Review Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 5
A Study of Impact of Gender on Sensory Marketing Activities In Hotel Industry
Bhatt Anand Y, Devi Ahilya University
Sharma Prachi, Devi Ahilya University
Citation Information: Anand, Y.B., & Sharma, P. (2022 A study of impact of gender on sensory marketing activities in hotel industry. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(5), 1-6.
Abstract
After 1970s, every year a new strategy was evolved and developed and still this evolution is witnessed in the business practices. Nowadays, the consumers seem to be fond of innovative and new products which they want to experience. The concept of sensory branding is quite new in the area of marketing. There have been some studies that have been focused on sensory branding and its significance and how the environment stimulus and the customer in emotional states are related but most of the researchers will limited either to the customers response or towards whether or not they are aware about the sensory marketing techniques. There is no reported research on sensory marketing techniques and its effect on customers of Pune region in particular. This study has been undertaken looking at the existing gap in the body of knowledge. The aim of the paper was to find the impact of gender on Sensory marketing activities.
Keywords
Sensory Marketing Activities, Hotel Industry, Business Practices, Consumers.
Introduction
Human wants are unlimited and these wants are satisfied by the various products that are available either naturally or by the market that is created by the different manufacturers and producers of products. Definition of a product as given by (Philip Kotler, 2008) can be stated as product is an offering that can satisfy a need or want. It is presented in terms of goods or services and even experiences and events also person, places, properties, organizations, information and ideas. Modern marketing has very deep roots in the history and needs to be studied very deeply. It is said that marketing is just as old as a human being. The origin of marketing can be understood as early as the eastern civilizations of the third millennium BC. The archaeologists claim that the barter system of trade which previously in the ancient illiterate tribes is the first form of the modern trade. When the barter exchange activity started functioning marketing was already born but the first light of the day was in the 20th century.
In 2004 marketing definition was changed as marketing is a hierarchical capacity and many procedures for making conveying and conveying and incentive to clients and also to be thought for as an activity that would seat clients connection in manners that advantage the association and its partners This definition brought about lot of exchanges in various articles with contradicting views. It is found that the largest portion of marketing budget is generally spent another advertisement because the consumers like this advertisement as they offer free entertainment it is also very important to note that spending too much on advertising campaigns have given results where there has been increased effectiveness because the consumers are not ready to accept the advertisements as they do not stimulate their sensory organs (Lindstrom, 2008). Consumer gets many advertising messages from the various stimuli that he received from the environment the consumers are also given different other means for brand recognition where there required to identify the brand and create a difference (North & Enslin, 2004). In simple words there is actually a need to develop a new and a different method where consumer’s minds can be stimulated as this method has to be different from the traditional tools.
Literature Review
Concept of sensory marketing is based on the idea that human being is destined to save written in find the mind where every of the five senses are included so by going outside the conventional marketing strategies the marketing media started focusing on site and branched came up with more longer and passionate association with the buyers.
Bitner (1992) Sensory marketing is a way to improve the service quality and alo increase the income of the restaurant. This has been proven by the various researches that are done in the previous times. The effect of sensory marketing is evident because of the effect it creates on the customers.
Lindstrom (2008) emphasized that the senses can be used to increase the relationship with the customers as the different senses can help in getting strong emotional Relationship with the customers as it is understood that the different sensors that a human being has can get different kind of strong emotional responses from the consumers. When we talk about both the smell and the sound they are deeply connected to the memory and a consumer can easily collect these to be very similar from A past experience that can make him feel better and nostalgic. Finally a brand can always create a strong bond with the consumers by using these five senses to increase the loyalty and have a long term relationship. A very effective way to increase the impact of sound would be to use a different type of a sound in logo. This means that a certain sound aur melody can be associated with the company logo and then this will help the consumers reconnect the brand as soon as they hear the sound.
Annica Isacsson, (2009) said that there are various types of marketing techniques can that can be used to produce the consumers to influence is buying behavior. When we talk about multi sensory branding it actually means to involve all the bodily sense is to promote the product amongst the potential consumers. He also describe the use of a proper design and using proper interaction between all the sensors to investigate the consumers relationship with the brand and hence I try to still in the brand as strong as it can be.
Pines, 1995 said that whatever we see smell feel aur here or even taste involves the use of more than billion of nerves that send messages as feedbacks to our brains and then these signals help us to correlate between the five senses and the brand immediately.
