Review Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 2S
Determinants of Mobile Marketing Acceptance and Adoption in Greater Visakhapatnam City
Pratima Merugu, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management
GNPV Babu, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management
M. Vijayabaskar, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management
Joseph Paul, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management
Chandana Valluripalli, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management
Citation Information: Merugu, P., Babu, GNPV., Vijayabaskar, M., Paul, J., & Valluripalli, C. (2024). Determinants of mobile marketing acceptance and adoption in greater visakhapatnam city. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(S2), 1-9.
Abstract
Purpose: This study empirically investigates the significant factors influencing consumer acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing. The research aims to develop a conceptual model of mobile marketing acceptance and adoption in Visakhapatnam City. Research Design/Methodology: Structural equation modeling to identify variables inducing the adoption of mobile advertising among buyers is applied. A total of 400 respondents' data was analyzed. The subjects of this study are general customers in Visakhapatnam City. The sampling method used is convenience sampling. Findings: The study's effects illustrate the role of selected variables: perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, information, entertainment, credibility, and privacy, to determine customer attitude and adoption of mobile marketing. Originality: The study conceptualized a framework for understanding consumer's acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing in Visakhapatnam city Managerial Implications: The findings of the study will help identify the indicators of consumers' adoption of mobile marketing and for companies to build appropriate strategies targeting potential buyers of this latest technology Limitations: The study examines the user's attitudes and adoption of mobile marketing in Visakhapatnam City alone. Further studies can focus on different geographical and cultural settings.
Keywords
Mobile Marketing, Consumers Attitude and Adoption, Information Technology.
Introduction
Technology convergence into marketing activities resulted in the e-marketing concept, resulting in quicker computing, communication, and content delivery around networked digital media platforms. Around the 2000s, mobile communication technology developed rapidly, and with the impact of social networks, it became widespread. Mobile technologies have made communication possible without restrictions as to place and time. Online Marketing has increased since 2011, with worldwide internet facilities and 4G services boosting mobile internet usage. The rise in smartphone technology has brought stores into customers' hands, where they can search and shop flexibly, and most marketers shifted to online mode to sell and promote their activities. The number of smartphone users worldwide has become lucrative for the business world.
Mobile Advertising is one of the significant components of Mobile Marketing. The ads that appear on smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices create an appeal to users. Recent reports state that users spend 40 percent of their internet time on Mobile devices and 89 percent of their mobile time on apps. It creates the most significant appeal for marketers to shift towards mobile marketing. Consumers are highly versatile and constantly changing. Mobile devices facilitate information search and product comparison and create a relationship with the marketer.
Review of Literature
Several researchers studied users' behaviour on their mobile usage and response to specific information about goods and services. A few of them conversed below.
Sham et al. (2014) explored the factors influencing consumers to accept mobile marketing. The study also examined the perspectives of the consumers on issues such as permission and privacy issues. The study revealed that information, irritation, credibility, entertainment, effects of modality and culture, and personalization influenced consumers' acceptance of mobile marketing.
Gurmeet Singh and Ramneet Kaur (2015) examined the factors inducing customers' attitudes toward mobile advertising. The study of 244 respondents confirms that informativeness, credibility, utility, and permission-based issues influence consumers' attitudes.
Further, the study highlighted that irritation and privacy negatively affect mobile advertising attitudes. Rekha and Pooja J. (2018) examined consumers' attitudes toward advertisements and mobile marketing in Delhi in their study. The findings revealed that consumers have a positive attitude toward mobile advertising and marketing. The results also showed that among mobile marketing tools, Mobile App was the most widely used mobile marketing tool, followed by text messages and mobile advertisement. Sivanenthira et al. (2018) explored the factors driving users' attitudes toward mobile advertising. The statistical results revealed that attitude influences consumers' acceptance of mobile advertising.
Surabhi Singh (2019) examined the determinants of mobile marketing satisfaction or consumer attitude towards mobile marketing. The study highlighted four elements, reliability, value for money, accuracy and social influence, and effective form of service, as the significant factors driving consumer satisfaction toward mobile marketing.
