Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 4S
A Proposed Framework for Classifying Preventive and Detective Fraud Controls
Abdullah Mohammad Al-Zoubi, Al al-Bayt University
Abstract
Fraud costs investors, society and companies a number of millions, even billions of dollars, and this points out an essential value to fight fraud, this reflects on adopting methods or controls, etc..,basically, this study aim to propose a framework to classify fraud detection and prevention controls, in order to stress the importance of the availability and accessibility as well as, to set out a clue which builds up a strong control systems, the Analytical descriptive approach was utilized to fulfill this objective, which contains literature reviews to collect controls specialized in fraud detection and prevention and go over them, along with finding a mutual linkage to classify it, it’s been accessed and finding out a common bond to be classified as well as it has been relied on the nature of the classification, and a framework has been proposed consists of four main controls: organizational controls, activity and event controls, developmental controls and security and protection controls, and these controls were included in four fields of study tool, a questionnaire to obtain a sample study on the possibility of adopting this classification or not, and were distributed to (234) internal and external auditor, The study found to the possibility of adopting the proposed framework, which combines previous four, it was recommending the need to adopt these controls companies to contribute to builds up a strong control systems to prevent and detect fraud operations and operations irregular and illegal events.
Keywords
Fraud, Fraud controls, Proposed Framework
Introduction
In light of the enormous technological developments that the world is witnessing changes growing on the working methods and data processing and acknowledge them, moreover that has helped many of individuals to commit crimes and internal frauds were or external to obtain benefits which is not of their rights, where the Australian Institute of crimes reported in his report for the year 2020 that The total losses of internal fraud amounted to (2775917) dollars and the losses of external fraud was (146876658) dollars (Teunissen et al., 2020) For a total of (149652575) dollars, as stated in the report Wc's Global Economic Crime and Fraud Survey For the year 2020 that 47% of companies have been for my business data fraud during the 24 months ago, in addition of this said Bekiaris & Papachristou (2017) that fraud costs the economy, companies, investors and society more than (3) trillion dollars every year. In addition, he mentioned Burzynska & Jablonska (2018) on the status of the weakness in controls preventive that would reduce the probability of occurrence of fraud, and that the companies do not have enough regulations in references to suggest and collect that allows prevention and detection rapid for fraud, and this is what stopped the researcher to see the available regulations in the literature and studies collected a proposal for a classification for it to be included in a general framework to facilitate dealing with it, as the nature of the controls in the classification was relied upon, and it was grouped into four classifications, which are: controls of their organizational nature, controls of their developmental nature, controls of their security and protection nature and finally controls of their nature activities and events according to the following form:
To make it clear; These controls considered to be all the procedures, policies, restrictions and population and divisions that are used to prevent and detect fraud, such as organizational controls that are related to the regulatory status of the company, for instance the organizational structure and the segregation of duties.., including development controls relating to the amendment to the mechanism of action or change or training, such as adjusted risk assessment and training programs for staff, including security and protection controls related to encryption, design and operating systems, for instance the design of accurate documents and records to obtain accurate data and encrypt data stored, including controls of activities and events that relate to practical steps to complete the work, such as restricting the activities of Personnel and risk management steps.
And this study is of particular importance in an attempt to provide a guide for those interested companies to guide the building systems strong oversight to control fraud and stop the bleeding for amounts that are losing companies as a result of frauds that are exposed as noted above, according to the classification contained in Figure (1).
Theory and Literature Review
The Concept of Fraud
The definitions are various which addressed the Fraud term; it's defined as obtaining a benefit dishonestly, or causing a loss by deception or any other ways. While.... (Attorney General's Department, 2017) defined fraud as the means which a person uses to obtain a benefit unfairly, from another person or concerns others.
Romney & Steinbart (2018) defined fraud as the means used by the person in order to get an unfair advantage from someone else or another person, The Institute of Internal Auditors Inc. (IIA) (2009) defined fraud as a wide group of irregularities or irregular illegal events, which is marked by deception or deliberate distortion.
as well, if we add the word corporate before the word fraud so it’d become (Corporate Fraud) Which is defined as a breach of trust where the administration doesn’t behave in favor of their owners, however, it acts opportunistically in order to benefit certain individuals from the owners of interest at the expense of others (Desai, 2020).
Through the previous presentation we extracted that the fraud takes the form of the offense or breach of confidence or action is unlawful or mismatch of the information produced with the regulations established by the order of misrepresentation or deception to reach the overall objective, which is the way to gain advantage or benefit given to non - owner.
Fraud Sections
Fraud has been Divided into Two Main Parts
1. Internal fraud, known as a fraud committed by officials against an entity. Fraud runs out by an official in the company as a result of non - compliance for the law (Attorney General's Department, 2017) Also known as a process of fraud that is committed inside the company or by the company itself (Donning et al., 2019).
2. External fraud, known as the fraud that is complementing from outside the company or any of the parties to external such as customers or providers of services (Service Providers) Or groups of criminal pain system Meh, and T text H companies to pay attention and attention to the risks of fraud pain contracts d (e Complex Fraud) Which is the collusion between its officials (internal parties) and the external parties (Attorney General's Department, 2017).
The implementer sets the previous sections apart. If the implementation was inside the company so it’s called internal fraud, on the other hand if the performance of fraud happened outside the company so this is what we call external fraud.
Literature Review
In this section we are going to review the Literature Review that mentioned the controls to prevent and detect fraud where it has been taken in consideration for including a comprehensive number of controls in addition to classifying the controls the Romney and Steinbart book mentioned.
