Research Article: 2022 Vol: 28 Issue: 3
A Systematic View On Value Congruence: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis
Tyagi Minakshi, Savitribai Phule Pune University
Citation Information: Minakshi, T. (2022). A systematic view on value congruence: A review and Bibliometric analysis. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(3), 1-17.
Abstract
Numerous researches have examined the positive associations between value congruence and the various outcomes. However, these studies on value congruence have been scattered across various literature. No study was done to consolidate and study this concept in an integrated and well organized manner. To fill this gap, we undertook a comprehensive and systematic bibliometric analysis of all value congruence publications and attempted to show the thematic metamorphosis of value congruence research in different contexts. Such a study will assist in understanding the extant of coverage of this concept across the various fields and also provide future research directions. In this endeavor, a total of 1120 publications related to value congruence across various areas were retrieved from the Scopus and EBSCO host databases. During the bibliometric analysis on value congruence, four major research areas were revealed: psychology, organizational behavior, relationship management, and consumer behavior. This concept, from across these four areas, was found to be extensively linked with outcomes like trust, satisfaction and identification. This article concludes by indicating future research areas and upcoming trends in value congruence. Finally, based on found information on value congruence, a conceptual model is proposed.
Keywords
Bibliometric Analysis, Organizational Behavior, Relationship Management.
Introduction
Congruence is the degree of similarity between the characteristics of an entity (an audience, a customer or a consumer) with the other entity (Kirmani & Shiv, 1998). Entity can refer to anything and can include things like product or brand, an employee, a consumer or even a value. Values are the compass, which helps individuals choose the behavior (Elizur & Sagie, 1999). Schwartz has done a lot of research on understanding the importance of values and has defined values as abstract goals or standards, which guide peoples’ interests and behaviors. There is an increased importance on the similarity of values between brands or companies and consumers, which drive their purchasing decisions. Based on congruity theory, organizations or brands develop marketing strategies to help employees or consumers realize the congruity of personal values and firm or brand’s values. The consumer behavior literature shows that values have impact on consumers’ purchasing decisions (Gutman, 1982). Thus, it can be seen that value congruence as a concept needs to be studied in detail so that it can be used as an effective tool for marketers in enhancing the preference of products or brands and hence increase customer base.
The objective of this bibliometric study is to systematically investigate all past researches of value congruence and evaluate its current status and major contributions (He & Harris, 2012). Due to the recent focus on understanding the significance of values in consumer behavior and the impact of the value congruence, between brands and consumers, on their purchase decisions, the study of value congruence is the prime focus of this study. The research on value congruence was spread across various areas of studies and no research has assembled and presented it in a coherent manner. Hence, this study attempted to understand and map the development of value congruence from various perspectives. It was revealed that value congruence was majorly covered in research areas like psychology, organizational behavior, and relationship management and consumer behavior and on the outcomes like satisfaction, trust and identification (Aoyagi, 1999).
An Overview Of Value Congruence
Value congruence, reflects the degree of similarity between values of customer and an object, which leads to a positive response with respect to such object (product, brand or organization) (Lee & Jeong, 2014). Johar & Sirgy (1991) defined value congruence as a cognitive comparison of the similarity of firm’s values and the consumer’s own values (Bitner, 1995). Value congruity is the degree of resemblance between two entities, like customers and brands or salesperson and depends on the similarity of the characteristics of the two entities (Tuškej et al., 2013). Byrne et al. (1967) Concept of value congruence is based on Similarity Attraction Theory (SAT). According to SAT theory, people will more likely maintain relationships with others who resemble them in some aspect (Byrne et al., 1967).
Value congruence has been studied from various perspectives: from psychological perspective to understand in psychological behavior (Gaunt, 2006), from organizational behavior perspective to understand organizational behavior outcomes (Bao et al., 2012), from relationship management perspectives to understand its effects on relationship management (Johnson et al., 2020), from consumer behavior perspective to understand its influence on the consumer’s behavior (Zhang & Bloemer, 2011) and in recent times in understanding its effect on green behavior (Bulmash, 2019). Researches in organization behavioral theories showed that the attitudinal outcomes of employees are linked with value congruence (Bao et al., 2012). From the relationship management perspective, the similarity-attraction theory states that individual stay in successful relationship if they see other individual as an extension of self (Philipp-Muller et al., 2020) Studies in consumer behavior literature has shown positive association between buying behavior and the value congruence of customer and salesperson (Brashear et al., 2003), brand and consumer (Sethi et al., 2001) and the seller and customer. The role of values congruence in guiding the human behavior (Schwartz, 2012), has been researched a lot in the psychological, relationship management, organizational behavior and consumer behavior, since earlier times. However, recent studies show a trend of researches in value congruence from the green behavior context (Gunden et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2018).). Green behavior is also known as pro-environmental behavior, where actions are dominantly supporting the environment.
Forthcoming sections will outline past researches on value congruence, present the process of analysis carried out on the collected data, describe the results of analysis, and finally conclude by providing research guidance for the future areas in value congruence.
