Research Article: 2021 Vol: 27 Issue: 3
Calendar Criteria for Selection of the Educational Supervisors in Secondary Schools From the Point of View of Teachers
Omar Azhar Ali, University of Baghdad
May Faisal Ahmed, University of Baghdad
Abstract
A field study aimed to identify the calendar selection criteria for the educational supervisors in secondary schools from the point of view of teachers, the research adopted the descriptive analytical approach. The research community, which consists of (3981) Faculty of education, was identified. The research sample was selected in a simple random way by (10%) of the research community, as the number of sample members (400) from my teaching. A questionnaire was built which included (36) paragraphs divided between areas (general terms, personal terms, technical terms and selection procedures). Make sure she's honest and consistent. The research data was analysed using the program (SPSS), and reached the most important results: that the rate of the year and the overall results of the questionnaire were very high and exceeded (91%), which is a high satisfaction index of the sample for the standards in their general form, and that the paragraph setting a schedule for all procedures has been In addition, a number of recommendations and proposals relating to the research were made.
Keywords
Transition Techniques, Students’ Behavior, Challenging Behavior.
Search Problem
It is necessary to select the appropriate educational supervisor .the qualitative change in the educational supervisor in theory and practice poses great challenges for those responsible for the educational supervisor to keep pace with this constant change. The most important of these challenges is the selection of the right person for the position of educational supervisor. This makes it necessary to review the basis and criteria for selecting the educational supervisor. Work to develop them to eventually produce the best elements for this difficult task.
The following search problem is summarized:
- What you say is the selection criteria for the educational supervisors in secondary schools from the point of view of teachers.
- Are there significant differences at the level of(0.05 =&) between the averages of the research sample answers in relation to the evaluation of the selection criteria of educational supervisors attributed to the following variables: (gender, number of years of Service).
Importance of Research
The Importance of Research is illustrated by
- The importance of educational supervision as a tool through the follow-up of educational and educational work.
- The importance of the calendar itself as a means by which to issue a judgment on the criteria adopted in the selection of Supervisors.
- The importance of the touchstones standards can be checked on the quality of the selection of educational supervisors.
- The theoretical and cognitive importance of the scientific material added by this research can enrich the educational library, especially with the scarcity of theoretical literature and previous studies in this subject.
- Applied importance, the research is expected to provide proposals and recommendations that can be used to evaluate the selection of standards of educational supervisors.
- The educational supervisor is one of the most important inputs to the educational system, which affects the processes involved in it and the resulting educational and educational outcomes.
- The educational Supervision Authority where it is expected to benefit from this research by standing on Strengths and weaknesses of the criteria for selecting pedagogical waveguides.
Research Objectives
The current research aims to identify the evaluation of the selection criteria of educational supervisors in secondary schools from the point of view of teachers, and the goal branched into the following two questions:
- Evaluation of the selection criteria for secondary school educational supervisors from the point of view of teachers.
- Are there statistically significant differences at level (0.05 =&) between the averages of the answers of the research sample in relation to the calendar selection criteria for the educational supervisors attributed variables following :(sex, experience).
Search Limits
Spatial boundaries: secondary schools in Riba districts (al-Rusafa /1 and Al-Karakh / 1)
Human Boundaries: teachers and female teachers in secondary schools in madriatin.
Time Limits: First Semester Academic Year 2019.
Definition of Terms
Calendar
Imam defined 1990 as: ((Provision of information, supplies and means to enable the evaluator to render judgment) (Imam, 1990).
And defined (Biggs & Collis, 1992) as: ((A process that involves making a judgment on the value or quantity of a particular object in the light of a particular criterion on the basis of a comparison between the reality of that object or the phenomenon that you want to recalibrate between the sources we have identified)) (Biggs & Collis, 1992).
Know her (Al-Azimi & Al-Halou, 2000): It is “a comprehensive process that involves making a particular judgment and in the light of which development and improvement is carried out” (Great, sweet, 200).
Procedural Definition of the Calendar
It is to make a judgment on the selection criteria of secondary school educational supervisors in the light of the responses of the sample search for the paragraphs of the tool used.
Standards
Standard Language: The intermediate lexicon stated in its statement that it is “a verifiable or perceived model of what should be on it the thing and combine criteria” (Median lexicon, PT: 639).
Know her (Fathallah, 2005): It is “a spoken expression of what the work should be” (Fathallah, 2005).
Know her (Al-Tanawi, 2005): “The basis of judgment is the knowledge of learners, and the extent to which progress is made in business to achieve consistency, coherence and consistency.” (Al-Tanawi, 2005)
Educational Supervision
“A collaborative leadership process that deals with the educational situation in all its elements, including curricula, means, environment, teacher and student, and aims to study and evaluate the factors affecting that situation to work towards its improvement and organization in order to achieve the best objectives of learning and education” (Al-Asadi & Ibrahim, 2003).
Educational Supervisor
An individual with Vision Critical, he can pay his scientific career to detect strengths and weaknesses in the process of translation school, especially related to education, then routed for more positive and tender (Morteza & Abu Noor, 2009).
Standards of Educational Supervisors
It is the basis on which the process of selecting educational supervisors is based, which determines the success of educational supervision in achieving its objectives to improve the educational process (Al-Azazi, 2016).
