Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 6S
An Empirical Study of Hospitality Industry with respect to Effect of Customer Experience on Customers Revisit Intention
Aparna J Varma, GSSSIETW
Ranjith P V, CMS Business School, Jain (Deemed-to-be-University)
Ashwini J, Bahadur Institute of Management Sciences
Keywords
Hospitality Industry, Customer Experience Management, Revisit Intention
Abstract
Customer experience management is the latest buzzword in the service and in the manufacturing industry. But the concept is highly relevant when it comes to service sector due to its characteristics of intangibility. There are many cues a customer will rely upon while choosing a service. This study focuses on the customer experience management of select resorts in Karnataka. Customer experience is shaped by the customers’ expectations and the service encounters which happens during a service interaction. This study has considered the role of five variables: Price, Food Quality, Ambience, Technology and Social environment that leads to customer revisit intention.
Introduction
Hospitality Industry in India is witnessing a healthy growth due to the major economic factors like increase in disposable income, growing middle class and double income families. The industry is continued to be the main drivers of economy due to the high potential of tourism in India. The contribution to the GDP from this sector accounts 7.5 percentages. The industry statistics shows that the hotels in India provide 42.6 million jobs and 8.1% of the total employment opportunities created in the country. The major challenge faced by heavily taxed industries ranging from 20-30 %, the growth in this industry is substantially high owed by the potential of tourism in India. The major revenue generation for a hotel happens through room rentals and food and beverages. All the hoteliers are investing their time in exploring the ways to increase this usage rate. One of the most promising strategies engaged for this is to enhance the customer experience management. Many studies in this filed have given valuable insight on the various factors affecting this strategy.
Literature Review
Customer experience is all about how a customer perceives his interaction with his service provider and encompasses all kind of factors like service environment, staff, physical evidence and self-service technologies (Sirapracha & Tocquer, 2012; Hwang & Seo, 2016). Different studies have proved that customer experience management can help a brand to achieve high brand equity (Bitner et al., 1992; Gilboa & Rafaeli, 2003; Berry & Carbone, 2007; Chang & Chieng, 2006).
The psychological perceptive of customer experience says that the cognitive and affective assessment of all service encounter will influence the purchase behavior of a customer (Lovelock et al., 2004; Verhoef et al., 2009; Lemke et al., 2011; Klaus & Maklan, 2013). Johnson et al., (2009) researched the role of perceived quality, price and emotions in customer experience. They could find a predominance of perceived quality than perceived price towards satisfaction. Morgan, et al., (2009) have come up with a new perceptive of theoretical metaphor in service delivery. This study throws light on the strategic evaluation of the critical incidents between three factors; restaurant, diner and other guests. The managers can play the service delivery act on by focusing on the extended Ps staff as People /actors, processes as script and physical evidence as stage to intensify the customer experience.
Satish & Venkatesh (2010) conducted a study on coffee lovers to know the factors influencing the experience that leads to customer satisfaction and loyalty. Staff service and product quality have emerged as the predominant factor affecting the dependent variables. Anderson and Mossberg (2004) have considered six factors to evaluate the expectation and perception to measure the dining experience of the customers. The authors have identified that customers gave more significance to social needs in the evening and physiological needs in the afternoon. Nambisan, et al., (2002 & 2007) have studied the relationship between customer, technology and new product development process. According to him technological advancement has created a great platform for a firms’ customer to be the co-creator in new product development process.
The role of employees in creating customer experience was widely researched in various industries (Ryu, 2008; Namasivayam et al., 2014; Schneider et al., 2014; Ren et al., 2016). Nasermoadeli, et al., (2013) have investigated the impact of social environment on customer experience and it was found that social environment is related to sensory and emotional experience. Research on pricing and customer experience management revealed that higher the price of a product/service higher will be the customer expectation for the experience. (Linda & Newton, 2006; Schmitt, 2010; Schmidt et al., 2012).
Objective of The Study
Customer experience management is a win-win strategy that can be designed by any business establishment to survive in today’s competition. Customer experience includes every point of interaction a customer will have with the business and related services. The authors could find comparatively very less research on this topic in the area of hospitality sector.
Hence the purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between select variables that shape customers’ experience in hospitality sector in Karnataka and its effect on their revisit intention.
