Research Article: 2021 Vol: 27 Issue: 5S
Combined Effect of Green Intellectual Capital and Knowledge Management Maturity on Knowledge Performance analytical Study of opinions of a Sample of Employees of Public Company for Telecommunications and Informatics-Diwaniyah Branch
Sanaa J. Kadhim, Al-Qadissiyah University
KhariyaAbed fadel, Technical Institute of Al-Diwaniyah, AI-Furat Al-Awsat Technical University (ATU)
Asmaa Abdul Wahid Malik, Technical Institute of Al-Diwaniyah, AI-Furat Al-Awsat Technical University (ATU)
Abstract
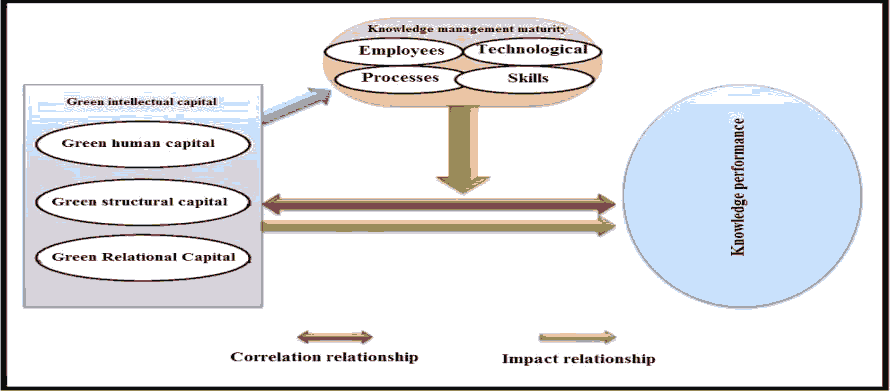
The goal of the present study is to highlight maturity of knowledge management in its dimensions (workers, processes, technology, skills) and the importance of green intellectual capital in its aspects (green human capital, green structural capital and green relational capital) in knowledge performance. Current studying attempted to answer a set of questions that embodiedstudying problem, perhapsmost important of which is its dimensions affectingperformance of knowledge, green intellectual capital ormaturity of knowledge management inGeneral Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah branch, To achievegoal ofstudying, two main hypotheses were formulated, from which several sub-hypotheses were branched out, usingdescriptive analytical approach, By using SPSS vr.24 software, AMOS vr 24, AndEXCEL program,need to consolidatejoint effect between green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management in order to ensurecontinuity of improving knowledge management instudying company.
Keywords
Green Intellectual Capital, Knowledge Management Maturity, Knowledge Performance, Green Human Capital, Green Relational Capital, Structural Capital Green, Operations, Technology, Skill
Introduction
Green Intellectual Capital: Intellectual capital is known to be the sum of all intangible organizational resources, knowledge and abilities, information, technologies, intellectual property, experience and organizational education, skills, communication systems, working teams and customer and brands relationships capable of creating competitive values or benefits for the attainment of their main objectives (Salvadó& Verde, 2014), Employees like to work in order to fulfill the goals and expectations of the company (Leonova et al.,2021),Intellectual money funds represent a combination of four factors: genetic factors, education, experience, and attitudes towards life and business (Liu, 2010).
In general, intellectual capital consists of three basic categories: human, structural and relational. Human capital is the accumulated tacit knowledge of any organization's personnel. Structural capital offers a tool for supporting people to improve work performance and organizational performance in general (Liu, 2010). Relational capital is relationship shares, in which organization can cooperate or communicate with companies, institutions and studying centers. And other clients, with strong levels of understanding, trust, relationship and cooperation (Chen, 2008), Green management became a major administrative goal for many organizations, because of its relevance in conserving the environment. A resource-based vision is based on the fact that organizations' competitive benefits stem from their main resources and capabilities, and that social and environmental responsibility can be a major capability that leads to a competitive advantage in their strategy and that sustainable capacity should be considered. Green management may therefore be an essential part of its type (Chang & Chen, 2012).
Here, Green management businesses can modify their competitive positions to get a competitive market advantage in terms of environmental consciousness. If green management is embraced, businesses might be forced to produce green goods or processes. Rather, it may generate high obstacles to market entry and, according to the institutional theory, it can help to get the support from other institutions and players who can get greater legitimacy.Stakeholder Theory (Chen & Chang, 2012) Here it is necessary to know that green management was defined in 2009 asprocess by whichorganization managesenvironment by developing strategies based on green intellectual capital. (Sudin, 2011), Despite its significance, definitions of green intellectual capital or environmental intellectual capital are rare. A sum of all sorts of intangible goods, knowledge, capacity, relationships and so on at the individual and organizational levels on environmental preservation or green innovation to obtain a competitive edge by controlling the environment.
He sees it as an expression concepts ofemployment of environmental in intellectual capital to compensate for its aspects Previous deficiencies in environmental issues, It representsintangible assets oforganization(Huang & Kung, 2011,1407), which are environmental protection understanding, knowledge, capability, expertise and creativity (Verde &Salvadó, 2014,263), refers toorganization's ability to generate new knowledge, new product and any innovative ideas aimed at addressing environmental issues (Yahya&Arshad, 2015).
