Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
Causal Factors Influencing Business Performance Effectiveness of Community Enterprises in Chumphon Province
Mallika Subongkod, King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang Prince of Chumphon Campus
Chanyaphak Lalaeng, King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang Prince of Chumphon Campus
Abstract
The research aimed to develop a structural equation model of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province and describe causal relationship of factors like production management skills, marketing skills, leadership skills, participation skills and networking skills that influence business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province. A questionnaire was used to collect data from 385 community enterprise entrepreneurs in Chumphon province. Probability random sampling technique was used to select the sample. Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling (SEM).
The study result revealed that the structural equation model was consistent with the empirical data while production management skills, leadership skills, participation skills and networking skills had an influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province, except marketing skills did not have an influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province. The study result is useful for supporting resource-based view theory which discovered that community enterprise entrepreneurs having production management skills, leadership skills, participation skills and networking skills contributed to business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province such as sales, profit, number of customers, and internal development in a better level. Besides, the study result is practically useful for community enterprises by giving importance to marketing skills and explicit planning for developing community enterprises in Chumphon province to achieve sustainability accordingly.
Keywords:
Production Management Skills, Marketing Skills, Leadership Skills, Participation Skills, Networking Skills, Business Performance Effectiveness
Citation Information:
Subongkod, M., & Lalaeng, C. (2021). Causal factors influencing business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in chumphon province. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(S1), 1-14.
Introduction
During the past several years, Thailand encountered economic downturn many times which have a severe impact on livelihood of people in the society. People experienced poverty and did not have economic security. Consequently, a policy on addressing the country poverty was formulated by using “community enterprise” as a tool to solve the problem as a whole since community enterprise is a business for community capital management by people in community in a creative manner in order to generate income and self-reliance of families, communities and among communities. Besides, community enterprise is a component of sufficiency economy and an economic activity important to drive community economy, build stable foundation to the country. As a consequence, community enterprise is truly a principle leading to stable and sustainable economic system at the national level. The government viewed that community economy including community enterprise were the foundation of sufficiency economy development. However, at present some community enterprises are not ready to reach trade competitiveness, both domestically and internationally. A development level has not been elevated as it should be. Therefore, knowledge and local wisdom should be promoted as well as income generation, helping each other, development of management skills and development of community enterprise model, making communities achieve self-reliance while community economic system will be strengthened to be ready for trade competitiveness in the future regardless of which levels including community enterprise development to small and medium enterprises accordingly.
Community enterprise is a mechanism that helps drive community economy by adopting knowledge, local wisdom and resources in locality to produce goods and services, giving rise to employment and generating income to communities. Moreover, it enables communities to have self-reliance, resulting in driving the economy at the national level. According to the report on statistics of community enterprises granted to register, the number of registered community enterprises in 2020 increased from the previous year, accounted for 1.1%. In 2020 (data updated as at 31 March 2020), there were 87,753 registered community enterprises and had 1,474,051 members. Classified by business, most of them produce goods, i.e., plant production (27.7%), livestock production (22.1%), food processing and production (11.2%). Community enterprises with service activities that registered the most were community savings (26.6%), community stores (12.6), and tourism (8.8%) respectively (Community Enterprise Promotion Division, 2020).
Today 80% of people in Chumphon province are farmers. Agricultural lands occupy 59% of the province area, bringing the major income to the province. Moreover, Chumphon is famous for a city of various kinds of fruits which sometimes oversupply problems occur. Therefore, a lot of agricultural products are processed to generate work and income to communities. However, the potential assessment of community enterprises in Chumphon at the end of the 2nd quarter, the fiscal year 2018 found 166 community enterprises were at a good level, accounted for 42.35%, 124 community enterprises were at a moderate level, accounted for 31.63%, and 102 community enterprises needed improvement, accounted for 26.02% (Community Enterprise Promotion Division, 2020). It can be seen that some community enterprises in Chumphon are ready for trade competitiveness while some are not ready since they have numerous problems and obstacles in operations, i.e., marketing as they cannot expand their markets and have to compete with large competitors, financial and accounting problems like lack of capital, being unable to access sources of finance, lack of a good accounting system, and lack of cash flow, management problems like lack of reliability in group leaders, lack of readiness to participate in group activities, lack of information technology and lack of continuous product development. Based on the aforementioned context, it can be seen that competitive status and trends to conduct community enterprise business have been changed (Juma, 2018). This study aimed to develop a structural equation model of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province so as to describe causal relationship of factors related to production management skills, marketing skills, leadership skills, participation skills and networking skills influencing business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province and to develop new body of knowledge showing the role of leaders, participation, network creation and importance of business performance of community enterprises that partially drive economy at regional and national levels to achieve sustainability, useful for other community enterprises, government agencies and relevant agencies as a guideline for setting a policy related to business promotion to community enterprises at the national level accordingly.
