Review Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 4
Consumer Engagement and Experience in the Era of Technology: A Structural Equation Modeling Study on Brand Loyalty and Customer Value
Chinmaya Kulshrestha, MDI, Gurgaon
Avinash Kapoor, MDI Gurgaon
Citation Information: Kulshrestha, C., & Kapoor, A. (2024). Consumer engagement and experience in the era of technology: a structural equation modeling study on brand loyalty and customer value. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(4), 1-13.
Abstract
This research paper explores the digital era's impact on consumer engagement and brand loyalty using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). The study reveals a strong correlation between digital consumer engagement and brand loyalty, with personalized and interactive digital experiences fostering consumer loyalty. The study also highlights the impact of digital engagement on customer value perception, with personalization, convenience, and digital brand interaction being key drivers. The findings have implications for digital marketing strategies, suggesting brands should prioritize digital engagement channels to enhance customer loyalty and perceived value. The research also addresses challenges like data privacy, the digital divide, and information overload, emphasizing the need for ethical practices in digital marketing. The paper underscores the importance of digital consumer engagement in modern marketing strategies and business success in the digital marketplace.
Keywords
Consumer Engagement, Brand Loyalty, Customer Value Perception, Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), Digital Marketing.
Introduction
The findings of a study that was carried out using structural equation modelling to investigate the relationship between customer value and brand loyalty are presented in an article. It was interesting in determining how customer value and brand loyalty are related to one another. This research analyses the complex dynamics of consumer engagement and experience in the digital era. Along with the influence that these dynamics have on customer value and brand loyalty, the study also looks at the consequences of these dynamics. In particular, the research focuses on the influence that these dynamics have on the situation. After conducting an investigation into the intricate connections that have been produced as a result of technological advancements over the course of time, the study makes an effort to fill in vast gaps that have been identified in the existing body of literature. This is accomplished by conducting an investigation into the intricate connections that have been produced. This goal may be reached by the use of structural equation modelling as the method of doing it (SEM). Putting an emphasis on the ever-changing expectations of consumers and the digital transformation, the purpose of this paper is to provide novel insights into the ways in which contemporary digital platforms and theories of consumer behaviour influence brand strategies.
Specifically, the paper will focus on the ways in which consumers use digital platforms. To be more specific, the article will concentrate on the techniques that customers use while using digital platforms. To be more precise, the paper will focus on the strategies that consumers use while using digital platforms with the intention of providing additional information. In addition to the fact that the real uses of these insights in marketing and commercial strategy will be very helpful, they will also give significant consequences for the research that is conducted in academic institutions.
Criticality of Understanding Consumer Behavior
To achieve success in a market that is becoming more competitive and technology-driven, it is vital to have a good grasp of consumer behaviour in the current digital environment. This awareness is crucial for marketing success. In order for marketing strategies and company models to be successful, this knowledge serves as the basis. The method in which customers engage with and perceive companies has been profoundly transformed as a result of the proliferation of digital platforms. The result of this is that the environment in which consumers operate is one in which their expectations are not only higher but also more varied. These expectations include customization, involvement in real time, and experiences that are seamless (Han, H. (2021). These expectations have not only grown in number, but they have also gotten more varied throughout time. It is very necessary for businesses to possess this level of in-depth information in order for them to properly modify their products and marketing efforts. This comprehension guarantees that the goods and marketing activities will connect with the populations who are being targeted and will encourage brand loyalty. Furthermore, as a consequence of the proliferation of data analytics and consumer insights, organisations today possess the tools that are required to delve more thoroughly into the psychographics of customers as well as the patterns of behaviour that consumers display.
On the other hand, this also poses a number of challenges, such as the need to handle difficulties with data privacy and the requirement to appreciate the intricacies of client behaviour across a range of digital platforms. In the end, understanding consumer behaviour in this digital era is not just about selling a product or service; rather, it is about establishing long-lasting connections with customers, which in turn fosters sustainable corporate development and innovation (Li, B., Gao, et. Al, (2021). This is because understanding consumer behaviour is about more than just selling a product or service. This knowledge becomes a vital component for businesses that have the purpose of prospering in a market that is controlled by technology and is always expanding. This is because of the reasons stated above.