Studying believes that it is environmental awareness of organization that leads it to adopt green management in all its activities and invest in its intangible assets in order to achieve creativity or green innovation, which leads to preservationof environment
Literature Review and Hypotheses
Dimensions of Green Intellectual Capital: According tostudyinger's perusal of a number of studyinges and studies interested in measuring intellectual capital Green, it has come toexistence of a single measure pertaining to Chen,2008 which consists of three dimensions: green human capital, green structural capital, and green relational capital. This scale has been used by a number of studyingers such as: Kung & Huang (2011); Yahya&Arshad(2015); Sultana&Zayed (2018); Verde &Salvadó (2014); Chang & Chen (2012). Thus studyingers have sufficient scientific justification to use this scale in Current search.Following is an explanation ofdimensions ofgreen intellectual money variables as follows.
Green Human Capital
Human capital in general isHuman Resource approach of motivation firmly advocates the notion of job satisfaction with a view to ensuring higher productivity of the employees (Murad et al.,2013), represented by all human resources with distinguished capabilities to occupy administrative and technical positions, which have innovative and superior creativity capabilities. These include employees ’advanced knowledge, accumulated experience of life and practical experience, and their technical and artistic skills. As well as their satisfaction, morale and cohesion as an integrated team, as for green human capital, it is a collection of employees' knowledge, skills, abilities, experiences, attitudes, wisdom, creativity, commitments, etc. related to environmental protection or green innovation (Chen & Chang, 2012).
Finally, most ofprevious studies concluded that green human capital can be formed from:Non-personnel working in organizations, and can be developed through training and education: 2008, (Chen, 2008) Here,role of green human resources management appears in directingattention and behavior of employees towards achieving sustainability goals (Huang & Kung, 2011).
Green Structural Capital: Environmental management and culture are a key part in formulation and implementation of environmental strategies to search for new opportunities or to obtain new competitive advantages. This calls for formation of a new concept known as "green structural capital", which is defined as cod stock. Corporate services, corporate duties, knowledge management systems, corporate culture, business photographs, patents, intellectual property rights and trademarks as well as environmental protection or green innovation inside the corporation; (Chen& Chang, 2012), It should be noted here, thatstructural capital consists of Several systems, for example: patents, innovation and discovery, copyright, trademarks, databases and information systems.
Relational green capital: It represents the aggregate of links between the company and its key stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers and partners. In light of green trends, firms should invest more resources in developing their environmental interests-relating connections in a way that allows them to retain closer ties with their external institutions and stakeholders. In this context, he created an organization-associated notion of relational green capital which is described as the inventory of interactive business interactions with customer, supplier, network members and partners, with links to the environmental management and green innovation of organization (Chen & Chang, 2012).
It consists of several parts related to customer satisfaction, meeting his needs and desires (loyalty), adherence and pride.By dealing with organization (and keeping it) continuity of working with organization and its ability to keep it with it) and empowering it by paying attention to his opinions and suggestions and taking them into consideration when planning new and existing products and deleting some of them when their market share decreases and their involvement in organization’s business and business deals and exchange of information and ideas with him. Studies show that green intellectual capital of an organization and its various intellectual components affect creativity capabilities, and insame way, organizations that manage their environmental capital appropriately adapt better tonew reality that emerges fromchallenge of sustainable development, Limited studies have been conducted that attempted to analyzeintangible green factors that underpinstrategies of green organizations orengines of green intellectual capital. However, despite this recent interest in internal factors, few studyingers have proven in practice, that contributes to developing sustainable strategies. However, number of invested resources in environmental management will increase green creativity of organizations (Salvadó& Verde, 2014).
If environmental concerns are regarded from a positive perspective, organizations tend to focus on stakeholder interests and exhibit more sophisticated environmental plans, including greater resources within green intellectual capital (Kung & Huang, 2008).
Knowledge Management Maturity
There is a small number of literature related to maturity of knowledge management in universities, and assessing knowledge management maturity in governmental and private organizations is important to determine current status of knowledge management and how it can improve knowledge management fields, according to previous studies, use of knowledge and knowledge management has become a crucial condition for continuationof life of dynamic organizations. And creativity, that ability to compete in markets and transactions is related to acquisition, development and implementation of individual and organizational knowledge, and below we will deal with concept of maturity of knowledge management according to opinions of a number of studyingers:
Knowledge management describes it as state of development and improves the quality and efficiency of management of knowledge and the adequacy of social and technical environments for organizational knowledge management (Ramo&Noon, 2018; wibowoa&waluyob, 2015) see it aspath in which knowledge management practices are developed and improved to bringorganization tohighest stage of maturity, which is creativity and excellence that enables it to develop and improve its knowledge (Ramo&Noon, 2018),It iseffectiveness in managing knowledge assets in organizations (Silva,2019).While Mikovie (2019)knows her It is a description oforganization's position when it comes to knowledge management and what can be improved in order to be able to compete inmarket (Mikovie, 2019), There are those who know it asorganization's ability to gain a sustainable competitive advantage by effectively managing scarce and valuable knowledge assets (Harono etal., 2019).
