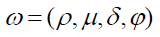Research Article: 2022 Vol: 14 Issue: 3
Customer Satisfaction of Mobile Users in the COVID-19 Situation: A Bangladesh Perspective Survey
Khondokar Oliullah, Jahangirnagar University
Mesbahuddin Sarker M, Jahangirnagar University
Abu Sayeed Arif, Jahangirnagar University
Adeyl Khan M, North South University
Citation Information: Oliullah, K., Sarker, M.M., Arif, A.S., & Khan, M.A. (2022). Customer satisfaction of mobile users in the Covid- 19 situation: A bangladesh perspective survey. Business Studies Journal, 14(3), 1-14.
Abstract
Since mobile phones have been engrained in Bangladesh's society, the telecommunications sector has made communication easier than it has ever been. Telecommunications have been more important than at any other time in delivering various services in the Covid-19 scenario. During the pandemic, mobile operators' internet services have become one of their most important offers. Because of the hard competition, businesses are attempting to gain as much market share as possible by providing attractive packages, special offers, and services with additional value to meet customers' requirements, desires, and expectations. Price, network quality, service quality, and user facilities, according to the literature, all impact consumer satisfaction in the mobile telecommunications sector. The goal of this study is to figure out what elements have the greatest impact on customer satisfaction in the Covid-19 scenario. A semi-structured questionnaire was used to obtain data from 267 respondents. These responses are analyzed using a mathematical model to determine how satisfied customers are with various aspects. The study's findings also show that, according to a direct questionnaire, all the framework factors are highly and positively related to overall customer satisfaction levels in Bangladesh's telecom industry.
Keywords
Customer Satisfaction, Mobile Telecommunications, COVID-19.
Introduction
The mobile phone, often known as a cell phone, is a device that has made communication easier for people in both urban and rural areas (Alam & Rubel, 2014). In the previous few decades, this industry has experienced phenomenal expansion. After China and India, Bangladesh is Asia's third largest telecom market. Grameen Phone (GP), Banglalink, Robi, Airtel, and Teletalk (government operator) are four mobile phone providers currently functioning in Bangladesh. At the end of July 2021, Bangladesh's mobile phone users reached more than 176.94 million (BTRC, 2021). The true number of mobile customers is likely to be lower, as many people use various service providers or SIM cards. Mobile users don't simply use their phones to make calls; they also use them for SMS, video calling, banking, social insurance, amusement, web-based shopping apps, and internet surfing.
In Bangladesh, mobile phone carriers are competing for a large part of the market. Operators are offering a variety of attractive packages, voice services, advertising offers, and services with additional value such as SMS, MMS, welcome tunes, games, electronic transactions, and web surfing, among other things (Saha et al., 2016). Students make up a significant portion of mobile phone users. They are extremely aware of phone call prices, net bundles, service quality, and various mobile phone operator offers.
Given the increased competition among operators, it is critical for them to realize their users' perceptions of service quality, brand image, and customers’ satisfaction (Pandiya et al., 2014). However, few researchers have focused on the telecom business to assess customer perception and satisfaction concerns, and there are no existing service quality evaluation scales, particularly in Bangladesh. This work aims to develop measuring factors for characteristics that influence customer satisfaction (Latif et al., 2020) in the Bangladeshi mobile telecommunications sector.
Client satisfaction refers to how satisfied a customer is with the degree to which their needs have been met (Bala et al., 2018). Consumer loyalty is often given more priority by service providers since it is seen as a prerequisite for customer retention. High customer loyalty promotes repeat item purchases and informal promotion to friends as a result of marketing efforts, but poor consumer loyalty has been linked to grabbing behavior. A happy client will occasionally continue loyal for longer and will most likely assist the company in the future. The most important indicator of customer purchasing intention and commitment is consumer loyalty (Kumar et al., 2020). Innovation and services in modern media transmission, like as mobile phones and the Internet, have provided the lives of ordinary people easier and more pleasant. Due to the extremely competitive nature of the industry, customer satisfaction has become a critical factor in retaining existing consumers and attracting new ones. If clients are not satisfied, they will transfer to another operator.
Bangladesh's mobile telecommunications sector is aiming for a high market penetration rate. With 4G network services, this industry has reached its mature stage in the telecommunications market. However, in our nation, 5G network services have just lately been introduced. The telecommunications industry's fierce competition (Mannan et al., 2017) has prompted incumbent mobile carriers to rethink their strategy and operations in order to maintain or strengthen their benefits in the marketplace. They are all competing for clients by offering a diverse range of services based on customer demand.