The study Donning, et al., (2019) introduced three different statistical arithmetical methods to detect financial fraud represented in First: data mining: which is sorting data into major groups in order to determine the patterns and making connections to detect fraud. Second: Meta Learning: it is a form of automated learning where automated learning algorithms are applied on descriptive data, Third: Machine learning: Where the algorithms detect patterns in big data and it can be classified into supervised machine learning and unsupervised machine learning, the supervised machine learning is considered to be the most commonly used method between those two, these two method differ in how they use the machine learning algorithms to determine the patterns in big data, the un-supervised machine learning works on determining processes and complicated patterns without any guidance or human interference which helps in solving problems that humans cannot solve.
Gibson (2018) study added many fraud preventive and detective tactics represented in evaluating the risks of fraud, fraud risks record, behavior methods, training on evaluating fraud, a policy and a plan to fight fraud, reviewing the internal control, the study Burzynska & Jablonska (2018) showed the increase interest between Entrepreneurs in executing objective independent internal audit, where it is considered the essence of good management and has a role in detecting different kinds of fraud, it also showed its growing role in the process of managing risks, the study Othman, et al., (2015) also reached a number of detecting and preventing fraud and they are: enforcing the audit commissions, improving the internal control, applying the policy of reporting fraud, forensic accounting, the study Sahiti & Bektashi (2015) also mentioned two controls to detect fraud and they are: regression which represents using the financial variables and the multivariable logistic regression. Second: to determine the connection between the factors related to fraud in financial data, the Decision Tree Which classifies notes into groups and selects many mutually exclusive features to share the best sample, as the study Banarescu (2015) determined the method of data analysis as a system to prevent and detect fraud where contains more than 24 types of analysis, and pointed to two types of classical analysis, namely: operational analysis and strategic analysis, study Lartey, et al., (2020) showed that the most common discovery regulations are the reconciliation of bank statements in which the discovery of contradictions happens through it, and added other regulations such as separation of duties for individuals and documentation appropriate for the assets purchased and updating records with clear details about the book values. The study Christ, et al., (2012) mentioned two types of regulations, First: controls preventive which represents adherence by the independence of the staff through the prohibition of the behavior of certain, such as not allowing employees to enter data or make a payment that has not allowed them to do so, II: controls discovery which provides immediate or late responses as an alert activation when entering payments in excess of a specified amount, the study Salihu & Jafari (2020) specified that the (implementation of whistle-blower policy)It is considered one of the anti-corruption methods that are listed under one of the prevention, detection and penal controls, and a study Yuniarti (2017) added that spreading awareness about anti-fraud among all parties of the company, such as managers and employees, has a significant and positive impact on preventing fraud, as by a study Manasseh, et al., (2015) indicated such things that affect positively in fraud prevention: the separation of duties, authority on transactions and control of sports and control of operational activity, The study Muritala, et al., (2017) recommended to promote and develop systems of internal control as well, the regulatory and supervisory associations improve their supervision by using all the available tools to investigate in an appropriate way in fraudulent operations. In order to fraudulent practices.
Study Badejo, et al., (2017) determined applying job applicants to test their ethics and integrity before hiring will reduce fraud. However, the study, Rahman & Anwar (2014) added that the password is one of the oldest means of defenses; nevertheless it remains the most effective and efficient way in control access as a way of preventing and detecting fraud, also, by changing the user password regularly and requesting password before access to jobs.
With regard to the Fraud prevention and detection controls, mentioned by Romney & Steinbart (2018), they have classified it into four categories, namely: decrease the possibility of fraud as little as possible, in order to increase the difficulty in committing fraud, as well, improve methods of detecting fraud, and finally reduce the losses of fraud, where they mentioned through these classifications a number of regulations, some of which are compatible and differ from what others are mentioned in the above studies, and as a result of the large number of regulations that Romney and Steinbart have mentioned In order to avoid its recurrence, it was not included here, and it was included in the study tool (the questionnaire) directly.
Methodology and Hypotheses
The fraud prevention and detection controls that were mentioned by both Romney & Steinbart (2018) and the controls are dealt with in the Literature review have been relying on them in the preparation of a tool to measure the study, a questionnaire, where the inclusion of these controls within the proposed classification which is based on the collection of controls that converge or are similar in nature with each other, and drawn four controls within the fields The next four:
The First Field: Organizational controls to prevent and detect fraud.
The Second Field: Developmental controls to prevent and detect fraud.
The Third Field: Security and Protection controls to prevent and detect fraud.
The Fourth Field: Activities and Events controls to prevent and detect fraud.
According to the above, the study hypotheses were formulated with a main hypothesis, which is:
H0: It’s Difficult to propose a framework for the classification of controls to prevent and detect fraud:
H0.1: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of Organizational controls to prevent and detect fraud.
H0.2: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of developmental controls to prevent and detect fraud.
H0.3: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of security and protection controls to prevent and detect fraud.
H0.4: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of activity and event controls to prevent and detect fraud.
To collect data on hypothesis testing to determine the possibility or difficulty of proposing classification for the four regulations, the questionnaire was distributed to (234) internal and external auditors out of the study population of (555) auditors, and the sample number is considered appropriate to its population based on the sample size table given to the size of the population (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016). Where the population was divided into: External Auditors who have the Jordan Certified Public Accountants (JCPA) Their number is (438) auditors (the Jordanian Association of Certified Public Accountants, 2020), and the number of internal auditors is approximately (117) who have the Certified Internal Auditor (CIA), Where he relied on them because they are the most understanding and informed on the systems for the control of internal and best able to identify useful controls in the prevention and detection of fraud and the possibility of classification.
