Research Article: 2018 Vol: 17 Issue: 4
An Empirical Study on Strategic Alliances of Multi-National Companies in the Modern Global Era-A Select Case Study
Kishore Vattikoti, Osmania University
Abdul Razak, Osmania University
Keywords
Strategic Alliance, Globalization, Liberalization, International Business.
Introduction
In this era of global competition, companies are adopting various forms of collaboration with domestic and international counterparts to find a space in the global marketplace and help in strengthening their competitive advantage (Dodgson, 2018). A strategic alliance is one of the major strategies for growth of international business companies. The present study analyses the conceptual framework of strategic alliances, various theories and motives behind formation of strategic alliances with special orientation to Indian Industry and firms (Crossan & Inkpen, 1995).
Strategic alliance is a contract between two or more organizations to cooperate in a particular business activity. By this, both the companies get benefits from the strengths of the other and achieve competitive advantage. The formation of strategic alliances has been advanced after the globalization and seen as a quick response to liberalization. This will lead to ambiguity and complication in the business environment, Xu et al. (2018). Strategic alliances include the knowledge sharing and expertise between the associates as well as the reduction of costs and risks in areas such as relationships with vendors and new product development and new technologies. Strategic alliances are rational and response timely to penetrate and make rapid changes in technology and economic activity (Khanna, 2018).
Strategic alliances become an important type of business activity in most of the industries particularly in view that companies are competing in the global world and should adapt and respond to the various changes driven by Liberalization, privatization and globalization, which increased customer needs and business complexity, Zaefarian et al. (2017). Strategic alliances are not a solution for each and every company at every situation. But, through strategic alliances firms can progress their competitive positioning, supplement critical skills, gain entry to new markets and share the cost and risk of major development assignments (Rothaermel, 2015).
Review Literature
Michael E. Porter, 1990- Strategic alliances are long-term agreements between firms that go beyond normal market transactions but fall short of merger. Forms include joint ventures, licenses, long-term supply agreements, and other kinds of inter-firm relationships.
Dussauge & Garrette (1995), an alliance is a cooperative agreement or association between two or more independent enterprises, which will manage one specific project, with a determined duration, for which they will be together in order to improve their competences. It is constituted to allow its partners to pool resources and coordinate efforts in order to achieve results that neither could obtain by acting alone. The key parameters surrounding alliances are opportunism, necessity and speed.
Yoshino & Rangan, (1995) a strategic alliance is a partnership between two or more firms that unite to pursue a set of agreed upon goals but remain independent subsequent to the formation of the alliance to contribute and to share benefits on a continuing basis in one or more key strategic areas, e.g. technology, products.
Gulati (1998) strategic alliances are voluntary arrangements between firms involving exchange, sharing, or co-development of products, technologies, or services. Strategic alliances are critical to organizations for a number of key reasons:
1. Organic growth alone is insufficient for meeting most organizations' required rate of growth and return.
2. Speed to market is very crucial and essential, and alliances greatly improve it.
3. Complexity is increasing in today’s global world, and no single firm has the required total expertise to serve the customer as good as possible.
4. Alliances can cover rising research and development costs and expenses.
5. Alliances facilitate access to global markets in marketing the products and services.
Strategic Alliances Have Some Characteristics
1. Two or more organizations (business units or companies) make an agreement to achieve objectives of a common interest considered important, while remaining independent with respect to the alliance (Cobianchi, 1994).
2. The partners share both the advantages and control of the management of the alliance for its entire duration.
3. The partners contribute, using their own resources and capabilities, to the development of one or more areas of the alliance (important for them).This could be technology, marketing, production, distribution, R&D or other areas (Beamish, 1998).
Benefits of the Strategic Alliances
There are four potential benefits that international business may realize from strategic alliances:
1. Ease of market entry: Advances in telecommunication, information technology and logistics and supply chain management have made entry into foreign markets by international firms very easier. Entering into foreign markets deliberates benefits such as economies of scale and increases opportunity in marketing and distribution (Anderson & Narus, 1984).The rate of entering an international business and international market may be beyond the capabilities of individual firm, but by entering into a strategic alliance with an international firm, it achieves the advantage of fast entry while keeping the cost low. Choosing a strategic partnership as the entry mode may overcome the hindrances like embedded competition and intimidating government rules and regulations de Villa et al. (2015).
