Research Article: 2020 Vol: 24 Issue: 3
Budgeting Development Under Conditions of Digital Economy
Alexander Bradul, Kryvyi Rih National University, Ukraine
Vira Shepeliuk, Kryvyi Rih National University, Ukraine
Zvenyslava Bandura, Ivan Franko University of Lviv, Ukraine
Yaroslava Kril, Ivan Franko University of Lviv, Ukraine
Nataliya Moskal, Ivan Franko University of Lviv, Ukraine
Abstract
The article gives a theoretical summary and suggests a new solution to the scientific problem regarding the substantiation of theoretical-methodical guidelines and development of practical recommendations on the improvement of organizational-methodical foundations of accounting and budgeting in the enterprise activity management system. The sophistication of the process of making effective managerial decisions due to the increasing degree of uncertainty of the external and internal economic environment conditions the need in rethinking of the role of budgeting in ensuring stable economic development of the enterprise. Based on the conducted retrospective analysis, the periodization of the historical development of budgeting was carried out, which confirmed the transition from the cost approach to understanding the content of budgeting (revenue and expenditure planning) to its perception as one of the subsystems of the overall enterprise management system. It is established that budgeting is an integral part of the enterprise management system, which is responsible for implementing efficient business activities and providing feedback between stages of the management process. Insufficient substantiation of the value of the budgeting process in the enterprise management system leads to a decrease in the quality of managerial decisions aimed at correction and improving the efficiency of the enterprise operation. In order to create a rational and flexible management system, it is proposed to introduce an integrated budgeting system in the activity of enterprises allowing to respond promptly to deviations from the planned budget indicators, which provides a qualitatively new level of planning and organization of internal (management) accounting with an orientation to the enterprise activity strategy. The introduction of an integrated budgeting system significantly increases the profitability of activities, helps identify areas of rational use of available resources, increase the solvency and investment attractiveness of the business entity based on improving the adaptability of the company to changes in the external and internal economic environment.
Keywords
Budgeting, Management Accounting, Enterprise Management, Integrated System, Digital Economy.
Introduction
The transformation of economic relations, the significant impact of changes in the external economic environment of the enterprise activity and the need to take them into account in the planning of activities condition the search for new methods of enterprise resource management, one of which is budgeting.
The use of this system at enterprises is the key to rational management of resources and their purposeful use, ensuring financial stability and adequate level of solvency, making sound and effective management decisions. With the help of a budgeting system it is possible to increase efficiency of enterprise activity and reduce activity costs for a reporting period at the expense of improvement of management quality, agreement and coordination of activity of separate enterprise divisions, and according to requests of management personnel of different levels.
Introduction of a budgeting system at an enterprise creates fundamentally new requirements for the content of information and methods of its provision, which provides for properly organized accounting at the synthetic and analytical levels. Accounting as the basis of the budgeting process should become an effective tool for ensuring the achievement of strategic goals of the enterprise activity on the basis of optimal implementation of budgets, eliminating the causes of deviations, identifying the reserves of unused opportunities and preventing the negative impact of risks.
The purpose of the study is to substantiate theoretical propositions and to develop practical recommendations on improving the organizational-methodical foundations of accounting and budgeting in the enterprise activity management system.
Review of Previous Studies
The organization of an effective management system at the enterprise level involves the introduction and use of modern management planning technologies including budgeting (Das, 2018; ?wilinski, 2019).
In the context of the uncertainty of the external and internal economic environment, budgeting is an effective method of managing the revenue and expenditure of a business entity and an instrument aimed at achieving the final goals of the activity (Bleyen et al., 2017).
Transformational changes in the system of economic relations and significant influence of the external economic environment on the activities of enterprises require the search for new methods of enterprise resource management, in particular on the basis of studying the genesis, principles and importance of budgeting in the enterprise management system (Drobyazko et al., 2019a: 2019b). This will allow further outline the theoretical aspects of accounting support for the budgeting process and find out the specifics of creation of an integrated risk-based budgeting system.
The integration of analytical systems, accounting as a single component of the budgeting process has evolved over a long period. Predicting future qualitative characteristics as a core strategy was emphasized (Weigel & Hiebl, 2018).