Methodology
A thorough review of the past academic literature on value congruence was done to determine the search keyword. Based on this, some keywords like “value congruence”, “value congruity” and “value similarity” were identified, for relevant data collection. Words like value congruity, value congruence and value similarity, were taken into conjunction, as separating them were giving unrelated articles not covering the area of interest of value congruence as a concept. To ensure that a maximum of related articles were covered, the “OR” operator was used to utilize all of the keywords. (Feng et al., 2017) The databases selected to shortlist research papers were EBSCOHOST and Scopus as these are the most widely used databases for literature review and bibliometric analyses (Morgan & Hunt, 1994).
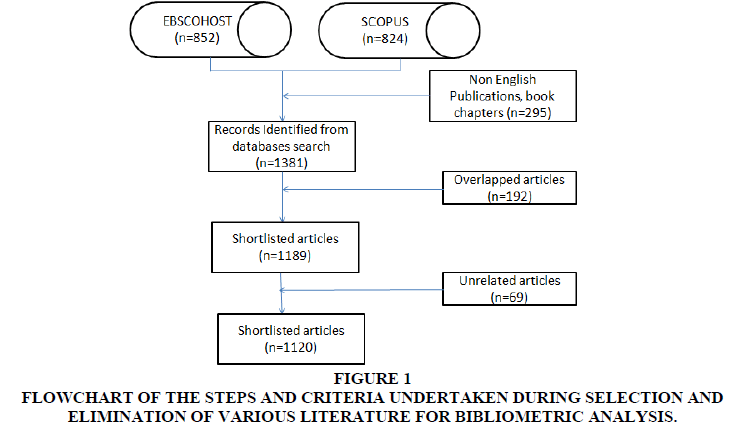
The result of the search and screening process of various literatures is shown in Figure 1. In the search from year 1966 through 2020, a total of 1676 publications were collected. The results of these publications were stored in csv format. The information saved for each publication was: the title, abstract, author name, indexed and author keywords, year, citations and publication journal.
Refinements in the Search Results
The collected 1676 publications consisted of documents like articles, book chapters, conference proceedings and literature reviews. For this study focus was only on academic journal articles, conference papers, and review papers. Hence, trade publications, papers from magazines, working progress, reports, books and book chapters were excluded from further considerations. It was found that most common language of collected publications was English, followed by Chinese, Japanese and Spanish. For the analysis only English papers were included. Based on these criteria, the obtained publications were further revised and 1381 publications were kept. It was seen that remaining publications had some duplications due to the presence of similar publication in both source database. For instance, the research paper by (Adkins et al., 1994) could be retrieved from two databases. Hence, the 1381 research papers were further scanned and 192 duplications were removed. The resulting 1189 articles were then reviewed for relevance criteria, based on current context of study. A total of 69 articles were not found relevant and final 1120 publications were finally shortlisted for statistical analyses (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Flowchart Of The Steps And Criteria Undertaken During Selection And Elimination Of Various Literature For Bibliometric Analysis.
Results and Data Statistics
There are numerous software and tools available for bibliometirc analysis, but for this study vosviewer and excel on csv files, were used in extracting diverse information fields. The statistics of results obtained by screening of past papers are shown as classifications, on the basis of the publication years, the journals of publications, popular themes, the countries of research origin, most contributing authors, and most found keywords in titles and papers.
Publication Trend of Research Papers by Years
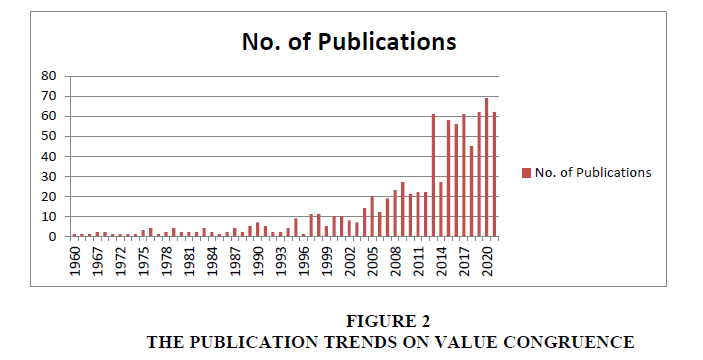
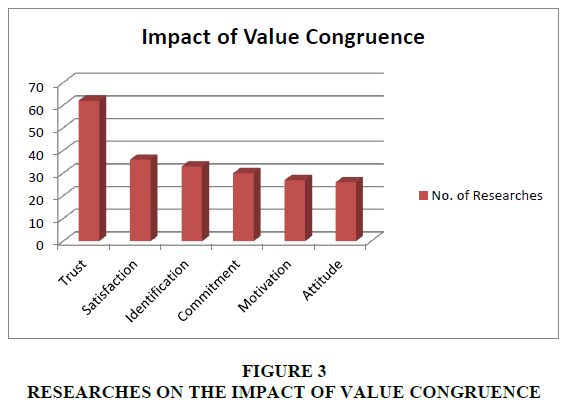
Data analysis captured the vast information on value congruence in a meaningful manner. From Figure 2, it is noticeable that the number of publications on value congruence showed a gradual increase over years. The emergence of publications on value congruence is seen between 1966 and 2004, with less than 10 articles published per year. Duration between 2004 and 2020 can be considered as the growth stage. Total publications in the growth stage comprised of more than 95% of total search results. This indicates that more academicians began to give attention towards this concept after 2004. It was observed that most of the studies happened in the area of psychology, relationship management, organizational behavior and consumer behavior. Figure 3 shows the impact of value congruence was majorly studied on trust, satisfaction and identification. By observing the publications on value congruence and its application in various fields over the years, it may be presumed that its publication related to organization behavior and consumer behavior will continue to proliferate in coming years. However, in recent years, 2018 till 2020, it is seen that value congruence is also studied in green behavior context (Gunden et al., 2020). But the studies on this aspect are very limited.