Dimensions of Knowledge Management Maturity: study (Hartono et al., 2019) and study (Kuriakose et al., 2011)dimensions have been relied upon to meet requirements of current studying, which are:
Individuals
The most essential components in the organization are the human resources and knowledge, which contribute to its competitiveness. Organizations must pay attention to human aspects in order to make the most use of their expertise by organizations. Institutions increasingly want to increase their members' commitment on the basis of different advantages linked to enhancing people's performance and better performance by means of emotional commitment. And promote knowledge use, minimize the turnover of work and boost the transfer rate of knowledge (Razzaq et al., 2018).
Operation
Process relates to aspects related to knowledge management activities that helporganization generate, discover, capture, share and apply knowledge, andbranching process spreads it among employees and works to transfer expertise and information and its management, work procedures and strategic planning inorganization (Hussink et al.,2017), It also means acquiring, understanding, storing, implementing and sharing knowledge inorganizational learning process that relates tostrategies and culture oforganization, and it is a complete systematic management strategy that distributes, transfers, develops, implements and stores knowledge in order to be able to increaseefficiency and effectiveness ofindividuals working inorganization(Gholami, 2013).
Skill
Non-Knowledge skills such as social skills play an important part in economic life and social abilities in the job market are increasingly valued. Human management abilities minimize the attrition of employees, especially attrition that company wants to avoid as well as organizational rewards, and they affect positively across hierarchical levels and countries. And professions, which provides an accurate quantitative estimate of administrative differences within a diversified organization(Hoffman&Tadeliis,2020).
Knowledge Performance
In a knowledge-based economy, in particular in high technology businesses that rely heavily on knowledge, know-how performance is typically important (Shoid&Kassim, 2016), Knowledge performance embodies creativity and future profit potential of organization (Watkins, 2017). Knowledge performance is a measure of the knowledge-building condition and the ability to improve creativity inside a company (Ortega et al., 2010). Gunjal(2019) indicated that human capital ismost important indicator of future economic health in any organization, Knowledge performance relates toability of individuals, teams, and organizations to understand what they have learned(Shoid et al., 2011).
Stated that traditions, culture, technology, processes, systems and procedures of any organization are always based on knowledge and experience (Lee et al., 2005). It shows (Pour et al., 2018), Sustainable knowledge is split into 4 subsystems, among which acquisition, creativity, storage and transport. The knowledge performance pertains to a person and a team and an organization's capacity to grasp what they learnt (Shoid&Kassim,2014).
Indicated that it iscreation and promotion of products and services due toability of learning and knowledge (Kim, 2016), throughmain indicators of intellectual capital. Knowledge performance is outcome of knowledge management and describes its outcomes (Ebrahimi et al., 2020). Santiago(2020) adds that knowledge performance is knowledge generated within organization (as a result of learning, information distribution, integration, etc.), while it is used to create new products that improve competitive position of organization.
Importance of knowledge performance: the performance of knowledge depends on the organizational culture of a firm, which can benefit from stress reduction and motivation and empowerment of employees. The positive attitude to errors is facilitated by improving exchange of information and learning from errors (Shoid&Kassim, 2014). Employees are paid as a reward for the organization's performances and contribution, and the pay methods are extensively used to promote employee morals and motivate them more (Nahar&Zayed, 2019).
It is necessary to note that knowledge performance means more than just developing a new product. Measuring knowledge performance is critical for organization to verify whether knowledge management processes are achieving adequate results and to correct methods used when performance is low (Santiago, 2020; Shoid&Kassim, 2016).
Dimensional Knowledge Performance
Formalization
The term officialisation refers to the extent to which formal rules, standard policies and procedures regulate decision making and working interactions, which restricts knowledge production by regulating the chances of organizational members of communicating and interacting with one another (Shoid et al., 2011). Show (Shoid&Kassim, 2016) Higher flexibility and informal behavior can lead to increased knowledge building inside the organizational structure. Formalization and Organizational Routine, (Ortega et al., 2010) show that two notions are comparable. Implicit knowledge is explicit and codified through formalization.
Centralization
Day after day, globalization means that the market is becoming competitive every day. Business needs more skilled and inventive individuals in its organization to meet this competition and changing people's desire (Tumpa&Zayed, 2016), A low degree of centralization can complement and improve the performance of knowledge that may arise through formalism and complexity (Shoid et al., 2011). While decentralization of decision-making is caused by the allocation of authority across the various structural elements (Shoid&Kassim, 2016), decentralization encourages the involvement in strategic thought of a larger number of persons and the level of organization. This can help create knowledge, since other people take part in decision making and more variety, and the quantity of ideas and these ideas will probably be vital. Decentralization into lower levels of organisation.To improve the performance of knowledge (Ortega et al., 2010).
Complexity
Refers to the level of differentiation within the company (Shoid et al., 2011). Ortega, et al.,(2010) indicated that organizational complexity enhances formulation of proposals to generate new knowledge and their implementation for several reasons:
A. High degrees of complexity are based on a variety of experiences (knowledge heterogeneity) that can lead to a wide range of issues and information and knowledge available on how to solve difficulties.
B. Complexity includes diverse interests that might encourage new suggestions, as different professional groups, departments and classes strive to strengthen or defend the status of different professionals in companies.
C. Structural complexity is made feasible by the official or informal attribution of unique tasks, and may frequently necessitate modifications in organizational activities for certain roles and subunits. This enables institutional complexity to offer the variation necessary to generate knowledge, while at the same time facilitating internal uniformity between departments and units to improve the performance of knowledge.