2. Shared risks: Sharing the risk is another common reason for undertaking a strategic alliance i.e., cooperative arrangement when a market has just opened up, or when there is much instability and ambiguity in a particular market where sharing risks becomes mainly important (Beamish, 1984). The competition and competitive nature of business makes it very difficult for a business to enter a new market or launch a new product. But by forming a strategic alliance, a firm can reduce or control its risks to the optimum (Doz & Hamel, 1998).
3. Shared knowledge and expertise: Many companies are competent in certain areas and lack expertise in few areas; as such, forming a strategic alliance can allow ready access to knowledge and expertise in an area that an organization lacks. The knowledge, expertise and information that an organization gains, can be used not only for the alliance project, but also for all other projects and purposes (Contractor, and Lorange, 1988). The knowledge, expertise and information can range from learning to deal with government rules & regulations, production knowledge, or learning how to acquire resources. A learning organization is always a growing organization (Bleeke & Ernst, 1991).
4. Synergy and competitive advantage: One of the reasons for firms enter into a Strategic alliance is for achieving synergy and competitive advantage. As compared to entering a market alone, forming a strategic alliance becomes a way to decrease the risk of market entry, research and development, international expansion, etc. (Sierra, 1995). Competition becomes more efficient and effective when both the partners leverage off each other's strengths, bringing synergy into the process that would be hard to achieve if attempting to enter a new market or industry Child et al. (1998).
Objectives of the Study
The main objective of the study is to understand the Strategic Alliances of Multi-National Companies in the present era and its plans in collaborating:
1. To trace the strategic alliance as a tool to harness the core competencies of strategic partners for strategic competitiveness.
2. To identify the motives of a firm to enter into strategic alliance.
3. To study the importance and benefits of Strategic alliance.
TYPES OF DATA SOURCES
Secondary Data: Main Source of Information
The access to the data and the information for analysis is obtained in documented form and the data is predominantly secondary in nature. The main sources of information are: (i) Records of Companies; (ii) Records of Income Tax Act, 1961 [Section 2(1A)]; (iii) Records of Industry; (iv) Books, journals, e-journals, periodicals and other published data and information.
Other Sources of Information: Primary Data
The second category of information and data relates to perceptions, opinions and views of knowledgeable people who are either actively involved in the transactions on either side, as well as those who are interested in the issue. The primary data necessary is generated through unstructured interviews schedule and personal interactions. These interviewees were essentially attempts to explore the views and judgments. The interviewees included top managerial personnel of various companies. This source of data enables where ever there exists information gap.
Data Collection
The study is made with respect to two large companies belonging to Private sector which were considered after examining Case studies from published sources. Tata Tea and Star Bucks on Strategic alliances are taken for the study.
Methodology
The present study is an evaluative study how the Strategic Management tools are adopted by the firms for strategic competitiveness. A case study method is chosen because it highlights the complexity of a single case and particularity and it is not designed to optimize on generalizations.
Limitations of the Study
Strategic alliance literature primarily focused on successful cases from secondary source of data and based on only interview schedule for primary source of data. However, case lacked exhaustive listing of causes and strategies due to non accessibility to some of the top officials who were directly associated with the Strategic alliances.
The present study is focused on specific Strategic tool used in managerial decisions. Therefore the study does not comprehensive cover the entire strategic management process of strategic formulation and implementation; rather it addresses one of the Strategic tools i.e., Strategic alliance used by the top management in crafting the strategies.
