Research Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 5
Adoption of AI and E-Commerce Improving Marketing Performance of SMEs
Anuj Kumar, Apeejay School of Management, Delhi, India
Anoop Pandey, HNB Garhwal University, Uttarakhand, India
Purvi Pujari, Confab 360 Degree, Delhi, India
Monika Arora, Amity University, Haryana, Gurugram
Citation Information: Kumar, A., Pandey, A., Pujari, P., & Arora, A. (2023). Adoption of ai and e-commerce improving marketing performance of smes. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 27(5), 1-10.
Abstract
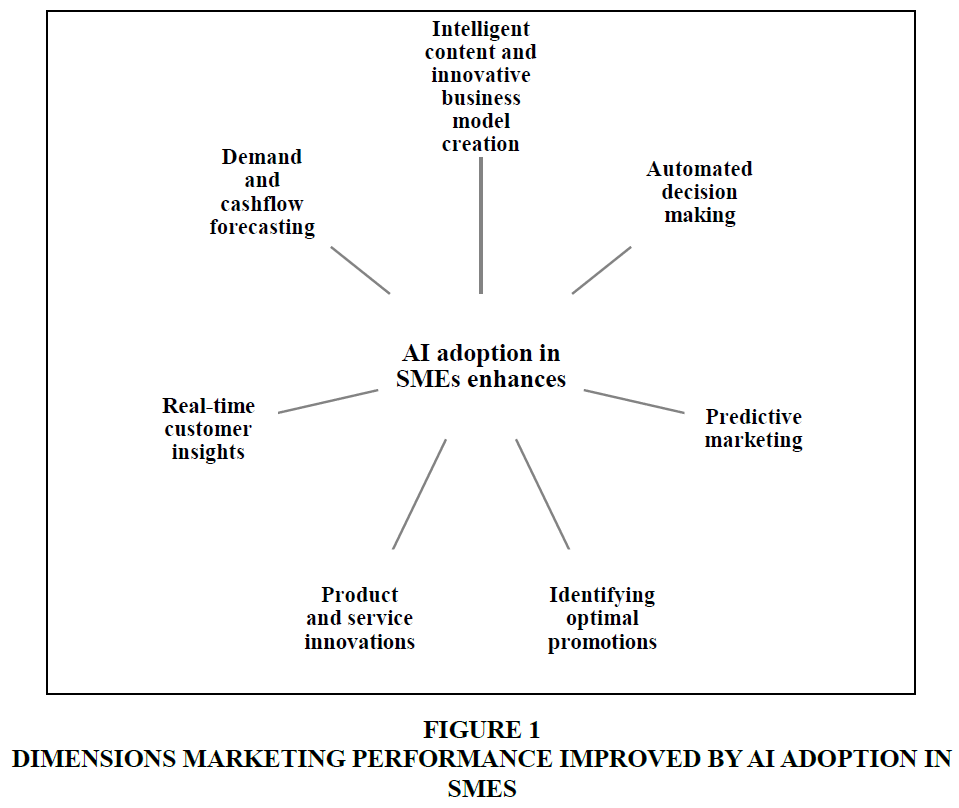
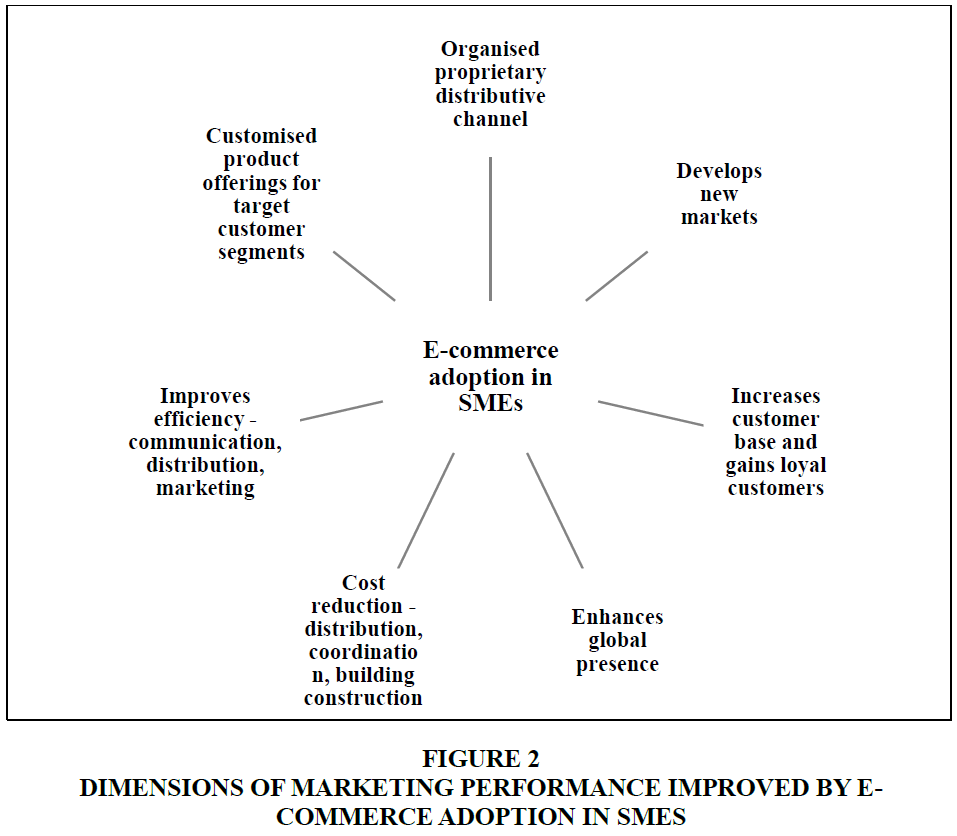
The focus of the study is to discuss the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and e-commerce in improving SME marketing performance. Hence, the main objective of the research is to explore how the marketing functions of SMEs could be improved by adopting AI and E-commerce. The methodology adopted for research is to review extant literature and research on the features of AI and e-commerce that could improve different dimensions of SME marketing processes. Besides, AI adoption in SMEs improved the creation of intelligent content and innovative business models, predictive modelling, automated decision making, real-time customer insights, product, and service innovations, identifying optimal promotions, and demand and cash flow forecasting. E-commerce adoption helped SMEs to develop new markets, increase their customer base and gain loyal customers, enhance global presence, improve communication, distribution, and marketing efficiency, reduce costs related to coordination, distribution, and building construction, develop an organized proprietary distributive channel, and provide customized product offerings to target explicit customer segments.
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence, SMEs, Marketing, Non financial performance, Management.
Acknowledgment
This research work has been done under the Major Research Project Grant titled "Strategic Technology Adoption and Acquisition: A Review of Policy Intervention and Impact on Performance of SMEs in India" sponsored by IMPRESS ICSSR (Govt. of India) in 2021-22.