Objectives of the Research
1. To develop a structural equation model of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
2. To describe causal relationship of factors related to production management skills, marketing skills, leadership skills, participation skills and networking skills influencing business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Theories and Research Conceptual Framework
Resource Based View Theory
Resource Based View Theory is the theory describing the importance of value creation on the bases of resource base. Jay Barney (1991) was the first scholar who studied the theory by proposing 4 significant attributes of resources that generate sustained competitive advantage to organizations, namely, they should be valuable (Value), rare (Rarity), imperfectly imitable (Imitability) and not substitutable (Non-Substitutable). The resource-based view requires 2 major components, i.e., resources and capabilities. Both components generate sustainable competitive advantage. Environmental changes both inside and outside organization in the globalization era encourage organizations not to stay in place. Without the improvement of organizational business performance, they fail to compete with competitors and cannot survive. Based on such competition, numerous organizations pay attention to what they already exist, namely, resources which are divided into tangible and intangible resources. Creating sustained competitive advantage for conducting business nowadays is considered important (Barney, 2001). Meanwhile organizations should allocate existing resources to reach maximum benefits in terms of efficiency and effectiveness including carrying out the operations to reach the set objectives and goals. Competitive advantage will be successful when organizations utilize existing resources to achieve sustainability by using organization resource mix in order to resist competitors’ capabilities not to imitate.
In this study the factor related to capabilities of community enterprises were employed since organizational survival generally depends on business management skills from working skills having an effect on business effectiveness and success. Therefore, the resource based view theory was adopted to determine the research conceptual framework modified from the conceptual framework of a study conducted by Tantasuntisakul (2015) to prove that factors existing in community enterprises, i.e., production management skills, marketing skills, leadership skills, participation skills, and networking skills will have an effect on effectiveness and success of community enterprise business performance.
Concept About Business Performance Effectiveness
Business performance effectiveness is the success of organizational operations for achieving the objectives within the set timeframe. Researchers define the meaning of effectiveness as capabilities of organizations to carry out production to produce products successful according to the set goals, consistent with Lawrence (2018) saying that organizational effectiveness is capabilities of organizations to achieve the set goals, both short-term and long-term goals that will lead to stable and sustainable progress of organizations. In the meantime, both government and private organizations are widely interested in and give importance to organizational performance assessment. Performance measurement is a process to assess organizational performance and progress to ensure the performance meets the set goals. According to the study of related research documents, the meaning of operational performance is given by several people; for example, Rekarti & Doktoralina, (2017) defines operational performance as outcomes produced when compared to the set goals. Anand, et al., (2017) define business performance as measuring of organizational capabilities in adapting themselves to keep pace with business environment such as customers, competitors and other factors that can change business performance. Valmohammadi & Roshanzamir, (2015) confirm that organizations having better management and strategies than competitors in conjunction with efficient financial plans will enjoy efficient business performance. Roman & Rastislav, (2015) claim that operational performance assessment of community enterprises can be divided into 3 perspectives, i.e., profit, product, and marketing. Business performance in terms of profit is measured from financial success that organizations determined. Business performance in terms of product depends on customer response and efficient employment. Business performance in terms of marketing depends on success in sales, market positioning, and market share. Therefore, in this study, the researcher determined effectiveness of business performance on the basis of finance, customers, internal process, learning and development which are indicators for the assessment of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Concept about Relationship between Production Management Skills and Business Performance Effectiveness
Production management skills are one of significant skills that entrepreneur in each organization should have since they consist of several important dimensions such as production skills, technology, innovation, quality standard, engineering design process, forecast, material requirement planning and other conditions related to the development of organizational competitive advantage necessary for organizational operations in an efficient manner. A research study conducted by Haleem, Jehangir & Baig, (2017) said that the competitive strategy having the highest influence was the lowest cost production management, followed by product quality strategy, flexibility strategy, and on-time delivery strategy. All these strategies result in business performance effectiveness and enable business performance to gain more efficiency. Lawrence, Amuhaya & Maurice, (2018) conducted a study on influence of competitive strategies on business performance of sugar industry in Kenya. The study result confirmed similarly that competitive strategies like production, cost, quality, delivery, and flexibility had a positive influence on business performance of sugar industry in Kenya. Based on the discussion mentioned earlier, production management skills seem to be one of the most significant skills having an effect on business performance of entrepreneurs and they must be further studied. The researcher determined research a research hypothesis as
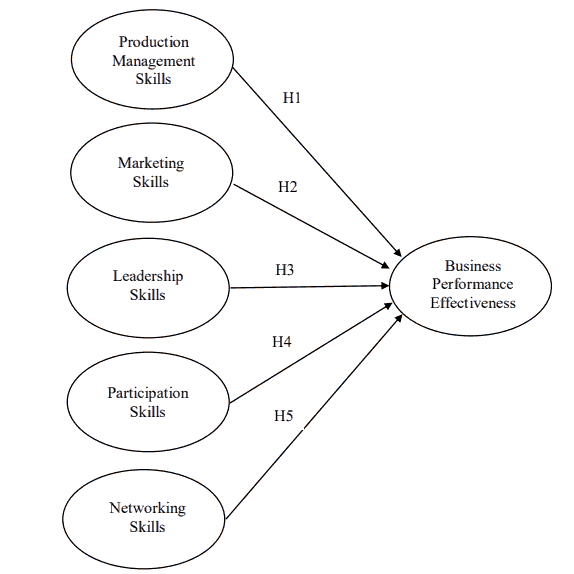
H1: Production management skills are positively related to business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Concept about Relationship between Marketing Skills and Business Performance Effectiveness