Analysis of Case Study
The case study I deal with the strategic alliance of Tata Coffee and Starbucks Corporation. The case analysis is done from the Strategic alliance perspective. The strategic alliance between both the companies is analyzed by conducting SWOT analysis, PEST analysis and Market analysis. These analyses are conducted to know how the core competences and strategic competitiveness are achieved by strategic partners through strategic alliances.
| Table 1 “Starbucks–a tata alliance”(tata starbucks ltd) Data sheet of the strategic alliance company |
|
| Year of Incorporation Commencement of Business |
January, 2012 October, 2012 |
| Head Office Registered Office | Starbucks coffee company– Seattle, Washington, US Tata Global Beverages Limited – Mumbai, Maharashtra, India Mumbai, Maharashtra |
| Project/Industry Founders Investors |
Strategic alliance/Coffee Industry R K Krishna Kumar and Howard Schultz Starbucks coffee company– Seattle, Washington, US Tata Global Beverages Limited–Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| Key People | Sumi Ghosh, Howard Schultz, R K Krishna Kumar |
| Chief Executive Officer Vision Mission No of Employees Daily Visits Stores Alliance |
Sumi Ghosh “To build a company with soul” “To inspire and nurture the human spirit–one person, one cup and one neighborhood at a time.” About +1200 employees 10500 Customers 101 Tata Global Beverages Ltd. And Starbucks Corporation |
| Focus Offers Initial Challenges |
Open Coffee outlets in all the cities in India Good Customer services and fixing prices and discounts as per Indian Standards Compete with domestic Coffee outlets like Café Day and International Coffee outlets like Barista |
| Building Trust Right Timing Helps Growth | 11 A.M. to 11 P.M Customer Service Wi-Fi service Home Delivery Starbucks entry to India with the alliance of Tata group Initially started with first store at Mumbai’s chatrapathi Shivaji International Airport and 2 stores at New Delhi Indira Gandhi International airport. And now 101 stores throughout India. |
| Statutory Dues | N.A. |
| Investment | $80 Million and additional $300 Million in 2015 |
Background
Tata Global Beverages Limited and Starbucks Coffee Company announced a strategic alliance between the second largest branded tea company and iconic international coffee brand in the world. The 50:50 joint venture, named TATA Starbucks Limited, owns and operates Starbucks cafés, branded as Starbucks Coffee “A Tata Alliance.” The first store has opened at Mumbai and subsequently 2 stores are opened at New Delhi in India on October, 2012. Presently, it owns and operates 60 stores in all the major cities in India (Vrushali, 2011). The alliance is expected to be very fruitful to both the companies in the long run. The report seeks to strategically assess the viability of this strategic alliance by peeping into its myriads of dimensions (Ruchi and Joel, 2011).
About Starbucks
Since 1971, Starbucks Coffee Company has been committed to ethically sourcing and roasting the highest-quality “Arabica” coffee in the world. Today, with more than 17,000 stores around the globe, the company is the premier roaster and retailer of specialty coffee in the world. Through our unwavering commitment to excellence and our guiding principles, we bring the unique “Starbucks Experience” to life for every customer through every cup.
About Tata Global Beverages
Tata Global Beverages is a part of the global Tata Group. Tata Global Beverages is a global beverage business and the world’s second largest tea company. The group’s annual turnover is US $1.5 bn and it employs around 3000 people worldwide. The Company focuses on “good for you” beverages and has a stable of innovative regional and global beverage brands, including “Tata Tea, Tetley, Himalayan natural mineral water and Eight O’clock Coffee.”
Strategic Intent
Starbucks Corporation aims India as its next major hub for big business. Starbucks want to repeat the success they had in United States and more recently, in china. Amazingly, their venture in China made more profits than that of United States. In India, Starbucks entered into an agreement with TATA Coffee Ltd, Asia's largest publicly traded coffee grower. This is, in particular, a non-binding agreement between two companies. The plans are to combine the trust and heritage of TATA coffee with the iconic brand image of Starbucks Coffee which can move on to development of Starbucks retail coffee chains in India and other parts of Asia. In addition to this, sourcing and roasting of coffee beans from TATA‘s Indian facilities, the companies will also work towards establishing and developing Starbucks stores in retail outlets and hotels (Herve, 2004).
Also, the Indian market is heavily driven by the upcoming youth culture which is totally driven by the western trends. With the success of Indian owned Cafe Coffee Day and Barista Coffee, it is a widely proven fact that there is lot of scope for the development of coffee cafe culture in India. Thus, Starbucks want to capitalize on this particular opportunity (Harold, 2011).