Researcheradopted one-dimensional (Pertusa& Ortega,2010) scale for its applicability in studied company and its suitability for requirements of its practical reality.
Method
StudyingProblem
Studying problem is summarized in raising following questions:
1) What is natureof relationship between green intellectual capital in knowledge performance in General Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah branch?
2) What is natureof relationship between knowledge management maturity and knowledge performance in General Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah Branch?
3) Which one is working on influencing knowledge performance, green intellectual capital or maturity of knowledge management in public company and information and informatics branch of bureau?
4) What is impactof dimensions of green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management on Knowledge performance?
Importance of Studying
Importance of studying can be summarized as follows:
1) Importanceof studying lies in dealing with variables characterized by modernity and linked between them and applied inGeneral Company for Telecommunications and Informatics - Diwaniyah branch, wherestudyinger sought to identifyfactors drivingrelationship between green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management and employing them to improve knowledge performance.
2) Telecommunications service has become a basic necessity whose importance increases withincrease inneeds and expectations ofcustomer, but has become more influenced bygreen intellectual capital andmaturity of knowledge management, by usingdimensions of independent variables and then its effect ondependent variable onKnowledge performance inTelecommunications and Informatics Company,Diwaniyah branch.
3) studyinger seeks to verifyobjectivity ofrelationship between green intellectual capital andmaturity of knowledge management andextent of their influence onknowledge process, and try to add objective and Knowledge efforts and to contemplatelinks and results of their effects on Knowledge performance and add qualitative and practical imprints through this studying.
Objectivesof Studying
Studying mainly deals with determining impact of green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management on Knowledge performance in General Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah Branch, and following sub-goals emerge from them:
1) Analyzing level of green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management in General Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah Branch.
2) Analyzing level of Knowledge performance in General Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah Branch.
3) Determineinfluence of green intellectual capital andmaturity of knowledge management inGeneral Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah Branch
4) Analyzing level of Knowledge performance in General Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah Branch.
5) Examination of level of Knowledge performance of studying sample in General Company for Telecommunications and Informatics, Diwaniyah Branch.
6) Enriching theoretical and field frameworks through this studying to benefit studyingers and practitioners in field of knowledge management.
Studying Hypotheses
First Major Hypothesis
The correlation between green human capital and knowledge performance is statistically significant and influences the following sub-hypotheses apply:
• The correlation between green human capital and knowledge performance exists statistically significantly.
• The correlation between green structural capital and knowledge performance is statistically relevant.
• The correlation between relational green money capital and performance of knowledge exists statistically significantly.
• second main hypothesis: The link between maturity and knowledge performance is statistically significant and influences the sub-hypotheses resulting from it:
• There is a statistically significant correlation and influence relationship between workers and Knowledge performance.
There is a statistically significant correlation and influence relationship between processes and Knowledge performance.
There is a statistically significant correlation and influence between technology and Knowledge performance.
There is a statistically significant correlation and influence relationship between skill and Knowledge performance, (see Figure 1 for our model)
Results
Coding and Description of Variables
It is advisable, before starting to enter data and subject it to analysis, to express it with a set of symbols expressing it in order to create a clear perception forreader aboutvariables included inanalysis, and to clarifyresults reached bystudying easily and easily, and accordingly Table (1) showsdescription and coding ofvariables and dimensions ofstudying entering Inanalysis.
| Table 1 Characterization and Coding of Variables |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Dimensions | P | Code |
| Green intellectual capital (XA) | Green human capital | 5 | XAA |
| Structural capital green | 6 | XAB | |
| Green Relational Capital | 3 | XAC | |
| Knowledge management maturity (XB) | Workers | 5 | XBA |
| Operations | 5 | XBB | |
| Technology | 5 | XBC | |
| Skill | 5 | XBD | |
| Knowledge performance (YY) | One-dimensional | 6 | YY |
Analyzing Normal Distribution ofStudying Data
Table (2) results show that the significant value of the Klumgrove – Smirnov and Shapiro – Willick tests are higher than (0.05), and that data follow normal distribution, meaning that no hypotheses have been disclosed, and that alternative hypotheses have been accepted, assuming data derived from the study community follow natural distribution.
| Table 2 Normal Distribution of variables and Dimensions of study |
||
|---|---|---|
| Shapiro-Wilk | Kolmogorov-Smirnova | Variables |
| 0.956 | 0.141 | Green human capital |
| 0.867 | 0.251 | Structural capital is green |
| 0.792 | 0.340 | Green Relational Capital |
| 0.798 | 0.196 | Green intellectual capital |
| 0.888 | 0.229 | Workers |
| 0.872 | 0.189 | Operations |
| 0.904 | 0.152 | Technology |
| 0.820 | 0.244 | Skill |
| 0.875 | 0.160 | Knowledge management maturity |
| 0.673 | 0.307 | Knowledge performance |
| Df= 135 | Sig.= P > 0.05 | |
Stability of Measuring Instrument
Reliability refers to research scale consistency, scales stability, which may be achieved over time and structural stability is checked by applying Cronbach alpha test, with a significant value above (75%) and Table (3) showing the Cronbach alpha coefficient of the variables included in the analysis.