Grameenphone is now the country's largest media communications service provider, with 82.48 million customers as of July 2021, providing consumers with access to web-based and other digital services. Furthermore, Robi's client growth rate is satisfactory. In our country, there are now four mobile operators. Grameen Phone Ltd. is in first place, with Robi in second place among four service providers, based on the number of endorsers and profitability. (Table 1) lists the mobile service providers in Bangladesh, as well as the number of subscribers for each. (BTRC, 2021).
| Table 1 Competitiveness Telecommunication Industry In Bangladesh | ||
| Mobile Operators | Active Subscribers (in millions) |
Comparative Market Share (%) |
| Grameen Phone | 82.48 | 46.61 |
| Robi | 51.81 | 29.28 |
| Banglalink | 36.57 | 20.67 |
| Teletalk Bangladesh Limited | 6.09 | 3.44 |
| Total | 176.94 | 100 |
The telecommunications market in Bangladesh is very competitive, and this trend is expected to continue. In order to preserve their market leadership, mobile operators must identify the characteristics associated with consumer loyalty (Uddin et al., 2014) and reliability. According to recent studies on growing client dissatisfaction due to poor service quality. Service quality would be a key factor of consumer happiness (Hafez & Akther, 2017) among Bangladesh telecoms customers. Besides, the customer demands in services have been shifted than earlier. Specially, internet service quality and data package have been major factors in the Covid-19 situation. As a result, the study focus should be on the elements that influence consumer satisfaction in Bangladesh's telecommunications industry during Covid-19 situation. Objectives of our work will be as:
1. To investigate the degree to which mobile telecommunications users are satisfied with the services provided by telecom companies.
2. Recognize the factors that mobile telecommunications users in Bangladesh evaluate while choosing between networks.
Section 2 of this paper discusses some related works. The technique and model are described in depth in Section 3. Section 4 discusses the survey results. Finally, in Section 5, we get to the end of our investigation.
Literature Review
Several researchers in Bangladesh and elsewhere have undertaken study on various aspects of customer retention in the telecommunications business. A few key precise study findings have been taken into account.
The objective of this research (Saha et al., 2016) is to learn more about customer happiness and the elements that influence it in Bangladesh's mobile telecommunications sector. Due to high competition, businesses are attempting to gain as much market share as possible by providing attractive packages, special offers, and services with additional value to meet customers' requirements, desires, and expectations. Price, network quality, product variety, and subscriber amenities, according to the literature, all impact consumer happiness in the mobile telecommunications sector. All of the distinguishing variables are strongly and positively linked with total customer satisfaction in the Bangladeshi mobile telecom market, according to this research. According to the conclusions of this work, mobile companies should design suitable strategies by considering their strengths in pleasing their subscribers as well as addressing their flaws by learning from one another's services.
In their research (Bala et al., 2018), they attempted to identify the important elements that most influence the level of satisfaction of mobile phone users among Bangladeshi college students. The data was collected using a questionnaire to conduct a research study from a diverse population. The findings revealed that coverage of the network, internet availability, and tariff availability are the most important factors impacting client retention and dependability.
Past researchers have emphasized the need of analyzing important aspects such as perceived value and service quality that may genuinely influence consumer loyalty in Malaysian mobile operators (Nurysh et al., 2017). The moderating effect of engaging quality of alternatives has also been tested across variables. As a result of the empirical conclusion, which is based on quantitative research and further supported by numerous regression analyses, both perceived value and service quality have a positive association with consumer loyalty. However, the adjudicator began by stating that communicating the two elements with the attractiveness of options has no effect on improving or upgrading contentment.
The goal of this study (Kumar et al., 2020) is to look at student satisfaction and how it relates to the cell phone business in Bangladesh. The participants in this study are 320 Grameenphone (GP) subscribers in Bangladesh. The recurrence rate, bar graphs, unshakable quality trial, KMO-Bartlett test, exploratory factor investigation, correlation, and linear regression inquiry were all used during the data analysis. The findings reveal a significant link between customer loyalty and service quality, network, call rate, online capability, and social responsibility. The results also suggest that all of these services are important markers of customer loyalty.
The objective of this study (Uddin et al., 2014) is to observe at consumer satisfaction and the elements that impact it in Bangladesh's mobile phone business. A questionnaire survey was used to obtain data from a diverse representative population. The data was analyzed using an iterated factor analysis using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and structural equation modeling (SEM), which included a measurement model and a structural model. The research findings show that service quality and fair pricing have an indirect impact on consumer happiness in the mass service business (i.e., mobile phone carriers) via perceived value. Quality, charge fairness, and pleasure are all mediated by perceived value. Furthermore, the findings suggest that a fair pricing has a favorable direct influence on customer satisfaction, but service quality has no significant direct influence on customer happiness.
Consumer satisfaction (Marinkovic & Kalinic, 2017) is an assessment of how well a company's products and services meet or exceed the expectations of its customers. It varies from person to person and service to service. Satisfaction is a result of a variety of psychological and physical matters that are linked to satisfaction behaviors. The term ‘satisfaction’ can be defined as (Kotler, 2000): “a person’s feeling of pleasure or disappointment resulting from comparing a product’s perceived performance (or outcome) in relation to his or her expectations”. The authors of (Hokanson, 1995) emphasize on responsive workers, well-mannered employees, educated employees, cooperative employees, correctness of billing, billing relevance, competitive price, service feature, excellent value, billing transparency, and rapid service as variables impacting customer happiness. Customers' satisfaction levels may change depending on the alternatives and products/services offered to them.
