Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 2S
An Impact of Covid-19 on Virtual Learning: The Innovative Study on Undergraduate Students of Mumbai Metropolitan Region.
Gaikar Vilas B, University of Mumbai
Joshi Bharat M, K. P. B. Hinduja College of Commerce
Bhadane Jaywant, University of Pune
Nilesh S. Mhatre, S.N.D.T University
K. Chitra, Madurai Kamaraj University
Sunitha Cheriyan, Madurai Kamaraj University
Rane Caroleena G, University of Mumbai
Keywords:
ICT, E-Learning, VLE, Perceptions, Satisfaction, Innovation, COVID-19
Abstract
The pandemic of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV2) infections was announced by the World Health Organization earlier in 2020 and the same has become a serious public health issue throughout the world. This virus stirred up and disturbed the lives of the world. Technological improvement has metamorphosed traditional brick-mortar classrooms into electronic virtual teaching-learning systems. The combination of an unprecedented growth in smart phone and tablet usage during the COVID- 19 pandemic and resultant lockdowns have created a gulf between the teachers and the learners and has facilitated a move towards application-based E- Learning (EL) as a dominating form of Virtual Learning Experience (VLE). The scope of the study is limited to the gratification level towards e-learning and perceptions towards VLE of undergraduate students of Mumbai Metro region. The Primary data was collected from 308 undergraduate students through a systematic convenient random sampling method. When the data was passed through descriptive Statistics and inferences analysis, an undeniable fact was thrown light that the e-learning has paved a way for innovative learning experience for better understanding and self-actualized knowledge of the subjects. There was a significant difference in perceptions of learners towards VLE. Further, it is also inferred that there is no significant correlation between gender and e-learning. The findings would be valuable for Virtual Learning Experience to build up an open innovation policy to further shape the field of scientific knowledge for the successful working of the education under conditions of absolute vulnerability. The study concludes with suggestions, recommendations and future research.
Introduction
Covid-19 virus changed all sections and sectors of the world beyond imagination. Its venom has been injected to all people regardless of one’s socio, economic and political status. The pandemic devastated the economy and has had an effect on various sectors. This worst pandemic situation of COVID-19 has generated online education as a common option for Higher Education (HE) institutions and maybe the only one Mulenga & Marban (2020); Almarzooq, Lopes & Kochar (2020); Wich, Selenski & Brunn (2020).
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) is undoubtedly a blessing to all sectors of education. With its immense potential to transcend boundaries and reaching a wider range of audience, ICT is being utilized with capacity to instruct geographically ubiquitous learners. Recent multiform technologies have made interactions between learner and instructors at free time with no location constraints, creating new arenas that are charged with potential. Existing technology in this area is competent in creating cost-effective and ductile learning environments and, thus, promoting directional efforts for creating a rentable teaching – learning paradigm of Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). Intellectual skills are developed through the systematic and scientific process of learning which may be in the form of imitation, beliefs, traditions or customs. Learning helps to acquire knowledge and/or skills through study or experience, thus bringing organization or modification in behaviour and confirmation of a new process.
William Arthur Ward (https://www.goodreads.com/quotes/166029-the-mediocre-teacher-tells-the-good-teacher-explains-the-superior) said, “The mediocre teacher tells, the good teacher explains, the superior teacher demonstrates, the great teacher inspires”. Virtual learning is a distinct form of teaching-learning experience, which is enhanced through the use of computer-based technology to convert the internet as a powerful medium to deliver education within and outside of the educational organization and within course work. Virtual teaching-learning is an online process in which the teacher and learners are geographically dispersed.
Thus, the Distance Learning is a convoy in Virtual Learning Environment with electronic resources, activities and interactions within course contents (synchronous) and structures designed for self-paced (asynchronous) or live web-conferencing. A web-based social learning environment provides an online/web-based interactive learning information system that promotes communication between different types of learners Al-Samarraie & Saeed (2018).
