Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 3
Decentralization, Centralization and Quality of Organizational Performance of Human Resources
Fory A. N Away, Universitas Negeri Gorontalo
Benget Simamora, Politeknik Negeri Media Kreatif
Salam Irianto Nadeak, Politeknik Negeri Media Kreatif
Mulyawan Safwandy Nugraha, Pascasarjana STAI Sukabumi
Indra Prasetia, Universitas Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utara
Prasetyono Hendriarto, Universitas Pakuan
Abstract
The success of an organization in achieving set goals is largely dependent on performance. A decentralized organization provides freedom of authority for lower managers to make decisions. This study, therefore, aims to analyse the effects of decentralization, centralization, and the quality of human resources on organizational performance. Data were randomly obtained from 105 people using the survey and quantitative approach. The study showed that the partial effect of decentralization (X1) has no significance so it isn’t accepted, Variable centralization (X2), and human resources (X3) on the organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks were positively and significantly accepted. Therefore, these three variables have an effect on improving organizational performance, thereby, delegating decision-making power to experts in need of knowledge on a particular issue, technology, product, or market. High centralization rates mean greater coordination and smaller flexibility, while decentralization is attributed to greater flexibility and less coordination.
Keywords
Decentralization, Centralization, Human Resources Quality, Organizational Performance.
Introduction
The activities associated with running companies or organizations always face problems irrespective of their performance. Almost all organizations use performance to measure their ability to succeed, fail and achieve predetermined goals effectively and efficiently. A person's performance, in a particular field of work, is largely determined by their level of competence, professionalism, and commitment in carrying out their jobs within an organization. Therefore, everyone needs to develop organizational commitments which ultimately improves performance and leads to success. In order to gain employee commitment to the organization, management need to implement several efforts to encourage strong teamwork culture, improve socializing, ensure transparency, set clear goals and expectations, communicate openly, maintain good work ethics, build trust, and encourage innovation, provide constructive feedback and not criticism, delegate tasks efficiently, and provide good incentives. In addition, performance appraisal plays an important role in identifying or measuring the success of a company or organization. Some examples of important success factors are increasing market share through current customers, providing excellent service, achieving perfection in carrying out on-line orders, and granting incentives & reward to employees. These factors need to be utilize by organizations to attain success especially in today’s globalization era where business competition is getting tougher and a lot of companies are emerging that operate in similar fields. The tight competition indirectly requires managers to be more observant in setting strategies and utilizing existing capabilities to excellently survive in their field irrespective of the existing problems. The inability of companies or organizations to compete with others, leads to their complete closure. Therefore, determining their competitors, and what they offer, help companies to make products, services and marketing strategies unique. Companies can also create marketing strategies that harnesses the weaknesses of their competitors, and improve performance. It also enables them to assess any threat posed by new and old competitors. In addition, innovating and improving employee performance helps to achieve predetermined goals and leads to organizational success. Presently, there are strict business measures and rules associated with prices in the global market due to the advent of technology; therefore, companies have obliged to use the use of reliable and creative human resources such as accurate price tags. They also make use of auto to develop and encourage corporate activities. The survival and growth of every organization, is dependent on the quality of human resources. This is because qualified human resources support companies to make quality decisions, minimize uncertainty, and reduce risks associated with choosing alternatives. Therefore, companies are permissible in the use of different marketing tools to conduct product innovations, and merging with others to achieve profits. According to Widodo (2019), the management of authority in an organization is grouped into centralizeation and decentralizeation. Centralization refers to the general manager, while decentralization is the delegation of authority from top management to subordinates. There are four main types of decentralization, namely political, administrative, fiscal, and market decentralization. However, the decentralized authority management expects decisions to be quick to avoid interference with the company's operations. In addition, with decentralization, decisions can be made by one party to eliminate confusion. Most of the Rural Banks have implemented the decentralization management process by safeguarding new products and services, determining large-scale investments, allocating budgets and determining selling prices, carrying out organizational strategy, and developing concepts as well as ideas. In decentralized organizations, decision security is made by all employees throughout the organization, with managers at various levels left to make important decisions according to the area and scope of their responsibilities. Therefore, decentralization focusess more on policies related to termination of employment, determination of small-scale investment, objective development in decision security, strategies, development varied