Results of the Study
The Study Results were Divided into Many Parts as Shown Below:
Part One: The Primary Tests to Show the Possibility of Approving the Study Tool and its Data.
Cronbachs Alpha Test
The range of consistency for the tests internal paragraphs, the Cronbachs alpha was used to determine the range of internal consistency for the Questionnaires internal paragraphs the review indicated a solid consistency for the Questionnaires paragraphs for each scale a part and for all parts combined as well as shown in table (1):
| Table 1 Consequences Cronbachs Alpha |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testing Fields | Fields | Combined Controls | ||||||||
| Organizational controls | activities and events Controls | Developmental controls | Security and protection controls | |||||||
| The ratio | Number of paragraphs | The ratio | Number of paragraphs | The ratio | Number of paragraphs | The ratio | Number of paragraphs | The ratio | Number of paragraphs | |
| Cronbach's alpha | 0.738 | 17 | 0.805 | 13 | 0.827 | 15th | 0.728 | 18 | 0.928 | 63 |
Normal Distribution Test
The Kolmogorov Smirnov normal distribution test was used; the analysis results indicated that the study’s data is distributed normally by exceeding the tests 5% as show in table (2)
| Table 2 Results Of Normal Distribution Kolmogorov Smirnov For Fields Of Study |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testing | Fields | |||
| Organizational controls | activities and events Controls | Developmental controls | Security and protection controls | |
| Kolmogorov Smirnov | 0.385 | 0.432 | 0.278 | 0.301 |
Part Two: The Characteristics of the Study’s Specimen (Sample)
Too describes the approved study specimen (sample) used for collecting the primary data and stating its characteristics its description was divided into six main elements as shown in the next table 3:
| Table 3 Frequencies and Percentages of the Study Sample Characteristics |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Statement | Frequencies | Percentages | Accumulated percentages |
| Academic Qualification | |||
| Bachelor | 172 | 73.5 | 73.5 |
| Master | 54 | 23.1 | 96.6 |
| PhD | 8 | 3.4 | 100 |
| The total | 234 | 100% | |
| Experience | |||
| less than 3 Years | 18 | 7.7 | 7.7 |
| From 3 to me 6 Years | 18 | 7.7 | 15.4 |
| From 6 to me 9 Years | 72 | 30.8 | 46.2 |
| more than 9 Years | 126 | 53.8 | 100 |
| The total | 234 | 100% | |
| Professional certifications | |||
| Jordan Certified Public Accountant (JCPA) | 144 | 61.5 | 61.5 |
| Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) | 18 | 7.7 | 69. 20 |
| without Certified | 72 | 30.8 | 100 |
| The total | 234 | 100% | |
| The nature of work for | |||
| Internal Auditor | 90 | 38.5 | 38.5 |
| External auditor | 144 | 61.5 | 100 |
| The total | 234 | The total | 234 |
| M was Uncle 's | |||
| Inside Jordan | 220 | 94 | 94 |
| Outside Jordan | 14 | 6 | 100 |
| The total | 234 | 100% | |
| Have you taken courses in fraud? | |||
| Yeah | 225 | 96.2 | 96.2 |
| No | 9 | 3.8 | 100 |
| The total | 234 | 100% | |
The previous table shows how the sample presents the study populations from many aspects:
1. Specimens (234 Auditor) formed a percentage of 44.162% of its population (117+438 Auditor) it's considered enough relying on the table of the specimens size depending on the population's size ( Sekaran & Bougie, 2016).
2. The distribution of the specimen on all population characteristics and not being narrowed on certain categories or specified characteristics.
3. The samples possess the experience powered with the nature of their work and professional certificates in a fair amount to be able to answer the questionnaire.
4. 96.2% of the sample have taken courses in fraud which gives the sample a new quality to be accounted on.
Part Three: Study Fields
In this part the amount of approval given by the study sample will be elaborated to the suggested classification on the individual level of the classifications passages and on the overall level for the fields represented by the mean, and elaborate the measure of dispersion in answering the passages represented by the standard deviation as in the tables below, and to clarify the means used to measure the degree of consistency we accounted on the lekerts tripartite level weights as in table 4:
| Table 4 Weights of The Answers to The Paragraphs of The Questionnaire |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statement | Yes | Neutral | No | The overall mean |
| Weight for an answer | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
The passage is approved if its gets a mean result higher than the weight of (2) which is the general mean calculated by summing all the three different weights divided on its number ((3+2+1)/3)
The First Field: Organizational Controls
| Table 5 Means and Standard Deviations for The Field of Regulatory Controls |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Paragraph | Mean | Standard deviation | The result |
| 1 | Company accredited on an organized Regulatory structure is considered one of the Organizational controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 2 | The audits commission supervision effectively and independently is considered one of the Organizational controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 3 | Determining the individuals access and the sections responsible for goals and holding it accountable is one of the Organizational controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 4 | Effective supervision procedures on the employees to monitor their performance and correcting their mistakes is considered one of the Organizational controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 5 | Company keeping all communication lines open with the employees, customers suppliers and external parties is considered one of the Organizational controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 6 | Duties rotation between employees to guarantee getting their annual vacations equally is one of the Organizational controls | 2.85 | 0.362 | Accept |