The need for innovative solutions to optimize educational endeavours has accelerated in the COVID-19 era. With emerging technology such as Zoom, blackboard, Google classroom, teams, slack and several VLE programs have tried to improvise. The key terms used for VLE are as under:
1. Content Management - Creation (Course Contents), Storage (for future reference), Access (to have in materials hand).
2. Curriculum Mapping and Planning - Lesson Planning (Assessment and Personalisation of the Learning Experience.
3. Learner Engagement and Administration -Access to learners’ information and resources, Progresses and Achievements.
4. Communication and Collaboration - emails, notices, chat, wikis, blogs.
5. Real Time Communication-live Audio-Video Conferencing
6. The key advantages and disadvantages of Virtual Learning Environment are penned down below (https://scand.com/company/blog/the-use-of-virtual-learning-environment-in education) as shows in Table 1.
| Table 1 Virtual Learning Environment : Advantages and Disadvantages |
||
|---|---|---|
| S. No | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1 | Time Flexibility | Quality of communication |
| 2 | Time Saving | Ask to be in self-disciplined |
| 3 | Location Independence | Lack of Practice |
| 4 | Cheaper | Delayed in Answer/Feedback |
| 5 | Improved Management | Difficult to Check Activeness Activities | 6 | Innovative Learning Material | - |
| 7 | Parallel Online Activities | - |
Rationale of the Problem Statement
Skill-knowledge based vocational education and its delivery is the prime concern to an underdeveloped country like India. The ICT in education, along with quality education, provides value education mainly on account of its ability to transcend geographical barriers. It has transformed the teaching-learning method from the chalkboard to smart boards to open-access online web-based courses, with cross-geographical access, around the clock. It makes teaching-learning active, interactive and participative at levels of education.
Scope for the further research
The current research has scope for further studies and possibilities as noted under:
a. A similar study or comparative study can be conducted for students of higher studies.
b. A comparative study of learning experience of the students of urban and rural areas can be vouched.
Significance of the Study
1. The present research study will help to understand the concept of e-learning and virtual learning.
2. The study will enable to understand the different modes of e-learning.
3. It will help learn the satisfaction level of target group.
4. It will enhance the perception with regard to VLE by the e-learners of undergraduate students.
Objectives of the Study
The present research is based on various objectives, as follows:
1. To understand the concept of Learning and Virtual Learning Environment.
2. To study the components of VLE.
3. To analyze the satisfaction level of undergraduate e-learners through VLE.
4. To analyze the perceptions of undergraduate e-learners with regard to VLE.
Hypothesis of the Study
The changes arising from the COVID-19 pandemic in the educational process like adaptation to emerging technology and various additional technical qualifications led to negative emotions like loss of hope and fears. Employment restrictions and stress have a negative impact on the dedication of teachers to work. On the other hand, a mechanism of resilience to stressors has been activated. The coping practices and the context of supporting work are positively related to job participation. The following related hypotheses provided the basis of this research. On the basis of the results of the literature review, the researchers investigate the following hypotheses.
Hypothesis 1 (H1) There is no significant difference in satisfaction level of undergraduate e-learners
Hypothesis 2 (H2) There is no significant association between gender and satisfaction level of e-learners.
Hypothesis 3 (H3) There is no significant association between aided and unaided sections and satisfaction level of e-learners.
Hypothesis 4 (H4) There is no significant difference in perceptions of e-learners towards VLE.
Hypothesis 5 (H5) There is no significant association between gender and perceptions of e-learners towards VLE.
Hypothesis 6 (H6) There is no significant association between aided and unaided sections of undergraduate e-learners and their perceptions of towards VLE.
Limitations of the Study
Following are the limitations of the study:
1. An online survey-questionnaire has been used.
2. The research covered e-learners of undergraduate students from two colleges in Mumbai only.
3. The researchers have drawn conclusions purely on the basis of data collected and inferences calculated.
Review of Literature
The review of literature has been taken from various journals, periodicals, articles, books and so on. November 17, 2019, officials in Wuhan City, China, first reported the first human cases of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel corona virus causing COVID-19, subsequently called SARS-CoV-2 (6. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/13/first-covid-19-case-happened-in-november-china-government-records-show-report). China informed the World Health Organization (WHO) on 31 December 2019 about cases of unidentified pneumonia found in Wuhan City, Hubei Province of China. The first case of infection with COVID-19 recorded in Kerala, India. On January 27, 2020, a 20-year-old woman with a one-day history of dry cough and sore throat was admitted to the Emergency Department in General Hospital, Thrissur, and Kerala in India. No history of fever, rhinitis or shortness of breath was observed. She announced that she had returned from Wuhan City, China, to Kerala, on January 23, 2020 due to the outbreak of Covid-19, Andrews, et al., (2020). Gradually, the pandemic spread throughout the country including the city of Mumbai. Virtual Learning Experience became an innovative way of learning to both the teachers and learners.
