Research Article: 2023 Vol: 22 Issue: 1
Academic Governance Strategies and their Impact on the Quality of Educational Performance
Ahmed Abdul Salam Ahmed, Samarra University
Firas Emad Ali, Samarra University
Mohammed Mahmood Taha, Samarra University
Citation Information: Ahmed, A.A.S., Ali, F.E., & Taha, M.M. (2023). Academic governance strategies and their impact on the quality of educational performance. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 22(1), 1-6.
Abstract
This study aims to determine the impact of academic governance in the Iraqi private colleges on the quality of university performance. The study was applied to the private colleges located in Baghdad, which were distinguished by their multiple departments, ten or more, and their number is (11) private colleges. The inspection unit was represented by members of the teaching and administrative staff in the colleges researched, and their number is (329) samples. Where the descriptive analytical approach was the basis of the work of this study, which reached several results, the most important of which is that the application of academic governance in private colleges was moderately, the researched colleges are working on developing the capabilities of employees through the learning channels and knowledge available to them in order to reach the quality of performance. Based on the results of the study, a set of recommendations were presented, the most important of which are: Private colleges should focus on practicing academic governance because it is a methodology suitable for working in a highly competitive environment, so it is opportunities for excellence in terms of performance for these colleges, working to provide integrated knowledge in order to achieve quality educational performance and according to the requirements of the labor market for various disciplines.
Keywords
Governance Strategies, Performance, Growth and Learning.
Introduction
The term governance is an old common concept in the economic literature, but it has been dealt with a lot recently, as we see its applications in all fields and all economic levels at organizations, institutions, associations, universities, governmental, public and private companies, as a good thing in making decisions characterized by rationality, enlightenment and transparency, and leads to achieving efficiency and effectiveness at the organizational level.
In view of the positive results achieved by governance in all fields, especially universities, which are considered the basis for building societies (Nuyten, 2022) and its role in increasing awareness and knowledge of individuals, Abu Juma’a (2017) referred to university governance as the key to universities reaching the highest levels of value and content. This requires the advancement of the functions of the university: teaching scientific research, community service, and this in turn will enhance the performance of the university. Higher education institutions are makers of knowledge as they produce and direct it for progress, and cooperate with their partners in making maximum use of this knowledge, exchanging with them visions, benefiting from it and benefiting from them, as they are partners in knowledge, development and destiny. University colleges are among the important institutions that contribute in most countries of the world to development in its various aspects, social, economic, administrative, political, health and others, and they are an important and vital part of the general community. It also has its reciprocal relations with this society, and in order for universities to achieve their goals and vision, they must have a wise modern administration that depends on several entrances, and one of the most important of these modern entrances is in management (Rowlands et al., 2017; Al-Hmoud & Al-Ghoul, 2022). Governance is the approach that has attracted the attention of researchers through its use in achieving quality and excellence in performance (Beunen et al., 2016; Fakeeh, 2016).
Accordingly, international rankings have increased pressure on universities with regard to the issue of quality performance on the one hand and governance on the other hand. Given the enormity of the challenge facing higher education institutions in Iraq, it is no longer possible to confront it with the traditional methods that have prevailed for a long period of time due to a significant development in various aspects Social, cultural and economic because higher education has not responded to these changes to the degree that keeps pace with the speed of modern technologies and communications in the world due to the preoccupation of these institutions with their daily problems that multiply with the increase in social demand for education (Scagnelli et al., 2019) All this prompted those universities to deepen the concept of academic governance to bring about change in the university’s framework in terms of the quality of educational performance on the one hand and facing current and future challenges on the other hand (Rowlands, 2018).
Based on the foregoing, academic governance is a necessary and prerequisite for deepening the independence of universities and higher education institutions, through the development of strategies, plans and university executive programs by the actual specialists in university and research work, and the proper use of the resources and means allocated, as well as taking full responsibilities to achieve the specific goals and objectives (Saha et al., 2010; Salam, 2013).
In this study, the study methodology that the researchers will follow in proving this study will be presented by defining the problem, the objectives that this study will achieve, and building a model prepared by researchers that shows the impact of academic governance on the quality of university performance in private colleges. A brief presentation shows the importance of academic governance and the quality of university performance through the study terms, in addition to the results and recommendations.
The Problem of the Study
Several studies have been conducted in order to determine the extent to which governance is practiced in business organizations in general, and due to the lack of studies that dealt with academic governance, researchers in this study sought to identify the degree of practice of the principles of governance by the private college, from the point of view of the members of the teaching and administrative staff in it, in addition to studying (Mahmoud, 2016), which recommended a study on the concept of academic governance.