| 7 | Making policies to chase fraud criminals is considered one of the Organizational controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 8 | Giving strict punishment to the fraud criminals is considered one of the Organizational controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 9 | Separating functional tasks is one of the Organizational controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 10 | Approving the dealings before making it by the supervisors is one of the Organizational controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 11 | Executing external audit regularly is one of the Organizational controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 12 | Executing internal audit on the dealing is one of the Organizational controls. | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 13 | Hiring security and computer consulters is one of the Organizational controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 14 | Encouraging the audit commissions is one of the Organizational controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 15 | Restricting the employees independency by restricting certain acts ( like not allowing employees to enter data unless they are allowed to ) is one of the Organizational controls | 2.77 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 16 | Making the correct authorization to the correct employee is one of the Organizational controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 17 | Testing the integrity and business ethics for the employees before hiring them is one of the Organizational controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| The overall mean of the field | 2.94 | |||
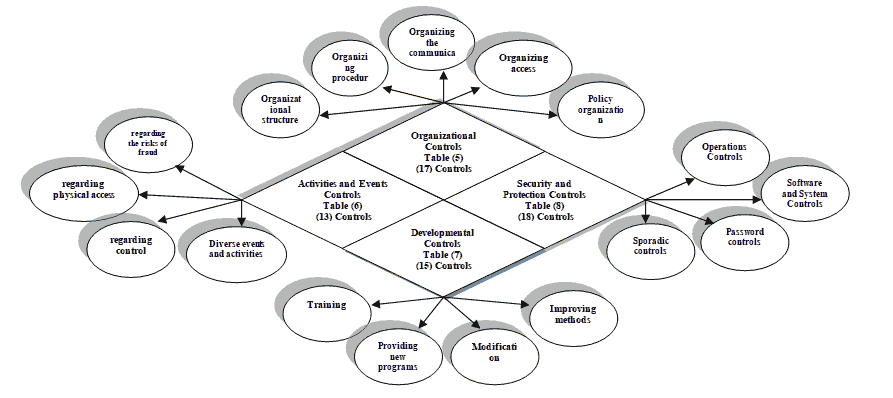
The previous table 5 reviews a passage represented by Organizational controls suggested by the researcher consisted by the study sample on the suggested classification, and the cause of this classification goes to the fact that the previous controls has the quality of Regulatory as below:
• Organizational structure: determines the access and responsibilities, Coordinates business and determines the relation between employees.
• Organizing procedures: this section takes the shape of variety because of the variation of dealings and its procedures for example audit the dealing internally and regularly, the commissions supervising actively independently, taking effective procedures regarding the employees to observe their performance, other procedures regarding employment as making tests for the candidates concerning their working ethics, the employment of security guards and computer consulters to minimize the amount of electronic fraud operations.
• Organizing access: this term is connected to the policy of separating between the functional tasks and restricting employees independence by banning certain behaviors with assigning the suitable job for a suitable employee.
• Policy organization: this term connects some policies such as special policies chasing the frauds and giving them strict punishments.
• Organizing the communicating operations internally and externally for the company by keeping the lines open between employees customers suppliers and external parties.
If we review the standard deviation we will find that the percentage is minor highly evaluated as (0.534) which means that the answers of the study sample is close and there is no dispersion, this enforces the approval of the sample to the suggested classification.
The Second Field: Activities and Events Controls
| Table 6 Means and Standard Deviations for The Field of Activities and Events Controls |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Paragraph | mean | standard deviation | The result |
| 1 | Selecting the events that increases the risks of fraud is one of the events and activities controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 2 | Selecting organized steps for managing the risks of fraud ( like banning, avoiding, sharing or accepting ) is one of the events and activities controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 3 | Making changes is one of the events and activities controls. | 2.85 | 0.362 | Accept |
| 4 | Restricting employees actions on physical re for the systems is one of the events and activities controls | 2.77 | 0.577 | Accept |
| 5 | Activities restricting that allows physical reach for the records and data is one of the events and activities controls | 2.54 | 0.931 | Accept |
| 6 | Independent performance tests like analytical reviews is one of the events and activities controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 7 | Monitoring the system activities to detect fraud cases is one of the events and activities controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 8 | Company working on recovering the ability to go back to work after disasters is one of the events and activities controls | 2.69 | 0.607 | Accept |
| 9 | Executing human resources policies like evaluation and promotion for the employees in a way that guarantees the ethical behavior and integrity is one of the events and activities controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 10 | Motivational activities for the employees by reporting the fraud cases like giving rewards for violations is one of the events and activities controls | 2.62 | 0.739 | Accept |
| 11 | Using the regressions analysis to detect fraud and its using the financial variables and multiple variables logistic regression to limit the relations between the factors regarding fraud in the financial data is one of the events and activities controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 12 | Making bank settlements is one of the events and activities controls | 2.69 | 0.723 | Accept |
| 13 | control the mathematical operations to check the accuracy of the numbers and summing is one of the events and activities controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| The overall mean of the field | 2.82 | |||
The previous table 6 shows a passage regarding the second classification of the events and activities controls where the mean acceding the general mean (2) indicates the samples approval of this classification, and the standard deviation mostly did not exceed (0.6) which means there is no dispersion in the answers of the sample and that encourages the approval on the classification by the sample. this classification can be included in several groups:
• Events and activities regarding the risks of fraud: where this events and activities connects to determining the events that can increase the risk of fraud to control it, it also connects to determining the organized steps to manage the risk of fraud accepting sharing or refusing it.
• Events and activities regarding physical access: these activities must restrict and ban the access of employees and individuals from inside and outside the company from getting physically to its data and records except those who are authorized to access it.
• Events and activities regarding control: here there are many activities regarding control such as independent performance tests, monitoring the system actions, executing human resources policies for evaluation, banks settlements that play a major role in adjusting the bank accounts and mathematical operations to verify the numbers and its summing.
