Research Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 4S
Customer Journey and Experience in the Banking Sector: A Comprehensive Analysis and Future Scope
Kanishka Sangwan, Delhi Technological University
Rajan Yadav, Delhi Technological University
Citation Information: Sangwan, K., & Yadav, R. (2024). Customer journey and experience in the banking sector: a comprehensive analysis and future scope. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(S4), 1-25.
Abstract
This study conducts a comprehensive scientific mapping analysis of significant publications regarding customer experience within the banking sector, placing special emphasis on the customer journey. While ground-breaking research has been conducted on customer experience, there exists a literature gap pertaining to the customer journey of a bank's clientele. Given the increasing awareness surrounding financial institutions and their services, it is imperative to scrutinize the available literature in this domain. The authors introduce a thematic analysis subsequent to presenting a bibliometric approach, aimed at exploring state-of-the-art research concerning customer experience in the banking sector through the lens of the customer journey. A total of 365 publications spanning a 20-year period on the aforementioned subject were sourced from the Web of Science. This study delineates the evolving volume of publications, the countries involved, sources, citations, authorship networks, and features a thematic map highlighting emerging themes. The results demonstrate a significant interest among both academicians and practitioners in investigating digital touchpoints and discerning the reasons underlying customer engagement with the digital customer journey. The study reveals that every banking customer prioritizes service quality and secures payments, necessitating the utmost attention from banks, as this directly leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty, thereby augmenting the overall customer experience. To ascertain the most prominently discussed themes within our dataset, we employed VosViewer to construct a graphical representation of the bibliometric data. We present five major clusters, elucidating customer personas, digital touchpoints consequent to the introduction of mobile banking as an emerging theme, direct impact of brand image on customer experience, and omnichannel banking. The paper concludes with a synthesis of the entire study, accompanied by its implications and outlines potential avenues for future research in this field.
Keywords
Customer Journey, Customer Experience, Touchpoints, Banking.
Introduction
For decades, marketers have endeavoured to ascertain the most effective means of providing an indelible and gratifying experience for their customer base. Businesses of all kinds acknowledge that customer satisfaction stands as a pivotal factor in constructing a prosperous organization. There exists substantial evidence demonstrating how customer satisfaction leads to recurrent sales (Szymanski et al., 2001; Bindroo et al., 2016), a cornerstone objective for any organization. Customer satisfaction serves as a precursor to the broader Customer experience, simultaneously occupying a central role in marketing campaigns. Furnishing a satisfactory experience to the customer constitutes the ultimate aim for individuals engaged in business, particularly within the service sector. In today’s contemporary landscape, there is widespread recognition of the criticality of managing customer experience through diverse strategies.
Given that the economy now predominantly revolves around experiences, scholars and practitioners are increasingly inclined to delve into this domain (Verhoef et al., 2009; Pine & Gilmore, 2011). To outshine competitors, especially within the service sector, companies must delve into the distinct characteristics of their customers and discern methods to augment their value (Walter & Ostrom, 2010). As customer experience assumes an increasingly pivotal role in steering a successful business, organizations are redirecting their focus towards comprehensive design and delivery of customer experiences to bestow superior customer value (Haeckel et al., 2003). Firms are recognizing the significance of fostering enduring and robust customer relationships, leading them to adopt novel techniques in managing customer experiences, such as customer journey mapping. To elucidate further, the customer journey can be likened to stepping into the customer's shoes (Holmlid and Evenson, 2008), providing a means to comprehend customer behaviour and experiences with greater precision. Conversely, mapping the customer journey entails visualizing all the touchpoints encountered by the customer. An enriching customer experience proves advantageous for both the company and its clientele, akin to positive word-of-mouth, culminating in heightened customer retention rates, augmented satisfaction, and fewer grievances, ultimately translating into heightened profitability (Reichheld et al., 2000). Customer experience is conceived as a comprehensive interactive process between the firm and its clientele. With the advent of digitalization, the frequency of interactions between businesses and customers has surged. A firm engages with its customers at myriad junctures along the customer journey, collectively termed as touchpoints. These touchpoints collectively mould the customer experience and perception. If a firm can discern all pertinent touchpoints in a sequential fashion, construct a visual representation of customer journeys, and craft strategic decisions accordingly, it can forge favourable customer experiences and cultivate a more loyal customer base. Consequently, dedicating more time and resources to crucial touchpoints emerges as a vital endeavour in satisfying customers (Aichner & Gruber, 2017).
Customers entrust banks with their hard-earned money, relying on them in times of crisis. Hence, customers hold high expectations for their interactions with their bank. Competition among banks, whether public or private, is exceptionally fierce. Therefore, banks are dedicating substantial resources to crafting and executing strategies aimed at retaining customers and enhancing their journeys. Customer experience has emerged as a pivotal determinant of customer loyalty and the sustenance of long-term relationships (Verhoef et al., 2015). Banks are increasingly cognizant of this reality, given the escalating competition in the industry. Moreover, technological advancements have prompted banks to engage in strategic marketing efforts, opening new avenues, particularly in the realm of digital banking.
As technology advances, banks are diversifying their services, underscoring the imperative of providing an optimal experience to customers throughout their journey. In the banking sector, the customer journey encompasses all touchpoints, representing various points of engagement where a bank interacts with its customers, including ATMs, physical branches, websites, applications, and more. Previous research urges practitioners to comprehend these touchpoints to elevate customer experience and satisfaction. The digitization of banking has prompted banks to strive for a seamless multichannel service for their clientele, posing formidable competition to traditional banking methods (Cortiñas et al., 2010). A study by Li and Xu (2020) underscores that banks excelling in providing an effective omnichannel experience tend to outperform competitors in terms of customer satisfaction and retention.
Evidently, both the customer journey and experience are burgeoning fields, drawing the attention of researchers worldwide. Through an exhaustive literature review, it is discerned that research in customer experience within the service sector is advancing at a commendable pace. However, there exists considerable room for further exploration, as few studies have delved into the journey of a bank customer to comprehend their experience. Expectations of customers in the banking sector have undergone significant evolution in recent years. Notably, convenience, speed, and personalized services have become paramount (Berry & Bendapudi, 2007). In their study, Williams and Johnson (2019) ascertain that customers anticipate seamless online and mobile banking experiences, in addition to highly personalized advice and support from their banks. Each interaction point serves as an opportunity for banks to gather valuable customer data, which can be leveraged to personalize services, target marketing endeavors, and enhance the overall customer experience (Smith & Johnson, 2017).
Considering the aforementioned perspectives and aiming to address the existing gap in the literature, this paper seeks to comprehensively explore, assess, and validate crucial aspects of customer experience within the banking sector, and throw some light on the how these dimensions shape the experience of the customers. The central objective of this paper is to conduct a thorough analysis of noteworthy research endeavours dedicated to investigating touchpoints and customer experience in the banking domain. Employing bibliometric analysis, this endeavour intends to contribute to the current body of literature in this field. The financial performance of banks is intrinsically tied to how customers perceive their experiences (Andaleeb et al., 2016). The study attempts to evaluate the current state of research on customer experience within the banking sector and identify the touchpoints that have garnered the most attention from academics, with the aim of aiding practitioners in refining customer experiences at these critical junctures. Another objective is to unearth prevailing trends in this domain and present future directions for the benefit of scholars and practitioners alike. Notably, no prior studies have tackled these interconnected themes in the literature.
By embarking on an investigation of "state-of-the-art research," this study aspires to compile the latest and most pertinent findings in the field, thereby bridging the existing literature gap. In addition to filling this gap, the study endeavours to provide a in-depth understanding of customer journey and experience within the banking industry. It also extends practical advice that banks can leverage to enhance their offerings and interactions with clients. Furthermore, this study is poised to provide future research avenues in this area, aiding academics and professionals in staying abreast of the most recent developments.
To achieve these objectives, the ensuing research questions have been formulated:
RQ1. What is the current state of research on customer experience in the banking sector, with a particular focus on the customer journey?
RQ2. What are the predominant themes and trends in the literature pertaining to customer experience and the customer journey in banking?
RQ3. Who are the influential journals, authors, and academic sources in this field, as identified through bibliometric analysis?
RQ4. How has the literature on customer experience and the customer journey in banking evolved over time, and are there emerging areas of interest?
RQ5. What practical insights can be derived from existing research to enhance customer experience strategies in the banking sector?
