Research Article: 2025 Vol: 28 Issue: 1S
A Study on the Challenges Faced By Women Entrepreneurs in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh
T. Devi, GITAM University, Vizag
B.Padma Narayan, SPMVV, Tirupati
A. Amala, SPMVV, Tirupati
Citation Information: Devi, T., Narayan, P., & Amala, A (2025) A Study on The Challenges Faced by Women Entrepreneurs in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 28(S1), 1-11.
Abstract
In India, gender disparity persists, with women often regarded as inferior to men, hindering their development across various spheres, particularly in entrepreneurship. Although the concept of women entrepreneurs in India has gained traction since the 1980s, thanks to economic liberalization, the journey towards gender equality in business remains challenging. Despite the rapid changes brought about by liberalization, privatization, globalization, and the IT revolution, women continue to face significant obstacles in establishing and growing businesses. While large corporations are predominantly led by men, women are carving out their niche in the business world through small and medium-sized enterprises, assuming roles as founders and leaders. Women's entrepreneurship not only contributes to a nation's economic growth but also enhances the financial well-being of individuals and communities. Despite governmental initiatives and incentives aimed at fostering women entrepreneurship, the growth rate remains modest. To address this issue, a study was conducted in Tirupati to identify the challenges faced by women entrepreneurs. A sample of 180 women entrepreneurs was surveyed using a questionnaire method. The results of the study shed light on the specific difficulties encountered by women entrepreneurs in Tirupati.
Keywords
Women, Entrepreneurship, Problems, Revolutions.
Introduction
To succeed in a dynamic global market and uphold excellence in entrepreneurship, it's crucial to nurture women entrepreneurs with the right traits and talents. Despite comprising half of India's population, women still face disparities compared to men in various areas. While women's literacy rates and employment opportunities have improved significantly over time, there's still progress to be made (Ansari, 2016). In recent years, there's been a notable surge in women's participation in diverse fields, including business and entrepreneurship. Both the Andhra Pradesh and Indian governments have actively promoted women's employment in industries, supported by financial institutions offering funding for new ventures (Brush, 1992). Consequently, women have been launching businesses, contributing to economic growth, and achieving remarkable success. Despite these strides, women in India continue to grapple with societal barriers that limit their full entrepreneurial potential. While there's been a shift towards recognizing and empowering women entrepreneurs, progress has been gradual. Efforts to advance women in entrepreneurship have been integrated into national plans, such as the Fifth Five Year Plan (1974–1978). Various laws and initiatives aimed at fostering female entrepreneurship are being implemented across India. However, cultural perceptions need to evolve to ensure women are granted the equal rights guaranteed by the Constitution. Additionally, addressing the issue of inadequate funding for policy initiatives is essential for accelerating progress towards gender equality in entrepreneurship (MeenuMaheshwari, 2015).
Objectives of the Women Entrepreneur
To present research and examine the main problems confront by women entrepreneurs. To provide remedial suggestions for overcoming these difficulties. Literature Review Singh and Raina (2013) examined the policies of the Indian government for women and detailed the main issues that women entrepreneurs in India face. The primary goal of the study was to ascertain the situation of Indian women entrepreneurs. According to the survey, women are becoming more and more entrepreneurs in modern India, particularly with MSMEs (Swarnalatha, 2016). Additionally, it noted that Indian women had carved out a place for themselves in a world dominated by men. It also demonstrated how well Indian women could handle both the responsibilities of the home and the demands at work.
Research on Issues Facing Women Entrepreneurs
Over the past 15 years, women entrepreneurs in the Andhra Pradesh (AP) area have witnessed a significant uptick in small-scale industries, indicating a high growth rate. This trend underscores a promising opportunity for further fostering the development of women entrepreneurs in the region (Thyagaraju, 2017). However, various challenges ranging from managerial and marketing issues to internal and external factors, as well as domestic concerns, have been identified and meticulously analysed to pinpoint their root causes. In addition to dissecting these challenges, the study also delves into the prospects for women entrepreneurs (Sugaraj, 2014). It scrutinizes factors such as their ability to outperform competitors and their overall success rate. By conducting this thorough analysis, researchers aim to shed light on the precise dynamics affecting women entrepreneurs in AP and provide valuable insights to inform strategies aimed at enhancing their growth and success (Sunil).