Introduction
SMEs have been known to be a strong contributor to an economy’s development. The SMEs create much needed GDP, employment, innovation, and balanced regional development for any developing economy. Unfortunately, most of these SMEs are not able to compete with the fierce competition posed by large organizations and MNCs. Many challenges these SMEs face include paucity of funds, poor technology adoption, lack of human and other resources, and lack of marketing skills. One of the major factors of poor performance of SMEs is their poor marketing performance vis à vis large firms. There have been many researchers all across the globe who have delved into the reasons behind this poor performance. Moreover, technology has been considered a catalyst for enhancing SMEs' performance. The most common technologies adopted by SMEs are social media (SM), E commerce (EM), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Robotics. These technologies have been known to bring improved productivity. However, most SMEs relied on traditional models for selling goods and services; besides, SMEs exhibited a low level of technological adoption despite gaining enormous benefits by leveraging the latest innovative technological trends (Hasan et al., 2021). One of the parameters has been the lack of technology acquisition and adoption. The reasons behind low technology adoption can range from lack of awareness, lack of accessibility, and lack of skills to use emerging technologies. As the world marches towards sustainable development, companies adopt novel technological strategies to maintain a dominant position for themselves in a highly competitive market. To achieve this, many firms adopt digitized technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), E commerce, social commerce, etc., to gain a sustainable competitive advantage so that they thrive in the dynamic business market. Technology adoption in SMEs drives business growth international markets by collaborating with new business partners, improves sales and increases customer satisfaction (Kumar, Syed, and Pandey, 2020b). Besides, the Covid 19 pandemic has increased business risks for SMEs. Latest technologies like AI enables SMEs to gain a competitive advantage in the areas of accounting, customer relations, e commerce, marketing, human resources, and manufacturing (Akpan, Soopramanien and Kwak, 2020). In addition, Drydakis (2022) indicated that AI adoption in SMEs reduced the pandemic induced business risks. Moreover, it has been projected that by 2030, nearly 70% of businesses will adopt AI to improve their business performance (Fonseka, Jaharadak and Raman, 2022). Also, the pandemic affected most of the business processes and overall functioning of micro, small, and medium sized enterprises (MSMEs) that they have to adopt numerous strategies to survive, and the two most impacting choices was the adoption of digital marketing strategies and e commerce (Gao et al. 2023). E commerce utilizes electronic technologies to advertise or sell products via the world wide web (Ramanathan et al. 2012). While covid 19 significantly increased e commerce revenue, most companies included e commerce technology adoption in their growth strategies; by 2024, e commerce revenue is predicted to grow up to $6.39 trillion (Statista, 2021).
Though companies that adopt AI will increase their operational efficiencies much ahead of their competitors, only a few small businesses have accommodated new technologies into their businesses. Two major barriers linked to the lack of technological adoption in SMEs are poor IT infrastructure and lack of talent (Jab?onska & Pólkowski, 2017). However, AI is expected to become much more accessible to businesses and people who are not experts in technology since AI is dynamically developing, and SMEs can use AIs to scale their business growth (Helfrich, 2022). Previously AI was perceived to be meant only for big companies, but many firms have realized that they can reduce costs, increase revenues and change the way firms operate. Thus, AI is getting into businesses of all sizes. Moreover, Kumar (2020) denoted that social media adoption in SMEs improved their sustainability meanwhile achieving their intended outputs too. And ICT adoption has become essential for organisations to thrive in the technological era.
Furthermore, the fourth industrial revolution is built upon the fusion of technology, and the innovations that leverage the internet could potentially influence global trade. E commerce adoption is one of the prominent elements in the fourth industrial revolution and has become a part of firms' business strategies (Fonseka et al., 2020). Also, e commerce channels and social commerce channels drive SMEs toward sustainable growth by globalising their products reach wider audience with limited time and lesser finance (Kumar, Syed, and Pandey, 2020a). Thus, AI and e commerce are two prominent technologies having the potential to improve SME marketing performance. Moreover, the number of articles related to AI adoption in SMEs is relatively sparse (Akpan et al. 2020; Jab?onska and Pólkowski, 2017), and marketing literature associated with AI is very limited (Davenport et al., 2019). Besides, many studies identified the influential impact of e commerce on the performance of organisations (Ramanathan, et al. 2012), and only a few focused on determining the impact of e commerce adoption on the marketing performance of SMEs. In addition, Audretsch and Thurik (2001) called for further research on how e commerce adoption could substitute traditional marketing channels in SMEs as the economy shifts from being more ‘managed’ to ‘entrepreneurial’. Though prior research incorporates subsets of these, this article integrates AI, e commerce, and their cumulative contribution to improving SMEs' marketing performance. Based on the background and the literature gap, the following research objectives are formulated.
