Research Article: 2021 Vol: 0 Issue: 0
Alienation in the urban structure and its impact on the individual and society
Abbas Hashem Sahan, University of Baghdad
Abstract
Alienation is a state of separation and a person’s distancing from his spiritual and material world and making him distant and unable to change the reality in which he lives. The alienation may be voluntary or involuntary and imposed on him. The concept of alienation came in many fields of knowledge, such as language, philosophy, sociology, and psychology, as well as the field of architecture, as it is a phenomenon of the modern era, and this is what led us to the need to address it in order to reveal its contents and forms. These introductions lead us to get acquainted with this concept and reveal the most important thing that it contains, as the link between the built environment and the physical components it carries with the human being as a social being has subjective and spiritual requirements that are taken into consideration and seriously to be met in that component that it will contain, which in turn alleviates the social problems resulting from the problems and crises of the rupture between man and the urban structure through creating a sense of belonging. The alienation contains multiple forms, including spatial, social and psychological alienation, all of which lead to the separation of the link between the individual as a social being and the place as a physical environment, which leads to the disintegration of the urban fabric and the formation of a contradictory urban structure in the chaos of the decaying urban spaces that were the cause of creating social problems and their failure to achieve Its social and psychological performance. The research problem came because of the lack of a clear perception of the direct connection between the built environment as a physical product with the human being as a social being that has spiritual subjective requirements that must be met in that product that it will contain, which leads to the creation of a kind of rupture between man and the built environment. As for the importance of research, it lies in the conflict of goals and objectives with the social environment standards to which the individual belongs. The aim of the research emphasizes the necessity of reaching the creation of places through which the individual can achieve correct communication with others, such as the existence of urban spaces that restore to man his comfort and psychological, emotional and social stability. This study came in two aspects: The theoretical aspect that dealt with previous concepts and studies and theories explaining alienation, its forms, the stages it goes through and its effects on the individual. The practical aspect, where the researcher studies two societies, the first is the spatial community to measure the effect of alienation in the urban structure on the individual, and the second is an academic community to find out the opinions of specialists about the physical effects on the individual and society. The study included many recommendations, including the direct link between built environment as a physical product and the human being as a social being with personal and spiritual requirements, and to alleviate social problems and ills resulting from crises of rupture between man and the surrounding urban environment. And get rid of the real causes behind the feeling of alienation.
Keywords
Alienation, Urban Structure, Spiritual, Philosophy, Sociology, Psychology
Introduction
The Conceptual Framework for the Research
First of all: The Research Problem
Not having a clear conception in the direct connection between the urban environment as a physical result and humankind as a social creature with spiritual inner needs that need to be fulfilled in his environment and not meeting his needs causes a termination between humankind and the urban environment where he exists.
Secondly: The purpose of the Research
Creating areas where a person is able to socialize and communicate and also fulfilling his social and psychological needs.
Thirdly: The Importance of the Research
The conflict between the individual purposes and desires with the urban environment standards where he lives leads to an occurrence of different types of alienation which are important to study.
Fourth: The Research Hypothesis
A. Human interaction gets affected by the urban environment positively and negatively.
B. The urban structure is just a concrete structure that doesn't affect people behavior and their psychological wellbeing.
Fifth: The Study Community
Al-asraa residential complex in Wasit Governorate, Al- Kut district which includes 504 families and also postgraduate students in the urban and regional planning center- Baghdad Univ.
Sixth: Research Areas
1. Spatial area: Wasit governorate, Al-Kut district, Al-asraa residential complex.
2. Human area: includes two communities, the first one is the families of Al-Asraa residential complex in Wasit governorate, Al-kut district, the other community are the postgraduate students in the urban and regional planning center because they present the academic category that relates to the residential environment planning issues and the spatial alienation.
3. Temporal area: it's the period between (1/9/2020) till (1/2/2021)
Seventh: The Research Method for the Study
(Social survey curriculum ), we can define this curriculum as (a method of social research that contains applying the scientific research steps scientifically about studying a phenomenon or a social issue or some social cases that are spreading in a particular geographic area so we can get enough information that describes the different sides of the studied phenomenon, after classification and analyzing the data we can get benefit from it for the scientific purposes, (Nahidaa Abd Al-Kareem, 1981).
It also defined as an organized attempt to reevaluate and explain the current situation for a social system or a community or a particular environment for reaching to data that can be classified and explained and enforced to get a benefit from it in the future for scientific purposes), This curriculum saves time and effort and searches in the events of human life and society phenomenon and cases and also benefit in specify the different circumstances and conflicts that affect people lives and their different circumstances from the social and economic and environmental point of view (Abd Al-Bassed Muhammad Hasan, 1985).
Eighth: The Research Tools
Questionnaire form, to get accurate and helpful information for the research, the researcher used two types of questionnaire forms, the first one to the Amal residential complex by a sample of 5%, and the second one to specialists from postgraduate students in the regional planning center with a 90% rate.