Anjana (2019) investigated the significant factors influencing consumer attitudes toward mobile marketing. The study identifies information quality, credibility, perceived utility, and attitude toward advertisements as the strongest drivers of mobile marketing acceptance. The findings revealed that customers positively react to mobile-based communications, provided they are customized according to their needs.
Rui Manuel Cruz et al. (2021) studied the influence of variables such as attitudes towards advertising, perceived utility, perceived risk, and attitudes towards mobile marketing on the behavioural intentions among college students. The research concludes that the variables' attitudes towards advertising and perceptual utility have more impact on the behavioural choice to the acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing.
Ismail et al. (2022) examined the determinants of mobile marketing services acceptance among Gen-y consumers by computing the consumers’ intentions. This research indicated that attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioural control, and perceived risk tend to influence the consumers' intention to use actual use for mobile marketing services.
Sarwat Jahan et al. (2022) analyzed the antecedents of the technological acceptance of marketing on mobile devices in the United Arab Emirates restaurant industry using the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). The study observed that the perceived ease of use and perceived utility of mobile marketing were significant predictors of intention to use. In addition, this study concludes that restaurant customers in the UAE have a positive attitude toward mobile marketing.
Statement of the Problem
The study fills the gap in the related literature by exploring factors influencing consumers' acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing in today's competitive markets. The study also examines how consumers' attitude affects consumer adoption in a rapidly developing city like Visakhapatnam, where survey on mobile marketing is scarce. A quantitative research design helped validate this study's theoretical framework and hypotheses.
Proposed Conceptual Framework for the Study
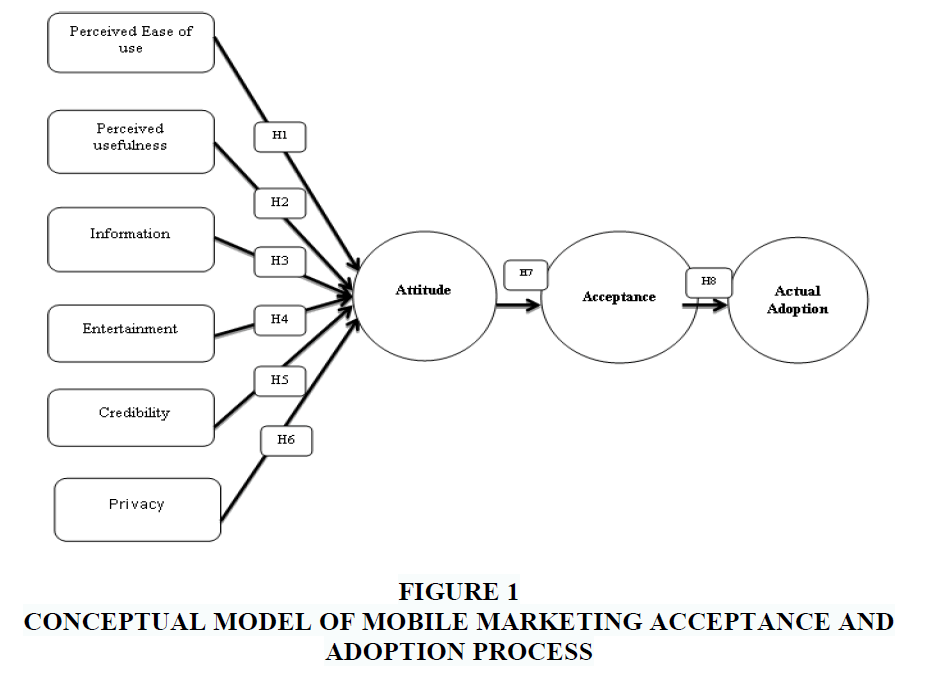
After examining the relevant literature review exploring Mobile Marketing acceptance and adoption, the study proposed a research model (Figure -1). Table -1 explains the constructs for the proposed model.
