Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 6
Analysis of entrepreneurial innovation on the business performance in Keerom district Indonesia
Westim Ratang, University of Cenderawasih
Citation Information: Ratang W. (2021). Analysis of entrepreneurial innovation on the business performance in keerom district indonesia. International Journal of Entrepreneurship, 25(4), 1- 8.
Abstract
The research objectives are to analyze entrepreneurship in terms of sustainability, cognitive aspects, accountability, transparency, affective aspects and conative aspects, partially and simultaneously effect on product innovation in Keerom Regency, and to analyze entrepreneurship partially and simultaneously influence business performance. This study also aimed at analyzing entrepreneurship affect business performance mediated by product innovation in Keerom Regency. This research was conducted at the dragon fruit farmer group in Keerom Regency with the number of respondents 50 farmers, qualitative descriptive analysis tools and Multiple Regression Analysis. The results of the simultaneous test state that all variables consisting of sustainability variables, cognitive variables, accountability variables, transparency variables, affective variables, conative variables and product innovation variables all affect business performance. The results of the simultaneous test state that all variables consisting of sustainability variables, cognitive variables, accountability variables, transparency variables, affective variables, conative variables all affect product innovation. The dominant influence on business performance mediated by product innovation is the cognitive aspect, meaning that there is a great need for training on entrepreneurship that makes it easier for farmers to become entrepreneurs.
Keywords
Innovation, Entrepreneurship, Sustainability, Business Performance.
Introduction
Fostering an entrepreneurial spirit is one of the efforts that can be expected to spur rural economic growth. The entrepreneurial spirit will change the orientation of farming from just production to being business-oriented. Farmers will begin to consider the types of plants to be planted, the time of planting and even the processing of agricultural products in order to obtain added value from these activities. The importance of entrepreneurship as a practice has received serious attention from the government. One form of this attention was the issuance of a government regulation in 1997 relating to efforts to foster the birth of new entrepreneurs. In 2011, the government's commitment to further encourage the emergence of new entrepreneurs was marked by the launching of the National Entrepreneurship Movement (GKN). It is time for entrepreneurial-minded farming to be introduced to the farming community. The strategic steps that need to be prepared are growing entrepreneurial interest by changing the mind set from production farming orientation to business; increasing knowledge and introduce various harvest processing techniques or derivative products to increase the added value of the product; introducing the market, namely conducting business cooperation with various business actors who use the product, and growing agribusiness institutions that are able to become the driving force of farmer's business.
The entrepreneurial spirit can grow and develop with the motivation and abilities possessed. When farmers have sufficient motivation, farmers must also have the ability to carry out the business. Creative ideas are the starting point for running entrepreneurship. Creative ideas can be trained with observing, imitating, and modifying or by making products that do not exist/need. The determination of the type of business must also be adjusted to the opportunities and potentials possessed. Farming with an entrepreneurial perspective is expected to be able to increase the added value of the product so that people's incomes can increase.
Dragon fruit is not an endemic plant in Papua. The fruit of this cactus-type plant is usually only sold in a number of supermarkets. These fruits are imported from a number of areas that were previously cultivated, such as from Java and other areas. However, recently, a number of fruit sellers on the side of the road have also started selling a lot of fruit which is believed to have great health benefits. Dragon fruit is one of the leading commodities in Keerom Regency, Papua, in addition to durian, banana, and matoa. In fact, it was originally developed with the intention of trying two transmigrants, Sobikhan and Samirun. The research objectives are to analyze entrepreneurship partially and simultaneously effect on product innovation in Keerom Regency, and to analyze entrepreneurship partially and simultaneously influence business performance. This study also aimed at analyzing entrepreneurship affect business performance mediated by product innovation in Keerom Regency.
Theoretical Basis
The development of a country is development that reflects the welfare of the majority of the country's population, where the majority of the population in Indonesia is farmers; therefore development in Indonesia should prioritize the agricultural sector (Subejo, 2020; Förster et al., 2011). In reality, it can be seen from the history of the economy and agricultural development in Indonesia, there have been ups and downs in the lives of farmers who received the impact of the policies of their time. In general, farmers always seem to be in a weak position and marginalized by various policies that are often impartial and do not have a real impact on improving their quality of life.