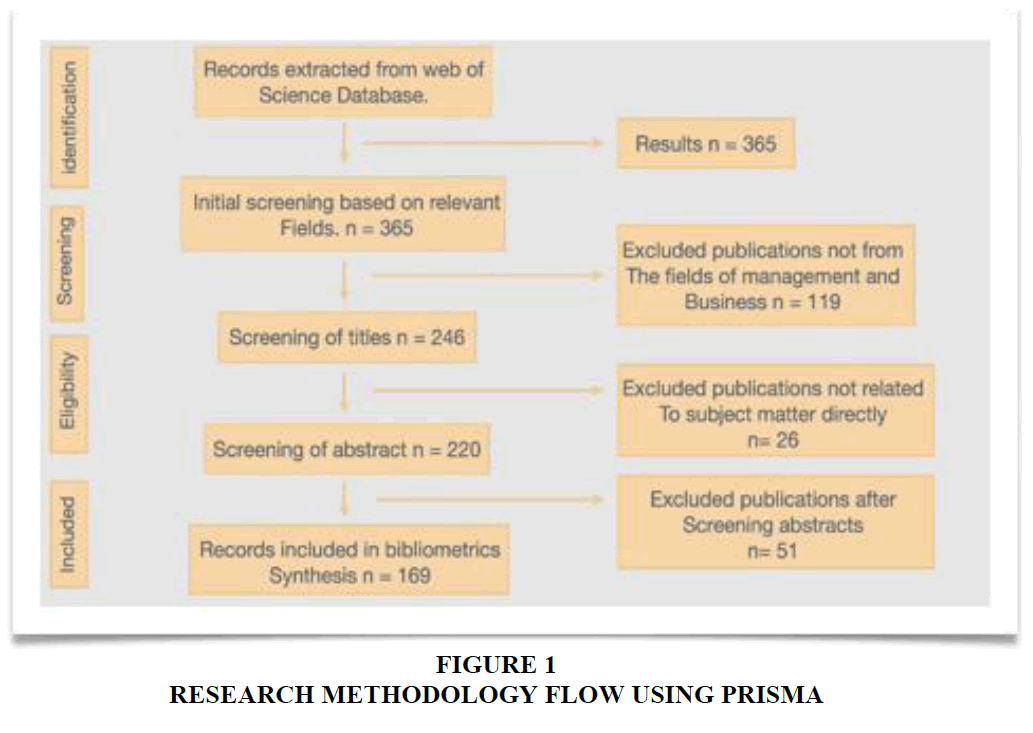
The ensuing section encompasses the research methodology, encompassing the research aim, procedure and data, inclusion and exclusion criteria, selection of pertinent studies, and analytical methods. It also elucidates the process of identifying relevant publications for this study using PRISMA. Section three will delve into the results and discussion, presenting a range of descriptive statistics, including graphical representation and clustering techniques employed in conducting a bibliometric analysis. Section four will address the research questions and present an overview of the diverse implications of this study. Furthermore, sections five and six respectively conclude the study and offer insights into limitations, as well as future scope and agenda for further research in this domain.
Research Methodology
This study aims to conduct a comprehensive analysis of significant publications concerning customer experience within the banking industry, with a specific emphasis on the customer journey. The method opted for this analysis is the bibliometric review. As Pine and Gilmore (1999) astutely observed, customer experience is a pivotal factor in distinguishing organizations in a service-driven economy. This assertion holds particular relevance within the banking sector, where a customer's entire experience is shaped by their interactions with the organization, starting from the initial contact. To gain a profound understanding of customer experience within the banking sector and scrutinize the existing body of literature on the subject, a literature review was deemed the most suitable approach, given its transparent and scientifically rigorous nature (Tranfield et al., 2003).
Bibliometric Analysis has emerged as the preferred choice for burgeoning researchers, owing to its potential in facilitating a comprehensive grasp of new topics, particularly in the realm of business research. This method aids in identifying influential authors, prominent journals, as well as key countries and institutions associated with pertinent publications in a specific field. It unveils the latest findings and provides valuable guidance for future research endeavors (Wang et al., 2014). Bibliometric analysis enables the interpretation of data extracted from a digital database with a high degree of objectivity. The accessibility of databases and the availability of qualitative tools have contributed to the upsurge in bibliometric studies in recent years (Zakaria, Ahmi, Ahmad, Othman, et al., 2021).
Procedure and Data
In this section, we will elucidate the methodology employed, encompassing the inclusion and exclusion criteria, to finalize the database for this review and present concrete findings. We adhered to the PRISMA flow diagram advocated by Moher et al. (2009) for our methodological approach. This diagram provides a comprehensive checklist of various items to facilitate the preparation of a suitable protocol for the review.
The initial step in a bibliometric review involves selecting a database that adequately covers publications for the review (Donthu et al., 2021). Database used for this study is Web of Science. This choice was predicated on the fact that Web of Science grants access to a wide array of publications encompassing cross-disciplinary research and allows for a detailed analysis of specific sub-fields within an academic or scientific area. Additionally, it is considered the preeminent database for citation analysis (Harzing & Alakangas, 2015). The selection of this database was guided by factors such as its widespread acceptance, frequent usage, and easy accessibility.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Among the various inclusion criteria, the foremost was to extract papers specifically pertaining to customer experience and the customer journey within the banking sector. A comprehensive topic search was conducted, employing the keywords "Customer Experience," "Customer Journey," and "Banking." The title, keywords, and abstract were scrutinized to identify relevant studies for this review. Another criterion considered was the time frame, as it was imperative to extract studies pertinent to the evolving landscape. Consequently, studies from 2003 to the end of 2022 were retrieved. A span of 20 years was selected based on the assertion by Arora & Chakraborty (2021) in their study, stating that it is an accepted timeframe for bibliometric analysis. This duration allows for a sufficient period to analyze citations and co-citations (Rey-Martí et al., 2016). Additionally, articles published in English were included as part of the inclusion criteria.
The initial exclusion criteria adopted for this study involved eliminating studies from the database that did not pertain to the fields of management and business. Given that the primary focus of this study is to synthesize the literature on customer experience and journey within the banking sector, all other studies were excluded from the final database through a rigorous screening of their titles. Conference proceedings and books were further excluded to ensure a refined source of knowledge (Rodriguez & Navarro, 2004). Furthermore, papers that did not align with the aim of the study were excluded following a meticulous and manual screening of their abstracts. As the central focus of our study is to present a comprehensive overview of publications on customer experience in the banking sector, along with the customer journey as a explored element, all other documents were removed from the final dataset.
Selection of Relevant Studies
An initial topic search yielded 364 results with the keywords "customer experience, customer journey, and banking" present in the title, abstract, or keywords of the publications. To ensure the inclusion of papers aligning with the purpose of this study, specific parameters were established, as mentioned above. After excluding papers based on the predetermined criteria of time frame, language, and fields, Web of Science yielded 246 results in this initial screening process on 7 June, 2023. Prior to finalizing the dataset for bibliometric analysis, a manual screening of abstracts was also conducted. During title screening, 26 publications that did not pertain to customer experience or journey in the banking sector were excluded. Furthermore, a review of the abstracts was undertaken to ascertain that the studies included were relevant to a specific banking touchpoint or encompassed the entirety of the customer journey and experience within the banking sector. In this process, 51 were excluded, resulting in a final list of 169 documents for the bibliometric analysis. The selection process was conducted with the primary objective of aligning with the core focus of the study. Only studies explicitly addressing the customer experience or journey within a bank or the banking industry, as their central theme, were incorporated into the final review. A comprehensive record of the selection process is meticulously illustrated in the flow chart presented in Figure 1.
Analytical Methods
In classifying the value of a paper, there exist multiple approaches (Podsakoff et al., 2008). With the core aim of this study in focus, bibliometric software was employed to analyze the database extracted from Web of Science. Specifically, Bibliometrix, an R-tool developed by Aria and Cuccurullo (2017), was used for the scientific mapping of the documents. This tool was designed to assist researchers in the dynamically evolving field of bibliometrics. The study seeks to identify the main themes, trends, and knowledge gaps within the domain. Bibliometric methods will be employed to assess the impact of authors, publications, and scholarly references (Glänzel & Moed, 2002). The ensuing bibliometric analysis will provide a comprehensive overview of the influential voices in the field and offer insights into the academic landscape of customer experience and the customer journey in banking. Additionally, the study will track the research evolution in this field, taking into consideration the dynamic nature of the banking industry and shifting consumer preferences. The finalized dataset was extracted in a bib text file to be processed using R Software. Relevant charts and tables were scrutinized to discern recent trends, the most frequently studied touchpoints in the banking sector, countries leading research in this field, as well as pertinent journals and authors.
Furthermore, the dataset was inputted into Orange software to analyze and visualize the keywords, culminating in the creation of a word cloud to grasp the major themes under examination. Orange, known for its reliability and quality in research, proved to be an appropriate tool for this purpose. Additionally, VosViewer, a software developed by Eck and Waltman (2009) for visualizing bibliometric networks, was utilized for clustering and identifying major themes and their interconnectivity. VosViewer offers data mining functionality that aids in visualizing the descriptive data and co-occurrence networks of relevant terms, making it particularly useful when dealing with a relatively large number of documents.