This study (Strenitzerova & Gana, 2018) provides information on customer loyalty to electronic communications services and demonstrates the results of using the European Customer Satisfaction Index (ECSI) model in the Slovak electronic communications market. According to the findings, the ECSI can present a better understanding of the complex relationships between client faithfulness and consumer loyalty, as well as their impact on the Slovak Telecom Supplier's manageability.
The focus of the research (Rizomyliotis et al., 2018) was to develop and evaluate a staggered model of client loyalty based on historical data from the UAE mobile telecommunications market. The authors want to look at how apparent service quality, perceived value, customer loyalty, and belief in client fidelity all interact. Except for perceived value, every studied variable had a significant positive impact on loyalty. Trust was discovered to be the strongest predictor of client loyalty. In light of these findings, the researchers provide supervisory proposals with the objective of enhancing service provider outcomes in the mobile telecom market.
The main goal of this research (Miah et al., 2018) is to determine the factors that influence consumer loyalty with telecom enterprises in Malaysia. The primary goal of this study is to identify these components and the extent to which they influence consumer loyalty for telecommunications services. This study looked at the different elements that impact or can build consumer loyalty, such as pricing, service quality, and brand reputation. Only the pricing and brand recognition of the telecom service provider have a crucial positive link with consumer loyalty to the telecom business, according to the findings of this investigation. However, no link was seen between the nature of service and consumer loyalty to the telecom industry in this study. Throughout this study, the researchers discovered several hidden and significant elements that have influenced the degree of pricing, service quality, and brand reputation, all of which influence customer loyalty to Malaysian telecommunication companies.
This research (Mohammed Ali, 2020) was carried out in Kochi's Ernakulam district, a worldwide metropolis renowned as Kerala's commercial center, where competition is fierce between Vodafone-Idea, Airtel, Jio, and BSNL. Rather than chasing down a new customer, business development efforts that use current loyalty are more cost efficient. To better understand customer perceptions of telecommunication service providers, the customer satisfaction model was used. As part of the descriptive study design, the researcher contacted 50 respondents using easy random selection. There is fierce rivalry among telecom operators these days, and maintaining customer satisfaction is essential if they want to grow their client base and keep their existing consumers (Momotaz, 2019). As a result, the researcher attempted to investigate the effect of customer satisfaction on customer loyalty.
The main objectives of this research (Kumar et al., 2021) are to determine the level of customer satisfaction in Bangladesh and to determine the elements that influence it, such as organizational efficiency, organizational competency, service quality, and product pricing. Primary and secondary data were employed to accomplish these goals. A simple random sample approach was employed to obtain primary data, and a 400-questionnaire was distributed. The data was analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) using the Smart PLS 3.2.3 method (Zin & Nor, 2017). The study discovered that people in their senior years and who are illiterate had no sentiments or thoughts regarding service offerings, prices, or internet capabilities. They want a strong network and plenty of chat time. However, educated individuals and young people are highly concerned about conversation time, network, service quality, internet access, and product offerings (Ahmad & Zhang, 2020), among other things. The study also found that the organization's organizational competency and efficiency had little impact on customer satisfaction. The research also reveals that product pricing and service quality have a major influence on consumer satisfaction in Bangladesh's telecom sector. In today's changing business climate, it's all about building and keeping a solid relationship with clients through the use of information the elements of customer satisfaction. Client happiness is the key to customer loyalty, and it is primarily determined by the service quality provided by service providers.
Methodology
For gathering information on the state of mobile phone users, the baseline research used a quantitative and qualitative method. Qualitative research is a technique of inquest that elucidates human and social science concepts by determining how individuals think and feel (Mohajan & Kumar, 2018). Quantitative research is a type of study that uses statistical, logical, and mathematical techniques to create numerical data. It's more accurate to think of them as relative points on a scale. Primary data is information that we collect directly from a field. A questionnaire survey was conducted to gather essential data such as age, gender, monthly income, monthly spending, tax, flat call rate, network quality, service quality, overall satisfactory level and so on. Secondary information was gathered from publications, newspapers, conference papers, and the annual report of the firm. Data was obtained from 267 people in total. This survey was performed in and around the university's campus. Students, professors, retailers, and car drivers are among those who took part in the poll. The study's full analysis was carried out using the SPSS (statistical program for social science) for Windows Statistics software (version 20). The SPSS for Windows format was used to enter the survey data. It was used to compute and record a variety of variables. This program was used to do some first-hand analyses, such as frequencies and testing.