Research Objectives
1. To determine how AI adoption influences marketing performance in SMEs
2. To explore the dimensions of marketing functions that could be improved by e commerce adoption in SMEs.
Research Methodology
This review article employs a research method in which the researchers reviewed existing literature on the adoption of artificial intelligence and e commerce in SMEs. Besides, the authors also explored how AI and e commerce contributed to SME business performance, particularly the marketing aspects associated with it. Thus, the various dimensions of marketing functions that could be improved by the adoption of these two technologies are determined. Further, the obtained information from various publications is analysed, and two theoretical frameworks are proposed.
Literature Review
The adoption of cutting edge technologies in business not only offered a competitive advantage and helped to contain the pandemic spread but also redefined the way companies survive, which continues to exist in the post pandemic era. Indeed, the onset of the Covid 19 pandemic further intensified the urgency of technology adoption that was fostered by the fourth industrial revolution. Technologies that enabled customer relationship management systems, the virtual reality technologies, and the Internet of Things (IoT) lowered the operational costs for business (Akpan, Soopramanien and Kwak, 2020). In addition, complex business decisions were enabled by predictive and visual analytics and big data. Additionally, usage of social media tools became indispensable for digital marketing during the pandemic and in the post pandemic era (Patil and Kumar, 2021). Moreover, the digitization of businesses has become the new normal, and SMEs must gain a huge advantage in terms of business growth, productivity, and technological competitiveness by integrating advanced AI systems into their work environment and processes (Jain, 2022).
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is defined as “the broad class of technology developed with the objective of collecting data in order to solve problems or make decisions” (Campbell et al., 2020). Besides, AI based marketing equips business decision makers with target customer needs and allows SMEs to acquire potential customers and retain existing customers (Bhalerao et al., 2022). Additionally, companies made their way out of the pandemic consequences from a state of ‘striving’ to ‘thriving’ by incorporating AI into their business functions (Pandey et al., 2021).
E commerce
According to Fonseka, Jaharadak and Raman (2022), e commerce “is a modern art of buying or selling goods or services using the internet.” E commerce was primarily interpreted only as transactions over the internet; later, it expanded to include several organizational activities, including buying, selling, logistics, doing business over information networks, and performing organization management activities via the internet. SMEs harness the potential of e commerce to improve their operational features like order processing, delivery, and order fulfilment, and marketing feature like online advertising (Ramanathan, Ramanathan and Hsiao, 2012). However, Shaikh et al. (2021) found compatibility and employees’ insufficient knowledge as two key issues for implementing e commerce in SMEs.
Influence of AI Adoption on SMEs’ Marketing Performance
AI techniques could be efficiently deployed to create intelligent content for marketing purposes and Kumar, Syed, and Pandey (2021b) stated that AIs could modulate the fortune of SMEs in different ways. Additionally, AI adoption in SMEs increases the firm’s dynamic capabilities to meet novel demands, reduces business risks and speeds up business operations by leveraging technology (Drydakis, 2022). Importantly, AI increases brand awareness, advances customer service, nurtures, and delivers passionate customers (Kose and Sert, 2017). Indeed, AI could improve the marketing performance of SMEs by automatizing consumer behaviour analysis. In this case, machine learning algorithms will be employed to construct more precise communication with target customers and to drive conclusions based on their behaviours. Indeed, AI based speech and language recognition is a key area in social media marketing. According to OECD (2021), AI applications benefit SMEs in the marketing and advertising sector. Moreover, AI marketing enhances marketing efficiency by pointing efforts, particularly towards the right customer. Besides, AI marketing could be viewed as a kind of direct marketing that leverages the potential of database marketing accompanied by AI based models and tools (Rekha, Abdulla and Asharaf, 2016). In fact, the study of Yaja and Kumar (2021) revealed the presence of lack of integrated marketing communication and long term branding approach in SMEs; however, Campbell et al. (2020); Kumar and Ayedee (2021) asserted that leveraging AI technology could improve marketing communication Table 1.
