Research Article: 2022 Vol: 28 Issue: 4S
Bayesian Independent Samples T-Test for Analysis Factor Entrepreneurial of Vocational School
Ariyono Setiawan, Universitas Negeri Surabaya
Munoto, Universitas Negeri Surabaya
Luthfiyah Nurlaela, Universitas Negeri Surabaya
Citation Information: Setiawan, A., Munoto, & Nurlaela, L. (2022). Bayesian independent samples T-test for analysis factor entrepreneurial of vocational school. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(S4), 1- 14.
Abstract
Entrepreneurship debriefing is one way that schools can do today to be able to equip students from an early age with motivation, knowledge about entrepreneurship. There are several factors that can be used as desire, motivation, character, and readiness. By doing survey respondents and data analysis because it uses conditional probability as the basis. In this Bayesian analysis, it is used as a determinant of factors that can influence a student to be open or ready to do entrepreneurship by using T test analysis as a comparative test to assess the difference between the factor value and the sample population value obtained from the factors of a student's interest in entrepreneurship and ready to practice entrepreneurship. Bayesian Independent Samples T-Test For Analysis Factor Entrepreneurial Of Vocational Schools with quantitative methods. Data analysis is carried out starting with organizing the data because the nature of quantitative data is generally very much and varied. The population in this study were all cadets in the ministry of air transportation. In this study, the population was about 585, but the data sample used by the author for the time being is a sample obtained by using a random sample method from the entire population.
Keywords
Vocational School, Entrepreneurship, Bayesian Independent, T-Test, Cadet
Introduction
Vocational schools that exist today are trying to make their students from job seeker to be job creator, there are many ways that vocational schools can be independent when students graduate or complete their studies. Entrepreneurship debriefing is one way that schools can do today to be able to equip students from an early age with motivation, knowledge about entrepreneurship. There are several factors that can be used as desire, motivation, character, and readiness. These factors can be seen from the student's interest that multiplying the potential in early entrepreneurship can be recognized, and then it can be directed to training and mentoring incubator to find suitable and appropriate entrepreneurs for each student.
Overview Theory
In this study, Bayesian analysis is used, namely to analyze uncertainty or can usually be reduced from the information data collected, so that it can perform a better analysis. By doing survey respondents and data analysis because it uses conditional probability as the basis. In this Bayesian analysis, it is used as a determinant of factors that can influence a student to be open or ready to do entrepreneurship by using T test analysis as a comparative test to assess the difference between the factor value and the sample population value obtained from the factors of a student's interest in entrepreneurship and ready to practice entrepreneurship.
Data Collection
In the process of finding answers to the problem formulation and research objectives, it is necessary to collect relevant data. The data collection was carried out in various ways, including library research, filling out questionnaires with several instruments from the variables of Interest, Efficacy, Knowledge, Motivation, Character, and Readiness.
Data Analysis
In this research, Bayesian Independent Samples T-Test For Analysis Factor Entrepreneurial Of Vocational Schools with quantitative methods. Data analysis is carried out starting with organizing the data because the nature of quantitative data is generally very much and varied. Organizing the data so that the data obtained is neat, structured, systematic, and complete. In the process of organizing the right data, researchers can obtain good quality data, document the analysis carried out, store the data and analyze it for the completion of the research carried out. Data analysis that is carried out is to use . The research location is an air transportation school with Bayesian Independent Samples T-Test For Analysis Factor Entrepreneurial Of Vocational School with a population of cadets, lecturers and the general public.
Research Methodology
Population and Sample
The population in this study were all cadets in the ministry of air transportation. In this study, the population was about 585, but the data sample used by the author for the time being is a sample obtained by using a random sample method from the entire population.
Intrument Questionnaire
The sample population in this study was obtained from the air transportation school ministry of transportation.