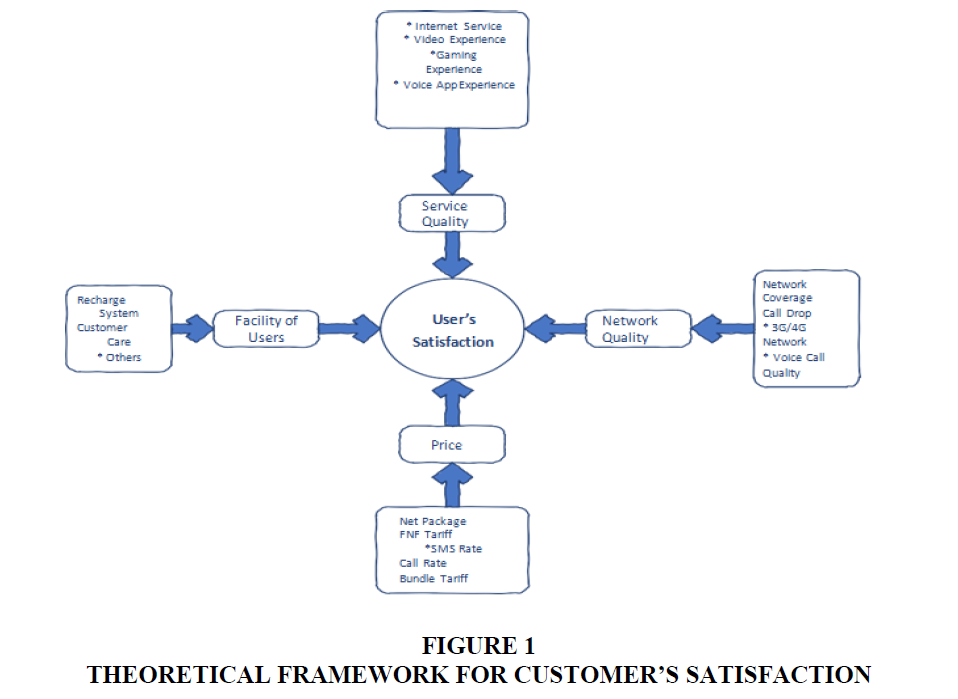
Theoretical Framework for Customers Satisfaction
The theoretical model for user’s satisfaction is designed with four criterions those are price, service quality, user’s facilities, and network quality. The service quality includes internet services like download/upload speed, video experiences (Zoom, Google Meet, etc.) gaming experiences, and voice application experiences (Whatsapp, Messenger, Telegram, etc.). Another important criterion, network quality, covers the network coverage, call drop rate, voice call quality, and 3G/4G network availability. Some extra facilities like recharge system, customer care services, different campaign notifications, etc. also play important role for customer satisfaction. Price is one of the most significant factors of customer satisfaction. Here, it includes the price of net package, fnf tariff, bundle tariff, sms rate, and call rate. The survey data will be analysed according to this model to define the satisfaction of mobile operator users.
Mathematical Model for Customer Satisfaction
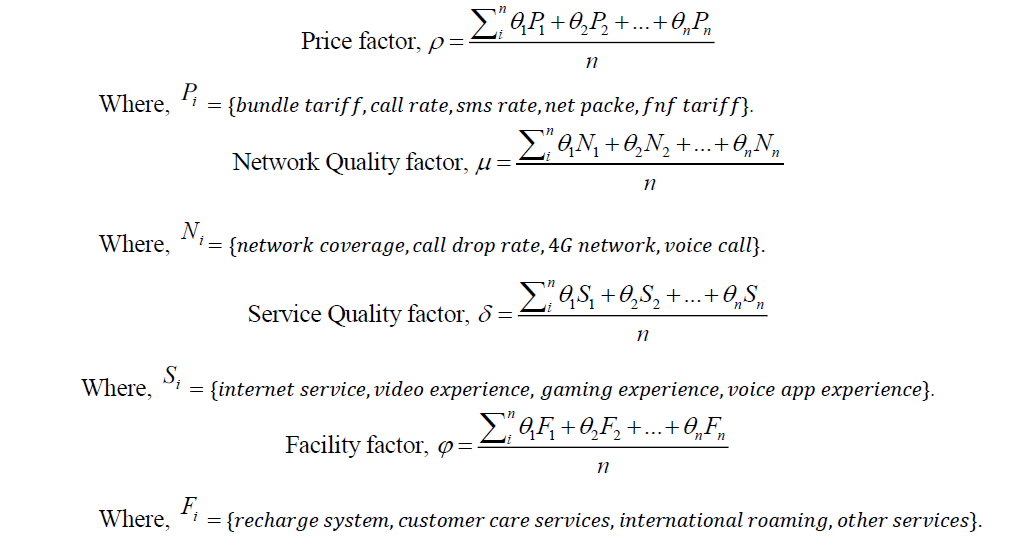
The mathematical model for the theoretical framework of customer satisfaction can be derived from different factor expressions considered in the framework earlier Figure 1. The factors can be formulated as:
In The above equations, the weighting factor, is a value assigned to a data point in order to give it a lesser or greater weight in a group.