In conclusion, the aim of this study is to synthesize the existing knowledge body to provide concrete insights. The objective is to present a structured overview of this knowledge domain, which will be valuable to the banking practitioners, as well as the academicians and scholars with an interest in this area. These insights will assist in curating superior customer experience strategies to meet dynamic environment and evolving customer expectations and needs.
Results and Discussion
This section provides an in-depth examination of the results of bibliometric mapping of 169 documents sourced from Web of Science spanning a 20-year horizon. It highlights the evolution of publications, citations, sources, countries, and keywords, in addition to analysis of clusters that define the core themes in this domain. The study also throws light on emerging topics and the relationships between the studies through thematic map and three-field plot graph. Moreover, this section concludes with an extensive discussion on the key clusters generated by the VosViewer software, illustrating some commonalities and prevailing themes amongst the diverse studies.
Description of the Corpus
This section provides critical insights into the dataset extracted from Web of Science. The time horizon for this study spans 20 years (2003-2022), encompassing the latest and most pertinent studies for a comprehensive overview. The corpus consists of a total of 607 keywords employed in the 169 papers selected for the study, underscoring the expansive scope of the domain. The average citation per document stands at 27.49, a metric derived from the main overview of the bibliometric interface used for this analysis, indicating a collective depth of knowledge within the subject, each study complementing the other. The number of citations serves as a valuable metric for understanding the influence and relevance of a paper (Svennson, 2010). Among the 394 authors contributing to this domain from this corpus, 29 documents are single-authored. Moreover, 28.99% of the articles exhibit international co-authorship, indicative of the global collaborative scope in this domain. A total of 9028 references were identified within the corpus, highlighting the extensive breadth encompassed by this domain.
Annual Scientific Production
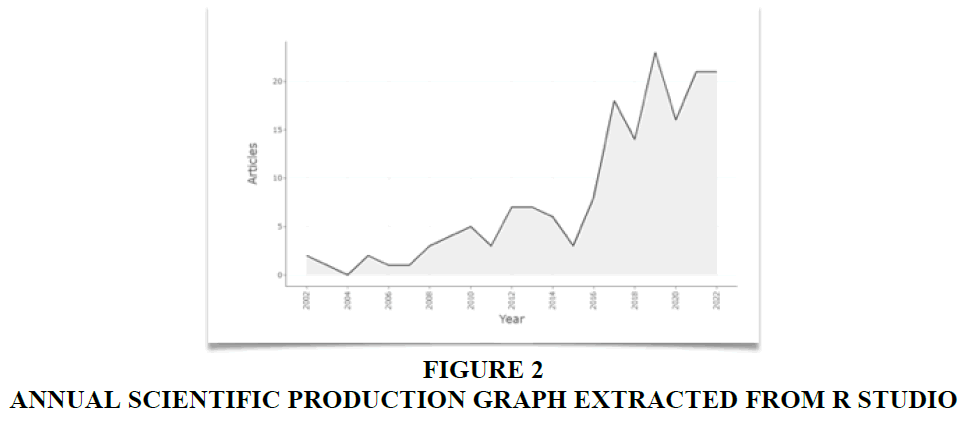
Figure 2 presents a chronological overview of publications spanning from 2002 to 2022. Up until 2015, the volume of publications in this domain exhibited fluctuations, indicating a broader exploration of customer experience rather than a specific focus on the banking sector. Notably, 2004 recorded the lowest number of publications. Subsequently, a substantial surge occurred after 2015, with 2019 marking the zenith at 25 publications. Following a slight dip in 2020, there was a resurgence in interest. This resurgence can be attributed to the heightened relevance of digital touchpoints and banking in the post-COVID era, prompting increased scholarly attention. Furthermore, it was observed that articles centred on customer journey were more dispersed around 2019. This aligns with Tueanrat et al.’s (2021) findings, which corroborate a sevenfold increase in publications focused on customer journey from 2012 to 2020.
Average Citation Per Year
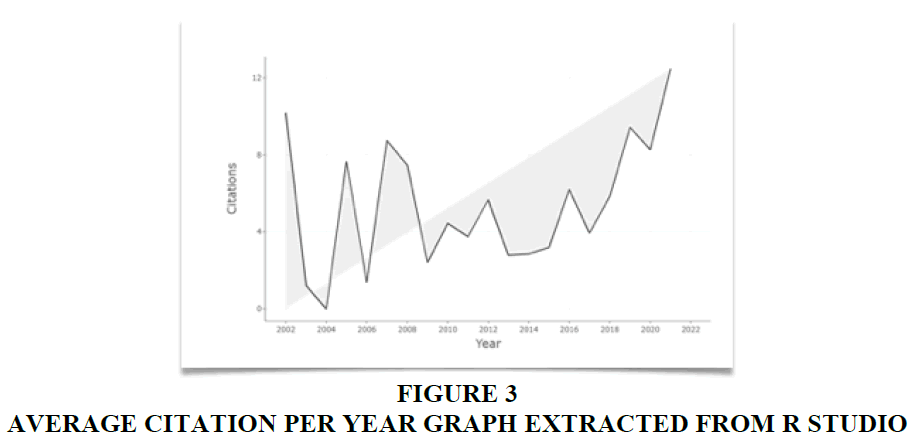
As depicted in Figure 3 below, the average citation per year in this subject matter reached its zenith in 2021. This suggests a burgeoning potential for future research in the realm of studying the customer banking experience, given its recent surge in influence. This upswing can be attributed to the rapid advancement of technology and the increasing proficiency of individuals in digitalization processes. Consequently, banking institutions are compelled to introduce more sophisticated digital channels for communication. The graph illustrates the evolving impact of this field on an annual basis. The average citation serves as a measure of the influence of specific topics, authors, and journals. Evidently, the influence of this domain experienced a significant upturn post-2020.
Source Dynamics
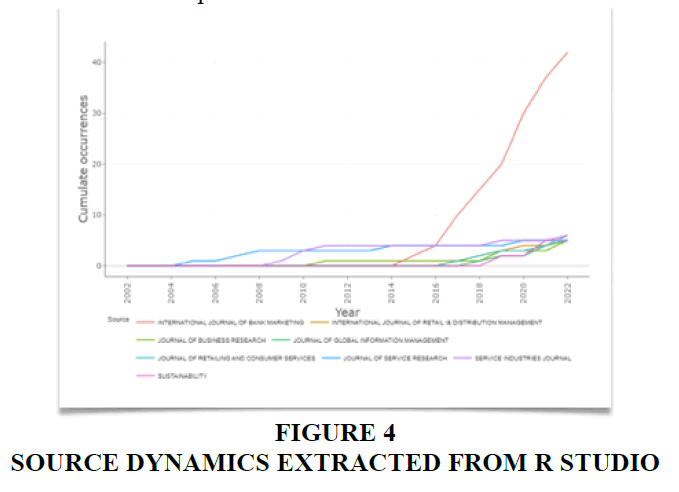
Source dynamics provide insights into the frequency distribution of publications from various outlets. It is evident from the graph below(Figure 4), that the Journal of Service Research emerged as the predominant publisher of articles advancing the study of customer experience and journey in the banking sector. Given that banking constitutes a substantial segment within the broader service sector, it is fitting to find extensive coverage in the pages of the Journal of Service Research. However, post-2014, the International Journal of Bank Marketing took the lead, becoming the primary publisher of manuscripts on this subject matter, and it has maintained this position ever since Figure 4.
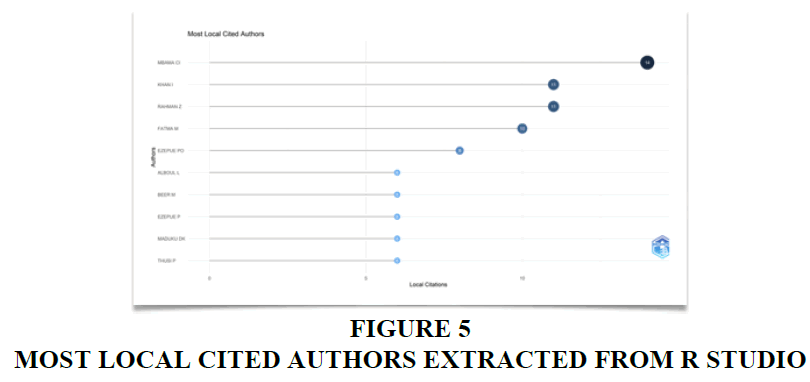
Most Local Cited Authors
The metric of Local Cited Authors pertains to authors whose foundational research has been referenced by other authors within the dataset, offering a significant gauge of a study's influence and productivity (Goyal and Kumar, 2021). In evaluating a publication's importance within a research domain, citations emerge as the most objective yardstick (Pieters & Baumgartner, 2002; Stremersch, et al. 2007). Consequently, through citation analysis, one can discern the most impactful contributions in a research field, illuminating the field's evolving dynamics. Figure 5 illustrates that Mbama's work boasts the highest citation frequency within this bibliometric collection, garnering 14 citations from other authors.