Starbucks Mission Statement
In early 1990, the senior executive team at Starbucks went to an offsite retreat to debate the company’s values and beliefs and draft a mission statement. Schultz wanted the mission statement to convey a strong sense of organizational purpose and to articulate the company’s fundamental beliefs and guiding principles. The draft was submitted to all employees for review and several changes were made based on employee comments. The resulting mission statement and guiding principles are “To inspire and nurture the human spirit–one person, one cup and one neighbourhood at a time.” In 2008, Starbucks partners from all across the company met for several months to refresh the mission statement and rephrase the underlying guiding principles (Flight, 2006).
Importance and Benefits of Strategic Alliance of Tata Coffee and Starbucks
Starbucks is very quality driven organization and is passionate about ethically sourcing the finest coffee beans, roasting them with great care and improving the lives of people who grow them. Starbucks call their employees as the partners and treat each other with respect and dignity. The employees at Starbucks get engaged with their customer and connect with them so as to laugh with them, uplift customers' lives even if it is just for moments. They believe in human connection and developing the sense of belonging. They believe in creating good neighbourhood and each store is nourished as a community (Ryan, 2008). Tata has made the cultural fit for Starbucks which will help in building core competencies of each other. (Tata has met all the stringent standards and conditions followed by Starbucks such as quality, soil, water, pest, waste and energy management, forest and biodiversity conservation to workers’ welfare, wages and benefits, living conditions, health, safety, etc.).1
Starbucks is committed to a role of environmental leadership in all facets of their business. They strive to fulfil this mission by a commitment to:
1. Understanding of environmental issues and sharing information with their partners.
2. Developing innovative and flexible solutions to bring about change.
3. Striving to buy, sell and use environmentally friendly products.
4. Recognizing that financial responsibility is essential to their environmental future.
5. Instilling environmental responsibility as a corporate value.
6. Measuring and monitoring the progress for each project.
7. Encouraging all partners to share in their mission.
Competitive advantage of starbucks
1. Strong brand image.
2. Starbucks specializes in coffee and related beverages.
3. Starbucks is the largest coffee house company in the world.
4. They have loyal customers worldwide.
Marketing strategy of starbucks
1. Starbucks started a community website, My Starbucks Idea.
2. It’s rare to find a Starbucks in a billboard, and space, newspaper or poster in places.
3. The company has went to great lengths to create a “Community atmosphere” among premium coffee lovers.
4. Starbucks operates primarily through alliances, joint ventures and licensing arrangements with consumer products business partners.
Competitive advantage of tata coffee
1. The largest integrated coffee plantation company in the world.
2. Its uniqueness lies in its ability to produce large quantities of estate specific, strain specific, special and premium coffee, while maintaining a strict consistency in quality.
3. It has a hand in every aspect of the coffee making process.
4. With the major coffee consumption markets being Arabica-centric, this lobby has been prevailing in international markets by Tata coffee.
About the deal
1. Starbucks made a strategic alliance with Tata coffee to start up its business in India.
2. Starbucks will explore setting up stores in the Tata group’s retail outlets and hotels, besides sourcing and roasting coffee beans at Tata Coffee’s Kodagu family.
3. This Agreement includes opening cafes, bean sourcing and roasting.
4. One of the hurdles that the two companies have to sort out is Starbucks’ franchisee-led model.2
Objective of tata coffee behind this alliance
1. The agreement will allow Tata coffee to provide roast coffee bean to Starbucks in India.
2. Get opportunity to jointly invest in additional facility for export to other markets.
3. Starbucks will help by providing new technologies for the promotion of responsible agronomy practices.
4. A long term relationship will be formed with this Memorandum of Understanding with Starbucks.
5. After this deal, Tata Coffee is poised to become Asia’s biggest publicly traded coffee grower.3
Objective of starbucks behind the deal
1. To tap huge emerging market of India.
2. Help increase its profitability due to its declining market and over dependence on US market.
3. To have access to the high quality Arabica coffee.
4. Starbucks aiming to enter in Indian market through this MoU.
5. Starbucks believe that India can be an important source of coffee in the domestic market, that’s why they entered in India.
