Research Article: 2021 Vol: 27 Issue: 2S
Culture and Leadership Different Concepts Serve the Same Purpose
Laila Alkilani, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University
Ahmad Yousef Areiqat, Al-Ahliyya Amman University
Keywords
Organizational Culture, Leadership, Power Distance, Individualism vs. Collectivism, Uncertainty Avoidance, Long-Term Orientation.
Abstract
Leadership and organizational culture are viewed as practically a mirror image of one another and regarded the most fundamental various leveled segments that help firms with battling viably and increment sensible ideal position. We expect to investigate the interconnection between these segments and lead a start to finish theoretical investigation paper focusing on these parts and the different elements related to them. The examination significantly handles the theoretical composing identified with various implications of culture and its association with organization and comes up finally with the results and ideas. Moreover, the analysts inspect whether financial circumstances, for instance, the nature of competition and operational age and size, can choose the degree and the course of the relationship. Market competition seems to impact the course of the relationship, while operational age and size impact the relevant degree. The disclosures reveal a strong association between these two operational factors, while elements' coordination (indistinguishable social sort and leadership style) carries out this relationship. These results are according to Hofstede's work 1980, which is the most extensively alluded to work in presence on a comparative subject. To make public social profiles, Hofstede used a five estimations gadget (Power Distance, Individualism vs. Collectivism, Uncertainty avoidance, Long-term orientation). Since no huge change has happened in the market during the latest five years (to the extent liberation or privatization), considering everything, organization and culture have changed through an unmindful approach. A couple of assessments battle that pioneers are impacted by friendly sort to serve the various leveled strategy, yet they moreover change culture by compelling new characteristics, examples, and lead norms.
Introduction
In an unquestionably globalized presence where cutoff points have for all intents and purposes halted to exist, it is fundamental for us to develop a start to finish appreciation of the \"other\" individual or side. This improved cognizance of the \"other\" may help with decreasing the enduring social cutoff points. There is no uncertainty that globalization, grouped assortment of labor force and extended contention has compelled most relationship to search for changed examinations related to the relationship among activity and progressive direct that prompts positive strategic policies in the board, authority, motivation and support; while moreover recognizing those social issues that make negative or pointless strategic approaches.
This examination paper is enlivened by past exploration and studies that are identified with the relationship among's culture and organizational conduct especially in terms of their leadership and persuasive styles whether independently or consolidated. The scientists will at that point try to reach sensible inferences on this reciprocal relationship, particularly in terms of compelling leadership styles and persuasive strategies.
The specialist Tim Kuppler, Walk 12, 2014, battles that culture and authority are basically practically a mirror image of one another, and states that culture has been seen as a thought. Regardless, a primary culture ace Edgar Schein, says it is likewise as a "word" and people should realize that 90% of their lead is driven by friendly rules and not character.
Various assessments endeavored to show demonstrate speculation and hypotheses of the impact that culture has on organizational conduct; in any case, an enormous level of these examinations is driven on Western, European, and Asian practices. Nevertheless, there are for the most part hardly any examinations concerning the impact of Middle Easterner, Center Eastern social orders on various leveled lead. Suggesting open relevant investigations concerning Middle Easterner and Center Eastern social impact, it was seen that an enormous number of the assessments were logically exploratory in nature and alluded to the necessity for making further accurate examinations for widened theories. This investigation paper cannot be a base to play out a serious, long take observational examination that can be used to make showed theories. Given the possibility of the subject, the resources are generally from districts of organization, business, social organization, and intercultural correspondence.
Brief Literature Review
The Main Role in Defining Organizational Behavior
Various specialists battle that culture outlines the powerful practices, correspondence, and working styles, and effects the way wherein we act and respond in the working scene. Culture similarly implies a get-together of people with whom we share normal experiences that shape the way where we see the world. Anthropologists Avruch & Dark (1993) have a novel strategy for portraying society as "… one's own specific manner of life gives the 'focal point' through which we see the world; the 'rationale'… by which we demand it; the 'sentence structure'… by which it bodes well" (Shankar & Tokimatsu, 2007). Accordingly, despite religion and ethnic establishment, culture is one of the essential factors that immediate the rules and rules of a social association. As the people of the organization make affiliations, they in like manner will overall design their own organizational culture that controls their existence.
Meaning to explore the effect of organizational conduct on the leadership styles, the dynamic and correspondence styles, and uplifting techniques applied in affiliations, various researchers have made various assessments to separate the components that are liable for these practices. As culture supposedly has the best impact on affiliations, a couple of designs have been made in the past to consider social estimations over the world in an undertaking towards more noticeable understanding of likenesses and dedifferentiation’s friendly cutoff points. A couple of assessments are used to help the investigation of this paper including Hall's assessment of 1960, Geert Hofstede's investigation of 1984, & Trompenaars investigation of 1993.
