Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 3
Corporate Governance and Earnings Quality: An Empirical in Indonesia
Aan Marlinah, Trisakti School of Management, Jakarta, Indonesia
Yulius Kurnia Susanto, Trisakti School of Management, Jakarta, Indonesia
Peggy Theodora, Trisakti School of Management, Jakarta, Indonesia
Citation Information: Marlinah, A., Susanto, Y.K., & Theodora, P. (2022). Corporate governance and earnings quality: an empirical in Indonesia. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 26(3), 1-08.
Abstract
Earnings quality is a media used by companies to communicate with external parties. Earnings quality increases if earning in the financial statement provide accurate information from company earnings accurately in company transactions and activities. The purpose of this research is to obtain empirical evidence and analyze the effect of corporate governance on earnings quality in manufacturing firms. The corporate governance are independent commissioners, audit committee, concentrated ownership, and external auditors. The period of this research is 2016 to 2018 and the sample required is a sample of manufacturing firms that are consistently listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX) from 2013 to 2019. The research sample is obtained using purposive sampling method. This research is using multiple regression methods. This study measures the earnings quality using accrual quality. The results of this research indicate that earnings quality is affected by independent commissioners and audit committee. But earnings quality is not affected by concentrated ownership and external auditors. The involvement of the audit committee in the company as part of corporate governance and fulfills the wishes of principal to oversee the management.
Keywords
Earnings Quality, Accrual Quality, Corporate Governance, Independent Commissioners, Audit Committee.
Introduction
The development of information technology in Indonesia makes it easy for parties who need information related to a company's financial statements to obtain it. The purpose of the financial statements is to present information about the financial position, company performance and changes in the composition of the financial statements that will be used as a decision-making tool. One of the information that becomes an important indicator in making decisions on financial statements is profit. Users of financial statements will perform calculations and estimate future earnings based on current earnings. The users of the report in question are company owners, company management, investors, and creditors. This encourages companies to present good financial reports in the midst of very tight competition between companies in one industry.
Earnings quality is an important part of the financial statements as contained in the income earned by the company. Earnings quality can be regarded as earnings information that can react to the market. There are two principles in the analysis that characterize the quality of the numbers presented in earnings, namely relevance and reliability (Egbunike & Odum, 2018). Companies that report an increase or decrease in earnings in large numbers and in an irrational way result in the information presented not showing the real situation and reducing the earnings quality, so that it can mislead users of financial statements in making decisions (Susanto et al., 2021).
The phenomenon in Indonesia that related to the presentation of earnings occurs in several companies, one of which is PT Garuda Indonesia. Based on Okefinance's 2019 online article, PT Garuda Indonesia included earnings from PT Mahata Aero Technology which has debts to PT Garuda Indonesia, resulting in a rapid increase in earnings in PT Garuda Indonesia's 2018 financial statements which were audited by KAP Tanubrata Sutanto Fahmi Bambang & Partners (Member of BDO International). The report caused debate because two commissioners of PT Garuda Indonesia, Chairal Tanjung and Dony Oskaria (currently no longer in office), considered PT Garuda Indonesia's 2018 financial statements to be inconsistent with Financial Accounting Standards. The collaboration between PT Garuda Indonesia and PT Mahata Aero Teknologi is a collaboration in providing on-board WiFi services that can be enjoyed free of charge. PT Mahata Aero Teknologi is a company that was only established at the end of 2017 with a capital of not more than Rp. 10 billion and signed a cooperation agreement by recording a debt of US$239 million to PT Garuda Indonesia, which was eventually recorded as revenue by PT Garuda Indonesia even though it had not been paid by PT. Mahata Aero Technology. Base of the gap between phenomena and agency theory, the problem statement is to provide empirical evidence about corporate governance on earnings quality in manufacturing firms. The corporate governance are board independence, audit committees, concentrated ownership, and external auditors.
Agency Theory
Agency theory is a theory that reveals the relationship between the principal, namely the investor and the agent, namely the manager, in the form of a cooperation contract (Jensen & Meckling, 1979). Agent is a party entrusted by the principal to manage the company in which the principal invests. The agent can make a decision on events that occur in the company because the decisions taken by the agent represent the decisions of the principal. In addition, the agent is a party directly involved in the company's activities, therefore the agent has more information and is considered capable of making the right decisions for the sustainability of the company. The principal is a party who is not directly involved in the company's activities and it is assumed that the principal only has an interest in the increasing financial results of the company.