Evolution of Consumer Engagement
The development of consumer involvement has experienced a tremendous transition, especially in the context of technology breakthroughs and the beginning of the digital revolution. Consumer involvement has traditionally been a one-way process, with corporations dictating market trends and consumers' decisions being mostly impacted by conventional advertising and restricted avenues of contact. Historically, this has been the case (Ubgade & Joshi, (2023). This dynamic, however, has been revolutionised by the introduction of the internet and subsequent digital technologies, which has resulted in a change in the power balance toward consumers. Consumer engagement in the modern period is defined by a two-way, interactive conversation. In this discussion, customers are not only passive receivers of marketing messages; rather, they are active players who have the ability to engage, criticise, and shape brand narratives. Consumers now have access to unprecedented channels through which they can voice their thoughts, discuss their experiences, and communicate directly with businesses.
These platforms include social media platforms, internet forums, and reviewed websites. This transformation has resulted in customers who are more educated and more powerful, and they are demanding that businesses provide them with increased individuality, authenticity, and responsiveness (Unnava, V., & Aravindakshan, A. (2021). When it comes to connecting with their audiences, companies need to embrace methods that are more nuanced and smarter in order to keep up with the current environment of consumer interaction, which is more complicated and diverse than ever before. Currently, it is necessary for brands to provide content that is not just engaging, relevant, and value-driven across a variety of digital platforms, but also to make use of data analytics in order to acquire more profound understandings of the preferences and behaviours of consumers. This development is indicative of a marketplace that is more democratic and centred on the customer, one in which participation is driven by meaningful interactions and connections rather than just transactions.
Engagement in the Digital Age
Engagement in the digital age represents a seismic shift away from traditional, linear models of consumer interaction and towards an approach that is more dynamic, interconnected, and user-centric for the purpose of fundamentally reshaping the way in which brands and consumers interact with one another. An ongoing, complex conversation in which customers take an active role in co-creating brand narratives and experiences is what we mean when we talk about engagement in this day and age. Engagement is no longer just about delivering messages to an audience that is not actively participating (Rasool, et. al (2021). Consumers now have a voice and a platform to express their opinions, preferences, and complaints thanks to the proliferation of digital platforms, notably social media, which have emerged as crucial avenues for this engagement. The power dynamics have shifted in favour of the consumer, allowing them unprecedented influence on brand reputations and market trends. This change has led to a democratisation of brand engagement, during which the power dynamics have shifted in favour of the customer. Companies are today confronted with the difficulty of navigating a world in which customers not only anticipate receiving high-quality goods and services, but also want authenticity, transparency, and individualised experiences. These expectations have been further enhanced as a result of the development of digital devices and the pervasiveness of the internet.
As a result, real-time engagement and responsiveness have become essential components of good customer interactions. In addition, the proliferation of data analytics and artificial intelligence has provided businesses with more profound insights into the behaviour of their customers. This has enabled them to customise their marketing campaigns with more accuracy and to cultivate relationships that are more meaningful. On the other hand, this increased reliance on technology also brings with it a number of challenges, such as the management of concerns regarding privacy and the possibility of digital overload, which occurs when consumers are constantly bombarded with digital content, which can lead to disengagement on their part (Yujie, et al, 2022). Therefore, engagement in the digital age necessitates striking a careful balance between using technical improvements to improve the experience of consumers and preserving a real, human-centred approach to the management of customer interactions. In the end, the success of a brand in this era is dependent on its capacity to not only attract the attention of customers, but also to engage them in a manner that is meaningful, sustainable, and ethically responsible. This is accomplished by cultivating a sense of community and belonging that goes beyond the conventional boundaries of business and customer interaction.