| Table 1 Constructs for the Proposed Model | |
| Constructs | Definition |
| Perceived Ease of Use | The degree to which users perceive how easy it is to use the technology |
| Perceived usefulness | The extent to which users believe how useful/beneficial the technology would be |
| Information | The ability to inform or persuade consumers of product benefits |
| Entertainment | The audience's needs for fun, enjoyment, or emotional pleasure |
| Credibility | Consumers' confidence and trust in the service/product |
| Privacy | The ability to protect consumer's personal and sensitive information when using the service |
| Attitude | The way buyers like or dislike feel towards a product /service. |
| Adoption | Acceptance of the product/service leads to actual usage or consumption. |
Need for the Study
This study aims to comprehend the factors influencing customer attitudes toward mobile marketing. Marketers can adapt mobile marketing techniques to showcase their products to customers. Mobile marketing has provided marketers with interactive communication, confidentiality, and continuity of response. The target response rate to mobile marketing campaigns is higher than that of the traditional advertising and promotion method. The results can help marketers adopt mobile marketing as the main channel for promoting goods and services to direct contact with customers. This study's findings will help marketers and policymakers identify the factors influencing consumers' acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing.
Objectives of the Study
To analyze the factors influencing consumer attitude toward mobile marketing
• To examine the drivers of consumer's acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing
• To suggest suitable strategies to promote mobile marketing usage.
Hypothesis of the Study
Based on the study's theoretical framework, this research hypothesizes as follows:
• H1: Perceived Ease of use influences consumer attitude toward mobile marketing
• H2: Perceived Usefulness affects consumer attitude toward mobile marketing
• H3: Information influences consumer attitude toward mobile marketing
• H4: Entertainment influences consumer attitude toward mobile marketing
• H5: Credibility influences consumer attitude toward mobile marketing
• H6: Privacy affects consumer attitude toward mobile marketing
• H7: Attitude influences consumer acceptance of mobile marketing
• H8: Acceptance of mobile marketing influences actual adoption among consumers.
Research Methodology
Sample selection: 400 respondents were chosen as the representative sample using a convenience sampling technique.
Sources of Data: the study gathered data through a structured questionnaire. The questionnaire before the actual distribution to the respondents was pretested and validated.
The study period: The research was for four months (January to April 2021). As the investigation is exploratory, a survey method was employed
Tools used for the study: The questionnaire includes six factors measured on a five-point Likert scale. The construct attitude and purchase intention were also measured using a Likert range. Twenty-eight items were studied using statistical tools like percentage analysis and structural equation model (SEM. Cronbach's Alpha test supported the reliability of the data. Table -2 reports the resulting values of Cronbach's reliability test.
| Table 2 Reliability Statistics | ||
| Cronbach's Alpha | Cronbach's Alpha Based on Standardized Items | No of Items |
| .945 | .950 | 24 |
Data Analysis
Table-3 shows the demographic summary of the sample selected for the study. The factors like age, gender, education, income, and occupation significantly impact the customers' Mobile Marketing prospects.
| Table 3 Demographic Profile | |||
| Variables | Particulars | No of Respondents | Percentage |
| Age Group (in Years) | Less than 20 | 134 | 33.5 |
| 21 – 30 | 92 | 23 | |
| 31 -40 | 86 | 21.5 | |
| 41 – 50 | 46 | 11.5 | |
| Above 50 | 42 | 10.5 | |
| Total | 400 | 100 | |
| Gender | Male | 226 | 56.5 |
| Female | 174 | 43.5 | |
| Total | 400 | 100 | |
| Level of Education | SSC /inter | 102 | 25.5 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 128 | 32 | |
| Postgraduate | 118 | 29.5 | |
| Others | 52 | 13 | |
| Total | 400 | 100 | |
| Income Level | Less than -Rs. 20000 | 76 | 19 |
| Rs. 20001 – Rs. 30000 | 121 | 30.25 | |
| Rs. 30001 – Rs. 50000 | 71 | 17.75 | |
| Rs. 50001 – Rs. 75000 | 52 | 13 | |
| Rs. 75001 – Rs. 100000 | 38 | 9.5 | |
| More than Rs. 100000 | 42 | 10.5 | |
| Total | 400 | 100 | |
| Occupation | Employed in private service | 104 | 26 |
| Employed in government service | 98 | 24.5 | |
| Business/self-employed | 81 | 20.25 | |
| Student | 92 | 23 | |
| Others | 25 | 6.25 | |
| Total | 400 | 100 | |
The study observed that most mobile users are below 30 years; this shows young people are well-versed in mobile and internet usage and show interest in mobile purchasing platforms. Males dominate mobile marketing activities, and females also make a significant share of mobile purchases. Women have a considerable influence in making family purchase decisions.