This relationship in agency theory can lead to asymmetric information. Asymmetric information is an information gap between principals who are given some or more information and principals who are less informed or not informed, this is because there are principals who know internal information that is not published. Thus, asymmetric information can cause a conflict of interest between the agent and the principal, because managers as agents are not encouraged to provide appropriate and informative disclosures (Chowdhury et al., 2018). This information gap can be used by agents to prioritize personal interests. Management who manipulates financial statements with the aim of achieving certain profit targets to obtain more rewards from the company will harm the principal and reduce the quality of earnings generated by the company (Sarawana & Destriana, 2015). When the agent tends to put his personal interests first by taking actions that are detrimental to the principal, then the manager's actions will cause agency problems.
Earnings Quality
Earnings quality is one of the most important characteristics in the financial reporting system (Mojtahedi, 2013). One of the benefits of financial statements is the means used for decision making. An important part of the financial statements that are used as the basis for making decisions is information related to the profits generated by the company. Earnings quality is able to represent the quality of financial accounting information within the company, so the higher the earnings quality, the higher the quality of financial accounting information owned by the company. The high quality of earnings is said to be able to attract the attention of investors and other users of financial statements.
Independent Commissioners
Al-Rassas & Kamardin (2015a) stated that an independent commissioner is the basic reason behind the board's supervisory mechanism which is directed to monitor the actions of management. Supervision carried out by independent commissioners is considered to be able to reduce agency problems, namely management that prioritizes personal interests. Management in general will do various things based on their own thinking, which can have an impact on decreasing the quality of earnings. It is necessary to carry out supervision by an independent commissioner to mitigate the decline in the quality of financial reporting based on the work of management. This is because the independent commissioner does not have a personal interest or interest in the company's finances where the independent commissioner carries out the assignment, so that the supervision carried out prioritizes an attitude of independence as it should be
Alves (2014), Al-Rassas & Kamardin (2015a), Kent et al. (2016), and Khafid & Arief (2017) say that there is a positive influence between independent commissioners on earnings quality. These results are consistent with Arniati et al. (2019). According to Al-Dhamari and Ku Ismail (2014) and Egbunike and Odum (2018), there is a negative effect of independent commissioners on earnings quality. In contrast to Iannielo (2013), Khan (2017), Adegbie et al. (2019), and Susanto, Pirzada, & Adrianne (2019) which argues that there is no effect between independent commissioners and earnings quality. Base on the research gap above, the hypothesis is:
H1: Independent commissioners has influence to earnings quality.
Audit Committee
The involvement of the audit committee in carrying out its duties serves to add value to the supervision. The audit committee is able to provide quality information in the financial statements where the information is given impartially to certain interests. In addition, a large number of audit committees have various experiences and expertise that are able to contribute to increasing effectiveness in management monitoring so as to direct companies to produce high earnings quality (Al-Rassas & Kamardin, 2015b). Al-Rassas & Kamardin (2015b), Kent et al. (2016) the audit committee has a positive effect on earnings quality. This is consistent with (SeTin & Murwaningsari, 2017; Sae-lim & Jermsittiparsert, 2019). Zhang & Huang (2017) state that there is a negative effect of the audit committee on earnings quality. The results are different from Piyawiboon (2015), Khafid & Arief (2017), and Adegbie et al. (2019) which argues that the audit committee does not affect earnings quality. Base on the research gap above, the hypothesis is:
H2: Audit committee has influence to earnings quality.
Concentrated Ownership
A concentrated ownership structure can be an internal mechanism that disciplines management actions to increase the effectiveness of supervision, because with a large number of ownership, significant information can be obtained by shareholders to balance the information contained in management. If this is done by shareholders, then moral hazard management actions can reduce actions in the form of earnings management so as to improve earnings quality. Kent et al. (2016), Sousa & Galdi (2016), Tambun et al. (2017), revealed that there is a positive influence between concentrated ownership on earnings quality. Al-Rassas & Kamardin (2015a) revealed that there is a negative relationship between concentrated ownership and earnings quality. According to Sarawana & Destriana (2015) there is no relationship between concentrated ownership and earnings quality. Base on the research gap above, the hypothesis is:
H3: Concentrated ownership has influence to earnings quality.