The Intersection of Technology and Consumer Experience
There is a significant turning point in the contemporary corporate world that is marked by the junction of technology and customer experience. This convergence is redefining the landscape of consumer contact and expectation in dramatic ways. The amalgamation of these two elements has resulted in the emergence of a new age in which technology improvements not only improve the experiences of consumers but also redefine them. Digital platforms, which include e-commerce websites, mobile applications, and social media, have become an essential part of the customer journey. These platforms provide experiences that are seamless, customised, and immersive, which were imagined at the beginning of the last few decades. Augmented reality, virtual reality, and personalization algorithms driven by artificial intelligence are all examples of how technology can be used to create experiences that are rich, engaging, and tailored to the individual (Farah, M. et. al 2019). This can completely change the way in which consumers discover, evaluate, and purchase products and services. By providing digital experiences that are both interactive and engaging, this technology integration goes beyond just facilitating transactional exchanges.
It helps to cultivate deeper emotional ties and a feeling of brand loyalty. Furthermore, the widespread availability of smartphones and the internet has resulted in the expectation of continuous connectivity and instant gratification. Customers are demanding that brands provide them with prompt responses, updates in real time, and accessibility around the clock when they are shopping. The use of data analytics is of critical importance in this paradigm because it enables companies to get insights into the behaviour and preferences of customers, which in turn allows them to develop marketing plans that are more targeted and relevant. Nevertheless, this junction also has a number of obstacles, including the need to navigate the intricacies of data privacy and digital security, as well as the possibility of consumers being overwhelmed with information (Bolton, et al. 2018). In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the ethical implications that are associated with the use of consumer data and the influence that digital technologies have on the mental health and well-being of society. In essence, the intersection of technology and consumer experience is a frontier that is both dynamic and evolving. It presents enormous opportunities for innovation and growth, but it also necessitates a careful balance between utilising technology for the benefit of businesses and ensuring that consumers are engaged in a responsible, ethical, and sustainable manner. The environment is one in which the experience that is delivered to the customer is just as essential, if not more so, than the product or service that is being supplied. This situation heralds the beginning of a new age of consumer-centric business models that are driven by technical capability.
Literature Review
Research Gap
While existing studies have explored various aspects of consumer engagement, customer experience, and brand loyalty, particularly in the context of digital platforms and online environments, there appears to be a lack of comprehensive understanding of how these elements interact in the increasingly technologically-driven marketplace. Specifically, there is a scarcity of research employing SEM to holistically examine the interrelationships between consumer engagement, customer experience, and brand loyalty while incorporating the nuances of customer value perception in the digital age. Additionally, the rapid evolution of technology and its impact on consumer behavior and brand interaction necessitates updated studies that reflect current trends and practices. Therefore, a study that integrates these components using SEM could provide a more integrated and contemporary perspective on how technology shapes consumer engagement, experience, and consequentially, brand loyalty and customer value.
Research Questions:
1. How does technology influence consumer engagement with brands?
2. What role does customer experience play in fostering brand loyalty in the era of technology?
3. In what ways does brand loyalty impact the perceived customer value in a digital context?
4. How can SEM be effectively applied to model the relationships between consumer engagement, customer experience, brand loyalty, and customer value?
Research Objectives:
1. To Examine the Impact of Technology on Consumer Engagement: Assess how advancements in technology, particularly digital platforms, affect the ways in which consumers engage with brands.
2. To Analyze the Role of Customer Experience in Brand Loyalty: Investigate the influence of customer experience on the development and sustenance of brand loyalty in the digital era.
Research Hypotheses:
H1: Technological advancements positively influence consumer engagement with brands.
H2: A positive customer experience significantly enhances brand loyalty in the digital age.
H3: There is a direct positive relationship between brand loyalty and the perceived value customers derive from a brand.