Ninth: The Honesty and Persistence of the Tool
The researcher designed the questionnaire relying on some specialists to put a specific question that clear the research issue, to test the honesty of the tool the form has been shown to the specialists who were ten people and this schedule clarifies their agreements on the questions and the adjustments they made (Table 1).
| Table 1 The Extent of The Experts' Agreement on The Questionnaire Questions |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| The experts | number of questions | Number of experts | percentage |
| Agreed without modifications | 16 of 19 questions | 7 | 90% |
| It was agreed to make some amendments | 2 of 19 questions | 2 | 8% |
| It was agreed to delete some questions | 1 | 1 | 2% |
The Persistence of the Questionnaire
One of the most important purposes of good research is getting good persistent notes; the calculation of persistence refers to retry the measures until getting stable grades from the syompls in a particular amount of time. (Al-maghribi, Aleeb albaheth, from the first community and the second community 5th scientific), for this matter, the researcher used a primary symbol from the audience of (25) and made sure to variegate the audience from the social type, housing area, to guarantee its presenting to the study community, after 14 days after the first test we repeated the attempt to test the persistence of the tool, the searcher used Pearson correlation coefficient to clarify the relationship between the first and second test as this schedule shows (Table 2):
| Table 2 Shows the Persistence of the Questionnaire |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persistence | Persistence symbol | Their number | Correlation | Indication | Result |
| The first persistence and after two weeks | Total respondents from the first and second community | 30 | 0.827 | 0.00 | strong correlation statistically |
The Theoretical Framework for the Research
Alienation is one of the most negative phenomena in the modern world and it had been a problem for several years and it varies in severity between the past and the present( the begging of the new renaissance and before), looking at it from this point of view makes it worse considering the cultural evolution in that era, in reverse with human belonging especially historically and religiously, alienation is a status of separation where the person feels distant from his spiritual world and feeling unable to change his reality, Alienation is the modern world issue that impacts many scientific fields like languages sociology, philosophy also psychology and architecture field this introduction leads us to know about this concept including the most important parts, the connection between the urbanism environment and the human who is a social creature with spiritual needs it should be taken seriously considered to meet these needs in his environment, this decreases the social issues and the feeling of not belonging the spatial alienation issues which leads to creating a distance between the person and the place and that causes a disintegration of the civilized texture which affects the urbanism structure formations which also leads to creating chaotic areas and that's the reason behind the failure of this structure to achieve its psychological and social purposes.
The researcher will discuss the alienation concept and the most important irrelevant subjects, also reviewing most important previous studies in this field, also reviewing theoretical explanation to it by reviewing its most important theories psychologically and socially besides understanding the phases that alienation is going through.
First of All: The Study Concepts
Alienation
The word is derived from the Greek word “alienation” which means cutting something off or change in property to something else, the word” alienation” derived from the verb”alienus” which means belonging to something else (Jamal Al-Dean & manthoor karma Al-Ansari, 1968).
Alienation Idiomatically
The alienation concept faced so much attention in an attempt to control it and considering the complication of it because of its philosophical roots and discussing it without it seems relatively new, Hegal is one of the most brilliant German philosophers. one of the founders of German idealism in philosophy in the late eighteenth century AD, developed the dialectical method that proved who During which the course of history and ideas is carried out with the existence of the thesis, then its contradiction, and then the synthesis between them, Hegel was the last constructor of the philosophical projects,The great thing in the modern era is that his estrangement means the separation of the human self as a spiritual entity separated from its existence as a being,Sociological as it was also considered in another proposal that man has given up his autonomy and his unification with the social essence, (Abd Al-Latif Khalifeh, 2003), after entering scientific use, several definitions were given to him, the most important of which were the definition of (secret honor). Professor of mental health at Al-Azhar University at the College of Human Studies, where he defined him as psychopaths expressing self-estrangement
On her identity, her distance from reality, her separation from society, her estrangement from herself, alienation from the world, and alienation among people. Source: (Zulekha Jadidi, 2012)
Urbanism
The word Imran refers to the verb (reconstruction), which is the acknowledgment of survival and the life of a thing throughout its life (Masseno & Lewis, 1976).
Urban Idiomatically
Conducting city planning by studying the concepts and theories that help meet the needs of people in housing,These cities depend on a number of social, economic and human measures, and on this basis, urbanization is planning Cities to provide three basic elements (shelter, employment, luxury) (Abdul Basit & Masoud Muhammad, 2006)This concept focuses on the elements of the human being, the place, the time), the human being is the social being, but the tangible aspect is The place through which the existence of that human being is geographically embodied, while the last element of time represents the existential and spiritual dimension, and through it Heritage, history and man are formed as these elements are one complementary to the other (Al-Tamimi & Shahba Ahmad Ali, 2011). In another definition of urbanism, he mentioned that it is the art of formulating restored physical elements with a specific spirit and pouring them into Boudqa Cultural into components of durability and functional utility, so here is the interaction on the part of the physical and the moral side, where here urbanization is a concept. Self-differs from one individual to another according to his upbringing stemming from his environment (Al-Ali Saad Hamid, 1997).
The Procedural Definition of Urbanism
It is a language that gives the individual a tangible material and moral value through which he can see his problems By beautifying urbanization as an appearance, texture and arrangement, urbanism here constitutes the environmental environment to which the person belongs, which organizes all his daily activities.
Structure
Structure Linguistically
Structure linguistically: that the etymological meaning of this word implies an architectural connotation by which the triple verb is (built Build, build) and the structure of a thing may be its formation (Source: Ibrahim, Zakaria, 1967).
Structure Idiomatically
An expression of the internal entity of a phenomenon or an identification of what is possible behind the external image of a thing and what the entity is. The internal, upon which the external image of the phenomenon is based, is also defined as a system of relationships and mutual rules of structure that The various boundaries of the same group connect and these relationships and these rules form the meaning of each of the elements (Kafani Aqeel Abd al-Amir Abd al-Hussein, 2004), an essential characteristic of all things, systems, and processes in the world, It is built of elements and parts that are related to each other by relatively stable relationships that have an internal arrangement and form the structure of the system from A set of essential relationships, (Alexander & Bassam Nachat, 2001). This term is derived from the word English is structure, which is of the Latin origin, which means the building or the way in which a building is constructed and that the old is used The word "structure" in European languages denotes the way in which Mabela praises and relates to how the composition of the parts is assembled Composition: The general appearance of an object (Hughes & Tunis, 1986) and through what he described the definition of structure (Roger Garaudy) The meaning of each of the elements (Garaudy, 1997).