External Auditor
Audit is the process of collecting and evaluating evidence to ensure that the financial statements produced by the company are protected from information asymmetric between management and shareholders. External auditors carry out audits and provide opinions on financial statements produced by the company to provide information for parties using financial statements (Piyawiboon, 2015). By carrying out his assignment, the auditor is expected to be able to evaluate the evidence obtained, assess the earnings quality by minimizing earnings management activities, so as to increase public confidence in the audited financial statements (Susanto et al., 2021). Sumiadji et al. (2019), Al-Rassas & Kamardin (2015b), Piyawiboon (2015), Slaheddine (2015), and Kent et al. (2016) revealed that there is a positive influence between external auditors and earnings quality. Contrary to Afifa et al. (2020), Susanto et al. (2019), and Susanto et al. (2019) which says that there is no influence between external auditors on earnings quality. Base on the research gap above, the hypothesis is:
H4: External auditor has infleunce to earnings quality.
Methods
The sample used as the object of research in this study are manufacturing companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX) and the period used is 2016 to 2018, but for the needs of this study, the sample data consists of manufacturing companies listed on IDX in 2013 to 2019. In this study, the sample to be selected using purposive sampling which can be seen in the following table 1:
| Tabel 1 Sampling Result |
||
|---|---|---|
| Criteria | Firm | Data |
| Manufacturing firms listing at IDX from 2013 until 2019 | 124 | 372 |
| Manufacturing firms do not reporting in Desember 31th | (5) | (15) |
| Manufacturing firms do not reporting in Indonesia Rupiah | (26) | (78) |
| Manufacturing firms do not have anual report | (3) | (9) |
| Total | 90 | 270 |
Earnings quality is an important driving component in improving the performance and reputation of a company (Huynh, 2018). Earnings quality in the study was measured using the model developed by McNichols (2002) and was used by Kent et al. (2016) to estimate Accruals quality with the following equation:
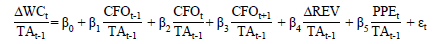
Where:
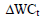 = Comprehensive measure of change working capital accrual (WCA) including changes in receivables, payables, current inventory, current investments, current provisions, current assets, and other current liabilities.
= Comprehensive measure of change working capital accrual (WCA) including changes in receivables, payables, current inventory, current investments, current provisions, current assets, and other current liabilities.
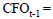 Cash flow from operations period t–1
Cash flow from operations period t–1
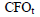 = Cash flow from operations period t
= Cash flow from operations period t
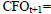 Cash flow from operations period t+1
Cash flow from operations period t+1
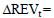 Change in net income
Change in net income
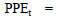 Property, Plant, and Equipment (PPE)
Property, Plant, and Equipment (PPE)
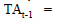 Total asset period t–1
Total asset period t–1
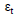 = Residual
= Residual
The working capital accrual (WCA) formula refers to the study conducted by Bradbury et al. (2006), with the following equations:
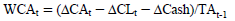
Where:

The regression equation for measuring earnings quality is calculated for three years for each study period, which results in three accrual qualities in each company's data in each period. Estimates of the overall accrual quality for each year were obtained from the standard deviation of the residual values for three years.
The independent commissioner is one of the important and effective role holders in the company to minimize the occurrence of earnings management (Arniati et al., 2019). The measurement of this variable uses the proportion of independent commissioners (Kent et al., 2016). A large number of audit committees have various experiences and expertise that can increase effectiveness in monitoring management activities (Al-Rassas & Kamardin, 2015b). This directs the company in achieving high earnings quality. The audit committee (AC) is measured by the number of members of the audit committee. The largest concentrated ownership is shareholding by the government, industrial investors, CEOs, and financial investors (Alucha & Kaminski, 2017). This variable uses the largest shareholder percentage (Conc) with the following formula (Sousa & Galdi, 2016):
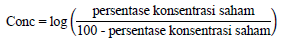
Investors as principals are more confident in the examinations carried out by external auditors, especially big four auditors because they are able to carry out higher supervision (Kent et al., 2016). External auditor is measured using a nominal scale with a dummy variable, namely 1 if the company's audit process is carried out by big four auditors, 0 for others. Company size is a measurement tool used to classify companies in the category of small, medium, or large companies (Kent et al, 2016). Firm size uses the logarithmic value of the total assets (Sarawana & Destriana, 2015).