| Table 1 Evidence in Support of AI Influencing Marketing Performance | |||
| Sl.No | Author(s) | Dimensions | Findings |
| 1. | Kose and Sert (2017) | Intelligent content creation | Companies could create interactive content by using AI |
| 2. | Jab?onska and Pólkowski (2017) | Rapid and automated decision making, efficient data analysis, Targeting the right customer, predictive marketing based on big data | AI-based tools improve the marketing processes of large as well as small and medium-sized enterprises. Despite likely menaces, the future of these companies greatly relies on these technologies. |
| 3. | Kumar and Kalse (2021) | Enhances customer deliverance, foreign market expansion | AI adoption will be highly beneficial for marketing and data capturing in SMEs. Besides, it improves foreign market expansion without any commercial risks |
| 4. | Kumar and Ayedee (2021) | Marketing communication, customer identification and prioritization | Deploying AI-based propensity models can provide solutions to identify potential customers and prioritize them towards increasing sales productivity |
| 5. | OECD (2021) | Enhance online shopping experience by deploying augmented reality (AR), click prediction systems through machine learning personalized by utilizing big data, advertising and pricing | AI technologies adoption in SMEs could improve marketing and advertising services by providing tailored marketing campaigns, offering online shopping markets, and enhancing targeting capacity |
| 6. | Drydakis (2022) | Facilitates HR activities, offers cashflow forecasting, reduces business risks | Companies using AI-based applications in their core services like marketing could boost their marketing performance efficiency and hence reduce business risks, which are identified in this study among SMEs in England |
| 7. | Davenport et al. (2019) | AI influences business models, customer service options, and sales processes | AI could substantially change customer behaviours and marketing strategies |
| 8. | Rekha, Abdulla and Asharaf (2016) | Optimal selection of contacts | Support Vector Data Description (SVDD) is a kind of machine learning algorithm used to make a proper choice of contacts for direct marketing |
| 9. | Campbell et al. (2020) | provides service assistance while interacting with customers, assists in determining optimal promotions | AI adoption in marketing has the potential to enhance marketing function in all nine stages of the marketing planning processes: (i) examining the current situation; (ii) interpreting markets and customers; (iii) segmenting, targeting, and positioning; (iv) planning objectives, direction, and marketing support; (v) building product strategy; (vi) constructing pricing strategy; (vii) developing logistics strategy and channels; (viii) building marketing communication and influence strategy; (ix) planning metrics and controlling implementation |
| 10. | Lu et al. (2022) | Real-time customer insights, business risk reduction, demand forecasting, process improvement and optimization, product and service innovations | SMEs struggling to overcome the negative impact of the pandemic, even in the post-pandemic era, could adopt digital technologies like AI to achieve sustainable development. Also, AI technology impacts work and organizational performance |
E commerce Adoption Influencing SMEs’ Marketing Performance
E commerce and digital marketing strategies are found crucial for the success and long term survival of micro, small, and medium sized enterprises (MSMEs) (Gao et al., 2023). Besides, e commerce adoption in firms reduced errors, improved customer satisfaction, increased the availability of information, and enabled companies to increase their customer base and develop new markets. Also, Santarelli and D’Altri (2003) challenge e commerce as a 'technological revolution' facilitating a cost minimized marketing channel. While e commerce adoption influenced marketing functions of SME performance, SME size and the number of employees moderated their association (Ramanathan, Ramanathan and Hsiao, 2012). Apart from this e commerce adoption enhances marketing performance of SMEs by establishing two way communication and improving company image positively impacting sales performance of SMEs (Kumar, et al. 2021a).
Moreover, SMEs primarily adopt e commerce for their communication requirements; however, they could benefit from e commerce adoption by making an easy market entry with reduced distributive costs to reach potential customers based on the availability of skills and knowledge base to handle the information and communication technologies (ICTs) (Santarelli and D’Altri, 2003). For instance, small companies with specialized production could reach a wide customer base beyond the borders, thus enhancing their capacity to compete with larger firms without having to build a high cost distributive channel across different areas or nations and eliminating hiring services from specialized dealers. Singh and Kumar (2020) stated that e commerce adoption in SMEs opens new opportunities to access the potential of untapped customer segments Table 2.