It is a system of mutual relationships and rules of synthesis that link the various boundaries of the same group, defining these relationships and these rules So, the urban structure is one of the social phenomena that are affected by thought, meaning that it is not sufficient to deal with it, but rather adds to it. It includes everything that exists from a natural environment and physical components that man interferes with its manufacture (Al-Kanani, Aqeel Abdel-Amir Abdul Hussein, 2004).
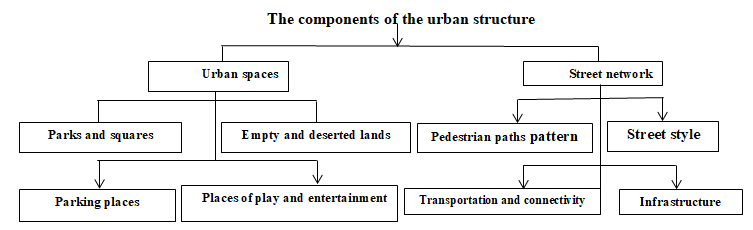
The procedural definition of the urban structure is the interactive framework that includes the components of the urban space and identifies the applicable uses on the neighborhood, city, its center, the municipality, and the village.
Figure 1: Illustrates the Organizational Structure of the Components of the Urban Structure Prepared by the Researcher
Society
Society is defined linguistically as a word derived from the verb (plural), meaning that people gather in a group.
A network or web of social relationships that exist between individuals or aim to satisfy their needs and achieve their near and far aspirations and goals (Max, Weber ) and society consists of a number of individuals, so the monkey is the smallest part of society he is considered an independent being and an explorer with a strong tendency to look forward to resilience deposits, to retain his entire personality in the face of environmental pressures (Sonya Hunt & Jennifer Helton, 1988). Society is a term derived from the Latin word “Societies”, which means society, which in turn is also derived from the name socius, which means companion, friend, ally, the adjective form is (socialis). It has been used to describe the bond or interaction between the parties (Mashkoor Ibrahim, 1975).
The procedural definition of a society as a group of individuals residing in a specific and recognized geographical area and adhering to a set of principles
Standards, evaluation, social ties and common goals are based on language and a common common destiny.
Second -Previous Studies on Alienation
Study of Hiti, Visited 2009 (Alienation in the Architectural Form|Study in the Alienation of Contemporary Iraqi Architecture
The study deals with alienation as a basic problem of the research, and a concept that is closely related to the concept of communication, in different formulas and vocabulary. Once as a result of lack of communication and again as a hindrance to communication in the case of a literal change of shapes or ideas from other societies to Communities that do not belong to it, and at other times he mentions it as a design plan that works to communicate by confusing the vision of the recipient and thus Raising his questions about this form, which returns his ideas in a way that enables him to correctly interpret the Results.
The study classified alienation on three levels as follows:
- Alienation of the designer
- The alienation of the outcome (form + meaning).
- Alienation of the recipient.
The study deals with the alienation levels of the architectural form (the second level) and identified four vocabulary words to explain the alienation of the form Architectural included: (What is the adopted intellectual position, the mechanisms of alienation, the causes of alienation, the nature of alienation).
Selecting the first three basic terms for the purpose of implementation and defining the fourth term as not associated with the product creation process
Klee and its association with other aspects outside the scope of the research, as the recipient’s psychology, which determines the characteristic of positive or negative alienation.
The study provided an analytical and descriptive method for the concept and the selected projects. The application was carried out by selecting seven residential role models (The post-nineties family) is characterized by strange, unfamiliar shapes and came up with a set of conclusions and recommendations in which I confirmed The need to raise awareness of both the producer and the recipient regarding the specificity of architecture and the reasons for its alienation, and the revival of styles
The study resulted in the architects ’tendency to adopt valuable references belonging to the killing of architecture in order to achieve strangers in their products, so that their understanding The old historical local, while not forgetting its link to the present and the future.
It is limited to the architectural elite only, and the alienation of the architectural form results from the changes, transformations, and loss Standards, loss of meaning, contradiction with context, and perception of the recipient of the production in addition to the multiplicity of the mechanisms adopted in the forms Expatriate architectural.
From what is taken from this Study
Its focus is on the architectural side only, and alienation in the city and at the urban level is not addressed, in addition to its focus on the strangeness of the product and its definition of the singularity of the nature of alienation and its relationship to the recipient, which is an essential focus in our biography.
Study of Dale L. Gibbs
The (Form) of Alienation: Architectural Theory in an Age of Change/1997
This study deals with the concept of alienation through its discussion of contemporary architectural ideas resulting in an era of rapid change taking place In society, it is difficult to formulate a viable architecture theory that appears only at the moment when social demands arise From architecture to an urgent degree, that modern technology, especially modern sciences such as bio-physics and new biology can It becomes the basis for a contemporary theory in architecture, and there are those who reject the idea that ideas of architecture can be constructed or based on traditions. Instead, pure forms can be visualized from pure ideas based on a contemporary knowledge of the forces of sociology and psychology. The study states that the contemporary architectural idea has been fragmented by the ideology of alienation resulting from the characteristics of or the manifestations of the current circumstance, which are considered among the causes of the occurrence of alienation, which are:
1. The struggle of values that was deposited by the technological
2. Culture The sense or meaning of the historical disconnection created by rapid change.
3. The architect's changing relationship with society.
4. The disintegration of the shape as a feature or characteristic of the current time or time.
That these reasons have shown an alienation from the historical tradition and a break with the instincts of consciousness and the unconscious that make up the collective unity and traditional cultural norms in society.