Problems of Women Entrepreneurship in India
Problem of Finance
Regardless of size, finance is regarded as the "life blood" of any company. Nevertheless, there are two explanations for the dearth of capital available to female business owners. First of all, most women do not own assets that can be used as collateral for loans from other lenders (Deshpande, 2020). Consequently, their access to external financing sources is limited. Second, banks prevent women from taking out credit and consider them to be less creditworthy since they believe that women can always quit their jobs. In situations like this, female business owners are compelled to depend on their own resources, if any, as well as modest, unavoidably combined loans from friends and family. Thus, women-owned enterprises fail due to a lack of capital (Vijayakumar, 2013).
Male-Dominated Society
In India, male chauvinism is still prevalent. The Indian constitution mentions gender equality. However, in reality, women are perceived as able—that is, as weak in every way. Women are regarded as the result of men's misgivings about their place in society and their capabilities. In short, women are not treated equally to males in the male-dominated Indian society. This thereby acts as a barrier to women's employment in the business world.
Lack of Raw Material
Lack of raw materials and other essential inputs is a problem for the majority of women-owned businesses. On the other hand, the exorbitant costs of raw materials add to this. One of the major problems that female entrepreneurs face is the lack of availability and scarcity of raw materials (SirumalarRajam, 2016). This is one of the factors contributing to the slow growth of women-owned businesses, and as a result, some women are expressing no interest in working in the innovative sector because it can be challenging to obtain raw materials from other sources at times. They wish to spend more money on transportation and the acquisition of raw materials. Many women worry about how they will adjust later if they spend a lot of money up front.
Tough Competition
The organizations that female entrepreneurs run are not designed to provide large sums of money for advertising and canvassing. As a result, they have to compete fiercely to sell their goods against both the organized sector and their male counterparts. The eventual outcome of this kind of competition is the closure of women-owned businesses (Baporikar, 2009).
Production Problems
The scarcity of raw materials is the most frequent problem in production that impacts women. The primary sources of production problems are a lack of machinery or equipment and a shortage of labour. Insufficient experience, insufficient training facilities, costly machinery requirements, and excessive labour and equipment expenses (Damwad, 2007).
Lack of Family Support
In India, taking care of the children and other family member’s falls primarily on the shoulders of the woman. Man only has a supporting role (Pettersson, 2012). A married lady must reconcile her obligations to her family and her career. Her whole focus on her family leaves little to no time or energy for her business. Wives' support and acceptance appear to be prerequisites for women entering the workforce. Consequently, women's involvement in commercial activities is positively influenced by their spouses' educational attainment and family history.
Lack of Education
The majority of women in India are still not literate. Illiteracy is the main factor contributing to socioeconomic problems. Due to their low educational attainment, women are less knowledgeable about business, technology, and market awareness. Furthermore, ignorant women are typically less driven to succeed. Consequently, a lack of knowledge makes it difficult for women to launch and run enterprises (Narendranath, 2020).
Marketing Problems
Women business owners encountered a number of challenges while promoting their products, including a bad shop location, limited transportation options, and fierce competition from more established and larger businesses (Dana, 2020).
Methodology
The main objective of the study is to find the problems faced by women entrepreneurs in the study area by using the questioner method (Franco, 2016). 180 Women entrepreneurs were chosen to collect the data. The primary data was collected by the questioner method, and the secondary data was collected from books, reports, journals, magazines, and websites. The results were tabulated and shown below.
Results and Discussion
The study was conducted on 180 women entrepreneurs engaged in different units. The required data were collected using the questioner method. The data were then analysed using various statistical methods. The results of the same are presented in this chapter.
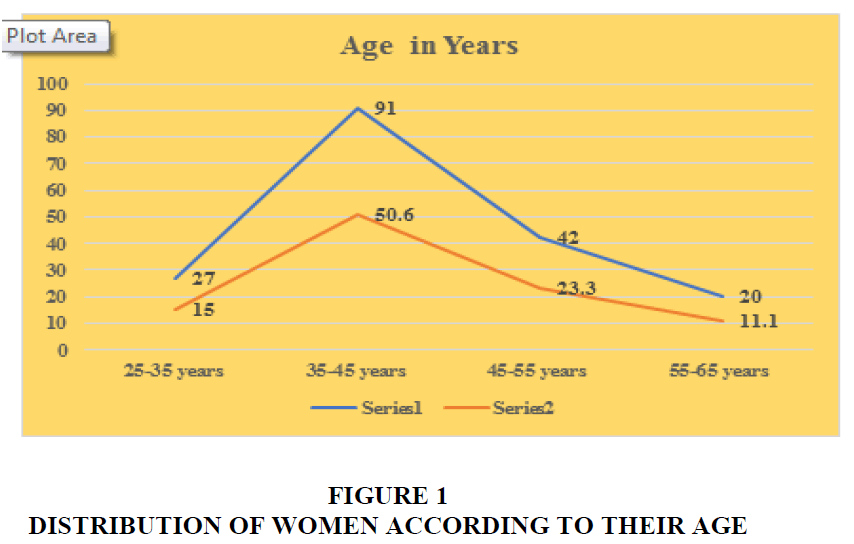
The Table 1 and Figure 1 indicates that the 15 percent of the women entrepreneurs were aged between25-35 years, 50.6 percent of the women entrepreneurs were 35-45 years, 23.3 percent of the women entrepreneurs were 55-65 years. Majority of the women entrepreneurs were aged between 35-45 in the selected area.