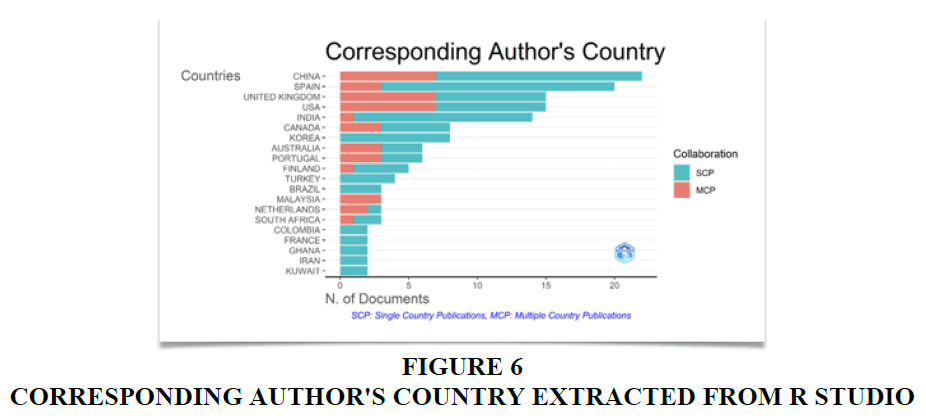
Corresponding Author's Country
Figure 5, 6 illustrates the prominent contributions of China and Spain in the realm of 'Customer Experience and Journey in the Banking Sector'. Notably, China takes the lead in overall authorship, encompassing both Single Country Publications (SCP) and Multiple Country Publications (MCP). Yet, when scrutinizing Single Country Publications specifically, the top positions are secured by China, the United Kingdom, and the USA. In the grander scope of overall contributions, India holds the fifth position, followed by Canada. However, in terms of Multiple Country Publications, Spain, India, and China emerge as the frontrunners among other nations. It is worth noting that in the context of Single Country Publications, there remains untapped potential for further exploration, particularly given India's status as a developing nation with an escalating rate of digital banking literacy and a substantial population. This context presents a valuable opportunity for an exhaustive examination of this subject matter in the Indian context, reinforcing the pertinence of this paper. Another insight drawn is that most of the developed and nations are in the lead which can be due to the fact that the customers of these nations are more tech savvy and informed, hence, they demand a superior customer experience.
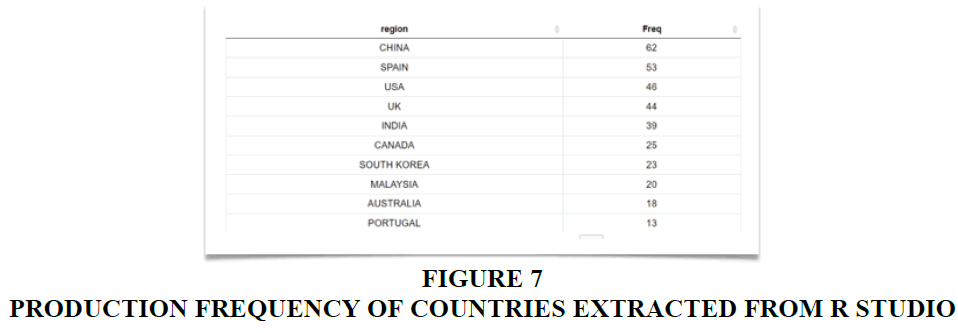
Country Scientific Production
The descriptive information in Figure 7 underscores China's prominent position in generating publications concerning customer experience and journey within the banking sector, as well as in the examination of associated touchpoints. China also exhibits the highest frequency of author contributions in this domain. Following closely, Spain emerges as the second-highest contributor in terms of country-specific scientific output. The USA and UK demonstrate similar levels of productivity, while India secures the fifth position. This pattern signifies a concerted effort in these countries towards the optimization of customer experience in the banking sector. It is apparent that these nations recognize the pivotal role of enhancing customer experience at critical touchpoints for bolstering the performance of banks in the future. This insight offers a snapshot of companies, whether in a developed or developing state, investing substantial research in these domains.
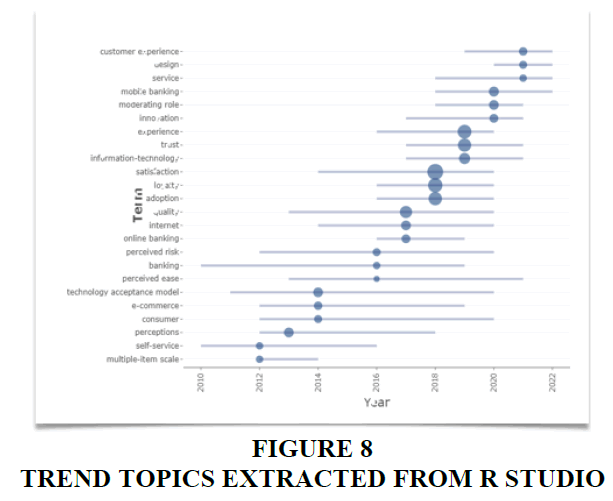
Trend Topics
The trending themes represent current, pertinent topics within the discipline that offer insights into the pressing issues in the industry. Figure 8 illustrates the yearly distribution of these trending themes. The line indicates the period when a specific topic gained prominence, while the circles indicate how frequently that particular topic was referenced. At present, customer experience stands out as the most prominent trend. There is no denying that customer experience is a burgeoning field, playing an indispensable role in the growth and success of a business. Many studies are also exploring the complex elements of service design to optimise customer experience. It can be seen that researchers are interested in examining mobile banking as a touchpoint in the customer journey considering the growing number of studies in this domain.
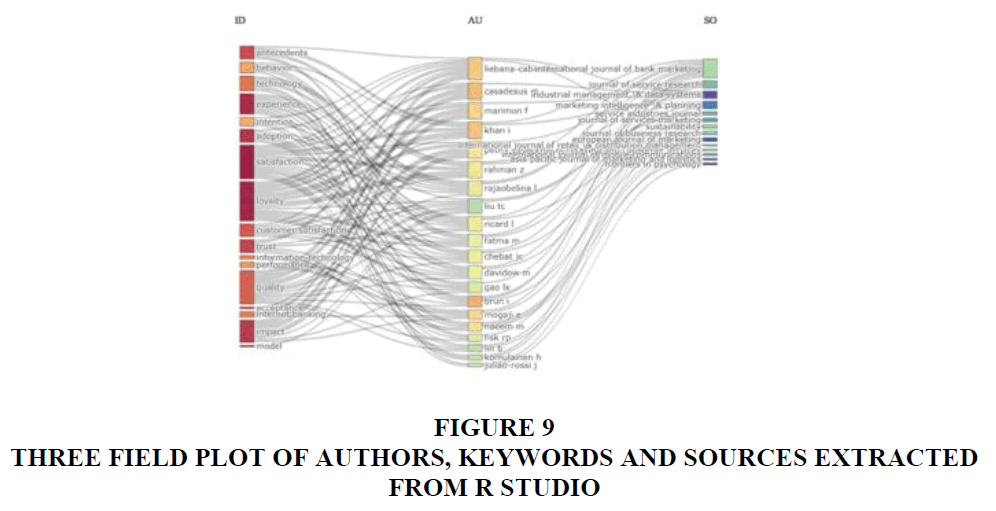
Three Field Plot
Figure 9 presents a Sankey diagram showcasing three key fields: keywords, authors, and sources. Analyzing these fields provides crucial insights into the connections between them. The diagram illustrates the relationships among the top keywords, authors, and influential journals. The leftmost field pertains to keywords, the middle field represents top authors, and the rightmost field focuses on influential sources (Journals). The width of the lines connecting these fields indicates the strength of the connection. From the diagram, it is evident that "satisfaction" and "loyalty" emerge as the most frequently used keywords or themes, affirming our earlier observations from the preceding charts. For those seeking information on authors active in a specific domain, they can trace the lines connecting authors with keywords. Additionally, one can explore the journals that have published papers in the same domain. Notably, "loyalty" emerges as the most extensively covered keyword, with Khan being the most prolific author in our database on this concept. The "International Journal of Bank Marketing" stands out as the most influential journal in this field, given its significant contribution to the literature, as evidenced by the highest incoming flow count.