| Table 1 Statistical description sample for sex |
||
|---|---|---|
| Descriptive Statistics | Sex | |
| Female | Male | |
| Valid | 198 | 387 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 |
| Mean | 7.727 | 7.850 |
| Std. Deviation | 2.534 | 2.560 |
| Minimum | 3.000 | 1.000 |
| Maximum | 10.000 | 10.000 |
With a sample value of 585 respondents, among them are 198 women and 387 men, resulting in the following calculation
| Table 2 Statistical description sample for status |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
| Status | |||
| Cadets | General | Lecturer | |
| Valid | 537 | 34 | 14 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mean | 7.784 | 8.206 | 7.786 |
| Std. Deviation | 2.564 | 2.508 | 2.155 |
| Minimum | 1.000 | 1.000 | 4.000 |
| Maximum | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
Respondents with cadet status as many as 537 respondents from the public as many as 34 respondents and from lecturers as many as 14 respondents
| Table 3 Descriptive statistics variable |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EFF1 | INT1 | MOT1 | KNW1 | CHA1 | RED1 | |||||||
| Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | |
| Valid | 198 | 387 | 198 | 387 | 198 | 387 | 198 | 387 | 198 | 387 | 198 | 387 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mean | 7.152 | 7.367 | 7.727 | 7.850 | 7.530 | 7.509 | 6.753 | 6.933 | 7.939 | 7.742 | 7.843 | 7.630 |
| Std. Deviation | 2.386 | 2.482 | 2.534 | 2.560 | 2.474 | 2.583 | 2.481 | 2.507 | 2.420 | 2.583 | 2.378 | 2.534 |
| Skewness | -0.573 | -0.774 | -0.780 | -0.969 | -0.775 | -0.823 | -0.364 | -0.554 | -0.910 | -0.873 | -0.857 | -0.826 |
| Std. Error of Skewness | 0.173 | 0.124 | 0.173 | 0.124 | 0.173 | 0.124 | 0.173 | 0.124 | 0.173 | 0.124 | 0.173 | 0.124 |
| Kurtosis | -0.960 | -0.740 | -0.989 | -0.575 | -0.788 | -0.742 | -1.114 | -0.949 | -0.677 | -0.743 | -0.700 | -0.748 |
| Std. Error of Kurtosis | 0.344 | 0.247 | 0.344 | 0.247 | 0.344 | 0.247 | 0.344 | 0.247 | 0.344 | 0.247 | 0.344 | 0.247 |
| Minimum | 2.000 | 1.000 | 3.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 3.000 | 1.000 | 3.000 | 1.000 |