And since the architectural structure represents the events going on around it, so when we are separated from the influences of our time, we do not have
A ground for developing a theory because it has a comprehensive goal or purpose. As a result of this process in architecture, the architect became estranged from the content the construction program, and it went after innumerable doctrines or pure beliefs to fill the gap in architecture.
Gibbs that he cannot generalize that all architects are expatriates, either in person or in their relations with society, and this is derived from He feels the meaning of diagnostic alienation and insecurity, as for others, they are not, and that the sense of loss or loss of a traditional position does not After the traditional architect is far from the mainstream of the society he serves, some architects feel strange, and some feel or An indifference to the future is a type of alienation, and that its roots lie in a new type of society, where strangers take the form of revolution or Social or economic, but increasingly at the present time the position of alienation has been chosen by the people as being
Rebellion without cause is rejected without vision and people in the past viewed alienation traditionally as imposed on them by circumstances Social or economic, But increasingly at the present time the position of alienation has been chosen by the people as their attitude towards society.
According to Kinston’s opinion, Gibbs defined the negative and the positive level of alienation, the negative side (feelings, Negative emotions): -
1. Existential pessimism with the futility of the attempt.
2. A sanctuary or sanctuary ... a search for certainty
3. Lack of trust in utopias or ideals, any commitment or commitment to the future.
As for the Positive Level, there is a Yearning or Aspiration for
1. Truthfulness or honesty.
2. Direct confrontation with an unpleasant or hateful truth.
3. The denial of the cosmic truth.
4. Emphasis on self-centeredness.
Gibbs also identified the main themes of alienation, namely
1. A yearning or ambition for cultural integration, assimilation or assimilation.
2. The pursuit of meeting an experience or an experience.
3. A sense of delinquency in the present moment.
From the above, it is clear that the study focused on the issue of alienation that occurs to the architect (the designer) as well as the positive dimensions.
The negativity of this concept, in addition to the main themes of alienation, and how the alienation of the designer stands an obstacle in the creation of or
Create an architectural idea that meets the needs of a society characterized by rapid, irregular change and in which the fixed ideology is Alienation biology.
The study has shown the reasons for this alienation into four influences
1. Technology forces, 2. Discontinuity, 3. Decomposition, 4. Cultural Change. The study in this way has been confined to the study of alienation from the side of the architectural idea only, and it is also not specified Individuals constituting the concept of alienation.
Study Baya in Al-Assoud 2002 (discontinuity in urban design, an analytical study using the catastrophe theory)
Basically, there is a relationship of dissonance and disconnection between the individual and (the part) and the social structure surrounding him (each), i.e., the social strangers. With the possibility of its transformation into an acute physical sector between man and the environment and then its subjective alienation, or what is termed environmental discontinuity and The study also indicates that the concept of spatial alienation in the alienation of the city is linked to two main factors, which are the concept of urban space. The missing in the sense that it lost the basic concepts and values that were characteristic of the traditional space and the concept of the silence of the sign-meaning
Cultural to him. Signs and signs emanating from the architectural forms are empty and do not reflect certain cultural values that achieve communication between the individual and his cultural storage.
The Position on the Study
The study investigated the concept of alienation in a partial and non-exhaustive manner within the main topic of the research, which is Discontinuity in urban design, considering alienation as one of the theoretical concepts most closely related to it through the transformation of that sense. Between the monkey (the part) and society (the whole) to an environmental disconnect between the individual (the part) and the environment (the whole), despite the researcher's approach to the concept of
Alienation is more clearly, but it has not been dealt with in a comprehensive manner within the main topic of the research.
Third: Theoretical Explanations of Alienation
The concept of alienation has acquired the right to a wide intellectual existence since the end of the eighteenth century and continues to this day.
Prominent intellectual concepts in sociology and psychology, and its uses have branched out and varied over the course of two centuries of thought
Scientific, social and European, starting from Hobbes & John Locke, passing by Jean-Jacques Rousseau, to Hegel, who occupies alienation. A central position in philosophy and in the works of Karl Marx is the alienation of man from his activity from his products and the alienation of man from what he is. As a human race (Faleh Abdul-Jabbar, 2012), and on this basis, the theoretical interpretations that addressed The topic is alienation. Some started on the psychological side, others from the social and economic side, and what follows is an offer the most important theories that explain alienation:-
Heikal Theory of Alienation
Hegel used the term alienation with two different faces. In the first sense, he spoke of the individual as estranged from himself and estranged. The self here means confining it to the private self and moving away from the social environment, while the other form of alienation from the self is The social structure is a mind in a modest form, so when the structure is estranged from the individual, it becomes a localized mind estranged from it. (Al - Mohammadi, 2001) So the struggle between the subject and the object I have (Hegel ) is the basis of the alienation, so man does not know what On himself, where this world becomes an estranged person, the individual here faces a problem between being a creative force that seeks self-realization and being A subjugation that is affected and shaped by others, while the second meaning is surrender or sacrifice, which refers to the meaning of abandonment, which is something includes a conscious concession or surrender with the intention of ensuring a desirable end, i.e., unity with the social environment through The photographer with the benefit and the established geometry (Rajab 1986) but Hegal data and knowledge, and he searched for ways to overcome this alienation, but he found only in a conscious level (Ziada, 1986).