Theoretical Background
Calendar
A calendar is an organized administrative process that analyzes all potential, information and performance results. Through it is known the accuracy in setting goals and the suitability of plans for the available possibilities, and know the problems that appear when implementing the plan and the size of the achievement achieved through the goals set, and the calendar is comprehensive, continuous and varied according to scientific foundations (Barhoum, 2006).
The administrative work of educational supervisors requires constant decision - making, some of which serve time-consuming purposes and some of which are related to distant goals, and these decisions are not correct if they are not based on the process of continuous evaluation of material and human resources (teachers), plans, programs, strategies used and the means used and the organization of time (Sammy, 2001).
The evaluation process clarifies the strengths and weaknesses of the performance of individuals and departments, identifies the sites and areas that need improvement and adjustment .it is one of the basic tasks of the educational institution. It does not assist in making administrative decisions on established grounds. In order to benefit from the evaluation process, the factors that are evaluated must be related to work, can be estimated and measured. The evaluation process is built on known and specific grounds and helps to compare the performance of the worker with the goals set, expectations or work requirements (Neriman, 2015).
Educational Supervision
The supervision process is one of the important educational processes that has undergone significant development over the past years .after being concerned with inspection and monitoring of teachers & apos; mistakes, it has become in the modern concept a cooperative process aimed at improving and developing the educational situation in all its elements and components by improving the performance of the teacher and equipping him with a set of necessary educational competencies and cooperating with him in diagnosing strengths to enhance them, diagnosing weaknesses and trying to remedy them to improve the educational situation and achieve the desired goals. The supervision process has been subjected to a range of concepts, which have been mentioned by a number of educators (Muhammad, 2007).
The system of educational supervision as part of the educational system as a whole, occupy considerable space studies, in each state select the criteria for the selection of staff, and expertise to be met for applying for a job stuff, in America, choose the foundations of the appointment of the staff from the national level to the local level, are selected on the basis of their understanding things to upgrade, and France is set to the educational supervisors need the degree, and teaching experience of not less than five years (Nariman, 2015).
It is required to evaluate teachers and work on their continuous training, and to activate research, creativity and educational production, as well as attention to the student in terms of his abilities, level, problems and needs, and work with the teacher to develop abilities and raise the level, solve problems and meet the needs; thus we get a diligent student, a lover of He represents the administration in the field of field work, is keen to implement the goals, policies and curricula and the directives approved by him. He is qualified to play a leading role in the field of education, because he is responsible for improving the educational and learning process by improving the performance of the teacher, and is charged with activating the educational development movement in the schools he oversees (Al-Azazi, 2016).
We can define the Objectives of Educational Supervision in the Following Matters
- Improve the teaching and learning process by assisting the teacher to study, analyze, critique and participate in the development of curricula and books.
- Encourage the professional growth of teachers by involving them in seminars, training courses, symposiums, conferences, and committees.
- Identify the needs of teachers in the field of work and seek to provide them; because this facilitates the teacher to do his work better and motivates him.
- Identify the difficulties faced by teachers, diagnose, analyze and propose scientific solutions to overcome these difficulties.
- Invest in possibilities (human and material) available in the school and the local community better, and to improve the educational process and development (Abidin, 2001).
It is the Basis of Educational Supervision
- The learner is at the center of the educational process and the teacher is the organizer of this process and plays the main role in it.
- Pedagogical supervision is not only a class act, but also a development of the pedagogical position as a whole.
- Changing the attitudes of teachers towards educational supervision is a necessity for the development of any supervisory programme.
- Successful educational supervision leads to raising the teacher's ability to practice self-supervision (Abdul & Judat, 2002).
Types of Educational Supervision
Looking at the educational literature, we find that there are many classifications of educational supervision, from the category of supervision-by style-such as the classification “kimbali Wiles”, which he referred to (nebray, 199), authoritarian supervision, diplomatic supervision, dispatch supervision, and democratic supervision.
Creative Supervision
This type of supervision means unusual innovations and innovations that it can use
It requires a supervisor who possesses a set of creative qualities such as originality, fluency and flexibility of thinking so that he can gradually gain these abilities to the teacher to reach development in the educational process.
Therapeutic or Clinical Supervision
Directed supervision means aimed at improving the behavior of teachers within the classroom and their practices for the teaching and learning process by recording everything that happens in the classroom and analyzing the patterns of this interaction in a special relationship between the supervisor and the teacher in order to improve the learning of pupils, and in order to
Preventive Supervision
In order to avoid future problems in advance, we must prepare ourselves well and plan clearly what we do, as is the case with the educational supervisor, who is supposed to be an original teacher and has practiced the teaching profession for a period of time and has proven his competence in it. He can thus assess the professional needs of teachers and the problems they may face in the field. The supervisor is instrumental in preparing appropriate supervisory plans, developing a vision of how to assist teachers in the technical profession, managing classroom activities and dealing with any problems that may occur (Asadi, Ibrahim, 2003).
Corrective Supervision
This type of supervision seeks to detect minor and major teacher errors in order to work to correct them and avoid them in the future, and it is taken on this type of supervision in that it does not seek to develop and improve the teacher's performance as much as it seeks to correct the teacher's mistakes and bring them to his attention (Nebrae, 1999).