Methodology:
A self-administered questionnaire was used to enquire. The responses were collected from 200 respondents using google forums following random sampling technique. Statical tools and tests are used to analyze the collected responses and derive the key findings of the study. IBM SPSS is used to perform the statistical analysis of the collected responses. SEM is used to analyze the path diagram. The value of coronach’s alpha is 0.977 for N = 14 (questions) Table 1.
| Table 1 Data Analysis | |||||
| Demographic Variables | |||||
| Statement | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Gender | Male | 168 | 84 | 84 | 84 |
| Female | 32 | 16 | 16 | 100 | |
| Age | 18-30 | 70 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| 31-40 | 90 | 45 | 45 | 80 | |
| 41-60 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 100 | |
| Educational Background | High School | 70 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| Bachelor's Degree | 66 | 33 | 33 | 68 | |
| Master’s Degree | 38 | 19 | 19 | 87 | |
| Other | 26 | 13 | 13 | 100 | |
| Locality | Urban | 136 | 68.0 | 68.0 | 68.0 |
| Rural | 64 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 | |
In terms of gender, the majority of respondents are male, accounting for 84% of the group, while females make up the remaining 16%. In terms of age distribution, the majority falls within the age range of 31-40, constituting 45% of the group. Those aged 18-30 make up 35% of the group, and individuals between the ages of 41-60 account for the remaining 20%. Regarding educational background, the data shows that respondents have diverse levels of education. The largest group, 35%, have a high school or equivalent education, followed closely by 33% who have obtained a bachelor's degree. 19% of respondents hold a master's degree, and the remaining 13% fall into the "Other" category, which may include individuals with different types of education or qualifications. Lastly, in terms of locality, the majority of respondents reside in urban areas, comprising 68% of the group, while 32% live in rural areas Table 2.
| Table 2 Consumer Engagement | |||||
| Statement | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| I frequently engage with brands through digital platforms such as social media, apps, or websites. | Strongly Disagree | 30 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Disagree | 54 | 27 | 27 | 42 | |
| Neutral | 50 | 25 | 25 | 67 | |
| Agree | 66 | 33 | 33 | 100 | |
| I find that digital technologies enhance my interaction with brands. | Strongly Disagree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Disagree | 48 | 24 | 24 | 49 | |
| Neutral | 44 | 22 | 22 | 71 | |
| Agree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 96 | |
| Strongly Agree | 8 | 4 | 4 | 100 | |
| I am more likely to engage with a brand that offers an innovative digital experience. | Strongly Disagree | 30 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Disagree | 54 | 27 | 27 | 42 | |
| Neutral | 50 | 25 | 25 | 67 | |
| Agree | 66 | 33 | 33 | 100 | |
In the first statement, respondents were asked about their frequency of engaging with brands through digital platforms like social media, apps, or websites. The responses varied, with 15% strongly disagreeing, 27% disagreeing, 25% being neutral, and 33% agreeing that they frequently engage with brands in the digital sphere. This indicates a diverse range of engagement levels among the surveyed individuals. The second statement explored how digital technologies enhance respondents' interactions with brands. Here, 25% strongly disagreed, 24% disagreed, 22% were neutral, 25% agreed, and 4% strongly agreed that digital technologies enhance their interaction with brands. The majority of respondents (49%) either disagreed or strongly disagreed, while a significant portion (29%) agreed or strongly agreed that digital technologies have a positive impact on their brand interactions. The third statement delved into the likelihood of respondents engaging with a brand that offers an innovative digital experience. Similar to the first statement, 15% strongly disagreed, 27% disagreed, 25% were neutral, and 33% agreed that they are more likely to engage with a brand that offers an innovative digital experience. This suggests that a substantial portion of respondents values innovative digital experiences when interacting with brands Table 3.