Marketing skills are one of important knowledge for entrepreneurs who strive for success. Entrepreneurs should develop business strategies from SWOT analysis and marketing activities planned to implement. According to a study conducted by Daniel (2018) on effects of marketing strategies on organizational performance, the findings from the study showed that marketing strategies comprising product, price, promotion, and place had an influence on sales, customers, organizational performance in a better level. A study conducted by AL Ashed & Hossain, (2019) proved that market focus, customer focus and brand focus had a positive influence on operational performance of SMEs. Besides, many researchers focus on electronic marketing strategies (e-Marketing). Adede, Kibera & Owino, (2017) confirm that e-Marketing is positively related to business performance. They further described that e-Marketing strategies used in any organization would help their business performance gain more efficiency. According to the review of literature related to marketing that influences on business performance effectiveness as mentioned earlier, the researcher determined a research hypothesis as
H2: Marketing skills are positively related to business performance of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Concept about Relationship between Leadership Skills and Business Performance
Leadership skills are one factor affecting a group process in order to achieve the set goals. They are also pressure producing collaboration that leads to efficient business performance. Firestone (1996) studied leadership skills and found that leaders with various skills would lead their organizations to succeed, consistent with a study conducted by Ojokuku, et al., (2012) finding that thinking skills among exchange leaders and transformational leaders have an effect on success in business performance at a high level. It is consistent with a study conducted by Sebahattin, et al., (2014) finding that leadership skills are important factors in management as they help elevate efficiency and effectiveness at work. In other words, the success or failure of organizations greatly depends on leadership. Good leaders shall develop co-workers to collaborate in planning, monitoring and describing operational performance regularly, making organizations strong and gain more competitive advantage. In addition, it is found that knowledge, attitude and action of community enterprise leaders of community products are related to business strength and operations, i.e., management structure, production and factors of production, and marketing. Based on the review of literature related to leaderships influencing business performance effectiveness, the researcher determined a hypothesis as
H3: Leadership skills are positively related to business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Concept about Relationship between Participation Skills and Business Performance Effectiveness
Participation skills play a significant role in economic and social development. Allowing a chance to members for participating in different activities of organizations will help communities and organizations receive both direct and indirect benefits and help build relationship among members, communities and societies, giving rise to knowledge exchange and sharing. A study conducted by Nazim (2014) found participatory management in organizations had an effect on efficiency at work. Participatory management of members in terms of trust and reliability, goal and objective setting, and independence at work contributes to efficiency at work in organizations, consistent with a study conducted by Rhokeun (2015) finding that participatory skills would give rise to better operational performance, better quality of decision-making, promote work improvement and high possibility, co-workers would be satisfied with the operations more and more. Benefits of participatory management increases efficiency at work, producing a higher amount of work done and effective organizational business performance. A study conducted by Joseph, et al., (2015) found participatory management among executives had an effect on organizational effectiveness in terms of organizational commitment, and organizational goal and objective setting. Consequently, member participation will help build satisfaction to a chance to grow and satisfaction at work of employees. Member participation encourages organizations to be able to set their goals and objectives, making the operations achieve the set goals easier. Based on the review of literature related to participation skill influencing business performance effectiveness, the researcher determined a research hypothesis as
H4: Participation skills are positively related to business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Concept about Relationship between Networking Skills and Business Performance Effectiveness
Networking skills are a part to enable business operations to achieve the set goals since they are techniques for self-adaptation of organizational survival. The gathering of many small sized organizations that can maintain their outstanding features will make changes to medium sized and small sized organizations in being able to operate their businesses for survival and build competitive advantage. Meanwhile, building alliances and relationship among government agencies, private agencies, and other relevant persons will allow organizations a chance to have knowledge sharing and be able to adapt themselves to blend with all time changing environment, making organizational operations stable and strong. A study conducted by Peter, et al., (2014) found business networks were positively related to operational performance of SMEs business since business networks enable organizations to access news, information, resources and knowledge. SMEs businesses have limited internal resources, making them seek and connect resources from agencies outside their organizations; for example, collaboration among industry groups in which SMEs are members. If large-sized industry networks give innovation assistance to SMEs, the overall industry costs of production will be decreased and uncertainty in delivering raw materials from SMEs will be reduced as well, giving rise to competitive advantage and an increase in business performance effectiveness (Nuryakin et al., 2018). Based on the review of literature related to networking influencing business performance effectiveness, the researcher determined a research hypothesis as shows in Figure 1.