Scope of The Study
The customers don’t buy product or services; they buy experience when they make their purchase decision. Also, it is evident from the various studies that retaining a customer is more profitable than gaining a new one. This study will help marketers to close the gap between what is expected by the customer and what is being delivered by reevaluating the marketing strategies.
Research Methodology
The study is descriptive in nature. A conceptual framework on customer experience management has proposed for the study based on the available researches in the area of interest.
The researchers have done primary data collection using convenient sampling method with the help of a structured questionnaire from 100 customers of select resorts in Mysore, Karnataka.
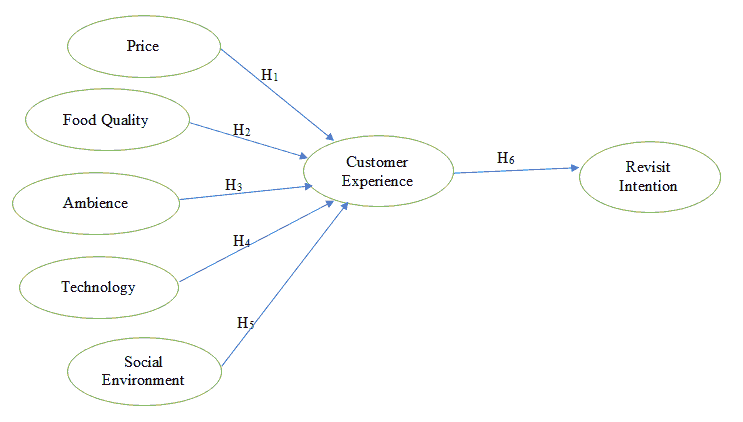
A field study approach was used to get authentic information from the respondents’ who were experiencing the service from the select resorts. All the statement was measured using a 5-point Likert scale from 1 strongly disagree to 5 strongly agree. Descriptive statistics has used to understand the demographic characteristics of the respondents meanwhile correlation study was used to know the strength of relationship between the select variables. Regression analysis has conducted to test the proposed hypotheses using SPSS version 21 (Figure 1).
Research Hypotheses
H1: There is a significant relationship between price and customer experience
H2: There is a significant relationship between food quality and customer Experience
H3: There is a significant relationship between ambience and customer Experience
H4: There is a significant relationship between technology and customer experience
H5: There is a significant relationship between social environment and customer experience
H6: There is a significant relationship between customer experience and revisit intention
Findings and Discussions
| Table 1 Profile of The Respondents |
||
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Category | Frequency |
| Gender | Male | 58 |
| Female | 42 | |
| Age | Less than 25 years | 30 |
| 25 years – 34 years | 34 | |
| 35 years – 44 years | 25 | |
| 45 years – 54 years | 8 | |
| 55 years and above | 3 | |
| Annual Income | Less than 5,00000 | 26 |
| 5,00000 – Less than 10,00,000 | 40 | |
| 10,00,000 – Less than 15,00,000 | 27 | |
| More than 15,00,000 | 7 | |
| Occupation | Home maker | 13 |
| Business | 32 | |
| Government sector | 15 | |
| Private sector | 40 | |
| Purpose of Visit | Official | 32 |
| Leisure trip | 68 | |
Reliability Test
Reliability test has been used to test the Reliability of the scale used for data collection. Cronbach's Alpha index was calculated to measure the Reliability of the questionnaire. The items having a coefficient value of 0.70 and more are considered as adequate. In this study 7 factors with 33 items are considered for the study with the help of SPSS 21. The overall reliability of all variables is 0.873, which means the results of all variables are reliable for further study” (Table 2 & Table 3).
| Table 2 RELIABILITY ANALYSIS |
|
|---|---|
| Cronbach’s Alpha | No. of Items |
| 0.873 | 33 |
| Table 3 Item -Total Statistics |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sl. No | Dimensions | Cronbach’s Alpha | No. of Items |
| 1 | Price | 0.855 | 4 |
| 2 | Food Quality | 0.848 | 3 |
| 3 | Ambience | 0.85 | 5 |
| 4 | Technology | 0.856 | 5 |
| 5 | Social Environment | 0.862 | 6 |
| 6 | Customer Experience | 0.845 | 4 |
| 7 | Revisit Intention | 0.844 | 6 |
Correlations
The correlation table explains the correlation between Customer Experience and Social Environment, Food, Technology, Price, Ambience (Table 4).
| Table 4 Correlation Matrix |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1. Price | 1 | |||||
| 2.Food | 0.575** | 1 | ||||
| 3.Ambience | 0.566** | 0.484** | 1 | |||
| 4.Technology | 0.442** | 0.478** | 0.563** | 1 | ||
| 5.Social Environment | 0.403** | 0.358** | 0.460** | 0.441** | 1 | |
| 6.Customer Experience | 0.441** | 0.481** | 0.494** | 0.324** | 0.614** | 1 |
From the above table it can be observed that social environment is showing a high positive correlation since the correlation value is 0.614.
