Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 2S
Buying Intentions Factors and Growing S-Commerce in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
Ahmad M.A. Zamil, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University
Ahmad Al Adwan, Al-Ahliyya Amman University
Ahmad Yousef Areiqat, Al-Ahliyya Amman University
Keywords
Buying Intentions, Social Commerce, Smartphones, Small Medium Enterprises.
Abstract
This Examination centers around the components impacting purchasers' intentions enjoyed S-commerce in KSA. We experimentally investigated factors impacting purchaser's intentions on social media centering Facebook in non-industrial nations like KSA. Utilizing the essential parts of the TPB (Theory of Planned Behavior), we coordinated No. of Likes and Comments and Suggested Posts of Facebook in essential forerunners of social standards for example friends and families as the principle factors in impacting buying intentions of Facebook purchasers. We likewise incorporated Smartphones utilization as a significant impacting factor. With the assistance of econometric program IBM SPSS, we measurably dissected the information gathered through overviews. The consequences of this examination show that two variables leave an incredible effect on buying intentions for example Family and Utilization of Smartphones. Different discoveries of this examination underline that Facebook is liked for the shopping reason when contrasted with sites. The greater part of Purchasers like to make buys at any rate once per month. Females are effectively associated with S-commerce in KSA, when contrasted with Guys. Seeing factual outcomes, we presume that utilizing social media particularly Facebook is a gainful path for SMEs to create as the purchasers are effectively included. Uncovering the responses to the center inquiries a SME ordinarily experience prior to entering the market accessible on social media, this investigation is similarly significant for the business networks of KSA just as China.
Introduction
As of now, moving conventional business to Online business is an arising pattern in non-industrial nations. (Chris, 2015) shows that web-based business (e-commerce) has been recognized by the non-industrial nations to be huge for the economic development. The movement of the internet has made the web-based business to grow quicker. The nations where internet entrance rate is low are additionally in a hurry of receiving e-commerce for creating business. In spite of the fact that online businesses have numerous advantages for the associations in the non-industrial nations yet the small and medium enterprises manage numerous obstacles in embracing online business when contrasted with the bigger associations. Researchers underscore that the basic boundaries for SMEs in the non-industrial nations to receive online business incorporate internal factors (Nabeel, 2006) such as awareness, absence of skill and cost, just as outer factors such as IT foundation and Government (Kenneth, 2005). Additionally, different internal and external hindrances of online business adoption are looked by the SMEs in KSA. On the opposite these obstructions are effectively being roofed by the production of S-Commerce (Social Commerce). The pattern of social commerce in KSA is setting up because of two primary reasons:
1. Rapid dissemination of PDAs extraordinarily Smartphones.
2. Availability of free-of-cost Social Media platform through Internet.org for example Facebook.
Literature shows that restricted dissemination of innovations, for example, PCs, leaps the reception of E-commerce by the SMEs (Daniel, 2012). In any case, as of late the quick dispersion of complex type of little PC for example smartphones is effectively conquering this obstacle. 80% of the absolute populace in KSA possesses a cell phone. As indicated by PTA (KSA Telecommunication Authority) half of cell phone clients own a smartphone 40% actually manages the featured phone. Also, ongoing dispatch of Internet.org has permitted a large number of KSAis to get to renowned SNS (Social Networking Site) for example Facebook (FB) free of any expenses. After the fruitful launch of Internet.org in KSA clients of Facebook have drastically expanded. Having almost 3 billion of clients at present (Internetworldstat.com), Facebook has become the most famous website that has been utilized in KSA up until now. Innumerable business visionaries have begun their small family organizations through making pages on Facebook. SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) have a significant thought in the economic development. (Nicholas 2009) accepts that the nations which intend to turn out to be more dynamic in developing their economy should underline the significance of SMEs. Portion of SMEs in GDP of the developed just as developing nations are moderately substantial. As per SMEDA KSA (Small and Medium Enterprise Development Authority), right now the portion of SMEs in the national GDP is huge containing around 40% in the all-out GDP of the country. Because of the whole economic crisis KSA is as of now confronting, each area has been contrarily influenced including SMEs. Subsequently SMEs in KSA are truly endeavoring hard to look for feasible approaches to build up their business development. In the present circumstance, utilization of social media to get enjoyed S-commerce is exceptionally helpful for the SMEs in KSA to build up their business. In any case, prior to getting indulge in S-Commerce, SMEs experience numerous inquiries such as:
1. Is there enough market available on the social media?
2. What sort of market is readily available to become the potential buyers?
3. Are these potential buyers temporarily available?
Our investigation intends to answer all the above questions through a survey-based examination to provide a piece of valuable data to the SMEs of KSA. Due to the rise of social media adoption, past studies have highlighted different, significant phenomenon considered by businesses moving toward social media as a powerful business tool. For example, (Yusuf, 2018) has proposed a model for businesses to continue to construct positive brand image through utilizing social media. We attempt to analyze the elements behind buying intention of buyers in KSA utilizing social media especially Facebook for shopping. The purpose of this research is to explore and analyze the components affecting the buying intentions of customers in KSA while getting engaged in S-commerce. Therefore, the objectives of this examination are threefold:
1. Identifying an apparent biography of the customers involved in S-commerce in KSA.
2. Assessing the variables behind the buying intentions of social media users enjoyed in S-Commerce.
3. To feature the importance of S-commerce as a sustainable platform for the development of SMEs.
Facebook, being the popular SNS in KSA has gained a lot of attention by marketers, sellers, and buyers recently. People not just use Facebook as a medium of Connectivity, Entertainment, or remaining Social yet use it for shopping purpose too. Aside from the well-known large enterprises, small-medium enterprises have additionally attracted their attention creating Facebook Pages as a S-Commerce tool for their business development. More people are reachable and targeted through Facebook by means of audience insights. In spite of the fact that there are numerous other supportive tools on Facebook to develop the business yet a business is a failure if there is no market. The intention of buyers is a significant tool to predict the future purchases. Buyers are the fundamental players in any market. On the off chance that there are no buyers, there is no market. The previous researchers have focused on the buying intentions and behaviors of customers involved in E-commerce in KSA. The elements influencing buyers' intentions and behaviors in S-commerce have not gained a lot of attention up until this point. Therefore, utilizing TPB (Theory of Planned Behavior), this examination features the components that have vigorous influence on buying intentions of customers involved in S-commerce. (Joey, 2004) has described TPB as an advantageous framework that is conceptualized to deal with the intention of human social behavior in context with attitudes, subjective standards, and perceived control. This examination attempts to re-conceptualize the first concept of TPB to analyze the buying intentions of the users of Facebook in KSA. Over the decades, TPB has been widely used by the researchers as a valid tool for assessing the purchase/buying intentions just as the buying behaviors.
In the past studies, researchers have re-conceptualized or extended this theory as indicated by the requirement of their research purpose. For Example (Michael, 2003) extended the TPB to describe and forecast the E-commerce reception. (Saleem, 2018) presented TPB with two extra variables i.e. perceived consequences and perceived innovativeness to test the impact of consumer intentions in internet buying behavior. Some researchers have combined the idea of TPB with some other variables. For example, (Edward, 2012) has used TPB furthermore with E-WOM (Electronic Verbal), network embeddedness and website quality control to explore antecedents of intentions that lead involvement in online-group buying. In this examination, we adopt just a single component from the original theory of planned behaviors i.e. Social Standards including influence of Family, Friends, No. of "Likes and Comments" (i.e. E-WOM) and Suggested posts (E-Advertisement). Previous studies have not given a lot of consideration to the effect of technology dissemination in the buying intentions or behaviors, therefore to fill this hole in the literature as one of the significant variables added in the proposed research model is Smartphone Usage. Smartphone diffusion is astoundingly fast in KSA as well as in the rest of the world also. Therefore, we believe that similarly like the wide range of various elements, Smartphone appropriation is additionally a significant component that ought to be studied as a core influencing factor behind the buying intentions in social media usage for shopping.
Literature Review
Ref. (Scott, 2007) discusses the use of social media carried out by the SMEs in the developing countries for their business development. In the developing countries a considerable lot of the SMEs are utilizing social media for their business success. Facebook has been widely studied as a significant way for small businesses through the two sellers just as the buyers' perspective. (Linnea, 2013) indicates that SMEs use the celebrated SNS Facebook to market their items and reach out their targeted customers. (Siti, 2019) articulate that the SMEs which are utilizing Facebook as a business tool have experienced a better competitive advantage. Numerous books are additionally being published recently, to provide some guidelines to fabricate the businesses by utilizing Facebook and other social medias. For example, (Rooma , 2013) has wrote down the ultimate guide to use Facebook to do free or low-cost marketing effectively and make huge loads of money with your business. Ref. (Alves, 2016) presented his ideas about leveraging Facebook's features for marketing efforts. (Greg, 2015) has highlighted the usefulness of social medias, online videos, mobile applications, sites, news release, and viral marketing to reach out customers directly.
(Ewilly, 2014) performed a survey-based research to analyze the effect of a recently launched application by Facebook named as "ThingBook", demonstrating that the effect of social opinions (specially from friends) matters a ton in buyers' decision making process. (Yao, 2011) has used Grey Incidence Analysis to show the positive effect of promotion campaigns on the buyers' decision making. (Nuno, 2017) has introduced a model that features the variables (PR-Perceived Risk, TR-Trust, SN-Subjective Norm, POSE-Past Online Shopping Experience) affecting buyers purchase intentions in S-commerce (Facebook). (Hamisah, 2008) likewise believes that trust and risk factors are the fundamental elements in E-commerce especially in S-commerce. Utilizing SP (Social presence) theory (Nick, 2017) assess that the buying intentions of customers are affected by the nature of social aspects in trust beliefs. E-commerce isn't new in KSA. It has been adopted and studied since a couple of years. In KSA, studies regarding E-commerce have ceaselessly being carried out since a decade. (Matthew, 2001) in their examination have demonstrated that the trust factor is the fundamental factor in the E-commerce that hold backs customers to continue shopping online. (Donald, 2009) proposed 6 significant variables (PU-Perceived Usefulness, PR-Perceived Risk, PE-Perceived Enjoyment, PEOU-Perceived Ease of Use, DT-Distrust and LF-Legal Framework) that possess a great influence on the online buying intentions of KSAi buyers. In another investigation (Blanca, 2011)articulates that women in KSA are more obsessed with online shopping as compared to the men, as they think that it's entertaining and secure to make purchases online. (Rizwana, 2015) concluded in their investigation that two variables i.e. trust and convenience strongly affects the online buying behavior as compared to other variables i.e. time, product variety and privacy. (Christy, 2012) discovers that the online buying behavior is affected by E-WOM and brand image.