Freud's Theory of Alienation
Freud believed that alienation comes as a result of the separation between the forces of feeling and the unconscious. He noted that there is a permanent conflict between the instincts and the release - the theory of alienation among Freud's supporters because he mentioned what was accepted for him into poetry and expresses the connection freely. As for the unspoken thoughts we find that they go to the feeling, and it is expressed by the person. Strange symbolic or imaginations and other methods, and for all this man is driven to alienation or escape from the lived reality of a better reality that he finds in his alienation, as he found that the expression is rooted in a person’s life between the ego, the idiom and the higher ego, and there is no room for satisfying the instinctive motives as it is impossible to reconcile them with regard to goals and demands. (Freud 1962). Human behavior is motivated to obtain certain goals if they are thwarted or prevented, which lead to the collapse of the human being due to the conflict with the outside world, which leads to his alienation and isolation from his society, (Al-Jubouri & Israa, 2014). From here Freud says that every individual is in fact the enemy of civilization, for civilization is based on suppressing instincts and does not allow him to satisfy them, in addition to the role of feeling in making the individual alienate from his society, which drives him to behaviors that preserve him to live within his society and he is convinced that the requirements of social construction contradict the essence of the self. Which becomes more dangerous as a result of the statelessness of the dominant natural existence, for his estrangement is a state of separation between the individual and the object, between the individual and the things surrounding him and between the individual and society (Khuraisan, 2015).
Marxist Theory of Alienation
Alienation is not explained by Marx as being of a material economic nature. Latent in the relations of production, hegemony and class, as man estranges from his work in capitalist society because he sells it, the nature of his work and the essence of social relations in the capitalist system is competition, here I mean the human feeling of the increasing dominance of personal bureaucratic procedures over his life, as what distinguishes man from animals is that the animal adapts to the environment. As for the human being, he controls it consciously and under the rule of (capitalism), the worker loses the element of control and becomes in the status of the animal, meaning that the human reference is directed. A goose collapsing to replace it with the reference latent in the animal, and the state of alienation can be abolished through the revolution and the change of production relations so that the worker becomes free to express his creative potential embodied by the fruit of his work, and human life will not become fragments, but rather it will become an integrated whole, and from here we conclude that alienation is nothing but a human struggle. With the dimensions of his existence, a struggle with economic, social, and political forces to determine his historical position of what revolves around him, so that the human being remains consumed and robbed of the self, crushing and distorting his human personality and escaping to the realm of imagination and proposing for humanity a spiritual basis instead of a realistic basis for it, and the conflict increases in this dimension as the awareness of man increases Itself that seems to him all What surrounds him is a dictation of horror, which leads to its distress, and from here the secret of his estrangement from the values with a bird of reality enters into the world of passers-by, the truth and its existence.
Social Functionalism Theory
The primary social theory, the primary secret bird in Nawaf al-Shaer and the escape to the corner of the bored and inclined to leave the theory. The wilderness, the thin wilderness, and the functional theory known by several names from the functional technical theory (The Structure Function Theory) The Theory of the Felic Bees (al-Hassan Ihssan Muhammad, 2015). This theory derives its general intellectual origins from the children of a group of traditional and contemporary social waters who appeared in particular in Western capitalist societies, where it was concerned with studying how societies maintain internal stability and survival over time and the interpretation of social cohesion and stability, and this is what was represented in the ideas and systems of the pioneers of Western sociology from Proverbs of Talcott Parsons (Robert Mercon). As for the concept of functional constructivism, it is composed of two parts:
1- Building - a term that refers to the way in which repetitive activities are organized in society.
2- Functional - and this refers to the term to contribute to a certain form of repeated activities in the preservation of Community stability and balance. (Hassan Imad & Leila Makari, 2006).
Fourth: Forms of Alienation
The Spatial Alienation
It is the disconnection of the connection between the individual and the place in which he is, so this type of alienation has arisen in the urban environment that suffers from the distortion of the image of it and the scattering of its parts and its lack of adherence to its failure to meet the human requirements, all of this leads to the disconnection of the individual Firstly the moral and then the physical, that the spatial alienation of the individual does not come by chance, but rather is the result of the changes that occur to the urban structure and the change in its shape, and this happens when there is a lack of connection between parts of the place and the tyranny of a system over the existing urban systems due to the removal and replacement of the original system, and this process includes stages that cause The disintegration of the urban structure (removal-discontinuity-intercalation). (Al-Bazzaz & Sami, 2007).
Psychological Alienation
One of the psychological characteristics of marginal and estranged people is affective binary in terms of duality of consciousness, attitudes, double loyalty, lack of belonging to self-confidence, excessive anxiety about the future, feeling of isolation, loneliness, feeling helpless and insults in one's choices What he wants and wishes, and what he achieves in the actual reality, affects his psychological structure in terms of his safety and disorder, and the sick individual feels that he is separate from himself and his feelings and separated from people for others and from society, so the phenomenon of alienation refers to a person’s relationship with the surrounding external world and to his relationship with himself, in this case the world and things appear. People and events are alien to the monkey, which he considers contradictory to, and he disagrees with it or rejects it, and there are feelings of isolation, loneliness, rejection, and the loss of ego or identity. The significance of these factors is a resource directed to its machines, the irrigation worker behind only (Sanna Adel Ibrahim, 2015).
M Social Alienation
It is stipulated in a price for a ball that has a dark ball for it and the other, and social coldness, i.e., from the bonds, and for God I feel affection and social harmony with them. And the inability to practice normal behavior (Zulekha, Hal & Al-Mughrabi, 2012). Cultural alienation-It refers to the individual's departure from the culture of his society, and the end of society is a coalition of customs and traditions prevailing in that society and the violation of the standards that control the ownership of its members, as you find the individual rejecting these elements and alienating them and not abiding by them, but preferring everything that is foreign and foreign to them (Zulekha & Hadidi, 2012).