The data analysis points out that the selected 1120 publications on value congruence were published in 561 journals. It can be seen that the concept of value congruence was covered in various fields and contexts. Table 1 shows the 36 journals in which most publications on value congruence has been done. Figure 2 reveals that studies on understanding the impacts of value congruence were majorly done on trust, satisfaction and identification. Further, from Table 1 we can infer that these studies were done in areas of organizational behavior, psychology, relationship management, and consumer behavior. Out of 1120 articles, 147 articles were published in these journals representing areas of organizational behavior, psychology, relationship management, and consumer behavior. This accounts for about 25% of all published articles.
| Table 1 The 36 Most Prolific Journals Or Proceedings Contributing To Product Placement Research |
||
|---|---|---|
| Journal Name | Total Number | Rank |
| Psychology | ||
| Journal of Applied Psychology | 7 | 5 |
| Journal of Applied Social Psychology | 7 | 5 |
| Journal of Personality & Social Psychology | 7 | 5 |
| Personnel Psychology | 7 | 5 |
| Journal of Managerial Psychology | 6 | 6 |
| Journal of Community & Applied Social Psychology | 4 | 8 |
| Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology | 4 | 8 |
| Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology | 4 | 8 |
| Journal of Social Psychology | 4 | 8 |
| British Journal of Social Psychology | 3 | 9 |
| Journal of Human Values | 3 | 9 |
| Organizational Behavior | ||
| Leadership Quarterly | 10 | 2 |
| International Journal of Human Resource Management | 8 | 4 |
| Personnel Review | 7 | 5 |
| Journal of Organizational Behavior | 6 | 6 |
| Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies | 5 | 7 |
| Human Resource Management Journal | 4 | 8 |
| Cross Cultural Management | 3 | 9 |
| Consumer Behavior | ||
| Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management | 8 | 4 |
| Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science | 6 | 6 |
| International Marketing Review | 3 | 9 |
| Industrial Marketing Management | 3 | 9 |
| Journal of nursing management | 4 | 8 |
| International Journal of Hospitality Management | 3 | 9 |
| Relationship Management | ||
| Family Science | 5 | 7 |
| Journal of Marriage & Family | 4 | 8 |
| Journal of Adolescence | 4 | 8 |
| Human Relations | 3 | 9 |
| International Journal of Conflict Management | 3 | 9 |
| Total | 147 | |
Author Influence
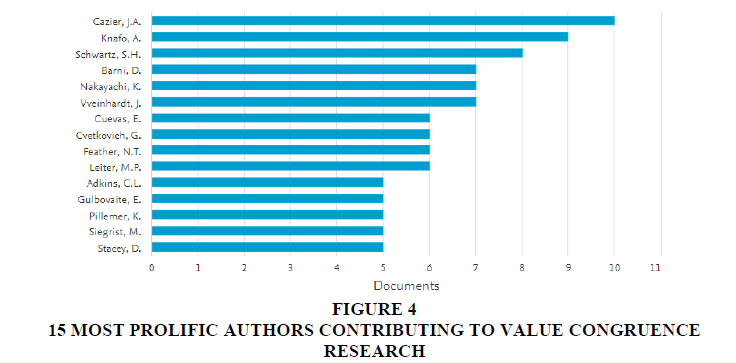
Top 15 influential authors with most contributions towards value congruence research are shown in Figure 4. It is evident that Cazier J. A is the most prolific author which is succeeded by Knafo A., Schwartz S.H., and Barni D. In Figure 5, academic collaborations between some prolific authors are shown. For example, there is a collaborative association between Knafo A., Barni D., Schwartz S.H., and Bohenke K., as they have co-authored many papers. From Figure 4, the most influential author was Cazier J. A., with 10 papers on value congruence. Out of these papers, most of his papers were on understanding the impact of value congruence on trust in consumer behavior context. Another influential author Knaof has given 9 papers on value congruence, with most papers on satisfaction in the psychological context. Adkins has researched value congruence’s impact on satisfaction from organizational behavior perspective. Barni D. has most of his researches on relationship management aspects. This shows that the most prolific authors’ work is distributed among areas like psychology, organization behavior, relationship management, and consumer behavior. From the works of various researchers, we see that Schwartz has majorly researched on the influence of value congruence on satisfaction, while Nakayachi, Cuevas and Cvetkovich has most of his papers on understanding trust related to value congruence and Knafo has mostly studied identification as constructs. Thus, it is evident that the impact of value congruence was majorly studied on trust, satisfaction and identification, in all four prominent domains of psychology, organizational behavior, relationship management, and consumer behavior.
