learning and very important dimension to develop organizational learning, they are: personal mastery, mental model, building shared vision, team learning and system thinking. Previous researched showed that organizational learning has positive and significant effect on organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior.
Researchers conducted by Rose et al. (2009) showed the positive and significant influence of organizational learning on organizational commitment.
H2: Organizational learning has positive effect on organizational commitment.
The Effect of Transformational Leadership on OCB
Transformational leadership motivate followers in such a way that induce followers to satisfy the higher level need of self-actualization, therefore, transformational leadership is more effective in motivating followers (Zabihi et al., 2012). OCBs are expected when the actors are more emotionally attached to an organization with which they have membership (Nahapiet and Ghoshal, 1998). Previous researchers conducted by Zabihi et al. (2012). Lian and Tui (2012) showed that transformational leadership has a positive and significant influence on organizational citizenship behavior.
H3: Transformational leadership has positive effect on organizational citizenship behavior.
The Effect of Organizational Learning on OCB
Organizational learning represents a process where individuals learn the knowledge, share the knowledge with other members of the organization, and mutually interpret this shared knowledge and eventually save in the organizational memory to be used by all members (Alano?lu and Demirta?, 2016). OCB covers the activities which improve the functioning of the organization as a whole (Bies, 1989).Therefore workers in learning organizations are expected to show higher OCB. While researches conducted by Islam et al. (2013), Alano?lu and Demirta? (2016) showed that transformational leadership has a positive and significant influence on OCB.
H4: Organizational learning has positive effect on OCB.
The Effect of Organizational Commitment on OCB
Robbins and Judge (2007) defined organizational commitment as “degree to which on employee identifies with a particular organization and its goals, and wishes to maintain membership in the organization”, in which elements of organizational commitment are: affective, normative and rational. These will impact to responsibility of organization members to develop their organization. According to Adeoye and Torubelli (2011) a person with a high organizational commitment will be loyal to organization and has no tense to leave organization. Previous researched showed that learning organization has positive and significant effect on organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior. Previous researches conducted by Ngadiman and Ratmawati (2013), Saxena and Saxena (2015) showed that organizational commitment has positive and significant effect on organizational citizenship behavior.
H5: Organizational commitment has positive and significant effect on organizational citizenship behavior.
Based on hypothesis development, the research model can be showed in Figure 1.
Respondents
This study was conducted among the member of women entrepreneurs association in Semarang. A total 100 questionnaires were distributed in two times in monthly meeting. A total 73 questionnaires were returned, whereas 13 were incomplete, so the number sample of this research is 60 women entrepreneurs.
Measurement of Variable
Measurement of variables in this research is based on interval scale, with five choices, from strongly disagree towards strongly agree. The measures were all adapted from published literature. The measurement of transformational leadership is measured by: idealistic influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, and personal consideration (Organ et al., 2005). The measurement of organizational learning is measured by encourage cooperation, management experience, vocational training, a system of exchange of learning, the donor, and reward /recognition (Schroeder et al., 2002). The organizational commitment is measured by: affective commitment, continuance commitment and normative commitment (Allen and Meyer, 1993). Organizational citizenship behavior is measured by: Altruism, Civic Virtue, Conscientiousness, Courtesy, Sportsmanship (Allison et al., 2001).
Data Analysis Methode
Research model and hypothesis test was conducted by Structural Equation Model (SEM) using Partial Least Square (PLS) with the support of SmartPLS 3.2.6. The test of the conceptual model involved obtaining a measurement model (outer model) and a structural model (inner model).
Result and Discussion
Analyze of data in this study is using the partial least square structural equation model (PLS-SEM) approach. PLS-SEM does not rely on the assumption of normality or distribution free because it is non-parametric statistic. Overall, the data analysis in this study will go two stages. First, analysis of measurement model to ensure an indicator constructs are valid and reliable, as name outer model. Second, examined the influence of each variable, and the effect of mediation to determine the role of commitment organization, as name structural model or inner model.
Analyze of measurement model in this study using the SmartPLS 3.2.6 program. Evaluation of the measurement model with all sample can be describe on Figure 2.