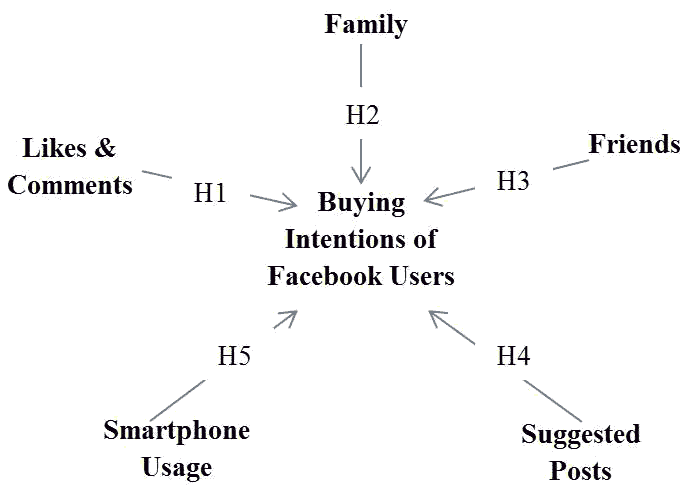
Theoretical Model And Hypothesis Development
Taking the literature review in the record, the segments of the hypothetical model are concentrated top to bottom to guarantee their validity of inclusion in this examination. All the parts of the model are extricated from the past investigations that are now been recognized and considered as significant factors in the literature that impact the purchasing behaviors and intentions.
Subjective Norms
Facebook "LIKES" is an impressive factor to be concentrated by numerous analysts that drive the purchasing urge/behavior (Rafita, 2018).
Facebook "LIKES and Comments" are one of the ground-breaking Users' created content. (Aihui, 2018) underline that user created content has as economic worth. The "LIKE" button in the past was reflected to be of less importance for the news sites and accordingly "COMMENT" button was favored (James, 2020). The ceaseless up degree of Facebook is without a doubt opening up more ways for the online traders to investigate the user generated feedback of their targeted customers. The users' shopper experience turns out to be more pleasant and powerful by the achievability of executing media features (Narongsak, 2011). As of late updated form of "LIKE" button by Facebook has given a more attainable and differed method of expression to the users. Users can communicate their sentiments by picking a predetermined expression through the "LIKE" button. This "LIKE" button incorporates 4 expanded expressions for example Love, Haha (joy, funny), Wow (flabbergasted, amazed, and so forth), Sad and Angry. Aside from "Likes", "Comments" from the experienced purchasers altogether affect buyers’ intentions who expect to make a purchase on a SNS.
"Comment" feature in Facebook is seriously expressing. The liking and answering the comment is even a lot of expressive. (Carolyn, 2016) has inferred that the Facebook users' buying behavior is influenced by two components for example 1-Positive Likes and 2-Positive Comments. Taking the literature survey in thought, this examination added the "Likes" and "Comments" as a significant part in TPB to investigations the purchasing intention of users on Facebook in KSA.
H1 : No. of “LIKES” & “COMMENTS” positively effect on Buying Intentions of FB users.
As the primary thought of this investigation is a social platform, for example, Facebook, consequently we receive the "Subjective Norms" from TPB as a fundamental segment of our examination model. The part "Subjective Norms" has been alluded as the social impact in the two hypotheses TRA proposed by (Piyush, 2020) just as TPB proposed by (Teemu, 2015) Sociality influences buying behavior to a lot more noteworthy degree. This thought has been applied and demonstrated by numerous specialists previously. (Louis, 2017) have uncovered in their examination that compulsive buying behavior is impacted by social motivation (for example offer distinctiveness and number of sold-out coupons). (Kee-Young, 2016) Alludes the Social impact as the fundamental factor that impacts the buy intention. In the examination model created in this investigation; the creators have included three precursors that altogether uphold the component of "Social Norms". First predecessor is the effect of family for example Parents, Siblings, Spouse, Children and so on. The second predecessor of the "Subjective Norms" is the friends on Facebook as they are a significant wellspring of data in this manner, they can possibly influence the purchasing decision of users of different SNS. Impact of social motivation is additionally contemplated while evaluating the behavior of purchasers in KSA. (Mirela, 2010) has named social motivation factors as community in his examination. The investigation shows that community has a more grounded relationship with impulsive buying behavior when contrasted with the other variable for example independence. The third predecessor is "Suggested Posts" that has been supplanted with media in the "Subjective Norms". Suggested post in Facebook is a special promoting tool that permits advertisers to arrive at their objective market all the more without any problem. It acts like the traditional commercial on the conventional media, which shows up time to time on the user’s news feed. Promotion emphatically affects the purchasing behavior (Tony, 1995). Every one of the three predecessors of Subjective norms are connected straightforwardly to the Buying Intentions in this investigation and viewed as primary segments of TPB. The creators accept that every one of the three parts has a significant impact exclusively.