Keyword Analysis
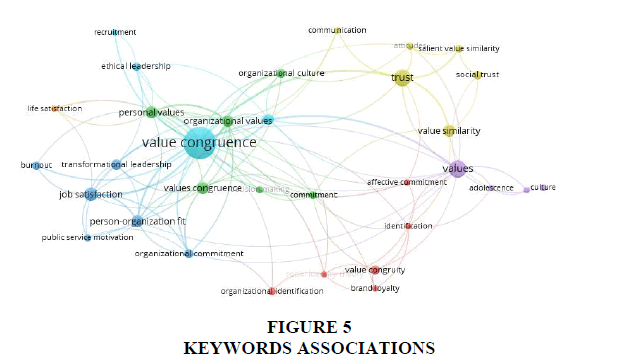
From the analysis of rate of occurrence of title words, author and indexed keywords, it is possible to identify current research interests in a particular area. Association strength of keywords is evaluated using VosViewer software. In this study, 3248 keywords were taken from the 1120 research publications. If strength of 3 keywords is chosen (minimum times a keyword should appear in shortlisted articles), then the total of 309 keywords, with 6627 links and total link strength of 12933 was obtained. The keywords associations are seen in Figure 5. The 20 most commonly used words in the research titles (Table 2) and author/indexed keywords (Table 3) fields. From Table 3, it is evident that major researches were done in behavioral aspects like trust, satisfaction and identification associated with value congruence. It was seen that trust was the studied in almost 85 papers, with identification and satisfaction in almost 54 and 55 papers respectively. Table 2 contains the most commonly found terms in the titles of research studies on value congruence. From the table 2, we can again see trust was majorly researched term and was found in 65 papers. This was followed by the next most found terms in value congruence studies, i.e. satisfaction and identification. The impact of value congruence on satisfaction was found in 35 papers and on identification was found in 34 papers. Also, comparing Tables 2 and 3, a consistency can be observed in the use of words in the title and keywords fields. For example, the words/phrases socialization, leadership, workplace, relationships, organization and consumer behavior were all frequently used in both the title and keywords fields. This indicates that value congruence was most studied in psychology, organization behavior, relationship management, and consumer behavior contexts. The popularity of keywords like trust, satisfaction and identification along with keywords like organizational, psychological, relationships and consumers indicate the area of major focus of past studies on value congruence.
| Table 2 Most Frequently Used Words In Research Paper Titles |
|
|---|---|
| Keywords | Score |
| Values-based/Values | 415 |
| Congruity | 182 |
| Similarity | 83 |
| Socialization | 76 |
| Workgroup/workplace/work | 76 |
| Leadership/Leader | 70 |
| Organizational/Organization | 65 |
| Relationships | 65 |
| Trust/Distrust | 63 |
| Role | 54 |
| Fit | 49 |
| Perception/Perceived | 42 |
| Satisfaction | 35 |
| Identification | 34 |
| Ethics | 30 |
| Job | 30 |
| Transmission | 29 |
| Consumer/Consumer Behavior | 28 |
| Cultures | 28 |
| Person-Organization | 27 |
| Commitment | 25 |
| Nurses' | 25 |
| Public | 25 |
| Attitude | 22 |
| Service | 23 |
| Table 3 Most Frequently Used Words In Research Papers |
|
|---|---|
| Keywords | Score |
| Value | 477 |
| Congruence | 183 |
| Organization | 147 |
| Social | 114 |
| Leader/Leadership | 110 |
| Similarity | 91 |
| Fit | 85 |
| Trust | 85 |
| Brand/Branding | 76 |
| Relation/Relationship | 68 |
| Behavior/behavioral | 65 |
| Job | 60 |
| Cultural/Culture | 59 |
| Work/Work-Place | 56 |
| Identification/Identity | 55 |
| Satisfaction | 54 |
| Employee | 52 |
| Perceived | 48 |
| Adult/Adulthood | 44 |
| Commitment | 43 |
| Model | 43 |
| Management | 42 |
| Person/Personal | 41 |
| Ethic | 40 |
From the VosViewer diagram in Figure 5, we can again see associations of the words like satisfaction, trust and identification along with value congruence. From the figure we can also see that these constructs were found in the major areas like psychology, organization behavior, relationship management, and consumer behavior. In addition, studies like commitment and attitudes were seen as also connected to value congruence. This is evidenced by the smaller and fainter keyword in Figure 5. However, the three major clusters that are evident from vosviewer are cluster 1: Trust associated with value congruence; 2: Identification associated with value congruence; 3: Satisfaction associated with value congruence.