Testing of Hypotheses
To test the hypotheses H1 to H5 multiple regression analysis was used (Table 5).
| Table 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Analysis between independent variables and customer experience | |||||
| R | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Standard error of Estimate | ||
| 0.712 | 0.508 | 0.481 | 2.33384 | ||
| ANOVA | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
| Regression | 527.789 | 5 | 105.558 | 19.38 | 0 |
| Residual | 512.001 | 94 | 5.447 | ||
| Total | 1039.79 | 99 | |||
| Coefficients | B | Std. error | b | T | Sig. |
| (Constant) | -0.551 | 1.746 | -0.316 | 0.753 | |
| Price | 0.206 | 0.103 | 0.195 | 1.994 | 0.041 |
| Food | 0.281 | 0.132 | 0.199 | 2.122 | 0.036 |
| Ambience | 0.162 | 0.099 | 0.162 | 1.631 | 0.106 |
| Technology | -0.134 | 0.084 | -0.149 | -1.592 | 0.115 |
| Social Environment | 0.376 | 0.071 | 0.455 | 5.329 | 0 |
From the above table it can be observed that the R Square score is 0.508 and adjusted R Square score is 0.481. These scores can be interpreted that the variables used to identify the effect of customer experience can explain the 50.8% of the equation. Also, it is evident that the Regression Model is significant since p<0.05. Also, the relationship between 3 variables price, food, and social environment with customer experience are significant since the p<0.05. Whereas the relationship between the other two variables like ambience and technology with customer experience are not significant since the p >0.05. If Food value increases one unit then customer experience ascends to 0.036 units. Similarly, if ambience increases one unit then customer experience ascends 0.106 units .
H6 : Regression analysis between customer experience and revisit intention
| Table 6 Regression Analysis |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Standard error of Estimate | ||
| 0.735 | 0.54 | 0.535 | 2.88174 | ||
| ANOVA | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
| Regression | 954.916 | 1 | 954.916 | 114.989 | 0 |
| Residual | 813.834 | 98 | 8.304 | ||
| Total | 1768.75 | 99 | |||
| Coefficients | B | Std. error | b | T | Sig. |
| (Constant) | 7.57 | 1.381 | 5.482 | 0 | |
| Customer Experience | 0.958 | 0.089 | 0.735 | 10.723 | 0 |
From the above table 6 it can be observed that R square score is 0.540 and adjusted R Square score is 0.535. These scores convey that the variables used to identify the effect of customer experience can explain the 54.0 % of the equation. From the above table 6 it is clear that there is a significant relationship between customer experiences and revisit intention since p<0.05.
Conclusion
Customer experience include all the interactions a customer will go through with the service provider during the purchase process (Kadampully, 2018). Henceforth it is necessary for any organization to provide a top-notch customer experience for its customers to build a long-term relationship (Chareon, 2003). This study elucidates the relationship of price, food, social environment, technology and ambience with customer experience management. Cronbach’s alpha is more than 0.8 which means that the study is reliable. The researcher could find a positive correlation between the select variables and customer experience. In this study it is statically proved that there is significant effect of price, food, and social environment in creating a positive customer experience. Also there is a positive correlation between customer experience and revisit intention. So, it can be concluded that a well-defined a holistic customer experience strategy is the need of the hour to earn the satisfaction and loyalty of the customers and the companies can concentrate on the above mentioned factors so as to make customer experience more worthwhile.
References
- Andersson, T.D., & Lena, M. (2004). “The dining experience: Do restaurants satisfy customer needs?” Food Service Technology, 4(4), 171-177.
- Leonard, L.B., & Lewis, P.C., (2007). Build loyalty through experience management. Quality Progress, 40(9), 26-32.
