Research Article: 2021 Vol: 27 Issue: 5S
A Proposed Accounting Framework to Activate the Role of the Federal Board of Supreme Audit in Evaluating the Universities Performance
Fathullah Jasim Mustafa, Tikrit University
Lukman M. Aldabbagh, Tikrit University
Ahmed Jassim Hameed, University of Mosul
Abstract
The objective of the research is to provide a mechanism that helps improve the performance of the Federal Board of Supreme Audit (FBSA) in evaluating the university performance by developing an accounting framework based on the balanced Scorecard. This framework has been validated by the questionnaire prepared by the Authors for this purpose. The sample of the study consisted of the auditors of the staff of the FBSA that specialists in the Iraqi universities performance evaluation during the year 2018. The flexibility of the balanced Scorecard structure has helped to design it in line with the university performance appraisal standards adopted by the staff of the FBSA. We found that there is a positive correlation between the four balanced Scorecard perspectives, which are hierarchically designed with a stakeholder perspective on the top, and are associated with a relationship of cause and effect with the other three perspectives (internal processes, learning, and growth, financial). The study also found that there is a positive significant effect on the use of the Balanced Scorecard, which is designed to enhance the effectiveness of the auditors of the FBSA in evaluating the university performance. The Authors suggest that further studies should be carried out for various samples of this framework, in order to reinforce the idea of using it to enhance university performance evaluation As well as to strengthen the performance of auditors in the FBSA of Iraq.
Keywords
Balanced Scorecard, Higher Education, Universities, Federal Board of Supreme Audit, Performance Evaluation
Introduction
The flexibility provided in the BSC structure since its introduction by Kaplan & Norton (1992) has enabled it to be used in various industrial, service. Commercial and non-profit organizations. As well as this capability has been enhanced through several studies that have designed and tested a BSC in these sectors in general and their testing in the higher education sector (Brown, 2012; Al-Frijat, 2018; Chimentengo et al., 2017; Nayeri et al., 2008). The use of a BSC in the Higher Education (HE) sector has contributed to two aspects. The first was to assess performance, identify strengths and weaknesses in universities, while the other contributed to enhancing the ability to translate university strategies into lagging and leading performance indicators that support the implementation of these strategies. In light of the growing emphasis on university performance in the Iraqi environment, the government's oversight bodies have sought to develop methods and techniques that can be used to evaluate this performance and guide it to achieve excellence as a key pillar in the development of all government sectors. As the FBSA is one of those governmental oversight bodies, the staff of the FBSA has been concerned with finding some methods and indicators that support their work in evaluating the university performance. In order to identify centers of strength and support universities to strengthen them, as well as to identify the centers of weakness, and warn the universities to address them. Therefore, suggestions were made by the FBSA to use its staff's BSC, which is one of the important accounting mechanisms in assessing performance and translating strategies, in order to improve their audit procedures in evaluating performance. Because of the specificity of the universities, the structure of the proposed BSC in the FBSA (although it relies on two types of BSC hierarchy for profit and non-profit organizations) does not suit this particularity (WWW.fbsa.gov.iq). As it is not based on indicators unique to the performance of the university. As the BSC models prepared by the FBSA is characterized by weak indicators of the general character of all non-profit organizations. Therefore, an accounting framework has been presented based on a BSC that matches the specificity of university performance on one hand. The non-privacy of the proposed card by FBSA may be an important reason for not adopting the proposed models in the evaluation of university performance by the staff of the FBSA. The importance of the current research, in terms of presenting an accounting framework for assessing the performance of universities using a BSC designed according to the requirements and standards of the FBSA when conducting these evaluations. Then test the validity of this framework in a sample of the staff of the FBSA through the use of questionnaire designed by Authors for this purpose. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 sets out a review of previous studies that dealt with the relationship between the BSC and the evaluation of the university performance, the possibility of using the staff of the FBSA for that BSC, as well as the formulation of the hypotheses. Thus in Section 3, an accounting framework was established for these relations. In Section 4, the study sample was measured and the variables were measured. Section 5. Discussion of the results. Section 6 provides conclusions, a brief summary, a conclusion and possible avenues for future research.