Recent studies have shown that e-learning is not only a technological solution to make learning easy and effective, but also a part of different factors such as social factors studied by Tarhini et al., and individual factors studied by Liaw & Huang (2011), organizational factor such as facilitating situations studied by Sun & Zhang (2005); Kim & More (2015) found that the social, individual, organizational, behavioural and cultural factors play an important role in order to make effective use of Information Technology in e-learning.
Moravec, et al., (2015) showed how e-learning tools impact students’ achievement. The study was attended by nearly 2000 students where the researchers found that the e-learning tools have affected the students’ results.
By using Cohen’s model, based on data collected from 15 documents from relevant research studies conducted on the effect of ICT based e-learning on academic achievement during 2010-2012, Mothibi (2020) examined the relationship between e-learning and students’ academic achievement in higher education. The researchers found that ICT had a statisticsally key positive influence on e-learning based students’ academic achievements. The results also indicated that ICT had a significant positive influence on students’ educational overall academic achievements.
A study conducted by Zitzmann, et al., (2020) on digital undergraduate education in dentistry stated that there is a need to develop widely agreed digital education standards in all countries. The opportunity to revolutionize the entire field of dental education is provided through digitalization. There will be more immersive and intuitive e-learning opportunities that inspire learners and provide a stimulating, enjoyable and meaningful education.
The Star of Mysore, a newspaper Chen, et al., (2020) quoted that the Covid-19 that hit the globe as a pandemic forced nation across the globe to turn to 'remote learning' or what is widely referred to as 'online teaching.' Due to the pandemic, school buildings are closed, campus gates locked, and with often recorded videos and occasionally live sessions, a new online teaching has arisen. He further opined that it would be virtually impossible in a digital class to ensure that every voice of the students is heard. Many sensitive parents have thought that whether it is possible to engage students in such vital processes in a digital class, such as self-awareness, involvement in groups or teams and healthy competition, bringing out interpersonal skills that are so important for school success first and later in life. The transition to remote teaching is so rapid that many rural teachers may not have thought of making a film, and now they have to deal with new teaching technology resources such as One Note and, to name a few, Microsoft Teams or Flip grid.
Chen, et al., (2020), in their study found that the social education, during Covid-19 pandemic moved from face-to-face to online to prevent large gatherings and crowds to block the spread of the virus.
Xie, et al., (2020) were of the opinion that A new standard has been developed by the global COVID-19 pandemic that further springboards such opportunities to introduce online education on a large scale. Because online education has the advantages of versatility, accessibility to content, global scope, equity, creativity, and effectiveness, distance learning and hybrid education programs are provided by an increasing number of educational institutions. Online education will co-exist with conventional education through the integration of artificial intelligence and mobile education to provide more educational opportunities, foster diversity in education, and enhance creativity in education.
A study conducted by Rajab, et al., (2015) showed that the COVID-19 pandemic had a positive effect on online medical education. In terms of communication, student evaluation, use of technology resources, online experience, pandemic-related anxiety or tension, time management and technophobia were the challenges posed by the pandemic. In spite these difficulties, according to their study, during the first few weeks of the pandemic, the experience of respondents raised their confidence in the efficacy of online education. Although pandemics have traditionally generated challenges, the first step in turning them into opportunities is to recognize these challenges. Online learning has evolved beyond intelligent acronyms and has reached mainstream education. More focus would almost certainly be put on formal online education programs across Asia Yuan, Powell & Olivier (2021); Palvia, et al., (2018); Liu, et al., (2020); Tartavulea (2020).
While studying the effects of the sudden move to online teaching due to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Tartavulea, et al., (2020) conducted a survey on 362 professors and students from 13 European countries and they found that universities and students have adapted to new developments very quickly and that they are actually using a combination of synchronous and asynchronous interaction and evaluation methods.
A study conducted by Maximiliane, et al., (2011) found that the students and lecturers of dental school of Justus-Liebig-University Giessen (Germany) displayed a largely optimistic outlook on the introduction of online learning, offering the ability to include online learning in the future curriculum beyond COVID-19
A study conducted by Daymont, et al., (2020) found that the Students who prefer face-to-face lessons cite the presence and learning benefits of the teacher. The media richness hypothesis is discussed by these writers as one interpretation. This theory argued that, because of superior communication through nonverbal indicators such as body language and auditory signals, face-to-face classes have advantages over online courses.
With regard to online education, Maharaj, Martín, et al., (2021); Gaikar & Sameer (2020) opined that, in the field of education, the COVID-19 epidemic may reflect an enduring transformation. However, it is critical that the perspectives be used by the academic education community and that a forward-thinking and realistic scholarly approach is prioritized as solutions to cope with current realities.