Education is a significant aspect that determines the mobile commerce market, knowledge, and understanding of the platform to create demand and loyalty. Most respondents have primary education, which helps them develop basic accounts and purchase mobile marketing platforms.
Occupation determines the respondent's income levels; income gives surplus money to consume goods and services, encouraging customers to spend time on mobile ads and activities. Most respondents are either professionals or employed in the private sector. Students and homemakers form a minor segment of the respondents' sample.
Over the years, Visakhapatnam is developing into a cosmopolitan city with several public sector companies and an Indian Navy base. There is a varied combination of people with different linguistics and culture. Whatever the background, a customer behaves like a customer in the marketplace who tries to obtain the maximum value of the expense made. The study surveyed 400 respondents to understand how people spend time on mobile phones.
Table 4 reports most respondents, i.e., 68 respondents, use mobile phones for chatting, messaging, and mail; the next majority of 66 respondents, or 16 per cent, use mobiles to play games. Another 62 respondents watch videos on their mobile phones. Some 12 per cent of respondents use mobiles for social networking. The most beautiful part is that around 45 respondents use mobile phones for online shopping, which is approximately 11.25 per cent, an attractive number for online marketers. This pandemic boosts online purchases as people avoid social contact and hang out in shopping malls. The study also observed that people use mobile phones for activities like making online payments, reading and internet surfing, listening to music, mobile banking, and navigation together account for 28 per cent of activities over mobile phones.
| Table 4 Consumers Preferred Activities Over Mobile Phones | ||
| Particulars | No. of Respondents | Percent (%) |
| Ordering and Online Shopping | 45 | 11.25 |
| Watching Videos | 62 | 15.5 |
| Social Networking | 50 | 12.5 |
| Playing Games | 66 | 16.5 |
| Making Payments | 31 | 7.75 |
| Reading and Internet Surfing | 24 | 6 |
| Listening to Music | 18 | 4.5 |
| Mobile Banking | 24 | 6 |
| Using GPS/Maps for Navigation | 12 | 3 |
| Chat, Messages, Text, and Emails) | 68 | 17 |
| TOTAL | 400 | 100 |
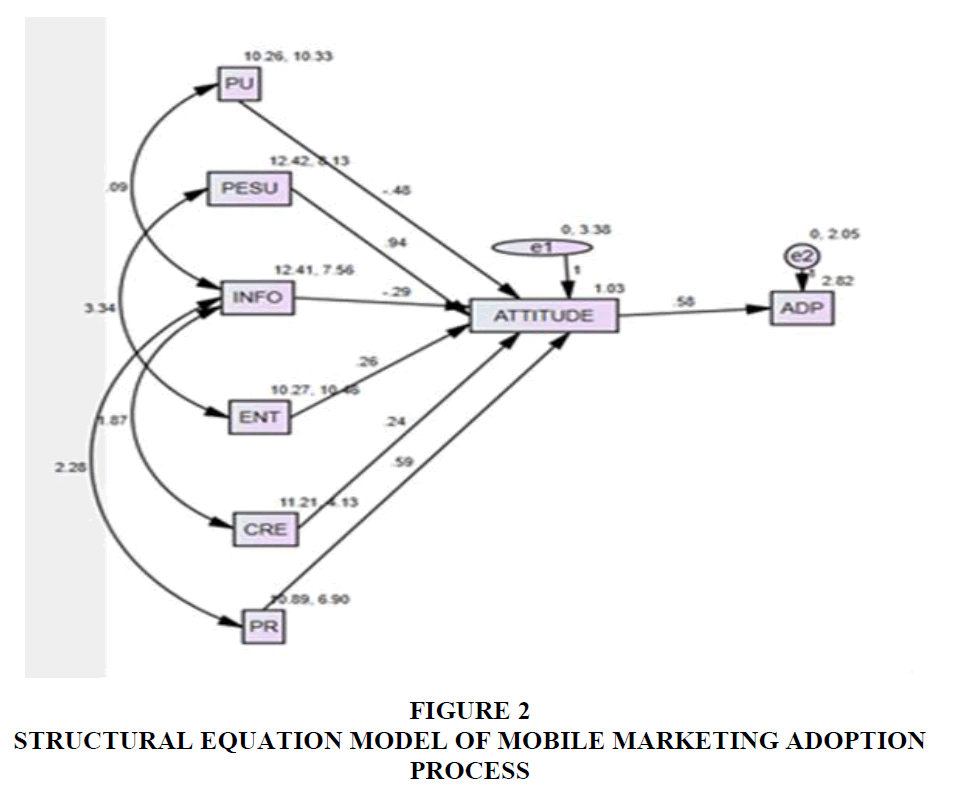