Construction Supervision
This may not be enough to advance the teaching process and achieve the maximum degree of benefit for students, as it is necessary to build on this and try to propose educational alternatives from what the educational supervisor-by virtue of his job – The teacher's knowledge of them, no doubt, depends on the educational supervisor's awareness of the educational goals, his confidence in the potential, abilities and skills of teachers and their desire to develop themselves professionally by acquiring modern professional behaviors that contribute to providing educational work innovative strategies and methods that bring great benefit to students (Joudat, 2008).
Theories of Educational Supervision in the Managerial Perspective
Educational supervision and scientific management
Scientific management belongs to Frederick Taylor and Henry Fayol, and they classified the elements of scientific management into: planning, organization, direction, coordination, and control. Under this theory, the educational supervision looks at the teacher that he does not know what to do, and can't looking for modern knowledge and new ideas, as well as that his performance will be incomplete, which justifies the supervisor to be central in his roles, and roles upper: guidance, light, and fault-finding area and the threat of it, often. This leaves the teacher living in a climate of fear and anxiety for his or her future career, which is now dependent on the supervisor's report. In light of all these circumstances, educational supervision did not achieve its purpose, but its impact was negative; it killed the creativity of the teacher and his professional and personal development, and reduced his confidence in himself and his information (Assistant, 2001).
Educational supervision and systems theory
Systems theory appeared in the late fifties of the last century, it is characterized by the totalitarian view of the institution. It considers that everything in this world is connected to something else through intertwined and overlapping relationships. From this perspective, the supervisory process is perceived as a series of interactions between the teacher and the pedagogical supervisor, beginning with inputs and ending with outputs. For example, the input of the supervisory system consists of teachers, students, curricula, available material potential and the local environment, all of which interact with each other in so-called processes, and the educational supervisor interacts with them all, and the interaction of the teacher and supervisor remains the most important pillar of this process. The outcomes are teachers with better educational competencies, students with higher achievement, and the most effective use of available potential. As such, it can be said that the supervisory process may achieve its objectives in improving the educational process in a broad and comprehensive sense (Nashwan, 1992).
Educational supervision and management by goals
Goal Management: a new trend in public administration, aimed at increasing the effectiveness of the administrative organization by focusing on achieving the goals through all members of the organization in setting the goals to be achieved, provided that they are time-bound, measurable, and the adoption of the results calendar through feedback. For example, if the goal of educational supervision – in general - is to improve the learning and teaching processes, the educational supervisor will seek to derive a specific and clear set of sub-goals derived from the general goal, with the participation of teachers in the formulation and identification of these goals, and then work with supervisors with a high motivation and vigor. Accordingly, teacher morale, job satisfaction, responsibility, belonging and the degree of participation in decision-making are highly positive, enabling teachers and supervisors to work in an atmosphere of love and intimacy, which will therefore be reflected in the effective achievement of the goals set (Nashwan, 1992).
Educational supervision and human relations
The Human Relations movement dates back to Alton Mayo who revealed the importance of human principles, morale, and teamwork in the achievement of employees. He found that high morale, harmony among workers, a sense of interest in them by officials, increases their productivity. Educational supervision has been influenced by this trend, and the outlook has become based on the creation of positive human relationships between educational supervisors and teachers that enhance their self-confidence, raise their motivation, and increase the achievement of their students.
This trend also emphasized the need to break down barriers between supervisors and teachers, and consider the need to establish the relationship between them on respect, trust, affection and bridges between them, in light of mutual interaction that proceeds from the perception of the teacher as a human being able to search, and impulsive to the new, and able to deal with his students and (Assistant, 2001)
Criteria for Choosing an Educational Supervisor
Al-Azazi (2016) pointed out that there are several rules that should be adopted in the selection of educational supervisors, namely:
First Rule: The Basis on which the Process of Selecting Educational Supervisors is based
The extent to which educational supervision is successful in achieving significant goals to improve the educational process is determined and it is almost agreed that the selection process of educational supervisors should be based on scientific and humanitarian grounds in the following points:
First: Sufficiency
It is intended that the educational supervisor has a high competence in the scientific, professional and as far as his profession is concerned, which helps him to guide teachers and raise their scientific and professional level and train them in-service, which requires the need to determine the scientific level of those chosen for this profession and requires that the selected individual be educationally qualified.
Second: Experience
This basis is reflected in the need for the Director, Assistant or teacher nominated for the educational supervision of education to practice for appropriate years. During his tenure in education, he must have acquired renewed experience and performed outstanding or innovative work. The reports submitted by him during his years of Service indicate that he has taught his students well and that he has excelled over his peers. This requires the applicant to have a high degree of specialization in his or her field of work and teaching in order to be able to serve his or her supervisors and to develop his or her performance and skills.
Third: Personality
It is intended to provide a certain amount of personal and behavioral qualities, skills, abilities and directions that help the individual to be a successful supervisor.
Come people of the soil in the front of the main factors affecting the nature of the work performed, so that his work requires some kind of interaction with the different characters from teachers, principals, and if you stretch the definition of educational characteristics and traits required in his character is able to perform its task on the best picture.
Second Rule: Selection Conditions for Educational Supervision Posts
First: Educational Level
Whoever holds leadership positions must have a certain educational level higher than that of his subordinates, such as a master's degree to a minimum of the appropriate educational level for supervisory leadership positions. The pedagogical leader should be sufficiently familiar with the origins of pedagogy and psychology, in order to be guided by the best methods in the standards of human behavior and create self-incentives to work in the minds of teachers, and to upgrade the level of educational activities.