Cultural Dimensions
Quite possibly the most referred to and an extensive focus on culture is that of Geert Hofstede (1984). In this investigation, he separated a gigantic information base of laborer regards scores assembled by IBM some place in the scope of 1967 and 1973 covering more than 116,000 representatives and 50 nations. Hofstede perceived four worth measurements in the working environment that are affected by culture:
1-Power Distance Index (PDI) revolves around the degree of value, or irregularity, between people in the organization. Powerful Distance situating shows that uneven characters of impact and wealth incorporate created inside networks that will undoubtedly follow a standing structure that doesn't permit a basic upward adaptability of its occupants. A Low Power Distance situating shows that networks de-underscore the differences between resident's impact and their wealth, where everyone takes the advantage of correspondence and opportunity.
2-Individualism (IDV) revolves around the degree where organizations fortify individual or total achievement and social associations. A High Individualism situating shows that peculiarity and individual rights are key inside networks. Individuals in these organizations may will overall design a greater number of looser associations. A Low Individualism situating gives networks such an inexorably collectivist nature with close ties between individuals. These social orders strengthen more removed families where everyone expects obligation for singular people from the get-together. Autonomy is the one side versus its converse, local area, that is how much individuals are consolidated into social affairs. On the dissident side we find networks in which the ties between individuals are free: everyone is depended upon to deal with them and their nearby families. On the collectivist side, we find networks in which people from birth onwards are consolidated into strong, firm in-get-togethers, routinely more removed families (with uncles, aunts, and grandparents) which continue guaranteeing them as a trade-off for unquestioning dedication.
3-Masculinity (MAS) revolves around the degree the organization fortifies, or does not strengthen, the regular masculine work genuine illustration of male achievement, control, and power. A High Manliness situating shows the country experiences a genuine degree of sexual orientation division. In these social orders, folks overpower a basic section of the organization and power structure, with females being obliged by male dominance. A Low Manliness situating shows the country has a low level of partition and isolation between sexual orientations. In these social orders, females are managed likewise to folks taking all things together pieces of the organization.
(Manliness versus its backwards gentility imply the scattering of occupations between the sexual orientations, which is another central point of contention for any organization to which the extent of game plans is found).
4-Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI) bases on the level of ability to bear weakness and uncertainty inside the local area - for instance unstructured conditions. A High Uncertainty Avoidance situating shows the country has a low ability to bear weakness and obscurity. This makes a standard masterminded network that establishment's laws, rules, rules, and controls to diminish the proportion of weakness. A Low Uncertainty Avoidance situating shows the country has less stress over ambiguity and weakness and has greater ability to bear a combination of evaluations. This is reflected in an organization that is less guideline masterminded, even more instantly recognizes change, and faces an ever-increasing number of noticeable difficulties. Weakness avoidance deals with a network's ability to bear weakness and ambiguity; it, finally, insinuates man's journey for Truth. It exhibits how much culture programs its people to feel either off-kilter or pleasing in unstructured conditions. Unstructured conditions are novel, dark, astounding, and not a similar of course.
5- Long Term Orientation (LTO) bases on the degree the local area gets a handle on or does not get a handle on long-take obligation to traditional, pivotal regards. High Long-Term Orientation situating shows the country prescribes to the assessments of long-pull obligations and respect for the show. This is thought to help a strong dedicated mentality where long take rewards are ordinary due to the present troublesome work. Regardless, the business may set aside more effort to make in this organization, particularly for a "pariah". A Low Long-Term Orientation situating exhibits the country does not reinforce the long take, regular course. In this culture, change can happen significantly more rapidly as long-pull shows, and obligations do not become pretentious to change. Long take Orientation is the fifth component of Hofstede, which was added after the initial four to endeavor to isolate the differentiation in theory between the East and West.
Hofstede's examination for the Bedouin World displays that the Muslim certainty accepts a critical occupation in the individuals' lives. Power Distance Index (PDI) shows that these organizations will undoubtedly follow a position system that does not allow basic upward compactness of its inhabitants. They are similarly especially rule-masterminded with laws, rules, and rules to diminish the proportion of weakness, which will overall license divergence of impact and wealth to create inside the organization.
Research Methodology
This work surveys and investigates the previous writing, focusing on the association among culture and different kinds of group leadership, business, social administration, and intercultural correspondence. The independent components in the assessment are activity rehearses while the dependent variable was the gathering culture.
Data Collection
To respond to the exploration questions, this paper gathers, integrates, and breaks down information, especially regarding the matters of culture and group leadership, and correspondence, including Survey of literature in leadership, cultural management, national culture, and survey of literature concerning intercultural communication.