Result
The results of descriptive statistics and hypothesis testing can be seen in the following table 2:
| Table 2 Descriptive Statisticds |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
| EQ | 270 | 0,0015 | 0,5198 | 0,074589 | 0,0709753 |
| KI | 270 | 0,2000 | 1,0000 | 0,417275 | 0,1150512 |
| KA | 270 | 0,0000 | 5,0000 | 3,033333 | 0,4904288 |
| Conc | 270 | -0,9876 | 1,4166 | 0,112904 | 0,5091026 |
| AE | 270 | 0,0000 | 1,0000 | 0,396296 | 0,4900356 |
| SIZE | 270 | 10,9510 | 14,5375 | 12,327745 | 0,7104999 |
Source: statistics output
| Table 3 Hypothesis Testing |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
| C | 0.284774 | 0.123456 | 2.306685 | 0.0218 |
| KI | 0.138033 | 0.043858 | 3.147253 | 0.0018 |
| KA | -0.019573 | 0.008775 | -2.230649 | 0.0265 |
| CONC | 0.002265 | 0.011842 | 0.191308 | 0.8484 |
| AE | 0.007032 | 0.014015 | 0.501780 | 0.6162 |
| SIZE | -0.017153 | 0.010269 | -1.670271 | 0.0961 |
Source: statistics output
Independent commissioner (KI) has a value of sig. of 0.0018 (α < 0.05), H1 is supported, meaning that the independent commissioner has an effect on earnings quality. The higher the value of the proportion of independent commissioners in the company, the lower the value of the earnings quality generated by the company. This is because independent commissioners are seen as parties who have little knowledge about the company's activities, so to obtain information about the company, independent commissioners depend on company management (Al-Dhamari & Ku Ismail, 2014). These results are in agreement with (Al-Dhamari & Ku Ismail, 2014; Egbunike & Odum, 2018).
value of the proportion of independent commissioners in the company, the lower the value of the earnings quality generated by the company. This is because independent commissioners are seen as parties who have little knowledge about the company's activities, so to obtain information about the company, independent commissioners depend on company management (Al-Dhamari & Ku Ismail, 2014). These results are in agreement with (Al-Dhamari & Ku Ismail, 2014; Egbunike & Odum, 2018).
Concentrated ownership (Conc) has a sig value. of 0.8484 (α > 0.05), H3 is not supported, meaning that the effect of concentrated ownership on earnings quality is not significant. Shareholdings that are concentrated in large numbers tend to focus on dividends that will be obtained from profits by encouraging high performance to management without being involved in the process of making financial statements. This study is consistent with (Sarawana & Destriana, 2015).
The external auditor (AE) has a sig. 0.6162 (α > 0.05), H4 is not supported, meaning that the influence of external auditors on earnings quality is not significant. External auditors do not affect the high or low earnings quality generated from company activities because the audit process carried out by the auditor occurs when the business processes and financial statements have been recorded in the relevant period by the management. This study is in accordance with (Afifa et al., 2020; Susanto et al., 2019; Susanto et al., 2019).
Conclusion
Independent commissioners and audit committees have an effect on earnings quality. Meanwhile, concentrated ownership and external auditors have no effect on earnings quality. Limitations in this study include the research period is only three years, the number of samples in the study is only manufacturing companies. Recommendations for further research related to earnings quality are increasing the research period, adding research samples from non-financial companies, adding independent variables not found in this study that may affect earnings quality such as institutional ownership and managerial ownership as corporate governance. This research is expected to be an additional reference for further research and provide information for investors to conduct in-depth analysis of the company's financial statements that will be used as a decision-making tool.
References
Afifa, M.A., Alsufy, F., & Abdallah, A. (2020). "Direct and Mediated Associations among Audit Quality, Earnings Quality, and Share Price: The Case of Jordan." International Journal of Economics and Business Administration, 8(3), 500-516.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Al-Dhamari, R.A., & Ku Ismail, K.N.I. (2014). The association between board characteristics and earnings quality: Malaysian evidence. Jurnal Pengurusan, 41, 43-55.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Al-Rassas, A.H., & Kamardin, H. (2015a). Directors’ Independence, Internal Audit Function, Ownership Concentration and Earnings Quality in Malaysia. Asian Social Science, 11(15), 244-256.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Al-Rassas, A.H., & Kamardin, H. (2015b). Internal and External Audit Attributes, Audit Committee Characteristics, Ownership Concentration and Earnings Quality: Evidence from Malaysia. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6(3), 458-470.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Alves, S. (2014). The Effect of Board Independence on the Earnings Quality: Evidence from Portuguese Listed Companies. Australasian Accounting Business and Finance Journal, 8(3), 21-44.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Arniati, T., Puspita, D.A., Amin, A., & Pirzada, K. (2019). The Implementation of Good Corporate Governance Model and Auditor Independence in Earnings' Quality Improvement. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 7(1), 189-200.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Egbunike, C.F., & Odum, A.N. (2018). Board leadership structure and earnings quality Evidence from quoted manufacturing firms in Nigeria. Asian Journal of Accounting Research, 3(1), 82-111.