| Table 1 Distribution of Women According to their Age | ||||
| S. No | Variable | Classification | Number | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Age in years | 25-35 years | 27 | 15 |
| 35-45 years | 91 | 50.6 | ||
| 45-55 years | 42 | 23.3 | ||
| 55-65 years | 20 | 11.1 | ||
| Total | 180 | 100 | ||
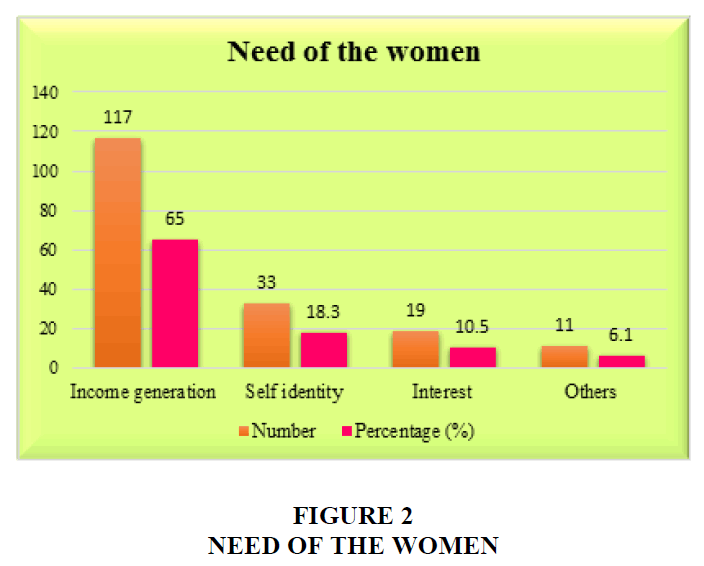
The Table 2 and Figure 2 connotes that the majority (65%) of the women entrepreneurs were started for income generation, 18.5 percent of them started for self- identity, 10.5 percent of the women started with interest and very less percent (6.1) were started with other purposes. Majority of the women want to support their families financially.
| Table 2 Need of the Women Entrepreneurs | |||
| S. No | Need of the women | Number | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Income generation | 117 | 65 |
| 2 | Self-identity | 33 | 18.3 |
| 3 | Interest | 19 | 10.5 |
| 4 | Others | 11 | 6.1 |
| Total | 180 | 100 | |
Table 3 shows that the 35 percent of the women entrepreneurs were a small labourer before starting their enterprise, 30 percent of the women were home maker, 18.3 percent of the were agricultural farmers and only 16.7 percent of the women were daily wage workers. Most of the women entrepreneurs were started their enterprise to earn more money to fulfil their family needs.
| Table 3 Status of the Women before Starting Enterprise | |||
| S. No | Women entrepreneurs | Number | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | A small labourer | 63 | 35 |
| 2 | Home maker | 54 | 30 |
| 3 | Farmer | 33 | 18.3 |
| 4 | Daily wage worker | 30 | 16.7 |
| Total | 180 | 100 | |
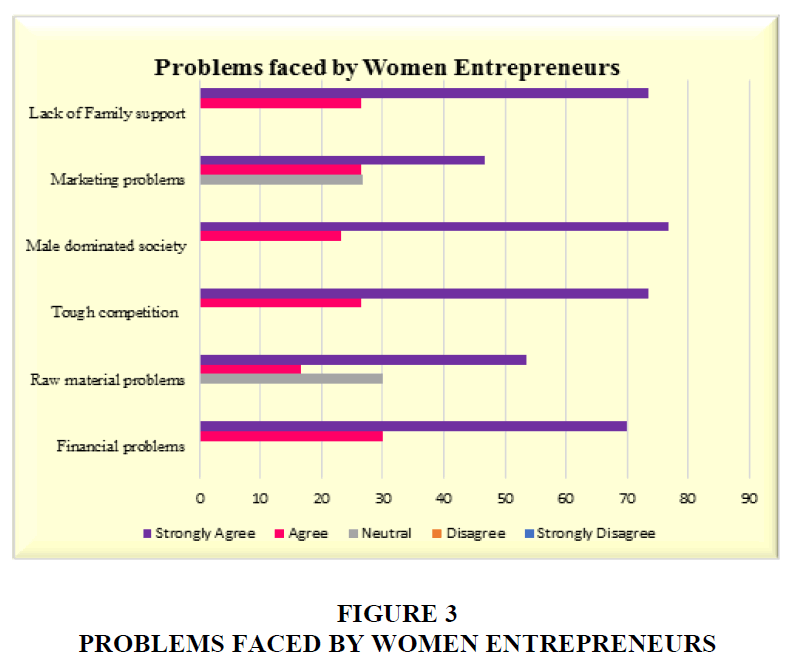
Table 4 and Figure 3 indicates that the majority of the women entrepreneurs were strongly agreed that they were faced financial, tough competition, male domination and lack of family support problems.