| Table 3 Consumer Experience with Technology | |||||
| Statement | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| The use of advanced technology (e.g., AR, VR, AI) by brands significantly improves my shopping experience. | Strongly Disagree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Disagree | 48 | 24 | 24 | 49 | |
| Neutral | 44 | 22 | 22 | 71 | |
| Agree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 96 | |
| Strongly Agree | 8 | 4 | 4 | 100 | |
| I value personalized experiences that are made possible through technology in my interactions with brands. | Strongly Disagree | 30 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Disagree | 54 | 27 | 27 | 42 | |
| Neutral | 50 | 25 | 25 | 67 | |
| Agree | 66 | 33 | 33 | 100 | |
| Brands that use technology effectively are more appealing to me. | Strongly Disagree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Disagree | 48 | 24 | 24 | 49 | |
| Neutral | 44 | 22 | 22 | 71 | |
| Agree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 96 | |
| Strongly Agree | 8 | 4 | 4 | 100 | |
In the first statement, respondents were asked about the effect of “advanced technology (such as Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Artificial Intelligence)” on their shopping experience. The responses indicate a range of opinions, with 25% strongly disagreeing, 24% disagreeing, 22% being neutral, 25% agreeing, and 4% strongly agreeing that the use of advanced technology by brands significantly improves their shopping experience. This suggests that there is a somewhat balanced mixture of opinions regarding the influence of advanced technology on shopping experiences.
The second statement explored respondents' preference for personalized experiences facilitated by technology in their interactions with brands. The data reveals that 15% strongly disagree, 27% disagree, 25% are neutral, and 33% agree, indicating that a notable portion of respondents values personalized experiences made possible through technology in their brand interactions.
The third statement assessed the appeal of brands that effectively use technology. Similar to the first statement, 25% strongly disagree, 24% disagree, 22% are neutral, 25% agree, and 4% strongly agree that brands using technology effectively are more appealing. This suggests a relatively even distribution of opinions on whether brands' effective use of technology enhances their appeal Table 4.
| Table 4 Customer Value | |||||
| Statement | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| I perceive greater value in brands that integrate technology seamlessly into their services. | Strongly Disagree | 30 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Disagree | 54 | 27 | 27 | 42 | |
| Neutral | 50 | 25 | 25 | 67 | |
| Agree | 66 | 33 | 33 | 100 | |
| My satisfaction with a brand is often linked to how it uses technology to improve its services or products. | Strongly Disagree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Disagree | 48 | 24 | 24 | 49 | |
| Neutral | 44 | 22 | 22 | 71 | |
| Agree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 96 | |
| Strongly Agree | 8 | 4 | 4 | 100 | |
| I am more likely to recommend a brand that uses technology in a way that adds value to the customer experience. | Strongly Disagree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Disagree | 48 | 24 | 24 | 49 | |
| Neutral | 44 | 22 | 22 | 71 | |
| Agree | 50 | 25 | 25 | 96 | |
| Strongly Agree | 8 | 4 | 4 | 100 | |
In the first statement, respondents were asked about their perception of greater value in brands that seamlessly integrate technology into their services. The responses indicate a range of opinions, with 15% strongly disagreeing, 27% disagreeing, 25% being neutral, and 33% agreeing that they perceive greater value in such brands. This suggests that there is a mix of viewpoints regarding the value of technology integration in brand services.
The second statement explores the link between customer satisfaction and a brand's use of technology to improve services or products. Here, 25% strongly disagree, 24% disagree, 22% are neutral, 25% agree, and 4% strongly agree that their satisfaction with a brand is often linked to how it uses technology. This data indicates that there is a fairly even distribution of opinions regarding the role of technology in customer satisfaction.