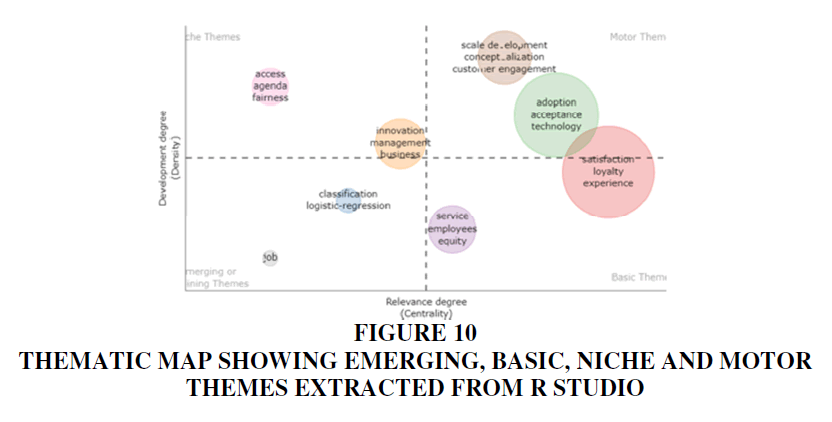
Thematic Map
The thematic analysis outcomes are presented in the respective gradients, as depicted in the figure above. Among the basic themes gradient, which encompasses major yet underdeveloped themes, we find "satisfaction," "loyalty," "experience," and "service employees equity," all of which offer significant potential for further research. Moving to the Emerging themes quadrant, which encompasses minor and underdeveloped themes, we encounter "innovation management," "business," and "job."
It's noteworthy that "innovation management" and "business" largely fall within the minor but developed category, indicating that only a few subsets of the broader term remain underexplored due to overlap. Within this quadrant (Niche themes), which addresses minor but developed themes, we also find "access," "agenda," and "fairness."
In the major and developed category (Motor theme), we encounter themes such as "social development," "conceptualization," and "customer engagement," which coexist with elements like "adoption," "acceptance," and "technology," exhibiting a minor overlap with a subset of "satisfaction," "loyalty," and "experience." This nuanced analysis helps identify the various dimensions within the field, shedding light on both established and potential areas for further exploration Figure 10.
Word Cloud using Orange Software
The Orange software, a robust data mining tool, provides capabilities for visualization, analysis, and various other functionalities, facilitated by both Python scripting and visual programming. In this study, the publications sourced from Web of Science were imported into the software, forming a corpus. Subsequently, Orange processed the text, generating a bag of words. Finally, this data was employed to construct a word cloud, effectively illustrating the current state of the corpus, including prevalent themes and keywords in use.
The sequential process, from uploading input as a corpus to obtaining an output, is outlined in the diagram below (Figure 11).
Word Cloud Analysis
Figure 11-13 provides a visual representation of the keywords and themes present in the publications within this dataset. The size of each term reflects its frequency of usage within the corpus. Major themes include 'customers', 'banking', 'customer service', 'experience', 'satisfaction', 'services', and 'perception'. These terms constitute the most prominent elements in the corpus. Additionally, keywords like 'loyalty', 'trust', 'relationship', 'brand', 'technology', and 'design' also feature prominently in the word cloud. The focus of our study is the analysis of documents pertaining to customers in the banking service sector. Consequently, these studies encompass a range of factors contributing to customer satisfaction, a pivotal aspect discussed in Section 1 of our study.
Using VosViewer
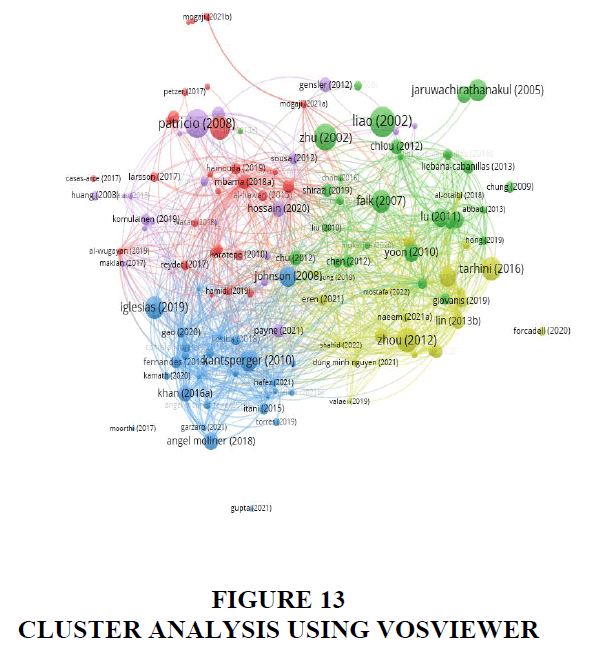
In this section, a cluster analysis has been conducted to gain an in-depth understanding of the subject matter and to identify the prevailing themes in the field of customer experience management within the banking sector. VosViewer, a tool known for graphical representation of bibliometric data, was employed for this purpose. A minimum citation threshold of 6 was set, given the specific focus on the banking sector, resulting in a limited pool of publications. Utilizing VosViewer, five clusters exhibiting high interconnectedness were generated (refer to Figure 13). Within this visualization, each circle represents a distinct study, while the lines signify the connections between them. Notably, the thickness of the lines indicates the strength of the interconnection.
Customer Persona
Cluster one encompasses publications that delve into the diverse personas of banking customers, examining their experiences across various countries. Recognizing that each customer's journey is distinct, it becomes crucial to create distinct personas and categorize them, thus facilitating a more streamlined comprehension of their experiences for organizations. Banks must exhibit sensitivity towards the needs of these different customer personas, given their varied perspectives towards service experiences (Wugayan, 2019). Ensuring equitable treatment, particularly for customers belonging to low-income groups, is imperative to mitigate any perception of neglect on the part of banking employees during service interactions (Kamran & Uusitalo, 2019).
Evaluating customer satisfaction can prove challenging, as dissatisfied customers are less likely to voice their concerns, potentially leaving the firm unaware of its shortcomings (Chebat et al., 2018). Therefore, prioritizing the study of different personas remains crucial. Undoubtedly, the advent of technology has opened up new avenues for firms to enhance their relationship marketing strategies, ultimately leading to satisfied customers. Banking institutions should be adept at identifying the specific factors that render a particular touchpoint satisfactory for various personas (Brun et al., 2013).
Moreover, it is pertinent for banks to acknowledge that a customer's age inversely correlates with their adoption rate of digital banking, with the older generation exhibiting a greater comfort with physical touchpoints over digital interfaces (Harris, 2016). Additionally, a customer's personality traits play a pivotal role in influencing their satisfaction levels, underscoring the need for banks to thoroughly study these characteristics and delineate distinct personas (Al-Hawari, 2015).
Establishing a set of well-defined personas tailored to a specific business can significantly aid in targeting the right audience, crafting more effective marketing campaigns, and personalizing these initiatives to provide enhanced services. Building personas ultimately fosters a deeper comprehension of customers' needs and preferences, facilitating the development of superior products and robust sales strategies. For the banking industry, delving into the profiles of ideal customers, or personas, holds the potential for innumerable benefits.
Factors Influencing the Adoption of E-banking
Cluster 2 delves into the adoption of e-banking and mobile banking services, and the various factors that influence their usage. The pandemic has significantly accelerated the shift towards online transactions, with safety being a paramount concern (Muneer M. Abbad, 2013). Understanding the variables that attract current online banking users is crucial for encouraging further adoption. The status quo theory suggests that customers tend to stick to channels they are already familiar with, such as traditional banking, and may be resistant to adopting newer, innovative channels like online banking (Falk et al., 2007).
Effective technical support is essential for ensuring continuous usage of mobile banking, particularly given the paramount importance of safety and reliability (Chung & Kwon, 2009). The usage rate of e-banking services is positively correlated with how customers perceive various service attributes, including information quality, performance, service quality, self-interest, experience, and satisfaction (Arora & Sandhu, 2018).
For reluctant customers, assurance of an enhanced customer experience after transitioning to e-banking services is essential. Satisfaction and trust significantly influence the intention to continue using mobile banking, indirectly influenced by technology readiness and service quality (Chen, 2012). According to the theory of bounded rationality, E-Service quality ensures increased e-loyalty through the development of satisfaction and trust (Chung et al., 2012).
As the future of banking lies in complete digitalization, banks should make a strong effort to spread awareness about the benefits of e-banking. With banking services now available around the clock, all customers are entitled to take advantage of the new banking models to enjoy the convenience and ease they offer. The focus should be on ensuring a seamless and secure digital banking experience for all customers.
Impact of Brand Image on Customer Experience
Cluster 3 emphasizes the significant impact of brand perception on consumer buying behaviour. Effectively managing the customer experience not only reinforces brand value but also ensures continued relevance and profitability in the market. This cluster focuses on the various factors influencing brand image and equity, which in turn shape the customer experience.
Elements such as the bank’s corporate visual identity, emotional experience, functionality, lifestyle, and self-identity collectively contribute to customer satisfaction and brand loyalty (Khan et al., 2016). While service quality is a crucial factor in shaping the experience of a customer, there are numerous other elements that shapes a customer’s perception of a service provider before they even experience the services.