| Table 2 Evidence in Support of E-Commerce Influencing Marketing Performance | |||
| Sl.No | Author(s) | Dimensions | Findings |
| 1. | Fonseka, Jaharadak and Raman (2022) | Improves company profit and workers' efficiency, payment facilities online, and provide real-time stock availability | Adopting e-commerce significantly influenced the SME business performance in Sri Lanka |
| 2. | Gao et al. (2023) | Digital marketing, financial performance, sustainability performance | E-commerce adoption influenced their financial performance and sustainability performance at MSMEs in Bangladesh amidst the pandemic |
| 3. | Ramanathan, Ramanathan and Hsiao (2012) | Improves internal functions, facilitates communication among partners in the supply chain | Adopting e-commerce significantly impacted the marketing aspects of Taiwan SMEs, and these marketing aspects strongly influenced SME performance |
| 4. | Santarelli and D’Altri (2003) | Customer communication, developing new markets, increasing customer base, reducing distribution cost, coordination costs, huge building costs, delivering more products with faster shipment even using overnight carriers, saving on building costs | The inter-firm diffusion of e-commerce would increase by 50% in 2003 for SMEs in Italy that have introduced e-commerce in their marketing channels. SMEs can increase customer density with an online catalogue and could accommodate more customers simultaneously from a central location, which otherwise requires a huge retail store |
| 5. | Bell and Loane (2010) | Stronger customer base, greater global presence | Firms with web access gain benefits like reduced marketing communication costs, lower information float time, greater chances for price standardization, redefined intermediary relationships, improved contact between sellers and buyers |
| 6. | Ismael and Lingtong (2022) | Improved customer relationships, Sales Growth | E-commerce implemented in innovative ways improves the overall business performance of SMEs in Saudi Arabia, including their marketing side, by positively impacting the development of the customer base |
| 7. | Octavia et al. (2020) | Creatively looking for existing market opportunities, studying market developments, meeting customer needs, gaining loyal customers | The research indicated a significant influence between market orientation and the adoption of e-commerce impacting SME business performance in Indonesia |
| 8. | Sugandini, Suwardi and Ghofar (2021) | Extensive admittance to items and data, improves distribution, communication and marketing efficiency, targets explicit customer segments by providing customized product offerings | E-commerce adoption in SMEs mediated the impact of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and relative advantage on marketing performance |
Analysis
AI based processes could significantly influence an organization's marketing performance as they provide highly interactive, flexible, and adaptive solutions depending on customers' needs and needs (Kose and Sert, 2017). AI is more versatile and can be deployed in almost any field. AI in e commerce could be used as recommendation algorithms and as marketing automatization systems. Besides, AI significantly moderates the impact of adopting e commerce technology on SME business performance (Fonseka, Jaharadak and Raman, 2022). The main goal of AI incorporated into e commerce is to deliver personalized content to target customers that would enhance the probability of purchase. Even with AI and e commerce, maintaining robust customer relationships is the key to acquiring marketing advantages (Ismael and Lingtong, 2022). Figure 1 depicts prominent marketing performance dimensions impacted by AI adoption in SMEs.
Apart from this, e commerce implemented across the marketing channels among the SMEs organised a proprietary distributive channel with low costs, and e commerce sales achieved a prominent level of penetration across those SMEs, which otherwise would have incurred high costs (Santarelli and D’Altri, 2003). On the SME side, e commerce yields coordination cost advantages since buyers eliminate the costs of finding potential suppliers, and customers easily do a price comparison and product purchase via the internet with exact information about the price, availability, and product characteristics. Whereas on the customer side, e commerce in SMEs reduces transportation costs for physically reaching the purchase venue and enriches with necessary information like customer ratings and reviews in addition to a descriptive product catalogue. All these increase the purchase intention of the customers, thus improving the marketing outcomes of the SMEs. Figure 2 depicts important marketing performance dimensions impacted by e commerce adoption in SMEs.