Students believe that they have full understanding of the use of email and speak, learning platforms such as Moodle Prado and Google classroom, video conferences such as Google meet, Skype and zoom, social networks such as twitter, Facebook and Instagram, collaborative work and network file management tools such as Google drive and drop box, knowledge search and publishing tools such as Google, yahoo and Wikipedia, and office tools such as Word, PowerPoint and Excel. They believe that teachers lack the information required as studied by Torres, et al. (2021).
In view of the challenges faced by educators during the COVID-19 pandemic, Opsahl, et al., (2020) found that the adaptability and versatility are crucial to advancing educational strategies to train current and potential clinicians. Innovative technology virtual platforms allow educators to deliver educational content to engage participants while retaining social distance criteria for pandemics.
Monroy, et al., (2020) said, in the transformation of learning models to meet present day demands, advanced education confronted significant challenges. It would be unthinkable, according to Lieza, et al., (2019), to have quality teaching and learning measures in advanced education without using innovative technology, particularly in 21st century. Several studies Gamage (2018); Mingorance, et al., (2019); Area, Hernandez & Sosa (2016); Wich, Selenski & Brunn (2020) have shown that the views on ICT educators are optimistic because they believe them to be instruments that facilitate profitable, rousing and intelligent learning and figure out how to regard the individual rhythms of the students.
E-networking, which is a form of social networking that incorporates life, both online and offline, can be generated through online learning. In a network environment, we can multiply information, as each person can contribute interesting ideas and good practices. It strengthens group cohesion and drives the group towards collective action and development as found by Wich (2020).
Research Methodology
Primary data was collected from two-degree colleges of Mumbai Metropolitan city on a convenient sampling basis, which had a total working population of 1423 employees. A self-administered questionnaire was developed for the survey and was distributed among 375 students of the total population. The researchers received 337 questionnaires back after 6 weeks, out of which 29 were rejected for incomplete information. 308 questionnaires were finally considered as sample which comprised of 184 males and 124 female learners. A convenient sampling was used with the help of the following formula. This sample was enough as per the following formula of sampling Gaikar & Sameer (2020); Cherian, et al., (2021); Rubina, et al., (2020).
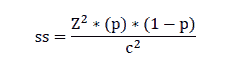
Where,
Z=Z value (e.g., 1.96 for 95% confidence level)
p=Percentage picking a choice, expressed as a decimal (0.5 used for sample size needed)
c=Confidence interval, expressed as a decimal (e.g., 0.05=±5)
The total population of 1423 was applied in the formula, and we arrived at the sample of 308 as given below.
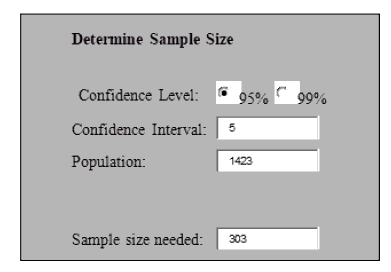
The questionnaires were presented in SPSS for data analysis as shows in Table 2.
| Table 2 Summary of Respondents |
||
|---|---|---|
| Sr.No | Criterion | Number of students |
| 1 | Total number of undergraduate students (Population Size) | 1423 |
| 2 | Decided to circulate questionnaire to (Sample Size Planned) | 375 (26.35%) |
| 3 | Received filled questionnaire (Sample Size Achieved) | 308 (21.64%) |
| 4 | Variance in Sample Size (not achieved) | 67 |
| 5 | Reason for Variance | Didn’t respond |
Secondary data has been collected from different electronic journals and articles. To clean up unwanted and unstructured data, the researcher has done data cleaning process as missing value. Primary data was screened to find out missing values, if any. As revealed in Table 3, there were no missing values.
| Table 3 Case Processing Summary of Demographic Profile, Satisfaction and Perception Statements |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Section | SVLE (1) 1,2 and 3 | SVLE 4 and 5 | PVLE (2) 1,2 3, 4 and 5 | ||
| N | Valid | 308 | 308 | 308 | 308 | 308 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
The researchers applied the ‘Test of Normality’ was applied using Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk test. The calculated test Statistics (W for S-W, D for K-S (from Table: 4 and 5) significance value is greater than 0.05, showed that the data related to satisfaction and perceptions towards VLE deviates significantly from normal distribution. The result of Normality of Data using Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk is as follows.