H5: Networking skills were positively related to business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Method Used to Conduct the Study
Population and sample: The study was conducted using a quantitative research method. A questionnaire was used to collect data from the sample. The research sample is 385 community enterprise entrepreneurs in Chumphon province. This is consistent with the advice of a lot of researchers such as Hair, Black, Babin & Anderson, (2010). The advice shows that the minimum sample size taken should be at least 200. Thus, the sample of 385 persons is enough for a structural equation modeling analysis (SEM) according to the aforesaid researchers’ advice and reasons.
Instrument Used for Data Collection
A questionnaire was used to collect data. The questionnaire divided into 3 parts as Part 1 is general information of respondents, i.e., gender, age, marital status, levels of education, monthly income, job position in community enterprise, and duration of membership; Part 2 is various factors influencing business performance effectiveness and part 3 is factors of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province. Independent variables in this study were improved from the study conducted by Tantasuntisaluk (2015) and Ruslee, et al., (2020), which include production management skills (4 items), marketing skills (5 items), leadership skills (4 items), participation skills (4 items), and networking skills (4 items). Dependent variable was business performance effectiveness improved from the study conducted by Collins (2007), in 4 aspects, i.e., finance (4 items), customer (4 items), internal process (4 items), and learning and development (5 items). Likert rating scale was employed to measure 5 levels of business performance. 1 means strongly disagree and 5 means strongly agree.
Before the questionnaire was brought to collect data, the researcher developed it by measuring its validity or index of item objective congruence (IOC). Its IOC value ranged from 0.67 to 1.00, higher than the 0.5 criterion (Rovineli & Hambleton, 1977). Reliability of the questionnaire was examined and Cronbach alpha’s coefficient ranged from 0.71 to 0.91, higher than the 0.7 criterion (Nunnally, 1978). Therefore, the questionnaire was suitable to collect data from the sample.
Statistics in Analysis
Before data analysis was performed, the researcher examined and screened completeness of data and analyzed preliminary data that were collected by using descriptive statistics, i.e., frequency and percentage. Before structural equation modeling analysis was performed, the researcher examined normal distribution, multicollinearity, construct validity of latent variable measurement in the model by using structural equation modeling analysis according to the hypotheses and the collected empirical data. The model was improved to be consistent with the empirical data as much as possible by considering index values appeared in analysis results in each procedure of the process in programming and creating the relationship model consistent with the collected empirical data. Effect size was analyzed, hypotheses were tested, and relationship among variables having a direct influence on the dependent variable in the research conceptual framework was described.
Research Results
Most respondents were women (70.4%) with 41-50 years of age (36.6%), married (66.0%). Most of them (82.1%) finished their education lower than a bachelor’s degree, had monthly income lower than 15,000 baht (69.3%). Their job position in community enterprises was members (90.1%). Most of their membership ranged from 5 to 10 years (55.6%). Details are shown in Table 1.
| Table 1 Number And Percentage Of Respondents Classified By Personal Information |
||
|---|---|---|
| Personal information | Number | Percentage |
| Gender -Male -Female |
114 271 |
29.6 70.4 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Age -20-30 years -31-40 years -41-50 years -50 years or more |
56 125 141 63 |
14.5 32.5 36.6 16.4 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Material status -Single -Married -Widow / Divorce |
316 66 3 |
82.1 17.1 0.8 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Levels of education -Lower than a bachelor’s degree. -A bachelor’s degree. -Higher than a bachelor’s degree. |
316 66 3 |
82.1 17.1 0.8 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Monthly income -Less than 15,000 baht -15,000 – 30,000 baht -30,001 – 45,000 baht -45,001 – 60,000 baht |
267 89 28 1 |
69.3 23.1 7.3 0.3 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
Testing construct validity using exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory factor analysis.