6. The knowledge and understanding of the Indian market can be brought by Tata Global Beverages, because it has been in this play for a while.
7. The Tata also have an arm in retail so there’s a synergy there as well.4
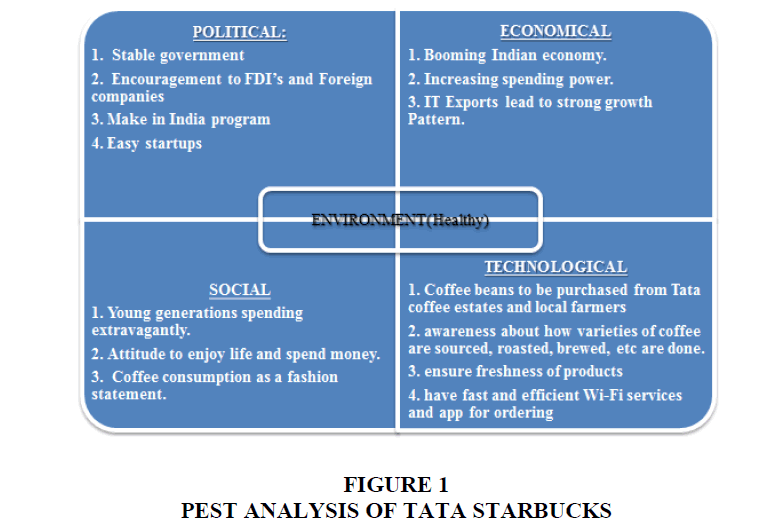
Scanning the Environment-Pest Analysis
Political factors
“India’s youth are becoming world-class consumers, and multinationals are taking note,” reads the sub header for an article titled “Hey, Big Spenders!” of TIME magazine. This change can be accredited to many factors. The new economic reforms of India went through a massive liberalization, globalization and privatization under the able leadership of the then Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao in 1991. Further, the government’s reform measures like approval to Foreign Direct Investment in multi brand retail for up to 51% will generate more investments in India.
Economic factors
The factors like insufficient infrastructure, regulatory and foreign investment controls, system of government, the condition of key products for small-scale and medium scale industries, and deficit in budgetary policy are constraints to economic growth in India. Due to the new industrial policy taken in 1991 opened the Indian economy to foreign trade and investment. This liberalization policy reduced controls, devalued the currency and decreased customs duties. It almost abolished licensing regulations and controls on private investment, reduced tax rates, and ruined public sector monopolies. The Indian government’s approval on Foreign Direct Investment up to 51% on retail industry made a boost up to foreign companies to invest in India. India being a major exporter of software and IT products and IT professionals, the IT industry shows the strong growth pattern. As the world is changing itself from industrial sector to an informational technology economy, India is to play a lead role in shaping the future of the globe.
Socio-cultural factors
The job opportunities increased drastically in India, due to liberalization of the economy and IT sector boom. This made the changes in the mind set of Indians by changing themselves from saving to spending. The India’s youth inspired by various job opportunities and spending money lavishly. The youth approach is to spend money and enjoy life.
However, Indians are habituated with tea consumption. According to market research studies, Coffee consumption is more in the urban areas (71%) and lesser in the rural areas (29%). The south Indians largely prefer coffee. The north Indians are not fond of coffee, but drink coffee in various flavours as a matter of fashion statement. The consumption of filter coffee and instant coffee is approximately equal on the national level. But region-wise, Filter coffee is more popular in Tamil Nadu and other south Indian states and percentage of instant coffee is very high in North India.