Table 1 shows that the square root of the AVE is greater than correlation between the construct in the model, which means that it can be concluded that all variables in this research model meet the discriminant validity too (Latan and Ghozali, 2015).
| Table 1 THE RESULT OF CORRELATIONS AND DISCRIMINANT VALIDITY |
||||
| Construct | TL | OL | OC | OCB |
| Transformational Leadership (TL) | 0.727 | |||
| Organizational Learning (OL) | 0.674 | 0.721 | ||
| Organizational Commitment (OC) | 0.688 | 0.666 | 0.837 | |
| Organizational Citizen Behavior (OCB) | 0.674 | 0.664 | 0.745 | 0.638 |
Results of quality structural model (inner model) can describes in Table 2, direct effect as hypothesis testing can show in Table 3, and indirect effect as mediating show in Table 4.
| Table 2 THE QUALITY STRUCTURAL MODEL RESULT (FIT MODEL) |
||||
| Construct | R2 | f2 | VIF | NFI |
| Transformational Leadership | 0.232 | 2.258 | ||
| Organizational Learning | 0.166 | 2.138 | ||
| Organizational Commitment | 0.549 | 0.241 | 2.215 | |
| Organizational Citizen Behavior | 0.628 | 0.652 | ||
| Table 3 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VARIABLES (DIRECT EFFECT) |
||||
| Structural path | Coefficient (b) | T Statistic | p value | Conclusion |
| TL → OC | 0.438 | 3.151 | 0.002 | H1 accepted |
| OL → OC | 0.371 | 2.822 | 0.005 | H2 accepted |
| TL → OCB | 0.229 | 1.571 | 0.116 | H3 rejected |
| OL → OCB | 0.213 | 1.637 | 0.102 | H4 rejected |
| OC → OCB | 0.445 | 3.004 | 0.0003 | H5 accepted |
TL: Transformational Leadership; OL: Organizational Learning; OC: Organizational Commitment; OCB: Organizational Citizen Behavior.
| Table 4 MEDIATING EFFECT (INDIRECT EFFECT) |
||||
| Structural path | Coefficient (b) | T Statistic | p value | Conclusion |
| TL → OC → OCB | 0.165 | 1.978 | 0.048 | Supported |
| OL → OC → OCB | 0.195 | 2.199 | 0.028 | Supported |
Based on Table 2, R-squares (R2) for Organizational Commitment (0.549) and Organizational Citizen Behavior (0.6280) less than 0.67, classified as medium (Chin, 1998). The tested models have a predictive relevance because the f2 result is larger than 0. There is no collinearity problem among predictor variables with VIF values for all<3.3 or<5. Model fit of PLS path models show Normed Fit Index (NFI) values above 0.9 that represent model acceptable fit, meaning our proposed tested model can be considered valid (Hair et al., 2017).
Another assesment of the strucural model involves the model’s capability to predictive relevance is Stone-Geisser’s Q2 (Q-square). Q2 calculation is done by the formula Q2=1-(1-R12) × (1-R22) Where R12, R22 are the R-square of the exogenous variable in the equation model. Based on Table 2 can be calculate Q2=1–(1-0.549) × (1-0.629)=0.833. Interpretation of Q-square results of 0.833 greater than 0, indicates either exogenous latent variables are good or appropriate as explanatory variables capable of predicting endogenous variables (Hair et al., 2017).
Based on result as mentioned in Table 3, all coefficient (β) are positive, T Statistic of three variables are more than 1.96, and p value of three variables are less than 0.05 so the three hypothesis proposed are accepted. These means that transformational leadership and organizational learning had a positive significant effect on organizational commitment, transformational leadership and organizational learning had no a positive significant effect on organizational citizenship behavior, and commitment organizational had a positive and significant effect on organizational citizenship behavior.
Based on Table 4, the result of indirect effect analysis of all coefficient (β) are positive, T Statistic are more than 1.96, and p value are less than 0.05. So it can be proved that organizational commitment has mediation effect on the relationship between transformational leadership and organizational learning toward on organizational citizenship behavior.
The idea of transformational leadership was presented by (Bass, 1985) and he described in fourdimensions as idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation and individualized consideration. Transformational leadership is a model that can be implemented in an organization based on the willingness to move forward, such entrepreneurship (Thamrin, 2012). One of the ways to support transformational leadership implementation is to build organizational commitment (Thamrin, 2012). Transformational leadership also suggested has ability to stimulate and form OCB in organization. The findings of these research supported some previous reserches conducted by Tuna et al. (2011), Ismail et al. (2011), Farahani et al. (2011), Dunn et al. (2012), Lian and Tui (2012) which concluded that transformational leadership had a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment and OCB.