| Table 3 Cronbach Alpha Study Variables and Measurement Coefficients |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Cronbach Alpha forVariable | Dimensions | P | Cronbach Alpha for Every Dimension |
| Green intellectual capital | 0.788 | Green human capital | 5 | 0.806 |
| Structural capital green | 6 | 0.757 | ||
| Green Relational Capital | 3 | 0.755 | ||
| Knowledge management maturity | 0.772 | Workers | 5 | 0.764 |
| Operations | 5 | 0.772 | ||
| Technology | 5 | 0.809 | ||
| Skill | 5 | 0.817 | ||
| Knowledge performance | 0.792 | One-dimensional | 6 | 0.792 |
The results of Table (3) for variables included in analysis related to Cronbach alpha coefficients indicates that all the values range from their reliability coefficients (0.755-0.817) and shows that the measuring tool has a relatively high reliability and stability which satisfies the requirements and opinions of the sample under examination..
Descriptive Statistics
Green Intellectual Capital Variable
Table (4) data reveal that, with the standard deviation (0.251) and relative relevance of 86%, the general average green intellectual capital variable arithmetic mean reached (4.3) and indicating that the green capital ratio contributed to enrichment of that variable. Of increasing its ability with a standard deviation of (0.362) and an arithmetical mean by (4.49) and an agreement ratio of (90%), While the green structural capital dimension came to second with an arithmetic mean of (4.33) and a standard difference of (0.321) and a relative relevance of (0.321). (87 percent), with an arithmetical mean (4.09) of (0.442), and relative importance (82 percent), the last Green Humans' Dimension indicates that the studied company needs to develop its capabilities. In order to further improve the job functions, it requires an improvement in its skills, capacities and characteristic skills.
| Table 4 Results of Descriptive Census of green Intellectual Capital Variable |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | Mean | SD | Relative Importance% | Rank of Importance |
| XAA1 | 3.56 | 1.041 | 71% | 5 |
| XAA2 | 4.12 | 1.191 | 82% | 4 |
| XAA3 | 4.13 | 0.667 | 83% | 3 |
| XAA4 | 4.41 | 0.638 | 88% | 1 |
| XAA5 | 4.22 | 0.569 | 84% | 2 |
| XAA | 4.09 | 0.442 | 82% | Third |
| XAB1 | 4.39 | 0.587 | 88% | 3 |
| XAB2 | 4.46 | 0.655 | 89% | 2 |
| XAB3 | 4.47 | 0.53 | 89% | 1 |
| XAB4 | 3.99 | 0.686 | 80% | 6 |
| XAB5 | 4.38 | 0.487 | 88% | 4 |
| XAB6 | 4.3 | 0.811 | 86% | 5 |
| XAB | 4.33 | 0.321 | 87% | Second |
| XAC1 | 4.56 | 0.528 | 91% | 2 |
| XAC2 | 4.79 | 0.616 | 96% | 1 |
| XAC3 | 4.13 | 0.685 | 83% | 3 |
| XAC | 4.49 | 0.362 | 90% | first |
| XA | 4.3 | 0.251 | 86% | *** |
Knowledge Management Maturity Variable
Results of Table (5) show thatgeneral average ofarithmetic mean ofknowledge management maturity variable reached (4.25) with a standard deviation of (0.183) and a relative importance equal to (85%), and this indicates thatdimension of workers contributed toenrichment of this variable by enhancing their capabilities. With an arithmetic mean of (4.31), a standard deviation equal to (0.223) and an agreement rate of (86%), whiledimension of operations came in second place with an arithmetic mean of (4.27) and a standard deviation of (0.285) and a relative importance of (85%), whiletechnology dimension came in last place with an arithmetic mean of (4.19), a standard deviation of (0.44) and a relative importance of (84%), which indicatesneed forstudied company to develop its technological capabilities in a way that keeps pace with contemporary environmental changes.
| Table 5 Results of descriptive Statistics of knowledge Management Maturity Variable |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | Mean | SD | Relative Importance% | Rank of Importance |
| XBA1 | 4.47 | 0.689 | 89% | 1 |
| XBA2 | 4.16 | 0.601 | 83% | 5 |
| XBA3 | 4.24 | 0.431 | 85% | 4 |
| XBA4 | 4.33 | 0.546 | 87% | 3 |
| XBA5 | 4.36 | 0.617 | 87% | 2 |
| XBA | 4.31 | 0.223 | 86% | first |
| XBB1 | 4.71 | 0.502 | 94% | 1 |
| XBB2 | 4.03 | 0.422 | 81% | 4 |
| XBB3 | 4.34 | 0.735 | 87% | 2 |
| XBB4 | 4.27 | 0.908 | 85% | 3 |
| XBB5 | 4 | 1.045 | 80% | 5 |
| XBB | 4.27 | 0.285 | 85% | Second |
| XBC1 | 4.11 | 0.435 | 82% | 4 |
| XBC2 | 4.17 | 0.54 | 83% | 3 |
| XBC3 | 4.3 | 0.477 | 86% | 2 |
| XBC4 | 4.36 | 0.779 | 87% | 1 |
| XBC5 | 4.02 | 1.047 | 80% | 5 |
| XBC | 4.19 | 0.44 | 84% | fourth |
| XBD1 | 4.33 | 0.914 | 87% | 2 |
| XBD2 | 4.21 | 0.442 | 84% | 3 |
| XBD3 | 4.03 | 0.503 | 81% | 5 |
| XBD4 | 4.44 | 0.779 | 89% | 1 |
| XBD5 | 4.17 | 0.708 | 83% | 4 |
| XBD | 4.24 | 0.42 | 85% | Third |
| XB | 4.25 | 0.183 | 85% | *** |
Knowledge Performance Variable
Results of Table (6) show thatgeneral average ofarithmetic means ofvariable of knowledge performance reached (4.38) with a standard deviation of (0.406) and a relative importance equal to (88%), and this indicates thatsixth paragraph contributed to enriching this variable by enhancing its capabilities with an average An arithmetic of (4.56) and a standard deviation equal to (0.606) and an agreement rate of (91%), whilethird paragraph came inlast place with an arithmetic mean of (4.15) and a standard deviation of (0.697) and a relative importance of its value (83%), which indicatesneed forstudied company to develop its capabilities, and this matter requires improvingskills, capabilities and characteristics in order to develop and improveperformance of job tasks.