| Maximum | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| 25th percentile | 5.000 | 5.000 | 5.000 | 6.000 | 5.250 | 5.000 | 4.000 | 4.000 | 6.000 | 5.000 | 6.000 | 5.000 |
| 50th percentile | 8.000 | 8.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 8.000 | 9.000 | 7.000 | 8.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 |
| 75th percentile | 9.000 | 9.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| 25th percentile | 5.000 | 5.000 | 5.000 | 6.000 | 5.250 | 5.000 | 4.000 | 4.000 | 6.000 | 5.000 | 6.000 | 5.000 |
| 50th percentile | 8.000 | 8.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 8.000 | 9.000 | 7.000 | 8.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 |
| 75th percentile | 9.000 | 9.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
Data Retrieval
In the process of finding answers to the formulation of the problem and the purpose of this research, it is very necessary to collect relevant data. These data were collected in various ways, including literature studies, filling out questionnaires with several instruments every variable.
Data analysis
This type of research is descriptive with quantitative methods. Data analysis was carried out starting with the organization of the data because the nature of quantitative data was generally very numerous and varied. Organizing the data so that the data obtained is neat, structured, systematic, and complete. In the process of organizing the right data, researchers can obtain good quality data, document the analysis carried out, store the data and analyze it for the completion of the research carried out. Data analysis that is carried out is by using Bayesian Independent Samples T-Test. The research location is an air transportation school with a population of lecturer cadets and the general public
Result and Discussion
Cluster is a collection of objects or data that have similarities with one another in the same cluster and are not similar to objects in different clusters (Jain, 2010).
| Table 4 Bayesian independent samples T-test |
||
|---|---|---|