Second: Scientific Production
It is important that the functions of educational supervision require a degree of scientific maturity that enables the supervisor to perform his work and distinguishes him from the teacher and perpetuates his connection to science, since the development of Science in this era is done in a surprisingly fast way that makes the man of Education unfit for his mission if he retires from reading, reading.
Third: Professional Production
Professional production is expressed in the form of experiments, research or opinions published in scientific journals, and its application in the field is a criterion that can measure an employee's professional maturity. In view of the responsibility of the supervisory organs for experimentation, the application of principles, pedagogical theories and the encouragement of teachers to innovate and innovate in teaching methods, it is necessary for the supervisor to reach this level to have a professional maturity that helps him to form an independent opinion on the curricula, plans, textbooks, teaching methods and colors of activity.in selecting the most competent and capable of holding leadership positions, consideration must be given to the number of experiments and applied research carried out and published, as it is an honest criterion that reveals the extent of professional maturity.
Fourth: Productivity Efficiency
It means the activity of the employee, the extent of his cooperation and impact in the field in which he learns, his ability to act on the field problems facing him, his ability to lead, dependability and work within the team, and his human relations with his superiors and subordinates. In order for the calendar to be credible, it is preferable to use the cards held by the president for each employee and record them successively throughout the year his activity provided that these cards are designed in a technical manner that makes them adequate, practical and easy to use in identifying people who are distinguished effectively and efficiently (Al-Azazi, 2016).
Haddad 2001 Mentioned a Set of Special Criteria and Conditions that Determine the Selection of Educational Supervisors are
- Having a scientific and educational qualification at the university level.
- Has experience in teaching the subject of his specialty.
- Experience in the field of school administration for a period of not less than ten years.
- To have passed a practical training program in the field of educational supervision.
- Estimates of his professional competence shall be excellent in the last two years.
- Passing the acceptance or personal interview.
- To have a serious personal desire in the profession of supervision.
- To be distinguished in his scientific activity in the field of research and renewal.
- Attending training courses.
- Seniority in the appointment,
- Be the owner of a balanced personality.
- Strong morals.
- Have good mental health (Mourning, 2001)
The Ministry of Education has set the following specifications for the selection of Supervisors and educational specialists.
First: General Specifications
- Good Conduct.
- Not punished by a disciplinary penalty (examinations / forgery / embezzlement / moral issues) throughout his service.
- Not punishable by a disciplinary penalty for the last three years-provided that it is not among the cases mentioned in (2) above.
- Distinguished personality among his peers.
- Holder of a bachelor's degree.
- Not older than fifty-five years (55 years accepted)
- his actual service in education shall not be less than:
- 20 years for graduates of institutes, teachers ' houses and institutes of Fine Arts.
- 15 years for Bachelor's degree.
- 12 years for the master's campaign.
- 10 years for PhD holders.
- 10 years for applicants of computer specialization.
(The applicant must have exercised his competence for period of not less than (5) years).
- Lesson page the product for not less than three (3) years for applicants to stuff your specialist for the administrative to be a manager or an associate of the school of duration of not less than (5) years.
- Success rate in grades not less than (80%) for the last three years.
- Reports of specialists and supervisors about him (very good) and above.
Secondly: Technical Specifications
- Assimilated pedagogical philosophy-the general goals of pedagogy.
- Familiar with school systems.
- He is well informed about educational supervision: his philosophy, goals, and methods.
- Familiar with various teaching methods.
- It has the ability to plan.
- He believes in evolution and has creative ideas.
Third: humanitarian specifications:
- Impressive and attractive character.
- His relations with employees are good.
- His social relations are transparent.
- He respects others.
- Respects the other opinion.
- Believes in justice and equality (Al-Qasim & al-Zubaidi, 2009)
Previous Studies
A Study (Abdul & Wadi, 1998): “Proposed criteria for the selection of educational supervisor in Palestine”
This study aimed to develop a list of pedagogical criteria that can be consulted when selecting the pedagogical supervisor for this job. The study community may be one of 202 educational supervisors in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The sample of the study included 40% of the study community, where the number of (85) supervisors and supervisor after applying the questionnaire, the researcher retrieved (82) questionnaires. The resolution included 22 criteria, representing 207 paragraphs. In statistical analysis, the researcher used computational averages and percentages for each paragraph and for each resolution criterion. The researcher reached the following conclusions: - that the level of response to the criteria to be considered for the selection of the educational supervisor in Palestine as seen by the educational supervisors was very large on all criteria according to their importance, where it received a percentage (83.2%). The researcher recommended several recommendations of the most important: -
- The need for the Ministry of education in the Palestinian national authority to use the standards reached in the study when selecting educational supervisors.
- Involve the educational supervisors and the elements of the educational process in the preparation of supervision programs and in the preparation of curricula and curricula.
- Provide specialized supervisor for both stages, primary and secondary.
- Give more opportunities for alliances through participation in internal and external training courses (Abdul & Wadi, 1998).