| Table 4 Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs | ||||
| S. No. | Problems faced by Women Entrepreneurs | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree |
| 1 | Financial problems | 90% | 30 | 70 |
| 2 | Raw material problems | 30 % | 16.7 | 53.3 |
| 3 | Tough competition | 85% | 26.7 | 73.3 |
| 4 | Male dominated society | 75% | 23.3 | 76.7 |
| 5 | Marketing problems | 26 % | 26.6 | 46.6 |
| 6 | Lack of Family support | 80% | 26.7 | 73.3 |
Opportunities for Women Entrepreneurs
Opportunities for women entrepreneurs abound in various sectors and industries, presenting avenues for growth, innovation, and success. Here are some key opportunities:
Technology and Innovation
The tech industry offers immense opportunities for women entrepreneurs, including software development, AI, fintech, and cybersecurity. Women can leverage their creativity and problem-solving skills to innovate in these fast-growing sectors.
E-commerce and Online Retail
With the rise of e-commerce platforms, there's a growing demand for women-led businesses in online retail. Opportunities exist in niche markets, artisanal products, and sustainable fashion, among others.
Health and Wellness
Women entrepreneurs can tap into the booming health and wellness industry by offering products and services focused on fitness, nutrition, mental health, and holistic wellness. This includes wellness coaching, organic skincare, and wellness retreats.
Sustainability and Green Technology
As environmental concerns grow, there's a rising demand for sustainable and eco-friendly solutions. Women entrepreneurs can capitalize on this trend by developing green technologies, renewable energy solutions, and sustainable fashion brands.
Education and Skill Development
Opportunities exist in the education sector for women entrepreneurs to offer tutoring services, online courses, and skill development programs. With the shift towards remote learning, there's a growing market for virtual educational resources.
Social Impact Ventures
Women entrepreneurs can make a difference by starting social impact ventures focused on addressing pressing social and environmental issues. This includes initiatives in areas such as education, healthcare, poverty alleviation, and women's empowerment.
Food and Beverage Industry
The food and beverage industry presents opportunities for women entrepreneurs to launch food start-ups, specialty food products, catering services, and innovative culinary experiences. This includes plant-based foods, artisanal beverages, and gourmet snacks.
Creative Industries
Women entrepreneurs can thrive in the creative industries, including design, fashion, art, and media. Opportunities exist for launching fashion labels, graphic design studios, art galleries, and digital media platforms.
This Figure 4 are just a few examples of the diverse opportunities available to women entrepreneurs. By leveraging their skills, expertise, and passion, women can carve out successful entrepreneurial ventures and contribute to economic growth and social change.
Suggestion to Promote Women’s Entrepreneurship
Popular belief suggests that every issue has at least one answer, and often two. For entrepreneurial women facing numerous challenges, it's crucial to address these issues head-on to foster growth and success in women's entrepreneurship.
Microfinancing Solutions
Microfinancing, increasingly prevalent in less developed nations, offers a promising avenue to alleviate the struggles faced by female entrepreneurs. By providing access to small loans and financial resources, microfinancing empowers women to start and grow their businesses.
Empowering Awareness Initiatives
Awareness initiatives should aim to educate and inform women about entrepreneurship. Access to necessary guidance and support when starting a new business is vital. By raising awareness and providing guidance, women can navigate the entrepreneurial landscape more effectively.
Skill Development and Training
Large-scale skill development initiatives, comprehensive technical training programs, and workshops can inspire individuals to pursue entrepreneurial endeavours. These initiatives equip women with the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed in business ventures.