Fifth: The Effect of Alienation on the Individual
The scholars have concluded that the physical framework of a place has a psychological and behavioral effect on the individual, so if this frame is a physical projection of the moral constituents, then its effect is no different from it. His action is homogeneous, and the nature of its constituents forms the character, spirit and conscience of the place through our extrapolation of historical and social data, that despite the spread of its physical and moral framework, the place still affects the collective conscience of individuals, and it still defines their behavior, which made us certain that the place has a memory that remains alive despite its demise It is derived from the strength of the urban and architectural presence within the existing fabric, so all activities and actions that take place within the space and repeat in it become a feature of its characteristics, and over time form the memory of the place, so the change of the physical framework to a degree that inevitably leads to a change in the internal behavior, as well as changing customs, traditions and activities Within the space there is a reason to change its physical framework, that making changes to the place without an in-depth and comprehensive study may lose its function and make the place not suitable for meetings and living, and this is what we did Many cities that he sought to evaluate by changing their centers and visiting vital ones that came to be innate, a job, and the establishment of new centers according to new architectural and urban patterns, the results came disappointing, where the restless soul usually falls under the shock of a strange and frightening emotional reality, so the sense of loss and fear remains attached to it. They are attached to this place whose features are unknown and as long as they are not aware of it. (Al-Bazzaz Sami, 2007).
Sixth: The Stages of Alienation
The Stage of Preparation for Alienation
This stage includes the concept of losing control in its two dimensions of the deprivation of knowledge and the deprivation of liberty and the concepts of loss of meaning and non-standardization in succession, when one feels injustice in the face of loss control over life and social situations and that he is powerless but even if things have their meanings as well, and accordingly there are no criteria that govern him and readings that can be.
The Stage of Rejection and Cultural Criticism
Which is the stage in which the choices of individuals are presented with the events and aspirations established, and it is the stage where the reality took place and what is financial and the consequent shutter objectives, and at this stage the individual is isolated from the emotional and cognitive components of his companions or seen as strangers, and at this point he is prepared to enter the third stage.
The Stage of Adaptation of the Expatriate
Or the stage of social isolation with its dimensions represented in positivity in its form of rebellion, revolution and negativity in its multiple forms reflected by withdrawal and isolation, at this stage the individual tries to adapt to situations in several ways, including:
• Integration, coping, and submission to all situations.
• Rebellion, revolution and protest, that is, the time takes an active, positive attitude and the individual takes the position of rejecting cultural goals, and in this case the person is at one of his feet within the social order and places the other outside it, which ultimately makes him a marginal person (Ahmad Amal & Bushra Ali, 2008).
The Practical Aspect and Analysis of Results
First: Study Population
Research Sample
Two different samples were identified for the first research, the Israa Residential Complex in Wasit Governorate, Al Kut District, for twenty-five families, 5% of the total number of 504 families.
As for the second sample, they are specialized academics represented by students of the Urban and Regional Planning Center, University of Baghdad, based on the answers students have with a scientific dimension and broad-based planning thinking, to benefit from them in city planning and achieve the individual's social and urban identity in the urban structure, and the size of the sample was determined. A 37student out of a total of 41 at a percentage of 90 %.
Second: The Questionnaire Form
The questionnaire is a set of questions that are directed to answer them by the interviewer in a direct personal confrontation situation with another person or through written questions, and here the questionnaire form consisted of a set of questions directed to the questionable persons to obtain information related to the research. The number of questions was 19, which were selected with extreme precision and presented to a number of arbitrators to amend them, and were chosen to see the validity and reliability of the answer.
Third: Analyzing the Results of the Questionnaire Questions
For the purpose of analyzing the answers to the questions addressed to the respondents. The researcher collected the answers in support of acceptance for each question and converted them into percentages to know the importance of each question and its impact on the study community and its position on the concept of alienation, and as shown in Table No. (3) Which are the most influential questions. With regard to expatriation, down to the least affected, according to the percentages that appeared in the responses of the brown housing community, and according to the results of the field survey. In order to find out the questions most influencing the alienation, down to the least influencing, and according to the percentages that appeared in the answers of specialists from the graduate students of the Urban Planning Center, the researcher made a table showing the results of the respondents' answers.
Where he analyzed the answers to the questions addressed to the respondents from the specialists from the graduate students of the Urban Planning Center and setting the answers in support of acceptance of each question and converting them into percentages to know the importance of each question and its impact on the study community and its position on the concept of alienation, see Table (3) & (4).