| BF10 | error % | |
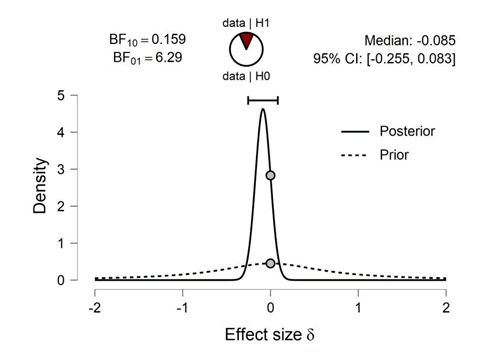
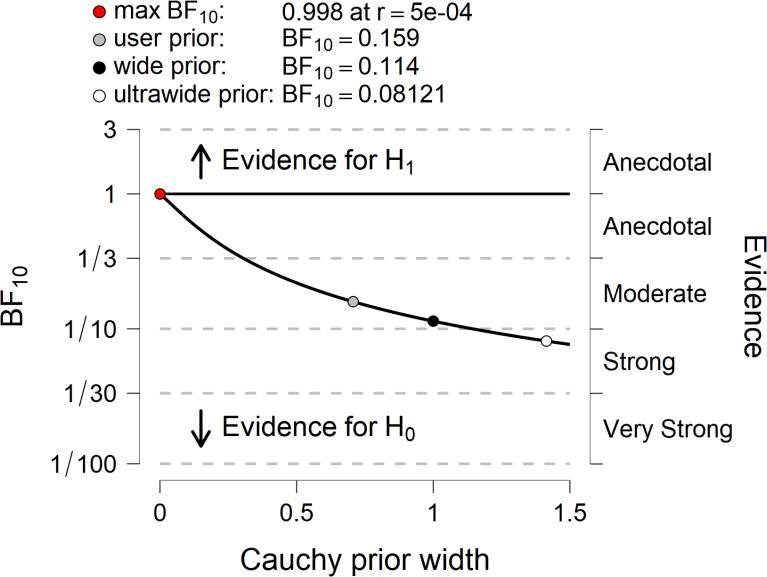
| EFF1 | 0.159 | 2.285e -4 |
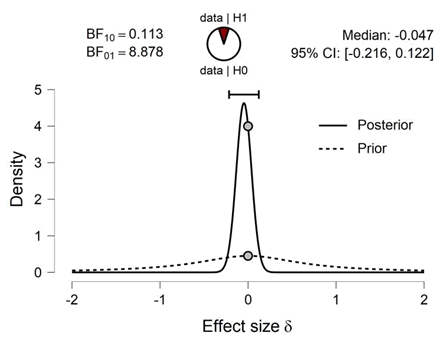
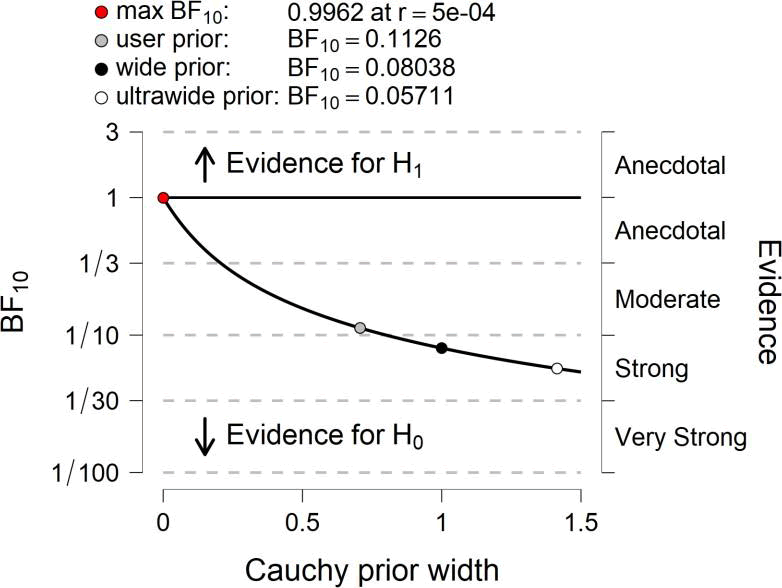
| INT1 | 0.113 | 3.296e -4 |
| MOT1 | 0.098 | 3.840e -4 |
| KNW1 | 0.135 | 2.710e -4 |
| CHA1 | 0.143 | 2.549e -4 |
| RED1 | 0.155 | 2.344e -4 |
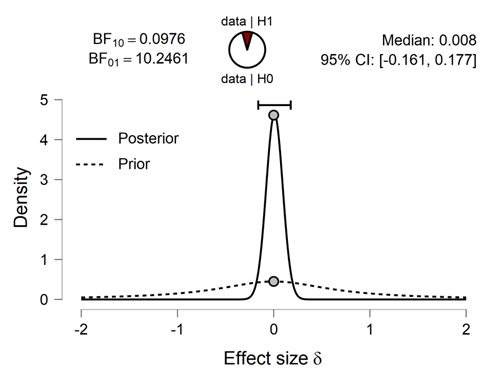
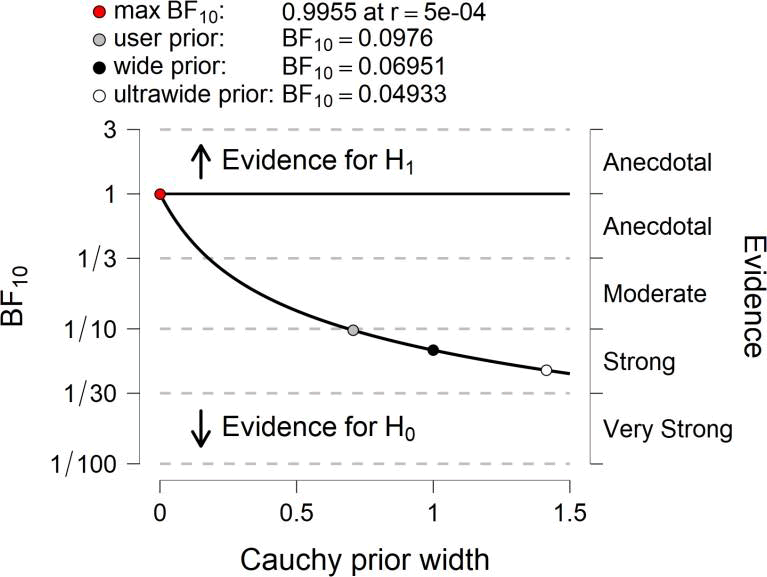
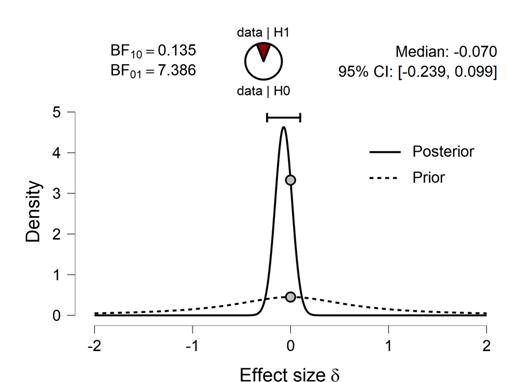
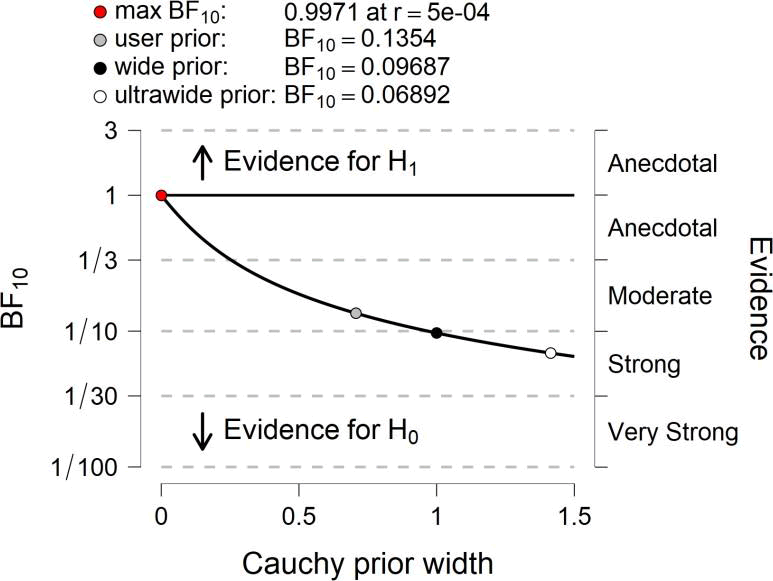
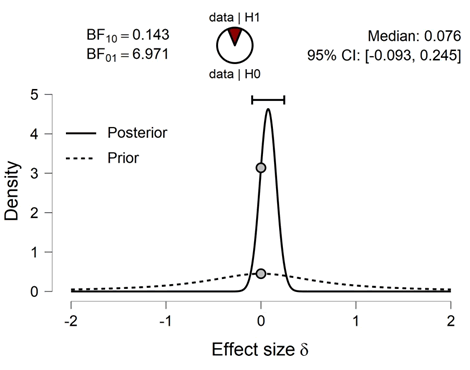
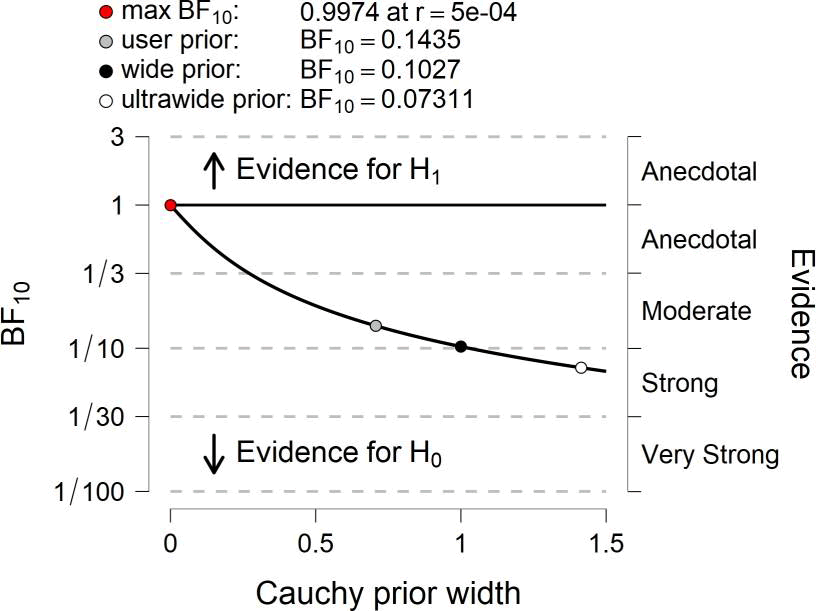
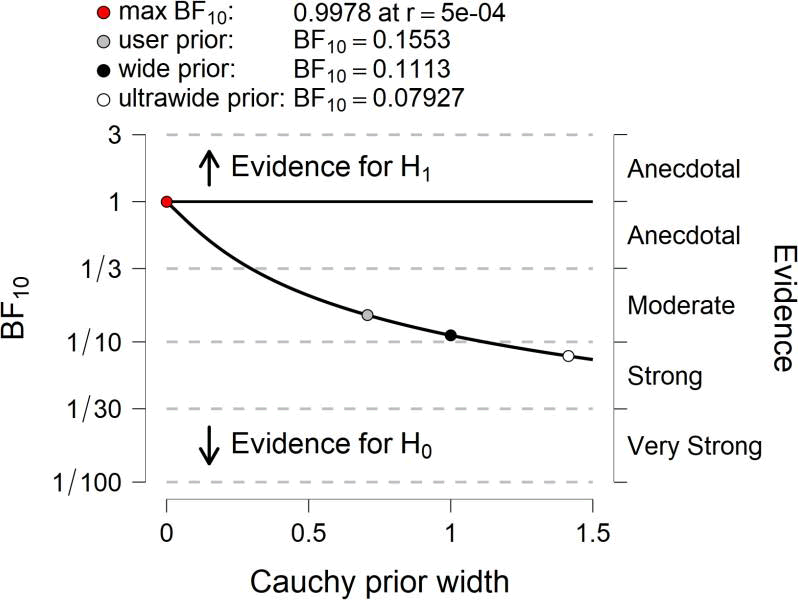
By analyzing data from each variable BF10 and error %, the results are as in the table
Prior and Posterior
| Table 5 Result with bayesian independent samples t-test |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% Credible Interval | |||||||
| Group | N | Mean | SD | SE | Lower | Upper | |
| EFF1 | Female | 198 | 7.152 | 2.386 | 0.170 | 6.817 | 7.486 |
| Male | 387 | 7.367 | 2.482 | 0.126 | 7.119 | 7.615 | |
| INT1 | Female | 198 | 7.727 | 2.534 | 0.180 | 7.372 | 8.082 |
| Male | 387 | 7.850 | 2.560 | 0.130 | 7.594 | 8.106 | |
| MOT1 | Female | 198 | 7.530 | 2.474 | 0.176 | 7.184 | 7.877 |
| Male | 387 | 7.509 | 2.583 | 0.131 | 7.251 | 7.767 | |
| KNW1 | Female | 198 | 6.753 | 2.481 | 0.176 | 6.405 | 7.100 |
| Male | 387 | 6.933 | 2.507 | 0.127 | 6.682 | 7.183 | |
| CHA1 | Female | 198 | 7.939 | 2.420 | 0.172 | 7.600 | 8.278 |
| Male | 387 | 7.742 | 2.583 | 0.131 | 7.483 | 8.000 | |
| RED1 | Female | 198 | 7.843 | 2.378 | 0.169 | 7.510 | 8.177 |
| Male | 387 | 7.630 | 2.534 | 0.129 | 7.377 | 7.884 | |
Conclusion
This research was conducted to see if there is Bayes method can only be used for classification problems with supervised learning and categorical data from the entrepreneurial interests of each cadet. The success rate of the test using the Bayes method is very dependent on the factors where students get learning about entrepreneurship that is given so that it affects the interest and readiness of the cadets to be able to start opening a business.