The Importance of the Study
The importance of this study stems from the importance of the topic it deals with, as the application of academic governance is one of the success tools of educational organizations. The importance of the study stems from the importance of applying governance and its impact on the quality of university performance, in addition to the importance of the findings of the current study, which benefit the employees of the colleges in question through their knowledge of academic governance, the mechanism of its application and the indicators indicating it.
The Hypotheses of the Study
There is no statistically significant effect at the level (a=0.05) of academic governance with its dimensions (information flow, training) on achieving the quality of educational performance in its dimensions (growth and learning, efficiency of internal processes) in private colleges.
H0: There is no statistically significant effect at the level (a=0.05) of academic governance on the quality of educational performance.
H1: There is a statistically significant effect at the level (a=0.05) of academic governance on the quality of educational performance.
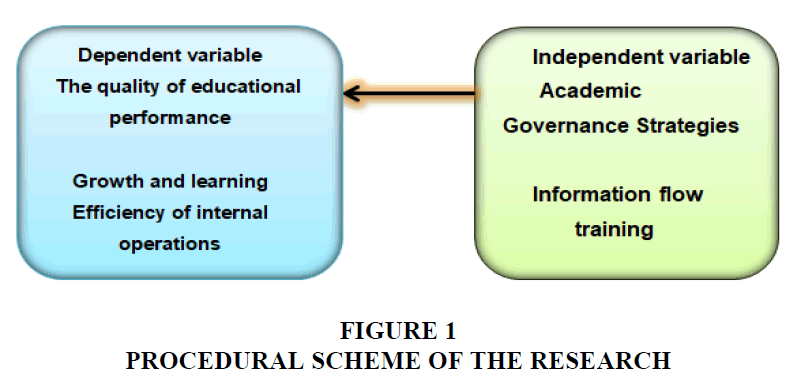
The Default Scheme for the Study
The procedural scheme of the research deals with the statistically significant impact of academic governance on the quality of educational performance, according to Figure 1.
Results
Arithmetic averages and standard deviations were calculated for the application of academic governance in its dimensions (information flow, training) as shown in Table 1.
| Table 1 Arithmetic Averages and Standard Deviations for Each Domain of Academic Governance | |||||
| No | Direction | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Rank | Degree |
| 1 | Information flow | 3.63 | 0.541 | 1 | Middle |
| 2 | Training | 3.21 | 0.402 | 2 | Middle |
| Academic governance | 3.42 | 0.471 | Middle | ||
It appears from Table 1 that the arithmetic averages of academic governance ranged between 3.63-3.21, the highest was after the information flow with an arithmetic mean of (3.63) at a medium degree, followed by the second dimension with an arithmetic average of (3.21) at a medium degree, where the arithmetic mean of academic governance as a whole (3.42) to a medium degree, and this indicates that the private colleges are working to transmit information and provide it with full transparency to the members of the teaching and administrative staff in order to prepare them in a way that achieves the desired goals of the colleges in question and through their training, and where they have positive trends towards the application of academic governance, but with middle degree.
As for the arithmetic averages and standard deviations of the quality of educational performance in its dimensions (growth and learning, efficiency of internal processes) they were as follows and as shown in Table 2.
| Table 2 Arithmetic Averages and Standard Deviations for each Domain of Educational Performance Quality | |||||
| No | Direction | Arithmetic Average | Standard Deviation | Rank | Degree |
| 1 | Growth And Learning | 3.66 | 0.794 | 1 | Middle |
| 2 | Efficiency of internal operations | 3.42 | 0.772 | 2 | Middle |
| The quality of educational performance | 3.54 | 0.783 | Middle | ||
Table 2 shows that the arithmetic averages and standard deviations in the field of university performance quality, which ranged between 3.42-3.66, were the highest in the first trend of growth and learning with an arithmetic average of 3.66 and a medium degree, followed by the second trend of the efficiency of internal operations with an arithmetic average of 3.42 and a medium degree, The arithmetic average for the axis of quality of university performance as a whole was 3.54, with a medium degree, and this indicates that the colleges in question is working on developing channels that link the learning of members of the administrative and academic members to the university’s policies through the adoption of modern technology means to exchange information and increase coordination between the different departments.