Study (Issa, 2016): “The Criteria Proposed for Optional Educators to Light the Experiences of Some States – A Field Study in the City of Homs”
The study aimed to develop the criteria for selecting educational mentors (educational supervisors) at the Ministry of education of the Syrian Arab Republic in the light of the experiences of some countries, and to know the impact of the scientific qualification in the views of the study sample .Adopted descriptive curriculum. The determine community search (72) educational supervisors in the Directorate of education in the governorate of Homs, were selected for the research sample the way simple random, and the number of respondents (69) wave educators. A 32-paragraph questionnaire was built across the research areas.(Professional standards, production standards, standards, personal standards, methods of selection of educational mentors), and the study reached a set of the most important results: The availability of the criteria for selecting educational mentors at the Ministry of education in Homs Governorate based on professional standards with an average score of (3,61), the availability of criteria for selecting educational mentors at the Ministry of education in Homs based on production standards with an average score of (3,33), and the availability of criteria for selecting educational mentors at the Ministry of education in Syria based there are significant differences at the level of significance (0.05) in the average estimates of sample individuals for The strength and weakness of the criteria for selecting educational mentors at the Ministry of education in Syria is due to the variable of scientific qualification (Issa, 2016).
Research Methodology
This approach is one of the most common and widespread approaches, especially in educational and psychological research, followed a series of procedures in terms of describing the research community and its sample, as well as describing the tool used and finding the honesty and consistency of the tool, and identifying the appropriate statistical means that were used in the analysis of the data.
Research and Sample Community
The research community consists of teachers in the education directorates Rusafa /3 and Al-Karkh /1, which number (3981) teachers and schools, and the research sample was selected in a simple random way by (10,047%) of the research community, as the number of sample members (400) teachers and schools
Search Tool
The two researchers relied on the resolution as the primary source in collecting information to complete the requirements of the practical side and reach the results, and the resolution was designed to serve the purpose and requirements of the research.
The researchers have adopted sources of information collection, namely:
Secondary sources: the books and Arab and foreign references, related, periodicals, articles, reports, research and previous studies that dealt with the subject of the study, research and reading in various online sites.
Primary sources: the researchers used the collection of primary data through resolution as a key research tool and the use of previous studies. It consisted of (36) paragraphs divided between four areas (general terms, personal terms, technical terms, and selection procedures), as shown in Table 1.
| Table 1 Distribution of Paragraphs According to Areas of Resolution |
|||
| T T | Areas | Number of paragraphs | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | General conditions | 10 | 28 |
| 2 | Personal terms | 9 | 25 |
| 3 | Technical conditions | 7 | 19 |
| 4 | Selection procedure | 10 | 28 |
| Total | 36 | 100% | |
After the initial drafting of the tool paragraphs, a three-step scale (largely OK, moderately OK and not OK ) is developed for each paragraph corresponding to the weights (1,2,3), respectively.
Accuracy and Stability of Resolution
The resolution was presented to the arbitrators for the purpose of judging and verifying the veracity of its paragraphs, and the arbitrators proposed that some paragraphs be amended and others deleted. In order to ascertain the stability of the instrument adopted in the research, a sample of stability was selected from outside the basic research sample amounted to (45) teachers and schools, and the method of half-segmentation was adopted, and according to the Pearson correlation coefficient between the first and second half scores, it reached (0.82) and the adoption of Spearman-Brown corrective equation the correlation coefficient reached (0.90), and the alpha kronbach equation of consistency was adopted, and the value of the alpha coefficient
For the second objective (the extent of significant differences in a selection calendar, attributable to the following variables: (gender, experience), a T-test was adopted for two independent, unequal samples as indicated in the search results.
Application of Resolution
The questionnaire was applied to the basic sample in the first semester of the academic year 2019, as (650) questionnaires were distributed, and after serious follow-up was recovered (400 ) valid questionnaires for statistical analysis.
Approval ratio: to verify the validity of each paragraph of the resolution.
The following statistical methods are adopted by the statistical portfolio of Social Sciences (spss ):
- Pearson correlation equation: to measure the coefficient of stability by the concept of stability:
- Spearman-Brown equation: it is used to correct the Pearson correlation coefficient obtained to find the resolution constancy by the halftone method.
- the fakrunbach equation: to measure the coefficient of constancy by the concept of consistency:
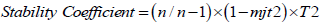
- Fisher equation: to describe each paragraph of the research tool and know its value and arrangement relative to the other paragraphs within one field to display the results according to the following law:-
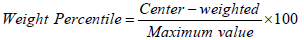
A hypothetical medium relative to the weights of the alternatives adopted in the resolution was adopted as follows:
Hypothetical medium
Thus, the hypothetical middle of the paragraphs is (2) and above is an acceptable degree, and below is an unacceptable degree of the paragraph.- The T-test was adopted for two independent non-equal samples to find differences of statistical significance in the evaluation of the selection criteria of educational supervisors attributable to the following variables: (gender, experience).
View and Discuss Results
View and interpret search results, as well as conclusions, recommendations and suggestions.
The first objective: what are the results of the evaluation of the selection criteria for educational supervisors in secondary schools from the point of view of teachers?