Technological factors
The green coffee beans and tea leaves is bought from the Indian farmers in order to support the agricultural sector, save transportation charges, get subsidies and gain tax benefits. Indians like to have more cream in the coffee. Starbucks alliance with the Tata Coffee Ltd for sourcing and roasting Arabica Coffee will surely help both the companies in the long run. In India, skim milk option is not necessary as many Indians do not following dieting. Indians specially like to have ginger and black clove in their tea and coffee. Additionally, the outlets are enabled with Wi-Fi services as everyone is using smart phones, laptops at the café. Indians like to connect with the traditional and rich heritage as well as its coming together with modernity. This may be reflected in the stores' ambience. Starbucks outlets are fully furnishes and creates awareness on how coffee beans are sourced, roasted, brewed, etc and makes customers more loyal to have a cup of coffee in Starbucks coffee outlets.
The inventory management is to keep the store stocked with coffee beans at the same time the outlets has to take care not to overstock of beans as it loses its freshness. Based on the everyday visit of the customers to the outlet, the policy is formulated accordingly.
Environmental factors
Starbucks believes in the ecofriendly products. It encourages on taking care of the globe and encourages others to do the same. Tata Starbucks purely relies on agricultural and ecofriendly products; it conducts its business in good sense. It engages in recycling, energy management, water conservation, green building, and in reducing carbon footprints wherever possible. With all these incorporated environmental responsibilities, Starbucks will clearly build its image even in India. The ecological issues regarding the cultivation of Arabica coffee should be addressed to ensure consistency in productivity.
SWOT Analysis of Tata Coffee and Starbucks
The core competence of Tata coffee and Starbucks has been its ability to efficiently and effectively leverage the cornerstone product differentiation strategies by offering a premium quality coffee and product mix of high quality beverages and snacks. Starbuck’s built its brand only by selling the finest quality coffee and related products, and it provided each customer a unique “Starbucks Experience”, that is consequent from ultimate customer service, clean environment and well-maintained stores that imitate the culture of the communities in which they operate. This resulted in high satisfaction and high degree of customer loyalty. The other core areas of Starbucks are human resource management's values-based approach that builds good internal and external relationships with vendors. This mainly drives successful deployment of Tata Starbucks business strategy of organic expansion into global markets Today, Starbucks is being recognized as the most respected brands in the world as it mainly prefers horizontal integration through acquisitions and alliances that maintains the long-term strategic plans.
Strengths
1. High Brand Visibility and Global Brand recognition.
2. Location and artistic appeal of its stores.
3. Superb Marketing and positioning skills of Starbucks.
4. Use of Technology and mobile outlets.
5. Diverse Product Mix.
6. Customer base loyalty.
7. Access to TATA's premium Robusta and Arabica coffees (Sourcing Agreement).
8. Both the companies are leading company in their sector.
9. Ethical and Environmental Practices.
10. High-quality green coffee beans.
11. Consider jointly investing in additional facilitates for exports to other foreign markets.
12. Tata coffee and Starbucks has a goodwill among customers due to Social Responsibility Initiatives.
13. Both the companies utilize the resources of each other in enhancing their core competency. Tata as a cultural fit for Starbucks will help in building core competencies of each other as Tata has met all the standard and conditions levied by the Starbucks such as quality, waste management, conservation of workers welfare, etc.).
Weakness
1. The Tata Starbucks is carrying the image of luxury coffee outlets. The people visiting coffee outlets are rare in India as the price per coffee is very high in the outlets.
2. Expensive products: High price of coffee is felt as a barrier among the Indian customers. (Starbucks coffee products are priced at a very high and the income of Indians are lesser when compared to other foreign markets where Starbucks already exists. Now, Tata Starbucks has to rethink to offer coffee at locally competitive prices).
3. Coffee dominant business. (Starbucks has to diversify its business from coffee to providing other snacks and food items to face the competition from rivalries which have already diversified).
4. Certain rigid standards and policies at outlets. (Starbucks follow the similar business models and formulas, despite of culture and traditions of the any country they are operating in like no smoking policy, etc.).
5. There is no uniqueness and exclusivity from these two companies i.e., Starbucks and Tata coffee.
Opportunities
1. India is the second most populated country in the world. There is scope for Tata Starbucks to capture the market because of huge market.