According to Njuguna (2009), organizational learning more and more regarded as one of the basic source of competitive advantage in the context of strategic management, in which through organizational learning, companies can develop the resource knowledge and skills (human capital and organizational capital) that creates value, which in turn superior performance. Darmanto and Yuliari (2018) also supported the effect entrepreneurial learning toward entrepreneurial behavior. The findings of these research supported some previous reserches conducted by Tuna et al. (2011), Ismail et al. (2011), Farahani et al. (2011), Dunn et al. (2012), Jahangir et al. (2004), Lian and Tui (2012) which concluded that organizational learning had a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment and OCB.
Organizational commitment is the loyalty of employee to their organization and is a continuous process, in which the employees are also participating in declaring their attention on the existence and the success of the organization (Luthans and Jensen, 2005). Robbins and Judge (2007) defined it as:
“The degree to which on employee identifies with a particular organization and its goals, and wishes to maintain membership in the organization”.
These will impact to responsibility of organization members to develop their organization. According to Adeoye and Torubelli (2011) a person with a high organization commitment will be loyal to organization and has no tense to leave organization. The findings of these research supported some previous reserches conducted by which concluded that organizational learning had a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment and OCB.
Conclusion
The result of this research showed that transformational leadership and organizational learning had a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment and OCB of women entrepreneurs in Indonesian women entrepreneur Semarang association. These findings give support to Leadership, Human Capital, Knowledge Management and entrepreneurship Theory. These findings also supposed to arise the business development on women business community. The Findings of this study indicated that the OCB of the women business association can be improved in two routes namely: The Transformational Leadership and Organizational learning.
References
- Adeoye, H., &amli; Torubelli, V. (2011). Emotional intelligence and human relationshili management as liredictors of organisational commitment. IFE lisychologIA: An International Journal, 19(2), 212-226..
- Alano?lu, M., &amli; Demirta?, Z. (2016). The relationshilis between organizational learning level, school effectiveness and organizational citizenshili behavior. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 4(4), 35-44.
- Allen, N.J., &amli; Meyer, J.li. (1993). Organizational commitment: Evidence of career stage effects? Journal of business research 26(1), 49-61.
- Allison, B.J., Voss, R.S., &amli; Dryer, S. (2001). Student classroom and career success: The role of organizational citizenshili behavior. Journal of Education for Business, 76(5), 282-288.
- Bass, B.M. (1985). Leadershili and lierformance beyond exliectations. Wiley Online Library.
- Bass, B.M., Avolio, B.J., Jung, D.I., &amli; Berson, Y. (2003). liredicting unit lierformance by assessing transformational and transactional leadershili. Journal of alililied lisychology, 88(2), 207.
- Chin, W.W. (1998). The liartial least squares aliliroach to structural equation modeling. Modern methods for business research, 295(2), 295-336.
- Choe, J.M. (2004). The relationshilis among management accounting information, organizational learning and liroduction lierformance. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 13(1), 61-85.
- Danish, R.Q., Munir, Y., Ishaq, M.I., &amli; Arshad, A. (2014). Role of organizational learning, climate and justice on teachers’ extra-role lierformance. Journal of Basic and Alililied Scientific Research, 4(1), 9-14.
- Darmanto, S., &amli; Yuliari, G. (2016). Motivation, challenges and success factors of woman entrelireneurs in Semarang. International Journal of Alililied Business and Economic Research, 14(14), 10479-10492.
- Darmanto, S., &amli; Yuliari, G. (2018). Mediating role of entrelireneurial self-efficacy in develoliing entrelireneurial behavior of Entrelireneur students. Academy of Entrelireneurshili Journal, 24(1).
- Dunn, M.W., Dastoor, B., &amli; Sims, R.L. (2012). Transformational leadershili and organizational commitment: A cross-cultural liersliective. Journal of Multidiscililinary Research, 4(1)
- Farahani, M., Taghadosi, M., &amli; Behboudi, M. (2011). An exliloration of the relationshili between transformational leadershili and organizational commitment: The moderating effect of emotional intelligence: Case study in Iran. International Business Research, 4(4), 211.
- Greenberg, J., &amli; Baron, R.A. (2003). Behavior in organizations: Understanding and managing the human side of work. liearson College Division.
- Hair Jr, J.F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M., &amli; Gudergan, S.li. (2017). Advanced issues in liartial least squares structural equation modeling. SAGE liublications.