• Diverse events and activities: there are many activities in this group that have a major role in controlling fraud like motivational activities for employees to report the cases of fraud, using regression analysis to reveal fraud, activities regarding the ability of the company to continue working after disasters.
The Third Field: Developmental Controls
| Table 7 Means and Standard Deviations for The Field of Developmental Controls |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Paragraph | Mean | Standard deviation | The result |
| 1 | Continuous modifications on the internal Control system are considered one of the development controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 2 | Continuous modification on the fraud risks evaluation and its size is considered one of the development controls | 2.77 | 0.577 | Accept |
| 3 | Providing security programs for computers and networks is considered one of the development controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 4 | Sorting data into large groups to determine the patters and making connections to reveal the fraud cases ( data’s mine ) is considered one of the development controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 5 | Automated learning algorithms with human interference and without human interference to determine the complicated patterns in large data for revealing the fraud cases is considered one of the development controls. | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 6 | Developing emergency plans against fraud is considered one of the development controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 7 | Training employees for the considerations of integrity and professional ethics is considered one of the development controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 8 | Developing the regulatory culture in the company to guarantee the integrity, ethical values and efficiency is considered one of the development controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 9 | Applying the means of forensic accounting to develop the operations of revealing fraud is considered one of the development controls | 2.62 | 0.626 | Accept |
| 10 | Developing a system able to analyze to data in order to prevent and detect fraud is considered one of the development controls | 2.77 | 0.577 | Accept |
| 11 | Using the decision tree method to detect fraud and this method separates the groups notes and choses similar characteristics correctly to share the best sample is considered one of the development controls | 2.54 | 0.636 | Accept |
| 12 | Spreading awareness about anti-fraud to al the company sections such as managers and employees is considered one of the development controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 13 | Improving the supervision activities and monitoring procedures on it is considered one of the development controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 14 | Developing a comprehensive group of security policies to design and execute the monitoring procedures is considered one of the development controls | 2.85 | 0.362 | Accept |
| 15 | Training employees on the safety procedures and preventing fraud is considered one of the development controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| The overall mean of the field | 2.84 | |||
The above table 7 the general mean estimated by (2.84) and the mean of all passages that exceeded the general mean for the study tool and the drop of the value of the standard deviation approves the consent of the sample for all of the passages of the classification as it undergoes the development controls which has the nature of development by
• Modification: As it relates to changing the internal control, the programs regarding the evaluation of fraud risks and the emergency plans against fraud that aim to improve.
• Improving Methods: These terms are represented in the organizational culture to guarantee the integrity, commitment to ethical values, efficiency, supervision activities, observing operations and also improving the security policies.
• Training: These terms relate to training the employees for the considerations of integrity, professional ethics and the safety procedures to prevent fraud.
• Providing New Programs: It relates by providing new safety programs for the computers and networks, using new methods such as decision tree to reveal fraud, the data sorting method by large groups of data, and the automated Algorithms with human intervention and without it to specify the complicated Patterns in large amounts of data, finally applying the Forensic accounting to develop the operations of revealing fraud cases.
Fourth field: Security and Protection Controls
| Table 8 Means and Standard Deviations of The Field of Security and Protection Controls |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Paragraph | Mean | Standard deviation | The result |
| 1 | Using well designed documents and records to get accurate data and making sure of processing it properly is one of the security and Protection controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 2 | Applying controls on entering data and processing, storing, transferring and reporting it is one of the security and Protection controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 3 | Decoding stored and transferred data and programs to protect it from unauthorized use is one of the security and Protection controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 4 | Getting rid of CDs safely to prevent the perpetrators from getting it is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.85 | 0.362 | Accept |
| 5 | Continuously improving the operating systems to get rid of the weakness points is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 6 | Developing security programs and programs for the applications is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| 7 | Evaluating controls and operations that prevent and detects possible fraud is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 8 | Creating a reviewing path in order to trace the transactions in the system to financial statements and from financial statements to transactions is considered one of the security and Protection controls. | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 9 | Executing audit procedures to protect the private networks is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.85 | 0.362 | Accept |
| 10 | Installing programs that prevents fraud is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 11 | Using descriptive data to understand and analyze data in order to detect the probability of fraud existence is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.85 | 0.362 | Accept |
| 12 | Contracting with insurance companies to make insurance in cases of fraud and stealing and other kinds of losses is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.69 | 0.723 | Accept |
| 13 | Making backups for the programs files and data in a safe place outside its location is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.85 | 0.534 | Accept |
| 14 | Using programs to detect system activities and recovery from fraud is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.92 | 0.267 | Accept |
| 15 | Documenting properly for the essential purchases and updating its records is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.77 | 0.577 | Accept |
| 16 | Providing immediate or delayed feedback is considered an alert activation when entering payments in excess of a specified amount of security and Protection controls. | 2.85 | 0.362 | Accept |
| 17 | Regularly changing the passwords is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 2.77 | 0.422 | Accept |
| 18 | Demanding passwords form the employees to make sure of their identities before making operations is considered one of the security and Protection controls | 3 | 0 | Accept |
| The overall mean of the field | 2.88 | |||
The previously (Table 8) given means appearing in the previous table which have exceeded the general mean shows the samples consent on classifying these controls as security and Protection controls and approved by the convergent answers that shows the decrease in value for the standard deviation that didn’t exceed 0.60 and its listed in the following groups:
• Software and System Controls: These controls are related to programs in terms of coding, security and application development, installing fraud detection programs and using programs to monitor system activities with storing backup copies of program files and data, as well as updating operating systems continuously.