1) Exploratory factor analysis result: preliminary factor extraction was conducted using principal component analysis. Factor extraction was determined with Eigen value greater than 1. Factor loading of variables was calculated using factor rotation, Varimax method. Variables whose factor loading greater than 0.50 were selected to join factors. Correlation coefficient matrix between each pair of variables was analyzed and it should be different from zero which was tested by Bartlett’s test of Sphericity with statistical significance and Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy (KMO) that should be close to 1. With regard to the exploratory factor analysis using different criteria mentioned earlier, variables had related factors. However, in this study the researcher cut observed variables of some skill factor variables, namely, production management skills - PMS3, marketing skills – MKS4 and MKT5, participation skills – PAS4, and networking skills – NWS4 since factor loadings were lower than the criteria. Details of suitable values of data for factor analysis are shown in Table 2.
| Table 2 Suitable Values of Data for Factor Analysis |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | KMO value | Barlet Test of Sphericity (BTOS) | df | P value |
| Production management skills | 0.617 | 88.209 | 3 | 0.000 |
| Marketing skills | 0.570 | 64.693 | 3 | 0.000 |
| Leadership skills | 0.701 | 324.584 | 6 | 0.000 |
| Participation skills | 0.622 | 170.789 | 3 | 0.000 |
| Networking skills | 0.628 | 157.186 | 6 | 0.000 |
| Business performance effectiveness | 0.822 | 771.740 | 6 | 0.000 |
2) Confirmatory factor analysis result found the relationship model between each latent variable and empirical was consistent with the empirical data. Besides, the test of goodness of fit of the measurement model using construct reliability (CR) and average variance extracted (AVE) of all latent variables found CR of all variables was above 0.70 and AVE of all variables was greater than 0.50, complying with the criteria (Hair et al., 2010). It means that the latent variable measurement model of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province has quality that meet the required criteria. Details are shown in Table 3.
| Table 3 Overall Consistency Test Result of the Measurement Model |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Sub-Construct | Factor Loading | CR (> 0.7) | AVE (> 0.5) |
| Production management skills | PMS1 | 0.76 | 0.769 | 0.526 |
| PMS2 | 0.70 | |||
| PMS4 | 0.72 | |||
| Marketing skills | MKS1 | 0.59 | 0.740 | 0.501 |
| MKS2 | 0.78 | |||
| MKS3 | 0.72 | |||
| Leadership skills | LSS1 | 0.82 | 0.831 | 0.552 |
| LSS2 | 0.70 | |||
| LSS3 | 0.74 | |||
| LSS4 | 0.70 | |||
| Participation skills | PAS1 | 0.82 | 0.812 | 0.591 |
| PAS2 | 0.68 | |||
| PAS3 | 0.80 | |||
| Networking skills | NWS1 | 0.83 | 0.782 | 0.547 |
| NWS2 | 0.66 | |||
| NWS3 | 0.72 | |||
| Business performance effectiveness | FIN | 0.88 | 0.912 | 0.723 |
| CUS | 0.87 | |||
| INP | 0.78 | |||
| LAD | 0.87 | |||
According to Table 3, parameter estimation result of the measurement model found the overall measurement model based on factor loadings of all observed variables had standardized factor loading in all observed variables above 0.65. It was found that standardized factor loadings met the criteria, ranging from 0.59 to 0.88 (Awang, 2010) construct reliability (CR) ranged from 0.740 to 0.912 which met the criteria. According to the criterion of Hair et al. (2010), construct reliability of good latent variables should be above 0.70, meaning that the construct validity of this model met the criteria. Average variance extracted (AVE) of latent variables ranged from 0.501 to 0.723, higher than 0.5 which is acceptable (Hair et al., 2010). It indicates that measurement error causing more variance in observed variables than in monitored latent variables did not occur.
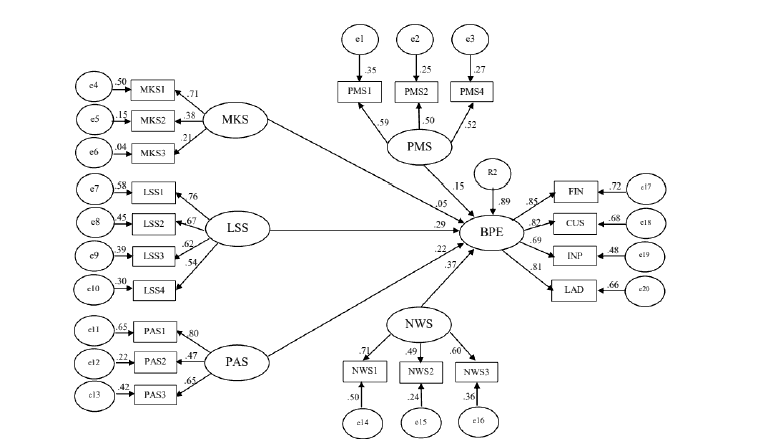
3) Structural equation modeling analysis result to test consistency of the structural equation model with the empirical data found the causal factor model influencing business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province was consistent or fit with the empirical data. Chi-square/Degree of Freedom (x2/df) was 1.966, TLI was 0.941, CFI was 0.957 and RMSEA was 0.050. The conformity of the structural equation model can be shown as shown in Table 4 and Figure 2.