Krishna (2012) showcases sensor in marketing as a marketing activities that draws in the customer's faculties and influences that practices he said that marketing is not what it used to be a stop in spite of the fact that more and more marketing assets are been included with the buyer's there are shoppers with a desire for advertisements and free amusement shopping. More attractive illustrations and quick alterations are required so that the customers can be increased for a greater period of time and this engagement need to continue also. Something new was required and this needs to be developed soon and in the quest for the something new going out of the normal and the most publishers model of marketing was the main requirement. It was required to understand what really charms the customer in ordinary circumstances. Sensory marketing means widening the scope of marketing and connecting with the purchaser senses and influence the decision making. From an administrative view point sensory marketing can be used to make triggers that characterize the impression of the customer about certain ideas about the product and brand and character.
Research Objectives
To study the Impact of gender on Sensory marketing activities in hotel industry.
Research Methodology
The study relies mainly on the data gathered from a Survey. The selection of a survey methodology in the form of a written questionnaire (appendix No 1) was used to serve the objective.Data was collected with the help of primary survey as well as secondary sources. The secondary data was collected through various resources like hand books and also through various journals and books. The primary data was collected with the help of a close ended, structured questionnaire designed on differential scale for the current and prospective customers.
Results and Discussion
The survey resulted in the following data collection.
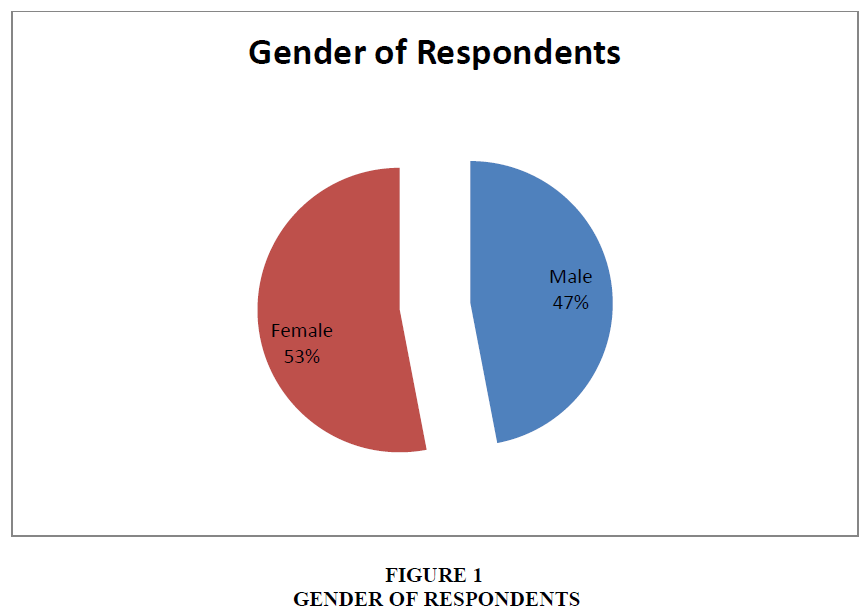
Gender of Respondents
The above figure 1 represents the gender of respondents. It is clear from the graph that out of 860 respondents, 47% i.e. 404 are male and 53% i.e. 456 are females (Tables 1-4).
| Table 1 Gender of Respondents | |
| Gender | No. of Respondents |
| Male | 404 |
| Female | 456 |
| Total | 860 |
| Table 2 Anova for Sight | |||||
| SIGHT | |||||
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| Between Groups | 515.012 | 1 | 515.012 | 18.494 | .000 |
| Within Groups | 23893.308 | 858 | 27.848 | ||
| Total | 24408.321 | 859 | |||
| Table 3 F Ratio for Smell | ||||||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval for Mean | ||
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| 1 | 404 | 12.59 | 5.873 | .292 | 12.02 | 13.17 |
| 2 | 456 | 10.94 | 4.869 | .228 | 10.49 | 11.39 |
| Total | 860 | 11.72 | 5.424 | .185 | 11.35 | 12.08 |
| Table 4 Anova for Hearing | |||||
| HEARING | |||||
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| Between Groups | 40.866 | 1 | 40.866 | 1.739 | .188 |
| Within Groups | 20158.767 | 858 | 23.495 | ||
| Total | 20199.633 | 859 | |||
Ho1: There is no significant relationship between atmosphere and gender of consumers.
Post hoc tests are not performed for Sight because there are fewer than three groups. It is found that F-ratio value is equal to 20.403. It is statistical significant at 5% level of significance. Given that p<0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between atmosphere of restaurant and gender of a customer.