| Table 4 Tests of Normality by Kolmogorov-Smirnov=(D) and Shapiro - Wilk =(W) of Satisfaction and Perceptions Statements. A. Lilliefors significance correction |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kolmogorov-Smirnova | Shapiro-Wilk | |||||
| Statistics | df | Sig. | Statistics | Df | Sig. | |
| SVLE1 I am able to complete my topic revision on time. |
0.248 | 308 | 0 | 0.877 | 308 | 0 |
| SVLE2 I learnt the topic contents of Organization of Commerce and Management subject in detail. |
0.242 | 308 | 0 | 0.882 | 308 | 0 |
| SVLE3 I admit that the time spent in e-learning is a totally new experience. |
0.232 | 308 | 0 | 0.851 | 308 | 0 |
| SVLE4 I acquired useful knowledge about Business, Commerce and Management. |
0.254 | 308 | 0 | 0.861 | 308 | 0 |
| SVLE5 At every new topic-contents discussion, I feel a sense of achievement and progress. |
0.245 | 308 | 0 | 0.871 | 308 | 0 |
Source : Compiled from Primary data
| Table 5 Tests of Normality by Kolmogorov-Smirnov=(D) and Shapiro-Wilk=(W) of Satisfaction and Perceptions Statements. A. Lilliefors Significance Correction |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kolmogorov- Smirnova | Shapiro-Wilk | |||||
| Statistics | df | Sig. | Statistics | Df | Sig. | |
| PVLE1 E-learning makes me more active than traditional classroom learning. |
0.183 | 308 | 0 | 0.908 | 308 | 0 |
| PVLE2 E-learning allows flexibility and no place constraints. |
0.257 | 308 | 0 | 0.876 | 308 | 0 |
| PVLE3 In Virtual Classrooms, I feel more Confident, Comfortable than in face-to-face classroom learning. |
0.172 | 308 | 0 | 0.905 | 308 | 0 |
| PVLE4 Virtual Learning, using computer, laptop, smart phones and tablets have much more virtual scope. |
0.24 | 308 | 0 | 0.879 | 308 | 0 |
| PVLE5 Is the virtual learning environment beneficial during the COVID-19 induced nationwide lockdown in India? |
0.248 | 308 | 0 | 0.852 | 308 | 0 |
Source : Compiled from Primary data
Reliability Analysis
Cronbach’s Alpha was found to be 0.925 for Satisfaction Statements that shows Excellent Internal Consistency and .835 for Perception Statements that shows Good Internal Consistency among variables. (Table: 6 and 7).
| Table 6 Reliability Statistics of Satisfaction and Perception Statements |
|
|---|---|
| Cronbach's Alpha (Satisfaction Statements) | Number of Items |
| 0.925 | 5 |
| Table 7 Reliability Statistics of Satisfaction and Perception Statements |
|
|---|---|
| Cronbach's Alpha (Peception Statements | Number of Items |
| 0.835 | 5 |
SPSS was used for Analytical study and Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk test was applied for the test of Normality. The test of Reliability is Cronbach’s’ Alpha. Other statistical tools like descriptive Statistics, frequency and percentage count, Kruskal-Wallis 1-Way ANOVA on Rank and Chi-square were also used in this research.
Analysis and Interpretation
The respondents were asked questions based on their gender and section (aided and unaided) to study the satisfaction level and perception toward e-learning and VLE. Further, questions based on ‘Likert Five Point Scale’ were also asked to measure their satisfaction level and perception of the respondents.
Descriptive Analysis
The researchers have described data as under:
Demographic Profile
Gender and Section of the Respondents
Gender was included to find out the significant relationship between the satisfaction and perceptions towards virtual learning as shows in Table 8 and 9.
| Table 8 Gender of the Respondents |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percentage | Cumulative Percentage | ||
| Valid | Male | 184 | 59.7 | 59.7 | 59.7 |
| Female | 124 | 40.3 | 40.3 | 100 | |
| Total | 308 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Table 9 Section of the Respondents |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Percentage | Valid Percentage | Cumulative Percentage | ||
| Valid | Aided Section | 130 | 42.2 | 42.2 | 42.2 |
| Unaided Section |
178 | 57.8 | 57.8 | 100 | |
| Total | 308 | 100 | 100 | ||
Satisfaction Statements as shows in Table 10.
| Table 10 Satisfaction Level of the Respondents Towards E-Learning. HD: Strongly Disagree; |
|---|