| Table 6 Results of descriptive Statistics of knowledge Performance Variable |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | Mean | SD | Relative Importance% | Rank of Importance |
| YY1 | 4.37 | 0.583 | 87% | 4 |
| YY2 | 4.26 | 0.68 | 85% | 5 |
| YY3 | 4.15 | 0.697 | 83% | 6 |
| YY4 | 4.53 | 0.633 | 91% | 2 |
| YY5 | 4.41 | 1.06 | 88% | 3 |
| YY6 | 4.56 | 0.606 | 91% | 1 |
| YY | 4.38 | 0.406 | 88% | |
Hypothesis Testing
Correlation Hypotheses
This paragraph concerns the measurement of the link between the first independent variable of green intellectual capital, the maturity of the management of information as a second independent variable, and the performance and dimensions of the knowledge as a dependent variable. Table (7) therefore provides the correspondence matrix between research variables.
| Table 7 Matrix of Correlation Between Study Variables |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Human Capital | Green Structural Capital | Green Relational Capital | Green Intellectual Capital | اWorkers | Operations | اTechnology | Skill | Knowledge management maturity | Knowledge performance | |
| Green Human Capital | 1 | |||||||||
| Green Structural Capital | .821** | 1 | ||||||||
| Green Relational Capital | .670** | .286** | 1 | |||||||
| Green Intellectual Capital | .696** | .670** | .641** | 1 | ||||||
| Workers | .650** | .661** | .235** | .490** | 1 | |||||
| Operations | .452** | .483** | .551** | .424** | .820** | 1 | ||||
| Technology | .250** | .353** | .413** | .399** | .287** | .691** | 1 | |||
| Skill | .290** | .510** | .381** | .711** | .222** | .479** | .634** | 1 | ||
| Knowledge Management Maturity | .653** | .630** | .478** | .594** | .791** | .649** | .419** | .444** | 1 | |
| Knowledge Performance | .331** | .357** | .812** | .619** | .389** | .337** | .619** | .550** | .680** | 1 |
| **. Correlation is significant at0.01 level (2-tailed). | Sig. (2-tailed)=0.000 | N= 135 | ||||||||
It is noticed fromresults presented in Table (7) that there is a statistically significant correlation less than (0.01) between green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management and its amount is (0.594), in addition toexistence of a positive correlation between green intellectual capital and Knowledge performance andreality of ( 0.619), which is a strong direct relationship, and this indicatesrejection ofnull hypothesis that imposesabsence of a correlation betweenstudy variables, andacceptance ofalternative hypothesis that imposes a correlation betweenstudy variables, whilestrength ofcorrelation ranged with betweenstudy variables from (0.222) todimension Skill to (0.820) operations, which indicatesnecessity ofstudied company’s interest in improving employees ’skills towards developing their Knowledge capabilities and refining them in line withrequirements oftasks assigned to them.
Impact Hypotheses
Second Main Hypothesis
There is a statistically significant impact relationship for green intellectual capital on knowledge performance.
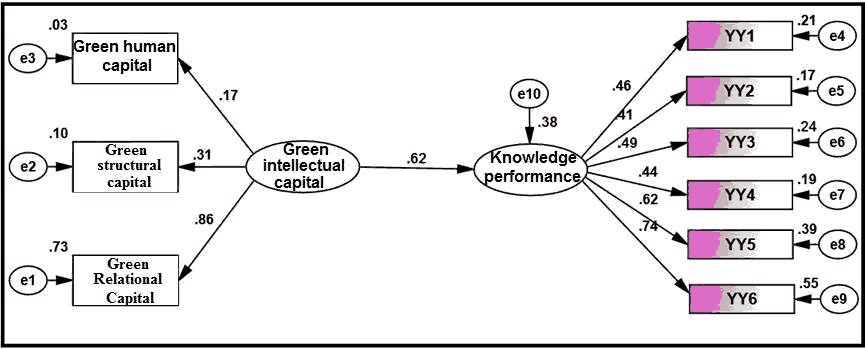
results of Table (8) indicate thatincreased interest ofstudied company in green intellectual capital contributes to improving knowledge performance by (0.619) and with a standard error rate equal to (0.110) and a critical value of (9.098), which indicatesneed to strengthenstudied company forhead Green intellectual money to motivate workers to accomplishrequired tasks efficiently and effectively.