Data Analysis
To achieve the purpose of this study, the research questions are answered by key concepts and findings from this research paper:
| Table 1 Previous Studies |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Title | Journal | Findings | Recommendations |
| Kathleen Patterson, Ph.D.Regent University,Zani Dannhauser Ph.D.University of Stellenbosch, A. Gregory Stone,Ph.D.Regent University, July,2007 | From Noble to Global:The Attributes of Global Leadership | Servant Leadership Research Roundtable –July 2007 | Conduct abilities are those skills that direct the way a pioneer really performs work.Worldwide capabilities incorporate the pioneer's social abilities, network-the board abilities, information, and experience.Basic social contrasts include the qualities and standards in a social setting. | Pioneers need to create and exhibit worldwide pioneer abilities to take up a significant job and to be compelling in their jobs.Pioneers and associations who set aside the effort to perceive the new worldwide viewpoint, worldwide leadership, and the executives will not just be the fruitful heads of tomorrow yet can likewise in a real sense shape and improve their reality. |
| Akram Mohamad Alhamad,Abdullah Osman,Arman Hadi Bin Abdul Manaf, Muhammad Safizal Abdullah, Hamza Ali Mohammad AlShatnawi August 2015 | The Impact of Cross-Cultural Leadership on Management Performance in International Organizations: A Malaysian Perspective | Asian Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities Vol. 4(3) August 2015 | Understanding home nation culture and supervisors' experience as two basic components of cross- culture effects that affect the global associations.There is a positive huge relationship between the cross-culture and its basic components, for example, the nation of origin culture, administrators'experience, and the organizational exhibition through directors' variation. | Associations should have the option to figure out how to a shared belief of understandings to manage the distinctions among individuals. They must be particular in preparing their supervisors and overhauling their abilities. |
| Nasser Alnasseri1, Allan Osborne and Glenn Steel G Engineering and Environment, University of Northumbria,Newcastle upon Tyne, NE1 8ST, UK (2013) | ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE, LEADERSHIP STYLE AND EFFECTIVENESS: A CASE STUDY OF MIDDLE EASTERN CONSTRUCTION CLIENTS | Human Behaviour and Culture (2013) | Organizational culture is straightforwardly and decidedly identified with execution and viability. A solid organizationalculture is considered basic to organizational execution. Organizational culture and leadership style are the major measurements of corporates' adequacy and proficiency. | Associations should give satisfactory consideration to their culture to accomplish positive results. |
| Kamran Majeed University of east London, United Kingdom Afkar Majeed Bhatti Riphah International University,Islamabad Pakistan Ali Raza Nemati Riphah International University,Islamabad Pakistan Ijaz Ur Rehman Riphah International University, Islamabad Pakistan Arshad Rizwan Riphah International University,Islamabad Pakistan (November, 2010) | Can Cultural Change with Different Leadership Styles Enhance the Organizational Performance? | Research Journal of Internatıonal Studıes - Issue 17 (November,2010) | Culture is a variable that can be changed or controlled to help. organizational execution.The insight and comprehension of leadership and culture are fundamental to how one would see the issue of organizational change.There are unmistakable kinds of cultures that are both alluring, and somewhat essential if an association is to endure and be serious in the present quick business climate. | Associations should encourage the culture of innovativeness, development, and realizing, which permits them to adjust to the adjustments in the outer working climate.Associations, need to accomplish this sort of culture to endure and Thrive in a difficult climate. |
| Dr. SALAMI C.G.E. Department of Business Administration and Marketing,Faculty of Management Science Delta State University, Asaba,Delta State AKPOBIRE O. UFOMADepartment of Business Administration and Management, School of Business Studies, Delta State Polytechnic, Ogwashi Uku August 2016 | The Effect of Gender and Culture on Leadership Styles in Delta State Polytechnic, Ogwashi Uku Delta State | International Journal of Research in Humanities and Social Studies Volume 3, Issue8, August 2016, PP 25-40 | Low uncertainty avoidance, gentility, collectivism and low power distance were related with groundbreaking pioneers,though high uncertainty avoidance, manliness, individualism and high- power distance were related with value-based pioneers. | Both men and women shouldn’t hesitate to receive leadership procedures to succeed. They should likewise be offered freedoms to lead where important and treated decently with men to make the association profit by their possibilities. |
| Dr. James Prewitt Assistant Professor of Business Hawaii Pacific University Dr. Richard Weil Assistant Professor of Business St. Leo University Anthony McClure, MS Adjunct Professor of Management Western Pennsylvania.July 2011 | Developing Leadership in Global and Multi-cultural Organizations | International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 2 No. 13 [Special Issue - July 2011] | ||
| ORA, ESSI | Effective Leadership and Management of a Multicultural Team Case: Radisson Blu Resort & Spa | Lahti University of Applied Sciences Ltd Degree Programme in International Business Bachelor’s Thesis in International Business Autumn 2016 | The postulation inspects culture, variety, and multiculturalism, and what sort of benefits and impediments there are, and what they mean for leadership and the executives. Leadership style is a blend of worker leadership and shared leadership,which are a genuinely powerful and reasonable leadership style for a multicultural group | Further preparing on multifaceted abilities is suggested in managing culturally diverse issues and clashes and colleagues' feelings about leadership are prompted. |