Table- 5 reveals the influential antecedents shaping users' attitudes (ATT) and behavioural intention (B.I.) towards mobile marketing in Visakhapatnam. All selected variables, perceived usefulness, perceived use, information, entertainment credibility, and privacy, are statistically significant, with p-values less than 0.01. The resulting standardized coefficient, as indicated in Table -5, reveals that the most critical factor is credibility (C.R.) 0.069, followed by privacy (PR) 0.053 and information (INFO) 0.053. The least important factor in perceived usefulness (PU) is 0.041.
| Table 5 Regression Weights of Proposed Variables | ||||||
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | P | Label | ||
| ATTITUDE <--- | PU | -.485 | .041 | -11.956 | *** | par_5 |
| ATTITUDE <--- | PESU | .939 | .049 | 19.152 | *** | par_6 |
| ATTITUDE <--- | INFO | -.294 | .053 | -5.503 | *** | par_7 |
| ATTITUDE <--- | ENT | .260 | .043 | 6.014 | *** | par_8 |
| ATTITUDE <--- | CRE | .244 | .069 | 3.557 | *** | par_9 |
| ATTITUDE <--- | PR | .589 | .053 | 11.170 | *** | par_10 |
| ADP<--- | ATTITUDE | .582 | .024 | 24.068 | *** | par_11 |
Table-6 reveals the significant correlation between the selected variables. The resulting values indicate that information privacy influences buyers' intention to accept and adopt mobile marketing. Similarly, credibility and information and perceived ease of entertainment use are significant.
| Table 6 Covariances of the Proposed Variables | |||||||
| Variables | Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | P | Label | ||
| PU | <--> | INFO | .089 | .556 | .160 | .873 | par_1 |
| INFO | <--> | PR | 2.281 | .509 | 4.483 | *** | par_2 |
| INFO | <--> | CRE | 1.865 | .398 | 4.681 | *** | par_3 |
| PESU | <--> | ENT | 3.337 | .695 | 4.799 | *** | par_4 |
Findings of the Study
The findings reveal that most mobile users are below 30 years old and well-versed in mobile and internet usage. Further, the male population is dominating the usage of mobile marketing activities with 56 percent. The study observed 30 per cent of respondents are graduates, and another 30 per cent are diploma holders. The study indicates that most respondents representing 50 per cent, are in the income band of Rs.75 000. The most beautiful part is around 45 percent of respondents use mobile phones for online shopping, which is an attractive number for online marketers, and that most respondents use mobile phones for chatting, messaging, and emails. The study observed that people use mobile phones for online payments, reading, internet surfing, listening to music, mobile banking, and navigation, accounting for 28 percent of activities over mobile phones. The variables, namely perceived usefulness, ease of use, information, entertainment, credibility, and privacy, are statistically significant in shaping users' attitudes and usage intention towards mobile marketing in Visakhapatnam.