Suggestion
Based on research data, then suggested for future researchers to develop research on the approach contextual through different methods or comparing several methods.
Conflicts of Interest Statement
The authors whose names are listed immediately below certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
References
Aji, S.P., Mulyadi, H., & Widjajanta, B. (2018). Keterampilan Wirausaha Untuk Keberhasilan Usaha (Entrepreneurial skills for business success). Journal of Business Management Education, 3(3), 111-122.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Ardiyanti, D.A., & Mora, Z. (2019). Pengaruh Minat Usaha dan Motivasi Usaha terhadap Keberhasilan Usaha Wirausaha Muda di Kota Langsa (The influence of business interest and business motivation on the success of young entrepreneurs in Langsa City). Ocean Journal of Economics and Business,10(2), 168-178.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Ariyono, S., Luthfiyah, N., & Munoto (2021). Grow up entrepreneurial interest for cadets in aviation polytechnic surabaya using CTL with demonstration methods. Technium Social Sciences Journal, 19, 156.
Abaho, E. (2017). How can teachers’ entrepreneurial competences be developed? A collaborative learning perspective. Educ þ Train, 57(8/9), 908–923.
Alma, B. (2007). Entrepreneurship, Revised Edition, Alfabeta Publishers, Bandung.
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. In: Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Belousova, O., Hattenberg, D.Y., Benoît, G. (2020). Corporate entrepreneurship: From structures to mindset. Studies on entrepreneurship, structural change and industrial dynamics. Springer, 2020.
Botsaris, C., & Vamvaka, V. (2016). Attitude toward entrepreneurship: Structure, prediction from behavioral beliefs, and relation to entrepreneurial intention. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 7(2), 433–460.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Corbetta, G., Huse, M., & Ravasi, D. (2004). Crossroads of entrepreneurship. Springer Science + Business Media, Inc, 1. New York: Kluwer Academic.