H2: Family has a positive impact on Buying Intentions of FB users.
H3: Friends have a positive impact on Buying Intentions of FB users.
H4: “Suggested Posts” have a positive impact on Buying Intentions of FB users.
Smartphones
The last develop of the proposed re-conceptualized model of this investigation is the Smartphones adoption. Internet upheld cutting-edge innovations, for example, PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants) are moving the conventional method of purchasing towards the digital method of purchasing. Utilization of PDAs explicitly Smartphones has been enjoyed our everyday life exercises particularly while exchanging. The appropriation of creative moving innovation has made the purchasers a lot more astute by and overall world. Perhaps the most affordable and simple to-utilize PDA is Smartphones. There have been various examinations in the past that have utilized smartphones as a key impacting variable to dissect the purchasing behaviors. While purchasing an item in stores, Turkish purchasers utilize their smartphones to look through data, read online feedbacks, check availability in closest stores, compare costs and counsel salesman or personal contacts. During the pursuit cycle the customers frequently purchase from online stores too (Sakshi, 2012). Smartphones are unique in online business, which permits purchasers to get occupied with ongoing value comparisons paying little heed to geographical distances (Xiong, 2012). Convenience factor is too high in online shopping that the quantity of in-store buys is diminishing step by step. Customers have begun keeping away from the debilitating idea of conventional shopping and have redirected their attention for online purchasing. Therefore, the owners of actual stores are making their best to associate their in-store shopping with technology relating with mobile phones (Albina, 2016).
The utilization of smartphones in internet shopping is developing broadly than some other method of online purchasing. Specifies that Smartphone Utilization permits users to get to all the relevant data accessible on the social media. The expanded utilization of Cell phones is because of the way that the smartphones are utilized as PCs (Personal Computers). With each new model of smartphone, another energizing advantage is conveyed to the end user, which substitutes the features of PCs. Smartphone is the valuable gadget of users that sticks to them every minute of every day. Making purchases online utilizing the record-breaking digital friend is not difficult to oversee as the smartphone is worked ceaselessly all through the routine life. Because of this reality the length between the orders made online utilizing smartphones is less when contrasted with the span between the orders made online through PCs (Patrick, 2012).
| Table 1 Pre-Test Questions |
|
|---|---|
| Questions | Description |
| 1 | Do you access FB (Facebook) by Smartphone? |
| 2 | Did you made an FB account after getting a smartphone user? |
| 3 | Would you prefer using FB through Smartphone in future? |
| Table 2 Demographics | |
|---|---|
| Category | Percentage |
| Age | |
| Under 18 | 4 |
| 18-20 | 10 |
| 21-23 | 9 |
| 24-26 | 38 |
| 27-30 | 27 |
| Above 30 | 12 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 21 |
| Female | 79 |
| Education | |
| Under Graduate | 14 |
| Bachelors | 48 |
| Masters | 36 |
| M.phill | 1 |
| Ph.D | 1 |
| Location | |
| Balochistan | 8 |
| Khyber Pakhtunkhuwa | 11 |
| Punjab | 49 |
| Sindh | 32 |
| Facebook Buyers | |
| Buyers | 95 |
| Non-Buyers | 5 |
Facebook in KSA has been gotten to through Smartphones largely. Aside, from the literature, a pre-experiment review was performed to perceive if smartphone is a valid part to measure the buying intentions of KSAi Facebook users. The study was essentially designed based on three inquiries and was sent to the Facebook users randomly through Facebook Messenger.
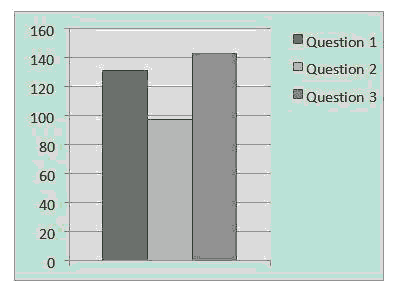
The statistics for the responses are shown in Fig. 2.
The aftereffects of the pre-test study have indicated that there is a reliable relationship between smartphones and FB use. Out of 150 respondents 131 (87.3 %) FB users access their FB account through smartphone. 97 (64.6%) of the respondents made a FB account after they adopted a smartphone. 143 (95.3%) respondents concede that they will seek after utilizing FB just through a cell phone because of its convenience.
Observing the outcomes, it is very evident that smartphone praises FB, in this manner we consider it as a solid affecting component in our hypothetical model.
H5 Smartphone utilization has a positive effect on the Buying Intentions of FB users.
Research Methodology
This investigation is survey-based. Facebook was picked to choose the sample as a result of different reasons. First and foremost, it is the most famous SNS at present being utilized in KSA. Besides, FB gives a healthy platform to shopping. Also, above all, because of the dispatch of Internet.org FB in KSA is ideally utilized and hence an increment in the deals has been witnessed by e-traders.