• Operations Controls: These controls relate to conducting audits to protect private networks with the establishment of a review path to enable tracking of transactions, and the use of metadata to understand and analyze operations, processes of entering, processing, storing, transferring and reporting data, and finally, an evaluation of the processes and controls used to ensure that Carry out what is required of it.
• Password Controls: These controls are concerned with password in terms of changing her regularly and ask her staff when entering the system or perform any action that requires the password.
• Sporadic Controls: these controls in terms of their work and are compatible in terms of security are varied and protection, such as the disposal of CDs, and contracting with insurance companies to maintain adequate insurance against cases of fraud and theft, and the use of documents and records properly designed to get accurate data with making sure processed true, and finally the documentation properly purchased the assets with the update records.
Part Four: The Statistically Significant Differences Attributable to the Sample Characteristics.
In order to determine the run and s data due to the characteristics of the sample relating to the areas of study relied on two tests:
*Test Independent-Samples T-Test for question with two levels.
*Test One-Way ANOVA For questions with three of the levels above.
When applying tests between the absence of differences of statistical significance between the answered data sample t attributed to the workplace and scientific qualification and experience, while he found some differences of statistical significance, which attributed E. Lee characteristics of professional certification, the nature of work and the sessions are as follows:
The First Difference: Statistical Differences Due to Characteristics of the Nature of Work and the Courses.
The statistical differences appear among the study sample answers in all study fields as it shown in Table (9). as well as, these differences attributed to the external auditor and those who gain courses in fraud field because the mean of the external auditor is higher than the mean of internal auditors, in order to the mean for those who have courses in fraud field is higher than who don't have any of fraud courses as it appears in Table (10), this means that the external auditor and the one who attend fraud courses are more responsive with the study paragraphs in all fields,
| Table 9 Statistical Significance Differences Between The Nature Of The Work And Courses For All Fields Of Study |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The field | Contrast data | work nature | Take courses | ||||
| T | DF | SIG | T | DF | SIG | ||
| Organizational controls | Equal Variances Assumed | -12.682 | 232 | 0 | 7.945 | 232 | 0 |
| Equal Variances not Assumed | -10.013 | 89,000 | 0 | 39.807 | 2,24,000 | 0 | |
| Activities and events | Equal Variances Assumed | -2.014 | 232 | 0.045 | 5.812 | 232 | 0 |
| Controls | Equal Variances not Assumed | -1.989 | 181.457 | 0.048 | 29.118 | 2,24,000 | 0 |
| Development controls | Equal Variances Assumed | -11.415 | 232 | 0 | 10.622 | 232 | 0 |
| Equal Variances not Assumed | -9.365 | 98.61 | 0 | 53.222 | 2,24,000 | 0 | |
| Security and protection controls | Equal Variances Assumed | -9.401 | 232 | 0 | 9.964 | 232 | 0 |
| Equal Variances not Assumed | -8.183 | 117.681 | 0 | 49.923 | 2,24,000 | 0 | |
| Table 10 Descriptive Census Results According To The Nature Of Work And Course Access |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The field | Work nature | Take courses | ||||||
| Job | Frequency | Mean | Standard deviation | Courses | Frequency | Mean | Standard deviation | |
| Organizational controls | Internal Auditor | 90 | 2.835 | 0.156 | Yeah | 225 | 2.948 | 0.113 |
| External auditor | 144 | 3 | 0 | No | 9 | 2.647 | 0 | |
| Total | 234 | 234 | ||||||
| activities and events Controls | Internal Auditor | 90 | 2.769 | 0.294 | Yeah | 225 | 2.837 | 0.273 |
| External auditor | 144 | 2.846 | 0.278 | No | 9 | 2.308 | 0 | |
| Total | 234 | 234 | ||||||
| Developmental controls | Internal Auditor | 90 | 2.653 | 0.301 | Yeah | 225 | 2.869 | 0.207 |
| External auditor | 144 | 2.958 | 0.088 | No | 9 | 2.133 | 0 | |
| Total | 234 | 234 | ||||||
| Security and protection controls | Internal Auditor | 90 | 2.778 | 0.187 | Yeah | 225 | 2.902 | 0.138 |
| External auditor | 144 | 2.951 | 0.094 | No | 9 | 2.444 | 0 | |
| Total | 234 | 234 | ||||||
This result was justified, that the external auditors are more interactive with fraud procedures cases than the internal auditor due to familiarizing them with many procedures back to several companies compared with the internal auditor who works with his company which gives them the ability to understand the suitable control for fraud procedures.
Also, the members who get courses in fraud fields are possibly informed with new fraud methods and cases which aren't faced by those who didn't get any courses.