Conclusion
The adoption of innovative technologies would aid SMEs to turn Covid 19 imposed challenges into opportunities and improve their survival rate by improving their performance. In this regard, the article sought to consolidate the developing body of knowledge regarding the impact of AI and e commerce in the marketing of SMEs. Moreover, AI enabled marketing in SMEs improves their performance through big data obtained from customers. Furthermore, the e commerce driven marketing performance of SMEs improves customer base, marketing efficiency, and market expansion and facilitates reduced costs. In either case, the effectiveness of deploying these technologies is highly dependent upon the availability of talent and resources in SMEs to deal with corresponding ICTs.
Therefore, to survive in the digital economy, SMEs have to equip their business models with novel digital communication tools. Additionally, AI and e commerce offer new prospects for SMEs to market their goods and services. This study enriches the theoretical knowledge of SME marketing management and the adoption of AI and e commerce. Though more empirical evidence on how AI and e commerce impact SME marketing performance is not available, this review article could be used as a background and starting point for future research.
References
Akpan, I.J., Soopramanien, D. and Kwak, D.-H. (Austin) (2020). Cutting-edge technologies for small business and innovation in the era of COVID-19 global health pandemic. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 33(6), 607-617.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Audretsch, D.B. and Thurik, A.R. (2001). What’s New about the New Economy? Sources of Growth in the Managed and Entrepreneurial Economies. Industrial and Corporate Change, 10(1), pp.267–315.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bell, J. and Loane, S. (2010). ‘New-wave’ global firms: Web 2.0 and SME internationalisation. Journal of Marketing Management, 26(3-4), pp.213–229.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bhalerao, K., Kumar, A., Kumar, A. and Pujari, P. (2022). A Study of Barriers and Benefits of Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Small and Medium Enterprise. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(S1), pp.1–6.
Campbell, C., Sands, S., Ferraro, C., Tsao, H.-Y. (Jody) and Mavrommatis, A. (2020). From data to action: How marketers can leverage AI. Business Horizons, 63(2), pp.1–17.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Davenport, T., Guha, A., Grewal, D. and Bressgott, T. (2019). How Artificial Intelligence Will Change the Future of Marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, [online] 48(1), pp.24–42.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Drydakis, N. (2022). Artificial Intelligence and Reduced SMEs’ Business Risks. A Dynamic Capabilities Analysis During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Information Systems Frontiers, 24, pp.1223–1247.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Fonseka, K., Jaharadak, A.A. and Raman, M. (2022). Impact of E-commerce adoption on business performance of SMEs in Sri Lanka; moderating role of artificial intelligence. International Journal of Social Economics, 49(10), pp.1518–1531.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Fonseka, K., Jaharadak, Dr.A.A., Raman, Dr.M. and Dharmaratne, Dr.I.R. (2020). Literature Review of Technology Adoption Models at Firm Level; Special Reference to E-Commerce Adoption. Global Journal of Management and Business Research, [online] 20(6), pp.1–9.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gao, J., Siddik, A.B., Khawar Abbas, S., Hamayun, M., Masukujjaman, M. and Alam, S.S. (2023). Impact of E-Commerce and Digital Marketing Adoption on the Financial and Sustainability Performance of MSMEs during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Empirical Study. Sustainability, 15(2), p.1594.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M.A., Singh, R.P. and Suman, R. (2022). Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature-based study. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, [online] 3, pp.119–132.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hasan, A., Amrusi, Musfiana and Mardhani, M. (2021). An overview of e-commerce adoption in Indonesian SMEs. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, [online] 1811(1), p.012104.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ismael, A.D. and Lingtong, Z. (2022). Impact of e-commerce adoption on the business performance of SMEs in Saudi Arabia. IJARIIE, [online] 8(2), pp.47–60.
Kose, U. and Sert, S. (2017). Improving Content Marketing Processes with the Approaches by Artificial Intelligence. Ecoforum, [online] 6(1), pp.1–8.
Kumar, A. (2020). Sustainable Development in SMEs Through Social Media Channels. International Journal of Management, Technology And Engineering, IX(VI), pp.1066–1075.