| Table 4 Consistency (Goodness of Fit Index ) of Structural Equation Model |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goodness of Fit Index | Criteria | Measured value | References | Consideration result |
| Chi-square/Degree of Freedom c2/df (Relative Chi-square) |
< 3 | 1.966 | Bagozzi and Yi (1988) | Passed the criteria |
| Tucker Lewis Index (the index used to detect noninvariance in the measurement invariance testing context) | >.90 | 0.941 | Hair et al., (2010) |
Passed the criteria |
| Comparative Fit Index (CFI) | >.90 | 0.957 | Hair et al., (2010) |
Passed the criteria |
| Root Mean Square Error of Approximate (RMSEA) | <.08 | 0.05 | Hair et al., (2010) |
Passed the criteria |
Figure 2: Structural Equation Modeling Analysis Result of Factors Influencing Business Performance Effectiveness of Community Enterprises in Chumphon Province.
Chi-square=269.281, df=137, p=0.000, CMIN/DF=1.966, RMSEA=0.050, CFI=0.957, GFI=0.934, TLI=0.941, RMR=0.008
The test results of hypotheses determined respectively are summarized in Table 5 as follow:
Hypothesis 1: The hypothesis test result found production management skills had a positive influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province with statistical significance (β=0.166, p<0.05). The hypothesis 1 was accepted.
Hypothesis 2: The hypothesis test result found marketing skills did not have an influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province with statistical significance (β=-0.121, p>0.05). The hypothesis 2 was rejected.
Hypothesis 3: The hypothesis test result found leadership skills had a positive influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province with statistical significance (β=0.356, p<0.05). The hypothesis 3 was accepted.
Hypothesis 4: The hypothesis test result found participation skills had a positive influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province with statistical significance (β=0.160, p<0.05). The hypothesis 4 was accepted.
Hypothesis 5: The hypothesis test result found networking skills had a positive influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province with statistical significance (β=0.349, p<0.05). The hypothesis 5 was accepted.
Furthermore, consideration of the variance (R2) of the structural equation model of factors influencing business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province found relationship among production management skills (PMS), marketing skills (MKS), leadership skills (LSS), participation skills (PAS), networking skills (NWS). The variance (R2) of community enterprises in Chumphon province was 0.89, meaning that this model could describe relationship among production management skills (PMS), marketing skills (MKS), leadership skills (LSS), participation skills (PAS), networking skills (NWS) to business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province by 89%. as shows in Table 5.
| Table 5 Path Analysis Result of Relationship Between Independent and Dependent Variables in the Structural Equation Model |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothesis | Constructs relationships | Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | P | Result | ||
| H1 | PMS | ---> | BPE | 0.166 | 0.082 | 2.030 | 0.042 | Significant |
| H2 | MKS | ---> | BPE | -0.121 | 0.294 | -0.410 | 0.682 | Not Significant |
| H3 | LSS | ---> | BPE | 0.356 | 0.130 | 2.727 | 0.006 | Significant |
| H4 | PAS | ---> | BPE | 0.160 | 0.074 | 2.144 | 0.032 | Significant |
| H5 | NWS | ---> | BPE | 0.349 | 0.107 | 3.269 | 0.001 | Significant |
Remark: R2=0.89, PMS=production management skills, MKS=marketing skills, LSS=leadership skills, PAS=participation skills, NWS=networking skills, BPE=business performance effectiveness.
Discussion and Conclusion
The study on causal factors influencing business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province found the causal factors influencing business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province were production management skills since production is a major factor to produce goods. It starts from preparedness of raw materials, calculation of raw materials used to meet requirements of production, preparedness of equipment, tools, machines for production, quality inspection of products and production capacity to ensure they meet customer requirements. They show readiness of businesses and enable businesses to achieve agility, consistent with a study conducted by Haleem, et al., (2017).
In this study shown that marketing skills have not influence on business performance effectiveness. Marketing skills does not have important role and impact on organizational performance. In essence, marketing skills are not useful tools for survival, sustenance and expansion of organizations (Prinka et al., 2019). Though marketing skills expenditures are funds of companies that are allocated to spending on advertising and other marketing communication activities such as digital and mobile marketing, press conferences, experiential marketing events and sales promotions (Seltuk et al., 2021). Marketing spending is an investment that will contribute value to the company in the future especially for emerging markets. It is easier for organization to raise new funds in times of high investor sentiment (or investment optimism) on the stock market, so companies generally decrease their advertising spending during periods of low investor sentiment. However, it is recommended to continue marketing investments even during the periods of investor pessimism and market recession because these investments contribute to company success during and after such downturn periods (Mian et al., 2018).
