Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 5
Artificial Intelligence In Digital Marketing Influences Consumer Behaviour: A Review And Theoretical Foundation For Future Research
Fazla Rabby, School of Business, University of Southern Queensland
Dr. Ranga Chimhundu, School of Business, University of Southern Queensland
Dr. Rumman Hassan, School of Business, University of Southern Queensland
Citation Information: Rabby., F. Chimhundu., R. & Hassan, R. (2021). Artificial intelligence in digital marketing influences consumer behaviour: a review and theoretical foundation for future research. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 25(5), 1-7.
Abstract
Tracking the customer journey has become more challenging because of the changing marketing environment. The market is getting bigger and better, with digital markets offering customers countless new options for shopping. Customers share their desires, attitudes, and beliefs through many avenues and mediums, as the need for exceptional customer experience grows across all digital platforms. Artificial intelligence (AI) is the answer to enhancing the digital experience while delivering personalised content. This seemingly endless source of customer- curated data is expanding. Many marketers turn to AI to extract the information and use it. AI empowers businesses to collect and act on detailed real-time customer insights, and through these insights, they can develop customised digital marketing experiences. Businesses have a long way to go before they adopt AI-based applications, but many see the critical benefit of integrating AI into digital marketing practices for building an exceptional customer experience during the buying process. This literature review looks at AI-based digital marketing applications that can enhance the online customer experience using the customer decision journey. It looks closely at how AI integrated digital marketing influences consumer buying behaviour.
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence, Technology, Trust, Digital Marketing, Consumer Behavior.
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is likely to transform digital marketing interactions with customers (Ransbotham et al. 2017). AI differs from human intuition because it is data- driven. Commonly referred to as human intelligence processes by machines, AI can transform data into strategies that guide meaningful consumer behaviour (Haenlein & Kaplan 2019). Higher customer satisfaction is more likely when businesses adopt digital marketing to influence consumer behaviour (Ransbotham et al. 2017). AI-based digital marketing, makes it even easier for businesses to reach the right customers at the right time (Ransbotham, et al. 2017). The unexpected benefit of deliberately promoting AI innovation to assist digital marketing shown in Picture 1, is a long-term partnership that helps customer satisfaction grow. Businesses are benefitting from AI through AI-controlled chatbots, big data and outputs from cognitive technologies. Retailers using AI powered marketing do 5 times better than traditional retailers. Consumer behaviour has changed dramatically due to digital marketing, with modern consumers expecting a more consistent and personalised experience.
Buyers may experience trust issues due to AI innovation in digital marketing and, as a result, clients are keen to spend more time educating themselves before they commit to a purchase (Singh et al. 2019). Because consumers are more educated today, they are more likely to do their research before purchasing a product or service (Yussaivi et al. 2019).
As of now, there is no way to know if AI-enabled digital marketing will be successful. According to research, if digital marketing is not done properly, it can have negative consequences (Roggeveen et al. 2021). This can be a challenge for businesses trying to implement AI into their operations (Aceto, Persico, & Pescapé 2018). Businesses that want to provide efficient AI-based digital marketing must have a robust IT infrastructure because AI requires appropriate and high-quality marketing data. Therefore, it is important to understand how customers perceive AI innovation as a component of their ability to learn and how this results in more attractive brands (Roggeveen et al. 2021). The after effects of an analysis of service quality result from a correlation between the read of service received and previous expectations for what that support can provide (Nagy & Hajdu 2021). In the current collection of studies, there is a dearth of research on clients' reactions to machine-controlled services, particularly AI-enabled service quality and shopping experience (Chopra 2020). Given that AI- enabled services are frequently built around self- management innovations, service quality in AI-enabled services is likely to differ significantly from service quality in social organisations (Guha et al. 2021).