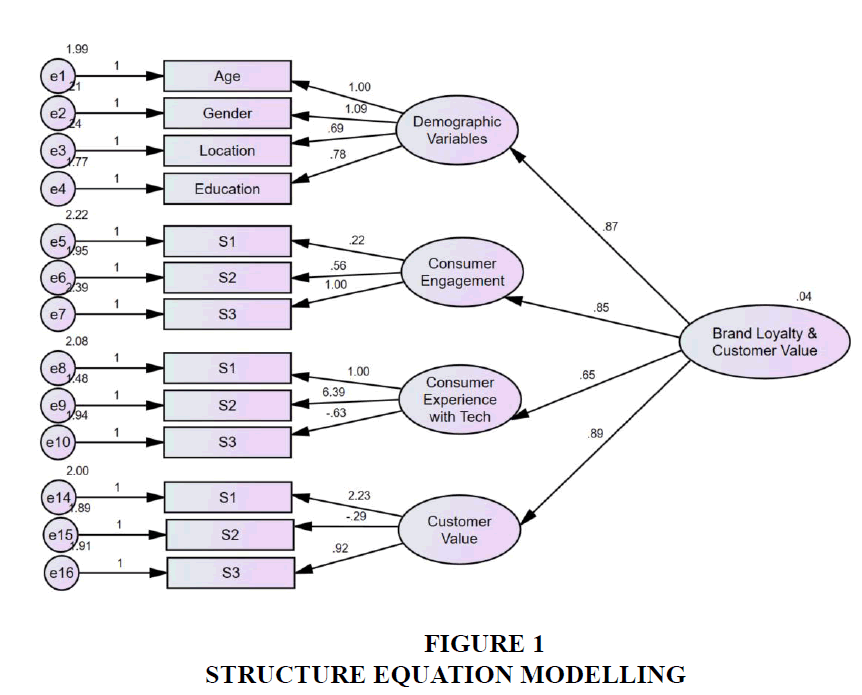
The third statement focuses on the likelihood of recommending a brand that uses technology to add value to the customer experience. Similar to the previous statements, 25% strongly disagree, 24% disagree, 22% are neutral, 25% agree, and 4% strongly agree that they are more likely to recommend such brands. This suggests that respondents' likelihood to recommend a brand is also influenced by a range of opinions regarding the impact of technology on the customer experience Figure 1.
Structure Equation Modelling
The Structural Equation Model (SEM) depicted in the diagram provides an academic examination of the relationships among demographic factors, consumer engagement, consumer experience with technology, customer value, and brand loyalty. This model is a reflection of the proposed hypotheses, aiming to measure the effect of technology on consumer behavior and brand perception in the digital age.
Demographic Variables: The model illustrates that demographic variables such as age, gender, location, and education have varying degrees of standardized path coefficients towards consumer engagement, with values of 0.22, 0.56, and 1.00 respectively. These coefficients suggest a potential influence of these variables on how consumers engage with brands, although the strength of these relationships varies.
Consumer Engagement: The consumer engagement construct, with statements S1 to S3, is operationalized through the frequency of engagement via digital platforms, the enhancement of interaction due to digital technologies, and a preference for brands that offer innovative digital experiences. The path from Consumer Engagement to Brand Loyalty & Customer Value is significant with a coefficient of 0.87, providing strong support for Hypothesis 1 (H1), which posits that technological advancements positively influence consumer engagement with brands.
Consumer Experience with Technology: This construct is defined by the impact of advanced technology on the shopping experience, the value of personalized experiences through technology, and the appeal of brands that use technology effectively. The SEM model shows a direct effect of Consumer Experience with Technology on Brand Loyalty & Customer Value, with a path coefficient of 0.65. This supports Hypothesis 2 (H2), suggesting that a positive customer experience with technology significantly enhances brand loyalty.
Customer Value: The statements for Customer Value focus on the perceived benefits of technology integration, satisfaction linked to technological improvements, and the likelihood of recommending technology-savvy brands. The path coefficient from Customer Value to Brand Loyalty & Customer Value is extremely robust at 0.89, underpinning Hypothesis 3 (H3), which asserts a direct positive relationship between the perceived value customers derive from a brand and their loyalty to it.
Brand Loyalty & Customer Value: As the focal construct, Brand Loyalty & Customer Value is influenced by both Consumer Engagement (β = 0.85) and Consumer Experience with Technology (β = 0.65), though to different extents. Interestingly, the direct path from Demographic Variables to Brand Loyalty & Customer Value is minimal (β = 0.04), suggesting that while demographics may affect engagement, they have a negligible direct effect on loyalty and value.