Testing the Hypotheses of the Study
To test the hypothesis, (Multiple-Regression) was used to measure academic governance in private colleges (information flow, training) on the quality of university performance (growth and learning, efficiency of internal processes) and the results indicate that there is a statistically significant effect on the level of ( (α≤0.05) for academic governance for all its dimensions on the quality of university performance, where the value of F reached (54,712), which is a statistically significant value at the level of (α≤0.05) and the value of R (0.379), The value of 2R was (0.143), which means that the independent variables of academic governance and its trends affect the dependent variable on the quality of university performance, and accordingly we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis that indicates: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05( for academic governance In private colleges (information flow, training) on the quality of university performance (growth and learning, efficiency of internal processes).
Conclusion
1. The benefits that private colleges obtain as a result of applying academic governance vary according to their specificity, including the creation of new jobs or the dispensation of some jobs in a way that enhances the need for new skills and capabilities, and thus works to provide the organization with new blood.
2. The success of the application of academic governance requires intellectual and cultural changes for individuals at different levels in the colleges in question, in addition to providing tools and techniques that help the successful application of this approach in order to reach the quality of educational performance.
3. It was noted that the colleges in question offer training courses and seminars on governance practices and prepare awareness programs for college and administrative staff members through seminars, lectures and workshops on governance, its principles and Fields of Application.
4. The researchers found that the application and implementation of the academic governance approach works within flexible criteria and responsive to developments in the surrounding environment.
5. The studied colleges are working on developing the capabilities of employees through the learning channels and knowledge available to them in order to reach the quality of educational performance.
6. Availability of sufficient financial allocations for private colleges with powers to spend on scientific and research activities to implement academic governance.
Recommendations
1. The application of academic governance in the colleges in question requires a sufficient preparation period to spread the culture of governance and administrative development in university institutions.
2. Private colleges should focus on practicing academic governance because it is an appropriate methodology for dealing with a highly competitive environment, and it is opportunities for excellence in terms of performance for these colleges.
3. Academic governance is not concepts and theories, but rather a field of application, and this requires great efforts by its pioneers to transfer it from the space of ideas to the field of implementation.
4. The application of the governance methodology requires the participation of all those concerned with academic work (administration, teaching staff, administrative staff, students) in its application.
5. Working to provide integrated knowledge in order to achieve the quality of educational performance and according to the requirements of the labor market for various disciplines.
6. The implementation of the academic governance approach requires legislation that is flexible and responsive to developments in the surrounding environment.
7. Availability of sufficient budgets for universities with powers to spend them on scientific and research activities is the essence of the quality of educational performance.
8. It is necessary to develop a system for selecting academic leaders (university presidents, deans, heads of scientific departments) as it is the most important success factor for the application of academic governance.
References
Abu Juma’a, M.H. (2017). University governance, a knowledge introduction to the conference on University Governance in Educational Institutions, Arab Universities Governance Council, March 13-11, Middle East University, Amman, Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan.
Al-Hmoud, A.M., & Al-Ghoul, K. (2022). The degree of implementation of governance and its relationship to organizational excellence in private Jordanian universities in the capital governorate “Amman”, from the viewpoint of teaching staff. Journal of the Association of Arab Universities for Research in Higher Education, 42(2), 29-50.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Beunen, R., Van Assche, K., & Duineveld, M. (2016). Evolutionary governance theory. Springer International Pu.
Fakeeh, K.A. (2016). The e-governance (e-gov) information management models. International Journal of Applied Information Systems, 11, 10-16.
Nuyten, T. (2022). Changing the course of faculty engagement in academic governance: Reconcilation through education.
Rowlands, J. (2018). Deepening understandings of Bourdieu’s academic and intellectual capital through a study of academic voice within academic governance. Studies in Higher Education, 43(11), 1823-1836.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rowlands, J., Rowlands, & Melchior. (2017). Academic governance in the contemporary university. Singapore: Springer.
Saha, S., Bhattacharyya, D., Kim, T.H., & Bandyopadhyay, S.K. (2010). Model based threat and vulnerability analysis of e-governance systems. International Journal of u- International Journal of u-and e-Service, Science and Techn Service, Science and Techn Service, Science and Technology, 3(2), 7-22.
Salam, M.A. (2013). E-governance for good governance through public service delivery: An assessment of district e-service centres in Bangladesh. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, BRAC University.
Scagnelli, S., Vasile, L., & Apostolov, M. (2019). Survival drivers of post-incubated start-ups: The effect of academic governance. International Journal of Innovation Management, 23(07), 1950062.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 19-Oct-22, Manuscript No. ASMJ-22-12696; Editor assigned: 21-Oct-22, PreQC No. ASMJ-22-12696(PQ); Reviewed: 04-Nov- 22, QC No. ASMJ-22-12696; Revised: 17-Nov-22, Manuscript No. ASMJ-22-12696(R); Published: 24-Nov-22