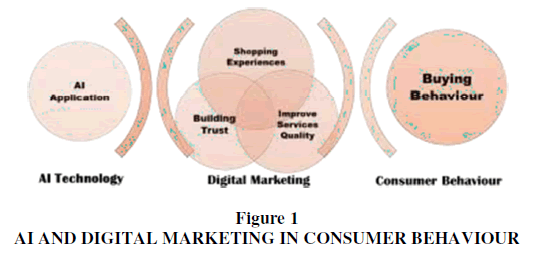
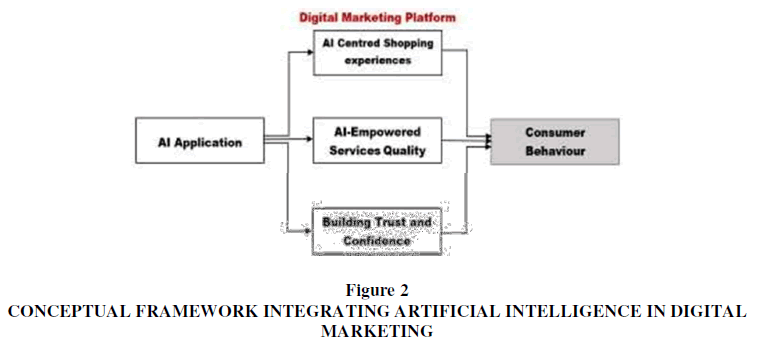
Here, we look into combining AI with digital marketing to improved client capability. We have developed a model in Figure 1, based on the AI centred shopping experience, service quality and trust-confidence hypothesis, which facilitates the learning of online consumer behaviours and attitudes. Our model includes trust and confidence to bridge the gap between quality, convenience and AI support to take advantage of technological development and promote prolific marketing campaigns. This study guides businesses to develop tailored AI experiences and ensures specific audiences benefit from the valuable insights gained through AI techniques employed. It also furthers our understanding of human collaboration with AI-powered services.
Objectives of the Study
To identify how consumer buying behaviour is influenced by integrating AI in digital marketing and how this supports better marketing decisions.
Literature Review
Advances in technology and the potential for AI in digital marketing are on the rise, and the possibilities are limitless. AI is being used more and more in operational markets for identifying risk, conducting consumer research, and identifying business functions to coordinate with target customers (Campbell et al. 2020). While the use of AI in digital marketing will influence marketing strategies, business models, marketing procedures, and consumer service options, it will also influence customers' behaviour. The main focus of AI in digital marketing is not based on replacing human dynamics in critical decisions but on developing a more robust dynamic digital marketing environment. It will allow advertisers to quickly assess the requirements of a potential customer and adjust the AI they employ in digital marketing to increase sales (Campbell et al. 2020). AI is expected to be critical for developing future digital products, particularly in digital marketing. Based on Juniper Research, in 2018, retailer spending on AI was 2 billion and is set to rise to $7.3 billion by 2022 (Smith 2018). Various sources, including AI-controlled chatbots, big data, and client information are being used in digital marketing to teach retailers how to use AI to influence consumer behaviour. Based on previous research, AI is expected to reach the highest level of customers in the digital marketing environment. Global company workplaces are unit-valuing conventional consumers at a rate that is multiple times that of retailers. As a result, high levels of personalisation and a significant commitment and better digital marketing material will be emphasised (Keiningham et al. 2017).
As Kiron and Schrage (2019) note, consumers and organisations may rely on technologies in value co- innovation, and they can connect and cooperate with one another through a digital platform. However, analysts are focusing on how AI is often used to develop new action plans—a possible outcome from both business and marketing composition use of the AI technique (Garbuio & Lin 2019). In the context of a digital environment, virtual consumer engagement can be defined as consumers' behavioural symptoms that happen as a result of their motivational drivers and occur while the business or brand is the focal point (Garbuio & Lin 2019). This advancement in AI digital marketing organisation, benefits from mechanising various aspects of marketing and data products that can be used to support AI (Bag et al. 2021). This means that AI use must be coordinated with digital marketing applications, data care must be taken naturally, and recommendations must be returned to these various areas (Haenlein & Kaplan 2019).