Model Fit Results
The provided fit indices for SEM indicate an overall strong fit of the model to the data. The (CMIN/DF) at 1.049 falls within the excellent range, suggesting that the model is a good representation of the observed data. Additionally, the (SRMR) value of 0.017 and the (RMSEA) value of 0.02 are both well within the thresholds for an excellent fit, further confirming the model's robustness. Although the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) is slightly below the ideal threshold at 0.875, it is still within an acceptable range. The PClose value of 0.07 also supports the model's adequacy. Collectively, these indices suggest that the model fits the data well, with minor areas for potential improvement.
Discussion
The findings from the SEM analysis underscore the integral role of technological advancements in enhancing consumer engagement, supporting H1. This is consistent with Elseidi & El-Baz (2016), who found a positive correlation between electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM) and consumer engagement. The significant path coefficient from consumer engagement to brand loyalty and customer value in the model (β = 0.87) suggests that the frequency and quality of digital interactions are crucial predictors of loyalty, mirroring Ashraf et al. (2018) who noted the positive impact of online brand experience on satisfaction and loyalty. Consumer experience with technology emerged as a significant predictor of brand loyalty and customer value (β = 0.65), supporting H2. This finding aligns with Rasool et al. (2020), who stressed the transformation of consumers into active participants in the digital age. Kumar & Mokha (2021) also highlighted the importance of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) in enhancing customer satisfaction and retention, further corroborating the model’s emphasis on the positive influence of personalized technological interactions. The model revealed a robust link between customer value and brand loyalty (β = 0.89), validating H3. This is in harmony with the insights provided by Leckie et al. (2016) and Rather et al. (2018), who emphasized the role of consumer-brand engagement and value congruity in fostering loyalty. Kaur et al. (2020) similarly identified the positive effects of community identification and rewards on consumer brand engagement and loyalty in virtual brand communities, which resonates with the model’s indication that perceived value derived from technology is a strong driver of loyalty. The SEM model’s fit and the supported hypotheses (H1-H3) suggest a strong theoretical and empirical foundation for understanding the intricate relationship between technology and consumer behavior. The validation of H4 through this fit indicates that SEM is a robust methodology for representing complex relationships in consumer studies, as Ahmad et al. (2022) utilized similar paradigms to establish connections between online experience and loyalty.
The discussion of the SEM analysis in the context of existing literature provides theoretical implications for the understanding of consumer behavior in the digital age. It also offers practical implications for brand managers and marketers, suggesting that investment in technology that enhances consumer engagement and experience can lead to greater brand loyalty and perceived customer value. The model encourages businesses to tailor their digital strategies to foster personalized and value-adding interactions with consumers.
Limitations and Future Research
While the model provides valuable insights, there are limitations to consider. The scope of demographic variables and their interaction with other constructs could be expanded to include more nuanced factors such as digital literacy or cultural differences. Future research might also explore longitudinal data to account for the evolving nature of technology and its impact on consumer behavior over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the research has delineated a clear and quantifiable relationship between technological advancements and consumer engagement, experience, and perceived value, which in turn significantly influences brand loyalty. The findings from the analysis reinforce the hypotheses that technological integration within brand strategies is not merely beneficial but essential in cultivating consumer engagement and loyalty. The research corroborates with previous literature that technology-enhanced interactions and personalized experiences are paramount in shaping consumer behavior and brand perception in the digital age. Despite demographic variables showing a degree of influence on consumer engagement, their impact on brand loyalty and customer value is comparatively minor, indicating that the quality of technological interaction outweighs the basic demographic factors in the digital consumer market. This study has theoretical and practical implications, suggesting that brands must prioritize innovation and personalization in their digital offerings to maintain competitive advantage and customer loyalty. However, it also acknowledges the limitations inherent in the scope of demographic variables and the necessity for future research to examine the evolving impact of technology on consumer-brand relationships over time.