In the course of development, farmers should have an entrepreneurial attitude in running their farming. Entrepreneurship is very necessary because every human being has the potential to develop themselves. Besides that, every human being also has an ever-increasing need, for that every human being will try to fulfill it as quickly as possible. The faster the desire to fulfill these needs, the higher the entrepreneurial spirit needed. When viewed more broadly, entrepreneurship is needed by a country because the wealth owned by a country must be explored, developed and utilized. These efforts must be carried out by the State itself, and will be successful if the nation has an entrepreneurial spirit, which is a spirit that always concentrates on increasing wealth values by exploring, developing and utilizing.
Priyanto (2004) revealed that studies in the agricultural sector prove that with entrepreneurship, farmers will be able to make strategic plans, be able and brave to implement these plans in farming activities and be able to monitor and evaluate the course of farming. Muatip (2008) states that entrepreneurial competence affects the productivity of farmers, in this case productivity describes the extent to which farmers are able to achieve business goals or objectives by managing resources appropriately. Rokhman (2008) explains that entrepreneurial orientation is very influential in getting fishery products that have quality assurance, are competitive and provide high added value. The entrepreneurial behavior affects the success rate of small businesses in the agro-industry (Koellinger et al., 2007; Dirlanudin, 2010; Ashilina et al, 2019).
Entrepreneurship is a creative endeavor that is built on innovation to produce something new, has added value, creates jobs and the results are useful for others. Entrepreneurship means entrepreneurship or entrepreneurship, which is a branch of economics that teaches how we can be independent in starting a business in order to achieve profit and develop all our economic potential.
The ability to create something new and different through creative thinking and innovative actions to create opportunities (Drucker, 1959; Steiner, 1963; Suryana, 2006). Entrepreneurship is everything that is important about an entrepreneur, namely a person who has the nature of working hard and sacrificing, concentrating all power and daring to take risks to realize his ideas (Soegoto, 2013; Ahmad & Seymour, 2008; Cunningham & Lischeron, 1991). In terms of his actions, he is able and sensitive to see business opportunities. From his actions, what stands out is taking concrete steps to combine or combine resources, whether or not they already have, to realize his idea of building a new business. From his work, it can be seen with the emergence of new companies with new products, new technologies, and new jobs.
A creative entrepreneur (entrepreneurships) is related to the ability and tenacity to develop new ideas by combining the resources they have, where they always observe previous situations and problems that were not or less attention to. In addition, they tend to have many alternatives to certain situations and use their subconscious mental emotional powers to create new things or products or new ways and so on. Entrepreneurs are people who are creative and innovative who are able to establish, build, develop, advance, and make their company superior (Soegoto, 2013; Ahmad & Seymour, 2008; Cunningham & Lischeron, 1991). An entrepreneur must be the soul of a person who is able to look ahead. Looking ahead is not empty daydreaming, but seeing, thinking calculatingly, looking for options from various alternative problems and solutions (Marbun, 1993; Cofriyanti & Hidayanto, 2013).
Research Method
This type of research is experimental research with a quantitative research approach. The population in this study was all Mekar Karya farmers in Keerom Regency with a total of 150 farmers. The sample is part of the number and characteristics possessed by the population. The number of samples is 79 respondents. The technique used in sampling is using purposive sampling technique, namely the technique of determining the sample with certain considerations (Sugiyono, 2013). The sample was selected by looking at the same characteristics.
As operational definition of research variables, sustainability is the knowledge respondents about entrepreneurship related to the belief respondents to be able to implement entrepreneurship and become successful entrepreneurs. The Cognitive Aspect is the belief respondents with the existence of an entrepreneurship program, which consists of an entrepreneurship program facilitator, an explanation of the entrepreneurship program, and the training held can provide understanding and practice in entrepreneurship. Accountability is the response respondents to entrepreneurship programs that will have a positive impact and enthusiasm for entrepreneurship and the entrepreneurial programs that are held are right on target. Transparency is the farmer's response to a complete explanation of the entrepreneurship program, getting clear information, facilitators provide in-depth assistance, facilitators control the results of activities, evaluate and see performance results from entrepreneurial programs.