One of the challenges that digital marketers face due to the increasing amount of data available is determining how to process and measure this data to provide valuable insights and build consumer trust (Wirth 2018). While emphasising the relationship between customer engagement behaviours and big data, it is important to analyse, in detail, how the organisation will build trust using big data and AI collaboration to influence consumer behaviour (Hoff & Bashir 2015). Fortunately, AI technologies help service providers manage and respond to large amounts of data in real-time, automating service interactions and offering tailored customer experiences (Bettencourt, Lusch & Vargo 2014). AI is becoming an essential marketing tool in critical situations (Abadir et al. 2020). The strategy and planning of AI has changed due to data collected by customer relationship managers about the actions and preferences of consumers (Dewnarain, Ramkissoon & Mavondo 2019).
In their review, Merendino and colleagues (2018) discovered that thedigitisation of information also impacts board decisions. According to Kim et al. (2019), AI’s reliance on data quality and quantity, as well as a scarcity of AI skills can slow progress even when AI is moderately implemented. Combining moderately important business and marketing transcription skills with AI capabilities could significantly increase output.
Chatbots are computer programs built by AI technology that guide customers to simplify human interaction in digital marketing platforms and support natural language conversational queries (Chopra 2020). Although they cannot seek human cooperation in promoting interactions, they can provide systematic research with a knowledgeable account (Brandtzaeg & Flstad 2017). When it comes to preferences, perceived value and transparency play an important role in determining opinions and conduct (Hoff & Bashir 2015). Chatbots have identified humanity, social intellect and the presence of society, trust, skills, and usability as regards to social demands (Chopra 2020). Various psychological types are recognised by Chatbots, and messages are generated that resonate with inclinations that produce individual recommending structures (Haenlein & Kaplan 2019). These AI-driven systems, which several companies already use, can provide digital marketing buyers with individualised guidelines to help customers find relevant products and services (Haenlein & Kaplan 2019). AI applications for customer decision-making are an unstudied field. This systematic review of the literature aims to fill this research gap.
Methodology
The methodology used was a systematic analysis of the literature. Scopus and Google Scholar databases were used to compile academic studies, papers, and publications over ten years from 2011 to the present. The papers were analysed in the review context, and keywords were focused on the title and research objectives.
Theoretical Framework and Discussion
Artificial Intelligence Centred Shopping Experiences
H1: Artificial intelligence can provide superior customer experiences and influence consumer behaviour to purchase goods and services.
In previous research, four aspects of customer experience were identified: cognitive, emotional, physical and social (Pires, et al. 2015). The social attitudes or the psychological character of a client's perception are also characterised by social elements (Keiningham et al. 2017). Jarrahi (2018) reports that AI innovations, common understanding of characteristic language handlings can encourage customer conclusion and customer input to be dissected by individuals in size, reality and surreal pace. Consequently, AI is likely one of the most important digital marketing tools for businesses to continuously improve customer capacity (Haenlein & Kaplan 2019). Different digital marketing technologies such as augmented-virtual realities, vision-driven imaging and predictive inventory management are widely associated with AI in online businesses (Singh et al. 2019). A thorough understanding of the customer and their preferences and past experiences are necessary to improve the customer experience. AI can contribute to speeding up understanding since AI devices use information and customer profiles to recommend customer communication in the digital marketing environment (Ransbotham et al. 2019).
Findings
AI can detect underlying patterns in consumer purchasing behaviour based on products purchased and it can make better-informed product recommendations to consumers, thereby encouraging them to make a final purchase.
Artificial Intelligence Empowered Service Quality
H2: Artificial intelligence in digital marketing improve service quality and operational efficiency.
It is possible to measure efficiency and service quality by how customers perceive a brand's service contributions. These measurements are verifiably set in light of the distinction between intended and acquired service contributions (Ransbotham et al. 2019). This definition of service quality is supported by the anticipation dis- affirmation hypothesis. The analysis of service quality and operational efficiency results from a relationship between the impression of service received and previous expectations for what that assistance can provide (Haenlein & Kaplan 2019). Even though current research is rich with a focus on the standard of social services, there is a dearth of research on clients' reactions to machine-controlled services, particularly those involving AI (Montes & Goertzel 2019). A significant difference between service quality and operational efficiency in AI- enabled services and social services is likely because AI- enabled services are frequently built around self- management advancements.