Ho2: There is no significant relationship between gender and frequency of visit.
Post hoc tests are not performed for smell because there are fewer than three groups. It is found that F-ratio value is equal to 20.403. It is statistical significant at 5% level of significance. Given that p<0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between smell of restaurant and gender of a customer.
Ho3: There is no significant relationship between music and gender of consumers who visit hotels.
Post hoc tests are not performed for music because there are fewer than three groups. It is found that F-ratio value is equal to 20.403. It is statistical significant at 5% level of significance. Given that p<0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between music played at a restaurant and gender of a customer.
To understand the relationship between Comfort and gender of the consumers following hypothesis was formed
Ho4c: There is no significant relationship between Comfort and gender of the consumers
Post hoc tests are not performed for music because there are fewer than three groups. It is found that F-ratio value is equal to 20.403. It is statistical significant at 5% level of significance. Given that p<0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between comfort offered at a hotel or restaurant and gender of a customer.
Ho5: There is no significant relationship between taste and gender of consumers.
Post hoc tests are not performed for music because there are fewer than three groups. It is found that F-ratio value is equal to 20.403. It is statistical significant at 5% level of significance. Given that p<0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between taste offered at a hotel or restaurant and gender of a customer (Tables 5 and 6).
| Table 5 Anova for Touch | |||||
| TOUCH | |||||
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| Between Groups | 208.063 | 1 | 208.063 | 7.504 | .006 |
| Within Groups | 23789.239 | 858 | 27.726 | ||
| Total | 23997.302 | 859 | |||
| Table 6 Anova for Gender | |||||
| TASTE | |||||
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| Between Groups | 980.978 | 1 | 980.978 | 26.173 | .000 |
| Within Groups | 32158.762 | 858 | 37.481 | ||
| Total | 33139.740 | 859 | |||
When we talk about brand image there are a lot of things that contribute in making a company's brand image positive that would in turn attract the customers towards the product. In hotel industry also a lot of radical changes have taken place in which in the way in which the marketing was done and assumed. Customer today wants to live experiences through its consumption. The market your noticed that sensory marketing had become the new adage that need to be followed to increase the market cap. The very reason sensory market came into existence was to affect the can the consumers emotions memories choices preferences and the various buying behaviors.
Multisensory marketing or sensory marketing as we call is a new trend in hotel industry its full potential is yet to be harnessed by the marketers. There are many studies that have been conducted in the past to understand the sensory marketing and how it can be implemented in hotel industry this study also aimed at finding out the impact of these sensors on the choice of hotels and restaurants amongst the it was found that there existed a strong relationship between all the five senses and it was found that there existed a strong relationship between all the five senses and the choice of hotel or restaurant hence we may say that it is very important for a market year or a manager of a hotel to develop its marketing strategies in such a way that these sensors can be stimulated and there would be repeat customers in his hotels.
Conclusion
It was understood that in hotel industry also whenever a customer revisit a hotel there is a past experience that he wants to relive. The above hypothesis testing proves that there exist a strong relationship between the five senses of human being and his choice of particular restaurant or a hotel that he wishes to reselect time and again. A restaurant owner or an hotelier needs to understand the importance of these five senses and must now make this a part of his marketing strategy so that he can increase the customer’s visits and in a way help his business grow.
References
Bitner, M. J. (1992). Servicescapes: The impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees. Journal of marketing, 56(2), 57-71.
Isacsson, A., Alakoski, L., & Bäck, A. (2009). Using multiple senses in tourism marketing: The Helsinki expert, Eckero line and Linnanmaki Amusement Park cases.
Kotler, P and Armstrong, G. 2001. Principles of marketing. 9thedition. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. (2011). Marketing management 14th edition. prentice Hall.
Krishna, A. (2012). An integrative review of sensory marketing: Engaging the senses to affect perception, judgment and behavior. Journal of consumer psychology, 22(3), 332-351.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross ref
Lindstrom, M. (2008). Brand sense: Sensory secrets behind the stuff we buy. Simon and Schuster.
North, E., & Enslin, C. (2004). Building brands through alternative brand contact communications: organisational, marketing and management communication. Communicatio: South African Journal of Communication Theory and Research, 30(1), 151-165.
Pines, M. (1995). Seeing, hearing, and smelling the world: new findings help scientists make sense of our senses. Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Received: 13-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12172; Editor assigned: 16-Jun-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-12172(PQ); Reviewed: 30-Jun-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-12172; Revised: 04-July-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12172(R); Published: 06-July-2022