| Table 3 Shows the Answers to the Questions that Most Affect the Alienation of the Israa Housing Community |
||
|---|---|---|
| Number | The question | % |
| 1 | The loss of social relations among the population in the city leads to a change in the traditional fabric of society | 85 |
| 2 | The individual’s perception of his tissue is related to the physiological aspects of the human being and to proportions related to the human scale, | 84 |
| When the scene is irregular and does not take into account the human scale, the individual feels distracted and lost | ||
| 3 | Neglecting an individual's opinion of changes occurring in the tissue leads to alienation | 82 |
| 4 | interaction and communication between the inhabitants is necessary and important | 80 |
| 5 | the science of the individual's self-isolation and isolation from people is a psychological alienation | 79 |
| 6 | the individual mixing with people from neighbors and weak social relations as a result of the disintegration of social values is considered social estrangement | 76 |
| 7 | alienation occurs as a result of interventions and differences between the individual culture inherited from tradition and acquired From the friction of the new culture | 74 |
| 8 | that the individual's pride in the fabric in it and his desire to preserve it is one of the advantages of belonging to the place | 73 |
| 9 | The individual feels alienated as a result of the change of the unique characteristics, the rise of the blocks and the traditional architectural styles that characterize the city and consequently the loss of the spatial identity | 71 |
| 10 | The alienation appears when the individual feels that the fabric does not belong to the fabric and is indifferent to what Protects from changes (alien behavior) | 69 |
| 11 | If the many transformations that occur on the fabric lead to loss of cohesion in the urban fabric and alter the identity of the place | 68 |
| 12 | the lack of coherence between parts of the urban fabric at the level of the plan or at the level of the facades leads to the disintegration of the fabric and the feeling of alienation | 66 |
| 13 | then the presence of buildings that correspond to the old urban building leads to a feeling of alienation | 64 |
| 14 | Loss. Space within the traditional urban fabric, from the public to the semi-public to the private, leads to a feeling of loss and a loss of awareness of the environment | 63 |
| 15 | diversity and the presence of a pattern that connects them creates a kind of harmony the structure with the infrastructure | 58 |
| 16 | Failure to take into account the overlap between the blocks and spaces complicates the relationship between the elements, making the recipient feel uncomfortable and bored | 46 |
| 17 | The new western culture lead to change in values and failure in facing social pressure which leads to feeling of alienation | 42 |
| 18 | Failure to preserve the heritage and the introduction of globalization led to the disintegration of the urban structure | 40 |
| 19 | The lack of visual continuity and the loss of orientation in the fabric leads to the creation of a feeling of alienation | 38 |
| Table 4 Analysis of Answers to the Specialists from Postgraduate Students of the Urban Planning Center |
||
|---|---|---|
| Number | The question | % |
| 1 | Not taking into account the overlap between all and distances affects the relationships between the elements, making the receiver feel uncomfortable and bored | 80 |
| 2 | Failure to achieve visual continuity and loss of direction in the tissue leads to creating a feeling of alienation | 74 |
| 3 | the individual's pride in the fabric in it and his desire for Preserving it is one of the advantages of belonging to a space place | 71 |
| 4 | the traditional urban fabric, from the public space to the semi-public to the private, which leads to a sense of loss and loss of sense of mobility for the environment | 67 |
| 5 | Neglecting the individual’s opinion about changes that occur in the fabric leads to alienation | 65 |
| 6 | Neglect of personal opinion in changes that lead to alienation | 63 |
| 7 | mixing with people from neighbors and weak social relations as a result of the disintegration of social values is considered social alienation | 64 |
| 8 | The individual’s introversion and isolation from people are considered psychological alienation | 63 |
| 9 | If the changes occurring on the fabric are many, which lead to a loss of cohesion in the urban fabric and a change of place identity | 62 |
| 10 | The presence of buildings that are compatible with the old urban building leads to feeling of alienation | 61 |
| 11 | The lack of interconnectedness between the parts of the urban fabric at the level of the plan or at the level of the façades leads to the disintegration of the fabric and the feeling of alienation | 60 |
| 12 | Repetition of the elements recognized in traditional areas of simple diversity and the presence of a pattern that connects them creates a kind of harmony with the urban structure. | 56 |
| 13 | The individual feels alienated as a result of changing characteristics. The uniqueness of the rise of the blocks and the traditional architectural styles that characterize the city Hence the loss of spatial identity | 54 |
| 14 | the loss of the spatial identity, the loss of social relations among the inhabitants of the city, leads to a change in the traditional values | 53 |
| 15 | The entry of Western culture into society and the disintegration of values and failure to face social pressures lead to the separation of the individual from his society | 49 |
| 16 | The failure to preserve the heritage and the entry of globalization led to the disintegration of the urban structure | 46 |
| 17 | Alienation occurs as a result of interventions and differences between the individual's culture inherited from tradition and gained from friction With the new culture | 41 |
| 18 | Perception of the individual from Galilee, and his message with the physiological body of the human being, proportions, and the human scale, when the scene is irregular and does not take into account the human scale. | 35 |
| 19 | The social interaction and contact between the inhabitants is necessary and important | 31 |
Table Analysis
By comparing the results of the answers of the first study population represented by the residents of the Israa housing complex with the results of the answers of a community of clumpines, we see to the questions of social location that had great importance in the formation of Arabs on the souls of the knife and almost gloriously reduced from the highest visibility to the least influence, as for the results of the responses of the study community The second, represented by academic specialists, shows the role of the urban structure and its great influence in Shaping the alienation of the individual and society, and there are some answers that were close between the respondents' answers to each of the first and second study societies. The interaction between place, man and place as a human content. As for the academic opinion of alienation, it becomes clear that the physical place has the greatest effect on the distancing of man from himself and the emergence of internal alienation has.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Conclusions Research
1- Through the field study and for both societies represented by the students of the Urban and Regional Planning Center for Postgraduate Studies, University of Baghdad and the Israa Residential Complex, we conclude that alienation in its two dimensions (material and intangible) leads the individual to move away from the urban environment in which he lives and becomes isolated and lost social interaction.
2- Through the field study, the loss of places that express their existence and their being through public spaces and means of security and urban safety emerged through their answers, and this in turn leads to alienation and the creation of a repellent environment.
3- The design of the urban structure that does not express the culture and values of the community becomes fragile and distorted, loses balance and becomes imbalanced, and this in turn increases the state of urban alienation.