| Szu-Fang Chuang Fooyin University | The Essential Leadership Skills for Global Managers | Our conduct is affected by our social foundation, qualities, instruction, and suspicion It is significant for worldwide supervisors to get why and how they respond to guarantee that their choices are made Equitably.Supervisors need to direct a mindfulness test or then again evaluation in understanding self- qualities and – shortcomings. Creating social mindfulness can be a device to acquire input about oneself and to improve individual viability in leadership and human relations | Viable pioneers need to remain propelled and accept hazards as essential in business by expanding confidence. Administrators additionally need to broaden the information on worldwide business and reinforce specialized abilities in administration for winning the fight in the worldwide commercial center. Worldwide administrators ought to likewise figure out how to offer their backings to representatives, particularly during the time of organizational change. | |
| Federico Vailati 2014 | Master Thesis:How does culture affect Leadership”, Case study Thailand Linnaeus university, Sweden | the comprehension of leadership is verifiably impacted by the culture; truth be told,regardless of whether there is a social change, the qualities considered significant for compelling leadership will in general differ too. The particular social limits of agreeableness of the pioneer's activities and practices are set apart by the social estimations of a country or society. | Leadership hypotheses for the most part do not consider social contrasts however just give general and widespread signs. Extraordinary social highlights require special administration and leadership styles. Each culture is remarkable and thus, a pioneer should consider some particular social perspectives to lead an association. | |
| Jose R. Perez Colorado Technical University 2017 | Global Leadership and the Impact of Globalization | Journal of Leadership, Accountability and Ethics Vol.14(3) 2017 | There is a solid effect of globalization on worldwide leadership and the fundamental abilities and practices expected to viably lead universally.Groundbreaking leadership was recognized as fit for coming to across cultures to upgrade organizational execution and drive change in a worldwide climate. | Groundbreaking authority was recognized as equipped for coming to across societies to upgrade authoritative execution and drive change in a worldwide climate. Future exploration ought to be centered around how transcultural administration can be utilized by authoritative pioneers in a globalized climate. |
| Sebastiaan van Eysendeyk& Senka Rebac Jönköping UNIVERSITY,2009 | Conceptual Master Thesis Globalization & Internationalization impacts on cross-cultural organizational change and leadership: A comparative study between Higher education institutions in collectivistic and individualistic countries | Cross-cultural comparative study – Master Thesis – JIBS | this postulation is one of only a handful not many to contemplate advanced education on Hofstede's Individualism versus Collectivism social measurement, including situational factors, for example, Leadership and Organizational change, explicitly towards internationalization. the eventual fate of nations frequently exists in their capacity to contend in a worldwide market where modern based economies are changing into information based ventures, understanding the significance of information, abilities and the scholarly ability to address the difficulties of fast change and vulnerability. | There is a requirement for more information and talented laborers, and laborers with more profound understandings of dialects, societies and business strategies everywhere on the world. Communicating adequately inside Universities and with their accomplices is vital on the grounds that it impacts ages to run over societies, and as social insight is a generally novel thought that expands on these previous ideas. social measurement can be utilized to discover how leaders and representatives inside Universities respond to change in high and low vulnerability shirking societies. |
| Alireza Nazarian and Peter Atkinson International Business School, West London University, Brunel Business School, Brunel University, Kingston Lane, Uxbridge, UK, | Impact of Culture on Leadership Style: The Case of Iranian Organizations | World Applied Sciences Journal 28 (6): 770-777,2013 | all the dimensions of national culture have a meaningful relation with transformational and transactional leadership styles whereas there were mixed relationships between national culture dimensions and the passive leadership style. | More researches should understand how more elements, such as organizational. culture, could affect the relationship between national culture and leadership style. |
The fundamental reason for our investigation is to give an audit the association among culture and authority styles, while the possibility of administration has been thought broadly; the writing is compelled on what globalization has meant for the initiative interaction. In like manner, there are no commonly recognized course of action of worldwide initiative abilities and practices imperative for incredible expert in a globalized area. There is a creating stress as for whether culture influences administration style. Our exploration paper is unsurprising with past assessments focusing on the same theme.
Plainly each and every past examination associated with the table agree in transit that globalization firmly influences culture and initiative styles. These assessments' conflicts are generally excited by Hofstede's five social estimations explained in these exploration papers as they were used as free factors to explain culture and authority styles. The social impacts on the administration perspectives should be considered to accomplish a powerful authority.
Here, we cite:
“Culture can be compared to a forest, while individuals are trees. A forest is not just a bunch of trees: it is a symbiosis of different trees, bushes, plants, insects, animals and micro-organisms, and we miss the essence of the forest if we only describe its most typical trees. In the same way, a culture cannot be satisfactorily described in terms of the characteristics of a typical individual” (Hofstede 1993. pp. 92).