In the meantime, leadership skills have an influence on business performance effectiveness. Successful organizations require leaders who possess knowledge, capability and are brave enough to make decision and are ready to learn and adapt themselves at all times. Leaders will be able to build influence or motivation and encourage other people to work on to achieve efficiency and build organizational success (Francis, 2018). Leadership is considered highly important to successful management. Organization development should start from building leadership in organization leaders. It begins with qualifications of self-leadership that other people can feel. Leaders must have a scientific approach and artistic approach, making them more outstanding than anyone in a group, being accepted and given trust and reliability that they can lead organizations to success by receiving collaboration. In addition, leaders must be respected, being a part to promote business operators as organization leaders to operate their business in a more efficient manner (Arhan, 2014).
Participation skills had an influence on business performance effectiveness since participation is a social dimension, consistent with a study conducted by Peter & David, (2018) finding that participation is social interaction of people in organizations under mental connection of a group of people who participate in business operations to generate benefits from collaboration. Participatory process can occur directly and indirectly. As soon as people in organizations work in collaboration and have responsibilities, the process of operations shall achieve the organizational goals. Emphasis should be placed on brainstorming, opinion giving, decision-making and operation planning for monitoring and assessment (Umair et al., 2020).
Networking skills have an influence on business performance effectiveness since running a business alone cannot succeed. Therefore, building relationship in running the business will make long-term growth in a sustainable manner. Running a business aims to seek mutual benefits by emphasizing the development of relationship with customers, employees, and suppliers of factors of production (Umrani et al., 2016). Meanwhile, interaction with government agencies, private agencies or relevant agencies will provide channels for business development while new technologies will be employed in businesses to meet success further in the future.
Conclusion and Suggestions
The study aimed (1) to develop the structural equation model of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province, (2) to describe casual relationship of factors related to production management skills, marketing skills, leadership skills, participation skills and network creation skills that have an influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province. Data were collected from community enterprise entrepreneurs in Chumphon province. Overall it can be concluded that the structural equation model of business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province, developed from related concepts and theories, is consistent with the empirical data. Causal relationship can be described that production management skills, leadership skills, participation skills, and network creation skills had an influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province. However, it is found that marketing skills did not have an influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises in Chumphon province.
Academic Suggestions
This study is a development of the causal model that comprises 2 theories, i.e., resource based view theory and concepts about business operational performance. It is found that production management skills, leadership skills, participation skills and network creation skills had an influence on business performance effectiveness of community enterprises.
Suggestions for Entrepreneurs
Community enterprise entrepreneurs can adopt the research result for their business planning and development to ensure the operations will meet the set goals and objectives. It can be used as a guideline for managing production, marketing, leadership, group participation, interaction with outside sources to ensure their products are known and produced to meet consumer requirements. This would help generate more sales, income, and number of customers, producing learning and business development in a sustainable manner at the same time.
Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research
1. This study was conducted using a quantitative study design based on the review of related literature and research studies in order to develop a research instrument. Data were collected and analyzed according to the concept of quantitative research to obtain overall data to be used as a guideline for developing other community enterprise groups in Chumphon province. Future research should be conducted on the basis of a qualitative study design through an in-depth interview or group discussion so as to obtain in-depth data for developing business operations of community enterprises in a more efficient manner.
2. Spatial restriction in this study was the sample. The sample was selected within Chumphon province, a province with community enterprise operations, making suggestion from this research is majorly beneficial to community enterprises in Chumphon province. For future research, the structural equation model developed from this research should be applied to the sample living outside Chumphon province so as to be useful and to be a guideline for community enterprise entrepreneurs in a more comprehensive manner.
References
- Adede, O.A., Kibera, F.N., & Owino, J.O. (2017). Electronic marketing practices, competitive environment and performance of telecommunications companies in Kenya. British Journal of Marketing Studies, 5(5), 60–67.
- Al Asheq, A., & Hossain, A.U. (2019). SME performance: Impact of market, customer and brand orientation. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 23(1), 1-9.
- Anand, P., Sanjay, K.J., Kapil, D.P., & Abhishek, K.S. (2017). Productivity, quality and business performance: An empirical study. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 66(1), 78-91.
- Arham, A.F. (2014). Leadership and performance: The case of Malaysian SMEs in the service sector. International Journal of Asian Social Science, 4(3), 343-355.
- Awang, Z.H. (2010). Research methodology for business and social science. Pusat Penerbitan Universiti: Universiti Teknologi MARA.
- Bagozzi, R.P., & Yi, Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation models. Journal of the academy of marketing science, 16(1), 74–94.
- Barney, J.B. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of management, 17(1), 99–120.
- Barney, J.B. (2001). Is the resources-based view a useful perspective for strategic management research? yes, Academy of Management Review, 26, 41–46.