Cafer, S. (2019). Enterpreneurial intentions of generation-z: Compare of social sciences and natural sciences undergraduate students at Bahcesehir University. Procedia.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Commarmond, I. (2017). In pursuit of a better understanding of and measure for entrepreneurial mindset contents. September, 34.
Cui, J., Sun, J., & Bell, R. (2019). The impact of entrepreneurship education on the entrepreneurial mindset of college students in China: The mediating role of inspiration and the role of educational attributes. The International Journal of Management Education, 100296.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Djaali. (2008). Teori Motivasi dan Aplikasinya (Motivation theory and its application). Jakarta: Earth Literacy.
Drucker, P.F. (1994). Innovation and Entrepreneurhip. New York: Harpercollins Publisher.
Davis, M., Hall, J., & Mayer, P. (2016). Measuring the entrepreneurial mindset: The development of the Entrepreneurial Mind set Profile (EMP), 727, 1–22.
Denanyoh, R., Adjei, K., & Nyemekye, G.E. (2015). Factors that impact on entrepreneurial intention of tertiary students in Ghana. International Journal of Business and Social Research, 5(3), 19–29.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Daz-Garc & Jimenez-Moreno, J. (2010). Entrepreneurial intention: The role of gender. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 6(3), 261–283.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Duong, C. (2019). Entrepreneurial self-efficacy and intention among vietnamese students: A meta-analytic path analysis based on the theory of planned behavior. Procedia ComputerScience.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Davis, M.H., Hall, J.A., & Mayer, P.S. (2015). Developing a new measure of entrepreneurial mindset: Reliability, validity, and implications for practitioners. Consulting Psychology Journal: Practice and Research, 67(4), 1– 28.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Elfving, J. (2008). Contextualizing entrepreneurial intentions: A multiple case study on entrepreneurial cognition and perception. Abo Akademi F€orlag.
Farny, S., Frederiksen, S.H., Hannibal, M., & Jones, S. (2016). A culture of entrepreneurship education. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 28(7–8), 514–535.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Fini, R., Grimaldi, R., Marzocchi, G.L., & Sobrero, M. (2012). The determinants of corporate entrepreneurial intention within small and newly established firms. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 36(2), 387–414.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Fahmi, I. (2013). Entrepreneurship. Bandung: Alphabeta.
Fuadi, I.F. (2009). "Hubungan Minat Berwirausaha Dengan Praktik Kerja Industri Siswa Kelas XII Teknik Otomatif SMK Negeri Adiwerna Kabupaten Tegal" SMK Negeri Adiwerna, Tegal Regency (The relationship of interest in entrepreneurship with industrial work practices for class XII students of automated engineering at SMK Negeri Adiwerna, Tegal Regency)”. PTM Journal, 9, 92-98.
Garaika. (2019). Self efficacy, self personality and self confidence on enterpreneurial intention study on young enterprises. Journal of Enterpreneurship Education.
Godwin, J.L., Neck, C.P., & D’Intino, R.S. (2016). Self-leadership, spirituality, and entrepreneur performance: a conceptual model. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religion, 13(1), 64–78.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Guerrero, M., Rialp, J., & Urbano, D. (2008). The impact of desirability and feasibility on entrepreneurial intentions: A structural equation model. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 4(1), 35– 50.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Hasibuan, A.H., Lubis, I., & Rujiman. (2019). The role of the management of the Indonesian young business (HIPMI) group in increasing business interest of young generation in Padangsidimpuan City. International Journal of Research & Review, 6(11), 327-354.
Hendro (2011). Entrepreneurial fundamentals. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Herdiani, N.M., & Hidayat, R. (2017). Faktor-Faktor Motivasi yang Mempengaruhi Mahasiswa Terhadap Minat Berwirausaha (Studi pada Mahasiswa Kelas Regular Pagi Politeknik Negeri Batam), (Motivational factors affecting students' interest in entrepreneurship (Study on morning regular class students at Batam State Polytechnic)). Journal of Applied Business Administration, 1(1), 139-146.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Hermana, D., Supardan, D., & Invite, G. (2010). Contextual teaching and learning (An initial guide in the development of PBM). Yogyakarta: PT. Diandra Primamitra Media.
Hisrich, R. (2001). Entrepreneurship kewirausahaan. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Hurlock, E. (2008). Psychology development. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Hadlock, H., Steven, W., Jemma, H., John, C., Nicholas, W., & James, B. (2008). From practice to entrepreneurship: Rethinking the learning factory approach. Proceeding of the 2008 IAJC IJME International Conference, ISBN 978-1- 60643-379-9.