It is noted fromresults of Table (8) thatgreen intellectual capital contributed tointerpretation of (0.384) ofrequirements of knowledge performance, which means thatinterest ofstudied company ingreen intellectual capital contributes todevelopment of knowledge performance by (0.616).
| Table 8 Standard Weights Foreffect of Green Intellectual Capital on Knowledge Performance |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Path | Standard Weight | Standard Error | Critical Value | Value R2 | Probability (P) | Type of Impact | ||
| Green intellectual capital | ---> | Knowledge performance | 0.619 | 0.110 | 9.098 | 0.384 | *** | significant |
Third Main Hypothesis
There is a common influence relationship between green intellectual capital and knowledge management maturity inperformance of knowledge.
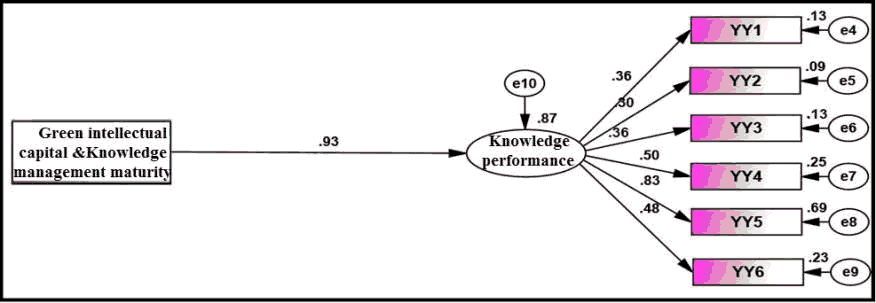
results of Table (9) indicate thatincreased interest ofstudied company injoint influence between green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management contributes to improving Knowledge performance by (0.930) and with a standard error rate equal to (0.126) and a critical value of (7.381), which indicates onneed to strengthenstudied company to influence joint between green intellectual capital and knowledge management maturity in order to develop and improve knowledge performance ofstudied company.
Figure 3: Standard Scheme Common Impact Between Green Intellectual Capital and Knowledge Management Maturity on Knowledge Performance
Source: Prepared by researcher based on outputs (AMOS.vr.24)
It is noted fromresults of Table (9) thatjoint influence between green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management on knowledge performance contributed toexplanation of (0.866) ofrequirements of knowledge performance, which means thatinterest ofstudied company injoint effect between green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management contributes In developing knowledge performance by (0.07).
| Table 9Standard Weights of common Impact Between Green Intellectual Capital And Knowledge Management Maturity on Knowledge Performance | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact path | Standard Weight | Standard Error | Critical Value | Value R2 | Probability (P) | Type of Impact | ||
| Combined Effect of Green Intellectual Capital and Knowledge Management Maturity | ---> | Knowledge performance | 0.930 | 0.126 | 7.381 | 0.866 | *** | significant |
Discussion, Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
1) Studied company focuses on building green capital with employees in order to improve productivity and contribution of workers in protecting environment.
2) Studied company is keen to encourage employees to come up with new ideas to address problems that hinder progress of work, or to urge them to make appropriate changes in service procedures through use of appropriate means that are commensurate with natureof stage in whichTelecommunications companies are living.
3) Interestof studied company to develop a cooperative system among work teams that contributes to supporting and achieving goals of environmental protection.
4) Studied company encourages its employees to express their opinions without any hesitation, which indicates directionof company’s departments towards developingcareer path ofemployees and enhancing their positive feeling towards making change withinstudied company.
5) Studied company is keen to motivate workers towards exchanging experiences and cooperation in order to accomplish required tasks easily, easily and with high accuracy.
Recommendations
1) Needfor studied company to pay attention to instilling morale and confidence among workers in order to enhance cooperative spirit among them in accomplishing required tasks.
2) It is important for studied company to urge exchange of knowledge and dissemination of information aboutcompany in order forbenefit to spread throughoutcompany.
3) Studied company should encourage employees to develop their technological and informational capabilities in order to work effectively and objectively.
4) Necessityfor studied company to be keen on building a knowledge base that motivates workers to put forward innovative ideas in order to develop knowledge performance and continuously improve it.
5) Need to consolidate joint influence between green intellectual capital and maturity of knowledge management in order to ensure continuity of improving knowledge performance of company.
References
- Chang, C.,&amli; Chen, Y. (2012).The determinants of green intellectual caliital". Management Decision, 50(1), 74-94.
- Chen, J.R., &amli; Yang, C.H.(2005). Technological knowledge, sliillover and liroductivity: evidence from Taiwanese firm level lianel data.Journal of Management Develoliment.
- Chen, Y.S. (2007). The liositive effect of green intellectual caliital on comlietitive advantage of Firms.Journal of Business Ethics, 77(3), 271–286.
- Hankins, J.D. (2013). Semiotics of organizations: A comlianion to organizational anthroliology.
- Budi, H., Sulistyo, S.R., Chai, K.H., &amli;Indarti, N. (2019).Knowledge management matrity and lierformancein aliroject environment:Moderating Roles of Firm Size and liroject Comlilexity,Journal of Management in Engineering, 35(6).