- Community Enterprise Promotion Division, Community Enterprise Registration and Information Group. (2020). Summary of the approved register number of community enterprises and community enterprise networks. Retrieved from http://www.sceb.doae.go.th/Documents/STC/310363.pdf
- Daniel, C.O. (2018). The effects of marketing strategies on organizational performance. International Journal of Business Marketing and Management, 3(9), 1–9.
- Firestone, W.A. (1996). Leadership: Roles or functions? k . leithvvood ve diğ. (eds.), International Fl and book of educational leadership and administration, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands: 395-418.
- Francis, O. (2018). The impact of leadership styles of small business owners/managers on firm performance. The International Journal of Business & Management, 5(8), 191-199.
- Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., & Anderson, R.E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
- Haleem, F., Jehangir, M., & Baig, A. (2017). Operations strategy practices of SMEs. Global economics review, 2(1), 12–23.
- Joseph, B., Richard, F., & Douglas, K. (2015). Do broad-based employee ownership, profit sharing and stock options help the best firms do even better?. British Journal of Industrial Relations, 54(1), 55–82.
- Juma, M. (2018). Factors affecting the competitiveness of small and medium muslim entrepreneur in three southern border provinces. Journal of Pacific Institute of Management Science, 4(1), 218–230
- Lawrence, O.O., Amuhaya, I.M., & Maurice, S. (2018). Effect of competitive priorities on the operations performance of sugar manufacturing firms in Kenya. The International Journal of Business & Management, 6(3).
- Mian, G.M., Sharma, P., & Gul, F.A. (2018), “Investor Sentiment and Advertising Expenditure”. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 35, 611-627.
- Nazim, H. (2014). Effect of direct participation on perceived organizational performance: A case study of banking sector of Pakistan. European Journal of Business and Management, 6(1).
- Nunnally, J.C. (1978). Psychometric Theory (2nd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- Nuryakin, R.W., & Indah, F. (2018). Network advantage: Mediating effect on business performance. Scientific Annals of Economics and Business, 65(4), 443-457.
- Ojokuku, R.M., Odetayo, T.A., & Sajuyigbe, A.S. (2012). Impact of leadership style on organizational performance: A case study of Nigerian banks, American Journal of Business and Management, 1(4), 202-207.
- Peter, B., & David, N. (2018). Effect of employee participation on organizational performance with organizational commitment as a moderator. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management, 6, 478-485.
- Peter, N., Ghasem, Z., Zhaleh, N.T., Saeed, N., & Reze, Z. (2014). The influence of network effects on SME performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 43(4), 630 – 641.
- Prinka, S.B., & Pankaj, S. (2019). Effects of marketing strategies on organizational performance. Conference Proceedings of International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, 1-7.
- Rekarti, E., & Doktoralina, C.M. (2017). Improving business performance: A proposed model for SMEs. European Research Studies Journal, 20(3), 613–623.
- Rhokeun, P. (2015). ‘Employee participation and outcomes: Organizational strategy does matter", employee relations, 37(5), 604 – 622. From www.emeraldinsight.com/0142-5455.htm.
- Roman, Z., & Rastislav, R. (2015). Strategic business performance management on the base of controlling and managerial information support. 4th World Conference on Business, Economics and Management, WCBEM. Proceeding of Economics and Finance, 769 – 776.
- Rovinelli, R.J., & Hambleton, R.K. (1977). On the use of content specialists in the assessment of criterion-referenced test item validity, Dutch. Journal of Educational Research, 2, 49–60.
- Ruslee, N., Tawat, N., & Aris, H. (2020). Causal factors affecting business performance of halal community enterprises in 3 provinces of Southern border. Journal of Business Management, 43(168), 58-82.
- Sebahattin, Y., Faruk, B., & İlknur, T.B. (2014). The effect of leadership and innovativeness on business performance. 10th International Strategic Management Conference Social and Behavioral Sciences, 785 – 793.
- Selçuk, K., Petek, T., & Mesut, D. (2021). The impact of marketing on the business performance of companies: a literature review. Journal of Social Sciences of Mus Alparslan University, 9(1), 63–74.
- Tantasuntisakul, W. (2015). Determinants of business performance among women entrepreneurs in Southern Thailand. PhD. University Utara Malaysia, Malaysia.
- Umair, A., Waheed, A.U., Umer, Z., Sheraz, M.R., & Tariq, A. (2020). Corporate entrepreneurship and business performance: The mediating role of employee engagement. 1-10.
From https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/. - Umrani, W.A., Mahmood, R., & Ahmed, U. (2016). Unveiling the direct effect of corporate entrepreneurship’s dimensions on the business performance: A case of big five banks in Pakistan. Studies in Business & Economics, 11(1), 181–195.
- Valmohammadi, C., & Roshanzamir, S. (2015), “The guidelines of improvement: Relations among organizational culture, TQM and performance”, International Journal of Production Economics, 164, 167-178.