Network Analysis Of Publications
This section presents citation analysis on data extracted from csv files by focusing on counts of authors and publications. Vosviewer was used as an analysis tool for visualizing networks in this study. Figure 6 shows the association between the various authors and their co-authorships. This shows various authors who have co-authored research papers on value congruence. From the 15 most prolific authors, it is seen that Schawrtz S.H, Barni and Adkins C.L. have written co-authored research papers. The connection between the authors of different countries, who were involved together in contributing to the researches on value congruence, has been shown in Figure 7. As seen from Figure 7, the maximum co-authorship across countries has been with the authors from America. There were 95 connections between different countries, out of which American authors co-authored 95% with all authors across nations. From the connection between 31 countries, only counties which were not connected with America were Russia, Finland, Malaysia, Sweden, Belgium and Lithuania. The 15 most prolific authors and the number of their papers cited in value congruence context. These are the authors who have contributed most on subject of value congruence. The number of papers, which each of the top contributing author has contributed on the study of value congruence. It also shows the number of research papers which have cited these authors in their research work. From the table it is evident, that though Stacey D. has contributed only 5 papers in the area of value congruence, but his papers are cited in 1042 papers in value congruence context. This is followed by the papers of Siegrist M., which are cited by 746 papers. The h-index for each prolific author is also shown in the table. The h-index is a measure for evaluating the cumulative impact of an author's research output and its performance. The highest h-index of 95 is of Adkins C.L., followed by Knafo A. The papers which were most cited by other authors in value congruence studies. It is seen that most of the papers cited by other authors are not by prolific authors. Only prolific author Cable D.M., Siegrist M. & Cvetkovich G. is found to be cited majorly in other papers.
Citation Analysis
The citation index is an important indicator to determine the impact of a particular researcher. The influence of researcher is determined with the number of citation. On the basis of these indicators, the statistical results of influential authors and publications are presented in Tables 4 and 5, respectively (Citation data were as of July, 2020).
| Table 4 The 15 Authors With Most Papers On Value Congruence |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Authors | No. of Papers | Cited Byin Value Congruence Context | H-Index of papers |
| Cazier, J. A. | 10 | 97 | 5 |
| Knafo A. | 9 | 239 | 36 |
| Schawrtz S.H | 8 | 246 | 7 |
| Barni D | 7 | 69 | 5 |
| Nakayachi, K. | 7 | 56 | 4 |
| Vveinhardt, J. | 7 | 24 | 2 |
| Cuevas, E. | 6 | 51 | 4 |
| Cvetkovich, G. | 6 | 646 | 6 |
| Feather, N.T. | 6 | 69 | 6 |
| Leiter, M.P. | 6 | 196 | 28 |
| Adkins, C.L. | 5 | 577 | 95 |
| Gulbovaite, E. | 5 | 8 | 1 |
| Pillemer, K. | 5 | 99 | 5 |
| Siegrist, M. | 5 | 746 | 5 |
| Stacey, D. | 5 | 1042 | 5 |
| Table 5 The 20 Most Cited Papers Of Value Congruence Research |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Most Cited Paper | Trust | Identification | Satisfaction | Cited By |
| (Rich et al., 2010) | ? | 1201 | ||
| (Fry LW, 2003) | ? | 731 | ||
| (Verquer et al., 2003) | ? | 493 | ||
| (Edwards & Cable, 2009) | ? | ? | ? | 465 |
| (Siegrist et al., 2000) | ? | 451 | ||
| (Meglino et al., 1989) | ? | 432 | ||
| (Jung & Avolio, 2000) | ? | ? | 415 | |
| (Cable & Edwards, 2004) | ? | ? | 405 | |
| (Jehn, 1994) | ? | 402 | ||
| (Jehn et al., 1997) | ? | 342 | ||
| (Klein et al., 1997) | 302 | |||
| (Robert et al., 2000) | ? | 279 | ||
| (Khazanchi et al., 2007). | 259 | |||
| (Fry et al., 2005) | ? | 229 | ||
| (Wright & Pandey, 2008) | ? | 224 | ||
| (Kramer & Hafner, 1989) | ? | 216 | ||
| (Tuškej et al., 2013) | ? | 210 | ||
| (Moynihan & Pandey, 2008) | ? | 208 | ||
| (Erdogan et al., 2004). | ? | 198 | ||
| (Siegrist et al., 2003) | ? | 188 | ||
Table 4 shows the top 10 researches whose papers were most cited. Table 5 shows that top cited researches were done on understanding the influence of value congruence on trust, satisfaction and identification in the fields of psychology, organizational behavior, relationship management, and consumer behavior. From citation-based indicators, Cable D.M., Stacey D, Adkins C.L., Leiter M.P. were the most influential researchers. However, if we see from Table 5, we see the papers which are most cited belong to most of the authors who are not included in Figure 4 and Table 4. This indicated that most referenced papers, in the value congruence research, are not from prolific authors. Based on citation score, Table 5 shows the top 20 most cited papers. The most cited article was written by (Rich et al., 2010) and published in the Academy of Management Journal. This article has often been cited by publications in this field. The paper studied the mediating effect of job satisfaction and engagement on relationships between value congruence, self-evaluations, and performance indicators like: task performance and organizational citizenship behavior. Besides this article, the studies (Fry, 2003), (Verquer et al., 2003); (Edwards & Cable, 2009) also are highly cited. These papers discussed the importance of value congruence in generating empowered teams, job satisfaction, communication, trust and other softer aspects of human behavior. Similarly, other highly referred article (Siegrist et al., 2000), mentioned the importance of value congruence in social context and the impact on social trust. (Meglino et al., 1989) discussed the importance of values congruence in creating a positive corporate culture. (Jung & Avolio, 2000) showed that value congruence mediates transformational leadership and the follower performance.