Then, the customer satisfaction is defined as,
Survey Results and Discussion
Data Analysis and Empirical Findings
Users of mobile phones were given the survey findings in Table 2 from the surveys, with 82% using GP, 22% Robi and Banglalink, 14% Teletalk, and 49.8% using various operators' services. In my poll, students make up 57.7% of users, service members make up 16.9%, and other occupations make up 25.5%. Monthly expenses for 33.0% of respondents are less than Tk. 300, 18.7% are between 300 and 500, 16.1% are between 700 and 1000 Tk, and 15.0% have more than 1000 Tk. Males account for 48.7% of responses, while females account for 51.3%. Post-paid connections are used by 89.1% of respondents, while prepaid connections are used by 10.9%.
| Table 2 Frequency Table | |||
| Monthly expense of MP the respondents |
Respondents income |
||
| Pearson Correlation | Monthly expense of mobile phone the respondents |
1 | 0.579** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | ||
| N | 267 | 267 | |
| Pearson Correlation |
Respondents income per month |
0.579** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | ||
| N |
|
267 | 267 |
Another major problem that we have gathered is the flat call rate and the imposition of rising taxes on the call rate. 70.0% of respondents are aware of the tax and are concerned about rising call rates, whereas 30.0% are unaware of the tax and believe it is a problem if they are aware of it (Mohajan, 2018). According to the above Table 3, at a 1% level of significance, there is a substantial positive association between monthly mobile phone costs and respondent's income.
| Table 3 Correlations Table | ||||
| Demographic Variable | Categories | Frequency | Percent % | Cumulative% % |
| Operator name | GP | 82 | 30.7 | 30.7 |
| Robi | 22 | 8.2 | 39.0 | |
| Banglalink | 22 | 8.2 | 47.2 | |
| Teletalk | 14 | 5.2 | 52.2 | |
| Use of multiple operator |
All operators | 40 | 15.0 | 67.4 |
| GP and Robi | 49 | 18.4 | 85.4 | |
| GP and Banglalink | 27 | 10.1 | 95.9 | |
| (GP, Robi, and Banglalink) |
11 | 4.1 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 267 | 100.0 | ||
| Monthly Expenditure | less than 300 taka | 88 | 33.0 | 33.0 |
| 300 to 500 taka | 50 | 18.7 | 51.7 | |
| 500 to 700 taka | 43 | 16.1 | 67.8 | |
| 700 to 1000 taka | 46 | 17.2 | 85.0 | |
| 1000 to above | 40 | 15.0 | 100.0 | |
| Profession | Students | 154 | 57.7 | 57.7 |
| Service holder | 45 | 16.9 | 74.5 | |
| Others | 68 | 25.5 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 267 | 100.0 | ||
| Gender | Male | 130 | 48.7 | 48.7 |
| Female | 137 | 51.3 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 267 | 100.0 | ||
| Type of connection | Pre-paid | 238 | 89.1 | 89.1 |
| Post-paid | 29 | 10.9 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 267 | 100.0 | ||
| Monthly income | Less 5000 to 5000 | 91 | 34.1 | 34.1 |
| 5000 to 10,000 | 85 | 31.8 | 65.9 | |
| 10,000 to 20,000 | 32 | 12.0 | 77.9 | |
| 20,000 to 30,000 | 11 | 4.1 | 82.0 | |
| 30,000 to above | 48 | 18.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 267 | 100.0 | ||
| Effect of flat call rate | Yes | 187 | 70.0 | 70.0 |
| No | 80 | 30.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 267 | 100.0 | ||
Findings According to the Framework
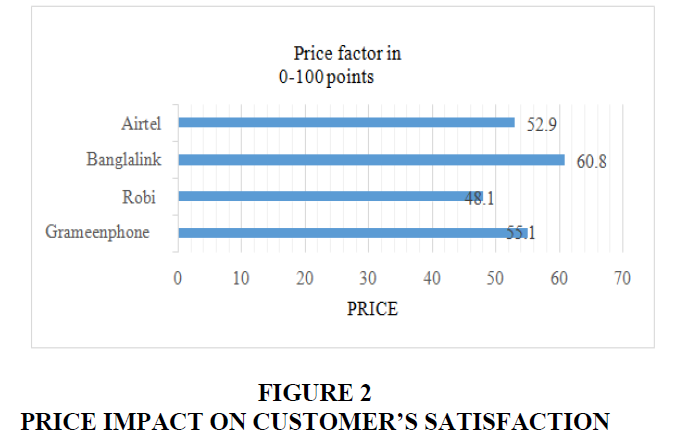
The price of different packages, tariff, and rates plays major role in User’s satisfaction of different mobile operators. The impact of the price factor can be derived from survey data based on the model and framework which is shown in the Figure 2.
The price impact is counted in 0 to 100 points. We can see that the banglalink, airtel, robi, and grameenphone obtain 60.8, 52.9, 48.1, and 55.1 points respectively. Customer satisfaction is influenced by a number of variables like services and network quality. Now, different service experiences are figured out below. The experiences are cast up in 0 to 100 points.