Hassi, A. (2016). Effectiveness of early entrepreneurship education at the primary school level: evidence from a field research in Morocco. Citizenship, Social and Economics Education, 15(2), 83–103.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Haynie, J.M., Shepherd, D., Mosakowski, E., & Earley, P.C. (2010). A situated metacognitive model of the entrepreneurial mindset. Journal of Business Venturing, 25(2), 217–229.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Houston, P., Connie, D., & Nicole, L. (2020). Entrepreneurial thinking: A signature pedagogy for an uncertain 21st century. The InternationalJournal of Management Education.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Hu, L.T., & Bentler, P.M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1–55.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Hussain, A., & Norashidah, D. (2015). Impact of entrepreneurial education on entrepreneurial intentions of Pakistani students. International Journal of Business Innovation and Research, 2(1), 43.
Indarto & Santoso, D. (2020). Karakteristik Wirausaha, Karakteristik Usaha dan Lingkungan Usaha Penentu Kesuksesan Usaha Mikro Kecil dan Menengah (Entrepreneurial characteristics, business characteristics and business environment determinants of the success of micro, small and medium enterprises). Journal of Economics and Business Research, 13(1), 54-69.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Indrityatni, L. (2013). Pengaruh Mata Kuliah Kewirausahaan Dalam Menumbuhkan Mahasiswa Untuk Berwirausaha (Studi Kasus Pada Mahasiswa STIE Pelita Nusantara Semarang), (The influence of entrepreneurship courses in growing students for entrepreneurship (Case study on students at STIE Pelita Nusantara Semarang)). Economic Focus, 8(1), 52-59.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Jabeen, F., Faisal, M.N., & Katsioloudes, M.I. (2017). Entrepreneurial mindset and the role of universities as strategic drivers of entrepreneurship: Evidence from the United Arab. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 24(1), 136-157.
Jena, R.K. (2020). Measuring the impact of business management Student’s attitude towards entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurial intention: A case study. Computers in Human Behavior, 107.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Katz J.A. (2003). The chronology and intellectual trajectory of American entrepreneurship education. Journal ofBusiness Venturing, 18(2), 283-300.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Katz, J., & Gartner, W. (1988). Properties of emerging organizations. Journal of Academy of Management Review, 13(3), 429-441.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Kuntowicaksono. (2012). Pengaruh pengetahuan wirausaha dan kemampuan memecahkan masalah wirausaha terhadap minat berwirausaha siswa sekolah menengah kejuruan. (The effect of entrepreneurial knowledge and ability to solve entrepreneurial problems on entrepreneurial interest of vocational high school students). Journal of Economic Education, 1(1), 45-52.
Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (1998). Entrepreneurship; Contemporary approach. Fort Worth: The Dryden Press.
Kurnianti, E.D. (2015). Kewirausahaan Industri, (Entrepreneurship industry). Yogyakarta: Depublish.
Krueger, N. (1993). The impact of prior entrepreneurial exposure on perceptions of new venture feasibility and desirability. Entrepreneurial Theory Practice, 18(1), 5–21.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Kasmir. (2007). Kewirausahaan, PT Raja Grafindo Perkasa, Jakarta.
Kawulur, A.F., Rumagit, M.C.N., & Tumiwa, R.A.F. (2019). Entrepreneurship conceptual model based on local economic potentials in coastal likupang beach North Minahasa district, Indonesia. Advances in Economics,Business and Management Research, 65, 737–741 (Icebef 2018).
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Kirkwood, J., Dwyer, K., & Gray, B. (2014). Students’ reflections on the value of an entrepreneurship education. The International Journal of Management Education, 12(3), 307–316.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Kouakou, K.K.E., Li, C., Akolgo, I.G., & Tchamekwen, A.M. (2019). Evolution view of entrepreneurial mindset theory. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 10(6).
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Krueger, N.F. ( 2003). The cognitive psychology of entrepreneurship. In: Acs, Z.J., Audretsch, D.B. (Editions), Handbook of Entrepreneurship Research: an Interdisciplinary Survey and Introduction (New York). Springer, New York.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Lambing, P.A., & Kuehl, C.R. (2007). Entrepreneurship. (4th Edition). New Jersey: PearsonPractice Hall.
Lee, S.H., & Wong, P.K. (2004). An exploratory study of technopreneurial intentions: A career anchor perspective. Journal of Business Venturing, 19(1), 7-28.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Lindner, J. (2019). Entrepreneurial spirit for the whole school–ways to become an e.e.si- Entrepreneurship School. Discourse and Communication for Sustainable Education, 10(2), 5-12.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Ludi, W. (2020). The impact of entrepreneurship education and students' entrepreneurial mindset: The mediating role of attitude and self-efficacy. Heliyon. Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Luthan. (2005). Organizational behavior, New Rok, Mc. Graw-hil companies, hlm. 186.
Martín-Guerrero, J.D., & Lucas, L. (2021). Quantum machine learning: A tutorial José D.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Masykur, W. (1994). Entrepreneurship: A series of lectures, Gunadarma, Jakarta.