The affective aspect is the respondent's attitude about entrepreneurship programs related to motivation in entrepreneurship, implementing all entrepreneurial programs, being motivated to sell fruit, easy and understanding entrepreneurial programs, easy entrepreneurship program procedures, control and evaluation. Conative aspects are aspects related to the results of respondents' understanding of the entrepreneurship program, namely providing knowledge, courage, independence, responsibility, commitment, being able to improve product quality, pride, control and evaluation. Product innovation is a innovation developed by farmers, the resulting product has a characteristic, is able to compete in existing markets, provides choices to consumers, products complement other products, provide more value, always make improvements, many choices, can compete in the culinary market and can increase sales volume. Business performance is the result of entrepreneurship which includes income development, facility development, being able to survive in difficult conditions, being able to provide fast service to consumers, critical thinking, evaluation, providing satisfaction to consumers and paying attention to employee welfare.
As to test the validity test and reliability, a construct or variable is said to be reliable if it is characterized by Cronbach Alpha > 0.60 Nunnaly (Ghozali, 2005). Validity test is used to measure the validity or validity of a questionnaire. A questionnaire is said to be valid if the questions on the questionnaire are able to reveal something that will be measured by the questionnaire. Measurement of validity in this study was carried out using the correct item-total correlation (Ghozali, 2005).
Before performing regression analysis, it is necessary to test the classical assumptions first, so that the processed sample data can truly represent the population as a whole. The tests include: (1) Data Normality Test, (2) Multicollinearity Test, (3) Heteroscedasticity Test, (4) Multiple Linear Regression Analysis.
Results and Discussion
Characteristics of respondents are showing an average age of 31-60 years, in general women, married, Islamic religion, the business they are engaged in is planting fruit, generally starting the business in 2016, the average education is elementary and junior high school, experienced in managing the business is 3 years, the workforce used is 1-3 people and generally are their own families, harvests are generally sold and some of the fruit is processed into products.
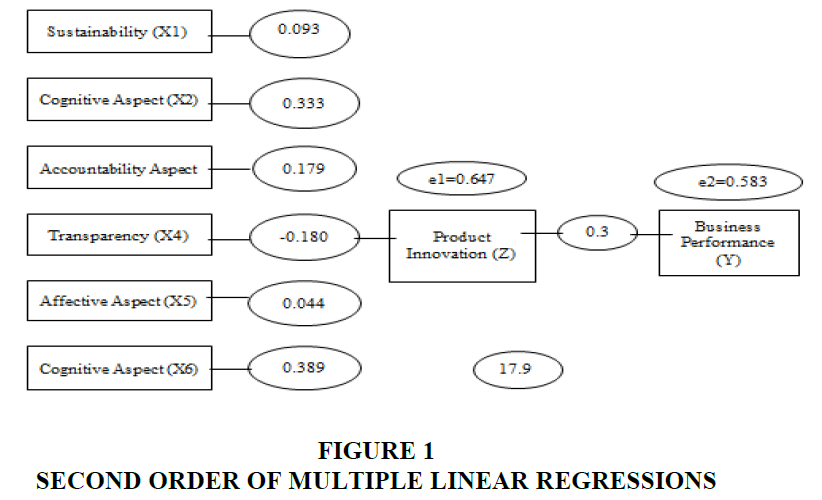
From the statistical testing, it is known that the value of 0.892 < 1.993 and the value of 0.37 > 0.05 with a large percentage of the influence of the sustainability variable on product innovation of 9.3% so that it is said that H1 is rejected. This means that the sustainability variable has a positive but not significant effect on product innovation. The results also showed that the value of 2.626 > 1.993 and the value of 0.01 < 0.05 with a large percentage of the influence of cognitive aspects on business performance is 33.3% so that it is said H2 is accepted. This means that the cognitive aspect variable has a positive and significant influence on product innovation.