ideas and concepts, and examining the communication gap between superiors and subordinates. A decentralized organization provides authority to the lower managers to make decisions, while a centralized company has a high level of hierarchy, authority and low participation rates in making decisions related to policies and resources. A decentralized company is characterized by a low hierarchical authority in which decision making is very participatory. Therefore, where only one or several individuals make decisions, the structure of the company is described as very centralized. Conversely, the most centralized corporate structure is where all employees in the company are responsible and involved in the decision making process. Components used to build effective organizational structures are nature of the task, workers’ location, manager ability to delegate responsibilities, number of interactions and feedback, and employees’ skill level. Another key factor that determines organizational effectiveness is centralization, which is related to the degree of centralized or distributed authority. Centralization is related to product safety, pricing of new services, determination of large-scale investment, and budget allocation. It is also defined as the concentration of power and authority at the top level of an organization which allows managers to develop a broad view of operations, carry out rigorous financial control exercises, and reduce costs by eliminating redundancy within the organization. However centralization may also mean that low-level personnel are not opportune to develop decision-making and leadership skills, therefore, the organizations are less able to quickly respond to customers’ demand. Decentralization is the process of encouraging authority in the decision making process of an organizational hierarchy, through the provision of a lower level personnel with more responsibility and power to make and execute decisions. Decentralized benefits include faster decision-making, increased levels of innovation and creativity, greater organizational flexibility, quicker development of low-level managers, and an increased level of job satisfaction as well as employee commitment. However decentralization can also be risky assuming low-level personnel do not have the necessary skills and training to effectively carry out their duties. In addition, decentralization increases the likelihood of an inefficient communication line, competing objectives, and duplication of effort. Some factors need to be considered when delegating decision-making to the entire organization, namely organizational size, speed of change in its environment, manager's willingness to give up authority, employees' willingness to accept more responsibility, and geographical dispersion. Previous studies on organizational performance and quality of human resources showed different results. In the context of decentralization, managers need excellent human resources (HR) to save time associated with information analysis and in directing organizational objectives. Human Resources (HR) is a central factor that aids in elaborating the resource theory, and function of a company to mobilize all resources or internal capabilities to face market interests as the main external factor. In a centralized structure, top managers make most of the major organization decisions with very little input from low-level employees (Karatepe & Aga, 2016). Conversely, in highly decentralized organizations, decision-making authorities are pushed down the organizational hierarchy, thereby, encouraging the lower level personnel more responsibility and power to make and execute decisions. Decentralization leads to faster decision making and increased innovation and responsiveness to customer preferences. According to Wirawan (2015) the quality of human resources is a combination of individuals' physical and non-physical abilities to enable them work, are creative, and possess the right organizational potential. The quality of human resources is determined by employees’ skills, level of knowledge, experience, maturity, and attitude. Quality human resources, in accordance with the needs of the job, increase employee effectiveness. Simamora (2012) stated that and increase in HR's ability, leads to a significant rise in work effectiveness. Amirul & Daud (2012) also stated that the quality of human resources had a significant effect on organizational effectiveness due to its ability to ease burden on top executives, facilitate diversification, provide market and product Emphasis, encourage managers’ development, and improve motivation.
Literature Review
Decentralizezation
Companies with a responsible center, usually have one or two decision protection approaches used to manage their complex and diverse activities, namely centralization or decentralization. In the centralized decision making process, various decisions are made by the top level managers, while those at the lower levels are responsible for the implementation of these policies. Meanwhile, the decentralized process allow managers at lower levels to make and implement decisions related to their area of responsibility. Many companies use the decentralization process to improve their overall efficiency. Garrison et al. (2015) stated that organizations utilize this process in decision-making allow mangers at various levels to make important decisions relating to their scope of responsibilities. Hansen & Mowen (2019) reported that decentralization is the practice of delegating decision-making authority to a lower level in order to achieve freedom of decision security. Meanwhile, according to Handoko (2011) decentralization is a broader concept and relates to how top management delegate authority down to divisions, branches, and other lower-level units of the organization. Decentralization is also the delegation of authority in making decisions and policies to managers or people at the lower level of an organizational structure. It improves and increases the effectiveness and productivity of an organization.