4- The loss of balance between economic and social aspects and levels leads to the emergence of a state of alienation and loss of belonging to the built environment
5- The side urban spaces have a great role in creating an urban environment that encourages interaction between residents, especially in residential complexes.
Recommendations
1- The urban environment is a physical product, so it is necessary to link it with the human being as a social product to create a wax for interaction, communication and spatial belonging, and this in turn will lead to the alleviation of university problems resulting from poor urban planning.
2- The need to take the opinion of the individual because of his great role in planning and the design of the urban structure.
3- The privacy of society, the group and the individual must be taken into account for its effective impact on the success of the planning process and the preservation of the urban structure from disintegration and collapse
4- The need to maintain a balance between the interactions and differences between the individual’s culture and the inherited tradition and cultural friction with the new culture...
5- The need to maintain the human scale by focusing on urban planning standards and taking into account aspects of sustainability.
6- The visual continuity is achieved by preserving the urban form and the balance between the old and the modern from the imported urban forms that make the individual far from his urban environment.
7- Creating places through which the individual can communicate to achieve social interaction, such as urban spaces and open spaces
8- The strength of social relations between residents in the city leads to the durability of the traditional fabric of society, and this is done by creating a human environment that attracts familiarity, love and harmony among members of a single community.
9- Emphasis on the spatial gradation within the traditional urban fabric, from the public to the quasi-public space to the private, which leads to a sense of inclusion within the urban structure.
10- The necessity to establish social clubs within the urban structure that work to encourage the mixing of the individual with society and enhance the positive social value and make him move away from his psychological, social and spatial alienation.
11- Attention to the interconnectedness between parts of the urban fabric and the social environment, which leads to the creation of a sense of comfort, aesthetics, and human interaction with the place.
References
- Angham, A.A.B., & Roni S.A. (2007). Alienation in the built environment. Freezer, 13(1), 225-236.
- Amal, A.A. (2008). Beshr my uncle, manifestations of alienation among Syrian students in some Egyptian universities. Academy Volume of Education, 24(1), 339-349.
- Abdul-Mutif, M.K. (2003). Studies in the psychology of alienation. Dar Gharib for Printing, Publishing and Distribution, Egypt.
- Awatif, A. (2015). A theoretical view of Belgrade. Adab Majlis Al-Mustansiriya, 71(71), 20-25.
- Aqeel Abdul, A.H.K. (2004). The dialectic of contemporary urban structure and influenced the formation of the Arab city. University of Baghdad, Iraq.
- Abd al-Qadir, M.M. (2001). The exile in the heritage of the Sufism of Islam, (1st Edition). House of Wisdom, Baghdad, Iraq.
- Bassam, N.I.J. (2001). The relationship between subject and object, an analytical study of the relationship between the kinematic and visual axes in the tissue. University of Baghdad, Lindseh quantity, Architectural Engineering Department, Iraq.
- Baya, M. (2002). Discontinuity in urban design, an interpretive study of disaster theory. MA Thesis, Algeri.
- Dale, L. (1997). The form of Alienation: Architectural theory in an Age of Change.
- Faleh Abdul, J. (2012). Classical introductions to the concept of alienation. Kufa, Academic Court Collections.
- Freud, S. (1962). The brief on psychological loading. Dar Al Maaref, Cairo, Egypt.
- Hassan, E.M., & Lime, H.A.S. (2006). Communication and investigations, the bill. The Lebanese House, Cairo.
- Ihssan, M.A.H. (1985). The fundamentals of social research. Dar Al-Tadamon Press, Cairo.
- Ihsan, M.A.H. (2015). Social theories. Wael Publishing House, Amman, Dar.
- Israa, A.J. (2014). Attributes of alienation in postmodern art. Economic Commons, 22(5).
- Jamal, I.M., Makram, A.A., & Lisan, A.A. (1932). Mujmed 15, (1st Edition). Dar Subuh, Lebanon.
- Kamil Muhammad, A.M. (2011). General research methods in human and social sciences, (4th Edition). House of Culture for Publishing and Distribution, Amman Jordan.
- Louis, M. (1979). The plans of Kufa and explanation of Mapatiya. Al-Ghary Press, Najaf, Iraq.
- Masoudi Muhammad, A.B. (2006). Contemporary architecture and urbanism between authenticity and contemporary, the case of the city of Biskra. University Center Elaraby Ben Maidi, Oum El Bouaghi, Teaching Assistant and Technologies, Algeria.
- Nayada, A.K. (1981). Introduction to social research design. Al Maaref Press, Baghdad, Iraq.
- Ragab, M. (1986). The expatriation. Dar Al Maaref, Cairo, Egypt.
- Roggio, G. (1979). Structuralism and the philosophy of the death of a person. Dar Al-Tumai'a, Beirut, Lebanon.
- Sanaa, A.I.K. (2015). The change of values and the relationship with the self-identity. Master Thesis, University of Salmiya.
- Sonya, H. (1988). The growth of the individual's social personality. House of General Cultural Affairs.
- Saad Hamid, A.A. (1997). Strategies of deconstructive architecture, theoretical and practice. Master Thesis, University Technology.
- Shaiba Ahmed, A.A.T. (2011). The role of urban in achieving sustainable urbanism. University of Baghdad.
- Weber Max. (1999). The theory of social and economic organization. Newyork, the free press.
- Zakaria, A. (1976). Infrastructure problem. Misr Printing House, Cairo, Egypt.
- Ziada, M. (n.d). The philosophical encyclopedia, (1st Edition). Beirut, Lebanon.
- Zulekha, J. (2012). The exile, society for the social public. Wadi Souf University, Algeria.