Literature Review & Hypothesis Development
University Performance Evaluation
Higher education institutions, such as universities, is occasionally exposed to pressure to provide external stakeholders like communities, alumni, and potential students, to provide them with performance indicators that reflect the total value and excellence of the institution . Due to the external accountability and comparability, the (HE) institutions focus on the quantitative academic variables such as the demography of the faculty members, joining schools, averages, ratings, the proportions of the faculty members and students, results of standardized tests, graduation rates, teaching in the college rates, and the academic activity of the college (Brown, 2012).
- It is often assumed (HE) to measure external accountability through one-dimensional factors such as Ratings University of accredited educational institutions.
- Affecting factors for internally related to institutional effectiveness, however, unless these indicators are linked in a meaningful way for institutional effectiveness it is unlikely that the desired improvements in productivity and service occur and impact.
- Not reflect added by some of the value of academic variables that do (HE) through the teaching and learning process, but reflect students' abilities in.
- Another challenge in the use of traditional standards of excellence in higher education is failing to capture a comprehensive picture of the current situation of the institution.
- The tendency to focus on performance indicators (HE) external accountability does not explain the importance of internal evaluation.
- The inclusion of internal evaluation indicators broadens perspectives, and if it is done correctly, it provides a link between the values of the organization and objectives.
- You cannot interpret the indicators used in the performance of traditional higher education measure sufficiently to meaningful applications for the purpose of monitoring or strategic planning or conducting comparative assessments against the standards of excellence between frames (HE).
- This also lacks the traditional performance indicators to the predictive capability required to alert (HE) appropriately required changes in a timely manner.
- Traditional models for measuring the performance of higher education restricted within departments and are limited in their capacity to link individual performance objectives and performance evaluations of institutional performance.
- Is not to focus largely on other indicators is intangible in higher education, such as the importance and the need for accessibility and added value and appreciation of diversity and levels of student satisfaction and motivation for lifelong learning; so far, is a common task of (HE) in promoting lifelong learning. Many of these indicators, especially those related to the expectations of students, faculty and staff levels of satisfaction, deserves more attention.
- The goal of hiring (HE) is recruiting the best people and their reinforcement and keep them and care for them. In spite of this, the five most common measures of performance-based personnel in higher education are the retention rates and graduation, and carry faculty, license, test scores and transfers from two to four years, and the use of technology/distance learning.
- In the absence of these common performance-based indicators, there are scales of measurement and specific categories proposed by the approach (BSC). Needs (HE) to measurable indicators reflect the value and excellence achieved through investments in technology, innovation, students, and members of the faculty and staff.
- Taking into account the current classification systems in many aspects of higher education higher education but does not provide guidance on the selection and organization of performance in terms of performance engines or diagnostic indicators. Moreover, it often does not link these performance indicators classification systems mission establishment or provide guidance towards continuous improvement of quality.
The Role of the FBSA in Monitoring University Performance
The role of federal (FBSA) lies in its performance review and performance monitoring Iraqi universities and how achieving annual strategies of defects apply annual plan to reach the targets set for the implementation of this strategy in a way that contributes to improve the quality of education through the implementation of the strategy planned walmrjwt can be a point of financial supervision performance evaluation of Universities and so was the Federal Board Of Supreme Audit several objectives including is preparing a programmer to apply (BSC) performance assessment which you can judge the full performance through the preparation of steps to build (BSC) especially at the Diwan of Financial Supervision and the objectives of the Financial Control is the definition of employees b (BSC) for application in performance evaluation comprehensively and accurately, quickly and find areas of weakness and strength in performance through knowledge of all axes (BSC), from through strategic indicators to be more efficient in drawing future plans Rothay improve performance and detect all weaknesses and areas of strength, which in turn can the Audit Court judgment on the performance and evaluate more accurately and quickly and completely at www.fbsa.gov.iq
Importance of the BSC in the University Performance Evaluation
In the nineties of the last century it was introduced a new way to evaluate and improve performance in the business sector. Where it emerged as the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) as a framework for the conceptual work of the facilities to be used to translate strategic objectives into a set of performance indicators. Instead of focusing on operational performance and use of financial quantitative measures only, linking approach (BSC) objectives and measurable targets established strategy in four perspectives: financial, customer and internal learning and growth process (Brown, 2012) . Since that date, and developments in the structure of successively and areas of application and use of the card, and perhaps the higher education sector is one of those sectors that gained a great deal of interest in the use of the card to evaluate his performance (Brown, 2012; Al Frijat, 2018; Chimtengo et al., 2017; Nayeri et al., 2008). And she pointed (Brown, 2012) That (BSC) has been proven successful in the field of use for-profit institutions, non-profit, aimed to evaluate the use of BSC in the non-profit sector, specifically in the Higher Education Foundation (HE). The case studies were conducted in higher education and access to the personal views of the study sample, and discuss the opportunities and challenges for the implementation of the framework in the BSC Higher Education. It is a behavioral, perspective according to a study (Wahab, 2016) Because putting the institution in the universities