Centralization
Centralization is the concentration of power and authority on a small number of managers at the top level of an organization. Robbins & Judge (2015) defined centralization as the degree to which decision making is centered on several positions in the company. Muharam & Chaniago (2019) stated that centralization means that authority or power is still largely held by a leader, and only a small portion is distributed throughout the organizational structure.
Quality of Human Resources
According to Cascio (2010), the quality of human resources is determined by the aspects of the skills, physical energy, education, level of knowledge, experience, attitude and values. Based on the above definition, it can be concluded that Human Resources are individuals, laborers, or employees that work for an organization. There are benchmarks or limits associated with identifing and determining qualified human resources which are the basis of one's personal quality. Sumarjan et al. (2013) stated that the quality of Indonesian human resources is dissected based on physical and non-physical qualities. From the above notions, it can be said that the quality of human resources is dependent on employees that make valuable contributions to achieving organizational goals in accordance with their skills, level of education, honesty, and experience. According to Thoha & Hutapea (2015), the Human Resource Quality Indicators are as follows: 1.) Understanding their respective fields, 2.) Knowledge, 3.) Ability, 4.) Work enthusiasm, and 5.) Ability to plan/organize.
Organizational Performance
Organizational performance is the periodic operational results of a manager based on the predetermined goals, standards, and criteria. It is also defined as the output that uses predetermined input during a certain period to achieve set goals. Evelyne & Juniarti (2003) stated that performance is the work achieved by a group of people in accordance with each authority and responsibilities to achieve organizational goals through planning, investigation, coordination, staffing arrangements, negotiation, representation, and overall performance. Rivai & Mulyadi (2012) stated that anyone in a managerial position is expected to achieve organizational goals, while organizational performance is abstract and complex. The managers mobilize the talents, abilities, and efforts of several other people within their authority (Banerjee, 2019). Organizational performance is one of the factors that improve effectiveness; therefore, a tool is needed to determine its quality. According to Mulyadi (2015) performance appraisal is a periodic determination of the operational effectiveness of an organization, parts of the organization, and its employees based on predetermined targets, standards, and criteria. Organizations are basically run by humans; therefore, performance appraisal is actually an assessment of human behavior in carrying out roles.
Methodology
Location, Objects and Samples
This research was conducted in Rural Banks in Indonesia. Data were obtained from 105 respondents in the category of general, branch, and public service managers from 35 Rural Banks.
Operational Definition of Variable
The Independent Variableles are as follows:
a. Decentralization (X1) which include policies on termination of employment, objective developments in decision security, development of small-scale investment, strategy and broader organizational environment, concepts, ideas, and poor communication gap between superiors and subordinates.
b. Centralization (X2) which include determining prices, new products and services, examining large-scale investments, allocating budgets, determining selling prices, smaller organizational strategy and environment, developing more limited concepts and ideas, communication gaps between leaders and employees.
c. The Quality of Human Resources (X3) this include understanding each field, knowledge, work ethos, and ability to plan/organize.
The Dependent Variablele
The dependent variable was measured using four-dimensional personal performance indicators, namely Planning, Organizing, Actuating, and Controlling.
The Technique of Data Analysis
Classical assumption test
Equation of multiple regression model of Ghozali (2014):
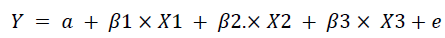
where :
Y = organizational performance
a = regression constant
β1, β2 = regression coefficient
X1 = variable of decentralization
X2 = variable of centralization
X3 = variable of the quality of human resources
X1, X2, and X3 = interaction between X1, X2, and X3 variables
Hypothesis test
T-Test (Partial Hypothesis Test), The T-test basically shows the effect of a certain independent variable individually in explaining the used variation.
F-Test (Hypothesis Test of Model Feasibility), The F-test is used to determine the ability of all independent variables included in a model to have simultaneous effects on the dependent.
Determination Coefficient Test, The determination coefficient test was used to identify the variance of dependent variables explained by the independent variables. The R2 was used to consider the number of independent variables in a model.
Results
Classical Assumption Test, The classical assumption test was first conducted to ensure that various deviations did not occur, in the regression model which is feasible to and used to carry out predictions.