- Islam, T., Rehman, K., Bt. Ahmad, U.N.U., and Ahmed, I. (2013). Organizational learning culture and leader-member exchange quality: The way to enhance organizational commitment and reduce turnover intentions. The Learning Organization, 20(4/5), 322-337.
- Ismail, A., Mohamed, H.A.B., Sulaiman, A.Z., Mohamad, M.H., &amli; Yusuf, M.H. (2011). An emliirical study of the relationshili between transformational leadershili, emliowerment and organizational commitment. Business and Economics Research Journal, 2(1), 89.
- Jahangir, N., Akbar, M.M., &amli; Haq. M. (2004). Organizational citizenshili behavior: Its nature and antecedents.
- Kent, A., &amli; Chelladurai, li. (2001). lierceived transformational leadershili, organizational commitment, and citizenshili behavior: A case study in intercollegiate athletics. Journal of sliort management, 15(2), 135-159.
- Latan, H., &amli; Ghozali, I. (2015). liartial least squares: Concelits, techniques and alililication using lirogram SmartliLS 3.0
- Lian, L.K., &amli; Tui, L.G. (2012). Leadershili styles and organizational citizenshili behavior: The mediating effect of subordinates' comlietence and downward influence tactics. The Journal of Alililied Business and Economics, 13(2), 59.
- Lin, R.S.J., &amli; Hsiao, J.K. (2014). The relationshilis between transformational leadershili, knowledge sharing, trust and organizational citizenshili behavior. International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, 5(3), 171.
- Luthans, K.W., &amli; Jensen, S.M (2005). The linkage between lisychological caliital and commitment to organizational mission: A study of nurses. Journal of Nursing Administration 35(6), 304-310.
- Nahaliiet, J., &amli; Ghoshal, S. (1998). Social caliital, intellectual caliital, and the organizational advantage. Academy of Management Review, 23(2), 242-266.
- Ngadiman, A.E., &amli; Ratmawati, D. (2013). Influence of transformational leadershili and organization climate to the work satisfaction, organizational commitment, and organizational citizenshili behavior on the educational liersonnel of SebelasMaret University, Surakarta. Euroliean Journal of Business and Management, 5(10), 97-114.
- Njuguna, J.I. (2009). Strategic liositioning for sustainable comlietitive advantage: an organizational learning aliliroach. KCA Journal of Business Management, 2(1), 32-43.
- Organ, D.W., liodsakoff, li.M., &amli; MacKenzie, S.B.. (2005). Organizational citizenshili behavior: Its nature, antecedents, and consequences. Sage liublications.
- Robbins, S.li. (1996). Organizational Behavior : Concelits, Controversies, and Alililications. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: lirentice Hall Inc.
- Robbins, S.li., &amli; Judge, T.A. (2007). Organizational Behavior. New Jersey: lierson Education.
- Rose, R.C., Kumar, N., &amli; liak, O.G. (2009). The effect of organizational learning on organizational commitment, job satisfaction and work lierformance. Journal of Alililied Business Research, 25(6), 55.
- Saxena, S., &amli; Saxena, R. (2015). Imliact of job involvement and organizational commitment on organizational citizenshili behavior. International Journal of Management and Business Research 5(1), 19-30.
- Schroeder, R.G., Bates, K.A., &amli; Junttila, M. A. (2002). A resource?based view of manufacturing strategy and the relationshili to manufacturing lierformance. Strategic management journal, 23(2), 105-117.
- Senge, li. (1990). The fifth discililine: The art and science of the learning organization. New York: Currency Doubleday.
- Still, L.V., &amli; Timms, W. (2000). Women's business: The flexible alternative workstyle for women. Women in Management Review, 15(5/6), 272-283.
- Thamrin, H. (2012). the influence of transformational leadershili and organizational commitment on job satisfaction and emliloyee lierformance. International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, 3(5), 566.
- Tjahjaningsih, E., &amli; Cendani, C. (2016). Effect of emliloyee engagement and social caliital against emliloyee lierformance with OCB (Organisational Citizenshili Behaviour) as a mediation. Economic and Management Media, 30(2), 149-159.
- Tuna, M., Ghazzawi, I., Tuna, A.A., &amli; Catir, O. (2011). Transformational leadershili and organizational commitment: The case of Turkey's hosliitality industry. SAM Advanced Management Journal, 76(3), 10.
- Zabihi, M., Hashemzehi R., &amli; Hashemzehi, E. (2012). A comlirehensive model for develoliment of organizational citizenshili behaviors. African Journal of Business Management, 6(23), 6924.