Findings and Future Opportunities In Value Congruence Research
The results of keywords, titles and abstract analysis revealed few clusters on trust, satisfaction and identification in areas like psychological studies, organizational behavior studies, relationship management and consumer behavior studies, were identified (Berry, 1995). Relationship studies included understanding the impact of value congruence between teachers and students, grandparents and grandchildren, parents and children (Johnson et al., 2020). In organizational behavior studies (Olubiyi et al., 2019), the impact of value congruence on employee-organization relation, retention, performance, loyalty, burnout and employee engagement was studied. Studies revealed that Person-Organization congruence’s criteria during the selection process impacts the team work, positive relations and trust among team members. Many studies were undertaken on understanding the impact of value congruence of leaders and team members. Also studies on value congruence in the consumer behavioral aspect were seen in service, brands and products (Risman et al., 2016). Few studies were on understanding the impact of value congruence on purchase intention, customer brand identification (Cazier et al., 2017). Some studies tried to understand the relation between value congruence on tourist’s behavioral intention. Studies related to psychology (Schippers & Ziegler, 2019), too were prominently seen.
Proposed Model
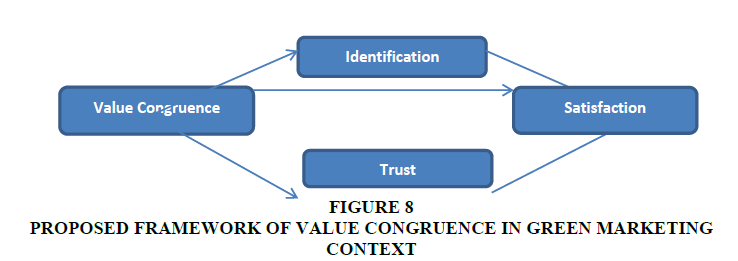
From the exploration of papers on value congruence in four major areas of studies, it was found that value congruence had influence on satisfaction, trust, and identification both positively and directly. Cazier et al. (2017) mentioned that value congruence is a significant constituent of perception and explained value congruence as “the amount of overlap between a consumer’s personal values and the values he perceives to exist in an organization”. Authors like stated that value congruity is important antecedent of brand identification. Congruence is a symbolic influencer of identification of consumer with a brand, and the consumers who perceive a brand as highly congruent with itself have increased levels of identification with the brand (Lam et al., 2013). Trust has been an important element of brand’s success. Cazier et al. (2017) argued that the intangible factors of value congruence have positive impact in generating trust among the customers. Value congruence has impact on some of the significant components of consumer-brand association, like satisfaction, loyalty and trust (Zhang & Bloemer, 2011). Social identity outlook of customer-brand association integrated brand identity and customer brand identification with value, trust and satisfaction in predicting brand loyalty (He et al., 2012). Edwards & Cable (2009) proved that value congruence is positively associated with identification and satisfaction. Most studies in social psychology mentioned that value congruence frequently predicts satisfaction in any relationship between two people (Byrne, 1997). In organizational behavior studies, researches indicated that value congruence has positive effect on job satisfaction of employees’ satisfaction (Arthur et al., 2006). From this we can propose a model on effects of value congruence on satisfaction, trust and identification.
Future Research Areas
The analysis of recent studies published between 2018 and 2020 was undertaken to understand the latest developments in value congruence and thereby determine future research directions. An interesting development in research has started focusing on value congruence in green behavior. The environmental impact of the individual’s actions has become recent trend in researches related to values and value congruence. The recent study on the employee’s green behavior (Wang et al., 2018) tried to understand the influence of green transformational leadership from value congruence perspective. Studies on green behavior was done with respect to consumers, to understand how green self-identity has a positive impact due to value congruence which further leads to green purchase behavior (Confente et al., 2020). In future, the proposed model (Figure 8) can be applied to study value congruence in context of green behavior. This can be a major breakthrough in green behavior studies, as past researches have shown the significance of understanding association of human values with pro-environmental behavior.
Conclusion
The systematic review of value congruence was undertaken using bibliometric methods. Initial bibliometric analysis captured the basic information about authors, year of publication, journals, citation score, the research titles, author and indexed keywords. To identify the number of authors in the network, the relationship between them and the most relevant authors in the network, network analysis was undertaken. It facilitated understanding of evolution of value congruence over years, determined recent research key areas, and laid foundation for further researches. The findings of the bibliometric analysis indicate that research related to value congruence started in 1966, gained momentum from 2004, and is still growing. From authors’ bibliometric analysis, it can be deduced that behavioral studies on value congruence, in relation to trust, satisfaction and identification were majorly studied in areas of psychology, organizational behavior, relationship management, and consumer behavior.
Limitations of the Study
Though interesting findings and implications were obtained from the methods used in the study, several limitations existed. First, while the Scopus and EBSCO host databases were used to collect publications on value congruence, some important papers not present in these two databases could have been missed. Also in future, a more detailed literature search including even full texts might be useful for more exploration.
Implications of the Study
This article can be considered as the first of kind of bibliometric study providing a comprehensive view on value congruence researches. The findings of this study can be helpful to academicians in determining future research opportunities in value congruence, especially in terms of applying the proposed model in green behavior context. This bibliometric analysis can assist other academic researchers to understand the various researches done in the area of value congruence and their recent developments. The results can provide significant insights to marketers and help them apply such analysis in their marketing strategies and decision making.