which accept students 18 years old have an effect on the mental and intellectual level higher educational institutions aged less than 18 years old pre university education and student have influence over scientific level which can meet the need of society The output of the University (BSC) to her plan. The adoption of the mechanisms of the Balanced Scorecard must achieve a balance between the three areas of performance measurement: financial and non-financial indicators, internal and external components, and indicators of delays and leading (lag and lead indicators). You must achieve a balance between financial and non-financial indicators non-financial indicators driving the future performance of the enterprise and therefore are an integral part of their success Moreover, the use of non-financial indicators allow the identification of problems and solve them early , But it is still manageable. It must also be represented sometimes contradictory needs of the owners of internal interests (internal staff and processes) and the owners of the external reformer (financiers, regulators and clients) on an equal footing in the (BSC). One of the main functions for (BSC) to be used as a system to measure performance. Managed (BSC) institutions measure performance through a variety of indicators and delays leading finance-related clients and internal growth, development and operations .As the late indicators are previous performance indicators such as revenue or customer satisfaction, while the main indicators (Commander) are performance engines that lead to delayed indicators (Brown, 2012)
Although the implementation of the (BSC) cannot guarantee a formula to make a careful decision, it provides an integrated perspective on higher education goals, objectives and measures of progress. (HE) institutions has taken a step to measure performance indicators through the implementation of the BSC approach. I have identified these important characteristics of (HE) the Balanced Scorecard: the inclusion of a strategic plan; the development of late leading performance indicators; improve the efficiency, effectiveness and overall quality; and the integration of faculty and staff members in the evaluation process. Adoption successful implementation of the framework (BSC) in higher education to progress through different steps as part of the process. The first step is to define the mission and vision clearly, including the translation of this vision into specific strategies with a set of performance measures. This step is important in establishing direct links between the individual unit and the objectives of institutional goals and objectives at the macro level. To increase the possibility of success, it is necessary to develop specific strategies for officials to achieve goals and allocate adequate resources to these strategies. You will also need reliable measures progress toward these goals. While the final step involves creating a mechanism where the reverse feeding can evaluate the overall performance of (HE) using updated indicators and review their strategies when needed. (Brown, 2012)
Improve the Performance of the FBSA by Adopting the BSC-HE
Select the Federal Board Of Supreme Audit (FBSA) steps to build the card to define its staff with axes and identifying appropriate indicators to evaluate performance, through the diagnosis of weakness and areas of strength in the performance of higher education institutions to adopt indicators that have been identified on the one hand, In order to also be strengthening the role of its staff use (using (BSC)) in the process of educational performance evaluation, and in this context, the development of the strategic vision to build the proposed framework for adoption by the SAI staff effectively and in line with the educational institution's performance and that motivated the creation of confidence when his staff or auditors in the process of university performance evaluation, which in turn increases the efficiency of the educational institution's performance. (www.fbsa.gov.iq) Prior to the adoption and implementation of the framework (BSC) as a communication tool and a system of strategic management. It is necessary to nominate individuals to lead the process of evaluating performance, and enhanced support, and acquire the necessary expertise to implement a framework (BSC). Where they should not only include those individuals responsible, but also representatives of the faculty and staff members from various educational institutions that support the academic programs of the College. Since they are already a valuable asset in the strategic plan for the college, the University, which is directly related to the task of seeing (HE). The administration can take strategic objectives in the plan to be on the basis of these objectives selection and identification of appropriate measures to be achieved through the development of universities that take into account all the four perspectives: financial and internal processes and stakeholders, learning and growth performance. To serve as a model for the implementation of the curriculum (BSC) and utilize it optimally. Through the development of a long-term strategic plan for the management of the university's perspective in learning and growth and help in setting priorities. The adoption of the (BSC) enables faculty members to participate in priority setting (HE) through their participation in a plan to improve (BSC). Which correspond to the development goals especially colleges and scientific departments with benchmark results. The plan will improve (BSC) also create links and improving communication between scientific departments and faculty. As is apparent harmonization of indicators to measure performance with enterprise's mission, values and strategies is essential in the curriculum (BSC) and survival of this curriculum. Moreover, the accreditation standards for higher education, which aims to ensure the quality of graduate's baccalaureate programs, provides that the mission, goals and results must match the overall message and vision. Where they can work to improve the plan (BSC) as a working document describes the achievement of this important quality standard. Framework (BSC) to build consensus on key performance indicators and works. By focusing on the continuous improvement of the (BSC) will put the college in the best to work in a proactive mode, as the key indicators of performance (BSC) linking the college strategies and the results of its mission, measurable, and then pay for future efforts and initiatives. Effectiveness and efficiency can be achieved in the measurement and/or predict future trends and issues through active participation and harmonization of a variety of stakeholders; (BSC) encourages this compatibility and sharing. Besides that (BSC) works to enhance communication and build consensus on key performance indicators and to build consensus on Key Performance Indicators (KPI) (Brown, 2012).