Normality Test, The normality test aimed to determine the ability of the residual variable in a normal or abnormal distribution. A good regression model shows normally distributed data which was carried out using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) statistical test as shown in Table 1. The normality test in Table 1 shows that the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) value is statistically the Asymp value. Sig. (2-tailed) is greater than 0.05, which means the data is normally distributed.
| Table 1 Results of Normality Test | ||
| One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test | ||
| Unstandardized Residual | ||
| N | 105 | |
| Normal Parametersa,b | Mean | 0 |
| Std. Deviation | 3.029489 | |
| Most Extreme Differences | Absolute | 0.083 |
| Positive | 0.07 | |
| Negative | -0.083 | |
| Test Statistic | 0.083 | |
| Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.069c | |
Source: Managed data, 2020
Multicollinearity Test
The results of multicollinearity are shown in Table 2.
| Table 2 Results of Multicollinearity Test | |
| Collinearity Statistics | |
| Tolerance | VIF |
| 0.933 | 1.071 |
| 0.815 | 1.228 |
| 0.866 | 1.154 |
Based on the multicollinearity test results in Table 2, the tolerance value of the independent variable is above 0.1, and the VIF value is below 10. Therefore, it is concluded that the model had no symptoms of multicollinearity.
Heteroscedasticity Test
The results of the heteroscedasticity test are presented in Table 3.
| Table 3 Results of Heteroscedasticity Test | ||||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 8.709 | 4.359 | 1.998 | 0.048 | |
| x1 | 0.021 | 0.044 | 0.048 | 0.479 | 0.633 | |
| x2 | -0.032 | 0.073 | -0.046 | -0.433 | 0.666 | |
| x3 | -0.101 | 0.047 | -0.221 | -2.134 | 0.135 | |
The heteroscedasticity test results in Table 3 shows that with the Glejser test the independent variables has a regressed estimated and absolute value of the unstandardized residual (ABS_RES) at a significance value above 5%. The independent variables are free from heteroscedasticity, which means that the variance value of the residual regression was similar to all observations.
Analysis of Multiple Regression
The results of the analysis are shown in Table 4.
| Table 4 Results of Multiple Linear Regression Analysis | ||||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 12.282 | 6.704 | 1.832 | 0.07 | |
| x1 | 0.073 | 0.068 | 0.099 | 1.08 | 0.283 | |
| x2 | 0.416 | 0.113 | 0.362 | 3.699 | 0 | |
| x3 | 0.098 | 0.073 | 0.128 | 1.352 | 0.18 | |
From Table 4, the obtained equations are as follows:
Y = a + b1X1 + b2X2 + b3X3
Y = 12.282 + 0.073X1 + 0.416X2 + 0.098X3
Regression equation can be explained as follows: The value of b1 = 0.073. This showed that the decentralization (X1) and organizational performance (Y) values increased, while the values of centralization (X2), and the quality of HR (X3) remained constant. The value of b2=0.416. This showed that the centralization value (X2) and organizational performance (Y) increased, while decentralization (X1), and quality of HR (X3) remained constant. The value of b3=0.098. This showed that the quality of HR (X3) and organizational performance (Y) values increased, while decentralization (X1) and centralization (X2) remained constant. The value of b1=0.073, b2=0.4161, and b3=0.098. This showed that the values of decentralization (X1), centralization (X2), quality of HR (X3) and organizational performance (Y) increased.
Multiple Correlation Analysis
This coefficient indicates the relationship between independent variables (X1, X2, and X3) simultaneously to the dependent (Y) as shown in Table 5.
| Table 5 Results of Multiple Correlation Analysis Test of Decentralization, Centralization, and the Quality of HR on Organizational Performance of Rural Banks | ||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate |
| 1 | 0.460a | 0.212 | 0.188 | 3.07415 |
Table 5 shows that the correlation coefficient of 0.460 is at the interval coefficient of 0.81 to 1.00. This means that decentralization, centralization, and the quality HR had a very strong relationship used to improve organizational performance.
Determination Analysis
Table 5 shows that the determination coefficient is 0.460 or 46%, which means that the variation of the relationship between decentralization, centralization, and the quality of HR to organizational performance was 46% while the remaining 54% was determined by other variables outside decentralization, centralization.
F-Test
This test was used to determine the ability of the independent variables (X1, X2, and X3) to significantly affect the dependent (Y). The testing steps were carried out as follows: determination of the F-count based on the calculation of SPSS 23.0 version for windows was 9.049.