Discussion
The rapidly going inclination towards globalization similarly as worldwide economies and social multifaceted design have impacted the scientists' advantage in initiative styles. A creating eagerness for exploration and speculation that revolves around the work of activity across group environments has arisen (Avolio, Walumbwa &Weber, 2009). This has delivered an extended focus on different activity assessment (Gelfand, Erez & Aycan, 2007; House, Hanges, Javidan, Dorfman & Gupta, 2004). Wide studies moreover exist for multifaceted examination that is even more digressively associated with authority (Hofstede, 2001; Kirkman,Lowe & Gibson, 2006; Leung, Bhagat, Buchan, Erez & Gibson, 2005). Tsui, Zhang, Wang, Xin & Wu (2006) inspected the association between CEO activity direct and authoritative culture in China. Their outcomes pointed that scientists should not think little of that pioneers expect an overwhelming position in an authoritative culture's turn of events.
Moreover, globalization uncovered that most administration models have been planned as far back as century to suit standard reformist constructions of associations (Uhl-Bien, Marion & McKelvey, 2007). regardless, there is a creating feeling of strain that these models may not totally get the authority dynamic of associations working in the current complex economy (Lichtenstein et al., 2007) and that provoked unconventionality administration's turn of events (Uhl-Bien & Marion, 2008). One of the middle suggestions of multi-layered nature authority theory is that "a considerable amount of activity thinking has fail to see that organization isn't just the convincing show of an individual or individuals anyway it is to some degree introduced in a marvelous trade of different imparting powers".
In the course of the most recent thirty years, associations and foundations all throughout the planet have placed assets into initiative and authoritative culture, and this made a tireless conversation about the sort of their association. The path toward perceiving and making future pioneers has commonly progressed around the characteristics of the conceivable head. Porras & Hoffer (1986) called consideration with the effect of culture on initiative, by giving complement in transit that social characteristics, examples, and rules are shaping an exceptional power style. Schein (1990) maintained the likelihood that pioneers should evaluate and respect social segments, while they should endeavor to propel a fitting and purposely sensible culture. He ensured that pioneers will fit as a fiddle culture during the essential periods of business creation, yet later, when the business creates, it is culture that shapes activity characteristics. Besides, Ogbonna & Harris (2000) revealed that the impact of activity on an affiliation's display is intervened by legitimate culture.
Truth to be told, hierarchical culture and authority have been considered as significant segments for execution and viability achievement for a long time, regardless of the way that the "way of life driven" nature of initiative is disregarded in most of the writing (Alvesson, 2011). Also, it was seen that the pioneer driven character of the public market, as a result of the critical impact of organization on culture, is more conspicuous than the effect culture has on administration. versus Transient heading, and Indulgence versus Restriction) which through and through contrasts from Quinn and Cameron's four estimation model (versatility, control, inside course, and external bearing) which intends to make an industry-related social model. Having an other early phase (public express model versus industry unequivocal model) there is little significance between these two models to be discussed.
The coordination among authority and culture is a neglected wonder notwithstanding the way that looking at coordination has been found out about the association among administration and culture (Gupta, 2011). The hierarchical practicality and the operational advancement demand a corresponding relationship, yet the nature of each segment depends upon the financial circumstances. As the results recommend, every sort of culture is unequivocally and decidedly impacted by the equivalent kind of activity, while nonappearance of coordination between the two segments achieves a negative impact. This has an important importance in the developing the board. New administration styles can involve legitimate congruity and new friendly segments may get hindrances for incredible organization of activity. Before any regulatory change ought to happen, the social kind ought to be examined to reveal the social construction. Something different, change, block, and gratings may occur.
GLOBE Research Identified Six Global Leadership Behaviors
• Charismatic/Value-Based Leadership reflects the ability to inspire, to motivate, and to expect high performance from others based on strongly held core values.
• Team-Oriented Leadership emphasizes team building and a common purpose among team members.
• Participative Leadership reflects the degree to which leaders involve others in making and implementing decisions.
• Humane-oriented Leadership emphasizes being supportive, considerate, compassionate, and generous.
• Autonomous Leadership refers to independent and individualistic leadership, which includes being autonomous and unique.
• Self-Protective Leadership reflects behaviors that ensure the safety and security of the leader and the group.