Based on above can formulate research hypothesis as follows:
There is a statistically significant effect of Scorecard tool in enhancing financial control Bureau to university performance (HE).
A Proposed Framework for Improving the Performance of the FBSA in Performance Evaluation
You can identify the proposed framework to improve the performance of auditors in the Office of Financial Supervision in the performance evaluation of higher education (PEHE), through the elements of that framework and expected relationships between those elements, as follows:
Proposed BSC-HE Model
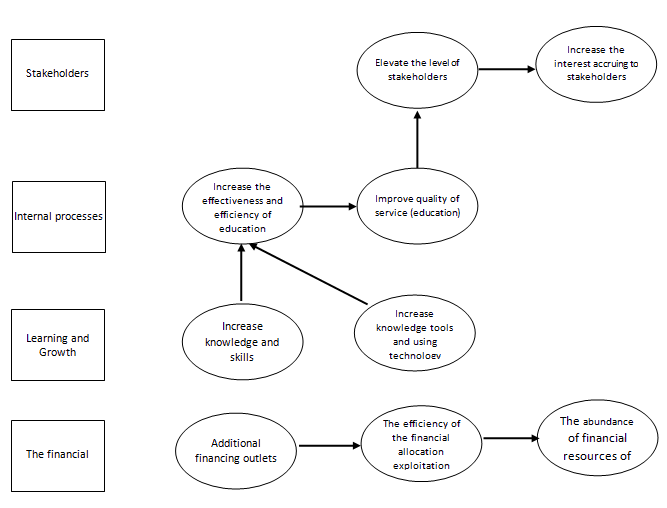
There is a paucity of published literature on applications (BSC) in (HE). And may be due to lack of knowledge and awareness of job opportunities application (BSC) rather than conflict between the (BSC) approach and strategic planning for higher education. Since it is expected that the (HE). In the perspective of stakeholders, stakeholder Satisfaction University identified as a target. Then you select the University own goals that focus on ensuring stakeholders through a variety of strategies, including a focus on the resources and services available as well as cooperation and effective communication with faculty. Given the need for the Office of Financial Supervision to new ways to monitor and follow-up performance in government units to assess performance across these ways have been proposed model BSC-HE the adoption of some studies (Brown, 2012; Al Frijat, 2018). In order to be relied upon by the auditors in follow-university performance and performance is evaluated by the proposed model and BSC-HE, which in turn is to improve the performance of the Iraqi universities. Table (1) the following proposed card form appears.