The test results, shows that the F-count> F-table at 9.049> 2.46, which means that Ho was rejected, and Hi was accepted. Table 6 shows that a significant value of 0.000 is smaller than 0.05, therefore, decentralization (X1), centralization (X2), and the quality of HR (X3) significantly influenced the organizational performance (Y) of Rural Banks. Table 6 shows that Fcount is 9,049 greater than Ftable, at 2.84, which means that the hypothesis was accepted. The variable of decentralization (X1), centralization (X2), and the quality of HR (X3) had a significant effect on organizational performance (Y).
| Table 6 Results of F-Test of the Effect of Decentralization, Centralization, and the Quality of HR on Organizational Performance of Rural Banks | ||||||
| ANOVAa | ||||||
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 256.556 | 3 | 85.519 | 9.049 | .000b |
| Residual | 954.491 | 101 | 9.45 | |||
| Total | 1211.05 | 104 | ||||
Source: Managed data, 2020
T-Test
This test was employed to determine whether in the regression model, the independent variables (X1, X2, and X3) partially affected the dependent variable (Y). The t-Test results are shown in Table 7.
| Table 7 Results of T-Test | ||||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 12.282 | 6.704 | 1.832 | 0.07 | |
| x1 | 0.073 | 0.068 | 0.099 | 1.08 | 0.283 | |
| x2 | 0.416 | 0.113 | 0.362 | 3.699 | 0 | |
| x3 | 0.098 | 0.073 | 0.128 | 1.352 | 0.18 | |
Based on the calculation of the SPSS 23.0 version for windows, the t-count value for decentralization (X1) was 1,080. Therefore, from the above test, it can be concluded that the t-count> t-table was 1,080<1.28967. It means that the effect of decentralization (X1) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks wasn’t significant. Therefore, Ho was accepted, and Hi was rejected.
T-Test: The Effect of Centralization on Organizational Performance
The t-count was determined based on the calculation of SPSS 23.0 version for windows with a degree of freedom of 50, and at centralization (X2) value of 1.352. This means that t-count> t-table, at 3,699 > 1.28967 which means that the effect of centralization (X2), on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was significant. Hence, Ho was rejected, and Hi was accepted.
T-Test: The Effect of the Quality of HR on Organizational Performance
The t-count was determined based on the calculation of SPSS 23.0 version for windows and a HR Quality (X3) value of 1.352. This means that t-count> t-table, at 1.352> 1.28967which means that the effect of the quality of HR (X3) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was significant. Therefore, Ho was rejected, and Hi was accepted.
Discussion
The results of the hypothesis test showed that the variables of decentralization, centralization, and HR quality influenced the organizational performance. The discussion for each hypothesis test result is elaborated as follows:
The Effect of Decentralization on Organizational Performance
The results showed that decentralization had no significant on organizational performance, which means that it must be improved and enhanced organizational performance. Establishing authorization for each of these divisions often motivate or encourage employees to improve their performance. This condition arises because it is easier to establish a decentralized system of activities through supervision and assessment. The authority here provides the understanding and right to determine the assignment, while responsibility is an obligation to achieve set goals. This means that the higher the level of decentralization, the greater the manager's ability to make autonomous decisions.
The Effect of Centralization on Organizational Performance
The results showed that centralization had a significant and positive effect on organizational performance variable. This means that the higher the centralization of employees in the company, the greater the organizational performance of the Rural Banks. Centralization means the focus of supervision from the center, as stated by detailed instructions from the central office on the work that needs to be conducted, i accordance with regular reports. Centralization is the concentration of authority at the top level of an organization. The impact of the interaction between the quality of HR and centralization significantly increases in organizational performance.
The Effect of the Quality of HR on Organizational Performance
The results showed that HR quality had a significant positive effect on organizational performance. This means that the organizational performance of the Rural Banks in increases, with a rise in employee HR quality which supports organizational structure. In an increasingly decentralized level, managers play a more significant role in making and implementing decisions. As a consequence of these conditions, they need human resources that provide precise, quality, and relevant information to support organizational performance.