The actual available analytical information was generated without reference to the regulatory indicators together with accounting ones, and the relevant indicators were not the subject of accounting documentation (Daumoser et al., 2018).
In certain cases, actual analytics were still compared to established fundamental indicators (van Helden & Reichard, 2018). The dominant importance of determining the final indicators by the results of the activity and the achieved result is observed. It can also be concluded that maintenance of estimate documentation also took place, which in turn provided for laying down certain established cost indicators and corresponding planning.
Budgeting has had considerable development and has spread in various institutions in the planning of operations and the generation of projected plans regarding revenue and expenditure (Hilorme, 2019a; 2019b).
The effort to implement certain measures as regards forecasting their own cost part of the processes indicates the desire to launch certain analytical systems, estimates that could optimize the activities (Ho, 2018).
At the same time, it should be noted that there is a lack of comprehensive studies of accounting problems together with the budgeting process in the enterprise management system. Particularly, such problems remain unresolved: scientific-theoretical substantiation of the place of internal economic (management) accounting and budgeting in the enterprise management system; development of accounting support for the management of production costs of enterprises in terms of budgeting; creation of information base of enterprise management in the conditions of budgeting automation; organization of accounting and reporting by centers of responsibility in the system of cost budgeting of enterprises; the use of organizational-methodical tools of control and modeling in the process of budgeting.
Methodology
In the process of the study, general scientific and special methods and techniques of cognition were used: methods of theoretical generalization and comparison (to find out the economic essence and components of structural elements of accounting and budgeting); methods of induction and deduction, analysis and synthesis (to create and improve the current classification attributes of budgets, and to define the elements of organization of accounting and reporting by the centers of responsibility in the system of enterprise cost budgeting); abstract-logical methods (to determine the basic characteristics of budget forms and their impact on budgeting in the management process. To evaluate the basic stages of implementation of a budgeting system and the formation of methodical support for its implementation, the association and analog methods were used. With the help of the empirical study method, the forms of budgets and plans by composition and content were examined.
Information base of the study is the works of scientists concerning the problems of accounting, control, economic theory, law and management, including monographs, articles in periodicals of scientific-practical character, materials of international scientific and scientific-practical conferences, normative-legal acts on the issues of organization and the methods of budgeting, organization of accounting, statistics, economic reviews and analytics, online resources, as well as the results of own studies of the author.
Results and Discussions
It is advisable to carry out the process of budgeting at enterprises using one of the variants of management concepts:
1. From strategic plans to operational plans (and then to budgets). In this case, corporate principles of the unity of purpose should be used. The purposes of business owners are usually based on psychological considerations and are unrelated to the current organizational basis. If the enterprise is undergoing business restructuring (entering new markets), operational plans should be used to implement the intention. To this end, the relationship of each direction of use of financial resources with the sources of financing is established.
2. From current budgets to developing strategic plans. The strategy is created "against the possible" by forecasting the development of the existing business, with its extrapolation calculated to the future and full use of existing opportunities: economic analysis, financial analysis (liquidity, profitability, etc.) are carried out, and prospects for production development, modeling of growth prospects are evaluated.
Organization of budgeting at an enterprise should be carried out on the basis of scientifically sound principles. The absence of a single approach to establishing the list and determining the essence of budgeting principles necessitated their systematization. The specified principles of budgeting establish the general features and essence of the management of companies, provide opportunities for their development, increase the efficiency of the enterprise activity and help to minimize the possible risks.
The creation of a system of budgeting at an enterprise and achieving the effectiveness of its practical application implies the need to generate the required economic information and to establish ways of its provision at the expense of a proper accounting organization, according to which data further control, analysis and planning can be carried out. Accordingly, the actual task is to substantiate the possibilities of integrating a budgeting system with the constituent elements of the enterprise management system.
Budgeting system is a system for planning of budget indicators based on the set goals and tasks of a company. In order to achieve the effectiveness of economic activity management in the process of activity and after the end of the reporting period, according to accounting data, deviations are identified, their causes are analyzed and appropriate management decisions are made.