The Second Difference: There are Statistical Differences due to the Feature of Vocational Certificates
Table (11) shows the statistical differences which attributed to the feature of vocational certificates to all study fields. Where the differences found in favor of those who hold the Jordanian Accountant Certificate Legal (JCPA) At the expense of those holding the Certified Internal Auditor Certificate (CIA) And also for those who do not hold professional certificates, and the differences came in favor of those who hold the certified internal auditor certificate at the expense of those who do not hold professional certificates, because mean for holders of the Jordanian Certified Accountant Certificate (JCPA) is Higher than the mean of the holders of the Certified Internal Auditor certificate(CIA)Those who do not hold professional certificates, and the mean for those who obtain the Certified Internal Auditor Certificate (CIA) It is higher than mean for those without professional degrees, and the mean appears in Table No. (12) with the two symbols (I) And (J( When subtracting )I( From )J) The result is either a positive or negative show, meaning that previous differences of holding (JCPA) For external auditor are more understand of fraud controls than who hold (CIA) For internal auditor, and this result praises the above previous one which elicits that the external auditors are more understandable to fraud control than the internal auditor.
| Table 11 Statistical Significance Differences Due To The Feature Of Vocational (Professional) Certificates |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The field | Sum of Squares | DF | Mean Squares | F | SIG. | |
| Organizational controls | Between Groups | 1.755 | 2 | 0.877 | 105.821 | 0 |
| Within Groups | 1.915 | 231 | 0.008 | |||
| Total | 3.67 | 233 | ||||
| activities and events Controls | Between Groups | 1.526 | 2 | 0.763 | 10.044 | 0 |
| Within Groups | 17,547 | 231 | 0.076 | |||
| Total | 19.073 | 233 | ||||
| Developmental | Between Groups | 5.636 | 2 | 2.818 | 74.911 | 0 |
| Controls | Within Groups | 8.69 | 231 | 0.038 | ||
| Total | 14.326 | 233 | ||||
| Security and protection controls | Between Groups | 1.669 | 2 | 0.835 | 44.001 | 0 |
| Within Groups | 4.382 | 231 | 0.019 | |||
| Total | 6.051 | 233 | ||||
| Table 12 The Results Of Descriptive Statistics According To Professional Certificates |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The field | (I) (J) | mean | STANDARD ERROR | SIG |
| (J-I) | ||||
| Organizational controls | JCPA CIA | 0.058 * | 0. 023 | 0. 028 |
| Without | 0.191 * | 0. 013 | 0. 000 | |
| CIA JCPA | - 0.588 * | 0. 023 | 0. 028 | |
| Without | 0.132 * | 0. 024 | 0. 000 | |
| Without JCPA | - 0.191 * | 0. 013 | 0. 000 | |
| CIA | - 0. 132 * | 0. 024 | 0. 000 | |
| activities and events Controls | JCPA CIA | 0.154 *- | 0.069 | 0.068 |
| Without | 0.135 * | 0.04 | 0.002 | |
| CIA JCPA | 0.154 * | 0.069 | 0.068 | |
| Without | 0.288 * | 0.073 | 0 | |
| Without JCPA | - 0.135 * | 0.04 | 0.002 | |
| CIA | 0.288 * | 0.073 | 0 | |
| Developmental Controls | JCPA CIA | 0.158 | 0.048 | 0.004 |
| Without | 0.342 | 0.028 | 0.001 | |
| CIA JCPA | -0.158 | 0.048 | 0.004 | |
| Without | 0.183 | 0.051 | 0.001 | |
| Without JCPA | -0.342 | 0.028 | 0 | |
| CIA | -0.183 | 0.051 | 0.001 | |
| Security and protection controls | JCPA CIA | 0.174 | 0.034 | 0 |
| Without | 0.174 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| CIA JCPA | -0.174 | 0.034 | 0 | |
| Without | 0 | 0.036 | 1 | |
| Without JCPA | -0.174 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| CIA | 0 | 0.036 | 1 | |
Part Five: Hypothesis Testing
The proposal hypotheses are classified into a main hypothesis, and four sub-hypotheses are branched out from it:
H0: It’s Difficult to propose a framework for the classification of controls to prevent and detect fraud.
H0.1: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of Organizational controls to prevent and detect fraud.
H0.2: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of developmental controls to prevent and detect fraud.
H0.3: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of security and protection controls to prevent and detect fraud.
H0.4: It’s Difficult to propose a classification of activity and event controls to prevent and detect fraud.
In order to reach the main result of the hypothesis will be tested first sub - hypotheses both separately, where test were used (One-Sample t-Test) to test it as follows shown in Table 13:
| Table 13 Hypothesis Test |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assumptions | T Tabular | T Calculated | SIQ. | mean | The result |
| Sub-hypotheses | |||||
| It’s difficult to propose a classification of Organizational controls to detect and prevent Fraud. | 1.96 | 114.165 | 0 | 2.94 | Rejected |
| It’s difficult to propose a classification of developmental controls to detect and prevent Fraud. | 1.96 | 51.884 | 0 | 2.84 | Rejected |
| It’s difficult to propose a classification of Security and protection controls to detect and prevent Fraud. | 1.96 | 83.969 | 0 | 2.88 | Rejected |
| It’s difficult to propose a classification of events and activity controls to detect and prevent Fraud. | 1.96 | 43.658 | 0 | 2.82 | Rejected |
| The main hypothesis | |||||
| It’s difficult to propose a classification of prevention and detection controls to detect and prevent Fraud. | Rejected | ||||
The null hypothesis is rejected if the counted (T Calculated greater than T Tabular) and Significant Less than (5%) (Al-Batsh & Abu Zina, 2007, 192), and based on the calculated values in the previous table, the four previous null hypotheses will be rejected and accepting the alternative hypotheses which state that:
•The possibility of proposing the Organizational classified controls to prevent and detect fraud.
•The possibility of proposing the developmental controls to prevent and detect fraud.
•The possibility of proposing the Security and protection controls to prevent and detect fraud.
•The possibility of proposing the activity and events controls to prevent and detect fraud.