2. The Middle Class with English speaking people is growing rapidly and the spending power of Indians is increasing.
3. The young population is increasing who shows more interest in visiting the cafes as a fashion statement. (Consumer of 20-45 years age group is emerging as the fastest increasing consumer group. As per the research, an average age of Indians is going to be 29 years by 2020.
4. Good and quality telecom infrastructure.
5. As Indians are habituated with Tea-based culture, this could be uses as an opportunity by Starbucks to offer tea-based drinks.
6. People prefer to have a cup of coffee outside home rather than tea outside home, specifically in the North-Eastern states of India. The southern states people like to consumer coffee. The North Indians are not generally coffee drinkers, but drink coffee as a fashion statement.
7. Tata coffee can increase its market share by providing the raw products to Global players who are in the Coffee outlets business. Cheap Labour, Fair availability of workforce (Quantity as well as skilled) and resources.
8. The expected growth rate of Coffee consumption in India is 6%, this can be used an opportunity to set up more outlets in many cities.
9. By this deal, Tata Coffee is able to lower the over dependence on the commodities market and shift to the branded Coffee retail market.
10. Brand extension: Starbucks and Tata coffee carries a good brand image in the international market. So, it can leverage it to extend its business by diversification and expansion of business while keeping brand image in consideration.
Threats
1. Indians are habituated with tea and have a tea-based culture. (The hot-beverage market of India is purely dominated by tea. As, India being a largest producer and consumer of tea in the world, its production is accounted for 29% and consumption is of 20%. Indians prefer to consume tea at least two times a day.
2. The domestic companies like Coffee Cafe Day that are home grown brands dominate the retail coffee market, followed by Barista coffee and Qwikys Coffee.
3. The standard of living of people and per capita income of Indians is low. The Coffee price of Tata Starbucks outlets is felt as a barrier for middle class income group to have a cup of coffee. So, Tata Starbucks has to reframe the pricing model as per the Indian standards and offer products at locally competitive prices.
4. The consumers are very conscious about their health. Due to increase in obesity, diabetes, Blood pressure, heart attacks, people prefer to go for health drinks. There is an opposition from many health groups worldwide on Starbucks that it sold high calorie and high fat products to its consumers.
5. Visiting coffee outlets and cafes are not a regular habit among most of the Indians. Instead they go occasionally.
6. Fast food chains like that of McDonalds, Dunkin Donuts, Burger King, etc., have already diversified their products and offering quality coffee to compete with Starbucks.
7. Rise in coffee prices are increasing pressure on the profit margins. So, Starbucks need to address pricing issues for India, since demand is highly elastic.
8. There are many competitors like Barista, café coffee day, etc in this sector for Starbucks.
| Table 2 Locations As Of July 2014, Starbucks Operates 63 Outlets In 7 Cities Of India |
|||
| State/Region | City | No. of Outlets | First outlet |
| Delhi | New Delhi | 14 | 24 January 2013 |
| Delhi NCR | Gurgaon | 4 | 10 July 2013 |
| Maharashtra | Mumbai | 25 | 19 October 2012 |
| Pune | 6 | 8 September 2013 | |
| Karnataka | Bangalore | 10 | 22 November 2013 |
| Tamil Nadu | Chennai | 1 | 8 July 2014 |
| Telangana | Hyderabad | 3 | 1 October 2014 |
Conclusion
Strategic alliances are an increasingly significant core element in many firm’s strategies to generate and sustain their competitive advantages in dynamic market environments. Alliance is like a nuptial where there may be no formal contract and no buying and selling of equity. But, there are few strictly binding provisions. It is an unfastened evolving kind of relationship. Both partners bring to an alliance a trust that they will be stronger together than they would be separately. Both judge that each has distinctive skills and functional abilities and both have to work assiduously over time to make the union flourishing. By developing strategic alliances, firms share their excess and/or complementary capabilities and resources with others and create a new entity to acquire competitive advantages. When alliances are efficiently managed, the participating firms can attain numerous benefits that eventually bring profitability. If companies utilizes proper strategic alliance, they can expand their product and service offerings substantially, without the usual corresponding investment in staff, equipment, and facilities. Strategic alliance benefits in the way of cost reduction, technology sharing, product development, market access etc. Sociocultural and ethical parameters that have an effect on company’s performance enhance the complexity of the environment in developing countries. The performance of strategic alliances would depend on the acknowledgement of these parameters. By taking advantage of the actual globalization context, strategic alliances may take part in a crucial responsibility in dipping the gap between economies in developed countries and those in developing countries which might be a subject of new research possibilities to prospective researchers in this particular field.