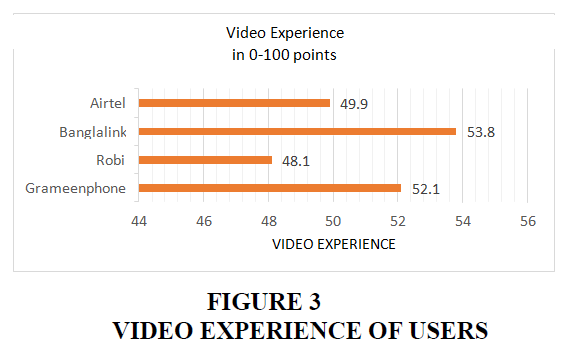
In Figure 3, the video experiences of users are displayed. We can see that the banglalink, airtel, robi, and grameenphone obtain 53.8, 49.9, 48.1, and 52.1 points respectively.
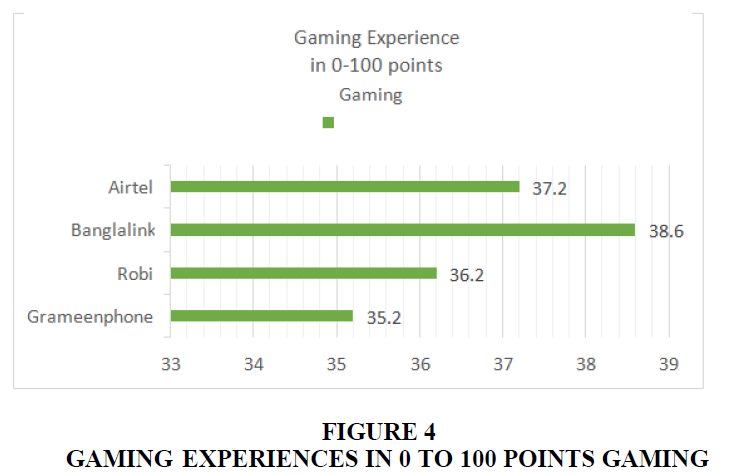
Users' gameplay experiences are depicted in Figure 4. Banglalink, Airtel, Robi, and Grameenphone all score 38.6, 37.2, 36.2, and 35.2 points, respectively.
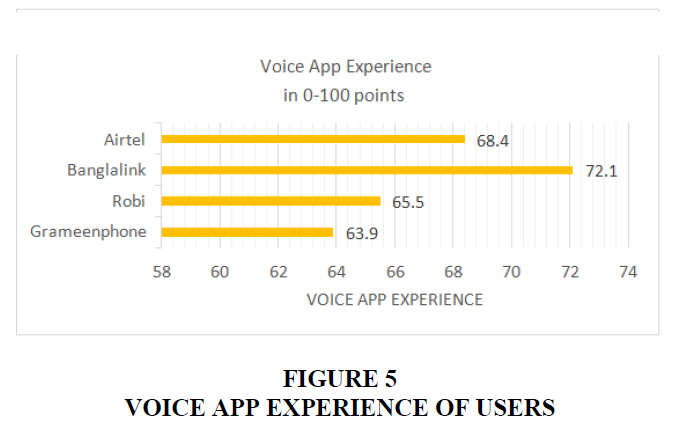
Figure 5 depicts users' experiences with the voce app. Banglalink, Airtel, Robi, and Grameenphone each receive 72.1, 68.4, 65.5, and 63.9 points.
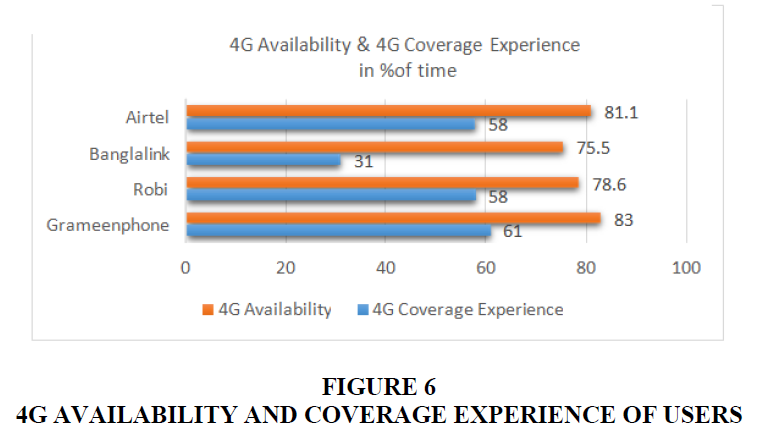
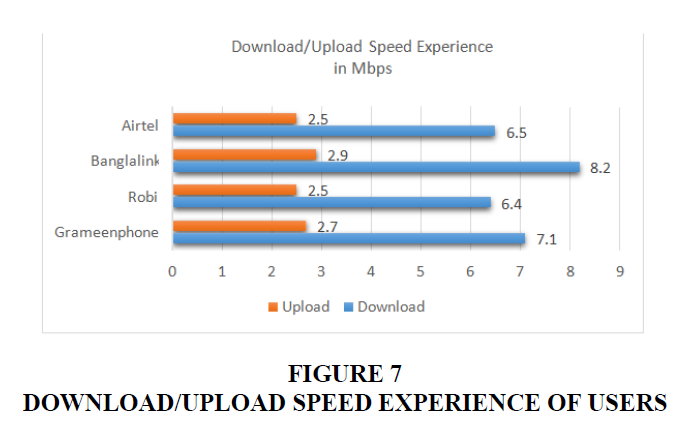
The network quality also is another important factor in customer satisfaction. Now, these services are figured out using a scale of 0 to 100 in% of time Figure 5. 4G network availability and coverage experiences are depicted in Figure 6. Banglalink, Airtel, Robi, and Grameenphone all score 75.5, 81.1, 78.6, and 83%, respectively. With the same sequence of mobile operator names, each coverage experiences scores 31, 58, 58, and 61%. Users' download/upload speeds in Mbps are depicted in Figure 7. Banglalink, Airtel, Robi, and Grameenphone all provide upload speeds of 2.9, 2.5, 2.5, and 2.7 Mbps, respectively. With the same sequence of mobile operator names, each delivers 8.2, 6.5, 6.4, and 7.1 Mbps for downloading something.