Kumar, A. and Ayedee, N. (2021). TECHNOLOGY ADOPTION: A SOLUTION FOR SMES TO OVERCOME PROBLEMS DURING COVID-19 | Source Details | Scope Database. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, [online] 25(1), pp.1–16.
Kumar, A. and Kalse, A. (2021). Usage and adoption of artificial intelligence in SMEs. Materials Today: Proceedings, pp.1–5.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kumar, A., Syed, A.A. and Pandey, A. (2020a). How Adoption of Online Resources Can Help Indian SMEs in Improving Performance during COVID-19 Pandemic. Test Engineering and Management Journal, pp.3394–3400.
Kumar, A., Syed, A.A. and Pandey, A. (2021a). Adoption of Online Resources to Improve the Marketing Performance of SMEs. Asia Pacific Journal of Health Management, 16(3), pp.137–144.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kumar, A., Syed, A.A. and Pandey, A. (2021b). Artificial intelligence (online resource): A panacea for SMES in healthcare. Asia Pacific Journal of Health Management, 16(4), pp.230–235.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kumar, M.A., Syed, D.A.A. and Pandey, D.A. (2020b). Impact of Online Resources/Technology Adoption on SMEs Performance. PIMT Journal of Research, [online] pp.1–11.
Lu, X., Wijayaratna, K., Huang, Y. and Qiu, A. (2022). AI-Enabled Opportunities and Transformation Challenges for SMEs in the Post-pandemic Era: A Review and Research Agenda. Frontiers in Public Health, [online] 10.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Octavia, A., Indrawijaya, S., Sriayudha, Y., Heriberta, Hasbullah, H. and Asrini (2020). Impact on E-Commerce Adoption on Entrepreneurial Orientation and Market Orientation in Business Performance of SMEs. Asian Economic and Financial Review, [online] 10(5), pp.516–525.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
OECD (2021). The Digital Transformation of SMEs. [online] OECD Studies on SMEs and Entrepreneurship. OECD.
Pandey, A., Kumar, A., Mangla, P. and Jain, C. (2021). How AI has Proved to be a Game-Changer for Organizations to Conquer Covid-19. Pacific Business Review International, [online] 13(12), pp.57–68.
Patil, V. and Kumar, A. (2021). A Viewpoint on Digital Marketing and Usage of Social Media Tools during COVID-19 Pandemic. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 25(2), pp.1–3.
Ramanathan, R., Ramanathan, U. and Hsiao, H.-L. (2012). The impact of e-commerce on Taiwanese SMEs: Marketing and operations effects. International Journal of Production Economics, [online] 140(2), pp.934–943.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rekha, A.G., Abdulla, M.S. and Asharaf, S. (2016). Artificial Intelligence Marketing: An application of a novel Lightly Trained Support Vector Data Description. Journal of Information and Optimization Sciences, 37(5), pp.681–691.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Santarelli, E. and D’Altri, S. (2003). The Diffusion of E-Commerce Among SMEs: Theoretical Implications and Empirical Evidence. Small Business Economics, [online] 21(3), pp.273–283.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Shaikh, A.A., Kumar, A., Syed, A.A. and Shaikh, M.Z. (2021). A Two-Decade Literature Review on Challenges Faced by SMEs in Technology Adoption. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 25(3), pp.1–13.
Singh, N. and Kumar, A. (2020). Role of E-business in SMEs. [online] pp.130–139.
Sugandini, D., Suwardi, S. and Ghofar, A. (2021). Impact of e-Commerce Adoption on Marketing Performance. RSF Conference Series: Business, Management and Social Sciences, 1(3), pp.277–284.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yaja, M. and Kumar, A. (2021). An empirical study of marketing of SMEs in the tourism sector. Small Enterprise Research, 28(3), pp.314–328.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 23-Mar-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13369; Editor assigned: 24-Mar-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13369(PQ); Reviewed: 23-Apr-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13369; Revised: 25-Jun-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13369(R); Published: 21-Jul-2023