The Effect of the Decentralization, Centralization and Quality of HR on Organizational Performance
The simultaneous effect of decentralization (X1), centralization (X2), and the quality of HR (X3) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. This conclusion is based on the results of the multiple linear correlation analysis, which was positive at 9.049. T-test analysis was conducted to determine the significant which resulted in F-count, and F-table of 9.049, and 2.84, which means F-count> F-table. Therefore, Hi was accepted. This means that the simultaneous effect of decentralization (X1), centralization (X2), and HR Quality (X3) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. Meanwhile, the value of determination showed 89.2%, and the remaining 10.8% was influenced by other variables not examined in this study
Conclusion
The research results is concluded as follows: The partial effect of decentralization (X1) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks is no significant. T-test analysis was conducted to determine the significance of the effect which resulted in t-test and t-table values of 1.080 and 1.28967, which means t-count> t-table. Therefore, Hi wasn’t accepted. This means that the partial effect of decentralization on organizational performance of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. The partial effect of centralization (X2) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. T-test analysis was conducted to determine the significance of the effect which resulted in t-test and t-table values of 3.699 and 1.28967, which means t-count> t-table. Therefore, Hi was accepted. This means that the partial effect of centralization (X2) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. The partial effect of the quality of HR (X3) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. T-test analysis was conducted to determine the significant effect which resulted in t-test and t-table values of 1.352 and 1.28967, which means t-count> t-table. Therefore, Hi was accepted. This means that the partial effect of the quality of HR (X3) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. The simultaneous effect of decentralization (X1), centralization (X2), and the quality of HR (X3) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. This conclusion is based on the results of the multiple linear correlation analysis, which was positive at 0.460. T-test analysis was conducted to determine the significant which resulted in F-count, and F-table of 9,049, and 2.84, which means F-count> F-table. Therefore, Hi was accepted. This means that the simultaneous effect of decentralization (X1), centralization (X2), and HR Quality (X3) on organizational performance (Y) of the Rural Banks was positive and significant. Meanwhile, the value of determination showed 46%, and the remaining 54% was influenced by other variables not examined in this study.
References
- Amirul, S., & Daud, H. (2012). A study on the relationship between leadership styles and leadership effectiveness in Malaysian GLCs. European Journal of Business and Management.
- Banerjee, A. (2019). Failure of employee retention and its consequences on organization through content analysis. International Journal of Research-Granthaalayah, 7 (3), 200-207.
- Cascio, W.F. (2010). Managing human resources: Productivity, quality of work life, profits.
- Evelyne, E., & Juniarti, J. (2003). The relationship of information characteristics produced by management accounting information systems on managerial performance in manufacturing companies in east java. Journal of Accounting and Finance, 5 (2), 110-122.
- Garrison, R., Noreen, E., & Pter Brewer. (2015). Managerial accounting. In McGraw Hill.
- Ghozali, I. (2014). Multivariate analysis application using SPSS. In Gramedia.
- Handoko, T.H. (2011). Personnel and human resources management. Introduction to Management.
- Hansen, D.R., & Mowen, M.M. (2019). Managerial accounting. In Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling.
- Karatepe, O.M., & Aga, M. (2016). The effects of organization mission fulfillment and perceived organizational support on job performance: The mediating role of work engagement. International Journal of Bank Marketing.
- Muharam, H., & Chaniago, H. (2019). The role of entrepreneurial personality on competitive advantages and corporate image based on digital. International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology.
- Mulyadi, M. (2015). Social change from agrarian society to industrial society in community development in Tamalate District, Makassar City. Bina Praja Journal: Journal of Home Affairs Governance, 7 (4), 311-322.
- Rivai, V., & Mulyadi, D. (2012). Leadership and Organizational Behavior. In Leadership and Organizational Behavior.
- Robbins, S.P., & Judge, T.A. (2015). Organizational behavior. In Boston: Pearson.
- Simamora, H. (2012). Management accounting. In Management Accounting.
- Sumarjan, N., Arendt, S.W., & Shelley, M. (2013). Incongruent quality management perceptions between Malaysian hotel managers and employees. The TQM Journal.
- Thoha, N., & Hutapea, P. (2015). Familiarization studies: Critical components in conducting successful fieldwork.
- Widodo. (2019). Models of community learning center (CLC) management. 5th International Conference on Education and Technology, ICET 2019.