Brand equity exerts a profound influence on customer experience, particularly in response to social influence, which has the potential to alter purchasing behaviour (Gao et al., 2020). The choice of the first bank to open an account is often influenced by recommendations from family or friends, underscoring the significance of brand image. Given the intense competition in the banking sector, understanding the switching behaviour of the customer is paramount.
Brand equity and customer satisfaction serve as mediators in the relationship between customer experience and loyalty, with behavioural and affective aspects of customer experience exerting the most influence on customer loyalty (Kamath et al., 2019). Positive customer-brand engagement, especially in online banking, not only enhances the customer experience but also bolsters brand performance (Imran Khan, Rahman 2006, Mobin Fatma, 2016).
A study by R. Bravo, E. Martinez, and J.M. Pina suggests that the online experience holds less importance compared to the offline experience, particularly concerning trust and brand commitment, both of which are closely tied to customer engagement. By presenting themselves in a personalized manner, banks are more likely to encourage electronic word of mouth and enhance their brand personality (Torres and Augusto, 2019).
For a customer to develop and maintain loyalty towards a brand, the brand should resonate with the customer's self-concept. However, it’s essential to not solely focus on online customers; the offline customer experience at bank branches still significantly impacts a brand's profitability, despite the surge in technology use (Moliner et al., 2018). Banks heavily rely on their reputation in the market, which is why a continuous evaluation of their brand image is of paramount importance to keep customers satisfied and maintain a loyal customer base.
Mobile Banking as a Significant Touchpoint
Cluster 4 delves into the profound effects of mobile banking on the banking industry, especially amid the rapid proliferation of internet technology and the heightened need for digitalization spurred by the Covid-19 pandemic. Managing digital touchpoints, particularly mobile banking, necessitates a deep understanding of the factors related to the usage intention of mobile banking.
Transitioning from trying mobile banking in emergencies to its continuous use involves distinct challenges. Therefore, banks must implement strategic measures to cultivate and maintain loyal e-banking customers. The perceived usefulness of mobile banking is significantly affected by the quality of information and system functionality. Initial trust plays an essential role in shaping customers' perceptions of the service's usefulness. Given that mobile banking entails low switching costs but carries a higher risk, building initial trust is crucial (Zhou, 2011).
The design and display of information on a mobile banking app, known as interface design, directly impact customer satisfaction (Al-Otaibi et al., 2018). Assurance emerges as a pivotal factor influencing the intention to use internet banking services (Rahi et al., 2019). The technology acceptance model provides valuable insights into customer perceptions and the perceived usefulness of internet banking services (Marakarkandy et al., 2017; Alsajjan & Dennis, 2010).
The actual usage experience is a decisive factor in determining whether a customer continues to engage with internet banking or not. Psychological factors like trust and commitment significantly influence customers' decisions in this regard (Yuan, Lai, and Chu, 2019). The banking infrastructure must be conducive to the seamless use of internet banking. Furthermore, internet banking not only fosters financial inclusion but also contributes to the development of a responsible society, highlighting the need for its promotion (Naeem and Ozuem, 2021).
In nations with limited access to traditional banking services, there is a heightened importance of promoting mobile banking to ensure broader inclusivity. To attract more users, mobile banking apps should prioritize authenticity and user-friendliness. Additionally, banks should demonstrate a strong commitment to combatting online fraud (Thusi and Maduku, 2020).
Addressing all the aforementioned factors that motivate customers to adopt mobile banking is important for banks seeking to increase their adoption rates. Customers must be guided through the entire adoption journey with a sense of security, guidance, and support from the bank.
Omnichannel Banking
In today's banking landscape, every financial institution is dedicated to providing multichannel services, aiming to enhance convenience, accessibility, and overall consumer satisfaction. The seamless integration of various channels, spanning from virtual platforms like mobile banking apps and internet banking to physical channels such as brick-and-mortar branches, forms a cornerstone of banks' business strategy.
Cluster 5 encompasses a series of publications that delve into the multichannel approach within the banking industry and elucidate how customers navigate the selection of specific channels for their interactions with a bank. Customers primarily base their channel preference on experiential requirements and general needs, rather than merely functional attributes or technological features (Patricio et al., 2003).
While the quality of e-service significantly impacts e-loyalty, its influence on channel behaviour is comparatively less pronounced. However, effective e-service can serve as a deterrent to customers switching to services offered by other providers, thereby averting defection (Sousa and Voss, 2012). Banks must diligently align all their channels to instil a sense of security and confidence in customers, encouraging them to adopt an omnichannel approach (Banerjee, 2014).
The absence of integration among channels may arise due to various challenges, including inconsistencies in managing customer data. If left unaddressed, this issue can lead to customers severing their relationship with the bank. Perceived service quality stands as a major dimension influencing the integration quality of various channels, consequently impacting channel selection (Hossain et al., 2020).
One of the key advantages of a multichannel approach is the convenience and ease it affords in conducting banking transactions. This approach proves time-saving and spares customers from the hassles associated with traditional banking methods, providing them with invaluable flexibility. Banks must ensure the seamless integration of customer data across all channels, guaranteeing a smooth and hassle-free experience for their clientele.
Findings and Implications
The study's first three research questions were comprehensively addressed through scientific mapping analysis and thematic analysis of relevant papers within the subject domain. The fourth research question, pertaining to the evolution of subjects, was elucidated during the review of selected papers. The research focus has shifted from enhancing physical satisfaction and reducing lead time at retail outlets to prioritizing online web browser engagement, and subsequently, the development of specific applications tailored to individual banks. Notably, convenience emerged as the paramount attribute in this transition, closely followed by safety considerations. This shift can be attributed, in part, to the rate at which customers are adopting new technologies. This presents banks with a valuable opportunity to further enhance customer interaction and satisfaction, particularly in light of the widespread prevalence of mobile banking apps.
Insights and Suggestions
The practical business insights derived from this study encompass a diverse range of aspects. These insights, accompanied by strategic recommendations, have been organized in Table 1 for easy reference and application.
| Table 1 Insights and Strategical Suggestions | ||
| S. No. | Insight | Strategic Recommendations by the Authors |
| 1. | There is a growing demand of Digital Accessibility and Convenience. Consumers appreciate digital channels because they are easily accessible and convenient (Chatterjee et al., 2016) | Hence, banks should formulate a strategy to invest in online and mobile banking platforms that prioritize simplicity, quick loading times, and intuitive layouts. |
| 2. | Verhoef et al. (2015) emphasize the importance of a seamless cross-channel experience, highlighting that it significantly enhances overall customer satisfaction. | Ensuring consistency of information and services across digital and physical touchpoints can greatly enhance the user experience, allowing for seamless transitions between these channels. |
| 3. | The study highlights the importance of customization of services and tailored suggestions which improve the online banking encounter (Ricci, 2011). | Banks should leverage customer data and AI algorithms to offer personalized product and service recommendations through digital channels. |
| 4. | Self-service alternatives for standard tasks are well-liked by customers (Lien et al., 2021). | We recommend banking firms to focus on improving self-service functions on digital platforms, such as simplifying fund transfers, bill payments, and balance inquiries for user convenience. |
| 5. | Perceptions are influenced by the physical branch environment, according to Mattila (2000). | To create a warm and professional atmosphere, banks should invest in the ambiance and design of their branches. Additionally, ensuring that staff is adequately trained to deliver exceptional in-branch experiences is crucial (Rust et al., 2019). |
| 6. | Customer journey mapping helps identify key touchpoints and pain points (Lemon & Verhoef, 2016). | We recommend that banks regularly update and analyze customer journey maps to gain a deeper understanding of the customer's path and to enhance interactions at critical stages |
| 7. | feedback collection is essential for continuous improvement (Kannan et al., 2016). | To foster a culture of continuous improvement, we advise banks to implement feedback mechanisms, encompassing both digital and in-branch channels. This approach will enable them to glean valuable customer insights and make informed, data-driven decisions (Bitner et al., 2008). |
| 8. | Security and trust are paramount for banking customers (Kumar & Lim, 2008). | To fortify the security of digital channels, we strongly recommend banking firms to allocate substantial resources towards implementing robust cybersecurity measures. Additionally, transparent communication about these efforts will go a long way in building trust with customers |
| 9. | Efficient problem resolution enhances overall satisfaction (Mattila & Mount, 2003). | Taking prompt and effective action to resolve customer complaints and providing timely solutions is a crucial step in enhancing the overall customer experience. This proactive approach demonstrates a strong commitment to customer satisfaction and builds trust in your services. |
| 10. | Well-trained staff are essential for positive in-branch interactions (Rust et al., 2019). | Implementing comprehensive training programs is essential to equip employees with the necessary knowledge and skills required to deliver exceptional customer service. This investment in employee development by the banks will directly contribute to an improved customer experience. |
| 11. | Data analytics can reveal valuable insights into customer behavior (Kannan et al., 2016). | Banks should harness the power of data analytics and predictive modeling to anticipate customer needs and offer proactive solutions. |
| Benchmarking against competitors can highlight areas for improvement (Reichheld & Teal, 2003). | Banks should continuously evaluate your customer experience against industry leaders and adjust strategies accordingly. | |
Integrating these insights from existing research with current practices and real-time data empowers banking institutions to develop and refine customer experience strategies that address the evolving needs and expectations of their customers, both in digital and physical interactions. These strategies play a pivotal role in building and sustaining strong, enduring customer relationships in the banking sector.