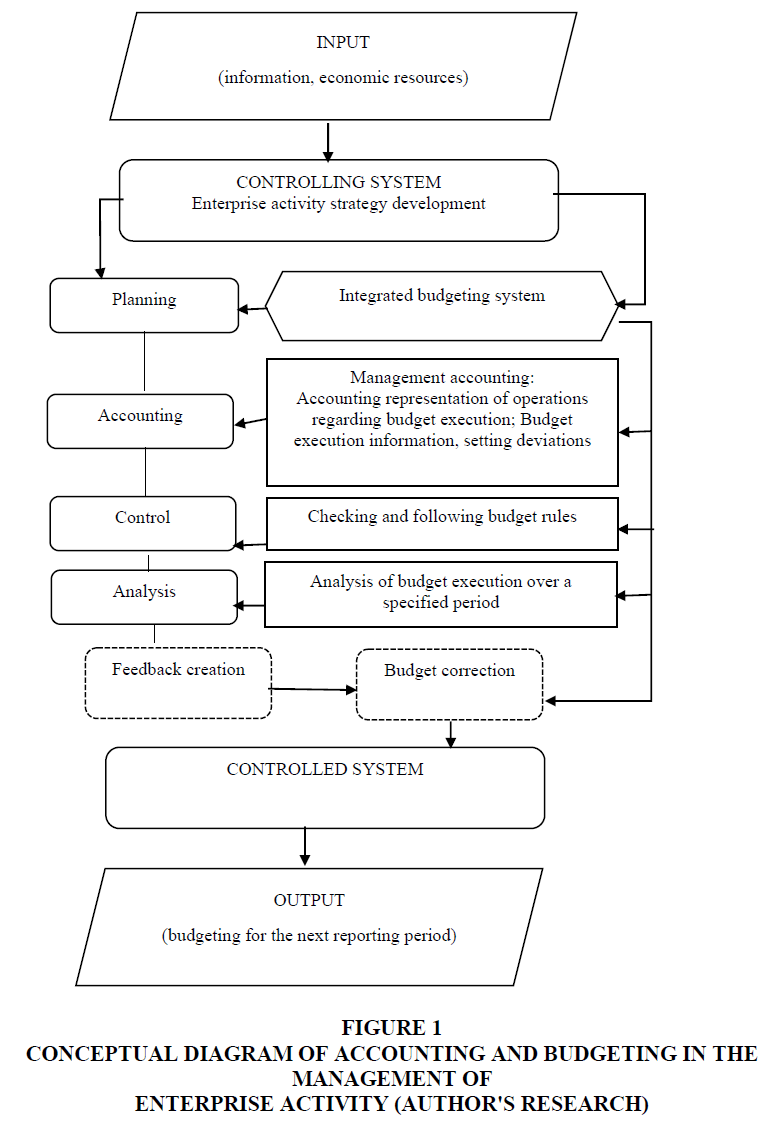
Ensuring consumer needs for quality products and development of new products that will contribute to improving the efficiency of the activity of enterprises of the industry in conditions of uncertain economic environment and financial-economic crisis is possible primarily based on the creation of integrated relationships between the budgeting system and such elements of management as planning, accounting, control and analysis (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Conceptual Diagram of Accounting and Budgeting in the Management of Enterprise Activity (Author's Research)
The presented diagram of integration of budgeting with components of a management system allows to define budgeting as an important component of planning of enterprise activity, since it provides for the development of directions of budgeting in relation to the strategic plan for achieving effective enterprise management. The system is based on developing a set of relationships between budgeting and elements of the management system in order to create an effective mechanism for ensuring the efficiency of operation and achievement of strategic goals of an enterprise.
Thus, the organization of an integrated budgeting system at an enterprise is ensured by the relationship of budgeting and accounting system on the basis of separation of single objects of accounting and budgeting, synthesis of budgeting tasks and internal economic (management) accounting, as well as development of information support of budgeting on the basis of data on the actual execution of budgets accumulated through the system of registers of internal (management) accounting.
At the stage of activity planning different types of budgets are created based on goal sets and taking into account the general strategy of an enterprise. Thus, for purposes of planning, a budget is strategic plans, on which basis medium-term plans are created and the operational tasks of an enterprise as a whole and of separate divisions are determined.