Regarding the influence of the accountability aspect variable on business performance, it is known that the value of 1.539 < 1.993 and the value of 0.12 > 0.05 with a large percentage of 17.9%, so it is said that H3 is rejected. This means that the accountability aspect variable does not have a significant positive effect on product innovation. Moreover, it is known that the value of 1.149 < 1.993 and the value of 0.25 > 0.05 with a large percentage of the influence of the transparency variable on product innovation of -18% so it is said that H4 is rejected. This means that the transparency variable has a significant positive effect on product innovation.
Regarding the influence of affective aspects on product innovation It is known that the value of 0.219 < 1.993 and the value of 0.82 > 0.05 with a large percentage of 4.4% so that it is said that H5 is rejected. This means that the affective aspect variable does not have a significant positive effect on product innovation. Lastly, it is known that the value of 2.407 > 1.993 and the value of 0.01 < 0.05 with a large percentage of the influence of the conative aspect variable on product innovation is 38.9% so that it is said H6 is accepted. This means that the conative aspect variable has a significant positive effect on product innovation in Table 1.
| Table 1 T-Test Results | |||||
| Coefficientsa | |||||
| Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | ||||
| Model | B | Std. Error | Beta | t | Sig. |
| 1 (Constant) | 6.009 | 2.162 | 2.78 | 0.007 | |
| Sustainability (X1) | 0.065 | 0.115 | 0.054 | 0.565 | 0.574 |
| Cognitive Aspect (X2) | 0.067 | 0.158 | 0.051 | 0.422 | 0.674 |
| Accountability Aspect (X3) | 0.425 | 0.293 | 0.156 | 1.448 | 0.152 |
| Transparency (X4) | -0.283 | 0.096 | -0.424 | -2.951 | 0.004 |
| Affective Aspect (X5) | 0.129 | 0.095 | 0.25 | 1.361 | 0.178 |
| Conative Aspect (X6) | 0.179 | 0.072 | 0.38 | 2.493 | 0.015 |
| Product Innovation (Z) | 0.069 | 0.381 | 3.564 | 0.001 | |
| a. Dependent Variable: Business performance (Y) | |||||
For simultaneous hypothesis testing in this study is 2.140. From the Table 2 simultaneous hypothesis testing above, it can be seen that the value of 17.940 > 2.140 and the value of 0.00 <0.05. Thus, the sustainability variables (X1), cognitive aspects (X2), accountability aspects (X3), transparency (X4), affective aspects (X5) and conative aspects (X6) have a significant positive effect simultaneously or simultaneously on performance variables effort (Z) in Figure 1.
| Table 2 Simultaneous F-Test Results | |||||
| ANOVA a | |||||
| Sum of Squares | Mean Square | ||||
| Model | df | F | Sig. | ||
| 1 Regression | 575.165 | 6 | 95.861 | 17.94 | .000 b |
| Residual | 384.733 | 72 | 5.344 | ||
| Total | 959.899 | 78 | |||
| a. Dependent Variable: Business Performance (Y) | |||||
Entrepreneurship partially and simultaneously influences the business performance in Keerom Regency. More specifically, sustainability variable is that there is still a lack of respondents in wanting to be successful in running innovation business, but farmers have a passion for success in the business, this shows that there is a need for training and knowledge related to entrepreneurship and innovation for fruit farmers. The statistical results show that the sustainability variable has an effect on business performance. In the cognitive aspect, the results of respondents' responses indicate that there is a great need for an Entrepreneurship Training program, especially on innovation, and the need for entrepreneurship training to provide positive knowledge for farmers. The results of respondents' responses to the accountability aspect show that respondents agree with the statement that entrepreneurship training will have a positive impact on the spirit of entrepreneurship, and what the government has done, namely the Entrepreneurship Training Program held is right on target. The results of statistical testing are that the effect of the accountability aspect variable on business performance is 17.9%, so it is said that H3 is accepted. This means that the accountability aspect variable has a positive but not significant effect on business performance. The transparency variable shows that the respondents received a complete explanation of the requirements for participating in the entrepreneurship training program. And they still lacked clear information about the entrepreneurship training procedures. In the affective aspect in general, farmers really need entrepreneurship training that is easy to understand and provides motivation and farmers are motivated to take part in entrepreneurship training programs. The conative aspect shows that there is a lack of evaluation carried out on activities related to entrepreneurship and is committed to improving the quality of products.