Suggestions
1. The Tata Starbucks has to minimize the cost as per the requirements of Indian customers in order to penetrate in Indian Market.
2. It has to switch on to new marketing strategy other than community website. It has to go for advertisement in Print and electronic media.
3. The company has to focus on how to offer convenient coffee locations and quality services to consumers.
Endnotes
1. http://news.starbucks.com/article_display.cfm?article_id=707 accessed on Oct 15, 2012
2. http://news.starbucks.com/article_display.cfm?article_id=703 accessed on Oct 15, 2012
3. http://www.starbucks.in/about-us/company-information/mission-statement accessed on Oct 15, 2012
4. http://www.tatacoffee.com/corporate/company_profile.htm accessed on Oct 15, 2012
References
- Anderson, J.C., & Narus, J.A. (1984). A model of the distributor's perspective of distributor-manufacturer working relationships. The journal of marketing, 48(4), 62-74.
- Beamish, P.W. (1988). Multinational joint ventures in developing countries. Routledge, London.
- Beamish, P.W. (1984). Joint-venture performance in developing countries. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Western Ontario, London Ontario.
- Bleeke, J., & Ernst, D. (1991). The way to win in cross-border alliances. Harvard business review, 69(6), 127-135.
- Child, J., & Faulkner, D. (1998). Strategies of cooperation: Managing alliances, networks and joint ventures. Oxford university press, oxford, UK.
- Cobianchi, T.T. (1994). Relationships among strategic alliance factors and strategic alliance success. Unpublished doctoral dissertation: US International University.
- Contractor, F.J., & Lorange, P. (1988). Competition vs. cooperation: a benefit cost frame work for choosing between fully owned investments and cooperative relationships. Management International Review, 5-18.
- Crossan, M. M., & Inkpen, A. C. (1995). The subtle art of learning through alliances. Business Quarterly, 60(2), 68-76.
- De la, C. (1995). Managing global alliances: Key steps for successful collaboration. Addison-Wesley.
- De Villa, M.A., Rajwani, T., & Lawton, T. (2015). Market entry modes in a multipolar world: Untangling the moderating effect of the political environment. International Business Review, 24(3), 419-429.
- Dodgson, M. (2018). Technological collaboration in industry: strategy, policy and internationalization in innovation. Routledge.
- Doz, Y.L., & Hamel, G. (1998). Alliance advantage: The art of creating value through partnering. Harvard Business Press.
- Flight, G. (2006). Grinding out success next to Starbucks. Business 2.0, 7(9), 62-63.
- Harold, B. (2011). External environmental analysis of starbucks and the coffee industry.
- Herve R. (2004). The starbucks corporation: Past, present and future.
- Khanna, R. (2018). Technical alliances as a strategy to create knowledge: analysis of patterns across Indian pharmaceutical firms. Journal of Business Thought, 7, 89-114.
- Larson, R.C. (2008). Starbucks a strategic analysis:Past decisions and future options.
- Rothaermel, F.T. (2015). Strategic management. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Ruchi, M., & Joel, S.T. (2011). Case: Starbucks coffee company, the Indian dilemma. Strategic management and business policy.
- Vrushali, P. (2011). International business plan starbucks India. A proposal.
- Xu, H., Guo, H., Zhang, J., & Dang, A. (2018). Facilitating dynamic marketing capabilities development for domestic and foreign firms in an emerging economy. Journal of Business Research, 86, 141-152.
- Zaefarian, G., Forkmann, S., Mitr?ga, M., & Henneberg, S.C. (2017). A capability perspective on relationship ending and its impact on product innovation success and firm performance. Long Range Planning, 50(2), 184-199.