Huynh, Q.L. (2018). Earnings Quality with Reputation and Performance. Asian Economic and Financial Review, 8(2), 269-278.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jensen, M.C, & Meckling, W.H. (1976). Theory of the Firm: Managerial Behaviour, Agency Costs and Ownership Structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(4), 305-360.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kent, P., Kent, R.A., Routledge, J., & Stewart, J. (2016). Choice of governance structure and earnings quality.Accounting Research Journal, 29(4), 372-390.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Khafid, M., & Arief, S. (2017). Managerial Ownership, Corporate Governance and Earnings Quality: The Role of Institutional Ownership as Moderating Variable. Pertanika Journals Social, Sciences & Humanities, 25(1), 241-254.
Khan, M.W. (2017). Corporate Governance and its Effect on Earnings Quality in Retail Industry of the United Kingdom. Asian Journal of Applied Sciences, 5(5), 849-857.
McNichols, M.F. (2002). Discussion of: The quality of accruals and earnings: The role of accruals estimation errors. The Accounting Review, Supplement, 77, 61-69.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Mojtahedi, P. (2013). The impact of intellectual capital on earning quality: Evidence from Malaysian firms.Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 7(2), 535-540.
Piyawiboon, C. (2015). Audit Quality, Effectiveness of Board Audit Committee and Earning Quality. Review of Integrative Business & Economics Research, 4(2), 366-377.
Sae-Lim, P., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2019). Audit Committee and Earnings Quality. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 6(2), 335-347.
Sarawana, S., & Destriana, N. (2015). Pengaruh Mekanisme Tata Kelola Perusahaan, Pendanaan Hutang Perusahaan, Dividen serta Ukuran Perusahaan terhadap Kualitas Laba. Jurnal Bisnis dan Akuntansi, 17(2), 156-167.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
SeTin, S., & Murwaningsari, E. (2018). The effect of Managerial Ability towards Earning Quality with Audit Committee as Moderating Variable. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 12(3), 178-189.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Slaheddine, T. (2015). Relationship between Earnings Quality and External Audit Quality. Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 5(2), 1-7.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sousa, E.F.d., & Galdi, F.C. (2016). The Relationship between Equity Ownership Concentration and Earnings Quality: Evidence from Brazil. Revista de Administração, 51(4), 331-343.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sumiadji, G.C., & Subiyantoro, E. (2019). Effect of Audit Quality on Earnings Quality: Evidence From Indonesia Stock Exchange. International Journal of Financial Research, 10(1), 86-97.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Susanto, Y.K., Pradipta, A., & Cecilia, E. (2019). Earnings Management: ESOP and Corporate Governance.Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 23(Spesial Issue 1).
Susanto, Y.K., Pirzada K., & Adrianne S. (2019). Is tax aggressiveness an indicator of earnings management? Polish Journal of Management Studies, 20(2), 516-527.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Susanto, Y.K., Pradipta, A., & Esther, S. (2021). Audit Decision: Interaction between Earnings Management and Audit Specialization. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 25(1), 1-8.
Susanto, Y.K., Pradipta, A., & Handojo, I. (2021). Institutional and Managerial Ownership on Earnings Management: Corporate Governance. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 25(6), 1-7.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Tambun, S., Sitorus, R.R., Panjaitan, I., & Hardiah, A.Z. (2017). The Effect of Good Corporate Governance and Audit Quality on The Earnings Quality Moderated by Firm Size. International Journal of Business, Economics and Law, 14(5), 48-56.
Zhang, C., & Huang, X. (2017). Involvement of Management, Audit Committee and Earnings Quality. Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, 37, 222-240.
Received: 09-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. AAFSJ-22-11137; Editor assigned: 11-Jan-2022, PreQC No. AAFSJ-22-11137(PQ); Reviewed: 27- Jan-2022, QC No. AAFSJ-22-11137; Revised: 16-Fab-2022, Manuscript No. AAFSJ-22-11137(R); Published: 23-Feb-2022