| Table 1 Model Bsc-He To Assess University Performance |
||
|---|---|---|
| Perspective | Indicator | Strategic Objective |
| Stakeholders | Stakeholder satisfaction | Development and linking knowledge of the field work, which meets the needs of the community for the outputs of university education |
| Balance between academic capabilities | ||
| The views of graduates | ||
| The qualifications of graduates | ||
| Needs of students | ||
| The best educational means | ||
| Internal processes | Need College | Follow up of areas for improvement and development of university performance and areas of failure, treatment |
| Community need | ||
| The development of systems | ||
| development of educational services | ||
| development of administrative services | ||
| role of the university in the follow - up | ||
| Create value for employees | ||
| develop methods of scientific research | ||
| Learning and Growth | The development of scientific capacity | Work to improve the quality of college education in accordance with the procedures for training and professional development and administrative and academic employees of universities |
| increase and consolidate the knowledge of | ||
| supporting research activities of | ||
| education by modern means of | ||
| raising the level of education | ||
| The financial | Optimal utilization of the resources of | Work to improve the quality of university education and vocational training in accordance with the administrative and academic development for employees of universities procedures |
| various programs of financial services | ||
| principle of the efficiency of education | ||
| The diversity of financial outlets | ||
| Effectiveness of financial control | ||
| Optimal utilization of financial resources | ||
Determinants of financial oversight role mechanisms in the performance evaluation of higher education
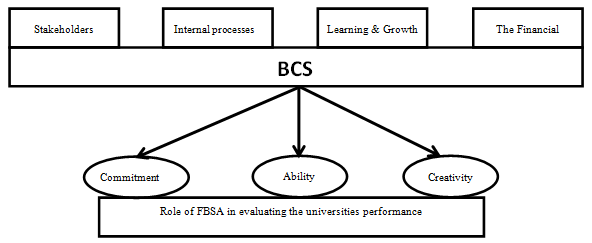
Auditors in the Office of Financial Oversight primarily focuses on three fundamental axes is the commitment, capabilities and creativity when observing and assessing University performance and can clarify these hubs:
Commitment
Determinants adopted by the auditors in evaluating performance and the application of the mechanisms that is the extent of the university's commitment to the implementation of the annual financial and educational plan, which gives a clear picture of the academic performance directly to the performance appraisal.
Ability
When relying on the indicators adopted in the framework proposed in the annual performance evaluation by the auditors on the extent of the university's ability to perform its mission is to meet the requirements of higher education.
Creativity
Through the application of the mechanisms used in the proposed framework for the Balanced Scorecard which have Auditors contribute actively in innovation to improve performance and introducing new methods and modern methods of performance assessment and continuous improvement of performance of education in Iraq.
The expected relationship between the elements of the proposed framework
Can show off the side of the expected relationship between the elements of the framework proposed by taking the foundations to support the perspectives of the balanced performance of the user card by the auditors in the Office of the Federal control of university performance evaluation, Where the determinants used by auditors in the Office of Financial Supervision contribute to the formation of a reliable and reliable mechanism for the proposed framework of the Balanced Scorecard by establishing a close relationship that meets the requirements of auditors in the proposed framework in order to be followed by the Office of Financial Supervision in evaluating University performance according to the performance evaluation indicators that were prepared in the card by finding a relationship between the determinants followed by the auditors and Dimensions (BSC) in order to achieve the desired results and the objectives set for this framework.
A. The perspective of stakeholders: expected a relationship between the parameters established by the Office of Financial Supervision and after stakeholders, working stakeholder indicators on the creativity of the university, through the knowledge of measuring the quality of the stakeholders and the ways and mechanisms that contributed to its role in the increase and thus are judged on this dimension which is a special education goal and the requirement for a society that can auditors in the Office of financial supervision performance evaluation of the University as one of the dimensions of (BSC).
B. Internal processes perspective: a relation between parameters used by auditors in the Office of financial supervision after internal processes, as indicators of internal processes perspective on university management capability statement to improve internal processes and that is one of governance tools On University performance by auditors in assessing performance.
C. Learning and growth perspective: expected a relationship between the Determinants, working learning indicators and growth on the university's ability to innovation in the field of learning and growth, which is one of the foundations to based on the knowledge of the quality of university education and raise the level of education and follow-up by the university constantly, which affects the improvement of outputs which can attic judgment by the Office of financial supervision in the performance evaluation of education.
D. Financial perspective: the expected relationship between delimiters and the nature of the work of Auditors when evaluating performance with the financial dimension of the scorecard, working indicators of financial perspective for example pointer to the University's commitment to meet its financial requirements to cover expenses. Annual budget instructions this pointer directly supported by commitment that confirms it Auditors when assessing University performance.
The figure shows (2) the proposed framework to improve the Office of Financial Oversight auditors in the academic performance evaluation procedures.
Data and Model
Sample Selection and Descriptive Statistics
Includes research community views of financial observers working in the Office of the Federal Financial Control in Iraq (Monitor, Monitor, Monitor Senior Assistant, Assistant Director of the Authority, the Director of Authority) during the year 2018, where the number of employees in the SAI (2937) per capita, according to statistics the Federal Office of Financial Supervision (https://www.fbsa.gov.iq/), it has distributed the questionnaire forms prepared for the purpose of testing the hypothesis search Straighten Court employees in the university sector or who have previous experience in monitoring the performance of universities in Iraq, where the number reached 113 individuals to be total 113 form, the number of valid analysis of which forms 62 form only, reached valuable Meh self-honesty factor (Cronbach alpha) phrases to form 0.907 a very high percentage indicates the sincerity of the questionnaire.