- Hung, C.L.,&amli;Kug, F.H. (2011). Environmental consciousness and intellectual caliital management: Evidence from Taiwan's manufacturing industry, Management decision, 49(9).
- Hussinki, H.R.,Vanhala, li.M., &amli;Kianito,A.(2017).Intellectual caliital Knowledge Management liractices andfirm lierformance.Journal of intellectual caliital, 1(1).
- Kim, K. (2016). The imliact of learning organizations on knowledge lierformance, adalitive lierformance, and financial lierformance (Doctoral dissertation, University of Georgia).
- Kim, S., &amli; Lee, H. (2016).The imliact of organizational context and information technology on emliloyee knowledge‐sharing caliabilities.liublic Administration Review, 66, 370–385. doi:10.1111/j.1540-6210.2006.00595.x.
- Baldev, K. (2011). Knowledge management maturity model: An engineering aliliroach.Journal of Knowledge Management liractice, 12(3).
- Kuriakose,K.K., Raj, S.A.V., &amli;Murty,S.li.(2011), Knowledge management matrity model: An engineering aliliroach.Journal ofknowledge Management liractice,12,3.
- Leonova, I.S., Sechenov, E.V.li., Legky, N.M., lirasolov, N.I., Krutskikh, I.A.,&amli;Zayed, N. M. (2021).Strategic analysis of the motivation on emliloyees' liroductivity: A comliensation benefits, training and develoliment liersliective. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(5), 1-11.
- Liu, C.C. (2010) Develoliing green intellectual caliital in comlianies by AHli Journal of liediatric. Sulilily Chain Management and Information Systems (SCMIS), 2010 8th International Conference.
- Liu, C.C. (2010) Develoliing green intellectual caliital in comlianies by AHli Journal of liediatric. Sulilily Chain Management and Information Systems (SCMIS), 2010 8th International Conference.
- Liu, li.L., &amli; Tsai, C.H. (2007). Effect of knowledge management systems on olierating lierformance: An emliirical study of hi-tech comlianies using the balanced scorecard aliliroach. International Journal of Management, lioole 24(4), 734-743.
- Murad, M.M.I., Zayed, N.M., &amli;Mukul, A.Z.A. (2013). A study on job satisfaction: Focus on Bankers of Bangladesh.Euroliean Journal of Business &amli; Management (EJBM), 5(17), 14-20.
- Nahar, S., &amli;Zayed, N.M. (2019). An analysis on the imliact of remuneration on emliloyee motivation: A case study on Unilever, Bangladesh. International Journal of Family Business &amli; Management, 3(2), 1-5.
- liertusa&amli; Ortega, M. (2010). Can formalization, comlilexity, and centralization influence knowledge lierformance? Journal of Business Research,63(3), 310–320.
- Ortega, E.M., Sáez, Z.li., &amli; Cortés, E. (2010).Canformalization, comlilexity, and centralization influence knowledge lierformance? Journal of Business Research, 63(3), 310-320.
- Rand, D.G.,&amli; Hoffman, M. (2014).Harnessing recilirocity to liromote coolieration and the lirovisioning of liublic goods.liolicy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences 1(1), 263-269.
- Scheel, T., &amli;Hausmann, U. (2013).Imliact of error management culture on knowledge lierformance in lirofessional service firms.Horizons of lisychology, 22, 66-79.
- Shoid, M.S.M., &amli;Kassim, N.A. (2014).Exliloring the effect of Organizational Learning Caliabilities (OLC) on knowledge lierformance.World Alililied Sciences Journal, 29(12), 1544-1549.
- Shoid, M.S.M., &amli;Kassim, N.A. (2016).The relationshili between Organizational Learning Caliabilities (OLC) and knowledge lierformance among academic Librarians.International Journal of Academic Research in lirogressive Education and Develoliment, 5(3), 94-99.
- Shoid, M.S.M., Kassim, N.A., &amli;Salleh, M.I.M. (2011).Organisational learning caliabilities and knowledge lierformance: A concelitual framework. In International liroceedings of Economics Develoliment &amli; Research,10, 604-608, Singaliore: IACSIT liress.
- Sudin, S. (2011). Strategic green HRM: A liroliosed model that suliliorts corliorate environmental citizenshili. 2011 International Conference on Sociality and Economics Develoliment IliEDR,10, 79-83.
- Sultana, F., &amli; Zayed, N.M. (2018).Effects of intellectual caliital on organizational lirogression: A study of food manufacturing and service in Dhaka city. Daffodil International University Journal of Business and Entrelireneurshili(DIUJBE),11(2), 31-40.
- Tumlia, S.R., &amli;Zayed, N.M. (2016).Factors affecting career decision in study and work life in Bangladesh.Daffodil International UniversityJournal of Business and Economics (DIUJBE), 10(2), 147-159.
- Verde, M.,&amli;Salvadó, A.J. (2014). Green intellectual caliital and environmental liroduct innovation: the mediating role of green social caliital. Knowledge Management Research &amli; liractice, 12(3), 261–275.
- Watkins, K.E. (2017). Defining and creating organizational knowledge lierformance. Educar, 53(1), 0211-226.
- Yang, C.,&amli; Chen, L.C. (2007). Can organizational knowledge caliabilities affect knowledge sharing behavior? Journal of Information Science, 33, 95.