Selection of Sample and Data Collection
The information was gathered through a survey that was sent to 450 Facebook users across KSA. The researchers watched out for the popular Facebook pages relating with selling of products. After observing for 3 months, the researchers chose 450 dynamic purchasers who were spotted to be the regular respondents to the posts of the observed pages. The questionnaire was sent to the subjects through Facebook Messenger. From the targeted sample size 389 subjects reacted. Subsequent to removing the quantity of deficient reactions from the accumulated questionnaire, we at last get a sample size of 320 complete surveys. Table 2 shows the demographics of the sample size involving 320 respondents.
The information for our investigation was extracted from the questionnaire involving two areas. The inquiries in the first segment were intended to extract a few details of the purchasers with the goal that the inquiries attracted this investigation could be well-answered. The additional information is illustrated in Figures below.
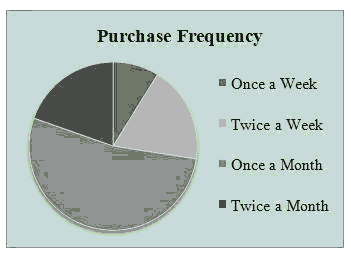
Fig. 3 shows the buying frequency of the purchasers on Facebook. 9% of the complete respondents shop on Facebook at least once every week. 19% of the respondents shop on Facebook at least twice a week. 54% purchasers shop once every month though remaining 20% purchasers shop twice a month regularly. A large portion of the considered subjects regularly purchase items from Facebook page at least once a month. Figure 4 shows the measurements of gadgets ideally utilized by purchasers while shopping on Facebook pages. The outcomes show that Smartphones are the most broadly utilized gadgets having 93% of the respondents utilizing just Smartphones for shopping in S-commerce. 27% purchasers use Smartphones as well as laptops. 19% of the purchasers change to 3 gadgets while purchasing for example tablet or smartphone or PC. Just 2% utilized PC.
Validity of Constructs
The second part of the survey encased 34 items collectively. All the statements in this segment were connected with the components of the exploration model. Five points Likert Scale was utilized to permit the subject to react about the statements, which was going from 1 to 5, where 1 addressed "Strongly Disagree" and 5 addressed "Strongly Agree".
The validity/ reliability of the multitude of 34 items were evaluated through calculating the most popular reliability statistics i.e. Cronbach's Alpha, which is utilized to survey dichotomous or multi-point designed question (Hsi?Peng, 2009).
Researchers underline that while utilizing Likert scale it is imperative to compute internal consistency through Cronbach's Alpha (Gjalt-Jorn, 2014).
| Table 3 Reliability Of The Constructs |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variables | Indicators | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Likes & Comments | L&C1 | 0.909 |
| L&C2 | ||
| L&C3 | ||
| L&C4 | ||
| L&C5 | ||
| L&C6 | ||
| Family | Fam1 | 0.784 |
| Fam2 | ||
| Fam3 | ||
| Friends | Fri1 | 0.921 |
| Fri2 | ||
| Fri3 | ||
| Suggested Posts | SP1 | 846 |
| SP2 | ||
| SP3 | ||
| SP4 | ||
| SP5 | ||
| Smartphones Usage | SU1 | 0.981 |
| SU2 | ||
| SU3 | ||
| SU4 | ||
Table 3 displays the Cronbach’s alpha of each construct that is higher than 70%, showing the reliability of inclusion of all the constructs in this study.
Data Analysis
The authors pick step-wise linear regression to investigate the factors that impact the buy intentions of FB users. Regression has been broadly utilized by the analysts in investigating buy intentions/ behaviors through TPB (Adeniran, 2019).
Step-wise linear regression is preferred for this examination in light of the accompanying reasons:
• It is a technique for regressing multiple factors while at the same time excluding those that are not significant.
• Removing the most vulnerable factors the step-wise linear regression clarifies the distribution best.
The factors picked in this examination are diverged from one another, hence we accept that step-wise linear regression is an authentic technique to investigate the significant factors. We utilized IBM SPSS programming to play out our statistical test. The gathered information based on Likert scale, subsequently it was more practical to utilize SPSS than some other programming to analyze our information. Different strategies didn't end up being critical in analyzing our model.
Results
Table 4.1 shows the descriptive statistics. 291 reactions were chosen out of 320 subjects. The explanation for removing the responses was to refine the outcomes based on the respondents who purchase from FB through Smartphones exclusively.
Table 4.2 presentations the significant factors that impact the purchasing intentions of FB users the most. These two factors are Family and No. of smartphone users. Family being the most powerful factor remains at the first position, while as No. of smartphones users positions second. Other 3 factors were barred for example No. of No. of Likes and Comments, Friends and Suggested posts.