With the help of planning, setting of specific goals and calculation of the indicators that the company desire to achieve are taking place. Planning is preceded by an analysis of financial and non-financial information for prior reporting periods. As financial information is accumulated in the accounting system, there is a direct relationship between the functions of accounting and planning. With the help of accounting feedback is also established: accounting data contribute to conducting the evaluation of the reality of the planned indicators, and hence, further making changes in the plans of an enterprise, taking measures to eliminate negative trends in activity.
The creation of a system of quality and timely information support for making management decisions by managers of different levels of management is carried out today through the establishment of clear links between the system of internal (management) accounting and the system of budgeting.
The integration of the system of budgeting and accounting as an element of the management system is that on the basis of budget items and indicators (planned indicators) and internal (management) accounting (actual values), key performance indicators are created such as the main guidelines for stimulation and motivation of personnel, improvement of business processes and achievement of financial stability of an enterprise. Additionally, the system of internal (management) accounting and budgeting system are integrated through the development of common information support. To create and control the execution of budget indicators, the information which is generated within the system of internal (management) accounting is required.
Internal (management) accounting of budget execution allows verification of qualitative and quantitative indicators in the activity of structural and separate divisions of an enterprise for reporting periods.
The creation of clear relationships between the budgeting system and internal (management) accounting allows to generate information taking into account the needs of managers of different levels of management for them to make effective decisions.
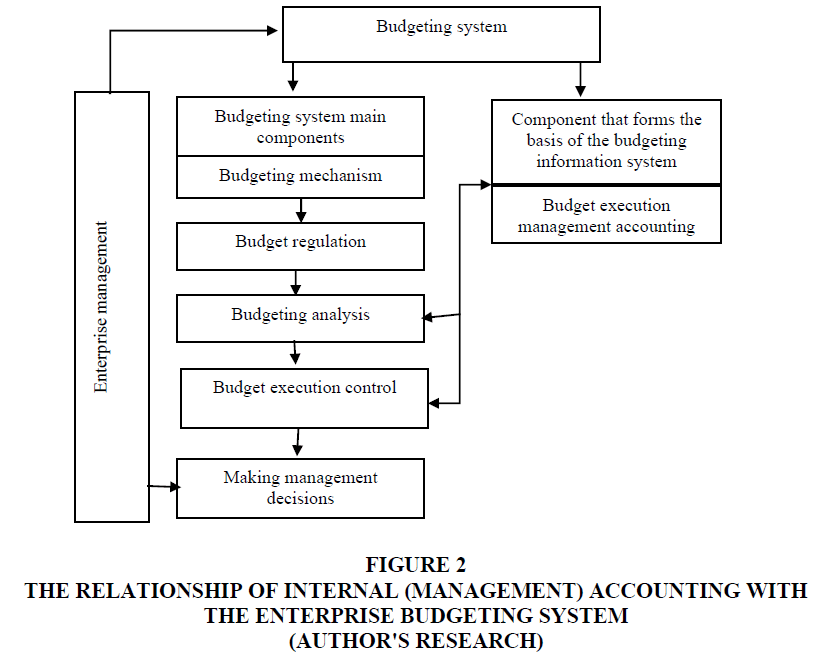
The relationship between the internal accounting (management) system and the budgeting system is presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2 The Relationship of Internal (Management) Accounting with the Enterprise Budgeting System (Author's Research)
To manage an enterprise quantitative information of an integrated budgeting system is used. At the same time, budgeting is an integral part of the internal (management) accounting system since it provides cost management and, on its basis, organic relationship and interaction with other management subsystems. At the same time, the role of internal (management) accounting in the budgeting system involves establishing the main tendencies in the development of an enterprise, the creation of an information base for making management decisions, the rational use of resources and the improvement of management mechanism.
The evaluation of the effectiveness of the planning and budgeting system at an enterprise should provide for the development of appropriate measures to control the degree of execution of budgets. To the priority tasks of control, you can refer verification of discrepancies of indicators in comparison with the set and forecasted ones, analysis of the factors that lead to this, provision of responsible employees with the required data set for making management decisions.
Control for the execution of budgets makes it possible to identify deviations from the planned actual data, the degree of their inconsistency with regulatory indicators.