Rahmadi, AN., & Heryanto, B. (2016). Analisis faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi minat berwirausaha pada mahasiswa program studi manajemen fakultas ekonomi Universitas Kadiri. (Analysis of factors affecting interest in entrepreneurship in management study program students, faculty of economics, Kadiri University). Journal of Economics,University of Kediri, 1(2), 153-169.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Riad, S. (2020). Stakeholder engagement for innovation management and entrepreneurial development: A meta-analysis. Journal of Business Research.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Santoso, D. (2013). Modul Pembelajaran Kewirausahaan. Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Pembelajaran dan Kemahasiswaan, Kementrian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. (Entrepreneurship learning module. Jakarta: Directorate general of learning and student affairs, ministry of education and culture).
Saragih, R. (2017). Membangun Usaha Kreatif, Inovatif, dan Bermanfaat Melalui Penerapan Kewirausahaan Sosial. (Building creative, innovative, and beneficial businesses through the application of social entrepreneurship). Journal of Entrepreneurship, 3(2), 26-34.
Semih, K. (2021). Completing the machine learning saga in fractional snow cover estimation from MODIS Terra reflectance data: Random forests versus support vector regression. Remote Sensing of Environment.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Slameto, S. (2010). Belajar dan faktor yang mempengaruhinya. (Learning and the factors that influence it). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Subandono, A. (2007). Minat Berwirausaha. Jakarta: Rajawali Pers.
Suharyono. (2017). Sikap dan Perilaku Wirausahawan. Jurnal Ilmu dan Budaya, 40(56), 6551-6586.
Crossref , GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Sunarya, P.A., & Saefullah, A. (2011). Kewirausahaan (Entrepreneurship). Andi Publisher.
Suparno, P. (2006). Teori Perkembangan Kognitif Jean Piaget. (Jean Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development). Yogyakarta: Kanisius.
Suryana. (2003). Kewirausahaan pedoman praktis: Kiat dan proses menuju sukses. (Practical guide entrepreneurship: Tips and process towards success). Jakarta: Salemba Empat. (Practical guide entrepreneurship: Tips and process towards success. Jakarta: Salemba Empat).
Timmons, J.A., & Spinelli, S., Jr. (2008). New venture creation. Kewirausahaan untuk Abad 21. Yogyakarta: Andi.(Buku asli New Venture Creation: Entrepreneurship for the 21st Century (6th Edition)).
Trianto. (2007). Model-Model Pembelajaran Inovatif Berorientasi Konstruktivistik. (Constructivistic oriented innovative learning models), Jakarta. Library Achievement.
Veronika, A., Roman, E., & Joanne, Y.C. (2021). A machine learning approach to cluster destination image on
Instagram. Tourism Management, 85.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Wahyono, B. (2013). ). Pengaruh Pendidikan Kewirausahaan terhadap Niat Berwirausaha Siswa SMK N 1 Medan Tahun 2013. Solo: Tesis Universitas Sebelas Maret Surakarta. (The effect of entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurial intentions of students at SMK N 1 Medan in 2013. Solo: Thesis of Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta.).
Widayati, E., Yunaz, H., Rambe, T., Siregar, B.W., Fauzi, A., & Romli, R. (2019). Pengembangan Kewirausahaan dengan Menciptakan Wirausaha Baru dan Mandiri. (Entrepreneurship development by creating new and independent entrepreneurs). Scientific Journal of Business Management and Innovation Sam Ratulangi University, 6(2), 98-105.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Widnyana, I.W., Widyawati, S.R., & Warmana, G.O. (2018). Pengaruh Pemberian Mata Kuliah Kewirausahaan dan Pelatihan Wirausaha Terhadap Minat Wirausaha Ekonomi Kreatif Pada Mahasiswa UNMAS Denpasar. (The effect of giving entrepreneurship courses and entrepreneurship training on creative economy entrepreneurial interest in UNMAS Denpasar students). Indonesian Community Service Journal, 1(1), 171-177.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Warhuus, J.P., & Basaiawmoit, R.V. (2014). Entrepreneurship education at Nordic technical higher education institutions: Comparing and contrasting program designs and content. International Journal of Managementin Education, 12(3), 317–332.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Winardi. (2003). Entrepreneur & Entrepreneurship, Kencana, Jakarta
Xuebin, Y., Hengyi, Lia., Kenshi, S., Kazuki, U., Aravinda, C.V, & Lin, M. (2020). Machine learning based Apathy classification on Doppler RadarImage for the elderly person. International Conference on Identification, Information and Knowledge in the internet of Things.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Zimmerer, T.W., & Scarborough, N.M. (2008). Kewirausahaan dan Manajemen Usaha Kecil. (Entrepreneurship and small business management. Jakarta: Four Salemba).
Received: 03-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-22-10686; Editor assigned: 05- Feb -2022, PreQC No. AEJ-22-10686 (PQ); Reviewed: 19- Feb-2022, QC No. AEJ-22-10686; Revised: 26-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-22-10686 (R); Published: 10-Mar-2022