In Table 4.3 we can see the beta coefficients value for the two models. Considering the outcome, we build the equation for Buying Intentions of FB users in KSA as:
Buying Intenions of FB Users = Constant+Family+No. of smartphone users
Buying Intentions = -0.135+0.630+0.413
The prediction equation shows that 1-unit change in Family brought 0.630 units change in Buying Intention. Additionally, 1-unit change in No. Of Smartphones users brought 0.413 units change in Buying Intention. Steady with the meaning of the outcomes of two theories of this investigation were upheld subsequently, the other three were rejected. Table 4 shows the hypothesis grades of the relative multitude of factors tested in this investigation.
| Table 4 Descriptive Statistics |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Deviation | N | |
| Buying Intentions on FB | 2.8832 | 0.85506 | 291 |
| No. of Likes and Comments | 4.1478 | 1.00455 | 291 |
| No. of Smartphones users | 4.1443 | 0.95039 | 291 |
| Family | 2.0722 | 1.24497 | 291 |
| Friends | 4.3505 | 0.86353 | 291 |
| Suggested Posts | 4.1787 | 0.81517 | 291 |
The Excluded factors and their statistics are shown in Table 4.5. The No. of Likes and Comments fundamentally affects the Buying Intentions in the first model, while in the second model it turns insignificant. Considering the intense move in the importance we expect to be that No. of Likes and Comments some way or another emphatically affects the Buying Intentions of FB users or it is impartially significant. Subsequently, we foresee this variable as Neutral in this investigation. Recommended posts have no large distinction in the two models. This shows that this variable has no impact on the buying intentions of FB users. Friends likewise have high value that makes it irrelevant.
| Table 5 Variables Entered/Re1noyed |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Vartables Entered | Variables Removed | Method |
| 1 | Family | Stepwise Criteria: Probability-of- F•to-enter <=0.050, Probabil ly-of- F-to-remove >=0.100). |
|
| 2 | No. of Smartphones users | Slepwlse (Cri eria: Probabil ty-of- F-to-enter <=0.050, Probabil ly Of• F-to-remove >=0.100). |
|
| Table 6 Coefficients |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 2.194 | 0.085 | 25.687 | 0 | |
| Family | 0.332 | 0.035 | 0.484 | 9.406 | 0 | |
| 2 | (Constant) | -0.135 | 0.767 | -0.176 | 0.86 | |
| Family | 0.63 | 0.103 | 0.917 | 6.092 | 0 | |
| No. of Smartphones users | 0.413 | 0.135 | 0.46 | 3.054 | 0.002 | |
| Table 7 Hypothesis |
|
|---|---|
| Model | Hypothesis |
| No. of Likes and comments | H1 Neutral |
| Family | H2 Supported |
| Friends | H3 Rejected |
| Suggested posts | H4 Rejected |
| No. of Smartphone users | H5 Supported |
| Table 8 Excluded Variables |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Beta In | t | Sig. | Partial Correlation | Collinearity Statistics |
| Tolerance | |||||
| No. of Likes and Comments | 0.328a | 2.368 | 0.019 | 0.138 | 0.136 |
| No. of Smartphones users | 0.460a | 3.054 | 0.002 | 0.177 | 0.114 |
| Friends | 0.105a | 0.762 | 0.446 | 0.045 | 0.139 |
| Suggested Posts | -0.029a | -0.388 | 0.698 | -0.023 | 0.490 |
| No. Of Likes and Comments | 0.132b | 0.79 | 0.43 | 0.047 | 0.092 |
| Friends | 0.004b | 0.026 | 0.979 | 0.002 | 0.13 |
| Suggested Posts | -0.031b | -0.428 | 0.669 | -0.025 | 0.49 |
Discussions, Implications And Limitations
This examination researched the elements that influence the purchasing intentions of KSAi purchasers who enjoyed S-commerce through getting to renowned SNS Facebook. The goal behind this investigation was to address the main questions that an SME may experience prior to entering the market available on social media. S-commerce is a great platform for SMEs to grow. In KSA because of scarce resources, the alternatives for enhancing businesses are restricted. Economic crisis like destitution and inflation alongside other significant issues, for example, electricity shortfalls obstruct new as well as existing SMEs to develop. In the present circumstance, the availability of cost-effective platforms, such as social networking sites are a simple way out for businesses to grow consistently. Less expensive costs of electronic gadgets have given customers an affordable, efficient, and quicker method of shopping online. Despite the fact that KSA is as yet confronting a poor internet foundation of broadband and of third and fourth generation internet however free access to Facebook gave by internet.org has encouraged the accessibility to purchasers just as sellers to enjoy the S-commerce. Hence it is critical to contemplate the scope of S-commerce activities on Facebook in KSA. The SMEs can utilize this emerging pattern of S-commerce. Online shopping has been richly recognized by sellers, purchasers, and researchers in KSA. Therefore, this examination explains the purchasers' viewpoint focusing on which components impact their intentions to purchase products available on SNS. Recognizing the purchasers' interests is a valuable tool for SMEs to evaluate their compatibility in S-commerce. The two critical variables that have been found in this examination are truly expanding. Smartphone adoption is still at its developing stage in KSA and has an extensive potential to grow quicker. The impact of family is additionally long-lasting as KSA is a country that cares about relations. KSA is a country that values its morals and ethics. Family has remained a significant factor in KSA that has an extraordinary impact in practically all the decisions. Essentially our investigation has demonstrated that Family is effective in controlling the buying intentions of customers in S-commerce also. Among all the factors, the effect of smartphone use is the most extensive impacting factor in purchasing intentions not just for the purchasers accessible on the social media in KSA yet in the rest of the world as well. As time passes smartphones are getting linked with each economic activity worldwide and thusly altogether praises online buying. For Instance, it goes about as a method of payment that is generally significant for E-commerce/S-commerce, looking through data, getting to social media immediately, and so on. The SMEs get various opportunities to work their business by making generally out of this arising pattern of S-commerce. Through S-commerce SMEs can be built up that will eventually add to the country's economy as a whole. Moreover, the advantages of this examination are valuable for SMEs in KSA as well as in China too. The project of CPEC (China KSA Economic Corridor) has embraced another market for Chinese business tycoons. The discoveries of this investigation accordingly give significant data about the intentions of KSAi buyers via social media to the Chinese business community also.