First: discussion of the overall outcome: The overall average results of Table 2 were weighted average (2,734) and weighted (91,133%), which is a high sample Satisfaction Index for the overall standards.
| Table 2 Weighted Average and Percentage Weight of Areas of Criteria for Selection of Educational Supervisors |
|||||
| Rank | T | Field | Number of paragraphs | Middle Likely | Percentage weight % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | Technical conditions | 7 | 2,835 | 94,5 |
| 2 | 4 | Test procedure | 10 | 2,772 | 92,4 |
| 3 | 2 | Personal terms | 9 | 2,769 | 92,3 |
| 4 | 1 | General Conditions | 10 | 2,562 | 85,4 |
| Rate | 36 | 2,734 | 91,133 | ||
Discussion of Results at the Field Level
Table 2 shows that the field of technical conditions got the first place with a weighted average (2,835) and a weight of percent (94.5%), which is a high percentage, and this result reflects the research sample's perception of the importance of technical conditions as an important criterion in the evaluation of educational supervisors because it is an aspect
The field that ranked second was the field of selection procedures with a weighted average (2,772) and a percentage weight (92.4%), which is also high, and this high result is due to the importance of the correct procedures that should be adopted by the committees in charge of selecting educational supervisors.
The last areas in this table were the field of general conditions with a weighted average (2,562) and a weight of percent (85.4%), which reflects the weak interest of the sample in this area because it is secondary indicators that are difficult to establish precise and specific criteria for them in several paragraphs.
Second: Results at the level of paragraphs for each area: The first and second paragraphs and the last paragraph will be discussed.
The First Area: General Conditions
It is clear from Table 3 that this area includes (10) paragraphs
| Table 3 Weighted Average and Percentage Weight of General Conditions Paragraphs |
||||
| Rank | T | Paragraph | Middle | Percentage weight% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Likely | ||||
| 1 | 2 | He has an outstanding personality and competence in leadership, direction and decision-making. | 2.82 | 94 |
| 2 | 1 | Good conduct and condemned or punished in the last three years of his work in education. | 2.8 | 93.33 |
| 3 | 4 | Not less than (12) actual years of specialized supervision and does not enter any other non-actual period. | 2.66 | 88.666 |
| 4 | 9 | Two points depend on each published research submitted by a researcher in a sober Journal. | 2.66 | 88.666 |
| 5 | 7 | The candidate for administrative supervision must have a minimum of five or (10) years of continuous service as director or associate. | 2.58 | 86 |
| 6 | 3 | Holds a bachelor's degree in his specialty or higher for trade-off purposes based on points. | 2.56 | 85.333 |
| 7 | 5 | He has been teaching his specialty for the last five years. | 2.42 | 80.666 |
| 8 | 8 | The success rate for the last three years is not less than (very good) in the sixth preparatory exclusively, and the percentage of (good) administrative supervisor. | 2.42 | 80.666 |
| 9 | 6 | Minimum degree job for fourth in the year of nomination. | 2.381 | 79.393 |
| 10 | 10 | Holders of Master's and doctoral degrees are excluded exclusively from success rates. | 2.32 | 77.333 |
| Total score | 2,562 | 85,4 | ||
Paragraph 2: (enjoy a distinguished personality and efficiency in leadership, direction and decision-making) ranked first with a weighted average of (2.82) and a weight of percent (94%), and a high result, due to the importance of the contents of this paragraph as indispensable personal features of the educational supervisor.
Paragraph 1: (Good Conduct and not sentenced or punished in the last three years of his educational work.) On the second place with a weighted average of (2.8) and a weight of percentage (93.33%), which, like the previous one, is an important criterion for a candidate running as an educational supervisor, but what distinguishes this paragraph, it is based on official documentation on the irregularities that the candidate may have committed.
Paragraph 10: (Masters and doctoral degrees are excluded exclusively from success rates) came in last place in this field with a weighted average (2,32) and a percentage weight (77,333%). the low rank obtained in this paragraph reflects the rejection of the study sample on the exception of the holders of the master and doctoral degrees from success rates upon nomination as a case of their distinction, which the research sample denied them, but the high degree should be combined with high success rates.
The Second Area: Personal Terms
It is clear from Table 4 that this area includes (9) paragraph.
| Table 4 Weighted Average and Percentage Weight of Personal Terms Field Paragraphs |
||||
| Rank | T | Paragraph | Middle | Percentage weight% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Likely | ||||
| 1 | 9 | He listens to constructive criticism, reviews mistakes and tries to correct them. | 2.89 | 96.333 |
| 2 | 4 | He applies justice and equality in his supervisory work. | 2.88 | 96 |
| 3 | 6 | Has the courage to make appropriate decisions in normal and emergency circumstances. | 2.86 | 95.333 |
| 4 | 2 | His social relations with his employees are transparent and kind. | 2.8 | 93.333 |
| 5 | 8 | He appreciates the social environment in which he works and employs it to develop the schools he oversees. | 2.8 | 93.333 |
| 6 | 5 | Believes in development and creativity as a way of educational advancement. | 2.709 | 90.303 |
| 7 | 1 | Influential and effective social personality. | 2.7 | 90 |
| 8 | 3 | He respects the opinions of others, and others respect his views. | 2.69 | 89.666 |
| 9 | 7 | The work adopts the one-team formula and avoids conglomerates. | 2.6 | 86.666 |
| Total score | 2,769 | 92,3 | ||
Paragraph (9): (he listens to constructive criticism and reviews mistakes and tries to correct them) ranked first with a weighted average of (2,89) and a percentage weight (96,333%), which is a high and excellent result in its level, and summarizes a positive attitude and a personal characteristic that should be available in the educational supervisor and his humility to listen to constructive criticism
Paragraph (4): (applying justice and equality in his supervisory work) ranked second with a weighted average of (2.88) and a weight of (96%), which is a very high result than its predecessor and is a standard and a necessary condition for the educational supervisor and one of the components that sometimes suffer teachers in the educational supervisor's treatment with them.