Findings
AI-powered customer experience shapes the customer's dynamic journey to make it convenient and satisfying by adding services performed by computers or machines to quality assessments.
Building Trust and Confidence
H3: Artificial intelligence helps to build trust in digital platforms.
In digital marketing, trust and accountability in a relationship play important roles in connecting customers and retailers (Jarrahi, 2018).
Over time, the hypothesis has been focused on a wide range of settings, including digital marketing, searching sites, complete connections in online networks, fan pages via web-based media, and online delivery conduct (Bag et al. 2021).
Any investigation considers the numerous roles that trust and partnership obligation play in interceded collaborations between consumers and retailers. The confidence- responsibility hypothesis benefits from one of the essential variables: trust (Wirth, 2018). Trust has made an essential contribution to the accomplishment of machine- controlled administrations because it portrays the relationship between people and robotization (Wirth, 2018). Hoff and Bashir (2015) consider security an essential component of trust, assuming that shoppers intend to maintain control over the use of their personal information by retailers. Furthermore, previous research has shown that confidence can alter relationships between various components in the context of AI use, to facilitate quality and accommodation for example (Xu et al. 2020).
Findings
AI is changing the future of digital marketing and helps build trust and create personalised experiences for consumer.
Conclusion
AI is a relatively new technology in digital marketing with the potential to improve the impact on consumer behaviour. AI marketing is a new marketing playbook that allows companies to move from marketing automation to marketing personalization more effectively. The impact of AI on digital marketing has accelerated in recent years allowing marketers to personalise sales and digital marketing efforts beyond expectations. Because of the vast amount of data available, marketers have personalised their sales and marketing efforts and exceeded their customers' expectations beyond what they imagined. AI engineering has the potential to change the way services and products are delivered to customers. Finally, we can say that digital marketing automation is more dynamic than ever before, and information for analysing buyer behaviour brings highly predictive results. AI's involvement helps businesses identify their target customers in digital marketing platforms, understand their customers’ needs and preferences and increasing transparency. AI tools in digital marketing platforms are integrated into live chat via Chatbots that engage consumers by promptly responding to inquiries in an easy-to-use interface. Using artificial digital marketing intelligence technologies together with human-produced data, companies can build trust in digital platforms and increase positive, personalised client experiences through a deep dive.
References
- Abadir, A.P., Ali, M.F., Karnes, W., & Samarasena, J.B. (2020). Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Clinical endoscopy, 53(2), 132.
- Aceto, G., Persico, V., & Pescapé, A. (2018). The role of Information and Communication Technologies in healthcare: taxonomies, perspectives, and challenges. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 107, 125-154.
- Bag, S., Gupta, S., Kumar, A., & Sivarajah, U. (2021). An integrated artificial intelligence framework for knowledge creation and B2B marketing rational decision making for improving firm performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 92, 178-189.
- Bettencourt, L.A., Lusch, R.F., & Vargo, S.L. (2014). A service lens on value creation: marketing's role in achieving strategic advantage. California management review, 57(1), 44-66.
- Brandtzaeg, P.B., & Følstad, A. (2017). Why people use chatbots. In International conference on internet science (pp. 377-392). Springer, Cham.
- Campbell, C., Sands, S., Ferraro, C., Tsao, H.Y.J., & Mavrommatis, A. (2020). From data to action: How marketers can leverage AI. Business Horizons, 63(2), 227-243.
- Chopra, S.S. (2020). Helping Entrepreneurs and Small Businesses Make the Digital Transformation. In The Evolution of Business in the Cyber Age (pp. 39-51). Apple Academic Press.
- Dewnarain, S., Ramkissoon, H., & Mavondo, F. (2019). Social customer relationship management: An integrated conceptual framework. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 28(2), 172-188.
- Garbuio, M., & Lin, N. (2019). Artificial intelligence as a growth engine for health care startups: Emerging business models. California Management Review, 61(2), 59-83.