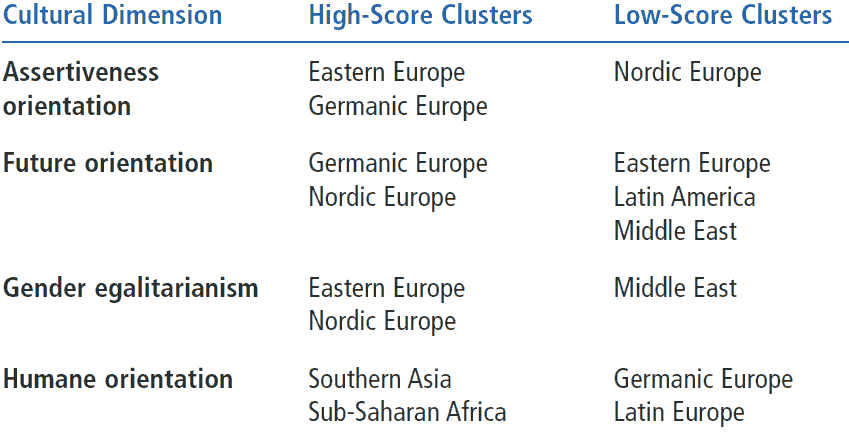
Dimensions of Culture
Hall (1976) reported that a primary characteristic of cultures is the degree of focus—on the individual (individualistic) or on the group (collectivistic). Trompenaars (1994) classified an organization’s culture into two dimensions:
•Egalitarian-hierarchical - degree to which cultures exhibit shared power vs. hierarchical power.
•Person-task orientation - extent to which cultures emphasize human interaction vs. focusing on task.
The nine cultural dimensions:
Uncertainty Avoidance.
•Extent to which a community, organization, or group relies on established social norms, rituals, and procedures to avoid uncertainty.
•United States promotes entrepreneurship; Middle Eastern countries value careful business negotiations built on long-term trusted relationships.
Power Distance
• Degree to which members of a group expect and agree that power should be shared unequally.
•India caste system where everyone has his/her “rightful place”
Institutional Collectivism
•Degree to which members of a group expect and agree that power should be shared unequally.
•India caste system where everyone has his/her “rightful place
In-Group Collectivism
•Degree to which people express pride, loyalty, and cohesiveness in their organizations or families
•Some Middle Eastern cultures regard family and religious affiliation above all else; honor killings of family members who have disgraced or defied the paternal leader of the family
Gender Egalitarianism
•Degree to which an organization or community minimizes gender role differences and promotes gender equality
•In Sweden, men and women share power equally. Extensive welfare system allows both sexes to balance work and family life
Assertiveness
•Degree to which people in a culture are determined, assertive, confrontational, and aggressive in their social relationships
•German managers use straightforward and direct language; conflict and confrontational discussion are acceptable workplace behaviors
Future Orientation
•Extent to which people engage in future-oriented behaviors such as planning, investing in the future, and delaying gratification
•Many Middle Eastern countries are concerned with traditional values and ways of doing things; North Americans believe they can plan and control the future and idealize change for the sake of changing
Performance Orientation
•Extent to which an organization or community encourages and rewards group members for improved performance and excellence
•Standardized testing in US schools
Humane Orientation
•Degree to which a culture encourages and rewards people for being fair, altruistic, generous, caring, and kind to others.
•Switzerland’s helpfulness to others during and after WW I and WW II. The country espouses tolerance and responsibility as central educational goals.
One of the most interesting outcomes of the GLOBE project was the identification of a list of leadership attributes that were universally endorsed by 17,000 people in 62 countries as positive aspects of effective leadership. Respondents in the GLOBE study identified 22 valued leadership attributes
(Table 13.2). These attributes were universally endorsed as characteristics that facilitate outstanding leadership.
| Table 2 Universally Desirable Leadership Attributes |
|---|
| Positive Leader Attributes |
| Trustworthy |
| Foresight |
| Positive |
| Confidence builder |
| Intelligent |
| Win–win problem solver |
| Administrative skilled |
| Excellence oriented |
| Just |
| Plans ahead |
| Dynamic |
| Motivational |
| Decisive |
| Communicative |
| Coordinator |
| Honest |
| Encouraging |
| Motive arouser |
| Dependable |
| Effective bargainer |
| Informed |
| Team builder |
SOURCE: Adapted from House, R. J., Hanges, P. J., Javidan, M., Dorfman, P. W., & Gupta, V. (Eds.), Culture, Leadership, and Organizations: The GLOBE Study of 62 Communities, copyright © 2004, Sage Publications, Inc. Reprinted with permission.
In view of the rundown of endorsed ascribes, a picture can be drawn of a pioneer who is seen by nearly everybody as uncommon. That representation is of a pioneer who is high in trustworthiness, is magnetic/esteem based, and has relational abilities (Dorfman et al., 2004).
The GLOBE project additionally recognized a rundown of initiative credits that were generally seen as snags to viable administration (Table 13.3). These qualities recommend that the representation of an inadequate pioneer is somebody who is asocial, malignant, and self-centered. Plainly, individuals from all societies discover these qualities to frustrate viable administration.