References
Adkins, C.L., Russell, C.J., & Werbel, J.D. (1994). Judgments of Fit in the Selection Process: The Role of Work Value Congruence. Personnel Psychology, 47(3), 605-623.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Arthur Jr, W., Bell, S.T., Villado, A.J., & Doverspike, D. (2006). The Use of Person-Organization Fit in Employment Decision Making: An Assessment of Its Criterion-Related Validity. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(4), 786.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Aoyagi, Midori. (1999). A Comparative Analysis of Citizen's Environmental Values and Pro-Environmental Behavior. Asian Geographer. 18, 123-134.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bao, Y.S.L.D., & Shay, S. Tzafrir (2012). Value Congruence in Organizations: Literature Review, Theoretical Perspectives, and Future Directions. Management of Journal, 8(48), 1-62.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Berry, L.L. (1995). Relationship Marketing of Services—Growing Interest, Emerging Perspectives. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 23(4), 236-245.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bitner, M.J. (1995). Building service relationships: it's all about promises. Journal of the Academy of marketing science, 23(4), 246-251.
Brashear, T.G., Boles, J.S., Bellenger, D.N., & Brooks, C.M. (2003). An Empirical Test of Trust-Building Processes and Outcomes in Sales Manager-Salesperson Relationships. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 31(2), 189.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bulmash, B. (2019). Green Anarchism: On Environmentalism and Hierarchical Domination. International Journal of Green Economics, 13(2), 139-145.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Byrne, D., Griffitt, W., & Stefaniak, D. (1967). Attraction and Similarity of Personality Characteristics. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 5(1), 82.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Byrne, D. (1997). An Overview (And Underview) Of Research and Theory within the Attraction Paradigm. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 14(3), 417-431.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cable, D.M., & Edwards, J.R. (2004). Complementary and Supplementary Fit: A Theoretical and Empirical Integration. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(5), 822.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cable, D.M., & Judge, T.A. (1997). Interviewers' Perceptions of Person–Organization Fit and Organizational Selection Decisions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 82(4), 546.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cazier, J., Shao, B., & Louis, R.S. (2017). Value Congruence, Trust, and Their Effects on Purchase Intention and Reservation Price. ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems (TMIS), 8(4), 1-28.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Confente, I., Scarpi, D., & Russo, I. (2020). Marketing a New Generation of Bio-Plastics Products for a Circular Economy: The Role of Green Self-Identity, Self-Congruity, and Perceived Value. Journal of Business Research, 112, 431-439.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Edwards, J.R., & Cable, D.M. (2009). The value of value Congruence. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(3), 654.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Elizur, D., & Sagie, A. (1999). Facets of Personal Values: A Structural Analysis of Life and Work Values. Applied Psychology, 48(1), 73-87.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Erdogan, B., Kraimer, M.L., & Liden, R.C. (2004). Work Value Congruence and Intrinsic Career Success: The Compensatory Roles of Leader?Member Exchange and Perceived Organizational Support. Personnel Psychology, 57(2), 305-332.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Feng, Y., Zhu, Q., & Lai, K.H. (2017). Corporate Social Responsibility for Supply Chain Management: A Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 158, 296-307.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Fry, L.W. (2003). Toward A Theory of Spiritual Leadership. The Leadership Quarterly, 14(6), 693-727.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Fry, L.W., Vitucci, S., & Cedillo, M. (2005). Spiritual Leadership and Army Transformation: Theory, Measurement, and Establishing a Baseline. The Leadership Quarterly, 16(5), 835-862.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gaunt, R. (2006). Couple Similarity and Marital Satisfaction: Are Similar Spouses Happier?. Journal of Personality, 74(5), 1401-1420.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gunden, C., Atis, E., & Salali, H.E. (2020). Investigating Consumers’ Green Values and Food?Related Behaviours in Turkey. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 44(1), 53-63.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gutman, J. (1982). A Means-End Chain Model Based on Consumer Categorization Processes. Journal of Marketing, 46(2), 60-72.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
He, H., Li, Y., & Harris, L. (2012). Social Identity Perspective on Brand Loyalty. Journal of Business Research, 65(5), 648-657.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jung, D.I., & Avolio, B.J. (2000). Opening the Black Box: An Experimental Investigation of the Mediating Effects of Trust and Value Congruence on Transformational and Transactional Leadership. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 21(8), 949-964.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kirmani, A., & Shiv, B. (1998). Effects of Source Congruity on Brand Attitudes and Beliefs: The Moderating Role of Issue?Relevant Elaboration. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 7(1), 25-47.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lee, S.A., & Jeong, M. (2014). Enhancing Online Brand Experiences: An Application of Congruity Theory. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 40, 49-58.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Morgan, R.M., & Hunt, S.D. (1994). The commitment-trust theory of relationship marketing. Journal of Marketing, 58(3), 20-38.