References
Ahmad, F., Mustafa, K., Hamid, S. A. R., Khawaja, K. F., Zada, S., Jamil, S., Qaisar, M. N., Vega-Muñoz, A., Contreras-Barraza, N., & Anwer, N. (2022). Online Customer Experience Leads to Loyalty via Customer Engagement: Moderating Role of Value Co-creation. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 897851.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ashraf, S., Iftikhar, A., Yameen, A., & Younas, S. (2018). Empirical relationship of customer brand engagement with satisfaction and loyalty through online brand experience. IUP Journal of Brand Management, 15(3), 23-48.
Bolton, R. N., McColl-Kennedy, J. R., Cheung, L., Gallan, A., Orsingher, C., Witell, L., & Zaki, M. (2018). Customer experience challenges: bringing together digital, physical and social realms. Journal of service management, 29(5), 776-808.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Elseidi, R. I., & El-Baz, D. (2016). Electronic word of mouth effects on consumers’ brand attitudes, brand image and purchase intention: An empirical study in Egypt. The Business & Management Review, 7(5), 268.
Farah, M. F., Ramadan, Z. B., & Harb, D. H. (2019). The examination of virtual reality at the intersection of consumer experience, shopping journey and physical retailing. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 48, 136-143.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kaur, H., Paruthi, M., Islam, J., & Hollebeek, L.D. (2020). The role of brand community identification and reward on consumer brand engagement and brand loyalty in virtual brand communities. Telematics and Informatics, 46, 101321.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kumar, P., & Mokha, A. K. (2021). Relationship between E-CRM, Customer Experience, Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty in Banking Industry: A Review of Literature. Research Review International Journal of Multidisciplinary, 6(2), 127–137.
Leckie, C., Nyadzayo, M. W., & Johnson, L. W. (2016). Antecedents of consumer brand engagement and brand loyalty. Journal of Marketing Management, 32(5–6), 558–578.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Leckie, C., Nyadzayo, M. W., & Johnson, L. W. (2018). Promoting brand engagement behaviors and loyalty through perceived service value and innovativeness. Journal of Services Marketing, 32(1), 70–82.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Li, B., Gao, Y., Zhang, S., & Wang, C. (2021). Understanding the effects of trust and conflict event criticality on conflict resolution behavior in construction projects: Mediating role of social motives. Journal of Management in Engineering, 37(6), 04021066.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Liladhar Rane, N., Achari, A., & Choudhary, S. P. (2023). Enhancing Customer Loyalty Through Quality Of Service: Effective Strategies To Improve Customer Satisfaction, Experience, Relationship, and Engagement.
Lim, W. M., & Rasul, T. (2022). Customer engagement and social media: Revisiting the past to inform the future. Journal of Business Research, 148, 325–342.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rasool, A., Shah, F. A., & Islam, J. U. (2020). Customer engagement in the digital age: A review and research agenda. Current Opinion in Psychology, 36, 96–100.
Rasool, A., Shah, F. A., & Tanveer, M. (2021). Relational Dynamics between Customer Engagement, Brand Experience, and Customer Loyalty: An Empirical Investigation. Journal of Internet Commerce, 20(3), 273–292.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rather, R. A., Tehseen, S., & Parrey, S. H. (2018). Promoting customer brand engagement and brand loyalty through customer brand identification and value congruity. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 22(3), 319–337.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ubgade, P. N., & Joshi, S. (2023). Evolution of Consumer Brand Engagement in Past Two Decades: A Systematic Analysis. Vision, 09722629231187913.
Unnava, V., & Aravindakshan, A. (2021). How does consumer engagement evolve when brands post across multiple social media?. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 49(5), 864-881.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yujie, Z., Al Imran Yasin, M., Alsagoff, S. A. B. S., & Hoon, A. L. (2022). The mediating role of new media engagement in this digital age. Frontiers in public health, 10, 879530.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 11-Jan-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14343; Editor assigned: 12-Jan-2024, PreQC No. AMSJ-24-14343(PQ); Reviewed: 29-Jan-2024, QC No. AMSJ-24-14343; Revised: 15-Apr-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14343(R); Published: 06-May-2024