The relationship between analysis and the budgeting system is to evaluate the execution of budgets by differentiated indicators, to study the directions and to create possible forecasts for achievement of the set goals, to identify possible causes that hinder these goals, to work out measures for solving these problems and to improve the quality indicators accordingly. Accordingly, the relationship between analysis and budgeting is due to the fact that, firstly, analysis should be carried out before budgeting, since it facilitates its substantiation; secondly, analysis should be carried out during budget execution and after the end of the planning period to identify deviations and the reasons that caused them to occur. With the help of budget target analytics, accounting data can be used to significantly improve the quality of enterprise planning.
Product analysis demonstrates that for computerization of business processes, including budgeting, in large corporations and holding companies they often use software products that belong to a certain class of integrated management systems (Table 1).
| Table 1 Main Classes of Integrated Management Systems (Systematized by the Author) | |
| Management system types | Content description |
| MRP (Manufacturing Requirements Planning) | Provides for production management only |
| MRP II (Manufacturing Resource Planning) | Includes business planning, planning of demand, sales, manufacturing, needs in material resource, production capacities, customer account management, evaluation of execution, etc. |
| ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) |
Provides for management of all types of enterprise resources, including modeling, various analytical tools, optimization of making management decisions (this standard transformed the system of MRP II and was supplemented by such functional modules as demand forecasting, management of project, costs, storehouses, processing of technological information, etc.) |
| ERP II (Enterprise Resource and Relationship Planning) | Creates possibilities for management (as opposed to previous systems) of external relationships of an enterprise with suppliers, customers, partners, etc. |
| S-MES (Standardised Manufacturing Executions System) | Provides control of the state and distribution of resources, manufacturing process scheduling, data collection and processing, manufacturing process management, manufacturing planning and support, product quality management, productivity analysis, work scheduling, workflow system creation, personnel management, manufacturing facilities management, etc. |
The integrated management systems will be able to increase the quality level of manufacturing processes, optimize manufacturing processes, increase the quality of products and workflow efficiency. However, the systems of such classes are extremely expensive, characterized by a low level of adaptability, a long period of implementation, setting and testing, and complex training of their users.
In the conditions of a highly competitive environment, enterprises need to implement a single integrated ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) management information system. Such system supports multi-dimensional data analysis, corporate database management, is characterized by a modular structure (separation of various functional blocks in the context of business processes), the use of common directories and analytical tools. Consolidation of information for the needs of management and interaction of all software modules are carried out at the expense of the compatibility of regulatory, technical and software support.
The efficiency of the computerization process of the budgeting process depends on the correct selection of the software product and the definition of clear criteria for its selection. According to the results of the study of the specificity of the enterprise activity (maintaining a large number of competing enterprises in the market; liquidation and conversion of large and medium-sized enterprises in order to attract foreign investment and small business development; creation of vertically integrated complexes that unite the entire production cycle from grain cultivation to the sale of finished products; creation of horizontally integrated associations at the expense of extension of manufacturing of products) the following criteria have been systematized that you should take into account before starting the automation of the budgeting process for choosing the software, which will be used for implementation of the process in the future.
Budgeting computerization software should allow you to import actual data from your accounting systems, be able to track limits by items, norms, and key targets of budget execution.
Conclusions
The effectiveness of the budgeting system is improved under the condition of close relationship between analysis, accounting and control at an enterprise. Identification of deviations from the regulatory indicators of separate components of the budget makes it possible to compare these indicators with the planned ones, which is actually achieved through control. Thus, analysis makes it possible to examine these deviations and the factors that lead to them, to identify ways of correcting the indicators and to take the necessary measures, which is actually its main function. Based on the results of control and analysis of budget execution, management decisions are made in terms of adjusting them to ensure cost minimization and achieve a high level of profitability and liquidity of an enterprise.
Thus, although in most cases the budgeting system has a positive effect on the enterprise activity, in case of improper organization and setting too high requirements for personnel involved in budget execution, unexpected results can be obtained, which in turn will complicate the achievement of the goals of an enterprise. Accordingly, before moving to budget application, it is necessary to objectively evaluate not only the financial condition of the enterprise, but also the qualification training of the personnel for development, implementation, control and analysis of budget targets.