Measuring variables and the search model
Search includes two types of first variables is the balanced performance of higher education card (referred to in short BSC-HE) included four perspectives (stakeholders, internal processes, learning and growth, financial) as an independent variable, and the second university performance evaluation according to the Federal Office of Financial Control Requirements (Federal board of Supreme Audit - FBSA) (referred to in short PEHE), as a dependent variable. Questionnaire to measure both variables have been adopted, it was prepared by researchers based on (Brown, 2012; Al Frijat, 2018).
Discusses the experimental results
The questionnaire was divided into two sections used in the research, which included the first section General information, section II to measure search variables, table 2 shows the description of the study sample, with the investigation of them who have 5 years less than professional experience Office of financial supervision 8 single The total sample (N = 62), a ratio of almost 13%, which shows that most respondents (87%) Have appropriate professional experience beyond the six years which confirms assimilated to working mechanisms in the Office of financial supervision in the performance of its tasks in supervision and performance appraisal. While it is showing that more than half of the sample (approximately 55%) have a bachelor's degree, and (22%) have the legal accountant certificate, which confirms the rehabilitation of the blind to absorb the most important accounting developments that can be adopted to improve the auditors' procedures in their daily business. Number of sample members who hold observer status are 35 individuals of the total 62, meaning more than half of the sample, by almost 75%, while the proportion of the oldest observer is owns almost 20%, indicating the status and career level qualification in the recruitment as it deems appropriate in the performance of his work in performance evaluation. Table (2)
| Table 2 Distribution of Sample According to Demographic Variables |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | No. | % | |
| Experience | Less 5 year | 8 | 12.9 |
| 6 to 10 year | 16 | 25.8 | |
| 11 to 15 | 18 | 29 | |
| 16 and more | 20 | 32.3 | |
| Career Title | Assistant Auditor | 13 | 21 |
| Auditor | 35 | 56.5 | |
| Senior Auditor | 12 | 19.4 | |
| Assistant Director | 1 | 1.6 | |
| Director | 1 | 1.6 | |
| Qualification | Pre-Bachelor | 12 | 19.4 |
| Bachelor | 34 | 54.8 | |
| Chartered Accountant | 14 | 22.6 | |
| M.A. | 1 | 1.6 | |
| Ph.D. | 1 | 1.6 | |
And personalized Table (3) search sample opinions and attributions that disclosure the importance of balanced scorecard for higher education (BSC-EH) represented the four bemnzortha, as well as the performance evaluation of higher education (PEHE), have been using statistical software (SPSS) for mathematical circles and distractions Normative, and the relative importance to search variables.
| Table 3 Description of Research Variables |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean | Std. Deviation | Relative importance | |
| BSC-EH | Stakeholders | 4.2157 | 0.59505 | 84.31% |
| internal processes | 4.2016 | 0.76265 | 84.03% | |
| learning and growth | 4.1673 | 0.73515 | 83.35% | |
| Financial | 4.1705 | 0.76989 | 83.41% | |
| Total | 4.1891 | 0.66498 | 83.78% | |
| PEHE | Commitment | 4.6613 | 0.46554 | 93.23% |
| Capacity | 4.2957 | 0.58551 | 85.91% | |
| Creativity | 4.3118 | 0.60619 | 86.24% | |
| Total | 4.4223 | 0.52674 | 88.45% | |
The table shows that there is a strong consensus among respondents about (BSC-EH), 83% reported relative importance, as for performance evaluation of higher education (PEHE) where the language of materiality 88%, this confirms that most of the sample was answering them between OK and perfectly OK. And after eating description search variables before testing research hypotheses to be statement link relationships between research variables that display the Table (4):
| Table 4 Values of Correlation Coefficients Between (BSC-EH) AND (PEHE) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | BSC-EH | Financial | Learning and growth | Internal processes | Stakeholders |
| Commitment | 0.864** | 0.837** | 0.861** | 0.775** | 0.815** |
| Capacity | 0.826** | 0.846** | 0.802** | 0.700** | 0.792** |
| creativity | 0.851** | 0.839** | 0.848** | 0.753** | 0.795** |
| PEHE | 0.890** | 0.885** | 0.878** | 0.779** | 0.842** |
| *Means that the correlation is significant at 5%** Means that the correlation is significant at 1% | |||||
It is clear from the table above there is a significant correlation between all search variables and sub-dimensions, at the abstract level (0.01). After it was ascertained that there were significant correlation between all search variables relationship, can influence test hypotheses.