- Guha, A., Grewal, D., Kopalle, P. K., Haenlein, M., Schneider, M.J., Jung, H., & Hawkins, G. (2021). How artificial intelligence will affect the future of retailing. Journal of Retailing, 97(1), 28-41.
- Haenlein, M., & Kaplan, A. (2019). A brief history of artificial intelligence: On the past, present, and future of artificial intelligence. California management review, 61(4), 5-14.
- Hoff, K.A., & Bashir, M. (2015). Trust in automation: Integrating empirical evidence on factors that influence trust. Human factors, 57(3), 407-434.
- Jarrahi., M.H. (2018), ‘Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making’, Business Horizons, vol. 61, no. 4, pp. 577-586.
- Keiningham, T., Ball, J., Benoit, S., Bruce, H.L., Buoye, A., Dzenkovska, J., & Zaki, M. (2017). The interplay of customer experience and commitment. Journal of Services Marketing.
- Kim, Y., Kim, C.K., Lee, D.K., Lee, H.W., & Andrada, R.I.T. (2019). Quantifying nature-based tourism in protected areas in developing countries by using social big data. Tourism Management, 72, 249-256.
- Kiron, D., & Schrage, M. (2019). Strategy for and with AI. MIT Sloan Management Review, 60(4), 30-35.
- Lysaght, T., Lim, H. Y., Xafis, V., & Ngiam, K.Y. (2019). AI-assisted decision-making in healthcare. Asian Bioethics Review, 11(3), 299-314.
- Merendino, A., Dibb, S., Meadows, M., Quinn, L., Wilson, D., Simkin, L., & Canhoto, A. (2018). Big data, big decisions: The impact of big data on board level decision-making. Journal of Business Research, 93, 67-78.
- Montes, G.A., & Goertzel, B. (2019). Distributed, decentralized, and democratized artificial intelligence. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 141, 354-358.
- Nagy, S., & Hajdú, N. (2021). Consumer Acceptance of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Online Shopping: Evidence from Hungary. Amfiteatru Economic, 23(56).
- Pires, G.D., Dean, A., & Rehman, M. (2015). Using service logic to redefine exchange in terms of customer and supplier participation. Journal of Business Research, 68(5), 925-932.
- Ransbotham, S., Kiron, D., Gerbert, P., & Reeves, M. (2017). Reshaping business with artificial intelligence: Closing the gap between ambition and action. MIT Sloan Management Review, 59(1).
- Roggeveen, A.L., Grewal, D., Karsberg, J., Noble, S.M., Nordfält, J., Patrick, V.M., & Olson, R. (2021). Forging meaningful consumer-brand relationships through creative merchandise offerings and innovative merchandising strategies. Journal of Retailing, 97(1), 81-98.
- Singh, J., Flaherty, K., Sohi, R.S., Deeter-Schmelz, D., Habel, J., Le Meunier-FitzHugh, K., & Onyemah, V. (2019). Sales profession and professionals in the age of digitization and artificial intelligence technologies: concepts, priorities, and questions. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 39(1), 2-22.
- Smith., S. (2018), Juniper Research: Retailer Spending on AI to Grow Nearly Fourfold, Reaching $7.3 Billion by 2022, Businesswire, viewed 30 March 2021, <https://www.businesswire.com/news-
- /home/20180131005068/en/Juniper-Research-Retailer-Spending-on-AI-to-Grow-Nearly- Fourfold-Reaching-7.3-Billion-by-2022>.
- Wirth, N. (2018). Hello marketing, what can artificial intelligence help you with?. International Journal of Market Research, 60(5), 435-438.
- Xu, Y., Shieh, C.H., van Esch, P., & Ling, I.L. (2020). AI customer service: Task complexity, problem-solving ability, and usage intention. Australasian marketing journal, 28(4), 189-199.
- Yussaivi, A.M., Lu, C.Y., Syarief, M.E., & Suhartanto, D. (2021). Millennial Experience with Mobile Banking and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled Mobile Banking: Evidence from Islamic Banks. International Journal of Applied Business Research, 39-53.