After applying the mathematical model on survey data it is found significant information which can lead to define satisfaction level of a user of different mobile operators. The analyzed data on price factor, network quality factor, service quality factor, and facility factor are represented in the Table 4. Here satisfaction level is labeled with increasing order. From this tabular data, it can be drawn that the most satisfactory services are provided by banglalink, grameenphone, airtel, and robi respectively.
| Table 4 Satisfaction Level of Mobile Users | |||||
| Mobile Operator |
Price Factor (ρ) |
Network Quality (μ) |
Service Quality |
Facility Factor (ψ) |
Satisfaction Level (ω) |
| Banglalink | 60.8 | 31.08 | 62.86 | 69.07 | 1 |
| Grameenphone | 55.1 | 38.15 | 58.05 | 65.33 | 2 |
| Airtel | 59.9 | 37.08 | 51.33 | 60.03 | 3 |
| Robi | 48.1 | 36.21 | 49.93 | 59.33 | 4 |
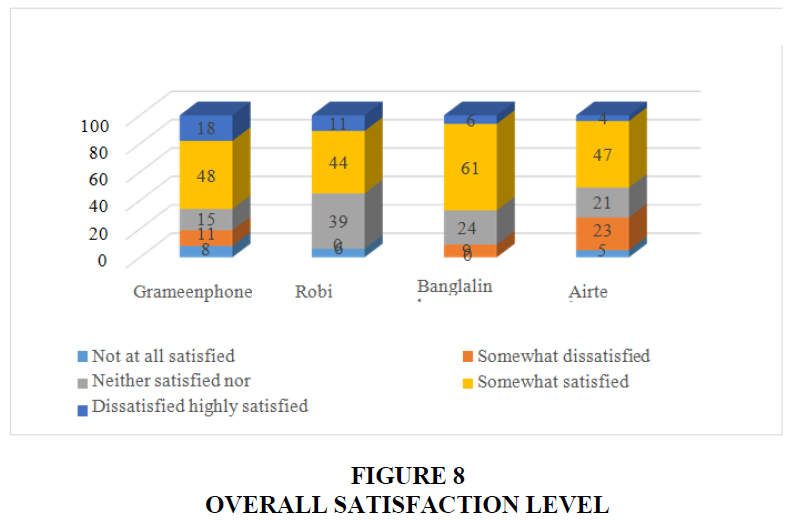
We also have gathered direct information from users to define overall satisfaction level. The overall satisfaction level of users of different mobile operator is figured out in the figure 8. The survey data is collected in five categories like Not at all satisfied, Somewhat dissatisfied, Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied, somewhat satisfied, and Highly satisfied (Table 4).
From Figure 8, it can be drawn with these categories that the most satisfactory services are provided by banglalink, grameenphone, robi, and airtel respectively. From the model and survey data it is evident that the satisfaction level of mobile users in covid-19 situation between table 4 data and survey data is almost similar.
Conclusion
The telecommunications sector has made communication in Bangladesh simpler than it has ever been before, since mobile phones have become ingrained in the country's culture. In covid-19 situation, the use of telecommunications has become more useful than any other times. Specially, mobile operators' internet services have become one of their most significant offerings during pandemic. As a result, they should continue to do study in order to identify the greatest possible approach to please users as the changing demands of customers are a continual process with situations.
This research has been conducted to determine the important factors impacting customer satisfaction in the Covid-19 scenario. A semi-structured based questionnaire was used to obtain data from 267 respondents. This survey was performed in and around the university's campus. Students, professors, retailers, and car drivers are among those who took part in the research.
After analyzing the data, the study's findings revealed that all the framework variables are strongly and positively associated with overall customer satisfaction levels in Bangladesh's telecom business, as determined by a direct questionnaire. According to the conclusions of this study, mobile operators should design their services with an emphasis on Internet services and network strength to survive in the post Covid-19 competitive market.