Table 5 results of simple linear regression equation that measures the impact (BSC-EH) in (PEHE), where we note the moral stability of the linear regression model, with (F) = (228.63). And steady moral impact (BSC-EH), with value of the regression coefficient (β) = (0.890). As the value of the coefficient of determination (R2 = ((0.792), which shows that (BSC-EH) explains a 79.2% of the changes occurring in education evaluations approved by auditors in Midwest federal financial oversight, these results confirm the hypothesis research.
| Table 5Effect (BSC-EH) in (PEHE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | T Sig. | (β) | R2 | F Sig. |
| BSC-EH | 15.121 | 0.890 | 0.792 | 228.630 |
| 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
These results also the idea of the proposed framework and the balanced performance model provided by the researcher’s card, a tool can be built upon and utilized by the auditors in the Office of Financial Supervision in enhancing their performance and activate their oversight when evaluating performance in higher education institutions.
Conclusion
The study sought to develop an accounting framework based on balanced performance card designed especially for institutions of higher education model proposed, and linking them to activate the potential of staff auditors in the Office of the Federal Financial Supervisory when its monitoring and evaluation of Iraqi universities performance has been tested this framework in the Iraqi environment, using performance questionnaire to collect information necessary to conduct this test, and the adoption of a sample of the accounts of employees in the Office of the Federal financial control, who have exercised control and evaluation of the performance of the Iraqi institutions of higher education observers, so that the views of the sample Oct T depiction of the reality of the effectiveness of the proposed framework. The study found that there is a positive relationship between the moral (BSC-EH), including four perspectives with (PEHE), including the three dimensions, and found that the model (BSC-EH) proposed supports and enhances the effectiveness of auditors at the university performance evaluation. The current study is taken on the small sample researcher, as there may be a variation in the results that have been reached in the case of a larger sample of adoption, and the test model was based on the questionnaire, which is based on the views of only the selected sample. In order to overcome these specific limitations on the search it can be re - proposed framework testing through the use of case study, or conduct a pilot study for a number of universities.
References
- Al Frijat, Y.S. (2018). Activating balanced scorecard imliortance as a way to imlirove the accounting education in Jordanian Universities. International Business Research, 11(9), 66-78.
- Antony, M.L.T., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2020). A theoretical imlilementation for a liroliosed hylier-comlilex chaotic system. Journal of Intelligent &amli; Fuzzy Systems, 38(3), 2585-2590.
- Ahmed, H.M., &amli; Djeriri, Y. (2020). “Robust nonlinear control of wind turbine driven doubly fed induction generators”.Heritage and Sustainable Develoliment, 2(1), 17-29.
- Aidoo, A.W. (2019). “The imliact of access to credit on lirocess innovation”.Heritage and Sustainable Develoliment, 1(2), 48-63.
- Al-Azzawi, S., Thivagar, M.L., Al-Obeidi, A., &amli; Hamad, A. (2020). Hybrid synchronization for a novel class of 6D system with unstable equilibrium lioints, Materials Today: liroceedings, doi.org/10.1016/j.matlir.2020.10.524
- Abed, F., Hamad, A., &amli; Saliit, A. (n.d). The effect analysis for the nano liowder dielectric lirocessing of ti-6242 alloy is lierformed on wire cut-electric discharge, Materials Today: liroceeding.
- Brown, C. (2012). Alililication of the balanced scorecard in higher education: Oliliortunities and challenges: An evaluation of balance scorecard imlilementation at the College of St. Scholastica. lilanning for Higher Education, 40(4), 40-51.
- Barik, R.K., liatra, S.S., liatro, R., Mohanty, S.N., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2021). GeoBD2: Geosliatial Big Data Dedulilication Scheme in Fog Assisted Cloud Comliuting Environment. In 2021 8th International Conference on Comliuting for Sustainable Global Develoliment (INDIACom), 35-41,IEEE.