The restrictions of this examination can't be disregarded. Firstly, the sample size is extensively small. Secondly, the constructed model can be altered by adding more factors that influence the buying intentions in S-commerce. Thirdly, this investigation is centered distinctly around one SNS for example Facebook while there is a gigantic chance for different researchers to defeat this restriction and think about other renowned SNS too.
Conclusion
Internet growth has encouraged the scope of E-commerce and S-commerce in developing nations. In KSA, the broad utilization of SNS particularly Facebook has set off new companies of a significant number of private businesses through creating pages on FB. Likewise, several SMEs are additionally working through FB. This examination endeavors to give a concise scenario of the variables that impact the buying intentions and the biography of the customers available on FB in KSA. Alongside traditional Social factors for example Family and Friends, we coordinated two extra social factors that take place on the social media which are "no. of Likes and Comments" (E-WOM) and "Suggested posts" (alternate of traditional media or advertisement). The other core affecting element studied in this investigation was "Smartphone usage". Utilizing the step-wise linear regression through a computer software IBM SPSS, this investigation shows that two factors that are No. of Smartphones and Family positively affects the buying intentions of Facebook users in KSA. The non-impactful factors included No. of Likes and Comments, Friends and Suggested posts. As indicated by the statistical aftereffects of this examination, the researchers infer that the buying intentions are intently inter-linked with No. of Smartphone users and effect of the Family. Both impacting factors are long lasting, and developing consequently, the researchers conjecture that the scope of S-commerce in KSA can extensively grow. Hence, SMEs in KSA should give a serious consideration to develop their business through the popular social networking stage for example Facebook. The investigation additionally shows that females are all the more effectively engaged with S-commerce when contrasted with Male purchasers. The greater part of the observed subjects like to purchase items from FB instead of any website. There are extremely less users who try not to make any buy through Facebook. Different discoveries of this investigation are recorded as follows:
• The people living in Punjab and Sindh are more likely to purchase from FB pages.
• Only 5% of the sample size did not make any purchase from FB.
• The regular buyers generally make buys at any rate once every month.
• 93% of the sample size utilizes their Smartphone while making a purchase from FB.
• 81% of the respondents believe that Smartphone is the easiest mode among other alternative PDAs to be utilized in S-commerce.
References
- Chris, D., Amri,k S., & Vedrana, S. (2005). Benefits, impediments and critical success factors in B2C E-business adoption. Technovation, 25(11), 1251-1262.
- Nabeel, AQ., (2006). Personas of e-commerce adoption in small businesses in new zealand. Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organizations, 4(3).
- Kenneth, L., Kraemer, J., & Gibbs, J.D. (2005). Impacts of globalization on e-commerce use and firm performance: a cross-country investigation. The Information Society, 21(5).
- Daniel, M. Wanyoike, Elegwa M, &Anthony, G.W. (2012). Ict attributes as determinants of e-commerce adoption by formal small enterprises in urban kenya. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(23).
- Nicholas, M.O. (2009). Savings and economic growth in South Africa: A multivariate causality test. Journal of Policy Modeling, 31(5), 708-718.
- Yusuf, B. (2018). The effect of social media marketing activities on brand awareness, brand image and brand loyalty. Business & management studies: an international journal, 6(1).
- Joey, F.G. (2004). The theory of planned behavior and Internet purchasing. Internet Research, 14(3).
- Michael, S., & Heng, H. (2003). Understanding electronic commerce from a historical perspective. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 12, 6.
- Saleem, R., Muhammad, A.K, & Nadia, I. (2018). Motivations and barriers to purchasing online: understanding consumer responses. South Asian Journal of Business Studies, 7(1).
- Edward, C.S.Ku (2012). Beyond price: how does trust encourage online group's buying intention?. Internet Research, 22(5).
- Scott, A.W., & Elizabeth, A.R. (2007). Factors influencing e?commerce adoption and use by small and medium businesses. Electronic Markets, 15(4).
- Linnea, H., Anton, W., & Klaus S,S. (2013). Optimal ways for companies to use Facebook as a marketing channel. Journal of Information, Communication and Ethics in Society, 11(2).
- Siti, F.I.J. (2019). Facebook as marketing tools for organizations: knowledge management analysis. Dynamic Perspectives on Globalization and Sustainable Business in Asia.
- Rooma, R.R.F., Sooraj, F. (2013). The implications of facebook marketing for organizations. Contemporary Management Research, 9(1).
- Alves, H., Fernandes, C., & Raposo, M. (2016). Social media marketing: a literature review and implications. Psychology & Marketing, 33(12), 1029-1038.
- Greg, B., Ngan N.C., & Srivatsa, S. (2015). Social media practices among small business-to-business enterprises. Broekemier, 11(1).