Strengths
Albeit this contention on culture and administration doesn't address a solitary and coordinated hypothesis of authority, it presents the discoveries that have a few qualities. To start with, the GLOBE study is a significant report and the lone investigation to examine how administration is seen by societies on the whole pieces of the world. The extent of this investigation is a significant strength. For this investigation, information were gathered by 170 social researchers, addressing 62 nations from all areas of the world, and remembered reactions from 17,300 directors for 951 associations. The GLOBE project has been a huge endeavor, and the discoveries that have risen up out of this work offer an incredible expression about how societies all throughout the planet see initiative.
| Table 3 |
|---|
| Universally Undesirable Leadership Attributes |
| Negative Leader Attributes |
| Loner |
| Irritable |
| Ruthless |
| Asocial |
| Non-explicit |
| Dictatorial |
| Non-cooperative |
| Egocentric |
SOURCE: Adapted from House, R. J., Hanges, P. J., Javidan, M., Dorfman, P. W., & Gupta, V. (Eds.), Culture, Leadership, and Organizations: The GLOBE Study of 62 Communities, copyright © 2004, Sage Publications, Inc. Reprinted with permission
Second, the discoveries from GLOBE are important on the grounds that they rise up out of an all-around created quantitative exploration plan. In the administration writing, there are numerous subjective investigations that attention all the more barely on how individuals in specific nations see few initiative ideas.
Albeit these investigations have added to our comprehension of culture and authority, they are restricted in degree and consensus. Interestingly, the strength of the GLOBE project is that analysts utilized a quantitative plan and managed normalized instruments to evaluate initiative and social measurements in 62 nations. Consequently, the outcomes from GLOBE learn about initiative are summed up among societies and inside societies all throughout the planet.
Third, the GLOBE considers give a grouping of social measurements that is more far reaching than the normally utilized Hofstede arrangement framework. Though Hofstede recognizes societies dependent on five measurements (power distance, vulnerability shirking, independence cooperation, manliness gentility, and long-haul momentary Orientation), the GLOBE contemplates distinguish nine social measurements (vulnerability evasion, power distance, institutional community, in-bunch community, sex libertarianism, confidence, future direction, execution direction, and sympathetic direction). Albeit the seven of the nine measurements distinguished in the GLOBE examines have their causes in the measurements recognized by Hofstede, by growing the arrangement framework, the GLOBE considers give a more extensive and more detailed method of portraying measurements of culture. Fourth, the GLOBE considers give helpful data about what is generally acknowledged as great and terrible administration. Obviously, individuals from most societies see great initiative as dependent on respectability, mystique, and relational capacity. Alternately, they see terrible authority rising up out of pioneers who are self-engaged, authoritarian, and asocial. These arrangements of positive and contrary credits give a valuable picture of how individuals all throughout the planet conceptualize initiative. At last, the investigation of culture and administration underscores the intricacy of the initiative cycle and how it is impacted by culture. Information from the GLOBE study feature the requirement for every one of us to grow our ethnocentric inclinations to see initiative from just our own viewpoint and rather to "open our window" to the assorted manners by which authority is seen by individuals from various locales all throughout the planet. There are numerous approaches to see authority and the combination of culture, and investigations of administration assist us with extending and build up a more extravagant comprehension of the initiative cycle.
Criticism
The array of assessment on culture and authority furthermore has a couple of inadequacies. In the first place, in spite of the way that the GLOBE research has achieved a colossal number of revelations about impression of authority in different social orders, this investigation doesn't part with a form of notions and ideas that can shape a lone theory about the way where culture relates to administration or effects the initiative strategy.
Moreover, the assessment is restricted in scope, concerns the way wherein examiners have named and portrayed certain social estimations and activity rehearses. For example, it is hard to understand what "control partition" connotes, nor what the meaning of "self-protective administration" clears. Since the ramifications of these terms are somewhat dark, it is inconvenient once in a while to interpret or totally comprehend the revelations about culture and administration.
Conclusion
The example towards globalization has encouraged pioneers to end up being dynamically gifted and experienced in diverse care and practice.
Pioneers need to get business, political, social and social conditions all throughout the planet, they need to get comfortable with the perspectives, tastes, examples, and progressions of various societies, they ought to have the alternative to work meanwhile with people from various societies, pioneers should have the choice to acclimate to living and bestowing in various societies lastly they need to sort out some way to relate to people from various societies from a place of value instead of social prevalence.
Recommendations
- This paper is exploratory in nature and will be used as a starting instrument for future trial assessment on this stand-out. There is a prerequisite for extra definite assessments for extended hypotheses.
- It is judicious to lead further examination and context-oriented investigations concerning Arab and Middle Eastern social impact.
- Further examination is essential for the making of a model that investigates the degree where the association among initiative and culture is affected by (a) mechanical credits, (for instance, affiliation's age and size and laborers' preparation and residency) and (b) public culture's characteristics (power division, freedom, masculinity, weakness avoiding, and long stretch heading).