Implications for the Banking Industry
The study highlights the significance of customer journey research, particularly in the banking sector. This is the first study to provide a thorough overview of customer journey and experience in the banking sector with the aim to advance the literature in this domain in several ways. It highlights that customer perception of service quality and experience plays a pivotal role in determining customer loyalty, especially in an industry where products and services are relatively similar across different banks. The study's bibliometric analysis and thematic clustering reveal key themes in customer experience management. These themes include the adoption of digital banking, continuous usage of internet banking, managing multichannel banking, studying different personas of bank customers, and strategically managing brand image. This provides a theoretical background for understanding and studying customer experience in the banking sector. The findings underline the growing importance of digital touchpoints in shaping customer satisfaction. With advancing technology, scholars and practitioners are increasingly focusing on factors influencing the adoption of digital banking, particularly mobile banking. Factors like initial trust, perceived usefulness, service quality, and service information emerge as dominant themes in this context.
The following managerial implications can be deduced from the study: First, traditional banks must invest in digital infrastructure and restructure their business practices to meet the demands of contemporary consumers for a seamless omni-channel experience (Verhoef et al., 2015). Second, the data-driven strategy of digital banking places a strong emphasis on efficient collection, processing, and utilization of client data. Traditional banks can adopt similar strategies to adapt to changing customer preferences and enhance overall customer experiences. Third, Striking the right balance between preserving physical branches and enhancing digital services is crucial for traditional banks. Informed decisions regarding branch consolidation and optimizing in-person customer interactions should be guided by research findings (Lemon & Verhoef, 2016). Fourth, to preserve and enhance trust in digital channels, traditional banks should prioritize strong cybersecurity defenses and maintain open lines of communication. These factors are essential for ensuring customer confidence in digital banking environments (Kumar & Lim, 2008). Fifth, traditional banks should invest in comprehensive staff training programs to ensure that in-person customer interactions remain exceptional and valuable. This can be informed by research on effective customer service and employee training methods (Rust et al., 2019). Sixth, some banks are adopting hybrid models that integrate robust digital services with physical branches. Studies can be leveraged to evaluate the effectiveness of these models and provide practical guidance for their implementation (Huang & Rust, 2018). Seventh, balancing the positive attributes of both traditional and digital banking models is essential. Prioritizing technology and data analytics, along with ensuring security and building customer trust in the digital realm, should be at the forefront of bank strategies. This approach enables banks to effectively meet the diverse demands and expectations of their clientele.
Conclusion
Managing customer experience is a paramount priority for service firms, particularly within the financial sector. Organizations widely recognize that a positive customer experience not only drives growth but also leads to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals from loyal customers. Even a minor shift in the proportion of loyal customers can significantly impact a firm's profits. This study specifically focuses on the banking sector, where customer loyalty hinges on their perception of service quality and overall experience, given that the products and services offered by different banks are largely comparable. The study holds both theoretical and managerial significance. The theoretical contribution is evidenced through bibliometric analysis, which helped identify contemporary themes, influential authors, and countries at the forefront of research in this domain. While the field has made substantial progress over the years, there remains a need for further research to delve deeper into understanding customer behavior in the banking sector. The centrality of customer satisfaction in determining overall customer experience is evident, as most authors concentrate their efforts in this area. Furthermore, through the clustering process in VosViewer, five distinct themes emerged: the adoption of digital banking, sustained usage of internet banking, effective management of multichannel banking, examination of various customer personas for enhanced experience management, and strategic maintenance of brand image to ensure ongoing customer satisfaction. It is now established that digital touchpoints wield the most influence over customer satisfaction levels, given the evolving landscape of technology, as extensively studied by scholars. Mobile banking, though an emerging feature, is yet to gain widespread popularity among consumers. Hence, much of the research has focused on identifying factors affecting user adoption of mobile banking. Dominant factors recognized in these studies include initial trust, perceived usefulness, service quality, and service information. The study carries significant managerial implications. Findings suggest various critical touchpoints that shape customer experience. Banking firms must meticulously track their customers' journey and concentrate on those touchpoints deemed important by the customers, rather than the touchpoints the company deems most relevant or profit-generating. Prioritizing the customer's perspective over the company's is key. Identifying relevant touchpoints, which predominantly are digital, empowers banks to serve their customers better and collaboratively create a secure platform. Moreover, a multichannel approach should be complemented by a robust strategy for effective management. This study underscores the importance of designing quality services to cultivate loyal customers. Banking firms should adeptly manage both online and offline customer experiences to fortify brand image in the minds of customers. This can be achieved through seamless integration of offline and online channels, ensuring a harmonious alignment for an enhanced customer experience.
To entice more customers towards digital touchpoints, incentives in the form of cost savings and convenience should be extended. Overall, while the study focuses on one service sector, its findings offer generalizable implications that can be applied to other sectors with careful analysis.
Limitations and Future Scope
This study was undertaken with the goal of contributing to the current body of literature on customer experience management, particularly in the banking sector. To achieve this, only one database, Web of Science, was utilized. Typically, it is recommended to assess multiple databases for conducting a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Therefore, in future research, academicians and scholars may consider conducting another comprehensive analysis using a different database such as Scopus. The study is exclusively focused on a single service sector, which may constrain the broader applicability of the findings. However, given that satisfaction is a predominant theme across most publications and is a crucial variable in nearly every type of service, the findings may still have relevance in other service sectors.
The following research avenues can be explored in the future studies: First, future studies could explore the individual themes identified in this study and develop a scale for their measurement. Second, a comparative study evaluating the online and offline customer experience and journey in the banking sector could be a valuable area for future exploration. Third, given the substantial shifts in customer behaviour, expectations, and company-specific capabilities in the post-pandemic landscape, further research is warranted to comprehensively assess these changes and to create strategies to the dynamically evolving market environment. Fourth, future studies could consider multiple databases for bibliometric analysis to provide a wider research landscape. Fifth, with the exponential rise of AI and other technologies, future studies could explore how banks can leverage these technologies to gain competitive advantage. Sixth, future studies can explore the ethical aspects of managing a bank’s customer experience in the digital realm encompassing privacy issues, transparency and data security. Seventh, future studies may assess the direct impact of customer experience on financial metrics like customer retention and profitability to present quantifiable benefits to the business.
The abovementioned future research directions have a wide scope and potential to deepen the understanding of customer experience management in the banking sector and further assist in the development of more effective strategies to enrich the experience throughout the customer journey.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The corresponding author on behalf of all the authors declares that there is no conflict of interest in relation to the study.
References
Abbad, M. M. (2013). E-banking in Jordan. Behaviour & Information Technology, 32(7), 681-694.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Aichner, T., & Gruber, B. (2017). Managing customer touchpoints and customer satisfaction in b2b mass customization: A case study. International journal of industrial engineering and management, 8(3), 131.
Al-Hawari, M. A. (2015). How the personality of retail bank customers interferes with the relationship between service quality and loyalty. International Journal of Bank Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Al-Otaibi, S., Aljohani, N. R., Hoque, M. R., & Alotaibi, F. S. (2018). The satisfaction of Saudi customers toward mobile banking in Saudi Arabia and the United Kingdom. Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM), 26(1), 85-103.
Alsajjan, B., & Dennis, C. (2010). Internet banking acceptance model: Cross-market examination. Journal of business research, 63(9-10), 957-963.
Andaleeb, S. S., Rashid, M., & Rahman, Q. A. (2016). A model of customer-centric banking practices for corporate clients in Bangladesh. International Journal of Bank Marketing.
Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of informetrics, 11(4), 959-975.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Arora, S. D., & Chakraborty, A. (2021). Intellectual structure of consumer complaining behavior (CCB) research: A bibliomet- ric analysis. Journal of Business Research, 122, 60–74.
Arora, S., & Sandhu, S. (2018). Usage based upon reasons: the case of electronic banking services in India. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 36(4), 680-700.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Banerjee, M. (2014). Misalignment and its influence on integration quality in multichannel services. Journal of Service Research, 17(4), 460-474.
Berry, L. L., & Bendapudi, N. (2007). Moments of truth in brand management: New directions in customer loyalty. Sloan Management Review, 53(3), 89-95.