Highlighting Entrepreneurial Benefits
Women should be encouraged to engage in entrepreneurship by highlighting the advantages and benefits. Emphasizing the opportunities for financial independence, creative expression, and personal fulfilment can motivate women to pursue entrepreneurial activities.
Promoting Literacy and Education
Recommendations to improve literacy rates among women include offering free education, scholarships, and encouragement to broaden their horizons. Access to training, real-world experience, and holistic personality development are essential for elevating the status of women entrepreneurs.
Addressing Gender-Specific Barriers
Gender-specific challenges, such as societal norms, access to resources, and work-life balance, must be identified and addressed. Measures to overcome these barriers may include providing mentorship programs, establishing support networks, and advocating for policy reforms that promote gender equality in entrepreneurship.
By implementing these proactive measures and addressing gender-specific barriers, we can create a more inclusive and supportive environment for women entrepreneurs to thrive and contribute to economic growth and development.
Conclusion
The interconnection between women's entrepreneurship, poverty alleviation, and economic advancement is unmistakable. Our first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, once said, "When women advance, the family, the village, and the country also advance." Despite the increasing recognition of female entrepreneurs, their journey towards success remains arduous. Transitioning from a stay-at-home mother to a thriving business owner is no simple feat. Similarly, sustaining and expanding a business presents ongoing challenges for women. It requires continual growth, adaptation, and the ability to overcome obstacles in their chosen field. To succeed, a woman entrepreneur must leverage her experiences, evolve, and confront the hurdles in her path. Every opportunity must be seized to mitigate weaknesses and creatively harness strengths to overcome threats. This serves as a guiding principle as she establishes and expands her enterprise. Women are enthusiastic about launching their ventures and contributing to their country's development. There's growing recognition of their significance, and efforts are underway to foster female entrepreneurship. The current imperative is for entrepreneurship to flourish once more. Women entrepreneurs need to be equipped with the requisite entrepreneurial attributes and skills to thrive in the local economy and navigate shifting trends and competitive global markets.
References
Ansari, D. A. (2016). Women entrepreneurship in India. AEIJST, 4(4), 1-14.
Baporikar, N. (2009). Entrepreneurship Development and project management (text and cases). Himalaya Publishing House.
Brush, C. G. (1992). Research on women business owners: Past trends, a new perspective and future directions. Entrepreneurship theory and practice, 16(4), 5-30.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dana, L. P., Sharma, N., & Acharya, S. R. (Eds.). (2020). Organising entrepreneurship and MSMEs across India (Vol. 11). World Scientific.
Deshpande, S., & Sethi, S. (2009). Women entrepreneurship in India. International Research Journal, 2(9), 13-17.
Franco, C. E., & Selvakumar, S. (2016). Entrepreneurship—A Key for Women Empowerment. Int. J. Res, 4, 45-51.
MeenuMaheshwari, M. P., & PriyaSodani, M. (2015). Women Entrepreneurship-A Literature Review. IOSR Journal of Business and management, 17(2), 6-13.
Pettersson, K. (2012). Supporting women’s entrepreneurship in Nordic sparsely populated areas. Stockholm, Sweden.
SirumalarRajam, P. M., & Soundararaja, D. K. (2016). Problems faced by women entrepreneurs. International Journal of Research–GRANTHAALAYAH, 4.
Sugaraj, J. M., & Salve, P. S. (2014). A study of women entrepreneurship and their problems in the development in Western Maharashtra. IOSR Journal of Economics and Finance, 3(2), 79-83.
Swarnalatha, K., & Anuradha, R. K. (2016). Women entrepreneurship in India-problems and prospects. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), 5(3), 1289-1291.
Thyagaraju, D. N. (2017). “WOMEN ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVOLOPMENT PRACTICES. IN INDIA-A REVIEW” Original Research Paper, Assistant Professor, Department of commerce, Sri ABR Government Degree College, Repalle, GUNTUR.
Vijayakumar, A., & Jayachitra, S. (2013). Women entrepreneurs in India-Emerging issues and challenges. International Journal of development research, 3(4), 12-17.
Received: 27-Sep-2024, Manuscript No. AJEE-24-15506; Editor assigned: 30-Sep-2024, PreQC No. AJEE-24-15506(PQ); Reviewed: 08-Oct- 2024, QC No. AJEE-24-15506; Revised: 21-Oct-2025, Manuscript No.AJEE-24-15506(R); Published: 30-Oct-2025