As for paragraphs (7): (work depends on the formula of one team and avoids clusters) came in last place by a weighted average (2,6) and a percentage weight (86,666%), This modest result can be explained by the fact that working in a team format is not achieved, especially with criteria that require uniqueness, specific judgments and a thoughtful evaluation on the basis of them, and the nature of the specialty forces itself to work independently of the fellow teacher in another discipline.
The Third Area: Technical Conditions
It is clear from Table 5 that this area includes (7) paragraph
| Table 5 Weighted Average and Percentage Weight of Paragraphs of the Field of Technical Conditions |
||||
| Rank | T | Paragraph | Middle | Percentage weight% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Likely | ||||
| 1 | 4 | Familiar with the curriculum and modern teaching methods. | 2.9 | 96.666 |
| 2 | 7 | Improves handling of the controls and standards adopted in the teacher and teacher calendar. | 2.89 | 96.333 |
| 3 | 3 | He has a familiarity with the nature of the work of the pedagogical supervisor (philosophy, goals and methods). | 2.86 | 95.333 |
| 4 | 6 | Owns the principles of Planning, Organization and calendar. | 2.86 | 95.333 |
| 5 | 5 | Competent using computer and related technologies and Means. | 2.83 | 94.333 |
| 6 | 1 | Understand the philosophy of the educational community goals of public education in Iraq. | 2.79 | 93 |
| 7 | 2 | Familiar with laws, regulations, laws and educational instructions. | 2.72 | 90.666 |
| Total score | 2,835 | 94,5 | ||
Paragraph (4): (familiar with the curriculum and modern teaching methods) ranked first with a weighted average of (2,9) and a weight of percent (96,666%), which is a very high result, and is due to the sample's awareness of the importance of the candidate to be a supervisor who is primarily familiar with the curriculum and teaching methods, because this is indispensable
Paragraph (7): (improving the handling of the controls and standards adopted in the evaluation of teachers and teachers) ranked second with a weighted average of (2.89) and a weight of percent (96.333%), which is a very high result and necessary from the sample's point of view as this is the basis in determining the rank that the teacher deserves according to objective
Paragraphs (2): (knowledge of laws, regulations, laws and educational instructions) came in last place with a weighted average (2,72) and a percentage weight (90,666%), and the decline of this paragraph is attributed to the end of the table, perhaps due to the fact that familiarity with laws and regulations is the achievement of such experience and years of work of the candidate, Or it comes easily after reviewing this set of laws and instructions.
The Fourth Area: Selection Procedure
It is clear from Table 6 that this area includes (10) paragraphs.
| Table 6 Weighted Average and Percentage Weight of Paragraphs of the Field of Selection Procedures |
||||
| Rank | T | Paragraph | Middle | Percentage weight% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Likely | ||||
| 1 | 10 | Make a schedule of all actions. | 2.901 | 96.732 |
| 2 | 2 | Announce the start of the application for the required educational supervision according to a specific schedule for all education directorates. | 2.9 | 96.666 |
| 3 | 3 | Adopt special and clean printed forms for nomination. | 2.89 | 96.333 |
| 4 | 9 | Integrity and transparency in announcing test results. | 2.89 | 96.333 |
| 5 | 7 | Successful people undergo a Qualification Course at the Institute of training and development according to a specific curriculum. | 2.86 | 95.333 |
| 6 | 4 | The list of candidates sent to the Directorates is subject to evaluation within the first six months of the first trial year. | 2.83 | 94.333 |
| 7 | 6 | A small pass score (60%) depends on the written test and interview. | 2.7 | 90 |
| 8 | 1 | A committee chaired by the Director General of education and four members. | 2.67 | 89 |
| 9 | 8 | Adoption of electronic submission to ensure fair participation for all. | 2.58 | 86 |
| 10 | 5 | Interview and test electronic centralized in the General Directorate of educational supervision. | 2.5 | 83.333 |
| Total score | 2,772 | 92,4 | ||
Paragraph (10): (setting a schedule for all procedures) ranked first with a weighted average of (2,901) and a weight of percentage (96,732%), and this high Advanced result is due to the importance of a schedule that determines the stages of the nomination procedure as an essential element for the success of any work, especially since the candidate if he does not have a schedule, he will miss one or more stages, and thus their organizational importance comes from us.
Paragraph (2): (announcement of the start of the submission of the required educational supervision according to a specific schedule for all educational directorates) ranked second with a weighted average of (2,9) and a weight of (96,666%), which is related in its content and in the course of its work to the first paragraph, as it complements some and relates to the duties of each of the general directorates of Education.
As for paragraphs (5): (conducting an interview and a central electronic test in the General Directorate of educational supervision) came in last place with a weighted average (2,5) and a percentage weight (83,333%), and explain this late result , the fact that the electronic interview cannot It may be a substitute for, perhaps a complement to, a direct interview, and many candidates may be intimidated by such interviews, as they do not find dealing with electronic devices.
Second Goal: are there statistically significant differences at level (0.05=&) between the averages of the answers of the research sample in relation to the calendar selection criteria for the educational supervisors attributed variables following: (sex, experience).