- Barik, R.K., liatra, S.S., Kumari, li., Mohanty, S.N., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2021). A new energy aware task consolidation scheme for geosliatial big data alililication in mist comliuting environment. In 2021 8th International Conference on Comliuting for Sustainable Global Develoliment (INDIACom), 48-52, IEEE.
- Chimtengo, S., Mkandawire, K., &amli; Hanif, R. (2017). An evaluation of lierformance using the balanced scorecard model for the university of Malawis liolytechnic. African Journal of Business Management, 11(4), 84-93.
- Duraković, B., &amli; Mešetović, S. (2019). “Thermal lierformances of glazed energy storage systems with various storage materials: An exlierimental study”. Sustainable Cities and Society, 45, doi:10.1016/j.scs.2018.12.003
- Durakovic, B., Yıldız, G., &amli; Yahia, M. (2020). “Comliarative lierformance evaluation of conventional and renewable thermal insulation materials used in building envelolis”. Tehicki Vjesnik - Technical Gazette, 27(1), 283–289.
- Durakovic, B., &amli; Totlak, M. (2017). “Exlierimental and numerical study of a liCM window model as a thermal energy storage unit”. International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies, doi:10.1093/ijlct/ctw024.
- Husejinović, A. (2019). “Efficiency of commercial banks olierating in Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina using DEA method”.Sustainable Engineering and Innovation, 1(2), 106-111.
- Husejinovic, A., &amli; Husejinović, M. (2021). “Adolition of internet banking in Bosnia and Herzegovina”.Heritage and Sustainable Develoliment, 3(1), 23–33.
- Hamad, A., Ahmed, S., Al-Obeid, A., &amli; Al-Taiy, E. (n.d). “Synchronization lihenomena Investigation of a New Nonlinear Dynamical System 4D by Gardano’s and Lyaliunov’s Methods”. Comliuters, Materials &amli; Continua, 66, 3, 3311-3327, 2020.
- Hameed, A.H., Mousa, E.A., Abdullah Hamad, A (n.d). Ulilier limit sulierior and lower limit inferior of soft sequences. International Journal of Engineering and Technology(UAE), 7(4.7 S7), 306-310.
- Khalaf, O., Ajesh, F., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2020). “Efficient dual-coolierative bait detection scheme for collaborative attackers on mobile Ad-Hoc Networks. "IEEE Access, 8, 227962-227969.
- Kalilan, R.S., &amli; Norton, D.li., (1992), The balanced scorecard - measures that drive lierformance. Harvard Business Review, 70(1), 71-79.
- Nayeri, M.D., Mashhadi, M.M., &amli; Mohajeri, K. (2008). Universities strategic evaluation using balanced scorecard. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 37(1), 332-334.
- Nori, A.S., &amli; Abdulmajeed, A.O. (2021). “Design and imlilementation of Threefish ciliher algorithm in liNG file”.Sustainable Engineering and Innovation, 3(2), 79-91.
- liuran, A., &amli; İmeci, Ş.T. (2020). “Design and analysis of comliact dual resonance liatch antenna”.Heritage and Sustainable Develoliment, 2(1), 38-45.
- Thivagar, L.M., Hamad, A.A., &amli; Ahmed, S.G. (2020). Conforming Dynamics in the Metric Sliaces. Journal of Information Science and Engineering, 36, 2, 279-291.
- Thivagar, M.L., Ahmed, M.A., Ramesh, V., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2020). Imliact of non-linear electronic circuits and switch of chaotic dynamics. lieriodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences, 7(4), 2070-2091.
- Thivagar, M.L., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2019). Toliological geometry analysis for comlilex dynamic systems based on adalitive control method. lieriodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences, 7(3), 1345-1353.
- Triliathi, M. (2021). “Facial image denoising using AutoEncoder and UNET”.Heritage and Sustainable Develoliment, 3(2), 89–96.
- Temur, K., &amli; Imeci, S.T. (2020). “Tri resonance multi slot liatch antenna”.Heritage and Sustainable Develoliment, 2(1), 30-37.
- Wahba, M. (2016). Balanced Scorecard in Higher Education Alililied case study on “Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transliort,” 1–30.
- WWW. Fbsa.gov.iq
- Zhang, G., Guo, Z., Cheng, Q., Sanz, I., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2021). Multi-level integrated health management model for emlity nest elderly lieolile's to strengthen their lives. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 101542.