- Mary-Jo, B. (1992). Servicescapes: The impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees. Journal of marketing, 56(2), 57-71.
- Mary-Jo, B. (2000). Servicescapes, in Handbook of Services Marketing and Management, T.A. Swartz & D. Iacobucci, editions. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 37-50.
- Bowen, D.E., & Schneider, B. (2014). A service climate synthesis and future research agenda. Journal of Service Research, 17(1), 5-22.
- Chang, P-L., & Ming-Hua, C. (2006). Building consumer–brand relationship: A cross-cultural experiential view. Psychology and Marketing, 23(11), 927–59.
- Gilboa, S., & Rafaeli, A. (2003). Store environment, emotions and approach behavior: Applying environmental aesthetics to retailing. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 13(2), 195-211.
- Grove, S.J., Fisk, R.P., & Bitner, M.J. (1992). Dramatizing the service experience: A managerial approach. Advances in services marketing and management, 1(1), 91-121.
- Johye, H., & Soobin, S. (2016). A critical review of research on customer experience management. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
- Johnson, M.D., Olsen, L.L., & Andreassen, T.W. (2009). Joy and disappointment in the hotel experience: Managing relationship segments. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal.
- Kandampully, J., Zhang, T.C., & Jaakkola, E. (2018), Customer experience management in hospitality. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
- Klaus, P.P., & Maklan, S. (2013). Towards a better measure of customer experience. International Journal of Market Research, 55(2), 227-246.
- Lemke, F., Clark, M., & Wilson, H. (2011). Customer experience quality: An exploration in business and consumer contexts using repertory grid technique. Journal of the academy of marketing science, 39(6), 846-869.
- Christopher, L & Wirtz, J. (2004). Services marketing: People, technology, strategy, (5th edition). Upper saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
- Maxie, S.S., Harley, M., & Carla, O. (2012). Pricing matters for customer experience professional.
- Morgan, M., Watson, P., & Hemmington, N. (2008). Drama in the dining room: Theatrical perspectives on the foodservice encounter. Journal of Foodservice, 19(2), 111-118.
- Karthik, N., Priyanko, G., & Lei, P. (2014). The influence of leader empowering behaviors and employee psychological empowerment on customer satisfaction. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 26(1), 69-84.
- Nambisan, S. (2002). Designing virtual customer environments for new product development: Toward a theory. Academy of management review, 27(3), 392-413.
- Nambisan, S., & Baron, R.A. (2007). Interactions in virtual customer environments: Implications for product support and customer relationship management. Journal of interactive marketing, 21(2), 42-62.
- Amir, N., Kwek, C.L., & Erfan, S. (2013). Exploring the relationship between social environment and customer experience. Asian Social Science, 9(1), 130.
- Nowak, L.I., & Sandra, N.K. (2006). Using the tasting room experience to create loyal customers. International Journal of Wine Marketing.
- Lianping, R., Hanquin, Q., Wang, P., & Pearl, L.M. (2016). Exploring customer experience with budget hotels: Dimensionality and satisfaction. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 52, 13-23.
- Charoen, R. (2003). “Customer experience management: The differential roles of search, experience, and reinforcement cue”. Doctoral Thesis, JDBA.
- Ryu, K., & Jang, S. (2008). DINESCAPE: A scale for customers' perception of dining environments. Journal of Foodservice Business Research, 11(1), 2-22.
- Sathish, A.S., & Venkatesakumar, R. (2011). Coffee experience and drivers of satisfaction, loyalty in a coffee outlet-with special reference to" café coffee day". Journal of Contemporary Management Research, 5(2), 1.
- Schmitt, B.H. (2010). Customer experience management: A revolutionary approach to connecting with your customers. John Wiley & Sons.
- Sirapracha, J., & Tocquer, G. (2012). Branding and customer experience in the wireless telecommunication industry. International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, 3(2), 103.
- Tourism & Hospitality Industry in India.
- Verhoef, P.C., Lemon, K.N., Parasuraman, A., Roggeveen, A., Tsiros, M., & Schlesinger, L.A., (2009). Customer experience creation: Determinants, dynamics and management strategies. Journal of retailing, 85(1), 31-41.
- Ward, J.C., Mary-Jo, B., & Barnes, J. (1992). Measuring the prototypically and meaning of retail environments. Journal of retailing, 68(2), 194.