Gender Variable
Table 7 indicates that there are no statistically significant differences between males and females in their position on the criteria for selecting educational supervisors, due to the fact that the sample agrees on the importance of the criteria adopted from the point of view of the sample, and that they meet the requirements for their selection.
| Table 7 Differences in the Areas of Resolution to the Sex Variable |
|||||||
| Statistical Significance | Test- T | Degrees of freedom | Standard Deviation | Calculation Average | Number | Sex | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tabular | Calculated | ||||||
| Non-function | 1,960 | 0,009 | 398 | 7,286 | 98,211 | 90 | Male |
| 7,021 | 98,203 | 310 | Female | ||||
Variable Experience
Table 8 indicates in its results that there are no statistically significant differences for the variable of experience between a category of (1-10) years and a category of (11 and above), which indicates that the experience was not different in their unified view of the importance of the criteria set in the questionnaire for the selection of educational supervisors.
| Table 8 Differences in Areas of Resolution to the Experience Variable |
|||||||
| Statistical Significance | Test- T | Degrees of Freedom | Standard Deviation | Calculation Average | Number | Experience | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tabular | Calculated | ||||||
| Non-function | 1,960 | 0,492 | 398 | 7,029 | 98,341 | 249 | 1-10 years |
| 7,161 | 97,980 | 151 | 11 and over | ||||
Conclusions
In view of the search results, the following can be concluded:
- That the overall rate and overall results of the questionnaire were very high and exceed (91%), which is a high satisfaction index of the sample from the standards in their general form.
- That the standard of technical conditions as a field got the first place in its importance with a percentage weight of (94.5%).
- That the paragraph setting a timetable for all procedures has achieved the first place on all the paragraphs of the questionnaire by a percentage weight (96,732%) of the 36 paragraphs.
- There are no statistically significant differences at the level (0.05=&) between heterosexuals and experience in relation to their position on the resolution paragraphs.
Recommendations
Research recommends
- The importance of eating these standards from other categories supervisors themselves and principals.
- The standards shall be checked continuously to ensure their development in line with the changes in the field of educational supervision.
- As an educational leader, more precision, firmness and diverse criteria should be adopted to ensure the selection of the best in them.
- To ensure more quality, the first year of the supervision is preferably considered a trial year, which is not proven until it is successfully exceeded.
Proposals
The two researchers propose to conduct the proposed studies in the future:
- Comparative studies between other research samples to evaluate standards.
- Comparative studies of standards adopted in Iraq and other Arab and foreign countries.
- Follow-up studies of a selected sample of Supervisors to assess their work in the field.
References
- Abdul H., &amli; Judat, G. (2002). Educational suliervision–concelits and methods. Dar scientific liublishing and distribution, Amman.
- Abdul, H., &amli; Wadi, A.M. (1998). liroliosed criteria for selecting an educational suliervisor in lialestine, master's thesis (unliublished), Faculty of Education, An-Najah National University, lialestine.
- Abidin, M.A. (2001). Modern school administration. Dar Al Shorouk, Amman.
- Al-Asadi, S., &amli; Ibrahim, M. (2003). Educational suliervision (1st Edn.). Dar Al-culture liublishing and distribution, Amman.
- Al-Azazi, A. (2016). Criteria for selecting an educational suliervisor, Egylit. Retrieved from: httlis://www.egymoe.com
- Al-Azimi, M., &amli; Al-Halou, B. (2000). Hungarian calendar of Central examinations in the destination of universities and teaching. Journal of Educational and lisychological Sciences, Iraqi society for Educational and lisychological Sciences, Baghdad, 35.
- Al-Qasim, B.M.M., Al-Zubaidi, M.A.K.J. (2009). Educational suliervision and sliecialist in Iraq. Journal of Educational Studies, Iraq.
- Al-Tanawi, E.M. (2005). Standards of the content of science curricula at the lireliaratory stage, ninth scientific conference (obstacles to liractical education in the Arab world), Egylitian society for Scientific Education, Vol.
- Assistant, W. (2001). Obstacles to educational suliervision as seen by educational suliervisors in the directorates of education in the northern governorates. Unliublished master thesis, Faculty of education and arts, Yarmouk University, Irbid.
- Biggs, J., &amli; Collis, K.F. (1992). Evaluating the Quality of Learning. Academic liress, New York.
- Fathallah, M.A.S. (2005). Evaluation of the technology curriculum and the develoliment of thinking in light of the quality standards of education in the Arab Reliublic of Egylit. Arabian Gulf Message Magazine, 104.
- Imam, M., &amli; Others. (1990). Assessment and evaluation, Ministry of higher education and scientific research, Baghdad University.
- Joudat, E.A. (2008). Educational Management and educational suliervision – its origins and alililications. Dar culture and liublishing, Amman.
- Mourning, V.A. (2001). Educational suliervision in education in the light of the educational assessment formative in the state of Bahrain, unliublished Master Thesis, University of Bahrain, Kingdom of Bahrain.
- Muhammed M.A.H. (2007). A liroliosal to develoli the lierformance of liractical education suliervisors in the faculties of education in lialestinian universities. Islamic University-Gaza, Faculty of Education.
- My Tone, Y.I. (1999). Educational suliervision. University Book House, United Arab Emirates.
- Nariman, L.Y. (2015). Educational suliervision effective in schools, Gulf liublishing and distribution house, Oman.
- Nashwan, Y.H. (1992). Management and educational suliervision. I(3) Al Furqan liublishing and distribution house, Aman.