Bindroo, V., He, X., & Echambadi, R. (2016). Satisfaction—repurchase intentions relationship: Exploring the contingent roles of consideration set size and Price consciousness. Customer Needs and Solutions, 3, 115-125.
Brun, I., Durif, F., & Ricard, L. (2014). E-relationship marketing: a cognitive mapping introspection in the banking sector. European Journal of Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chebat, J. C., Davidow, M., & Codjovi, I. (2005). Silent voices: why some dissatisfied consumers fail to complain. Journal of service research, 7(4), 328-342.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chen, S. C. (2012). To use or not to use: Understanding the factors affecting continuance intention of mobile banking. International Journal of Mobile Communications, 10(5), 490-507.
Chung, N., & Kwon, S. J. (2009). The effects of customers' mobile experience and technical support on the intention to use mobile banking. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 12(5), 539-543.
Cortiñas, M., Chocarro, R., & Villanueva, M. L. (2010). Understanding multi-channel banking customers. Journal of Business Research, 63(11), 1215-1221.
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 133, 285-296.
Falk, T., Schepers, J., Hammerschmidt, M., & Bauer, H. H. (2007). Identifying cross-channel dissynergies for multichannel service providers. Journal of Service Research, 10(2), 143-160.
Gao, L., Melero-Polo, I., & Sese, F. J. (2020). Customer equity drivers, customer experience quality, and customer profitability in banking services: The moderating role of social influence. Journal of Service Research, 23(2), 174-193.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Glänzel, W., & Moed, H. F. (2002). Journal impact measures in bibliometric research. Scientometrics, 53, 171-193.
Goyal, K., & Kumar, S. (2021). Financial literacy: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 45(1), 80-105.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Haeckel, S. H., Carbone, L. P., & Berry, L. L. (2003). How to lead the customer experience. Marketing Management, 12(1), 18-18.
Harris, M., Cox, K. C., Musgrove, C. F., & Ernstberger, K. W. (2016). Consumer preferences for banking technologies by age groups. International Journal of Bank Marketing.
Harzing, A. W., & Alakangas, S. (2016). Google Scholar, Scopus and the Web of Science: a longitudinal and cross-disciplinary comparison. Scientometrics, 106, 787-804.
Holmlid, S., & Evenson, S. (2008). Bringing service design to service sciences, management and engineering. In Service science, management and engineering education for the 21st century (pp. 341-345). Springer, Boston, MA.
Hossain, T. M. T., Akter, S., Kattiyapornpong, U., & Dwivedi, Y. (2020). Reconceptualizing integration quality dynamics for omnichannel marketing. Industrial Marketing Management, 87, 225-241.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Huang, M. H., & Rust, R. T. (2018). Artificial intelligence in service. Journal of service research, 21(2), 155-172.
Kamath, P. R., Pai, Y. P., & Prabhu, N. K. (2019). Building customer loyalty in retail banking: a serial-mediation approach. International Journal of Bank Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kamran, S., & Uusitalo, O. (2019). Banks’ unfairness and the vulnerability of low-income unbanked consumers. The Service Industries Journal, 39(1), 65-85.
Khan, I., Rahman, Z., & Fatma, M. (2016). The concept of online corporate brand experience: an empirical assessment. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 34(5), 711-730.
Khan, I., Rahman, Z., & Fatma, M. (2016). The role of customer brand engagement and brand experience in online banking. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 34(7), 1025-1041.
Lemon, K. N., & Verhoef, P. C. (2016). Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. Journal of marketing, 80(6), 69-96.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lien, C. H., Hsu, M. K., Shang, J. Z., & Wang, S. W. (2021). Self-service technology adoption by air passengers: a case study of fast air travel services in Taiwan. The Service Industries Journal, 41(9-10), 671-695.
Marakarkandy, B., Yajnik, N., & Dasgupta, C. (2017). Enabling internet banking adoption: An empirical examination with an augmented technology acceptance model (TAM). Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 30(2), 263-294.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D.G. and the Prisma Group (2009), “Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement”, Annals of Internal Medicine, 151. 264-269.
Moliner, M. Á., Monferrer-Tirado, D., & Estrada-Guillén, M. (2018). Consequences of customer engagement and customer self-brand connection. Journal of Services Marketing.
Naeem, M., & Ozuem, W. (2021). The role of social media in internet banking transition during COVID-19 pandemic: Using multiple methods and sources in qualitative research. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 60, 102483.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Patricio, L., Cunha, J., Fisk, R. P., & Pastor, O. (2003, July). Essential Use Cases in the Design of Multi-channel Service Offerings—A Study of Internet Banking. In International Conference on Web Engineering (pp. 468-471). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Pieters, R., & Baumgartner, H. (2002). Who talks to whom? Intra-and interdisciplinary communication of economics journals. Journal of Economic Literature, 40(2), 483-509.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakoff, N. P., & Bachrach, D. G. (2008). Scholarly influence in the field of management: A bibliometric analysis of the determinants of university and author impact in the management literature in the past quarter century. Journal of Management, 34(4), 641-720.
Rahi, S., Mansour, M. M. O., Alghizzawi, M., & Alnaser, F. M. (2019). Integration of UTAUT model in internet banking adoption context: The mediating role of performance expectancy and effort expectancy. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rahman, Z. (2006). Customer experience management—A case study of an Indian bank. Journal of Database Marketing & Customer Strategy Management, 13(3), 203-221.
Reichheld, F. F., Markey Jr, R. G., & Hopton, C. (2000). The loyalty effect-the relationship between loyalty and profits. European business journal, 12(3), 134.
Rey-Martí, A., Ribeiro-Soriano, D., & Palacios-Marqués, D. (2016). A bibliometric analysis of social entrepreneurship. Journal of Business Research, 69(5), 1651–1655.
Rust, R. T. (2020). The future of marketing. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 37(1), 15-26.
Smith, A. B., & Johnson, M. (2017). Digital transformation in banking: Challenges, opportunities, and customer expectations. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 35(5), 738-759.
Sousa, R., & Voss, C. (2012). The impacts of e-service quality on customer behaviour in multi-channel e-services. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 23(7-8), 789-806.
Stremersch, S., Verniers, I., & Verhoef, P. C. (2007). The quest for citations: Drivers of article impact. Journal of Marketing, 71(3), 171-193.
Szymanski, D. M., & Henard, D. H. (2001). Customer satisfaction: A meta-analysis of the empirical evidence. Journal of the academy of marketing science, 29(1), 16-35.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Thusi, P., & Maduku, D. K. (2020). South African millennials’ acceptance and use of retail mobile banking apps: An integrated perspective. Computers in Human Behavior, 111, 106405.
Torres, P., & Augusto, M. (2019). Building resilience to negative information and increasing purchase intentions in a digital environment. Journal of Business Research, 101, 528-535.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., & Smart, P. (2003). Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British journal of management, 14(3), 207–222.
Tueanrat, Y., Papagiannidis, S., & Alamanos, E. (2021). Going on a journey: A review of the customer journey literature. Journal of Business Research, 125, 336-353.
Verhoef, P. C., Lemon, K. N., Parasuraman, A., Roggeveen, A., Tsiros, M., & Schlesinger, L. A. (2009). Customer experience creation: Determinants, dynamics and management strategies. Journal of retailing, 85(1), 31-41.
Verhoef, P. C., Lemon, K. N., Parasuraman, A., Roggeveen, A., Tsiros, M., Schlesinger, L. A., & McColl-Kennedy, J. (2015). Customer experience creation: Determinants, dynamics, and management strategies. Journal of Retailing, 91(1), 31-41.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Walter, U., Edvardsson, B., & Öström, Å. (2010). Drivers of customers' service experiences: a study in the restaurant industry. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 20(3), 236-258.
Wang, Bing, et al. "An overview of climate change vulnerability: a bibliometric analysis based on Web of Science database." Natural hazards 74.3 (2014): 1649-1666.
Williams, J., & Johnson, M. (2019). The impact of technology on the banking industry. Journal of Digital Banking, 3(1), 1-15.
Yuan, Y., Lai, F., & Chu, Z. (2019). Continuous usage intention of Internet banking: a commitment-trust model. Information Systems and e-Business Management, 17(1), 1-25.
Zakaria, R., Ahmi, A., Ahmad, A. H., Othman, Z., Azman, K. F., Ab Aziz, C. B., & Shafin, N. (2021). Visualising and mapping a decade of literature on honey research: a bibliometric analysis from 2011 to 2020. Journal of Apicultural Research, 60(3), 359-368.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zhou, T. (2011). An empirical examination of initial trust in mobile banking. Internet Research.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 31-Oct-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-14132; Editor assigned: 01-Nov-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-14132(PQ); Reviewed: 29-Dec- 2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-14132; Revised: 29-Mar-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-14132(R); Published: 07-Apr-2024