Since the null hypotheses were rejected and the alternative hypotheses were accepted, so this result will be rejected in the main hypothesis by rejecting the sub-main hypothesis and accepting the alternative, which states:
"The possibility of a proposal framework for the classification of controls to prevent and detect fraud"
Conclusion
After the fraud controls has classified in a framework, which contains four proposed groups : Organizational controls, activities and events, development, and finally security and protection, adding the data analysis which has collected and testing hypotheses and survey, concluded the study found that the possibility of adoption the proposed framework with its four previous controls which will accomplish the usability and accessibility of dealing with it, plus stopping the bleeding of the sums that companies lose, and this framework will be a guide for companies that will guide them in building strong control systems to control fraud and reduce the possibility of their occurrence through the prevention and rapid detection of fraud, additionally, the frame can be shown in the following figure that shows the four main controls The groups that belong to each officer and the number of sub-controls that are listed under it :
Recommendations
The study, however, has shown many controls in a number of the mentioned groups in the above results, the researcher recommends to adopt these controls in industrial companies and other companies in order to contribute in building strong control systems which detect and prevent the fraud operations, in addition, to find out the irregular actions and illegal operations which classified as fraud operations, as well as, which cause the loss of companies in millions even billions of dollars.
References
- Al-Batsh, M.W., & Abu Zina, F.K. (2007). Scientific research methods "research design and statistical analysis", (1st Edition). Dar Al-Masirah for Publishing, Distribution and Printing, Amman-Jordan.
- Attorney Generals Department. (2017). Preventing, detecting and dealing with fraud, "Resource Management Guide No. 201". Australian Government, Commonwealth of Australia
- Badejo, B.A., Okuneye, B.A., & Taiwo, M.R. (2017). Fraud detection in the banking system in Nigeria challenges and prospects. Journal of Economics and Business, 2(3), 255-281.
- Bekiaris, M., & Papachristou, G. (2017). Corporate and accounting fraud: Types, causes and fraudster's business profile. Corporate Ownership & Control, 15(1), 467-475.
- Banarescu, A. (2015). Detecting and preventing fraud with data analytics. Procedia Economics and Finance, 32, 1827-1836.
- Burzynska, D., & Jablonska, M. (2018). The role of internal audit as a tool for detecting fraud. Economic and Environmental Studies, 18(2) (46/2018), 483-497.
- Christ, M.H., Emett, S.A., Summers, S.L., & Wood, D.A. (2012). The effects of preventive and detective controls on employee performance and motivation. Contemporary Accounting Research, 29 (2), 432-452.
- Desai, N. (2020). Understanding the theoretical underpinnings of corporate fraud. The Journal for Decision Makers, 45(1), 1-7.
- Donning, H., Eriksson, M., Martikainen, M., & Lehner, O.M. (2019). Prevention and detection for risk and fraud in the digital age-The current situation. ACRN Journal of Finance and Risk Perspectives, Special Issue Digital Accounting, (8), 86-97.
- Gibson M.R (2018). An analysis of fraud prevention and detection in not-for-profit organizations in the state of South Carolina. Thesis Doctoral, Liberty University. Jordanian Association of Certified Public Accountants. (2020),
- Lartey, P.Y., Kong, Y., Maci-Bah F.B., Santosh, R.J., & Gumah, I.A. (2020). Determinants of internal control compliance in public organizations; Using preventive, detective, corrective and directive controls, International Journal of Public Administration, 43(8), 711 - 723.
- Manasseh, H., Linus, M.L., & Bitrus, R.W. (2015). Impacts of control activities on fraud prevention and control in the bursary departments of tertiary institution: A critical study and appraisal of Kwararafa University Wukari, Taraba State Nigeria. The International Journal of Business & Management, 3(11), 326-337.
- Muritala, T.A. Ijaiya M.A., & Adeniran, D.S. (2017). Fraud and bank performance nexus. Evidence from Nigeria using vector error correction model. J. Bus. Financ, 03(01), 21-29.
- Othman, R., Abdul A.N., Mardziyah, A., Zainan, N., & Amin, N.M. (2015). Fraud detection and prevention methods in the Malaysian public sector: Accountants 'and internal auditors' perceptions. 7th International Conference on Financial Criminology, 13-14 April, Wadham College, Oxford, United Kingdom, Procedia Economics and Finance 28, 59 - 67.
- PwC's Global Economic Crime and Fraud Survey. (2020). Fighting fraud: A never-ending battle.
- Rahman, R.A., & Anwar, I.S.K. (2014). Effectiveness of fraud prevention and detection techniques in Malaysian Islamic banks. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 145, 97-102.
- Romney, M.B., & Steinbart, P.J. (2018). Accounting Information Systems, (14th Edition). Pearson Education Limited, England.
- Sahiti, A., & Bektashi, M. (2015). Detection techniques of fraud in accounting. European Journal of Economics and Business Studies, 2(1), 96-101.
- Salihu, H.A., & Jafari, A. (2020). Corruption and anti-corruption strategies in Iran: An overview of the preventive, detective and punitive measures. Journal of Money Laundering Control, 23 (1), 77-89.
- Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2016). Research Methods for Business "A Skill-Building Approach", (7th edition). John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
- Teunissen, C., Smith, R.G., & Jorna, P. (2020). Within and against fraud the commonwealth: The harmful by most Frauds 2016-17 To 2018-19 “the AIS the Reports Statistical 26. Report”. Australia: Australian Institute of Criminology.
- The Institute of Internal Auditors Inc. (IIA). (2009). Fraud Prevention and detection in an Automated world, Global Technology Audit Guide 13.
- Yuniarti, R.D. (2017). The effect of internal control and anti-fraud awareness on fraud prevention (A survey on inter-governmental organizations). Journal of Economics, Business, and Accountancy Ventura, 20(1), 113 – 124.