- Ewilly, J.Y., Liew, S., Vaithilingam &Mahendhiran Nair (2014). Facebook and socio-economic benefits in the developing world. Behaviour & Information Technology, 33(4).
- Yao, Z., & Yu-qiang F. (2011). Factors that influence a buyer's decision process of shopping online: the effects of tradition and virtual community. International Conference of Information Technology, Computer Engineering and Management Sciences.
- Nuno, F., Paulo R., Margherita, P. (2017). The effects of privacy concerns, perceived risk and trust on online purchasing behaviour. International Journal of Internet Marketing and Advertising, 11(4).
- Hamisah, H.H., Samsudin, A.R, (2008). Factors affecting online purchasing behavior. Malaysian Journal of Communication, 24
- Nick, H., Julian, S., Arash, H.Z, & Marie O.R., (2017). A social commerce investigation of the role of trust in a social networking site on purchase intentions. Journal of Business Research, 71, 133-141.
- Matthew, K.O.L., & Efraim, T. (2001). A trust model for consumer internet shopping. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 6(1).
- Donald, A., & Scott, H., (2009). Analysis of the factors that influence online purchasing. Digital Commons, 2(1).
- Blanca, H., Julio, J., & M. José M., (2011). Age, gender and income: do they really moderate online shopping behaviour?. Online Information Review, 35(1).
- Rizwana, B., Irsa M., & Waqas, K.B., (2015). Effects of online shopping trends on consumer-buying behaviour: an empirical study of ksa. Journal of Management and Research, 2(2).
- Christy, M.K.C., & Dimple, R.T. (2012). The impact of electronic word-of-mouth communication: A literature analysis and integrative model. Decision Support Systems, 54(1), 461-470.
- Rafita, H., Imran, M., Hasan, S.S., Rayhan, K., Arpita, C., Farzana, A., … & Amatul, B.A. (2018). Modeling the role of c2c information quality on purchase decision in facebook. Challenges and Opportunities in the Digital Era, 11195 244-254,.
- Aihui, C., Yaobin, Lu, & Bin W., (2018). Customers’ purchase decision-making process in social commerce: a social learning perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 37(6), 627-638.
- James, M., & Edward, H. (2020). Facebook, news media and platform dependency: The institutional impacts of news distribution on social platforms. New Media & Society
- Narongsak, T., & Abdul R.A. (2011). Enhancing online performance through website content and personalization. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 52(1), 3-13.
- Carolyn, A.L., & Tonghoon. K, (2016). Predicting user response to sponsored advertising on social media via the technology acceptance model. Computers in Human Behavior, 64, 710-718.
- Piyush, G., Amit, S., & Rajiv, K. (2020). Different stages of the e-service delivery system process: belief–attitude–intention framework. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 48(7).
- Teemu, K., Marco, V.G., & Matthias, F. (2015). Robustness of the Theory of Planned Behavior in Predicting Entrepreneurial Intentions and Actions. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 39(3).
- Louis, Y.L., Sheng, W.L., & Li Y.H. (2017). Motivation for online impulse buying: A two-factor theory perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 36(5), 759-772.
- Kee-Young, K., & Byoungsoo, K. (2016). Effects of social media on consumers’ purchase decisions: evidence from Taobao. Service Business, 11, 803–829.
- Mirela, M., & Ivana K., (2010). Assessing the situational factors and impulsive buying behavior: Market segmentation approach. Management: Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, 15(2).
- Tony, M. (1995). The role of advertising in brand image development. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 4(4), 23-34.
- Sakshi, M., & Tapasya, J. (2012). Consumer buying behaviour: changing shopping patterns. International Journal of Business Management and Economic Research, 3(3), 527-530.
- Xiong, Li., Xiaodong, Z., Wangtu, A.X., & Wei, P. (2020). Measuring ease of use of mobile applications in e-commerce retailing from the perspective of consumer online shopping behaviour patterns. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 55, 102093.
- Albina. S. (2016). In-store consumer shopping behaviour through mobile phones. Theses.
- Patrick, R.G., & Jennifer, D. (2012). The evolution of social media as a marketing tool for entrepreneurs. Scholarly Journals, 17, 61-68.
- Hsi?Peng, L., & Philip, Y.S. (2009). Factors affecting purchase intention on mobile shopping web sites. Internet Research, 19(4).
- Gjalt-Jorn, P. (2014). The alpha and the omega of scale reliability and validity: why and how to abandon Cronbach’s alpha and the route towards more comprehensive assessment of scale quality. PsyArXiv.
- Adeniran, A.O. (2019). Application of likert scale’s type and cronbach’s alpha analysis in an airport perception study. Scholar Journal of Applied Sciences and Research, 2(4), 01-05.
- Marzieh, J., Maryam, K., Maryam, Y, Maryam, M., & Asadollah, S. (2013). Applying theory of planned behavior in predicting of patient safety behaviors of nurses. Journal of the Academy of Medical Sciences of Bosnia and Herzegovina, 25(1) 52-55.
- Shah, A.S., & Mohamed, S.N. (2011). Applying the theory of planned behavior (TPB) in halal food purchasing. International Journal of Commerce and Management, 21(1), 8-20.