Entrepreneurship partially and simultaneously influence product innovation in Keerom Regency. The effect of the sustainability variable on product innovation is 9.3%, so it is said that H1 is rejected. This means that the sustainability variable has a positive but not significant effect on product innovation. The effect of the sustainability variable on product innovation is 47.3%, so it is said that H1 is accepted. This means that product innovation variables can mediate and have a significant positive effect on business performance. The results of statistical tests show that the percentage of the influence of cognitive aspects on business performance is 33.3%, so it is said that H2 is accepted. This means that the cognitive aspect variable has a positive and significant influence on product innovation. The effect of cognitive variables on product innovation is 71.3% so that it is said that H1 is accepted. This means that product innovation variables can mediate and have a significant positive effect on business performance.
The effect of the accountability variable on product innovation is 55.9%, so it is said that H1 is accepted. This means that product innovation variables can mediate and have a significant positive effect on business performance. The result of statistical test is that the effect of the transparency variable on product innovation is -18%, so it is said that H4 is rejected. This means that the transparency variable does not have a significant positive effect on product innovation. This means that the accountability aspect variable does not have a significant positive effect on product innovation. The effect of the transparency variable on product innovation is 20%, so it is said that H1 is rejected. This means that product innovation variables can mediate and have a positive but not significant effect on business performance. The influence of the affective aspect variable on product innovation is 4.4% so that it is said that H5 is accepted. This means that the affective aspect variable has a significant positive effect on product innovation.
In analyzing entrepreneurship affect business performance mediated by product innovation in Keerom Regency. The effect of the affective variable on product innovation is 42.4%, so it is said that H4 is accepted. This means that product innovation variables can mediate and have a significant positive effect on business performance. The results of statistical tests show that the influence of the conative aspect variable on product innovation is 38.9%, so it is said that H6 is accepted. This means that the conative aspect variable has a significant positive effect on product innovation. The effect of the conative variable on product innovation is 76% so it is said that H4 is accepted. This means that product innovation variables can mediate and have a significant positive effect on business performance.
The innovation of products has not been developed by farmers. Also, farmers are trying to develop new markets in the culinary world. The meaning of the word 'innovative' is to create something that has never existed before or to create something completely different. These are the things that entrepreneurs really need. Entrepreneurs are entrepreneurs, but not all entrepreneurs are entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are pioneers in business, innovators, risk bearers who have a vision for the future and have advantages in achieving in the business field. The function of creativity in the innovation process is the generation of ideas that result in improving the effectiveness and efficiency of a system.
The results of this study are in line with the results of Priyanto's (2004) research, revealing that studies in the agricultural sector prove that with entrepreneurship, farmers will be able to make strategic plans, be able and brave to implement these plans in farming activities and be able to monitor and evaluate the course of farming. The entrepreneurial behavior affects the level of success of small businesses (Koellinger et al., 2007; Dirlanudin, 2010; Ashilina et al, 2019). In the aspect of business performance, it shows that farmers try to maintain relationships with customers and as business owners always provide fast service to customers. The results of the simultaneous test state that all variables consisting of sustainability variables, cognitive variables, accountability variables, transparency variables, affective variables, conative variables and product innovation variables all affect business performance. This means that in improving business performance, these variables are needed and the dominant one that affects business performance is the cognitive aspect variable which is 38.9% directly on business performance. The dominant influence on business performance mediated by product innovation is the cognitive aspect, meaning that there is a great need for training on entrepreneurship that makes it easier for farmers to become entrepreneurs.
Conclusions
Simultaneous test results state that all variables consisting of sustainability variables, cognitive variables, accountability variables, transparency variables, affective variables, conative variables and product innovation variables all affect business performance. This means that in improving business performance, these variables are needed and the dominant one that affects business performance is the cognitive aspect variable directly on business performance.