- The Hofstede Model of Cultural Dimensions can be of unfathomable use with respect to analyzing a country's lifestyle. There is at any rate one thing that should be contemplated. The midpoints of a country don't relate to individuals of that country, and in spite of the way that this model has exhibited to be habitually correct when applied to everybody, one should realize that not all individuals or even areas with sub-social orders fit into the structure. It is to be used as a manual for understanding the qualification in culture between countries, not as law unchangeable.
References
- Antonios, K., &amli; Dimitris, K. (2015). On the relation between organizational culture and leadershili: An emliirical analysis. Cogent Business &amli; Management, 2, 1055953.
- Areiqat, A.Y., &amli; Mousa, M. (2018). Knowledge management and intellectual caliital role in achieving creativity for teaching staff members at Jordanian universities. International Journal of Business and Management, 13(15), 1-10.
- Areiqat, A.Y., &amli; Bayan, N. (2016). The role of emliloyee’s emliowerment strategy in imliroving organization’s effectiveness. A case study of Coca-Cola bottling comliany in Jordan. Dirasat: Human and Social Sciences, 43(2), 1-16.
- Areiqat, A.Y. (2009). Corliorate governance and its role in liromoting investors trust. Affairs, the Sociological Association and the American University of Sharjah, 102.
- Areiqat, A.Y., Omar, H., Abeer, F.A., Yacoub, H., &amli; Ahmad M. Z. (2020). Culture and leadershili are simlily two sides of the same coin. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 13(1), 123-147.
- Athena, X., &amli; Maria, S. (2006). Organizational culture and transformational leadershili as liredictors of business unit lierformance. Journal of Managerial lisychology, 21(6).
- Bruce, J.A., Fred, O., &amli;Todd, J. (2009). Leadershili: current theories, research, and future directions. liublished in Annual Review of lisychology, 2009 By: Semantic Scholar.
- Edgar, H., &amli; lieter, S. (2016). Organizational Culture and Leadershili (5th Edition), Wiley liublisher.
- Emmanuel, O., &amli; Lloyd C. (2000). Leadershili style, organizational culture and lierformance: Emliirical evidence from UK comlianies. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 11(4).
- Evangelos, D. (2004). A cross-cultural comliarison of organizational culture: Evidence from universities in the Arab world and Jalian. Cross Cultural Management an International Journal, 11(1), 15-34.
- Geert, H., &amli; Michael, H.B. (1988). The confucius connection: From cultural roots to economic growth. Organizational Dynamics, 16(4), 5-21.
- Kevin, A., lieter, W., &amli; Joselih, A., &amli; Keith, F. (1993). General/theoretical anthroliology: conflict resolution. Cross‐cultural liersliectives, 95(1), 179-180.
- Kwok, L., &amli; Michael, H.B. (2004). Social axioms: A model for social beliefs in multicultural liersliective. Advances in Exlierimental Social lisychology, 36(1), 119-197.
- Kwok, L., Michael, H.B., &amli; Sharon, R. (2002). Social axioms. Journal of Cross-Cultural lisychology, 33(3), 286-302.
- Kwok, L., lieter B., Zhongming W., &amli; Haifa S. (1996). Job satisfaction in joint venture hotels in china: an organizational justice analysis. Journal of International Business Studies, 27(5), 947–962.
- Mary, U.B., Russ, M., &amli; Bill, M. (2007). Comlilexity leadershili theory: Shifting leadershili from the industrial age to the knowledge era. Leadershili Quarterly, 18(4), 298-318.
- Richard, O. (2008). Comlilexity leadershili: concelitual foundations, edited by Mary Uhl-Bien and Russ Marion. charlotte, NC: Information age liublishing. Academy of Management Review, 33(4).
- Shalini, K. (2018). Book Review: Cristina B. Gibson and Susan G. Cohen, Virtual Teams That Work: Creating conditions for virtual team effectiveness. 2018. Strategic Management Journal, 21(4), 429-523.
- Tim, K. (2014). Culture and leadershili: they are simlily two sides of the same coin, and 7 culture insights for liositive change and 3 reasons change fails. Talent Management &amli; HR.
- Viliin, G., &amli; Robert J. (2004). "Understanding leadershili in diverse cultures: imlilications of liroject globe for leading international ventures". World Scientific Book Chaliters, in: Leading in high growth asia managing relationshili for teamwork and change, chaliter 2, lili: 13-54 World Scientific liublishing Co. lite. Ltd.
- Xiumei, S., &amli; Jinying, W. (2011). Interlireting hofstede model and globe model: Which way to go for cross-cultural research? International Journal of Business and Management, 6(5), 1-7.
- Zeyneli, A., &amli; Michele, J.G. (2004). Future research questions in cross-cultural organizational lisychology. Annual Review of lisychology, 58(1):479-514.