References
Ahmad, W., & Zhang, Q. (2020). Green purchase intention: Effects of electronic service quality and customer green psychology. Journal of Cleaner Production, 267, 122053.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Alam, N., & Rubel, A.K. (2014). Impacts of corporate social responsibility on customer satisfaction in telecom industry of Bangladesh. ABC Journal Of Advanced Research, 3(2), 93-104.
Indexedat, GoogleScholar, CrossRef
Bala, T., Hossain, I., & Mondal, G.R. (2018). Measurement of Customer Satisfaction of Different Mobile Operators in Bangladesh; a Study on Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University, Gopalganj, Bangladesh. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM), 20 (3), 38-47.
Hafez, M., & Akther, N. (2017). Determinants of Customer Loyalty in Mobile Telecommunication Industry in Bangladesh. Global Journal of Management and Business Research.
Hokanson, S. (1995). The deeper you analyze, the more you satisfy customers. Marketing news, 29(1), 16-16.
http://www.btrc.gov.bd/content/mobile-phone-subscribers-bangladesh-july-2021
Kotler, P. (2000). Marketing in the twenty-first century. Marketing Management, 10th Edition, Millenium, New Jersey.
Kumar, D., Haque, A., & Dhar, P. (2021). Exploring the Critical Influencing Factors of Customer Satisfaction in Telecommunication Sector in Bangladesh. Asia-Pacific Journal of Management and Technology, 1(4), 11-21.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kumar, D., Mukherjee, S., Haque, A., & Anis, Z. (2020). Measuring Student Satisfaction towards Mobile Service Provider in Bangladesh: With Special Reference to Grameen Phone Limited. Journal of Xidian University, 14(5), 184-200.
Latif, M., Huq, M., Sammy, H., Beg, T., & Afrina, T. (2020). Factors affecting customer satisfaction of cell phone users in Dhaka city of Bangladesh. International Journal of Information Systems and Social, 11(1), 01-09.
Mannan, M., Mohiuddin, M.F., Chowdhury, N., & Sarker, P. (2017). Customer satisfaction, switching intentions, perceived switching costs, and perceived alternative attractiveness in Bangladesh mobile telecommunications market. South Asian Journal of Business Studies.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Marinkovic, V., & Kalinic, Z. (2017). Antecedents of customer satisfaction in mobile commerce: Exploring the moderating effect of customization. Online Information Review.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Miah, I., Azad, A.K., & Ferdous, J. (2018). Factors Influencing Customer Satisfaction on Local and Foreign Telecommunication Companies in Malaysia. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 9(4), 1374-1413.
Mohajan, H.K. (2018). Qualitative research methodology in social sciences and related subjects. Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People, 7(1), 23-48.
Mohammed Ali, S. (2020). To study the Impact of Customer Satisfaction on Customer Loyalty in mobile telecom at Ernakulam District. To Study the Impact of Customer Satisfaction on Customer Loyalty in Mobile Telecom at Ernakulam District (May 1, 2020).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Momotaz, S.N. (2019). Effects of Service Quality and Perceived Value on Customer Satisfaction to Mobile Internet Service: Evidence from Bangladesh. International Review of Business Research Papers, 15(1), 60-68.
Nurysh, N., Naghavi, N., Benjamin., & Fah, C.Y. (2017). Study on Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction in Mobile Telecommunication Industry in Malaysia, International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE), 7(5S), 299- 316.
Pandiya, D.K., Kumar, B., & Choudhury, M.H. (2014). A study of customer satisfaction on telecom service providers. Indian Journal of Research, 3(5), 57-60.
Rizomyliotis, I., Konstantoulaki, K., Kaminakis, K., Giovanis, A., & Papastathopoulos, A. (2018). Antecedents of customer loyalty in the mobile telecommunication market. A cross-cultural investigation. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 22(4), 1-10.
Saha, N., Islam, M., & Hoque, A. (2016). Factors affecting customers’ satisfaction of mobile phone subscribers: an empirical study on mobile telecommunication Industry in Bangladesh. International Journal of Business and Management, 11(6), 252.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Strenitzerova, M., & Gana, J. (2018). Customer satisfaction and loyalty as a part of customer-based corporate sustainability in the sector of mobile communications services. Sustainability, 10(5), 1657.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Uddin, M.R., Haque, M.E., & Bristy, J.F. (2014). Customer satisfaction of telecom industry in Khulna City, Bangladesh. European Journal of Business and Management, 6(23), 87-94.
Zin, M.I.M., & Nor, M.M. (2017). Instrumen soalselidik kajian melalui model pengukuran reflektif dalam partial least square structural equation modeling (pls-sem) menggunakan smart pls 3.2.3. JuKu: Journal Kurikulum & Pengajaran Asia Pasifik, 4(3), 20-37.
Received: 03-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. BSJ-22-11434; Editor assigned: 04- Mar-2022, Pre QC No. BSJ-22-11434(PQ); Reviewed: 19- Mar-2022, QC No. BSJ-22-11434; Revised: 11-May-2022, Manuscript No. BSJ-22-11434(R); Published: 18-May-2022