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Meglino, B.M., Ravlin, E.C., & Adkins, C.L. (1989). A Work Values Approach to Corporate Culture: A Field Test of the Value Congruence Process and Its Relationship to Individual Outcomes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 74(3), 424.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jehn, K.A. (1994). Enhancing Effectiveness: An Investigation of Advantages and Disadvantages of Value?Based Intragroup Conflict. International Journal of Conflict Management, 5(3), 223–238.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jehn, K.A., Chadwick, C., & Thatcher, S.M. (1997). To Agree or not to Agree: The Effects of Value Congruence, Individual Demographic Dissimilarity, And Conflict on Workgroup Outcomes. International Journal of Conflict Management, 8, 287-305.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Johar, J.S., & Sirgy, M.J. (1991). Value-expressive versus Utilitarian Advertising Appeals: When and why to use which Appeal. Journal of Advertising, 20(3), 23-33.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Johnson, M.K., Mortimer, J.T., & Heckhausen, J. (2020). Work Value Transmission from Parents to Children: Early Socialization and Delayed Activation. Work and Occupations, 47(1), 83-119.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Khazanchi, S., Lewis, M.W., & Boyer, K.K. (2007). Innovation-supportive Culture: The Impact of Organizational Values on Process Innovation. Journal of Operations Management, 25(4), 871-884.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Klein, K.J., Lim, B.C., Saltz, J.L., & Mayer, D.M. (2004). How Do They Get There? An Examination of the Antecedents of Centrality In Team Networks. Academy of Management Journal, 47(6), 952-963.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kramer, M., & Hafner, L.P. (1989). Shared Values: Impact on Staff Nurse Job Satisfaction and Perceived Productivity. Nursing Research.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lam, S.K., Ahearne, M., Mullins, R., Hayati, B., & Schillewaert, N. (2013). Exploring the Dynamics of Antecedents to Consumer–Brand Identification with a New Brand. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 41(2), 234-252.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Moynihan, D.P., & Pandey, S.K. (2008). The Ties That Bind: Social Networks, Person-Organization Value Fit, and Turnover Intention. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 18(2), 205-227.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Olubiyi, O., Smiley, G., Luckel, H., & Melaragno, R. (2019). A Qualitative Case Study of Employee Turnover in Retail Business. Heliyon, 5(6), e01796.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Philipp-Muller, A., Wallace, L.E., Sawicki, V., Patton, K.M., & Wegener, D.T. (2020). Understanding When Similarity-Induced Affective Attraction Predicts Willingness to Affiliate: An Attitude Strength Perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 1919.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rich, B.L., Lepine, J.A., & Crawford, E.R. (2010). Job Engagement: Antecedents and Effects on Job Performance. Academy of Management Journal, 53(3), 617-635.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Risman, K.L., Erickson, R.J., & Diefendorff, J.M. (2016). The Impact of Person-Organization Fit on Nurse Job Satisfaction and Patient Care Quality. Applied Nursing Research, 31, 121-125.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Robert, C., Probst, T.M., Martocchio, J.J., Drasgow, F., & Lawler, J.J. (2000). Empowerment and Continuous Improvement in the United States, Mexico, Poland, and India: Predicting Fit on The Basis of the Dimensions of Power Distance and Individualism. Journal of Applied Psychology, 85(5), 643.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Schippers, M.C., & Ziegler, N. (2019). Life Crafting as a Way to Find Purpose and Meaning in Life. Frontiers in Psychology, 10.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Schwartz, S.H. (2012). An Overview of the Schwartz Theory of Basic Values. Online readings in Psychology and Culture, 2(1), 2307-0919.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sethi, R., Smith, D.C., & Park, C.W. (2001). Cross-Functional Product Development Teams, Creativity, and the Innovativeness of New Consumer Products. Journal of Marketing Research, 38(1), 73-85.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Siegrist, M., Cvetkovich, G., & Roth, C. (2000). Salient Value Similarity, Social Trust, and Risk/Benefit Perception. Risk Analysis, 20(3), 353-362.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Siegrist, M., Earle, T.C., & Gutscher, H. (2003). Test of a Trust and Confidence Model in the Applied Context of Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Risks. Risk Analysis: An International Journal, 23(4), 705-716.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Tuškej, U., Golob, U., & Podnar, K. (2013). The role of consumer–brand identification in building brand relationships. Journal of Business Research, 66(1), 53-59.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Verquer, M.L., Beehr, T.A., & Wagner, S.H. (2003). A Meta-Analysis of Relations between Person–Organization Fit and Work Attitudes. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 63(3), 473-489.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wang, X., Zhou, K., & Liu, W. (2018). Value Congruence: A Study of Green Transformational Leadership and Employee Green Behavior. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1946.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wright, B.E., & Pandey, S.K. (2008). Public Service Motivation and the Assumption of Person—Organization Fit: Testing the Mediating Effect of Value Congruence. Administration & Society, 40(5), 502-521.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zhang, Jing & Bloemer, Josée. (2011). Impact of Value Congruence on Affective Commitment: Examining the Moderating Effects. Journal of Service Management. 22, 160-182.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 23-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-22-10959; Editor assigned: 25-Jan-2022, PreQC No. AEJ-22-10959(PQ); Reviewed: 07-Feb-2022, QC No. AEJ-22-10959; Revised: 18-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-22-10959(R); Published: 23-Feb-2022.