Suggestions
1.Retailers should develop better apps with more security over transactions to promote users' acceptance and usage of mobile commerce.
2.Information is wealth. M-commerce platforms should continue promoting their activities through SMS and frequent information calls.
3.E-tailers should have a more personalized approach, as different customers have different leisure time and applicability; m-marketers should take note of customers' convenience and approach them accordingly.
Conclusion
This pandemic boosts online purchases as people avoid social contact and hang out in shopping malls. The study identifies the critical predictors of mobile marketing acceptance and adoption in Visakhapatnam City. The resulting values signify the importance of the variables, namely perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, information, entertainment, credibility, and privacy, in predicting the attitude and adoption of mobile marketing. The regression weights are significant in predicting mobile marketing acceptance and adoption drivers. The findings can help policymakers and mobile service providers formulate and implement suitable strategies for attracting and retaining existing users.
Limitations of the Study
1. The study sheds light on consumers' opinions in Vizag City alone. The findings may not apply to other geographical areas.
2. Further studies on other variables like perceived social and emotional values and sacrifices can be an exciting area to explore
3. Researchers can further explore the impact of information on consumers' attitudes towards acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing in rural areas.
Scope for further Studies
Buyer behaviour's dynamic nature may change consumers' tastes and preferences. Furthermore, similar studies with larger sample sizes and geography can be exciting.
A similar study on social marketing and networking influence can be undertaken.
References
Al-Maroof, R. S., Salloum, S. A., AlHamadand, A. Q., & Shaalan, K. (2020). Understanding an Extension Technology Acceptance Model of Google Translation: A Multi-Cultural Study in United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (IJIM), 14(03), 157-178.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Anjana, S. (2019). A study on factors influencing customers' attitudes towards mobile marketing. International Journal of Business and Management Invention, 8(2), 28-30.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chhonker, M. S., Verma, D., & Kar, A. K. (2017). Review of technology adoption frameworks in mobile commerce. Procedia Computer Science, 122, 888-895.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cruz, R. M. N., Rosário, A. T., & Rio, G. (2021). The factors that influence the acceptance and adoption of mobile marketing by university students. International Journal of Business and Systems Research, 15(4), 527-543.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gurmeet Singh & Ramneet Kaur (2015). Consumers attitudes towards mobile advertising: An empirical study in the Indian context. Advances in Economics and Business Management, 2(5), 450-456.
Hajarian, M., Camilleri, M. A., Díaz, P., & Aedo, I. (2021). A taxonomy of online marketing methods. In M. A. Camilleri (Ed.), Strategic corporate communication in the digital age (pp. 235-250). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ismail, M., Razak, R. C., Hakimin Yusoff, M. N., Wan Zulkiffli, W. F., & Wan Mohd Nasir, W. M. N. (2022). The Determinants of Mobile Marketing Services Acceptance among Gen-Y Consumers. International Journal of Criminology and Sociology, 9, 2277–2284.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Muchran, M., & Ahmar, A. S. (2019). Application of TAM model to the use of information technology. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.11358.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Pongiannan, K. (2013) An Evocative appraisal of the traits and values of advertisements in TV and web media. Smart Journal of Business Management Studies, 9(1), 51-64.
Rekha, & Jain, P. (2018). Consumers' Attitude Towards Mobile Marketing: An Empirical Investigation. PACIFIC BUSINESS REVIEW INTERNATIONAL, 11(4), 49-63.
Singh, D. S. (2019) Investigating consumer satisfaction towards mobile marketing. Journal of International Technology and Information Management, 28(2), 93-108.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sivanenthira, S., E, R., & D, S. (2018). A study of consumer attitudes towards mobile advertising among the University of Jaffna Srilanka undergraduates. The International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Invention, 5(8), 4918-4922.
Received: 27-Jul-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13932; Editor assigned: 28-Jul-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13932(PQ); Reviewed: 26-Oct-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13932; Revised: 02-Nov-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13932(R); Published: 11-Dec-2023