Taking into account substantiated budgeting principles and complex conditions of enterprise activity at the uncertainty of the economic environment, the necessity of creating integrated relationships between the budgeting system and such elements of management as planning, accounting, control and analysis has been proven.
The proposed integrated budgeting system is an organizationally ordered system by its content, which is based on establishing a set of relationships between budgeting and elements of the management system in order to develop an effective mechanism for ensuring the efficiency of operation and achievement of strategic goals of an enterprise.
Taking into account the requirements for creating the conditions for the operation of the integrated budgeting system helps to identify the risks of activities in order to develop alternative measures to eliminate potential hazards or to use favorable situations. In order to minimize the negative effects of the threats of the economic environment, a mechanism for managing financial and entrepreneurial risks in the budgeting system for enterprises has been developed, in particular in terms of goals, objectives, methods of risk assessment, evaluation procedures, risk detection and their identification, control of results, which contributes to purposeful influence on the possible consequences of the occurrence of risks.
The need for automation of internal (managerial) accounting is due to the needs of accurate systematization of information, prompt response to changes in the conditions of the external environment, as well as conducting a comprehensive analysis of the results of the enterprise activity in the reporting and previous periods.
Therefore, it is advisable for enterprises to create a single integrated enterprise management system that includes a computerized subsystem of budgeting and internal (management) accounting.
Systematized criteria of software selection for computerization of the budgeting process (software functionality; cost and labor costs for implementation; implementation period; adequacy of enterprise size), critical analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of existing software products facilitated the substantiation of the feasibility of using an automated software complex adapted to the specifics of the activity of enterprises.
References
- Bleyen, P., Klimovský, D., Bouckaert, G., & Reichard, C. (2017). Linking budgeting to results? Evidence about performance budgets in European municipalities based on a comparative analytical model. Public Management Review, 19(7), 932-953.
- Das, S.K. (2018). Accrual budgeting. In public budgeting in india (143-162). Springer, New Delhi. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-81-322-3917-8_9
- Daumoser, C., Hirsch, B., & Sohn, M. (2018). Honesty in budgeting: a review of morality and control aspects in the budgetary slack literature. Journal of Management Control, 29(2), 115-159.
- Drobyazko, S., Bondarevska, O., Klymenko, D., Pletenetska, S., & Pylypenko, O. (2019). Model for forming of optimal credit portfolio of commercial bank. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 22(4), 501-506.
- Drobyazko, S., Pavlova, H., Suhak, T., Kulyk, V., & Khodjimukhamedova, S. (2019). Formation of hybrid costing system accounting model at the enterprise. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 23(6).
- Hilorme, T., Sokolova, L., Portna, O., Lysiak, L., & Boretskaya, N. (2019). The model of evaluation of the renewable energy resources development under conditions of efficient energy consumption. Proceedings of the 33rd International Business Information Management Association Conference, IBIMA 2019: Education Excellence and Innovation Management through Vision 2020. pp. 7514-7526. https://ibima.org/accepted-paper/the-model-of-evaluation-of-the-renewable-energy-resources-development-under-conditions-of-efficient-energy-consumption/
- Hilorme, T., Sokolova, L., Portna, O., Lysiak, L., & Boretskaya, N. (2019). Smart Grid Concept as a Perspective for The Development of Ukrainian Energy Platform. IBIMA Business Review, Retrieved from https://ibimapublishing.com/articles/IBIMABR/2019/923814/
- Ho, A.T.K. (2018). From performance budgeting to performance budget management: Theory and practice. Public Administration Review, 78(5), 748-758.
- ?wilinski, A. (2019). Implementation of Blockchain Technology in Accounting Sphere. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 23(SI2), 1528-2635-23-SI-2-412: 1-6.
- van Helden, J., & Reichard, C. (2018). Cash or accruals for budgeting? Why some governments in Europe changed their budgeting mode and others not. OECD Journal on Budgeting, 18(1), 91-113.
- Weigel, C., & Hiebl, M.R. (2018). Beyond budgeting: review and research agenda. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change , 14(3).