Simultaneous test results state that all variables consisting of sustainability variables, cognitive variables, accountability variables, transparency variables, affective variables, conative variables all affect product innovation. This means that in producing product innovation these variables are needed, with product innovation it will have an impact on the income respondents and entrepreneurship training is needed. The dominant influence on business performance mediated by product innovation is the cognitive aspect, meaning that there is a great need for training on entrepreneurship that makes it easier for farmers to become entrepreneurs.
References
- Ahmad, N., & Seymour, R.G. (2008). Defining Entrepreneurial Activity: Definitions Supporting Frameworks for Data Collection. OECD Statistics Working Papers, (1), 1.
- Ashilina, H., Baga, L.M., & Jahroh, S. (2019). The influence of farmers’ entrepreneurial behavior on the business performance of dairy farmers in west Bandung Regency, Indonesia. International Society for Southeast Asian Agricultural Sciences, 25(2), 143-154.
- Cofriyanti, E., & Hidayanto, A.N. (2013). The relationship among organisations’ factors, information technology, innovation and performance: an Indonesian SMEs study. International Journal of Innovation and Learning, 14(3-4), 422-443.
- Cunningham, J.B., & Lischeron, J. (1991). Defining entrepreneurship. Journal of small business management, 29(1), 45-61.
- Dirlanudin, D. (2010). Perilaku Wirausaha Dan Keberdayaan Pengusaha Kecil Industri Agro (Kasus Di Kabupaten Serang Provinsi Banten). Doctoral Dissertation, Institut Pertanian Bogor (Unpublished).
- Drucker, P.F. (1959). Long-range planning challenge to management science. Management science, 5(3), 238-249.
- Förster, H., Sterzel, T., Pape, C.A., Moneo-Lain, M., Niemeyer, I., Boer, R., & Kropp, J.P. (2011). Sea-level rise in Indonesia: on adaptation priorities in the agricultural sector. Regional Environmental Change, 11(4), 893-904.
- Ghozali, I. (2005). Structural Equation Model. Semarang: Badan Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro.
- Koellinger, P., Minniti, M., & Schade, C. (2007). “I think I can, I think I can”: Overconfidence and entrepreneurial behavior. Journal of economic psychology, 28(4), 502-527.
- Marbun, B.N. (1993). Kekuatan dan kelemahan Perusahaan kecil. Jakarta: Pustaka Binaman Pressindo.
- Muatip, K. (2008). Kompetensi kewirausahaan peternak sapi perah: kasus peternak sapi perah rakyat di Kabupaten Pasuruan Jawa timur dan Kabupaten Bandung Jawa Barat. Doctoral Dissertation, Institut Pertanian Bogor (Unpublished).
- Priyanto, S.H. (2004). Pengaruh Faktor Lingkungan, Kewirausahaan Dan Kapasitas Manajemen Terhadap Kinerja Usahatani (Studi Empiris Pada Petani Tembakau di Jawa Tengah). Doctoral dissertation, Universitas Brawijaya Malang (Unpublished).
- Rokhman, A. (2008). Peranan Kebijakan Publik, Orientasi Kewirausahaan Dan Kompetensi Sumberdaya Manusia Dalam Pengembangan Produk Perikanan Prima. Doctoral Dissertation, Institut Pertanian Bogor (Unpublished).
- Soegoto, E.S. (2013). Entrepreneurship menjadi pebisnis ulung. Jakarta: Elex Media Komputindo.
- Steiner, G.A. (1963). Managerial long-range planning. McGraw-Hill Book Company.
- Subejo, S. (2020). Memahami dan mengkritisi kebijakan pembangunan pertanian di Indonesia (comprehending and perceiving to agriculture development policy in Indonesia). Jurnal Ilmu-Ilmu Pertanian, 3(1), 14.
- Sugiyono, S. (2013). Metode Penelitian Kuantitaif, Kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
- Suryana, D. (2006). Kewirausahaan: Pedoman Praktis (Kiat dan proses menuju sukses). Jakarta: Salemba Empat.